Genome-Wide Characterization and Evolutionary Analyses of Purple Acid Phosphatase (PAP) Gene Family with Their Expression Profiles in Response to Low Phosphorus Stresses in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions and Treatments
2.2. Determination of Root Morphology, Phosphorus Content and Acid Phosphatase Activity
2.3. Database Search for Moso Bamboo PAP Genes
2.4. Phylogenetic, Conserved Domain and Motif Recognition Analyses
2.5. Analysis of Regulatory Elements in the Promoter Regions of the PePAP Gene Family
2.6. RNA Extraction and qRT–PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
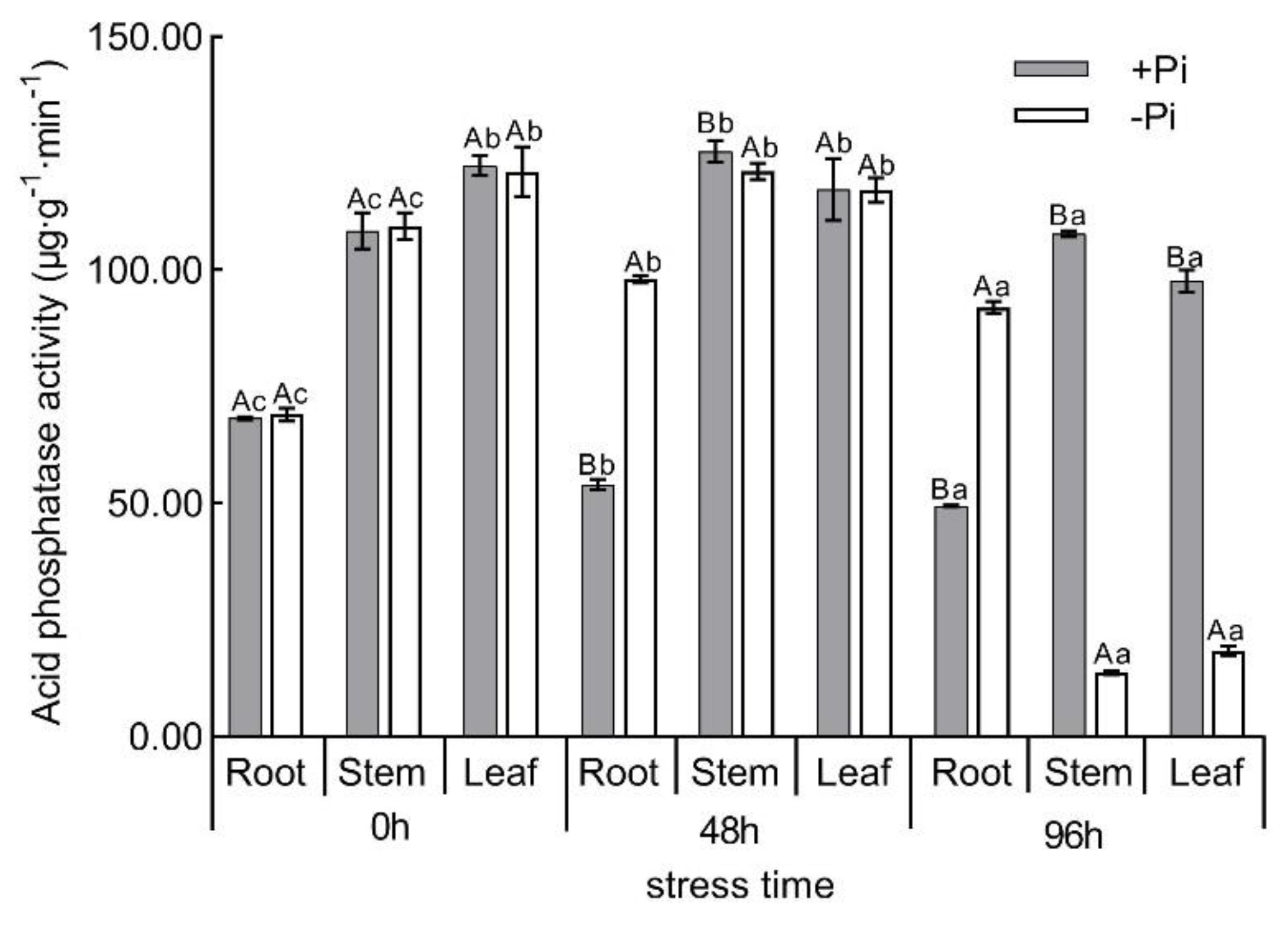
3.1. Physiological and Biochemical Analysis of Moso Bamboo under Low Phosphorus
3.2. Genome-Wide Characterization of PAP Genes in Moso Bamboo
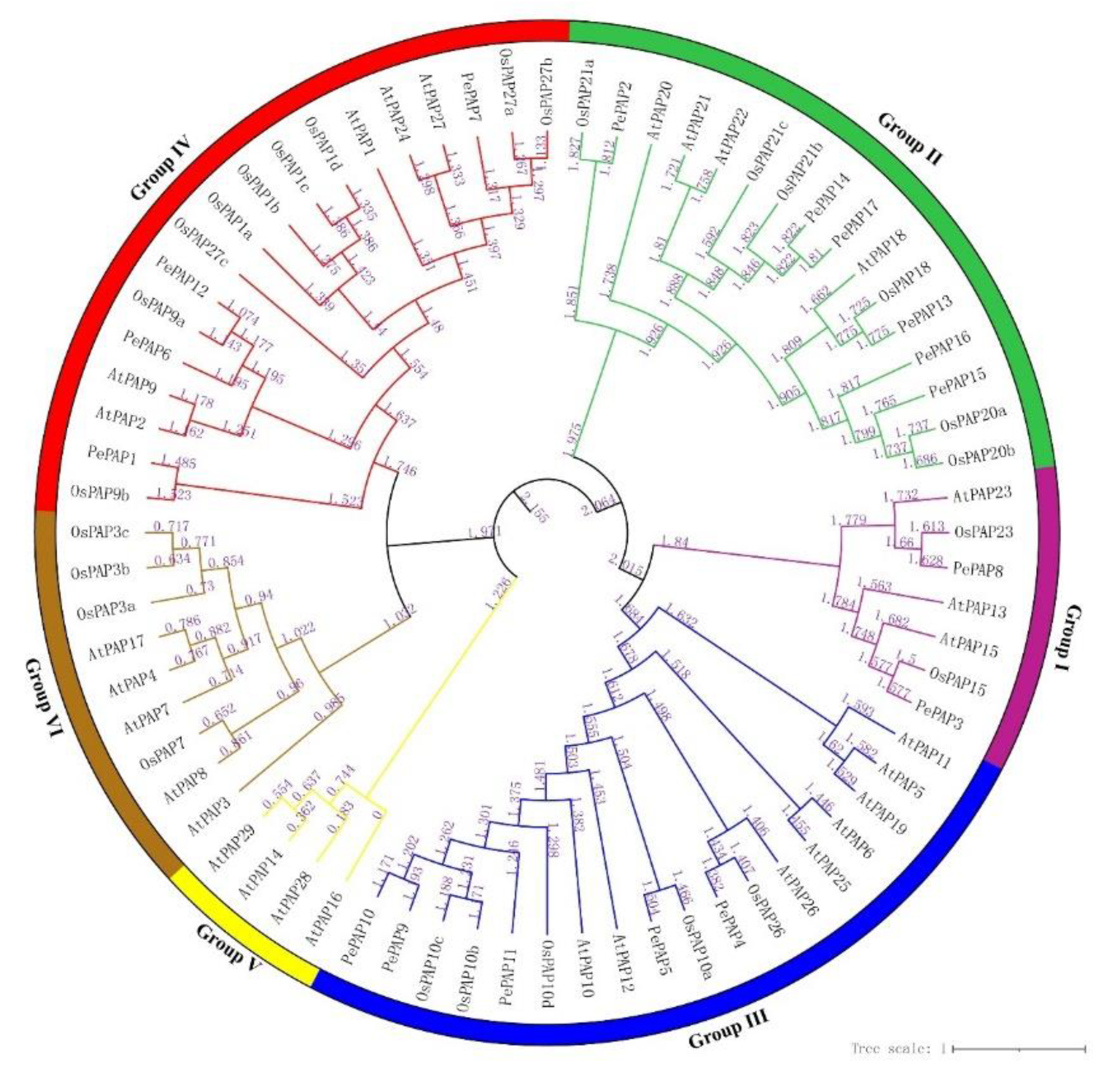
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Bamboo PAP Genes
3.4. The Conservation of PAP Motifs and Structure In Moso Bamboo PAP Proteins
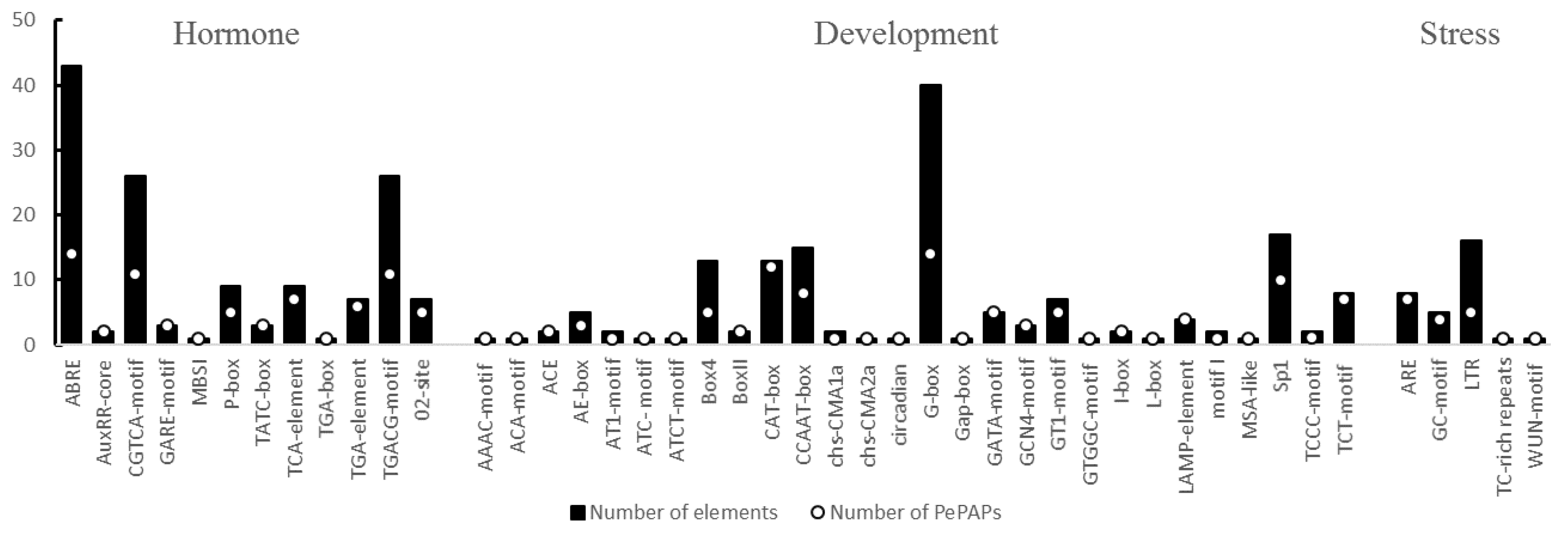
3.5. Characterization of Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Regions of PePAPs
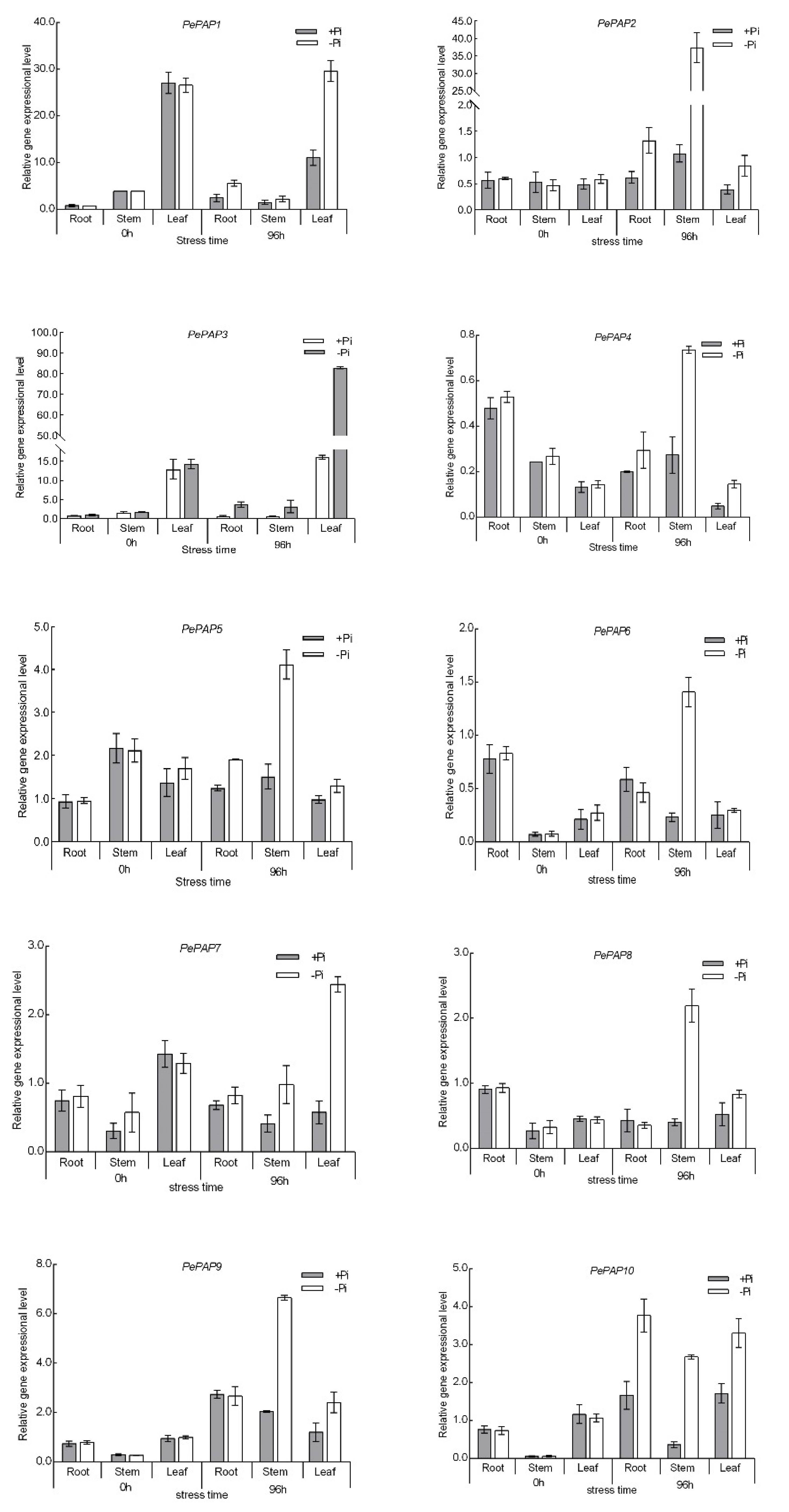
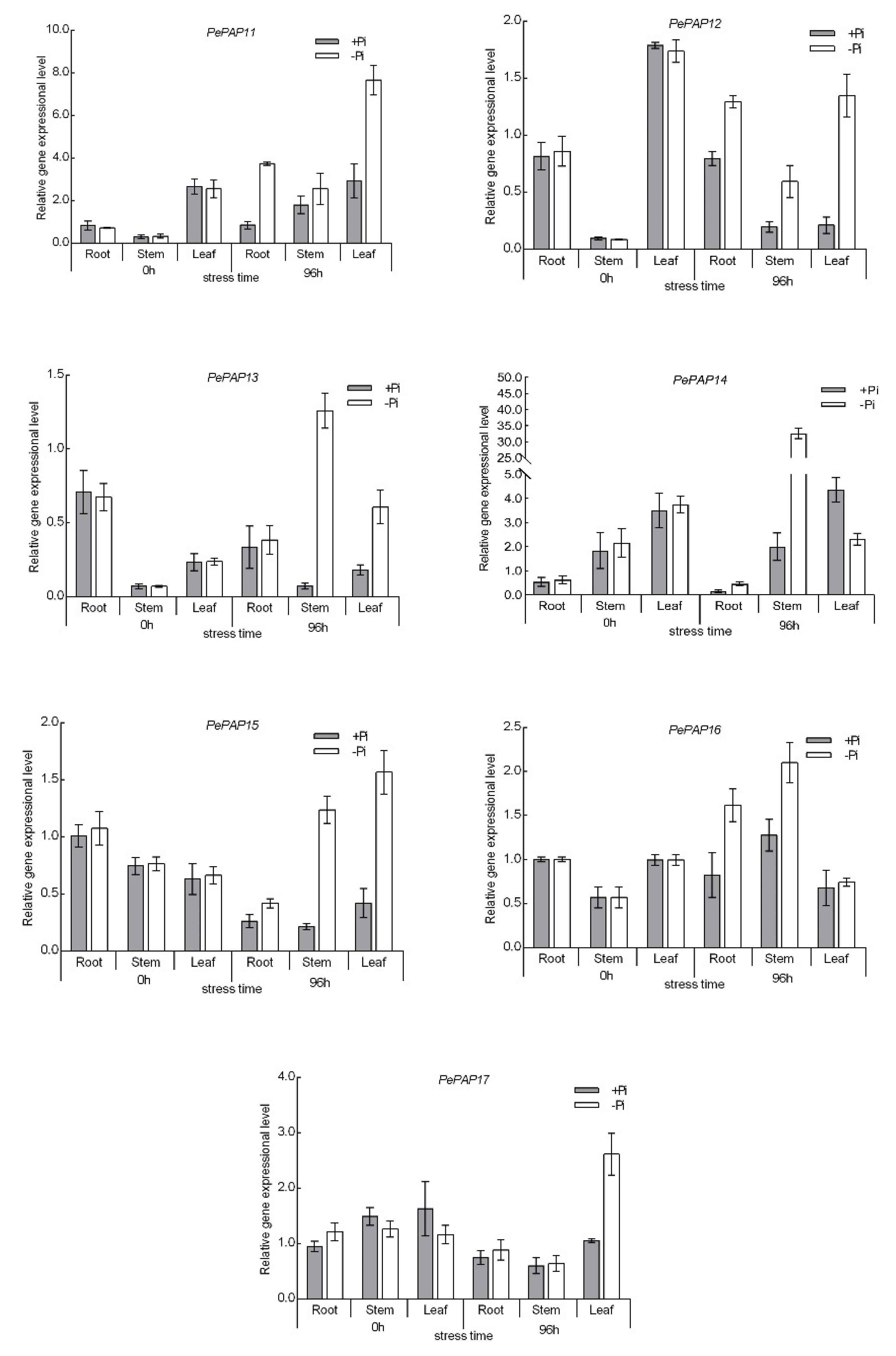
3.6. Expression Pattern of PePAP Genes in Moso Bamboo under Low Phosphorus Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.T.; Li, Q.Z.; Lou, S.T.; Yang, Y.; Peng, L.F.; Lin, Z.Z.; Hu, Q.; Ma, L.Y. GSK3/shaggy-like kinase 1 ubiquitously regu-lates cell growth from A. to Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Plant Sci. 2019, 283, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Lou, S.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lin, C.; Ma, L. Genome-Wide Characterization and Gene Expression Analyses of GATA Transcription Factors in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, Y.Z.; Fang, L.; Yu, L.Z.; Liang, H.Q.; Fang, Z.G.; Hui, P. Structural variability and differentiation of niches in the rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiome of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Feder, D.; McGeary, R.P.; Mitić, N.; Lonhienne, T.; Furtado, A.; Schulz, B.L.; Henry, R.J.; Schmidt, S.; Guddat, L.W.; Schenk, G. Structural elements that modulate the substrate specificity of plant purple acid phosphatases: Avenues for improved phosphorus acquisition