Drought Stress Can Induce the Pathogenicity of Cryptostroma corticale, the Causal Agent of Sooty Bark Disease of Sycamore Maple
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
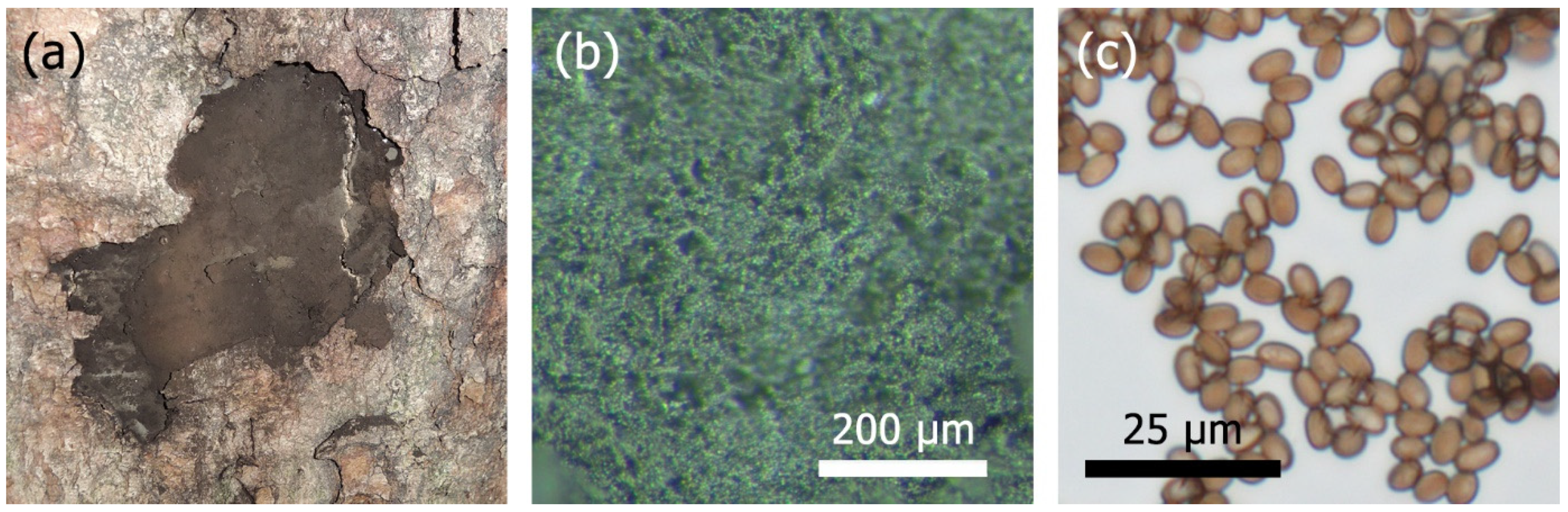
2.1. Identification
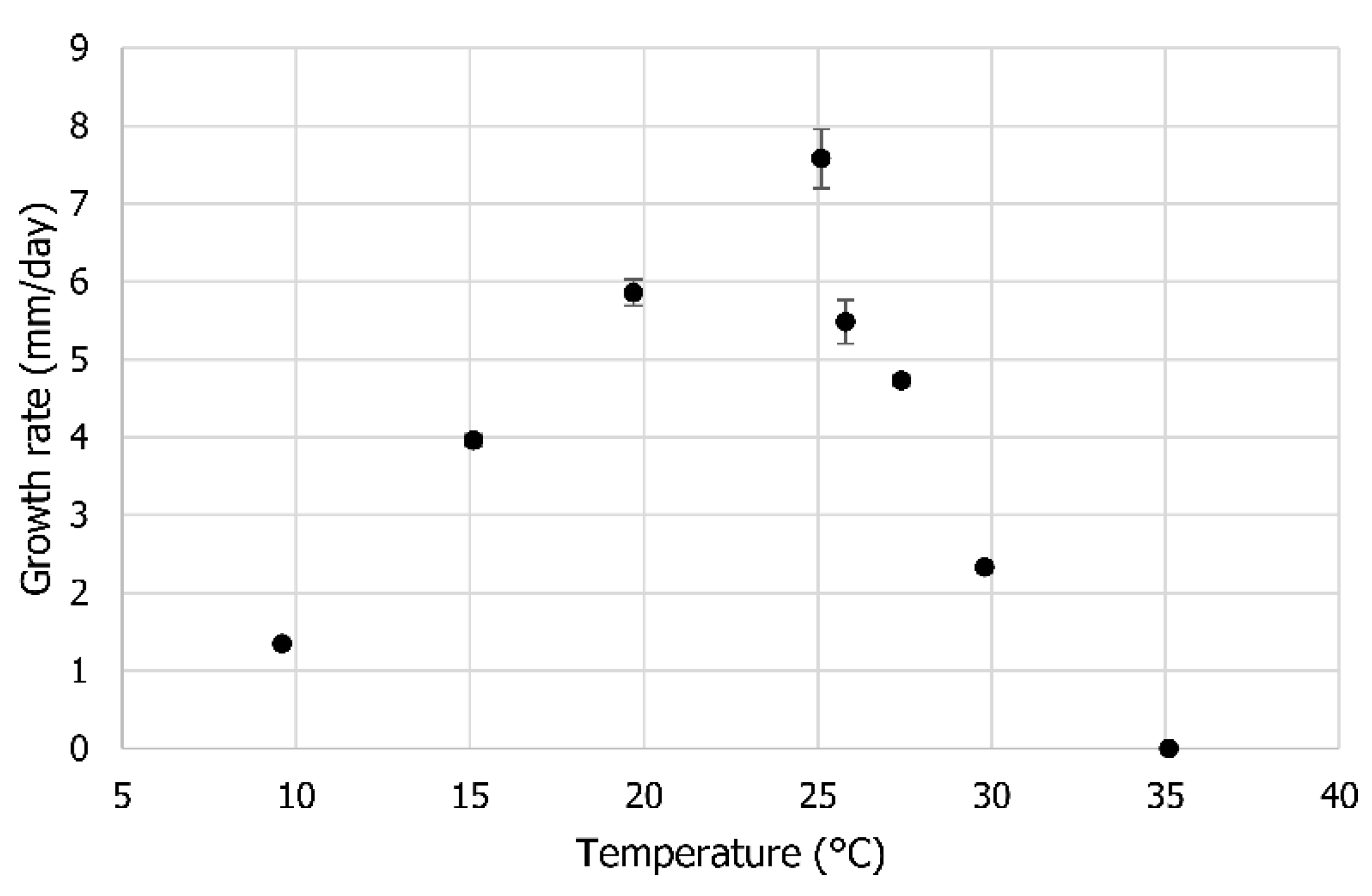
2.2. Optimum Temperature
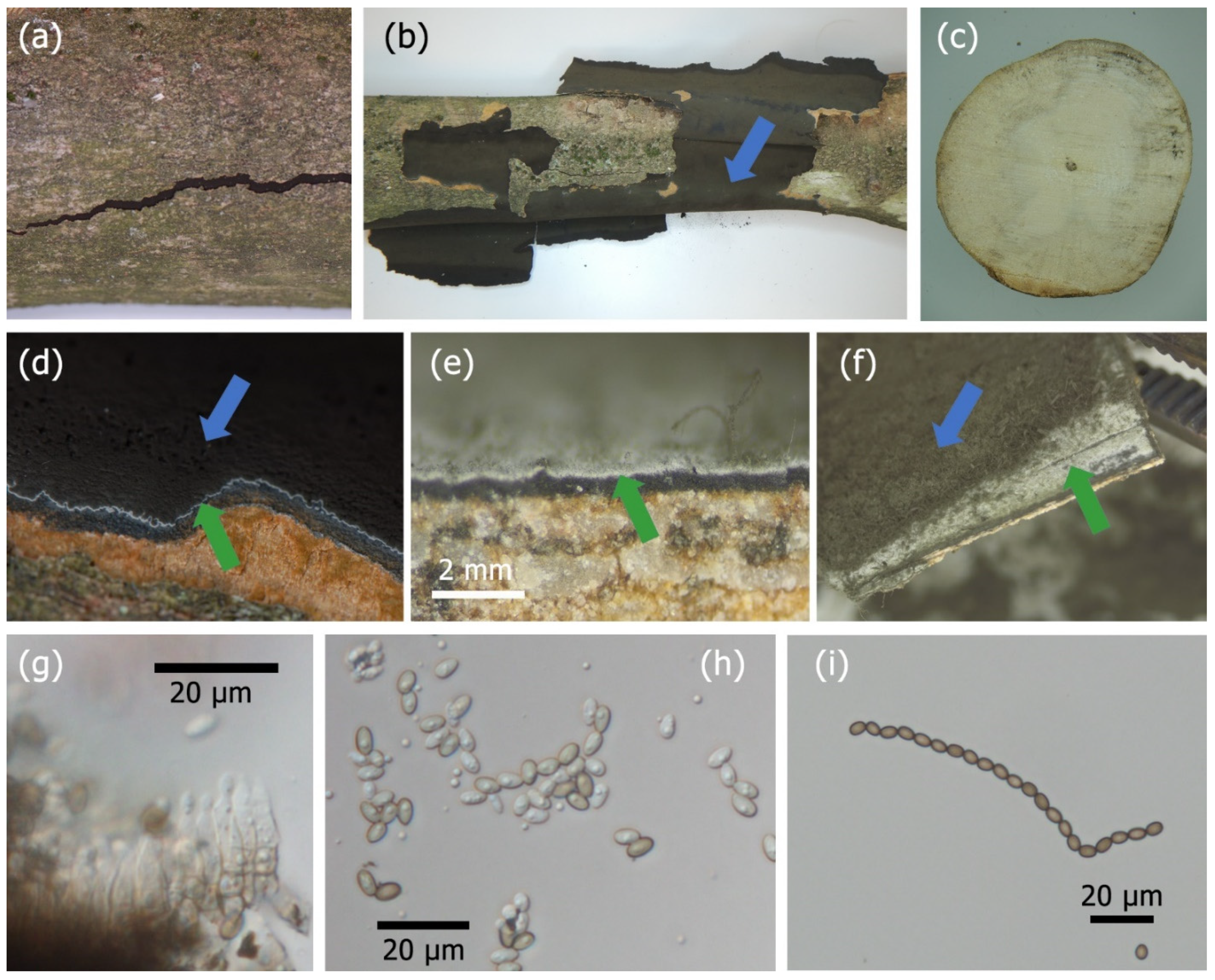
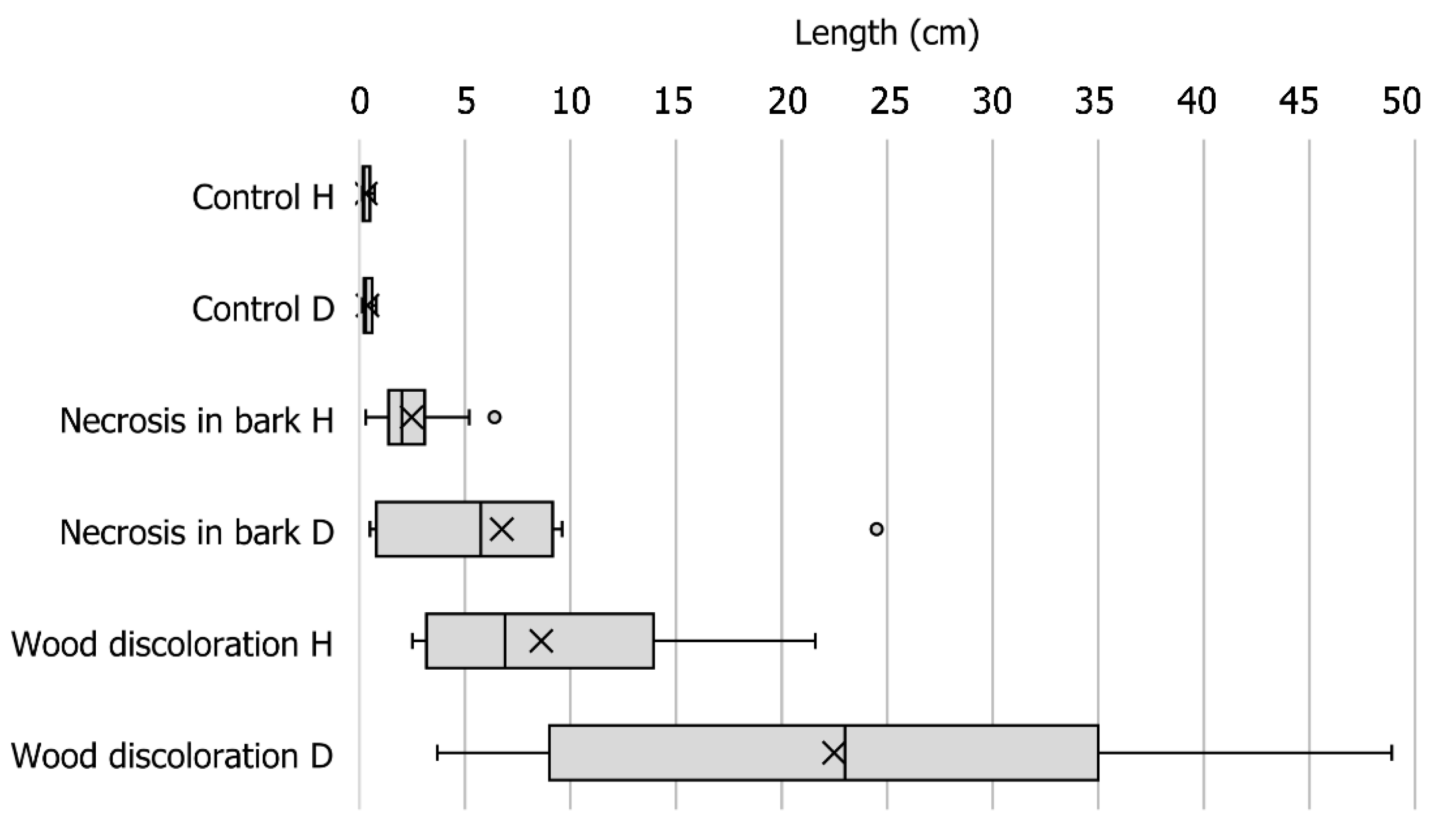
2.3. Pathogenicity Tests
2.4. Mass Loss of Wood
3. Results
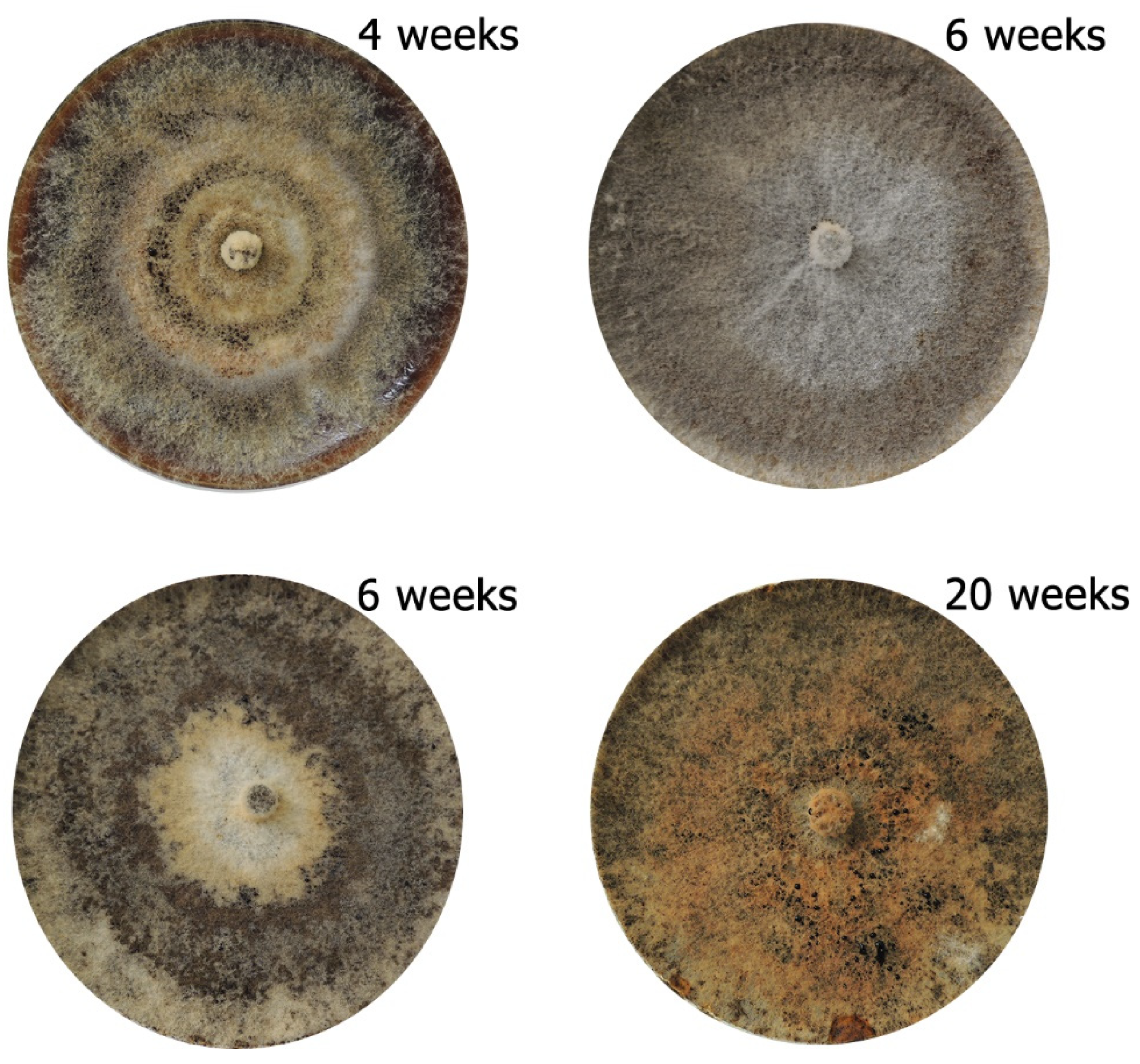
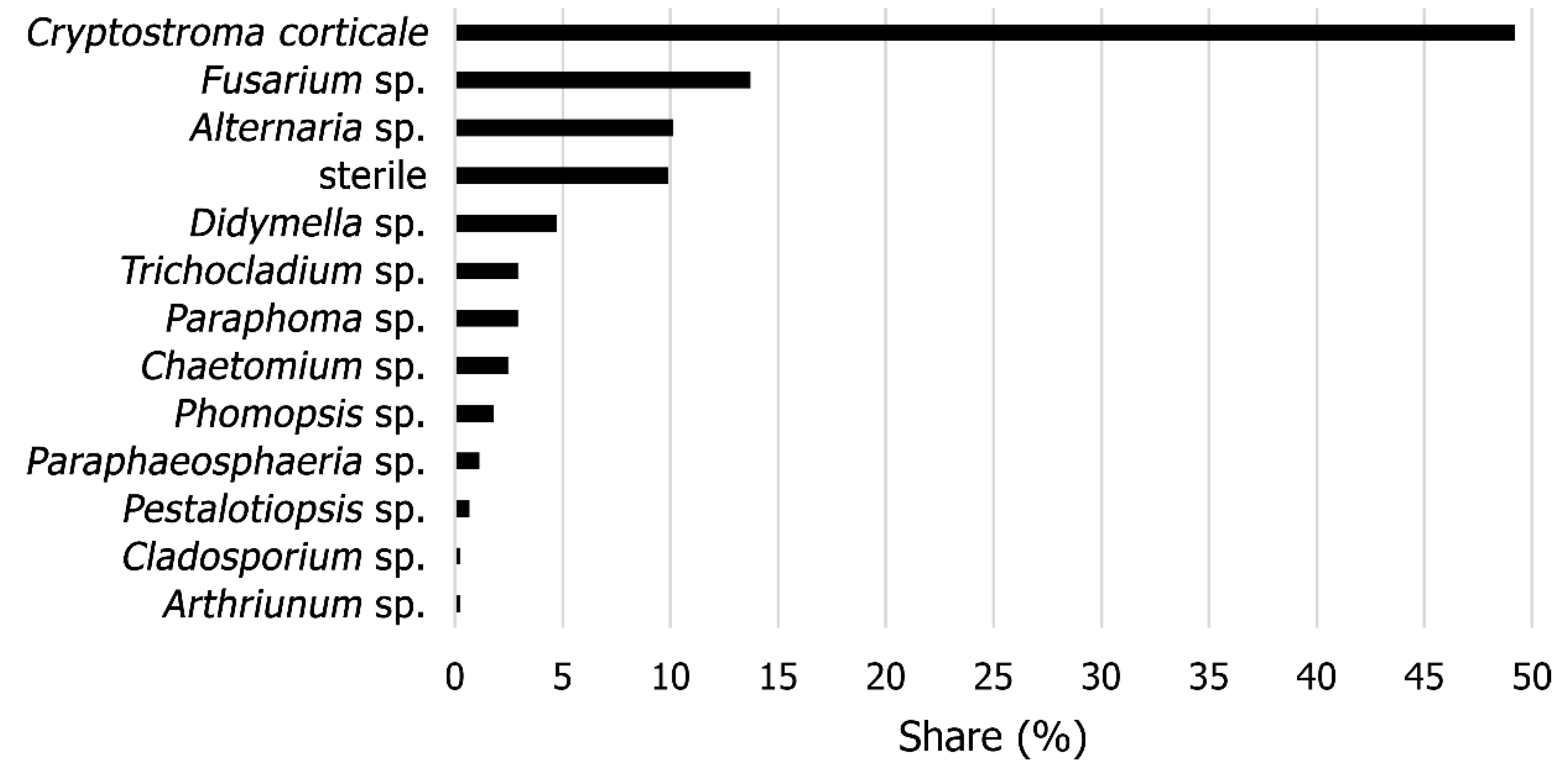
3.1. Identification
3.2. Optimum Temperature
3.3. Pathogenicity Tests
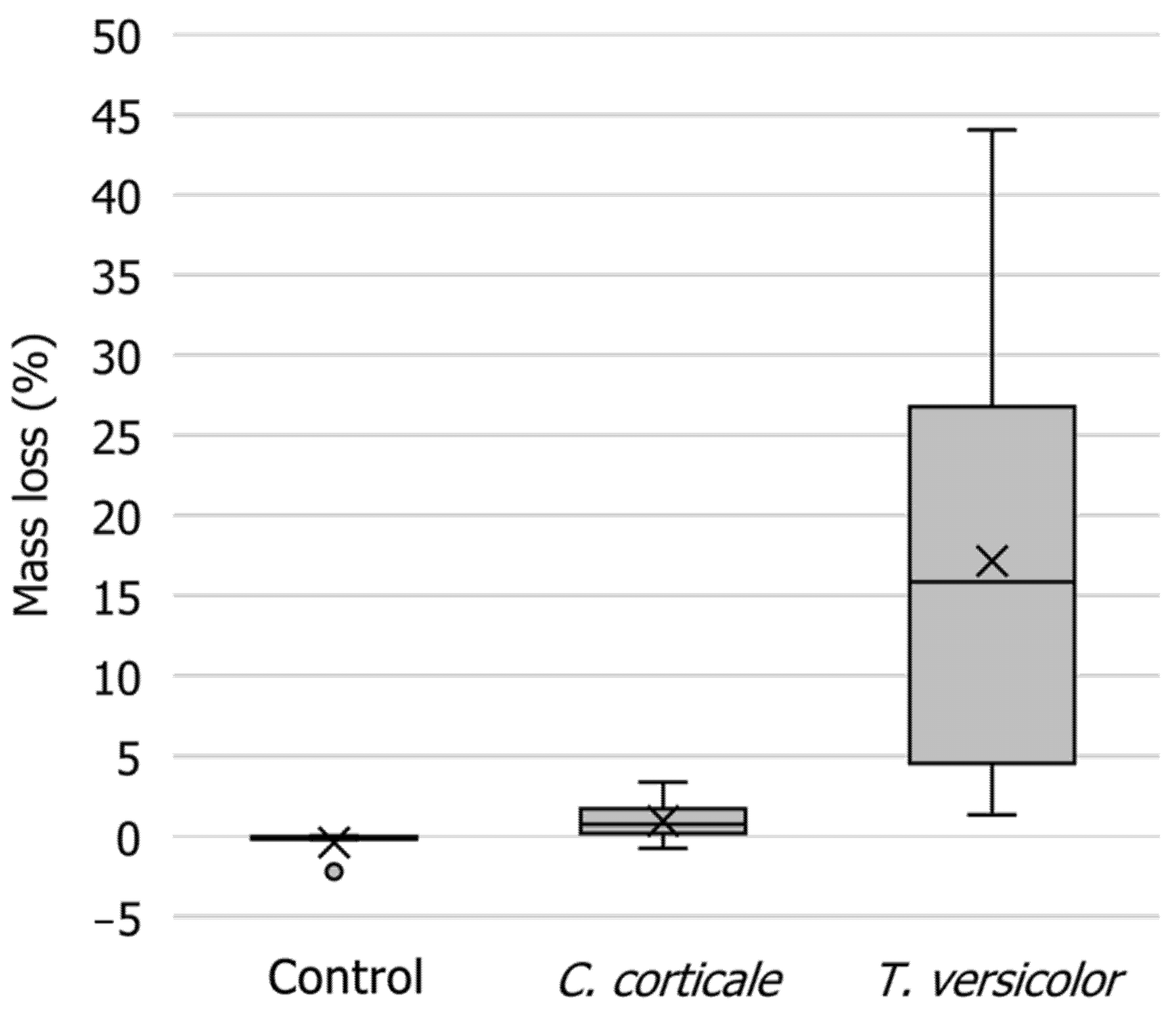
3.4. Mass Loss of Wood
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification
4.2. Optimum Temperature
4.3. Pathogenicity Tests
4.4. Mass Loss of Wood
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregory, P.H.; Waller, S. Cryptostroma corticale and sooty bark disease of sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus). Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1951, 34, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goree, H. Occurrence of Cryptostroma corticale in northwestern United States. Plant Dis. Rep. 1969, 53, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Bevercombe, G.P.; Rayner, A.D.M. Population structure of Cryptostroma corticate, the causal fungus of sooty bark disease of sycamore. Plant Pathol. 1984, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPPO. EPPO Global Database. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/ (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- NPPO. Quick Scan Number: QS. Myc 417, Cryptostroma corticale. Available online: https://pra.eppo.int/getfile/d67aa42f-b317-4a89-97e3-9b14aaf42408 (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- OWSF. Observatoire Wallon de la Sante des Forets. La News de l’OWSF (Avril 2019). Available online: http://owsf.environnement.wallonie.be/fr/26-04-2019-owsf-news-avril-2019.html?IDC=5792&IDD=6073 (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Robeck, P. Die Russrindenkrankheit (Cryptostroma corticale) des Ahorns in Deutschland; GRIN Verlag: München, Germany, 2007; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Bork, K. Rußrindenkrankheit an Ahorn–Erstfund in Bayern. AZV Der Wald 2018, 20, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kelnarová, I.; Černý, K.; Zahradník, D.; Koukol, O. Widespread latent infection of Cryptostroma corticale in asymptomatic Acer pseudoplatanus as a risk for urban plantations. For. Pathol. 2017, 47, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukol, O.; Kelnarová, I.; Černý, K. Recent observations of sooty bark disease of sycamore maple in Prague (Czech Republic) and the phylogenetic placement of Cryptostroma corticale. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.L. Remarkable pathogens in 2004. Forstsch. Aktuell 2004, 32, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cech, T.L. Sooty bark disease endangers stands of Sycamore maple in Lower Austria. Forstsch. Aktuell 2019, 65, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira Longa, C.M.; Vai, N.; Maresi, G. Cryptostroma corticale in the northern Apennines (Italy). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2016, 55, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochard, B.; Crovadore, J.; Bovigny, P.Y.; Chablais, R.; Lefort, F. First reports of Cryptostroma corticale causing sooty bark disease in Acer sp. in Canton Geneva, Switzerland. New Dis. Rep. 2015, 31, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bencheva, S. First report of Cryptostroma corticale (Ellis & Everh.) P.H. Greg. & S. Waller on Acer platanoides L. in Bulgaria. Silva Balc. 2014, 15, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Abbey, S.D. The Morphology and Physiology of Cryptostroma corticale. Ph.D. Thesis, Loughborough University of Technology, Loughborough, UK, 1978; p. 177. [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson, S.J. Biology of Cryptostroma corticale and the sooty bark disease of sycamore. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science of the University of London, Berkshire, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, B. Cryptostroma corticale on Acer pseudoplatanus in Germany after the drought period of 2003. Mitt. Biol. Bundesanst. Land Forstw. 2006, 400, 161–162. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, M.; Klingelhöfer, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Sooty bark disease of maples: The risk for hypersensitivity pneumonitis by fungal spores not only for woodman. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brglez, A.; Piškur, B.; Ogris, N. Eutypella parasitica and other frequently isolated fungi in wood of dead branches of young sycamore maple (Acer pseudoplatanus) in Slovenia. Forests 2020, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcock, S.; Wheeler, B.E.J. Variability of Cryptostroma corticale, the causal fungus of sooty bark disease of sycamore. Plant Pathol. 1983, 32, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Bravery, F. A miniaturised wood-block test for the rapid evaluation of wood preservative fungicides. In Proceedings of the International Research Group on Wood Protection, Peebles, UK, 18–22 September 1978; pp. 