Assessment of Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling the Spatial Distribution of Bark Beetle Infestation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
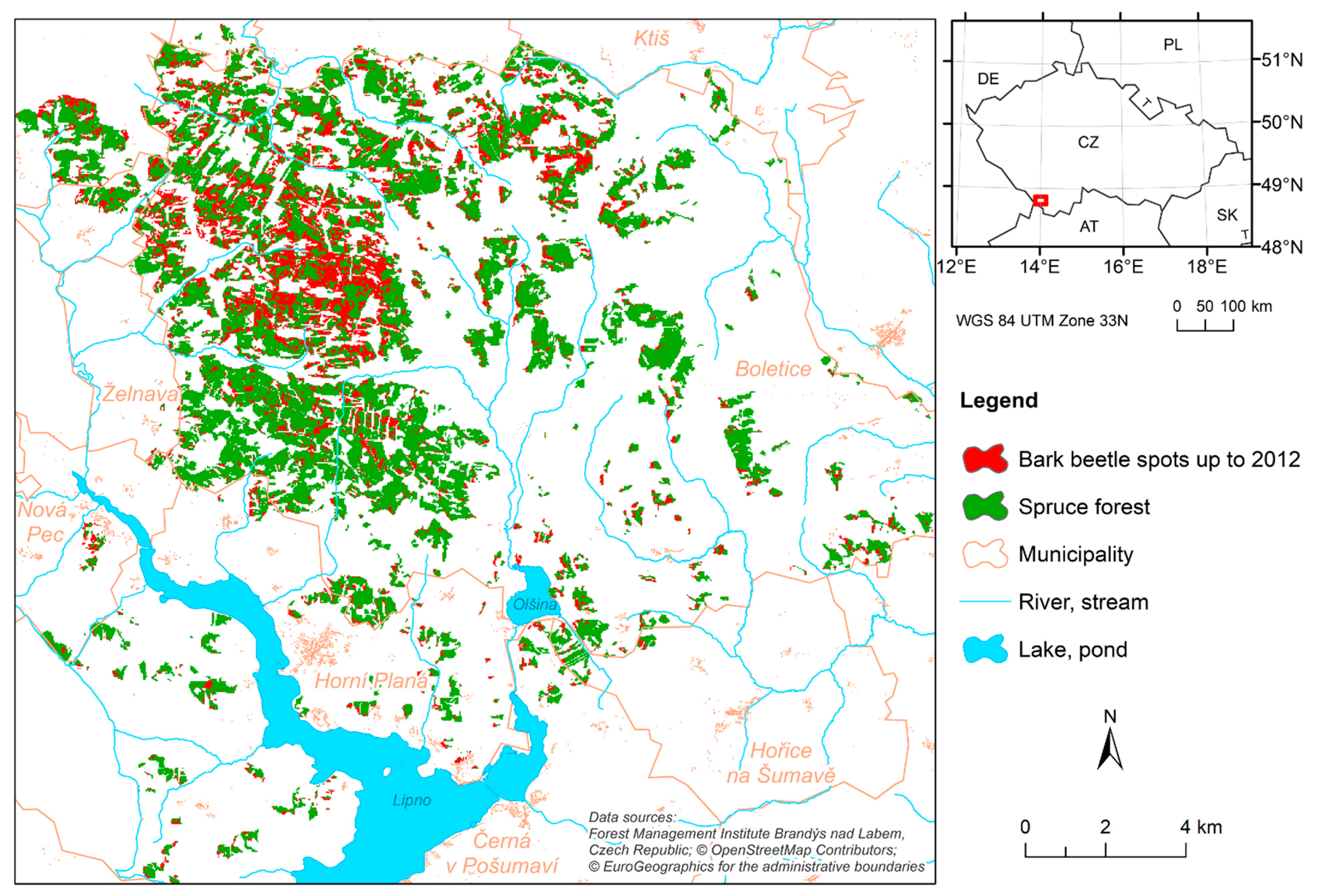
2.1. Study Area
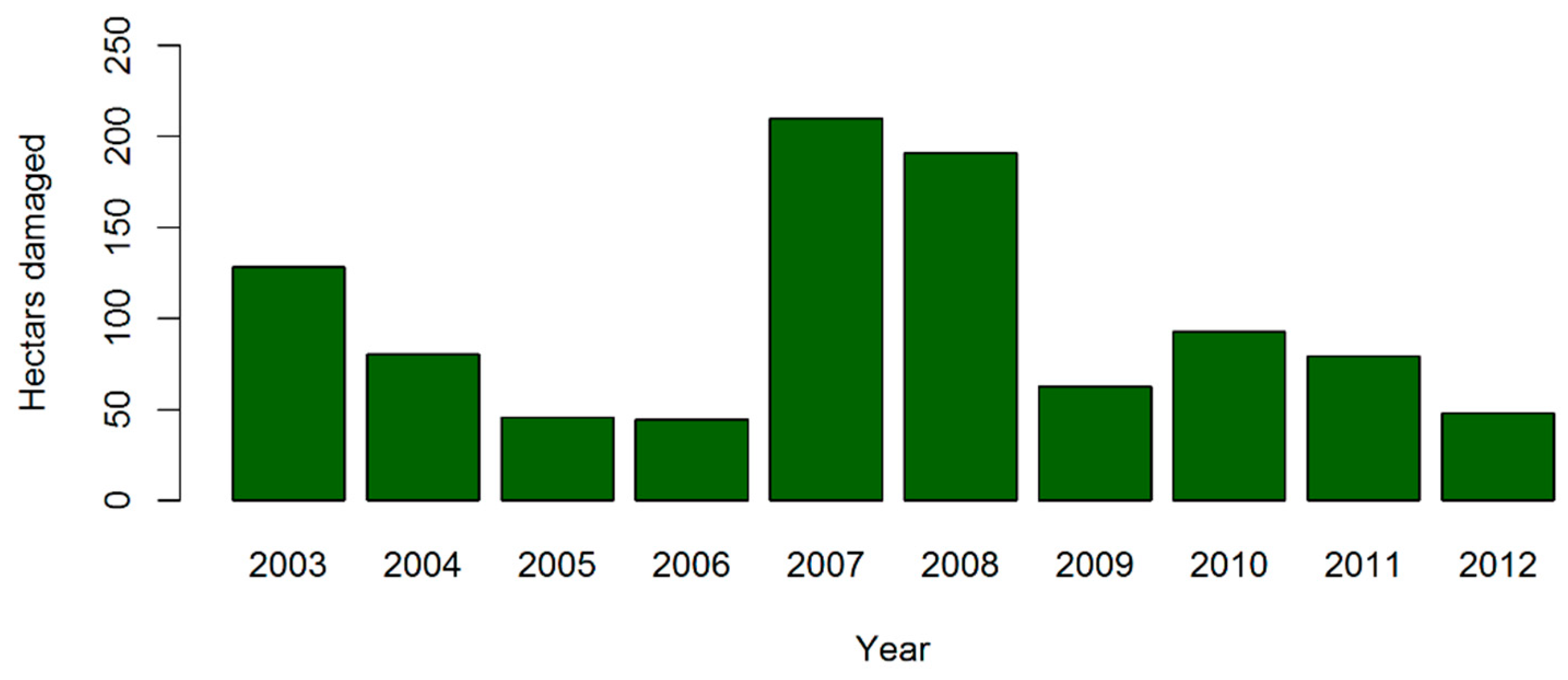
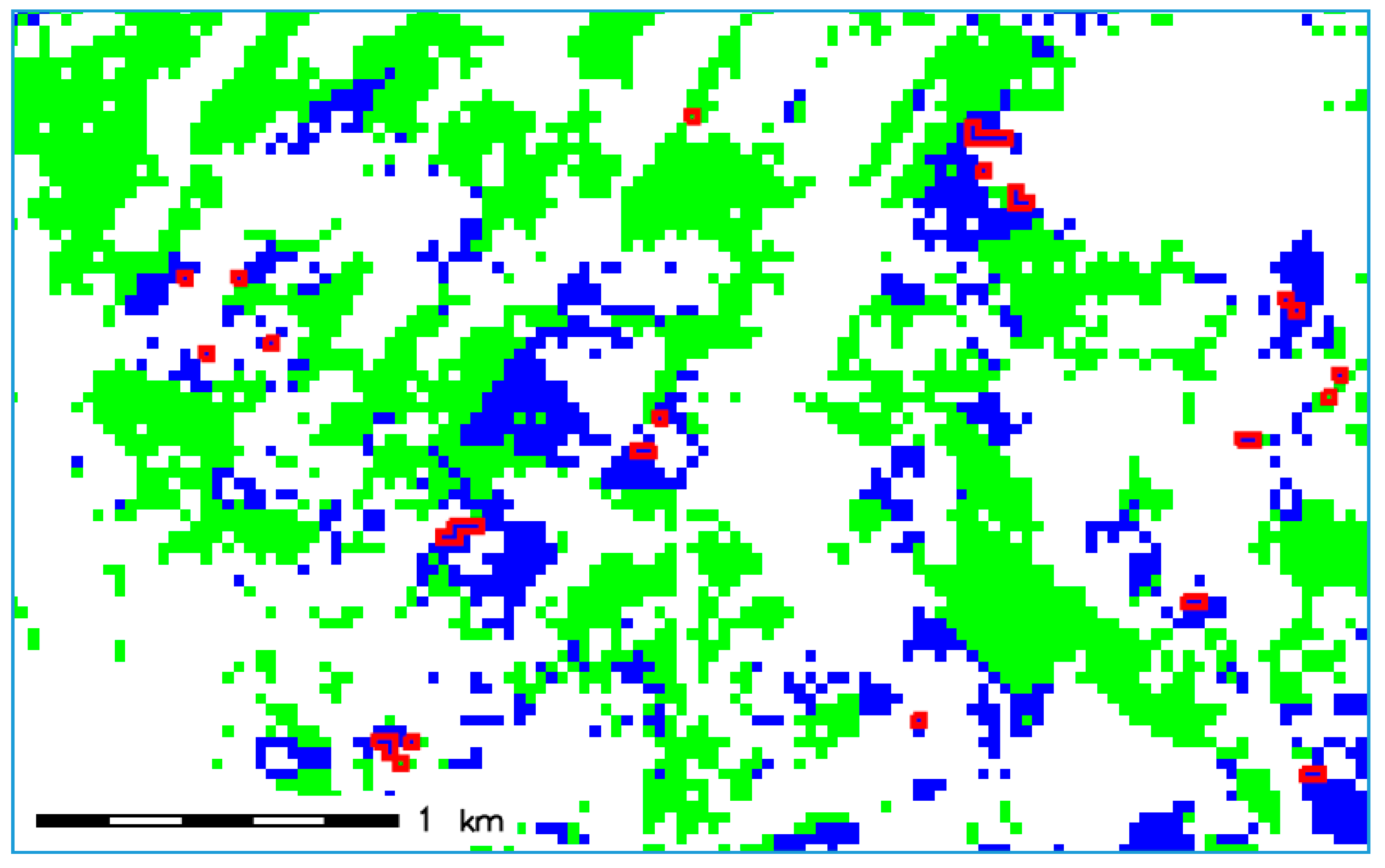
2.2. Input Data
2.3. Computer Simulations and Data Processing
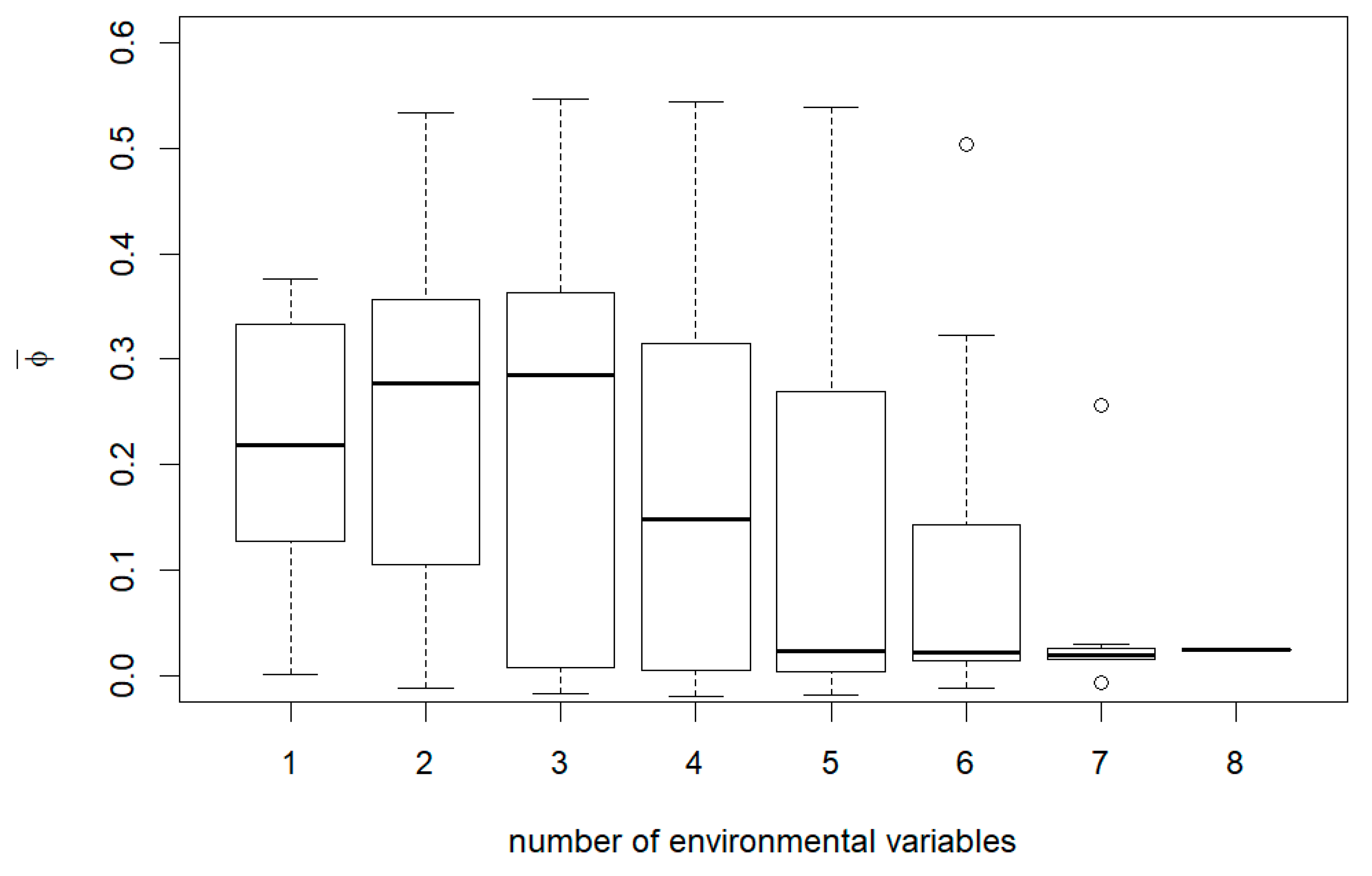
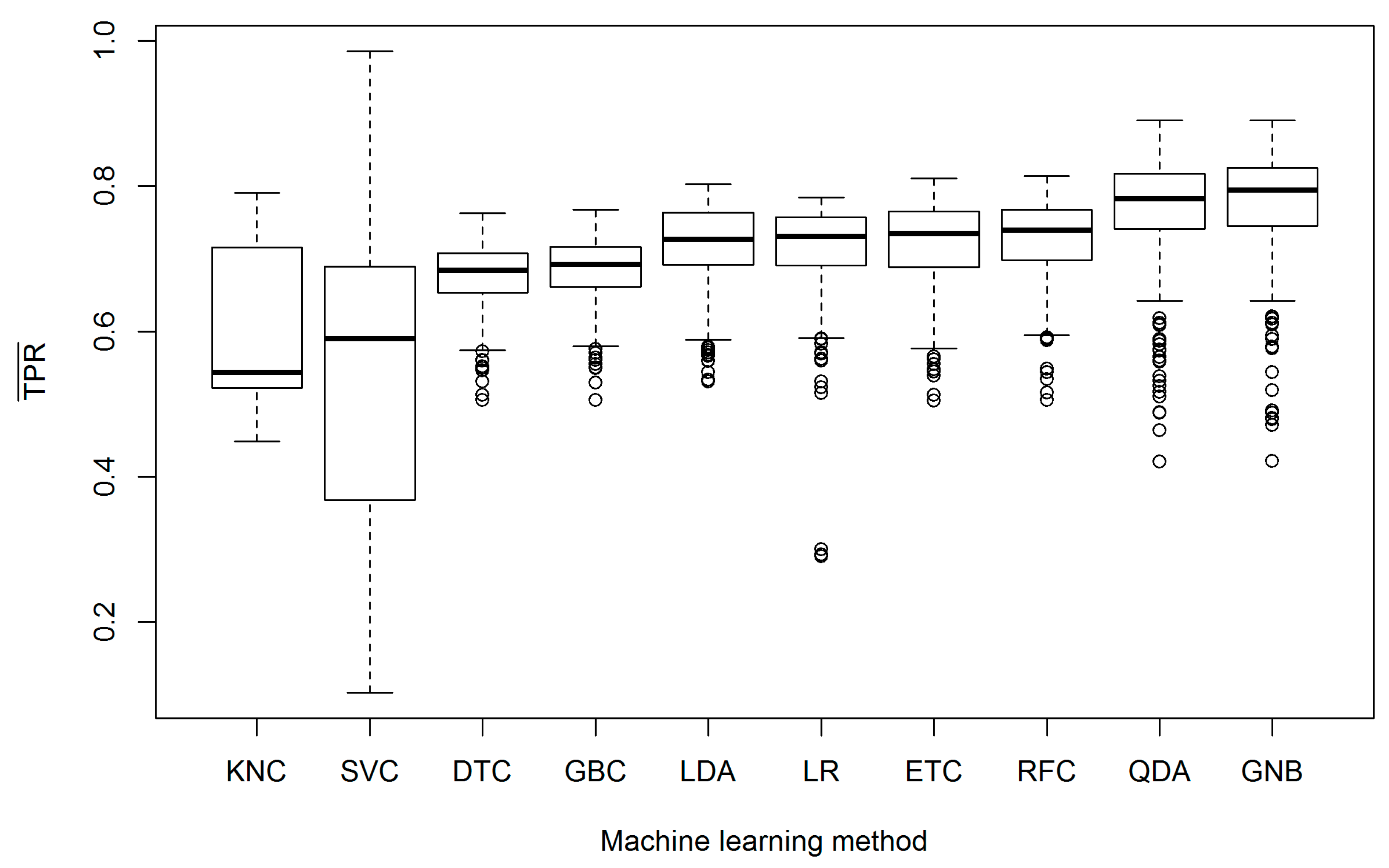
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

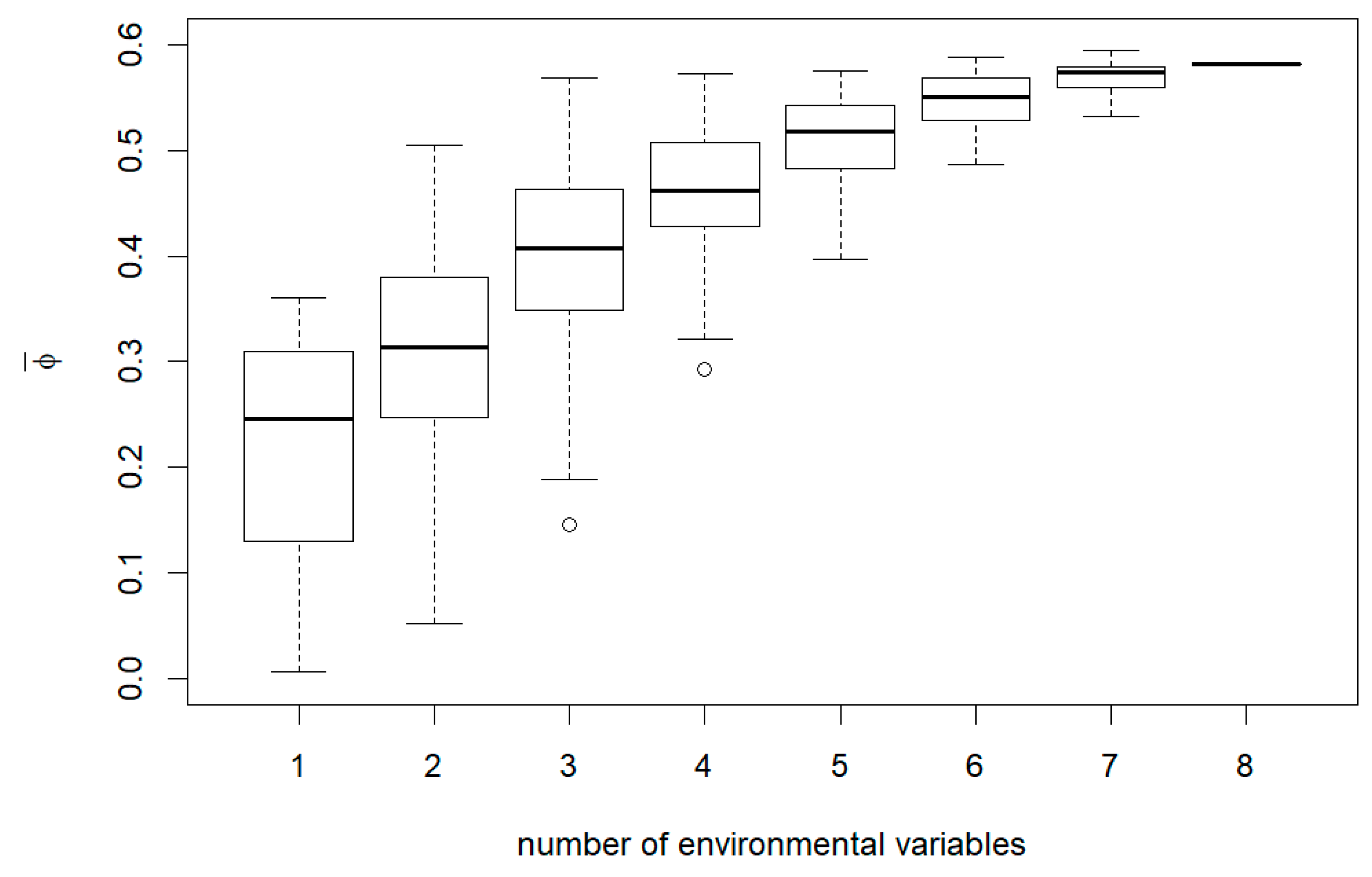
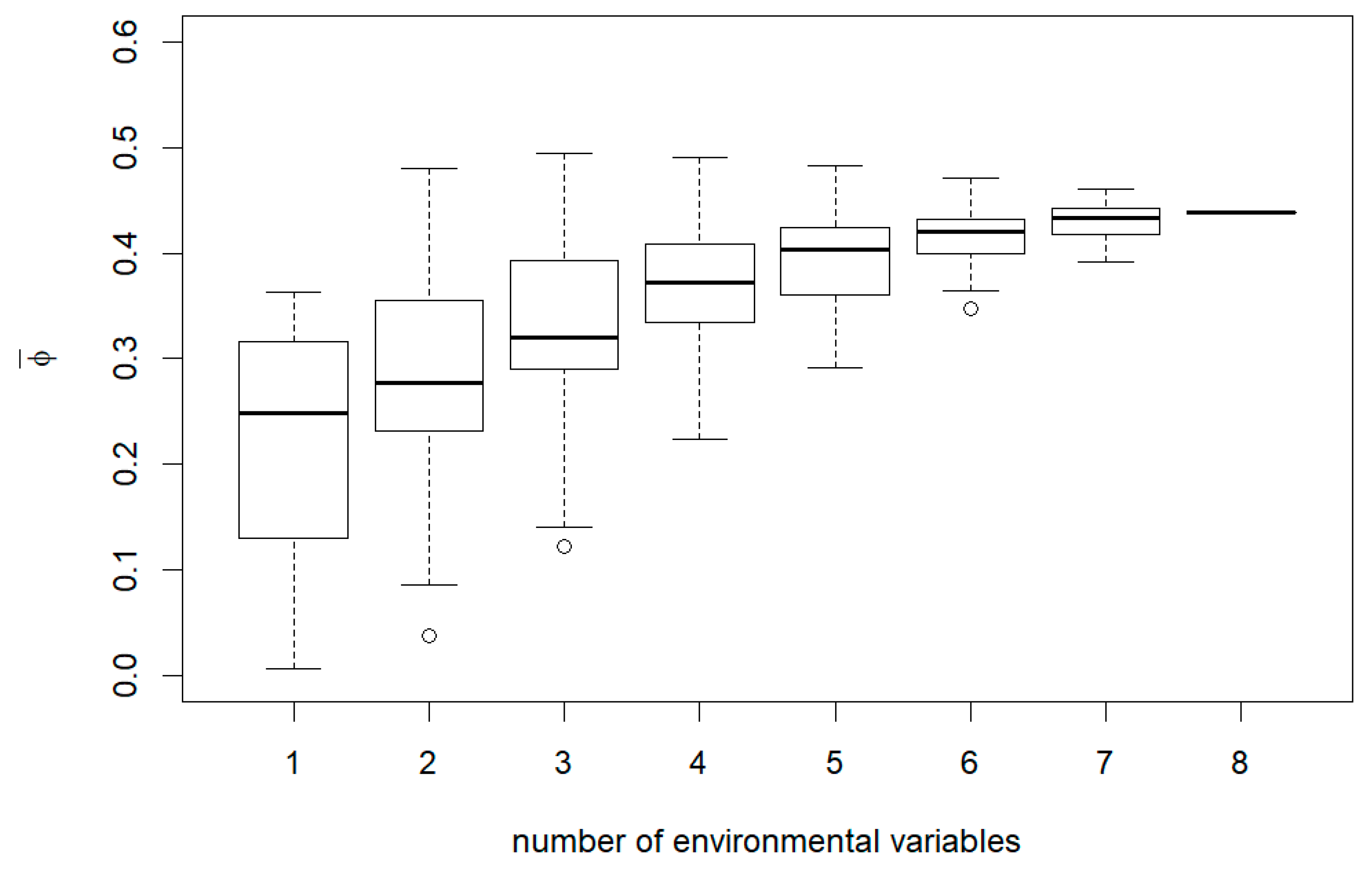
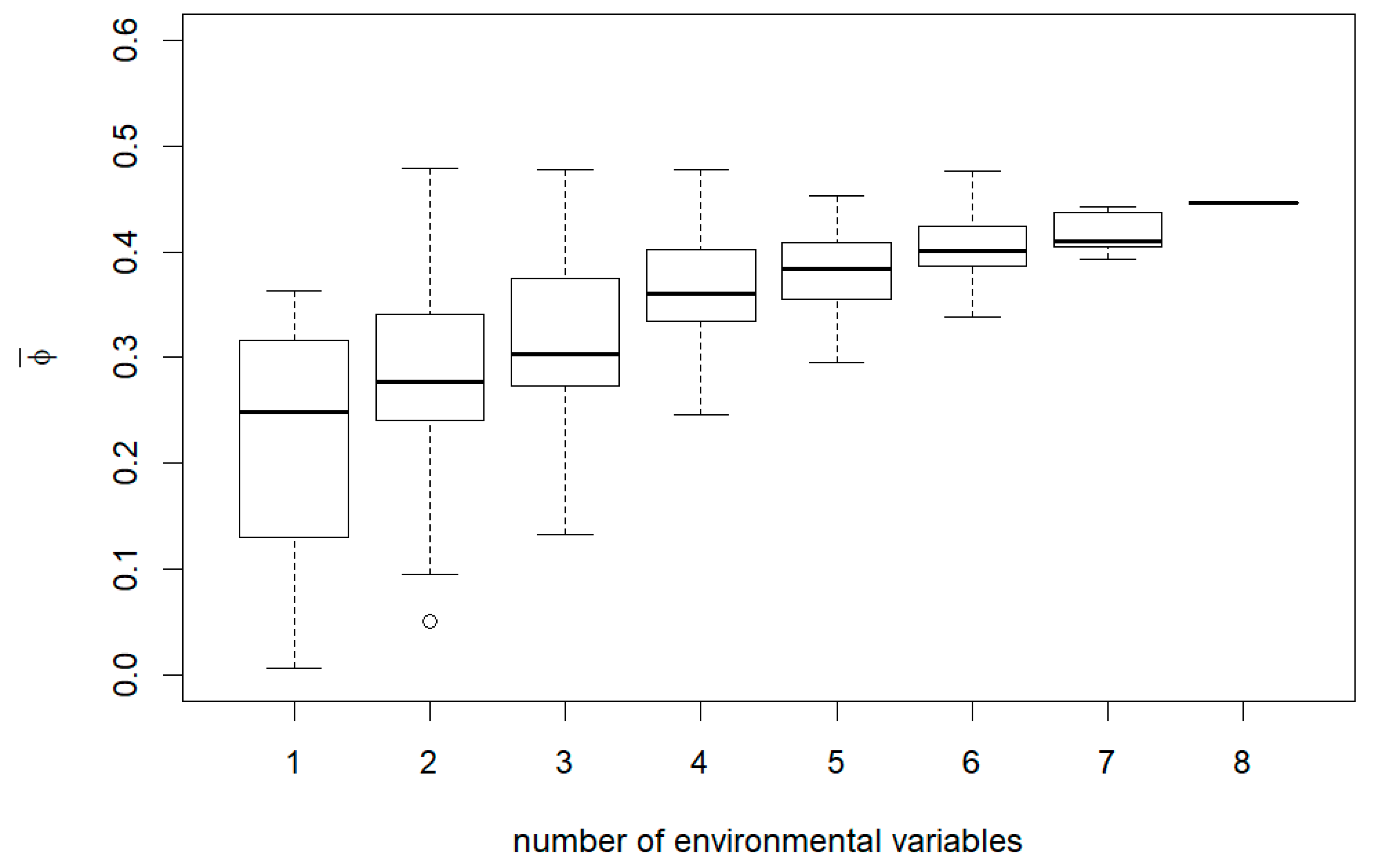
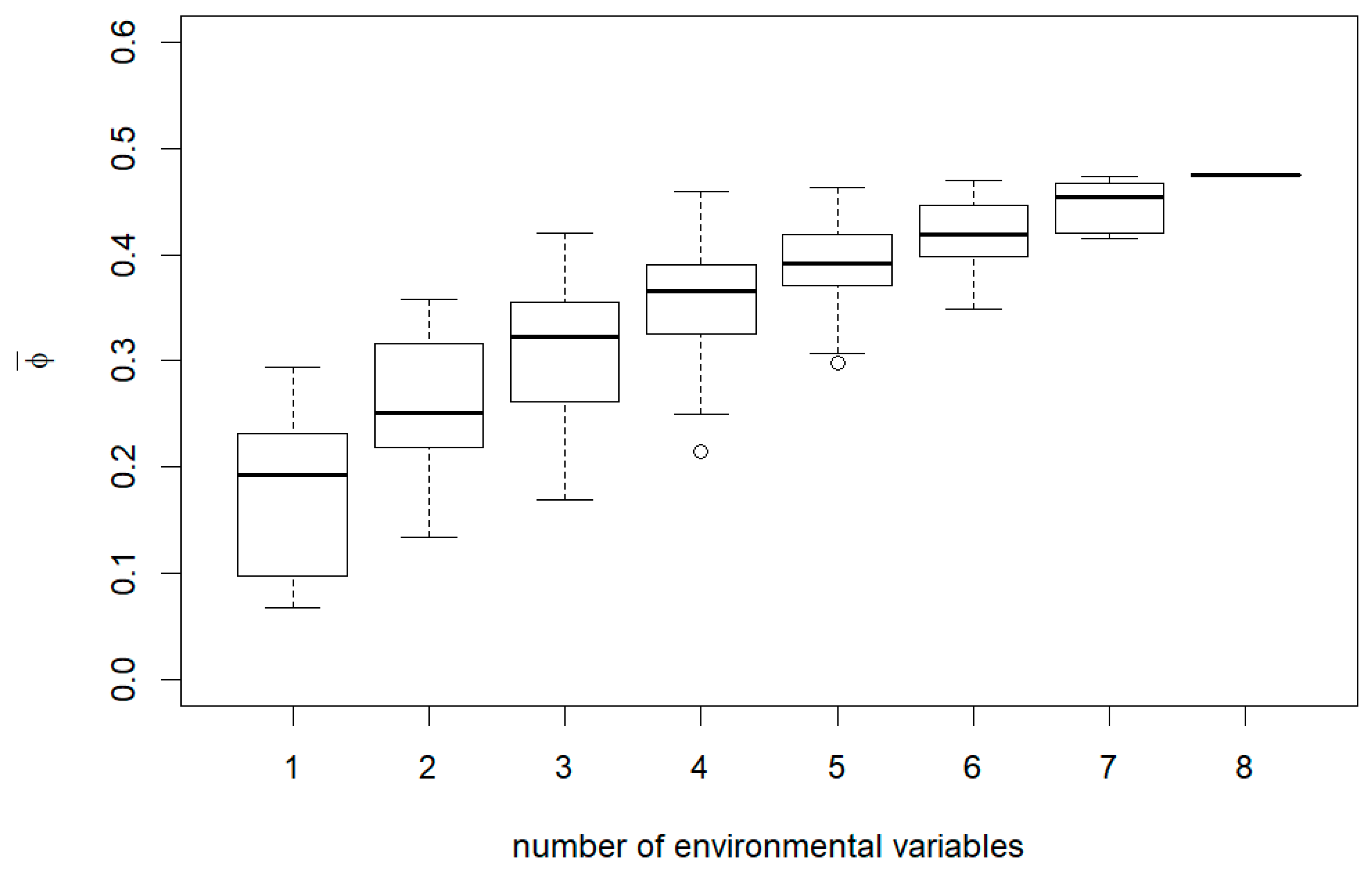
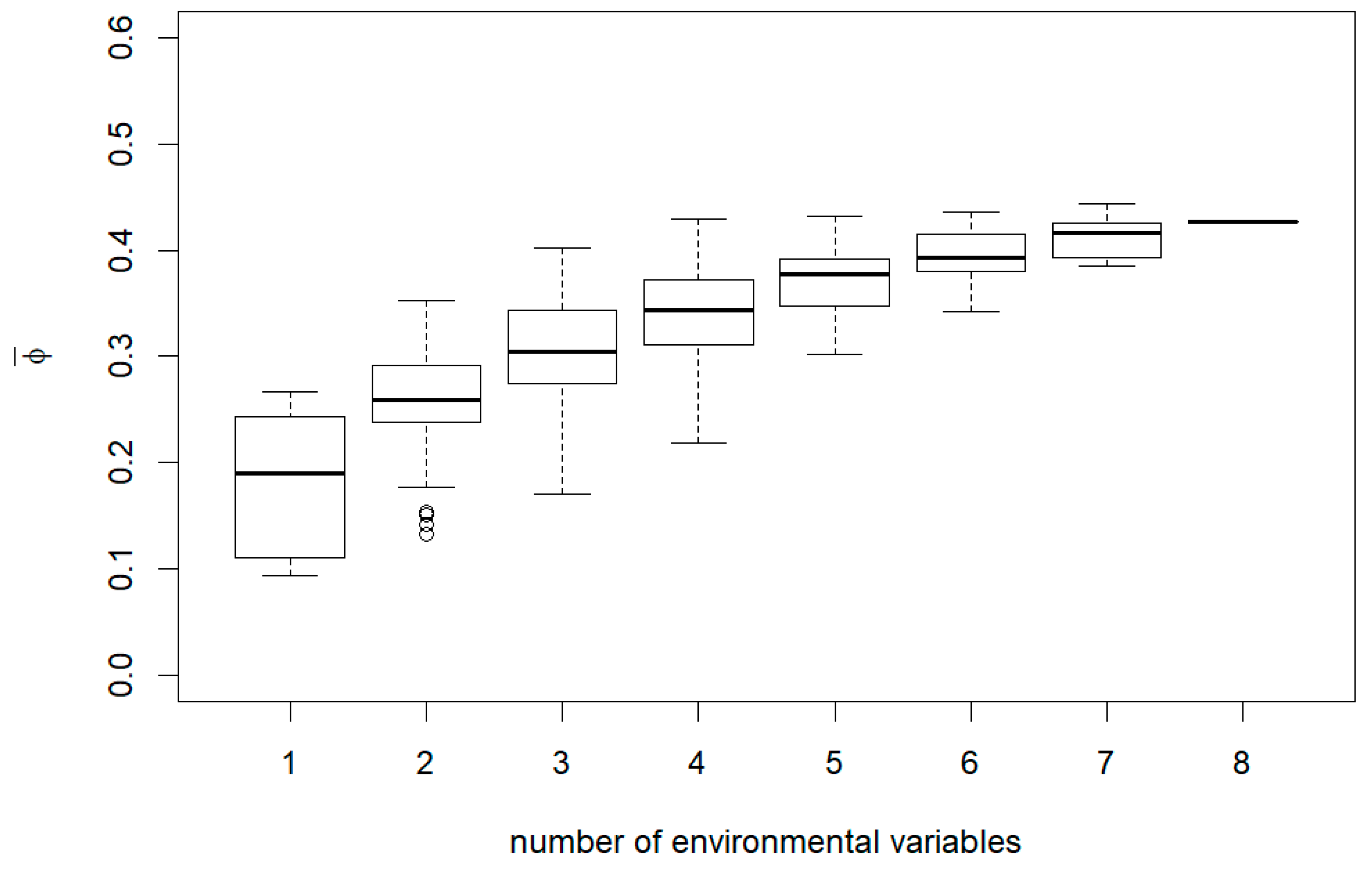
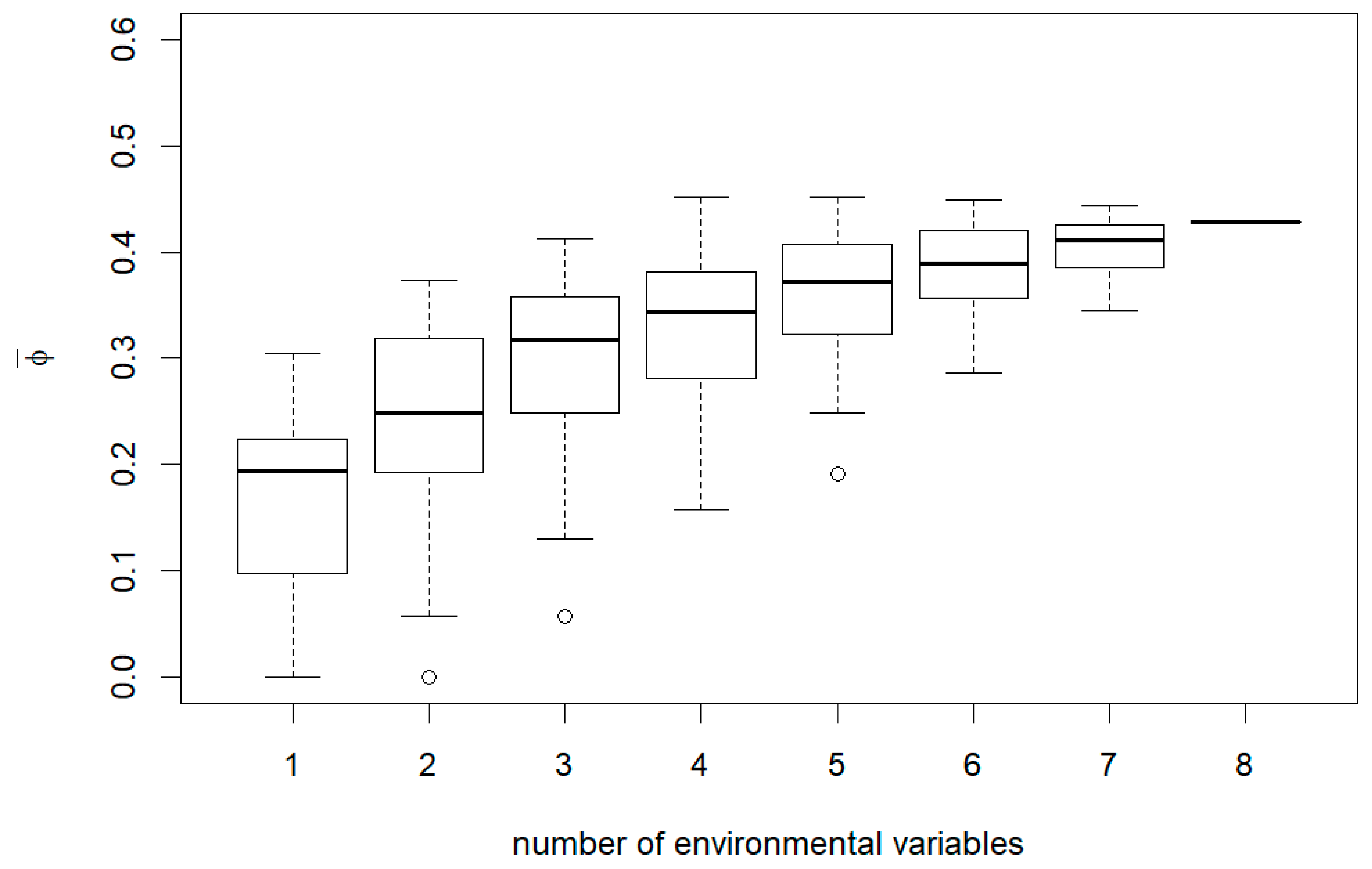
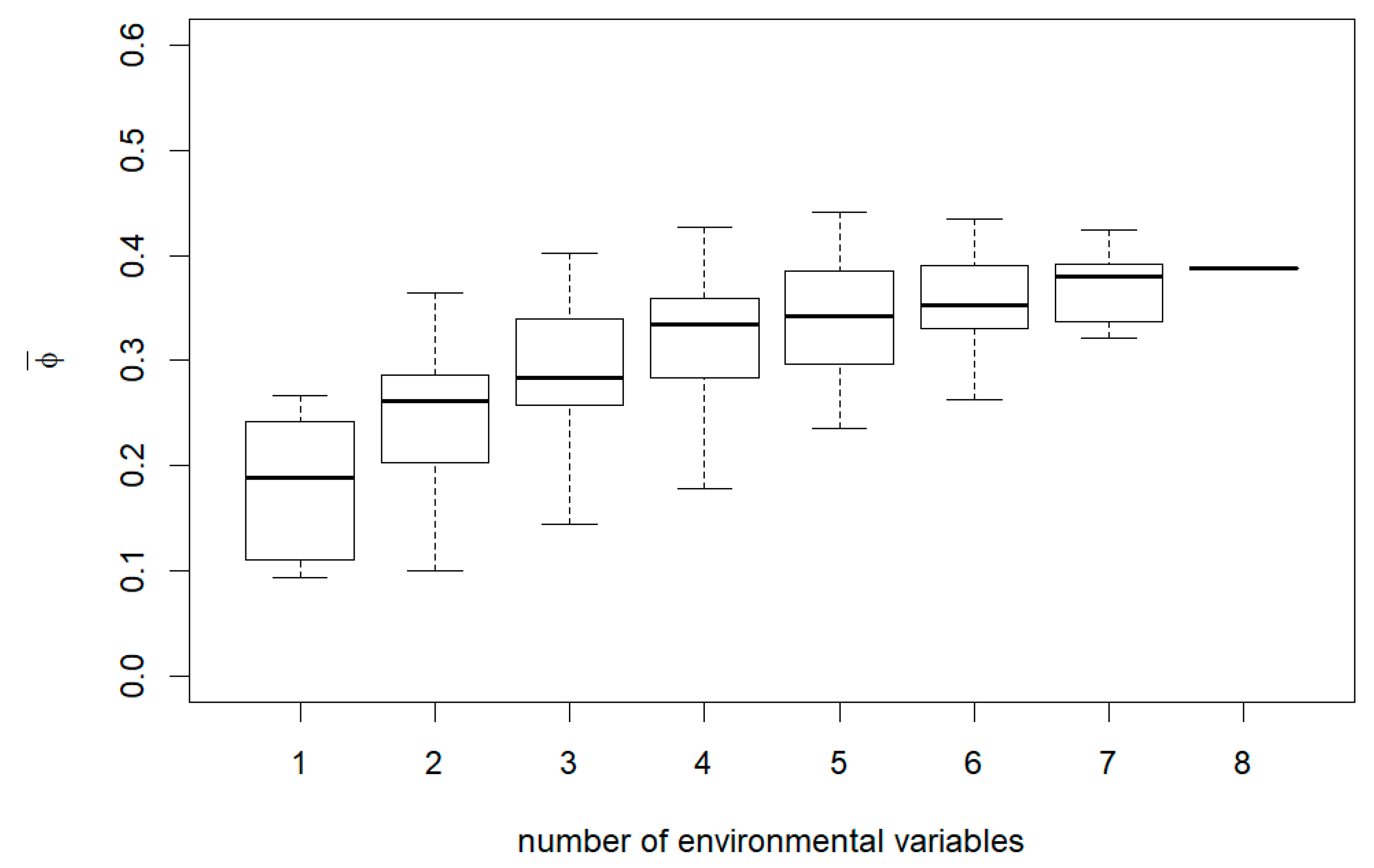
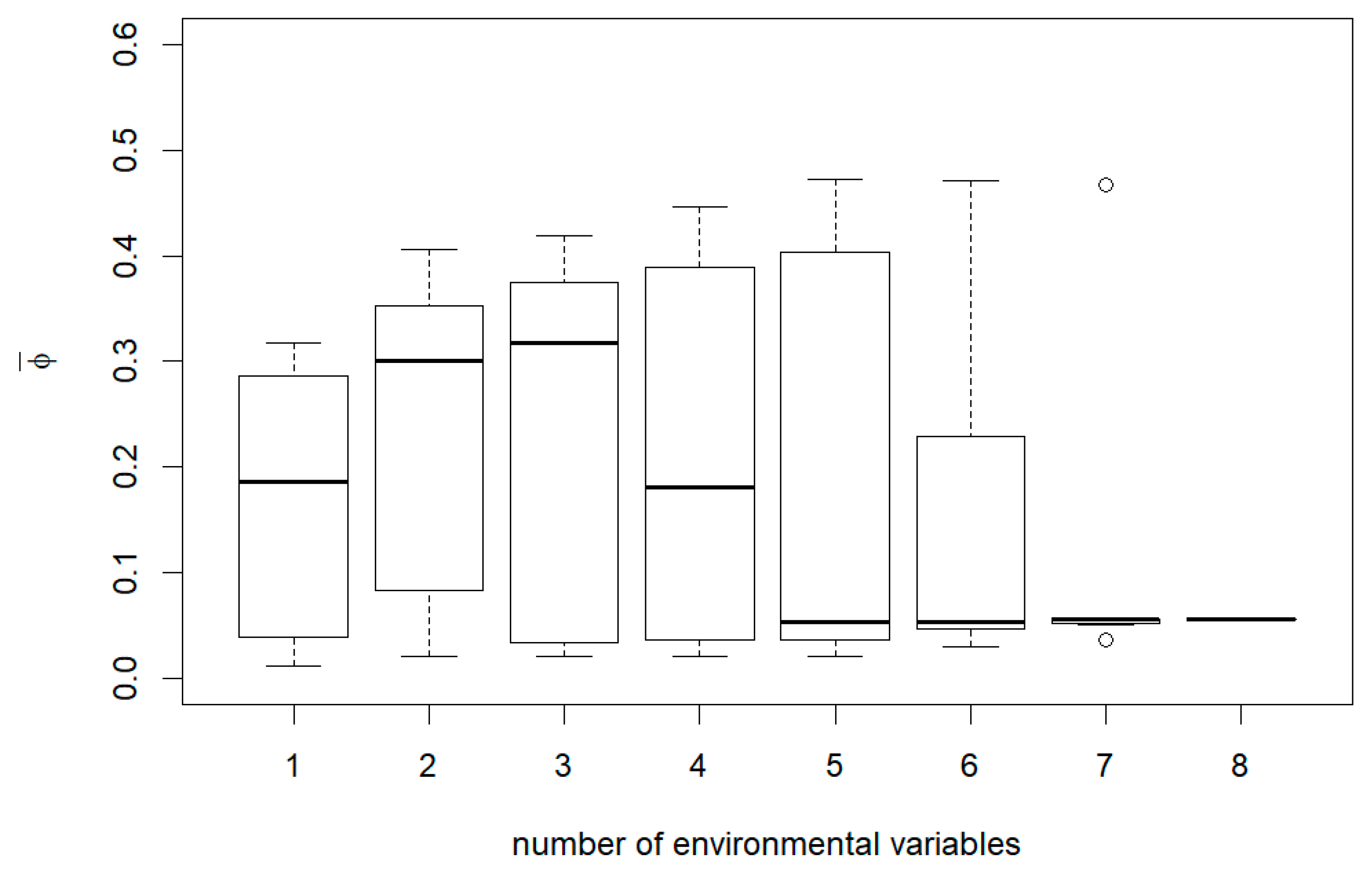
Appendix B
| r 1 | nV 2 | MLA 3 | Variable 4 | 7 | p 8 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | DFE | PSR | NDVI | AGE | PCT | VOL | STO | |||||||
| 1 | ETC | 5 | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8043 | 0.8002 | 0.6052 | - | |||
| 2 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7927 | 0.8058 | 0.5997 | 0.5537 | |
| 3 | ETC | 8 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8038 | 0.7905 | 0.5959 | 0.5037 |
| 4 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8045 | 0.7898 | 0.5957 | 0.4998 | |
| 5 | RFC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8140 | 0.7782 | 0.5937 | 0.2509 | |