in crops. Plant Sci. 2020, 294, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; Linhares, F.; Solano, R.; Martín, A.C.; Iglesias, J.; Leyva, A.; Paz-Ares, J. A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press 2001, 15, 2122–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abel, S.; Ticconi, C.A.; Delatorre, C.A. Phosphate sensing in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.D.; Carson, I.; Ying, S.; Ellis, K.; Plaxton, W.C. Eliminating the purple acid phosphatase At PAP 26 in A. thaliana delays leaf senescence and impairs phosphorus remobilization. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.H.U.; Tigabu, M.; Chen, H.; Farooq, T.H.; Ma, X.; Wu, P. Calcium-mediated adaptive responses to low phosphorus stress in Chinese fir. Trees 2020, 34, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, D.; Ma, G.; Jia, L.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; Tong, Z.; Lu, Y.-Q. Response of Chinese fir seedlings to low phosphorus stress and analysis of gene expression differences. J. For. Res. 2018, 30, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Z.; Xie, Y.; Dai, A.Y.; Liu, L.F.; Li, Z.C. Root and shoot traits responses to phosphorus deficiency and QTL analysis at seed-ling stage using introgression lines of rice. J. Genet. Genom. = Yi Chuan Xue Bao 2009, 36, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, L.; Gao, X.; Shi, Y.; Du, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G. Effects of different planting approaches and site conditions on aboveground carbon storage along a 10-year chronosequence after moso bamboo reforestation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, W.; Xu, F.; Shi, L.; Shou, H.; Wang, C. Purple acid phosphatase 10c encodes a major acid phosphatase that regulates plant growth under phosphate-deficient conditions in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4321–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, W.T.; Lee, S.W.; Baek, D.; Li, M.S.; Kim, D.H. The Burholderia pyrrocinia Purple Acid Phosphatase Pap9 Mediates Phosphate Acquisition in Plants. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Du, H.; Zhang, C. GmPAP12 Is Required for Nodule Development and Nitrogen Fixation Under Phosphorus Starvation in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Lu, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, C.; Shou, H. OsPAP26 Encodes a Major Purple Acid Phosphatase and Regulates Phosphate Remobilization in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Hurley, B.A.; Plaxton, W.C. Feeding hungry plants: The role of purple acid phosphatases in phosphate nutrition. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jersey, J.D.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Fan, H.K.; Gary, S.; Luke, G.; Hamilton, S. Mammalian-like Purple Acid Phosphatases in Plants. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2006, 22, 263–264. [Google Scholar]
- The Role of Intracellular and Secreted Purple Acid Phosphatases in Plant Phosphorus Scavenging and Recycling; Plaxton, W.C.; Lambers, H. (Eds.) John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 265–287. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, G.; Römheld, V. Root excretion of carboxylic acids and protons in phosphorus-deficient plants. Plant Soil 1999, 211, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Tian, J.; Lam, H.-M.; Lim, B.L.; Yan, X.; Liao, H. Biochemical and Molecular Characterization of PvPAP3, a Novel Purple Acid Phosphatase Isolated from Common Bean Enhancing Extracellular ATP Utilization. Plant Physiol. 2009, 152, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olczak, M.; Morawiecka, B.; Watorek, W. Plant purple acid phosphatases—Genes, structures and biological function. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Vecchio, H.A.; Ying, S.; Park, J.; Knowles, V.L.; Kanno, S.; Tanoi, K.; She, Y.-M.; Plaxton, W.C. The cell wall-targeted purple acid phosphatase AtPAP25 is critical for acclimation of A. thaliana to nutritional phosphorus deprivation. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 80, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Regierer, B.; Kossmann, J.; Frossard, E.; Amrhein, N.; Bucher, M. Differential Expression of Three Purple Acid Phosphatases from Potato. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, X.Q.; Liu, D. Comparative genetic analysis of A. purple acid phosphatases AtPAP10, AtPAP12, and AtPAP26 provides new insights into their roles in plant adaptation to phosphate deprivation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Tian, J.; Li, K.; Shou, H. Identification of rice purple acid phosphatases related to phosphate starvation signalling. Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gui, S.; Yang, T.; Walk, T.; Wang, X.; Liao, H. Identification of soybean purple acid phosphatase genes and their expression responses to phosphorus availability and symbiosis. Ann. Bot. 2011, 109, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Suen, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Carrie, C.; Whelan, J.; Ward, J.L.; Hawkins, N.D.; Jiang, L.; Lim, B.L. A dual-targeted purple acid phosphatase in A. thaliana moderates carbon metabolism and its overexpression leads to faster plant growth and higher seed yield. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Gruszewski, H.A.; Chevone, B.I.; Nessler, C.L. An A. Purple Acid Phosphatase with Phytase Activity Increases Foliar Ascorbate. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sridhar, R.; Sophia, L.S.; Bernhard, B.; Balakrishnan, P. Purple Acid Phosphatase5 is required for maintaining basal resistance against Pseudomonas syringae in A. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Baskar, V.; Dhivya, S.; Sathishkumar, R. Genome-wide analysis of purple acid phosphatase (PAP) family proteins in Jatropha curcas L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 123, 648–656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, G.J.; Wen, X.P. Cloning and expression pattern analysis of ectomycorrhizal purple acid phosphatase gene in Pinus massoniana Lamb. For. Res. Beijing 2016, 29, 797–806. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Cai, S.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, C.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals the crucial biological pathways involved in cold response in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Tree Physiol. 2019, 40, 538–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Gao, Z.; Lu, H.; Hu, T.; Yao, N.; Liu, K.; et al. The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozano, R.; Hamblin, M.T.; Prochnik, S.; Jannink, J.L. Identification and distribution of the NBS-LRR gene family in the Cassava genome. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, A.-Y.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.