Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- testing the diurnal self-preservation hypothesis and different ET upscaling methods based on in-situ flux measurements;
- evaluating the SEBAL model’s performance in estimating instantaneous surface energy fluxes over Mediterranean maquis using the evaporative fraction;
- evaluating the upscaling methods for retrieving daily actual ET values from instantaneous SEBAL evapotranspiration estimates of Mediterranean maquis.
2. Materials and Methods
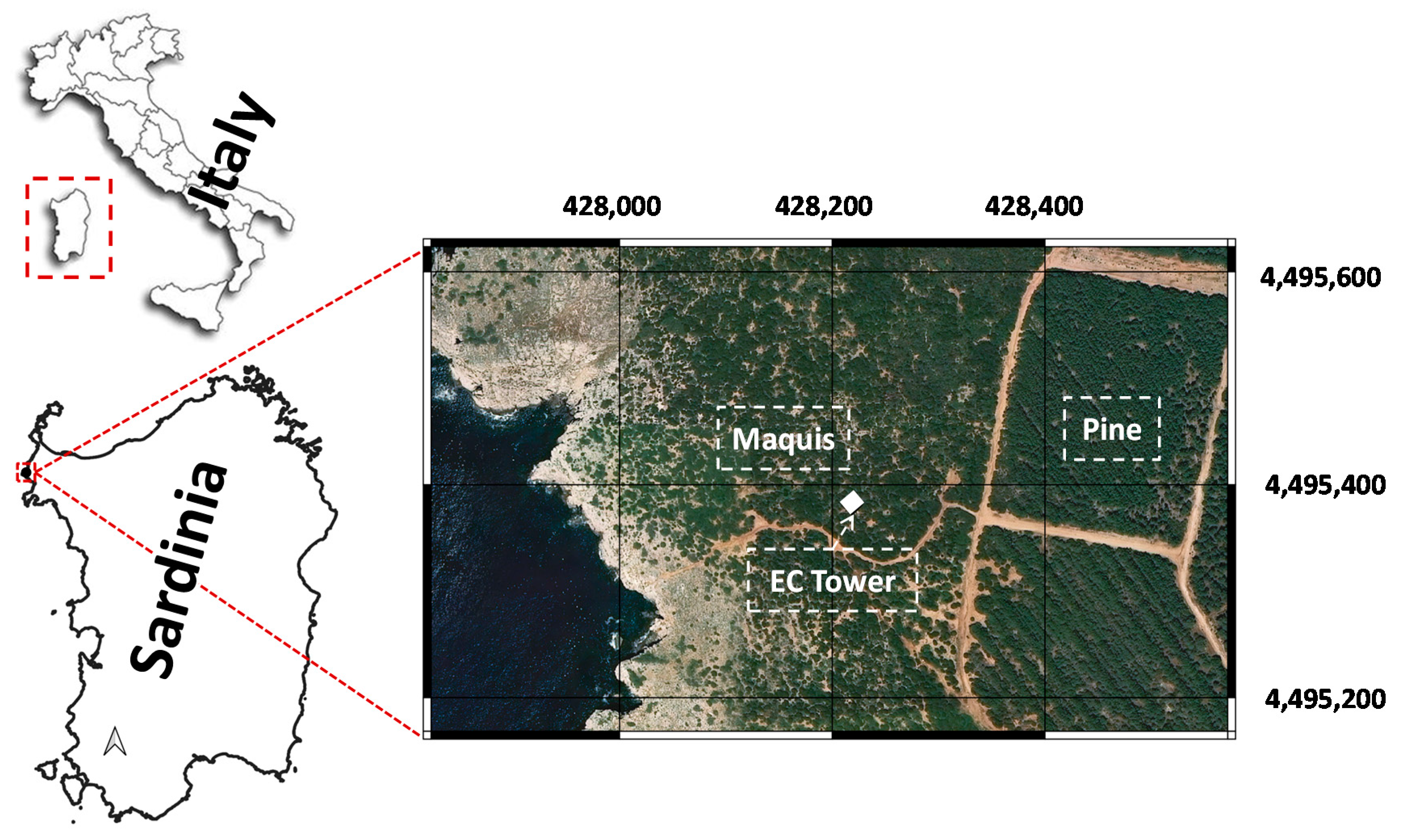
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Micrometeorological and Eddy Covariance Measurements
2.3. Landsat Satellites Datasets and Processing
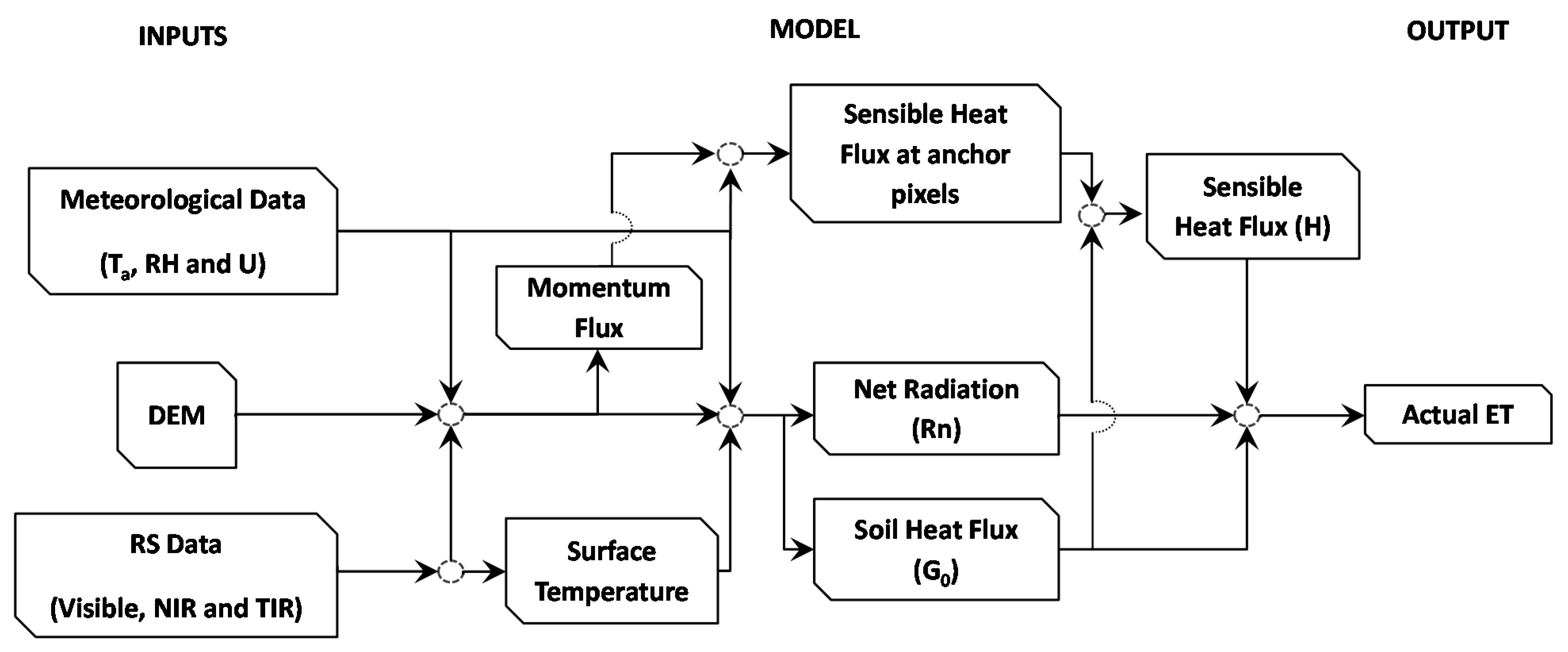
2.4. The Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) Model
2.5. Upscaling Instantaneous to Daily Evapotranspiration
2.6. SEBAL Data Extraction
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Measured Energy Fluxes
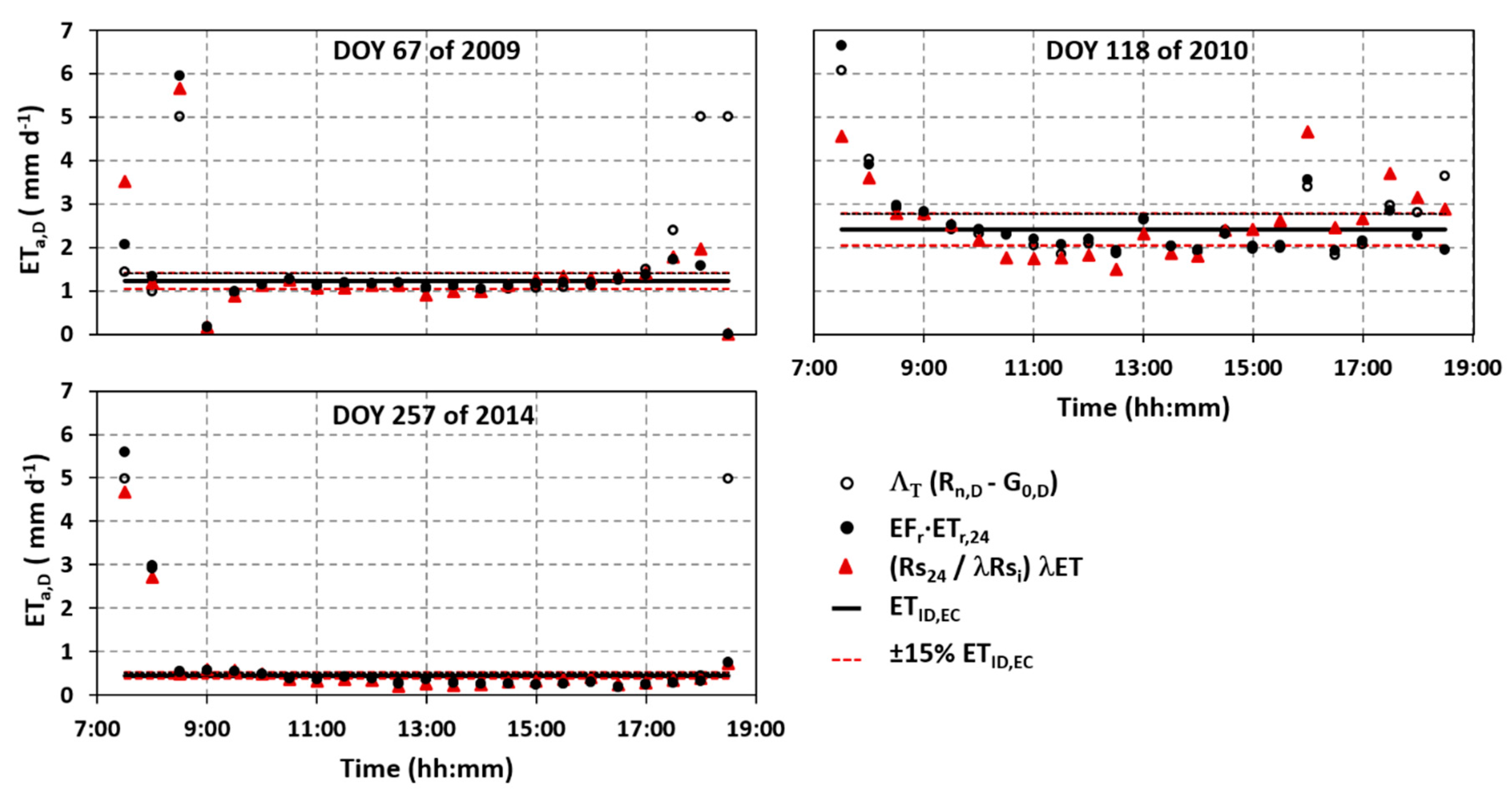
3.2. Diurnal Self-Preservation and Performance of Tower-Derived Upscaling Factors
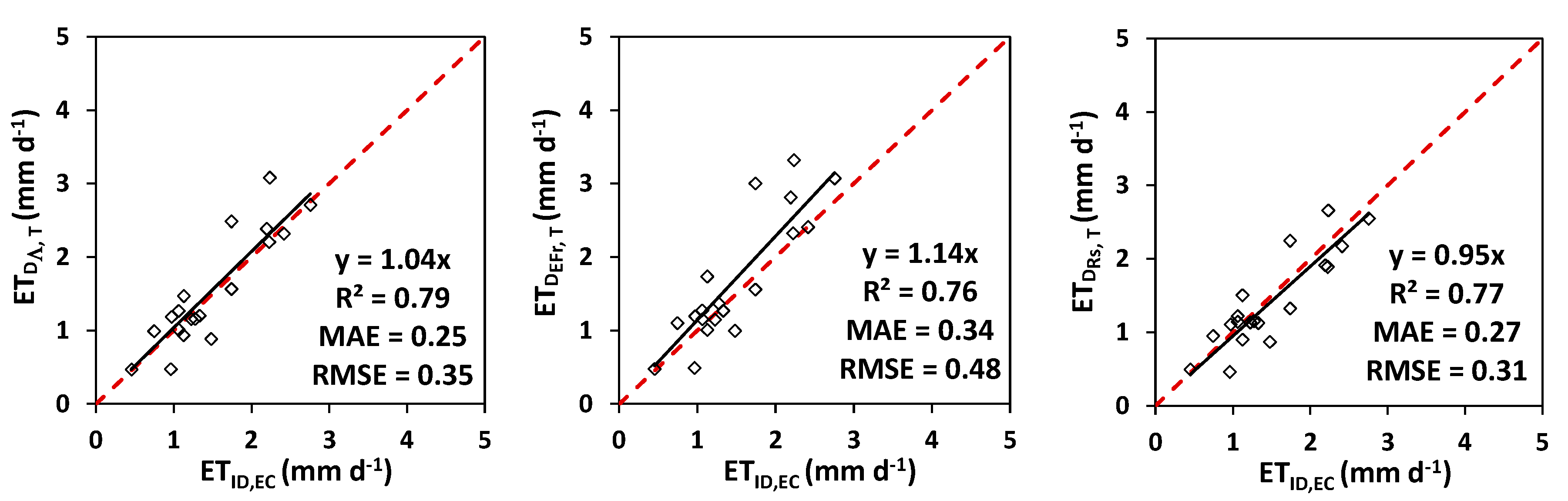
3.3. Validation of the SEBAL Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagener, T.; Sivapalan, M.; Troch, P.A.; McGlynn, B.L.; Harman, C.J.; Gupta, H.V.; Kumar, P.; Rao, P.S.C.; Basu, N.B.; Wilson, J.S. The Future of Hydrology: An Evolving Science for a Changing World. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, P. Overview of Ecohydrological Models and Systems at the Watershed Scale. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 9, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spano, D.; Snyder, R.L.; Sirca, C.; Duce, P. ECOWAT—A Model for Ecosystem Evapotranspiration Estimation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R.; Hollinger, D.; Running, S.; Anthoni, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Davis, K.; Evans, R.; et al. FLUXNET: A New Tool to Study the Temporal and Spatial Variability of Ecosystem-Scale Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, and Energy Flux Densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M.; Vesala, T.; Papale, D. (Eds.) Eddy Covariance: A Practical Guide to Measurement and Data Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilos, M.; Stahl, C.; Burban, B.; Hérault, B.; Courtois, E.; Coste, S.; Wagner, F.; Ziegler, C.; Takagi, K.; Bonal, D. Interannual and Seasonal Variations in Ecosystem Transpiration and Water Use Efficiency in a Tropical Rainforest. Forests 2019, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemakumara, H.M.; Chandrapala, L.; Moene, A.F. Evapotranspiration Fluxes over Mixed Vegetation Areas Measured from Large Aperture Scintillometer. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesely, M.L. A Comparison of Two Optical Methods for Measuring Line Averages of Thermal Exchanges above Warm Water Surfaces. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1976, 15, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angus, D.E.; Watts, P.J. Evapotranspiration—How Good Is the Bowen Ratio Method? Agric. Water Manag. 