Abstract
Revealing the pedogenesis of soil on carbonate rocks is a key step in determining the boundaries of soil types along a climosequence. However, related research is lacking for a subtropical mountain. In this study, eight pedons were sampled across an elevation gradient (789–2322 m) having large variation in mean annual precipitation (MAP) (1189–1764 mm) and mean annual temperature (MAT) (5.7–14.9 °C). General processes were performed, including physical, chemical, and morphological characterizations, X-ray diffraction (XRD), total elements’ content, and soil classification of the carbonate rock. In the climo-toposequence, the illite had been transformed into illite-smectite below 1300–1500 m of elevation, 1300–1370 mm of MAP, and above 10.5–11.5 °C of MAT, and into vermiculite above this climate. These findings indicated that the effects of temperature on soil mineral transformation had weakened with the gradual increases in elevation. The pedon at 861 m of elevation, 1206 mm of MAP, and 14.5 °C of MAT, which accounted for the argic horizons, was divided into Argosols after human activities. The finding revealed that changes from forest to cultivated land could potentially accelerate the formation of argic horizons, and it provided a theoretical basis for global carbonate rocks’ weathering conditions and ecological problems in subtropical mountains. When the soils reached approximately 1100–1200 m of elevation, 1250–1300 mm of MAP, and 11.5–13.5 °C of MAT, the argic horizons of the soil could be accounted for, as evolved from the Cambosols in Chinese Soil Taxonomy (CST) (Inceptisols in Soil Taxonomy (ST), Cambisols in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB)) to the Argosols in CST (Alfisols in ST, Luvisols or Alisols in WRB) under natural vegetation. Therefore, it was indicated that the soil types changed significantly in the CST, ST, and WRB with increases of MAP and decreases of MAT, which provides a reference for determining the boundaries of the soil types along a climosequence in subtropical mountains.
1. Introduction
On a global scale, carbonate rocks’ formations occupy substantial amounts of land area (approximately 12%), which substantiates their importance in global weathering and biogeochemical cycling processes [1]. In China, carbonate rocks have an estimated distribution area greater than 3.44 × 106 km2, accounting for approximately one-third of the total land area. The total exposed area of carbonate rocks is estimated at greater than 9 × 105 km2, which is close to one-tenth of the total land area [2]. Chemical weathering of carbonate minerals has been proposed to consume atmospheric CO2 on a relatively short-term scale, and most mobile elements are leached due to the high dissolution rates of calcite and dolomite. Carbonate rocks play a more important role in regulating CO2 content and may be the sinks of carbon dioxide on a long-term scale during weathering [3]. In addition, carbonate weathering accounts for one-third of annual CO2 consumption, which is closely related to annual precipitation and temperature [4]. Additionally, the slow soil formation processes, as well as the pedogenesis of the soil derived from carbonate rocks, represent key components in the global carbon cycle via the preservation of soil organic carbon and weathering-induced CO2 consumption [5]. Due to the strong chemical weathering of carbonate rocks, the area where it is located has the ineffective water and soil conservation abilities, inadequate natural disaster resistance abilities, and improper development. Thus, serious soil erosion and rocky desertification occur in the area of carbonate rocks, which are enhanced by the geomorphic slopes of the carbonate rocks’ formations [6,7]. Therefore, the study of soil pedogenesis and its environmental effects is of major scientific and practical significance for solving a series of resource and environmental problems related to carbonate rocks.
Climate conditions are known to have significant impacts on soil pedogenesis and evolution [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Usually, the elevation can influence mean annual temperature and precipitation in a certain region and is an important factor affecting soil pedogenesis [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. The weathering and diagenesis processes tend to alter the geochemical characteristics of the elements, clay mineralogy, vegetation, and the types of carbonate-derived soils [23,24,25,26]. The easily weathered minerals (calcite and dolomite) in carbonate rocks are gradually dissolved to soluble salts, which are carried away, along with the karst water system, and the insoluble minerals such as clay minerals and quartz remain. Secondly, the solution gradually changes from alkaline to acidic, then montmorillonite and illite transform to kaolinite. Finally, aluminosilicate minerals are completely decomposed to form limonite, gibbsite, and hard and pyrolusite in situ, then form iron oxide and manganese layers with clay minerals to cover the surface [27]. However, there is little research on how climosequence affects the pedogenesis of soil derived from carbonate rocks in subtropical mountains.