-C. GSDS: A gene structure display server. Hereditas 2007, 29, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Wu, R.H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Lu, C.F. Genome-wide identification and characterization of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase family genes in moso bamboo and functional analysis of PeUGDH4 in hemicellulose synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, Q.; Tian, J.; Liang, C. Association of extracellular dNTP utilization with a GmPAP1-like protein identified in cell wall proteomic analysis of soybean roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Bai, Y.; Lei, X.; Pei, D. Genome-Wide Identification of WOX Gene Family and Expression Analysis during Rejuvenational Rhizogenesis in Walnut (Juglans regia L.). Forests 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta c (t)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.N.; Chen, M.H.; Liang, C.Y.; Xue, Y.B.; Lin, S.L.; Tian, J. Characterization of Purple Acid Phosphatase Family and Functional Analysis of GmPAP7a / 7b Involved in Extracellular ATP Utilization in Soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wang, F.; Fan, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, W. Identification of Tea Plant Purple Acid Phosphatase Genes and Their Expression Responses to Excess Iron. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Yan, G.; Zhang, C. GmPAP4, a novel purple acid phosphatase gene isolated from soybean (Glycine max), enhanced extracellular phytate utilization in A. thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, H. A purple acid phosphatase, GmPAP33, participates in arbuscule degeneration during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in soybean. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, R.; Chan, K.-H.; Yeung, E.; Lim, B.L. Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of AtPAP15, a Purple Acid Phosphatase with Phytase Activity, in A. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dionisio, G.; Madsen, C.K.; Holm, P.B.; Welinder, K.G.; Jørgensen, M.; Stoger, E.; Arcalis, E.; Brinch-Pedersen, H. Cloning and Characterization of Purple Acid Phosphatase Phytases from Wheat, Barley, Maize, and Rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhadouria, J.; Singh, A.P.; Mehra, P.; Verma, L.; Srivastawa, R.; Parida, S.K.; Giri, J. Identification of Purple Acid Phosphatases