| 6 | ETC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7910 | 0.8001 | 0.5919 | 0.1819 | ||
| 7 | ETC | 5 | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8035 | 0.7856 | 0.5902 | 0.1029 | |||
| 8 | ETC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8103 | 0.7782 | 0.5898 | 0.2369 | ||
| 9 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7989 | 0.7890 | 0.5897 | 0.2859 | |
| 10 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8004 | 0.7869 | 0.5896 | 0.1759 | |
| 12 | ETC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7807 | 0.8069 | 0.5888 | 0.1829 | ||
| 13 | RFC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.8036 | 0.7833 | 0.5882 | 0.0770 | ||
| 14 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7980 | 0.7882 | 0.5877 | 0.1479 | |
| 16 | ETC | 4 | + | + | + | + | 0.8004 | 0.7844 | 0.5855 | 0.0800 | ||||
| 18 | ETC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7813 | 0.8027 | 0.5851 | 0.0860 | ||
| 21 | ETC | 6 | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7983 | 0.7787 | 0.5783 | 0.0820 | ||
| 36 | ETC | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.7881 | 0.7798 | 0.5693 | 0.0510 | |
References
- Brázdil, R.; Stucki, P.; Szabó, P.; Řezníčková, L.; Dolák, L.; Dobrovolný, P.; Tolasz, R.; Kotyza, O.; Chromá, K.; Suchánková, S. Windstorms and Forest Disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 