When soil quantitative classifications and soil cartography are completed in carbonate-rocks areas under subtropical mountain climate conditions, it was found that the determinations of the boundaries of the soil types along a climosequence had not yet been completely solved, and few similar research investigations have been conducted. It is considered that deepening the understanding of those interactions will be critical in order to clearly determine the effects of the weathering and soil formation processes on the carbonate rocks’ formations in China, as well as similar regions throughout the world. However, several of the previous research investigations regarding the soil pedogenesis of carbonate rocks have not effectively focused on subtropical mountain environments. In this study, in order to address these issues, the Ta-pa Mountains of China were taken as an example. A general soil characterization was completed, and the total elements’ content was conducted. The mineralogical data of an elevation sequence, which included eight soil pedons, were determined and discussed.
The objective of this work was to evaluate how the climate controls carbonate rocks’ weathering and pedogenesis across a steep environmental gradient in a subtropical mountain area of China. Specifically, we evaluated the influence of climosequence conditions on the degrees of weathering and pedogenetic evolution of soil under subtropical mountain in order to solve the problems related to the determinations of soil-type boundaries in China, as well as similar regions around the world.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geological Setting
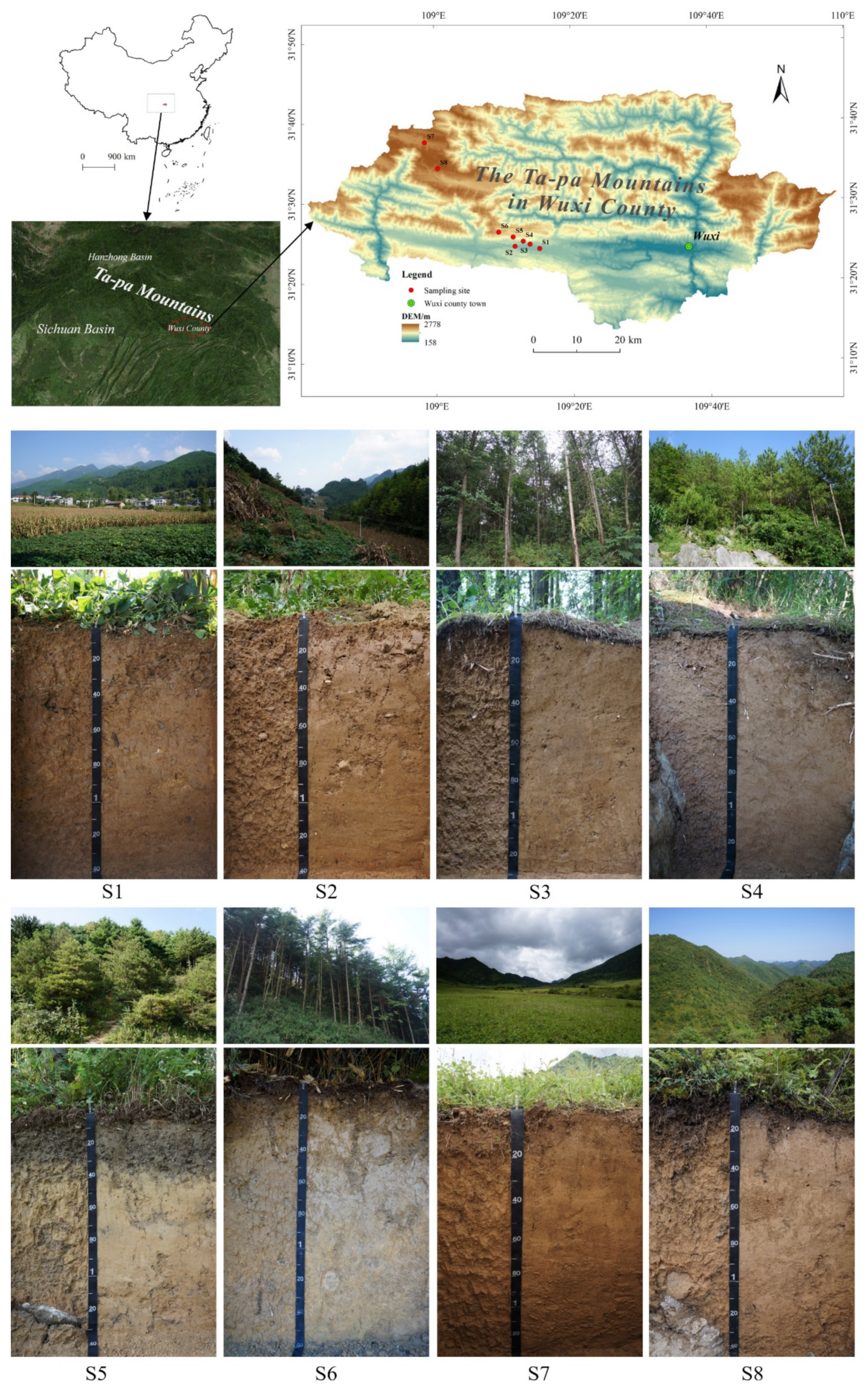
The Ta-pa Mountains region is located in western China and is the generally used term for the mountainous areas bordering the Shaanxi, Sichuan, and Hubei Provinces. The region stretches for more than 500 km from east to west and provides a watershed between the Jialing and Han Rivers. In addition, it is the geographical boundary between the Sichuan Basin and the Hanzhong Basin [28]. In China, there are tropical climate, subtropical climate, temperate climate, temperate continental climate, and alpine plateau climate. The subtropical climate is divided into north subtropical climate, middle subtropical climate, and south subtropical climate. The boundary between the middle subtropical climate and north subtropical climate from west to east passes through the northern edge of