1984, 8, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, I.S. The Ratio of Heat Losses by Conduction and by Evaporation from Any Water Surface. Phys. Rev. 1926, 27, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paw, U.K.; Qiu, J.; Su, H.-B.; Watanabe, T.; Brunet, Y. Surface Renewal Analysis: A New Method to Obtain Scalar Fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 74, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, D.; Snyder, R.L.; Duce, P.; Paw, U.K.T. Surface Renewal Analysis for Sensible Heat Flux Density Using Structure Functions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 86, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, W.R.N. Precision Weighing Lysimetry for Trees, Using a Simplified Tared-Balance Design. Tree Physiol. 1986, 1, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.E.; Burman, R.D.; Allen, R.G. Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirements; ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice No. 70; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Marek, T.H.; Schneider, A.D.; Howell, T.A.; Ebeling, L.L. Design and Construction of Large Weighing Monolithic Lysimeters. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 477–0484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, R.H.; Stangel, D.E.; Kelly, S.F. Soil Water Balance in a Boreal Forest. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 29355–29365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastham, J.; Rose, C.W.; Cameron, D.M.; Rance, S.J.; Talsma, T. The Effect of Tree Spacing on Evaporation from an Agroforestry Experiment. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1988, 42, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, A. Une nouvelle méthode pour la mesure du flux de sève brute dans le tronc des arbres. Ann. For. Sci. 1985, 42, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Allen, S.J. Measurement of Sap Flow in Plant Stems. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Beyazgül, M.; Kayam, Y.; Kite, G.W.; Murray-Rust, H. Distributed Agro-Hydrological Modeling of an Irrigation System in Western Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaddad, A.; Garcia, L.A. Surface Energy Balance-Based Model for Estimating Evapotranspiration Taking into Account Spatial Variability in Weather. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.P.; Skaggs, T.H. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Time-Stable Characteristics of Soil Moisture within Remote Sensing Footprints with Varying Soil, Slope, and Vegetation. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.H.; Running, S.W. Forest Ecosystems: Analysis at Multiple Scales, 3rd ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-12-370605-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, P.G. Scaling Processes and Problems. Plant Cell Environ. 1995, 18, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A Remote Sensing Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, A.; Awada, H.; Capodici, F.; Ciraolo, G.; La Loggia, G.; Rallo, G. On the Use of the Eddy Covariance Latent Heat Flux and Sap Flow Transpiration for the Validation of a Surface Energy Balance Model. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minacapilli, M.; Cammalleri, C.; Ciraolo, G.; Rallo, G.; Provenzano, G. Using Scintillometry to Assess Reference Evapotranspiration Methods and Their Impact on the Water Balance of Olive Groves. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 170, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source Approach for Estimating Soil and Vegetation Energy Fluxes in Observations of Directional Radiometric Surface Temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A Simple Remote Sensing Algorithm to Estimate the Surface Energy Balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for Estimation of Turbulent Heat Fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, P.; Bhattarai, N.; Gowda, P.H.; Kakani, V.G. Performance of Five Surface Energy Balance Models for Estimating Daily Evapotranspiration in High Biomass Sorghum. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Scott, R.L.; Shang, S. Modeling Evapotranspiration and Its Partitioning over a Semiarid Shrub Ecosystem from Satellite Imagery: A Multiple Validation. JARS 2013, 7, 073495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, H.; Ciraolo, G.; Maltese, A.; Provenzano, G.; Moreno Hidalgo, M.A.; Còrcoles, J.I. Assessing the Performance of a Large-Scale Irrigation System by Estimations of Actual Evapotranspiration Obtained by Landsat Satellite Images Resampled with Cubic Convolution. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 75, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.F.; Roerink, G.J.; van der Wal, T. A Remote Sensing Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL).: Part 2: Validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Shaw, S.B.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Im, J.; Niraula, R. Evaluating Five Remote Sensing Based Single-Source Surface Energy Balance Models for Estimating Daily Evapotranspiration in a Humid Subtropical Climate. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 49, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, W.J.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; French, A.N. An Intercomparison of the Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) and the Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) Modeling Schemes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Brito, R.A.L.; Bos, M.G.; Souza, R.A.; Cavalcanti, E.B.; Bakker, M.M. Low Cost Satellite Data for Monthly Irrigation Performance Monitoring: Benchmarks from Nilo Coelho, Brazil. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2001, 15, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Van der Wal, T.; Visser, T.N.M. Diagnosis of Regional Evaporation by Remote Sensing to Support Irrigation Performance Assessment. Irrig. Drain. Syst 1996, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Schauer, M.; Friedrichs, M.; Velpuri, N.M.; Singh, R.K. Satellite-Based Water Use Dynamics Using Historical Landsat Data (1984–2014) in the Southwestern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Sakthivadivel, R. Water Accounting to Assess Use and Productivity of Water. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1999, 15, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Toomanian, N.; Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Gieske, A. Monitoring Irrigation Performance in Esfahan, Iran, Using NOAA Satellite Imagery. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zayed, I.S.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Spatio-Temporal Performance of Large-Scale Gezira Irrigation Scheme, Sudan. Agric. Syst. 2015, 133, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatchford, M.L.; Karimi, P.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Nouri, H. From Global Goals to Local Gains—A Framework for Crop Water Productivity. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; de Fraiture, C.; Molden, D.J. A Global Benchmark Map of Water Productivity for Rainfed and Irrigated Wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.D.; Kirby, M.; Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.J.; Islam, M.M. Groundwater Use for Irrigation and Its Productivity: Status and Opportunities for Crop Intensification for Food Security in Bangladesh. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.-D.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Feddes, R.A. A New Technique to Estimate Net Groundwater Use across Large Irrigated Areas by Combining Remote Sensing and Water Balance Approaches, Rechna Doab, Pakistan. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-Based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cammalleri, C.; Agnese, C.; Ciraolo, G.; Minacapilli, M.; Provenzano, G.; Rallo, G. Actual Evapotranspiration Assessment by Means of a Coupled Energy/Hydrologic Balance Model: Validation over an Olive Grove by Means of Scintillometry and Measurements of Soil Water Contents. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Bastiaanssen, W. Irrigation Performance Using Hydrological and Remote Sensing Modeling. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2002, 128, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P. Calibration of a Distributed Hydrological Model Based on Satellite Evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuwatta, L.P.; Ahmad, M.-D.; Bos, M.G.; Rientjes, T.H.M. Assessment of Water Availability and Consumption in the Karkheh River Basin, Iran—Using Remote Sensing and Geo-Statistics. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 459–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaselli, R. The Degradation of the Mediterranean Maquis. Ambio 1977, 6, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Palahi, M.; Mavsar, R.; Gracia, C.; Birot, Y. Mediterranean Forests under Focus. Int. For. Rev. 2008, 10, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirastru, M.; Niedda, M.; Castellini, M. Effects of Maquis Clearing on the Properties of the Soil and on the