250–251, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, P.; Grodzki, W.; Blaženec, M.; Jakuš, R. Factors Influencing the Wind–Bark Beetles’ Disturbance System in the Course of an Ips Typographus Outbreak in the Tatra Mountains. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 312, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Thom, D.; Kautz, M.; Martin-Benito, D.; Peltoniemi, M.; Vacchiano, G.; Wild, J.; Ascoli, D.; Petr, M.; Honkaniemi, J.; et al. Forest Disturbances under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schurman, J.S.; Trotsiuk, V.; Bače, R.; Čada, V.; Fraver, S.; Janda, P.; Kulakowski, D.; Labusova, J.; Mikoláš, M.; Nagel, T.A.; et al. Large-Scale Disturbance Legacies and the Climate Sensitivity of Primary Picea Abies Forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezei, P.; Jakuš, R.; Pennerstorfer, J.; Havašová, M.; Škvarenina, J.; Ferenčík, J.; Slivinský, J.; Bičárová, S.; Bilčík, D.; Blaženec, M.; et al. Storms, Temperature Maxima and the Eurasian Spruce Bark Beetle Ips Typographus—An Infernal Trio in Norway Spruce Forests of the Central European High Tatra Mountains. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 242, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, V.; Bertheau, C.; Doležal, P.; Krumböck, S.; Okrouhlík, J.; Stauffer, C.; Moodley, Y. How Differential Management Strategies Affect Ips Typographus L. Dispersal. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 360, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Heurich, M.; Fahse, L. Spatio-Temporal Infestation Patterns of Ips Typographus (L.) in the Bavarian Forest National Park, Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 31, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Økland, B.; Nikolov, C.; Krokene, P.; Vakula, J. Transition from Windfall- to Patch-Driven Outbreak Dynamics of the Spruce Bark Beetle Ips Typographus. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 363, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M.; Ogris, N. Short-Term Forecasting of Bark Beetle Outbreaks on Two Economically Important Conifer Tree Species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 450, 117495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Ray, D.; Maroto, C. Decision Support Systems for Forest Management: A Comparative Analysis and Assessment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 101, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Seidl, R.; Hostert, P. Remote Sensing of Forest Insect Disturbances: Current State and Future Directions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oeser, J.; Pflugmacher, D.; Senf, C.; Heurich, M.; Hostert, P. Using Intra-Annual Landsat Time Series for Attributing Forest Disturbance Agents in Central Europe. Forests 2017, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.C.; Nuske, R.S.; Ahrends, B.; Panferov, O.; Albert, M.; Staupendahl, K.; Junghans, U.; Jansen, M.; Saborowski, J. Climate Change Impact Assessment—A Simulation Experiment with Norway Spruce for a Forest District in Central Europe. Ecol. Model. 