Sichuan Basin, then follows the Ta-pa Mountain-Wudang Mountain watershed, and then stretches along the southern edge of Dongting Lake Basin, the north of Poyang Lake and the southern edge of Taihu Lake Plain, in turn. Thus, the Ta-pa Mountains are an important geographical region across the northern and middle part of the subtropical climate zone. The MAT is 13.5–16.5 °C and the MAP is 900–1300 mm in the north subtropical zone, while the MAT is 16.0–20.0 °C and the MAP is 1000–1500 mm in the middle subtropical zone. From a geomorphological perspective, the study area protrudes in an arc shape toward the southwest. Within the mountain range, the river is cut deeper and the terrain of the piedmont basin is relatively flat. At the same time, new tectonic stress continues to pass eastward from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. It has been found that when encountering the strong dome of the Huang Di Mausoleum, the stress becomes concentrated in the Shennongjia and Three Gorges areas of the Yangtze River, which resulted in a vertical uplift zone in the study area [29]. From a geological perspective, the study area is consisting almost entirely of rocks formed from Triassic carbonate material, including limestone and dolomite. There is evidence of soluble crags, which resulted in the abnormal development of a karst geomorphology. This study was conducted in the eastern section of the Ta-pa Mountains, located in the northern region of China’s Sichuan Basin at Wenfeng Town, Wuxi County, Chongqing Municipality (Figure 1). The region is characterized by a humid monsoon climate in a subtropical environment. The current climatic data indicate a mean annual rainfall ranging from 1030 mm to 1950 mm, the majority of which falls during the months ranging from November to April. It has been determined that the temperatures range on average from 5 °C to 20 °C during the winter seasons and from 25 °C to 40 °C during the summer seasons, with an average temperature of approximately 18 °C over the course of a year. The study area below about 1000 m is cultivated land, intercropping of corn and sweet potato, and above about 1000 m is forest land (mainly including Pinus massoniana Lamb, Pinus armandii Franch) or pastureland (mainly including Cyclobalanopsis glauca (Thunberg) Oersted, Pinus tabulaeformis Car, Trifolium pratense Linn.).

Figure 1.
General position of the eight soil profiles in relation to China and pictures of the eight soil profiles.