in Chickpea and Potential Roles of CaPAP7 in Seed Phytate Accumulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajat, S.; Akash, P.; Parida, A.; Kumar, C.P.; Rahul, K. Identification, structure analysis, and transcript profiling of purple acid phosphatases under Pi deficiency in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and its wild relatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2020, 165, 2253–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Föhse, D.; Claassen, N.; Jungk, A. Phosphorus efficiency of plants. Plant Soil 1991, 132, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghinoni, I.; Barber, S.A. Phosphorus Influx and Growth Characteristics of Corn Roots as Influenced by Phosphorus Supply 1. Agron. J. 1980, 72, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.; Mackay, A. Root growth and phosphorus and potassium uptake by two corn genotypes in the field. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1986, 10, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doris, F.; Claassen, N.; Jungk, A. Phosphorus efficiency of plants: I. External and internal P requirement and P uptake efficiency of different plant species. Plant Soil 1988, 110, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dinkelaker, B.; Romheld, V.; Marschner, H. Citric acid excretion and precipitation of calcium citrate in the rhizosphere of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Plant Cell Environ. 1989, 12, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, J.W.; Becquer, A.; Haling, R.E.; Simpson, R.J.; Flavel, R.J.; Guppy, C.N. Intrinsic root morphology determines the phosphorus acquisition efficiency of five annual pasture legumes irrespective of mycorrhizal colonisation. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 48, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde-Stone, C.; Allan, D.L. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Qiu, W.; Gao, W.; Tyerman, S.D.; Shou, H.; Wang, C. OsPAP10c, a novel secreted acid phosphatase in rice, plays an important role in the utilization of external organic phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Liao, H.; Wang, X. The purple acid phosphatase GmPAP21 enhances internal phosphorus utilization and possibly plays a role in symbiosis with rhizobia in soybean. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 159, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-Y.F.; Shao, G.; Lam, H.-M. Ectopic expression of GmPAP3 alleviates oxidative damage caused by salinity and osmotic stresses. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Wong, F.-L.; Phang, T.-H.; Cheung, M.-Y.; Li, W.-Y.F.; Shao, G.; Yan, X.; Lam, H.-M. GmPAP3, a novel purple acid phosphatase-like gene in soybean induced by NaCl stress but not phosphorus deficiency. Gene 2003, 318, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliécer, G.M.; Aida-Odette, A.V.; Chávez, M.R.A.; Stefan, D.F.; Liliana, A.H.; Cei, A.G.; Sawers, R.J.H. The maize (Zea mays ssp. mays var. B73) genome encodes 33 members of the purple acid phosphatase family. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.F.; Qian, W.Q.; Lu, X.Z.; Li, D.P.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.F.; Wang, D.W. Expression Patterns of Purple Acid Phosphatase Genesin A. Organs and Functional Analysis of AtPAP23 Predominantly Transcribed in Flower. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Name | Gene ID | Location | ORF Length (bp) | Size (aa) | MW (kDa) | PI | Predicted Location(s) | Phylogenetic Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PePAP1 | PH02Gene03873.t1 | 64125824–64134183 (+strand) | 1887 | 628 | 68.89 | 6.63 | Nucleus | IV |
| PePAP2 | PH02Gene06180.t2 | 41970818–41973326 (+strand) | 1638 | 545 | 60.43 | 6.76 | Nucleus | II |
| PePAP3 | PH02Gene08370.t1 | 100943784–100947526 (−strand) | 1626 | 541 | 60.50 | 5.72 | Cell wall, Nucleus | I |
| PePAP4 | PH02Gene13885.t1 | 36547136–36557904 (+strand) | 1431 | 476 | 55.33 | 7.04 | Extracellular | III |
| PePAP5 | PH02Gene17860.t1 | 61935055–61946690 (−strand) | 1404 | 467 | 53.10 | 6.85 | Extracellular | III |
| PePAP6 | PH02Gene18076.t1 | 61150761–61154907 (+strand) | 1968 | 655 | 74.15 | 6.03 | Cell wall, Nucleus | IV |
| PePAP7 | PH02Gene19604.t1 | 10147974–10154225 (+strand) | 1854 | 617 | 68.93 | 6.55 | Cell wall, Nucleus | IV |
| PePAP8 | PH02Gene21481.t4 | 86205603–86209154 (−strand) | 1863 | 620 | 68.38 | 6.26 | Nucleus | I |
| PePAP9 | PH02Gene27343.t1 | 49726678–49738431 (−strand) | 1383 | 460 | 52.43 | 6.51 | Extracellular | III |
| PePAP10 | PH02Gene27344.t1 | 49720108–49723291 (−strand) | 1383 | 460 | 52.48 | 6.08 | Extracellular | III |