2017, 346, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Müller, J.; Hothorn, T.; Bässler, C.; Heurich, M.; Kautz, M. Small Beetle, Large-Scale Drivers: How Regional and Landscape Factors Affect Outbreaks of the European Spruce Bark Beetle. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, A.A.; Carvalho, M.C.; de Mello, J.M.; Gomide, L.R.; Ferraz Filho, A.C.; Acerbi Junior, F.W. Spatial Prediction of Basal Area and Volume in Eucalyptus Stands Using Landsat TM Data: An Assessment of Prediction Methods. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2018, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hickey, C.; Kelly, S.; Carroll, P.; O’Connor, J. Prediction of Forestry Planned End Products Using Dirichlet Regression and Neural Networks. For. Sci. 2015, 61, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Görgens, E.B.; Montaghi, A.; Rodriguez, L.C.E. A Performance Comparison of Machine Learning Methods to Estimate the Fast-Growing Forest Plantation Yield Based on Laser Scanning Metrics. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; de la Riva, J. An Insight into Machine-Learning Algorithms to Model Human-Caused Wildfire Occurrence. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 57, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, H.; Smith, C.; Gallagher, M.; Hockings, M. Use of Freely Available Datasets and Machine Learning Methods in Predicting Deforestation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 87, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castelli, M.; Vanneschi, L.; Popovič, A. Predicting Burned Areas of Forest Fires: An Artificial Intelligence Approach. Fire Ecol. 2015, 11, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, H. Integrating Remote Sensing, GIS and Dynamic Models for Landscape-Level Simulation of Forest Insect Disturbance. Ecol. Model. 2017, 354, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hlásny, T.; Turčáni, M. Persisting Bark Beetle Outbreak Indicates the Unsustainability of Secondary Norway Spruce Forests: Case Study from Central Europe. Ann. For. Sci. 2013, 70, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Military Forests and Farms of the Czech Republic, State Enterprise. Available online: https://www.vls.cz/en (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Culek, M.; Grulich, V.; Laštůvka, Z.; Divíšek, J. Biogeografické Regiony České Republiky; Masarykova Univerzita: Brno, Czech Republic, 2013; ISBN 978-80-210-6693-9. [Google Scholar]