2.2. Field Site Locations
In the present study, a series of soil pedons, which all derived from the carbonate rocks, was sampled on a slope located in the eastern section of the Ta-pa Mountain region, across an elevation gradient ranging between 789 m and 2322 m above sea level, along a climosequence of mean annual precipitation ranging between 1189 mm and 1764 mm and mean annual soil temperature ranging between 5.7 °C and 14.9 °C. The sampling sites had elevation differences ranging between 200 m and 300 m, with the exception of the cultivated land sites. According to the difference in land use and vegetation at different altitudes in the study areas, sampling areas with similar slopes’ gradient (between gently sloping and steep) at different altitudes were selected. Then, locations suitable for digging soil profiles in the sampling areas were selected as sampling sites. This study collected samples, excavated profiles, divided horizons, and recorded the morphological characteristics of the soil profiles [30]. This study’s field sites were located between 31°24.23′ N and 109°15.20′ E to 31°37.60′ N and 108°58.53′ E and situated near Wenfeng Town, Wuxi County, Chongqing Municipality, China (Figure 1). The slope classes of the test soil ranged from gently sloping to steep [31], and the mean annual precipitation levels ranged from 1100 mm to 1800 mm. Site S7 was located in the center of a rainstorm area known to have heavy rainfall occurrences, which was located at the climate station with the highest rainfall in Chongqing [32]. The mean annual temperature range was 5 °C to 15 °C as detailed in Table 1. The specific locations of the pedons were determined according to the environmental characteristics of the testing sites [33]. The source of the parent material, with the exception of the carbonate rocks’ weathering residue, included a small amount of material sourced as slope-diluvial deposit mixture (the mixture of the weathering products transported by sheet erosion and accumulations formed by temporary floods) caused by topographic factors. Among them, the parent material of the S1 testing site was a slope-diluvial deposit mixture of weathering materials, mainly including limestone and a small amount of dolomite of Triassic. The S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 testing sites were composed of slope deposit (the weathering products transported by sheet erosion and deposited on different slop positions) and such weathering material as Triassic limestone. The parent rocks exposed around the sites S4 and S8 collected along all sites were found to be limestone with a hardness of 3–4. The dominant primary mineral was calcite, with a small amount of dolomite, quartz, feldspar, and muscovite in these limestones [34,35].

Table 1.
Site characteristics for soils derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
2.3. Physical and Chemical Analyses
This study’s acquired soil samples were air-dried to constant weight. Then, visible pieces of plant debris were removed, and the samples were ground and sieved (2 mm) in order to produce the fine earth necessary for physical, chemical, and mineralogical analyses [36,37,38]. The Munsell soil color charts were utilized to determine the soil colors in dry and wet soil conditions [39]. The pH levels of the soil samples were measured (soil:water = 1:2.5) by SX836 Model. The particle-size distributions were determined using sieving and sedimentation processes and a pipette method [40]. Prior to the commencement of the dispersion process, the samples were treated in order to remove the carbonates (dissolution by HCl), organic matter (oxidation by 30% H2O2), and soluble salts (leaching). Then, NaOH was added to prevent the re-flocculation of the colloidal material. The bulk densities of the soil samples (three replicates per horizon) were measured in the field using a hammer corer device for one pedon at each site. The soil organic carbon (SOC) was measured using a potassium dichromate oxidation method. The cation exchange capacities (CEC) and the content levels of exchangeable bases (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+) were determined by NaOAc-EDTA at a pH of 7.0 method. The CEC was extracted by 1 M NH4OAc. Then, the NH4+ exchanged with soil cation was measured by automatic Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer. The cations were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometer [41]. The base saturation refers to the ratio of the base exchange capacity to the cation exchange capacity (pH < 7; when the pH > 7, it is usually considered to be saturated). The CaCO3 was measured by the NaOH titration reacted by HCl. In this study, sodium citrate- bicarbonate-dithionite was used to extract the free iron oxide (Fed), following a sequence of three successive extractions. Subsequently, o-phenanthroline was added to the extracting solution for completing color reaction, and the absorbance of the solution was determined at wavelength 520 nm by UV-1200 spectrophotometer [42]. Finally, the Fed concentration in the solution was calculated by a regression equation of Fe concentration on absorbance for Fe standard solutions [38].
The most stable horizons (the main soil horizons that affect the migration and transformation of materials in the soil and root activities) were selected from the middle of the pedons and the clay particles were extracted. Then, the mineralogical compositions and total elements’ content levels were analyzed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was performed on the clay (<2 μm), and the XRD analysis results of the clay fractions were collected from 3.2° to 30° 2-theta with Rigaku D/max-rA-produced Cu-Kα radiation generated with a 40-kV accelerating potential and a 40 mA tube current. The clay was oriented on glass slides using the following standard treatments: glycol solvated (EG), air-dried mounts (AD), and glycol-solvated samples heated at 550 °C (K550) [40]. The total elements’ content of the fine-earth fractions and clay fractions (a stable horizon of each pedon) was performed using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with panalytical Axios FAST-PW4400/40 [43,44].