Near-Surface Hydrological Processes in a Semi-Arid Mediterranean Environment. J. Agric. Eng. 2014, 45, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folton, N.; Martin, E.; Arnaud, P.; L’Hermite, P.; Tolsa, M. A 50-Year Analysis of Hydrological Trends and Processes in a Mediterranean Catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2699–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedda, M.; Pirastru, M. Field Investigation and Modelling of Coupled Stream Discharge and Shallow Water-Table Dynamics in a Small Mediterranean Catchment (Sardinia). Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5423–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL-Based Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes in the Irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Noordman, E.J.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.P.; Allen, R.G. SEBAL Model with Remotely Sensed Data to Improve Water-Resources Management under Actual Field Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, C.; Cox, P.M.; Lenton, T.M. Contrasting Responses of a Simple Terrestrial Ecosystem Model to Global Change. Ecol. Model. 2000, 134, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minacapilli, M.; Agnese, C.; Blanda, F.; Cammalleri, C.; Ciraolo, G.; D’Urso, G.; Iovino, M.; Pumo, D.; Provenzano, G.; Rallo, G. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration of Mediterranean Perennial Crops by Means of Remote-Sensing Based Surface Energy Balance Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.; Irmak, A.; Trezza, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kjaersgaard, J. Satellite-Based ET Estimation in Agriculture Using SEBAL and METRIC. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4011–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Soppe, R.W.O.; Allen, R.G.; Thoreson, B.P.; de C. Teixeira, A.H. Thermal-Infrared Technology for Local and Regional Scale Irrigation Analyses in Horticultural Systems. In Proceedings of the Acta Horticulturae, Leuven, Belgium, 30 June 2008; International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS): Mildura, VIC, Australia, 2008; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Ciraolo, G.; D’Urso, G.; Kustas, W.P.; La Loggia, G.; Minacapilli, M. Applications of a Remote Sensing-Based Two-Source Energy Balance Algorithm for Mapping Surface Fluxes without in Situ Air Temperature Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, J.L.; Neale, C.M.U.; Prueger, J.H.; Kustas, W.P. Daily Evapotranspiration Estimates from Extrapolating Instantaneous Airborne Remote Sensing ET Values. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 27, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crago, R.D. Conservation and Variability of the Evaporative Fraction during the Daytime. J. Hydrol. 1996, 180, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, A.; Capodici, F.; Ciraolo, G.; Loggia, G.L.; Rallo, G. Assessing Daily Actual Evapotranspiration through Energy Balance: An Experiment to Evaluate the Selfpreservation Hypothesis with Acquisition Time. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XV, Dresden, Germany, 16 October 2013; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8887, p. 888718. [Google Scholar]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P. Upscaling of Evapotranspiration Fluxes from Instantaneous to Daytime Scales for Thermal Remote Sensing Applications. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trezza, R. Evapotranspiration Using a Satellite-Based Surface Energy Balance with Standardized Ground Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Utah State University, Logan, UT, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.D.; Hatfield, J.L.; Reginato, R.J.; Idso, S.B.; Pinter, P.J. Estimation of Daily Evapotranspiration from One Time-of-Day Measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 1983, 7, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lemeur, R. Evaluation of Daily Evapotranspiration Estimates from Instantaneous Measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 74, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, G.; Trotta, C.; Canfora, E.; Chu, H.; Christianson, D.; Cheah, Y.-W.; Poindexter, C.; Chen, J.; Elbashandy, A.; Humphrey, M.; et al. The FLUXNET2015 Dataset and the ONEFlux Processing Pipeline for Eddy Covariance Data. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C.; et al. Energy Balance Closure at FLUXNET Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foken, T. The Energy Balance Closure Problem: An Overview. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoy, P.C.; Mauder, M.; Foken, T.; Marcolla, B.; Boegh, E.; Ibrom, A.; Arain, M.A.; Arneth, A.; Aurela, M.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. A Data-Driven Analysis of Energy Balance Closure across FLUXNET Research Sites: The Role of Landscape Scale Heterogeneity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171–172, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueger, J.H.; Hatfield, J.L.; Parkin, T.B.; Kustas, W.P.; Hipps, L.E.; Neale, C.M.U.; MacPherson, J.I.; Eichinger, W.E.; Cooper, D.I. Tower and Aircraft Eddy Covariance Measurements of Water Vapor, Energy, and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes during SMACEX. J. Hydrometeors 2005, 6, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Saleous, N.E.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Privette, J.L.; Remer, L.; Roger, J.C.; Tanré, D. Atmospheric Correction of Visible to Middle-Infrared EOS-MODIS Data over Land Surfaces: Background, Operational Algorithm and Validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17131–17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of Landsat Thermal Imagery in Monitoring Evapotranspiration and Managing Water Resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentine, P.; Entekhabi, D.; Polcher, J. The Diurnal Behavior of Evaporative Fraction in the Soil–Vegetation–Atmospheric Boundary Layer Continuum. J. Hydrometeors 2011, 12, 1530–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Foken, T.; Wichura, B. Tools for Quality Assessment of Surface-Based Flux Measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1996, 78, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, G.N.; Tetzlaff, G.; Raabe, A. Inhomogeneity of the Land Surface and Problems in TheParameterization of Surface Fluxes in Natural Conditions. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1998, 60, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T.; Wimmer, F.; Mauder, M.; Thomas, C.; Liebethal, C. Some Aspects of the Energy Balance Closure Problem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4395–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masseroni, D.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Limitations and Improvements of the Energy Balance Closure with Reference to Experimental Data Measured over a Maize Field. Atmósfera 2014, 27, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brutsaert, W.; Sugita, M. Application of Self-Preservation in the Diurnal Evolution of the Surface Energy Budget to Determine Daily Evaporation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 18377–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L.; Unsworth, M.H. Principles of Environmental Physics: Plants, Animals, and the Atmosphere, 4th ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-12-386910-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Use of Remote Sensing for Evapotranspiration Monitoring over Land Surfaces. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Brutsaert, W. Daily Evaporation over a Region from Lower Boundary Layer Profiles Measured with Radiosondes. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Schmugge, T.J.; Anderson, M.C. Mapping surface energy fluxes with radiometric temperature. In Thermal Remote Sensing in Land Surface Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Volume 2004, pp. 205–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Evaluation of Soil and Vegetation Heat Flux Predictions Using a Simple Two-Source Model with Radiometric Temperatures for Partial Canopy Cover. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 94, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Neale, C.M.U.; Jackson, T.J. Utility of Remote Sensing–Based Two-Source Energy Balance Model under Low- and High-Vegetation Cover Conditions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Diak, G.R. Validation of GOES-Based Insolation Estimates Using Data from the U.S. Climate Reference Network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristóbal, J.; Anderson, M.C. Validation of a Meteosat Second Generation Solar Radiation Dataset over the Northeastern Iberian Peninsula. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Image | Acquisition Day (dd/mm/yyyy) | DOY | Platform | Acquisition Time (Scene Center) (hh:mm UTC) | Pass | Row | Cloud Cover (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8/3/2009 | 67 | LS5 | 9:52 | 193 | 32 | 0 |
| 2 | 11/5/2009 | 131 | LS5 | 9:53 | 193 | 32 | 2 |
| 3 | 19/6/2009 | 170 | LS5 | 10:00 | 194 | 32 | 0 |
| 4 | 21/7/2009 | 202 | LS5 | 10:01 | 194 | 32 | 0 |