- Forestry and Game Management Research Institute, Czech Republic. Available online: https://www.vulhm.cz/en/ (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Forest Management Institute (FMI), Czech Republic. Available online: http://www.uhul.cz/home (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Henzlik, V. Forests and Air Pollution in the Czech Republic. In Restoration of Forests; Gutkowski, R.M., Winnicki, T., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 133–149. ISBN 978-0-7923-4634-0. [Google Scholar]
- Havašová, M.; Ferenčík, J.; Jakuš, R. Interactions between Windthrow, Bark Beetles and Forest Management in the Tatra National Parks. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 391, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďuračiová, R.; Muňko, M.; Barka, I.; Koreň, M.; Resnerová, K.; Holuša, J.; Blaženec, M.; Potterf, M.; Jakuš, R. A Bark Beetle Infestation Predictive Model Based on Satellite Data in the Frame of Decision Support System TANABBO. IForest Biogeosci. For. 2020, 13, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Šúri, M. The Solar Radiation Model for Open Source GIS: Implementation and Applications. In Proceedings of the Open Source GIS—GRASS Users Conference 2002, Trento, Italy, 11–13 September 2002; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- EU-DEM v1.1—Copernicus Land Monitoring Service. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/imagery-in-situ/eu-dem/eu-dem-v1.1 (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- GRASS GIS. Available online: https://grass.osgeo.org/ (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018.