2.4. Data Analysis Results
2.4.1. Weathering Indices and Elemental Concentrations
The fine-earth fraction elemental data were used to calculate the weathering indices. The weight percentage oxide data were converted into molar values and used to calculate the base-alumina ratio (ba values) following the method introduced by Hans [45]: ba = (Na2O+ CaO+K2O)/Al2O3. The ba reflects the leaching of potassium, sodium, and calcium, and the relative accumulation of aluminum. The molar ratios of the free Fe-oxide (citrate-dithionite extractable) to the total elemental Fe-oxide (Fed/FeT) and total elemental Si:Al were calculated as additional weathering indices in this study. XRD data were analyzed using JADE version 6. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using Canoco5 [46].
2.4.2. Soil Classification
Quantitative systems with defined diagnostic horizons and diagnostic characteristics are generally used in soil classifications around the world [47]. Currently, several major global soil classification systems are in use, including the Soil Taxonomy (ST) [48,49,50,51] and the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) [52,53,54,55]. China also had a standard research on soil taxonomic classification (Chinese Soil Taxonomy, CST) [56,57]. In the present study, based on the comparative analysis results, the Chinese Soil Taxonomy (CST), genetic characteristics, and classifications of the soil relative to the elevation gradient were discussed. The diagnostic horizons and diagnostic characteristics of the soil were successfully determined. In this study, the examined soil samples were attributed to soil subgroups in CST by referencing the Chinese Soil Taxonomy (third version) [58]. In addition, in accordance with the standards provide in the Illustrated Guide to Soil Taxonomy and Keys to Soil Taxonomy (10th Edition, 2006) [59] and the World Reference Base for Soil Resources, 2014 (updated 2015), the Soil Taxonomy (ST) of the subgroups and WRB were determined [60].
3. Results
3.1. General Soil Characterization