| PePAP11 | PH02Gene27346.t1 | 49685388–49688197 (−strand) | 1452 | 483 | 54.56 | 6.38 | Extracellular | III |
| PePAP12 | PH02Gene28188.t1 | 24090526–24094241 (−strand) | 1953 | 650 | 73.66 | 6.79 | Cell wall, Nucleus | IV |
| PePAP13 | PH02Gene29678.t1 | 19498663–19503808 (−strand) | 2322 | 773 | 87.83 | 6.59 | Chloroplast, Nucleus | II |
| PePAP14 | PH02Gene33883.t3 | 32855977–32859136 (−strand) | 1809 | 602 | 67.37 | 7.76 | Nucleus | II |
| PePAP15 | PH02Gene33886.t1 | 32922514–32926606 (+strand) | 1329 | 443 | 48.00 | 5.62 | Cell wall, Nucleus | II |
| PePAP16 | PH02Gene42583.t1 | 4108516–4112174 (+strand) | 1374 | 457 | 50.12 | 5.16 | Cell wall, Nucleus | II |
| PePAP17 | PH02Gene48530.t1 | 5657804–5664682 (−strand) | 1587 | 528 | 59.56 | 6.52 | Cell wall, Nucleus | II |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, X. Genome-Wide Characterization and Evolutionary Analyses of Purple Acid Phosphatase (PAP) Gene Family with Their Expression Profiles in Response to Low Phosphorus Stresses in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Forests 2021, 12, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030326
Zhou M, Chen W, Zhao M, Li Y, Li M, Hu X. Genome-Wide Characterization and Evolutionary Analyses of Purple Acid Phosphatase (PAP) Gene Family with Their Expression Profiles in Response to Low Phosphorus Stresses in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Forests. 2021; 12(3):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030326
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Mengyan, Wanting Chen, Mingzhen Zhao, Yachao Li, Ming Li, and Xia Hu. 2021. "Genome-Wide Characterization and Evolutionary Analyses of Purple Acid Phosphatase (PAP) Gene Family with Their Expression Profiles in Response to Low Phosphorus Stresses in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis)" Forests 12, no. 3: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030326
APA StyleZhou, M., Chen, W., Zhao, M., Li, Y., Li, M., & Hu, X. (2021). Genome-Wide Characterization and Evolutionary Analyses of Purple Acid Phosphatase (PAP) Gene Family with Their Expression Profiles in Response to Low Phosphorus Stresses in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Forests, 12(3), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030326