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammer, W.; Seidl, R. Harnessing Deep Learning in Ecology: An Example Predicting Bark Beetle Outbreaks. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.J.; Saborio, J.; Ramsey, R.D.; Rivera, S. Likelihood of Occurrence of Bark Beetle Attacks on Conifer Forests in Honduras under Normal and Climate Change Scenarios. Geocarto Int. 2012, 27, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Huettmann, F.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Wen, L. Why Choose Random Forest to Predict Rare Species Distribution with Few Samples in Large Undersampled Areas? Three Asian Crane Species Models Provide Supporting Evidence. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geurts, P.; Ernst, D.; Wehenkel, L. Extremely Randomized Trees. Mach. Learn. 2006, 63, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angst, A.; Rüegg, R.; Forster, B. Declining Bark Beetle Densities (Ips Typographus, Coleoptera: Scolytinae) from Infested Norway Spruce Stands and Possible Implications for Management. Psyche J. Entomol. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, M.; Schopf, R.; Ohser, J. The “Sun-Effect”: Microclimatic Alterations Predispose Forest Edges to Bark Beetle Infestations. Eur. J. For. Res. 2013, 132, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann, G.; Bugmann, H.; Wermelinger, B.; Meier, F.; Bigler, C. A Predictive Framework to Assess Spatio-Temporal Variability of Infestations by the European Spruce Bark Beetle. Ecography 2013, 36, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stereńczak, K.; Mielcarek, M.; Kamińska, A.; Kraszewski, B.; Piasecka, Ż.; Miścicki, S.; Heurich, M. Influence of Selected Habitat and Stand Factors on Bark Beetle Ips Typographus (L.) Outbreak in the Białowieża Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 459, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Code | Explanatory Variable |
|---|---|
| DAS | distance to forest damage spots from previous year |
| DFE | distance to spruce forest edge |
| PSR | potential global solar radiation |
| NDVI | normalized difference vegetation index |
| AGE | spruce forest age |
| PCT | percentage of spruce |
| VOL | volume of spruce wood per hectare |
| STO | stocking |
| Date | Scene |
|---|---|
| 16.07.2003 | LT05_L1TP_191026_20030716_20161205_01_T1 |
| 10.08.2004 | LT05_L1TP_192026_20040810_20161130_01_T1 |
| 28.07.2005 29.08.2005 | LT05_L1TP_192026_20050728_20161125_01_T1 LT05_L1TP_192026_20050829_20161125_01_T1 |
| 15.07.2006 24.07.2006 | LT05_L1TP_192026_20060715_20161120_01_T1 LT05_L1TP_191026_20060724_20161120_01_T1 |
| 25.06.2007 19.07.2007 | LT05_L1TP_191026_20070625_20161112_01_T1 LE07_L1TP_191026_20070719_20170102_01_T1 |
| 29.06.2008 21.08.2008 | LT05_L1TP_191026_20070625_20161112_01_T1 LT05_L1TP_192026_20080821_20180116_01_T1 |
| 24.08.2009 | LT05_L1TP_192026_20090824_20161021_01_T1 |
| 10.07.2010 | LT05_L1TP_192026_20100710_20161014_01_T1 |
| 23.08.2011 | LT05_L1TP_191026_20110823_20161007_01_T1 |
| 23.07.2012 01.08.2012 | LE07_L1TP_192026_20120723_20161130_01_T1 LE07_L1TP_191026_20120801_20161130_01_T1 |
| Code | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| LR | logistic regression |
| LDA | linear discriminant analysis |
| QDA | quadratic discriminant analysis |
| KNC | k-nearest neighbors classifier |
| GNB | Gaussian naive Bayes |
| DTC | decision tree classifier |
| RFC | random forest classifier |
| ETC | extra trees classifier |
| GBC | gradient boosting classifier |
| SVC | support vector classification |
| r 1 | nV 2 | MLA 3 | Variable 4 | 7 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | DFE | PSR | NDVI | AGE | PCT | VOL | STO | ||||||
| 1 | 5 | ETC | + | + | + | + | + | 0.804 | 0.800 | 0.605 | |||
| 5 | 7 | RFC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.814 | 0.778 | 0.594 | |
| 89 | 3 | SVC | + | + | + | 0.724 | 0.818 | 0.546 | |||||
| 219 | 3 | GBC | + | + | + | 0.761 | 0.733 | 0.495 | |||||
| 273 | 2 | DTC | + | + | 0.750 | 0.728 | 0.479 | ||||||
| 286 | 8 | LDA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.764 | 0.707 | 0.474 |
| 295 | 5 | KNC | + | + | + | + | + | 0.790 | 0.678 | 0.472 | |||
| 388 | 4 | LR | + | + | + | + | 0.769 | 0.679 | 0.452 | ||||
| 421 | 7 | QDA | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.815 | 0.618 | 0.444 | |
| 436 | 5 | GNB | + | + | + | + | + | 0.827 | 0.602 | 0.441 | |||
| MLA 1 | GNB | QDA | LR | KNC | LDA | DTC | GBC | SVC | RFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDA | 0.827 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LR | 0.338 | 0.687 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KNC | 0.338 | 0.406 | 0.348 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LDA | 0.020 | 0.154 | 0.054 | 0.906 | - | - | - | - | - |
| DTC | 0.124 | 0.202 | 0.177 | 0.827 | 0.851 | - | - | - | - |
| GBC | 0.073 | 0.124 | 0.124 | 0.576 | 0.338 | 0.126 | - | - | - |
| SVC | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.034 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | - | - |
| RFC | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.020 | - |
| ETC | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.312 |
| r 1 | nV 2 | MLA 3 | Variable 4 | 7 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | DFE | PSR | NDVI | AGE | PCT | VOL | STO | ||||||
| 1055 | 1 | SVC | + | 0.691 | 0.685 | 0.376 | |||||||
| 116 | 2 | SVC | + | + | 0.719 | 0.811 | 0.534 | ||||||
| 43 | 3 | RFC | + | + | + | 0.794 | 0.773 | 0.568 | |||||
| 16 | 4 | ETC | + | + | + | + | 0.800 | 0.784 | 0.585 | ||||
| 1 | 5 | ETC | + | + | + | + | + | 0.804 | 0.800 | 0.605 | |||
| 6 | 6 | ETC | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.791 | 0.800 | 0.592 | ||
| 2 | 7 | ETC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.793 | 0.806 | 0.600 | |
| 3 | 8 | ETC | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.804 | 0.790 | 0.596 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koreň, M.; Jakuš, R.; Zápotocký, M.; Barka, I.; Holuša, J.; Ďuračiová, R.; Blaženec, M. Assessment of Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling the Spatial Distribution of Bark Beetle Infestation. Forests 2021, 12, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040395
Koreň M, Jakuš R, Zápotocký M, Barka I, Holuša J, Ďuračiová R, Blaženec M. Assessment of Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling the Spatial Distribution of Bark Beetle Infestation. Forests. 2021; 12(4):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040395
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoreň, Milan, Rastislav Jakuš, Martin Zápotocký, Ivan Barka, Jaroslav Holuša, Renata Ďuračiová, and Miroslav Blaženec. 2021. "Assessment of Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling the Spatial Distribution of Bark Beetle Infestation" Forests 12, no. 4: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040395
APA StyleKoreň, M., Jakuš, R., Zápotocký, M., Barka, I., Holuša, J., Ďuračiová, R., & Blaženec, M. (2021). Assessment of Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling the Spatial Distribution of Bark Beetle Infestation. Forests, 12(4), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12040395