It was observed in this study that the general morphological, physical, and chemical properties varied substantially across the examined elevation gradient (Table 2). There was an O horizon observed in the S3, S4, S5, S6, and S8 pedons. Additionally, with the exception of the S8 pedon, which had an R horizon at 141 cm, there were no R horizons in the remainder of pedons within the excavation depths. The moist soil colors included a wide range of Munsell hues, with yellowish colors of 10YR and 2.5Y observed in S5, and 10YR observed in S1, S2, S3, S4, S6, S7, and S8 pedons, respectively. The dry soil colors ranged from 5 to 7 in value and 3 to 6 in chroma, and the moist soil colors ranged from 4 to 6 in value and 3 to 6 in chroma, with the exception of a surface horizon in S5 pedon (chroma of 1).

Table 2.
Morphological, physical, and chemical properties for soils derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
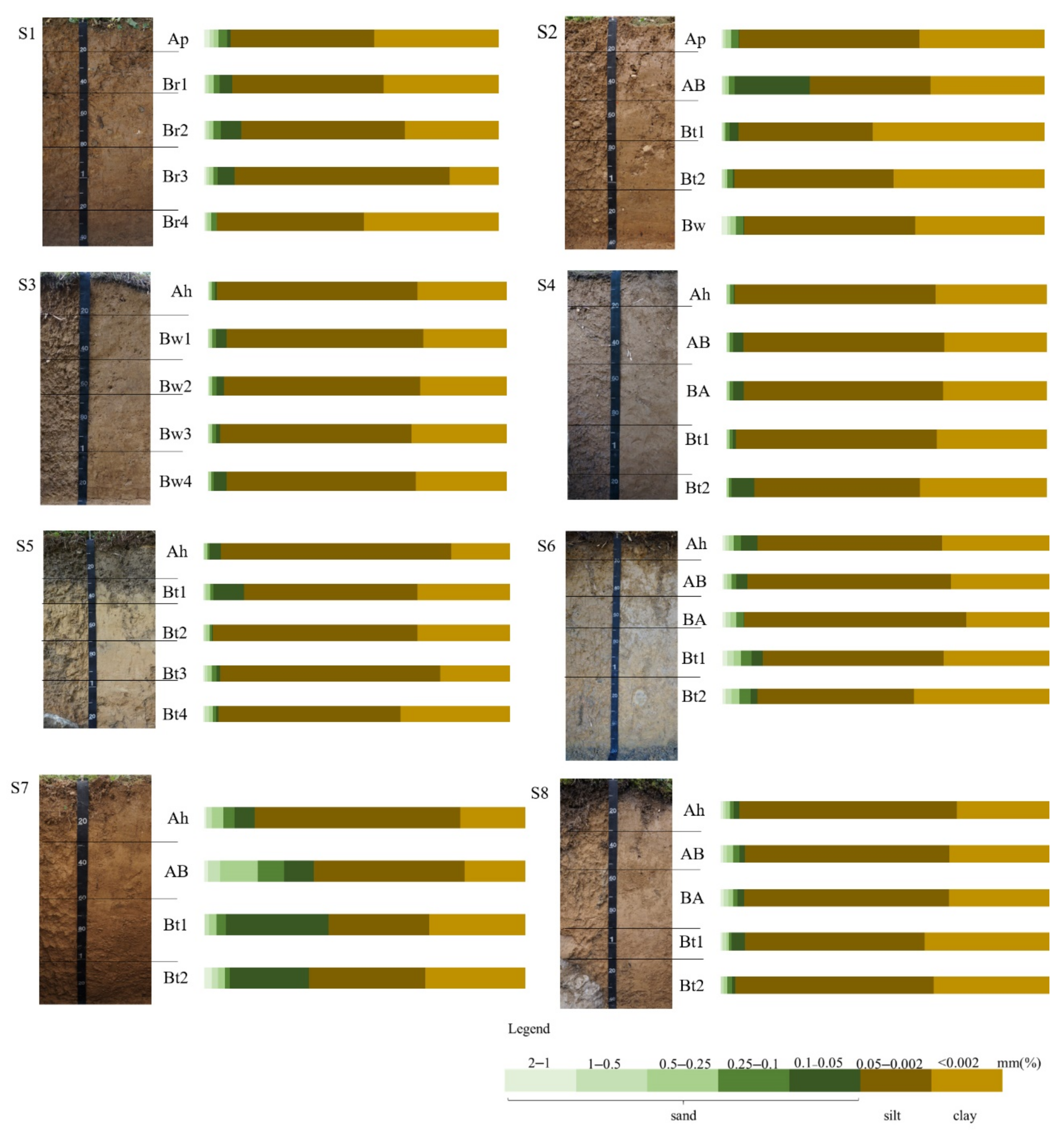
Figure 2 shows the depth plots of grain size distribution within eight soil profiles tested. The measurements of the particle size distributions (Table 2) revealed that the amount of clay had generally reached a maximum in the Bt horizon in the S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 pedons. The clay content levels exhibited relative extremes in the S2 and S1 pedons. For example, 53% in the Bt1 horizon of the S2 pedon and 16% in the Br3 horizon of the S1 pedon. As shown in Figure 2, clay and silt accounted for the majority of soil particles in the eight soil profiles. Except AB horizon of S2 and all horizon of S7, the content of sand (2–0.05 mm) is less than 15%, the content of sand in AB horizon of S2 and Ah horizon of S7 is between 15% and 30%, while the content of sand in AB, Bt1, and Bt2 horizons of S7 is more than 30%. The eluviation and illuviation of the clay occurred in pedons S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8, respectively, with the content of clay in the subsurface horizons observed to be obviously higher than that in the overlying horizons, or argillan was observed in the pedons.
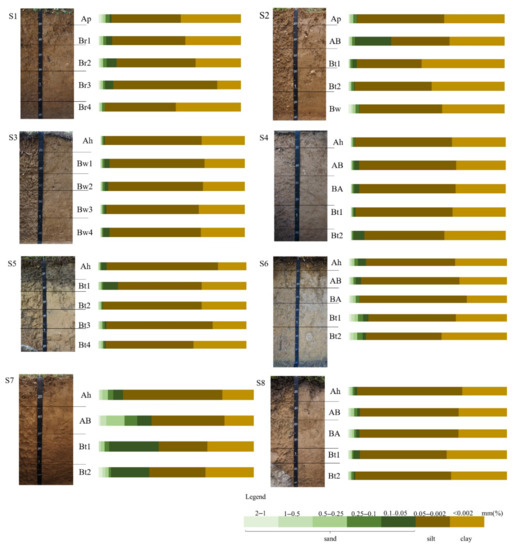
Figure 2.
Depth plots of grain size distribution within soil profiles.
