Plant Regeneration and In Vitro Growth Performance of Male-Sterile Somatic Plantlets of Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica) Derived from Different Embryogenic Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, SE Initiation, and Maintenance and Proliferation of ECLs
2.2. Selection of Male-Sterile ECLs
2.3. Maturation of Somatic Embryos
2.4. Somatic Embryo Germination and Plantlet Conversion
2.5. In Vitro Growth of Somatic Plantlets
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
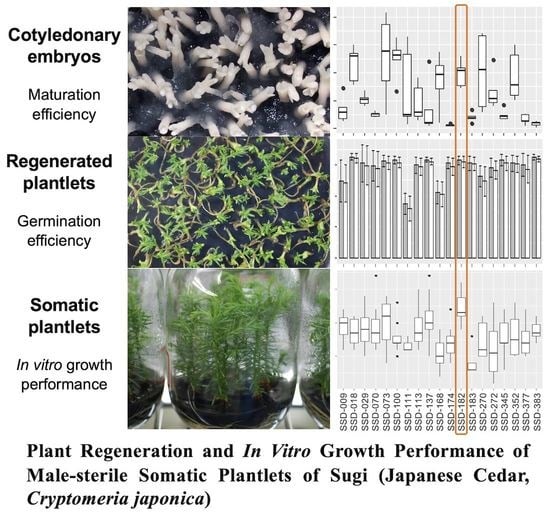
3.1. Somatic Embryo Maturation
3.2. Somatic Embryo Germination and Plantlet Conversion
3.3. In Vitro Growth of Somatic Plantlets and Seedlings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020 Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; 186p. [Google Scholar]
- Forestry Agency. Statistical Handbook of Forest and Forestry; Forestry Agency, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries: Tokyo, Japan, 2020; pp. 8–9. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara, A.; Sakashita, M.; Gotoh, M.; Kawashima, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Kondo, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeno, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Urashima, M.; et al. Epidemiological Survey of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan 2019. Nippon. Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 2020, 123, 485–490, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Hirayama, S.; Kaneeda, T.; Moriguchi, Y. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don, Cupressaceae) seed families by marker assisted selection for the male sterility allele ms1. Plants 2020, 9, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Barret, J.D.; Bonga, J.M. Application of somatic embryogenesis in high-value clonal forestry: Deployment, genetic control, and stability of cryopreserves clones. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1998, 34, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Trontin, J.F.; Becwar, M.R.; Devillard, C.; Park, Y.S.; Lelu-Walter, M.A. Recent progress in somatic embryogenesis of four Pinus spp. Tree For. Sci. Biotechol. 2007, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Bonga, J.M.; Klimaszewska, K.; von Aderkas, P. Recalcitrance in clonal propagation, in particular of conifers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 100, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Cyr, D.R. Conifer somatic embryogenesis: I. Development. Dendrobiology 2002, 48, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y. Progress in somatic embryogenesis of Japanese pines. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Tanaka, T.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K.; Morohoshi, N. Embryogenic cell culture, protoplast regeneration, cryopreservation, biolistic gene transfer and plant regeneration in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Plant Biotechnol. 2000, 17, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y.; Futamura, N.; Saito, M. Initiation of embryogenic cultures from immature seeds of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2014, 65, 107–110, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Miyazawa, S.; Ueno, S.; Onishi, N.; Totsuka, S.; Iwai, J.; Moriguchi, Y. Differences among families on embryogenic cell induction from seed of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) produced at the Niigata prefecture. Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2018, 69, 1–2, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, T.; Konagaya, K.; Nanasato, Y. Somatic embryogenesis in artificially pollinated seed families of 2nd generation plus trees and cryopreservation of embryogenic tissue in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don (sugi). Plant Biotechnol. 2020, 37, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, T.; Sato, T.; Akashi, N.; Mohri, T.; Maruyama, E.; Kinoshita, I.; Walter, C.; Shinohara, K. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 22, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igasaki, T.; Akashi, N.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Sakagami, Y.; Shinohara, K. Phytosulfokine stimulates somatic embryogenesis in Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, R.; Ogita, S.; Kubo, T.; Funada, R. Effect of polyamines and L-ornithine on the development of proembryogenic masses of Cryptomeria japonica. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2006, 85, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y. Polyethylene glycol enhance somatic embryo production in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Propag. Ornam. Plants 2007, 7, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y.; Miyazawa, S.; Ueno, S.; Onishi, N.; Totsuka, S.; Iwai, J.; Moriguchi, Y. Pollen-free plant regeneration from embryogenic cells derived from sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2019, 70, 37–40, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Hosoi, Y.; Miyazawa, S.I.; Mori, H.; Kaneeda, T.; Bamba, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Hirayama, S.; Kawakami, K.; et al. Somatic embryogenesis initiation in sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don): Responses from male-fertile, male-sterile, and polycoss-pollinated-derived seed explants. Plants 2021, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Mori, H.; Kaneeda, T.; Moriguchi, Y. Factors influencing somatic embryo maturation in sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica (Thunb. ex L.f.) D. Don). Plants 2021, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, K.-A.; Bozhkov, P.V.; Von Arnold, S. Early selection improves clonal performance and reduces intraclonal variation of Norway spruce plants propagated by somatic embryogenesis. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Ueno, S.; Wei, F.J.; Matsumoto, A.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Fujino, T.; Shigenobu, S.; et al. Development of diagnostic PCR and LAMP markers for MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, S.; Uchiyama, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Ujino-Ihara, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Wei, F.J.; Saito, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Futamura, N.; Kanamori, H.; et al. Scanning RNA-Seq and RAD-Seq approach to develop SNP markers closely linked to MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Breed. Sci. 2019, 69, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuruta, M.; Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Moriguchi, Y. Marker-assisted selection for pollen-free somatic plants of sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica): A simple and effective methodology for selecting male-sterile mutants with ms1-1 and ms1-2. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 748110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretz, F.; Hothorn, T.; Westfall, P. Multiple Comparisons Using R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Maruyama, E.; Hosoi, Y.; Ishii, K. Somatic embryogenesis in Sawara cypress (Chamaecyparis pisifera Sieb. et Zucc.) for stable and efficient plant regeneration, propagation and protoplast culture. J. For. Res. 2002, 7, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, E.; Ishii, K.; Hosoi, Y. Efficient plant regeneration of Hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa Sieb. et Zucc.) via somatic embryogenesis. J. For. Res. 2005, 10, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y.; Katsuki, T. Plant regeneration of Yatsugataketouhi (Picea koyamae) through somatic embryogenesis. Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2011, 62, 127–130. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y.; Katsuki, T. Somatic embryo induction from embryogenic cells of Himebaramomi (Picea maximowiczii Regel ex Mast.). Kanto Shinrin Kenkyu 2012, 63, 67–71, (In Japanese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Garin, E.; Isabel, N.; Plourde, A. Screening of large numbers of seed families of Pinus strobus L. for somatic embryogenesis from immature and mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 1998, 18, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Goncalves, S.; Tereso, S.; Marum, L.; Maroco, J.; Oliveira, M. Somatic embryogenesis from 20 open-pollinated families of Portuguese plus trees of maritime pine. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2004, 76, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Bucalo, K.; Determann, R.O.; Cruse-Sanders, J.M.; Pullman, G.S. Somatic embryogenesis, plant regeneration, and cryopreservation for Torreya taxifolia, a highly endangered coniferous species. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2012, 48, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.H.; Tull, A.R.; Montello, P.M.; Merkle, S.A. A clonal propagation system for Atlantic white cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) via somatic embryogenesis without the use of plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 130, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossnickle, S.C.; Major, J.E.; Folk, R.S. Interior spruce seedlings compared with emblings produced from somatic embryogenesis. I. Nursery development, fall acclimation, and over-winter storage. Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, C.; Welty, D.; Herold, G. Performance and genetic parameters of somatic and zygotic progenies of coastal Douglas-fir at 7 ½-years across Washington and Oregon, USA. Silvae Genet. 2009, 58, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoi, Y.; Kuramoto, N.; Maruyama, T.E. Screening RAPD primers to assess clonal fidelity in somatic embryos of Sawara cypress (Chamaecyparis pisifera Sieb. et Zucc.) and field performance of somatic embryo-derived trees. Plant Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, S.; Moriguchi, Y.; Taira, H. Comparison of traits between male sterile and fertile Cryptomeria japonica D. Don trees in selected stands. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2009, 91, 290–294, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakamata, T.; Kondo, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Saito, M. Growth of containerized Japanese ceder seedlings crossing with mother trees having male sterile gene. Chubu For. Res. 2017, 65, 3–4. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Lamhamedi, M.S.; Chamberland, H.; Bernier, P.Y.; Tremblay, F.M. Clonal variation in morphology, growth, physiology, anatomy and ultrastructure of container-grown white spruce somatic plants. Tree Physiol. 2000, 20, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossnickle, S.C.; Folk, R.S. Field performance potential of a somatic interior spruce seedlot. New For. 2007, 34, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, N.; Rainville, A.; Lamhamedi, M.; Margolis, H.; Beaulieu, J.; Deblois, J. Genetic parameters and performance stability of white spruce somatic seedlings in clonal tests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 270, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puentes, A.; Högberg, K.A.; Björklund, N.; Nordlander, G. Novel avenues for plant protection: Plant propagation by somatic embryogenesis enhances resistance to insect feeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneeda, T.; Moriguchi, Y.; Maruyama, T.E.; Tsuruta, M.; Ueno, S.; (Niigata University, Niigata, Japan). Unpublished work. 2021.
- Kurinobu, S.; Toda, T. Genetic variation in height growth curves observed in three clonal tests of Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) in Kyushu. J. For. Res. 2000, 5, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Fukatsu, E.; Hiraoka, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Takahashi, M. The effect of genotype and planting density on the growth patterns and selection of local varieties of Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica). J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2016, 98, 45–52, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuruta, M.; Maruyama, T.E.; Ueno, S.; Kaneeda, T.; Moriguchi, Y. Plant Regeneration and In Vitro Growth Performance of Male-Sterile Somatic Plantlets of Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica) Derived from Different Embryogenic Cell Lines. Forests 2021, 12, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111592
Tsuruta M, Maruyama TE, Ueno S, Kaneeda T, Moriguchi Y. Plant Regeneration and In Vitro Growth Performance of Male-Sterile Somatic Plantlets of Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica) Derived from Different Embryogenic Cell Lines. Forests. 2021; 12(11):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111592
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuruta, Momi, Tsuyoshi E. Maruyama, Saneyoshi Ueno, Takumi Kaneeda, and Yoshinari Moriguchi. 2021. "Plant Regeneration and In Vitro Growth Performance of Male-Sterile Somatic Plantlets of Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica) Derived from Different Embryogenic Cell Lines" Forests 12, no. 11: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111592
APA StyleTsuruta, M., Maruyama, T. E., Ueno, S., Kaneeda, T., & Moriguchi, Y. (2021). Plant Regeneration and In Vitro Growth Performance of Male-Sterile Somatic Plantlets of Sugi (Japanese Cedar, Cryptomeria japonica) Derived from Different Embryogenic Cell Lines. Forests, 12(11), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12111592