| 5 | 30/7/2009 | 211 | LS5 | 9:55 | 193 | 32 | 0 |
| 6 | 6/8/2009 | 218 | LS5 | 10:01 | 194 | 32 | 0 |
| 7 | 15/8/2009 | 227 | LS5 | 9:55 | 193 | 32 | 0 |
| 8 | 22/8/2009 | 234 | LS5 | 10:01 | 194 | 32 | 0 |
| 9 | 31/8/2009 | 243 | LS5 | 9:55 | 193 | 32 | 4 |
| 10 | 7/9/2009 | 250 | LS5 | 10:01 | 194 | 32 | 0 |
| 11 | 2/10/2009 | 275 | LS5 | 9:56 | 193 | 32 | 14 |
| 12 | 28/4/2010 | 118 | LS5 | 9:56 | 193 | 32 | 7 |
| 13 | 17/7/2010 | 198 | LS5 | 9:56 | 193 | 32 | 0 |
| 14 | 6/11/2010 | 310 | LS5 | 9:55 | 193 | 32 | 1 |
| 15 | 10/8/2013 | 222 | LS8 | 10:07 | 193 | 32 | 6 |
| 16 | 29/10/2013 | 302 | LS8 | 10:07 | 193 | 32 | 10 |
| 17 | 10/6/2014 | 161 | LS8 | 10:05 | 193 | 32 | 1 |
| 18 | 28/7/2014 | 209 | LS8 | 10:05 | 193 | 32 | 2 |
| 19 | 14/9/2014 | 257 | LS8 | 10:06 | 193 | 32 | 8 |
| Year | DOY | CR at Near-Image Acquisition Time (At 10:00) | Slope of Linear Regression Equation of Diurnal CR (Zero Intercept) | Coefficient of Determination (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 67 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| 2009 | 131 | 1.13 | 1.05 | 0.73 |
| 2009 | 170 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.85 |
| 2009 | 202 | 1.18 | 1.1 | 0.84 |
| 2009 | 211 | 1.05 | 0.96 | 0.86 |
| 2009 | 218 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 0.8 |
| 2009 | 227 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.59 |
| 2009 | 234 | 1.04 | 0.96 | 0.81 |
| 2009 | 243 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.85 |
| 2009 | 250 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.87 |
| 2009 | 275 | 1.04 | 0.87 | 0.95 |
| 2010 | 118 | 1.04 | 1.05 | 0.91 |
| 2010 | 198 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 0.69 |
| 2010 | 310 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.92 |
| 2013 | 222 | 1.07 | 1.03 | 0.64 |
| 2013 | 302 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 0.96 |
| 2014 | 161 | 1.36 | 1.1 | 0.56 |
| 2014 | 209 | 0.87 | 1.11 | 0.78 |
| 2014 | 257 | 1.05 | 1.12 | 0.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awada, H.; Di Prima, S.; Sirca, C.; Giadrossich, F.; Marras, S.; Spano, D.; Pirastru, M. Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach. Forests 2021, 12, 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020189
Awada H, Di Prima S, Sirca C, Giadrossich F, Marras S, Spano D, Pirastru M. Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach. Forests. 2021; 12(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020189
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwada, Hassan, Simone Di Prima, Costantino Sirca, Filippo Giadrossich, Serena Marras, Donatella Spano, and Mario Pirastru. 2021. "Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach" Forests 12, no. 2: 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020189
APA StyleAwada, H., Di Prima, S., Sirca, C., Giadrossich, F., Marras, S., Spano, D., & Pirastru, M. (2021). Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach. Forests, 12(2), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12020189