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sutter, H.P. A new technique for screening fungicides for wood preservatives. Int. Biodeterior. 1987, 14, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Caswell, S.; Williams, G.R. Development of miniblock test method for rapid evaluation of preservative performance against Basidiomycete fungi. In Proceedings of the International Research Group on Wood Preservation, Kyoto, Japan, 20–24 May 1991; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson, S.; Wheeler, B.E.J. Effects of temperature, and water stress in sycamore, on growth of Cryptostroma corticale. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1981, 76, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P.M. (Eds.) Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Towey, J.W.; Sweany, H.C.; Huron, W.H. Severe bronchial asthma apparently due to fungus spores found in maple bark. J. Am. Med Assoc. 1932, 99, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, K.J.; Ohman, J.H. Cryptostroma corticale-allergen, plant pathogen, saprophyte. Phytopathology 1965, 55, 811–812. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, D.A.; Wenzel, F.J.; Lawton, B.R. Pneumonitis due to Cryptostroma corticale (Maple-Bark Disease). N. Engl. J. Med. 1966, 274, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, R.A.; Stretton, R.J. Lesions experimentally produced by fungi implicated in extrinsic allergic alveolitis. J. Hyg. 1974, 73, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CEN. EN 113. Wood Preservatives-Test Method for Determining the Protective Effectiveness against Wood Destroying Basidiomycetes-Determination of the Toxic Values; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2002; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, R.B.; Fisher, B.J.; Carpenter, T.A.; Hall, L.D. Water distribution in fungal lesions in the wood of sycamore, Acer pseudoplatanus, determined gravimetrically and using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. New Phytol. 1997, 135, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogris, N.; Brglez, A.; Piškur, B. Drought Stress Can Induce the Pathogenicity of Cryptostroma corticale, the Causal Agent of Sooty Bark Disease of Sycamore Maple. Forests 2021, 12, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030377
Ogris N, Brglez A, Piškur B. Drought Stress Can Induce the Pathogenicity of Cryptostroma corticale, the Causal Agent of Sooty Bark Disease of Sycamore Maple. Forests. 2021; 12(3):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030377
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgris, Nikica, Ana Brglez, and Barbara Piškur. 2021. "Drought Stress Can Induce the Pathogenicity of Cryptostroma corticale, the Causal Agent of Sooty Bark Disease of Sycamore Maple" Forests 12, no. 3: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030377
APA StyleOgris, N., Brglez, A., & Piškur, B. (2021). Drought Stress Can Induce the Pathogenicity of Cryptostroma corticale, the Causal Agent of Sooty Bark Disease of Sycamore Maple. Forests, 12(3), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030377