The soil pH in the H2O was determined to range from 4.5 to 7.7, with the highest values noted in the Bt1 horizon of pedon S2, and the lowest values noted in the surface horizon of pedon S7. Therefore, there was no distinct trend with elevation observed (Table 2). The content levels of rocks’ fragments were less than 3% in eight pedons. For pedons S1, S2, S3, and S4, the soil bulk densities were greater than 1.50 g cm−3 in all the horizons except the surface horizons, while the soil bulk densities of S5, S6, and S8 were less than 1.50 g cm−3 in all the horizons. At the same time, the decreasing bulk density of surface horizon was found from pedon S1 to S8 (Table 2). Therefore, the bulk densities tended to decrease with the increasing elevations, particularly in regard to the surface horizons. Furthermore, it was observed that, with the increases in the soil profile depths, the bulk densities of the soil gradually increased (Table 2). The soil cation exchange capacity at pH 7.0 ranged from 10.51 cmol kg−1 to 46.36 cmol kg−1 in the Ah horizon of pedon S3 and the Bt2 horizon of pedon S7, respectively. The content levels of calcium carbonate equivalent ranged between 2.53 g kg−1 and 16.37 g kg−1 in the Bt1 horizon of pedon S7 and the Bw horizon of pedon S2, respectively. It was found that the exchange Ca2+ content ranged from 4.45 cmol kg−1 (Ah horizon of pedon S4) to 27.20 cmol kg−1 (Bt1 horizon of pedon S2) and gradually increased with the depths of the pedons (with the exception of the S1 pedon). The pH values of some horizons (Bw1, Bw2, and Bw3) in the S1 and all horizons in S2 pedons were greater than 7.0. Therefore, the base saturation of those pedons was not determined in this study but generally considered to be greater than 50%. In addition, pedon S7 was determined to have a base saturation <50% for all horizons, while some or all horizons of the other soil pedons were determined to be >50% (Table 2).
3.2. Total Elements’ Content
3.2.1. Fine-Earth Fractions
The total elements’ content results of the fine-earth fractions indicated some variations in the elemental concentrations among the pedons (Table 3). The eight soils were determined to have SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3 as major elements, always in that sequence. The secondary elements were K2O, MgO, and CaO. In regard to the Al2O3 and K2O, there was no tendency of accumulation observed in the S1 and S2, but in the other pedons we observed that the increasing tendency with the depth of the profile. In the case of the MgO, there was no tendency of accumulation observed in the S1, S2, S3, and S4, but it tended to increase toward the surface in S4, S5, S7, and S8. In addition, the content levels of Fe2O3 gradually increased with the depths, with the exception of pedon S2. The content levels of CaO gradually decreased in the pedons, with the exception of pedons S1, S2, and S4, and the content levels of MnO were observed to only vary slightly within all the pedons. The ba for the pedons varied from 0.25 to 0.40 and there were only slight differences observed within the pedons. The lowest values of the ba were noted in the Br2 horizon of pedon S1 and the highest values were noted in the surface horizon of pedon S8. The molar ratio of Si:Al ranged between 5.52 to 10.39, with the highest values noted in the surface horizon of pedon S3 and the lowest values noted in the Bt2 horizon of pedon S8. The molar ratio of Si:Al varied little within each pedon. It was found that, as the elevation increased, the molar ratio of the Si:Al gradually increased from pedon S1 to pedon S3 and varied little from S3 to S8. The Fed:FeT values reflected the degrees of weathering of the soil pedons and ranged from 25.89% (Bt1 horizon of pedon S7) to 66.05% (Br2 horizon of pedon S1) in the tested soil. Additionally, it was found that pedon S7 had the lowest content among all of the pedons. The Fed:FeT values also indicated the differences in the soil weathering intensities. It was observed in this study that, as the depth of the profiles increased, the Fed:FeT of the S2, S3, and S8 pedons gradually decreased. Meanwhile, the other pedons gradually increased with the profile depth. In addition, the Fed:FeT values of pedons S1 and S2 were found to be higher than those of the other pedons.

Table 3.
Total major element composition and total elements’ content data for soils derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
3.2.2. Clay Fractions
The molar ratios of Si:Al and Si:(Al + Fe) of the middle horizons were calculated in order to reflect the pedogenesis and soil weathering degrees. The results of the middle horizons of each pedon are detailed in Table 4. The molar ratios Si:Al and Si:(Al + Fe) in the soil were used to determine the degrees of allitization. The Bt1 horizon of the S2 pedon was found to have the highest molar ratio of Si:Al and Si:(Al + Fe). Meanwhile, the Br2 horizon of the S1 pedon had the lowest molar ratio of Si:Al, and the S1 and S5 pedons had the lowest molar ratios of Si:(Al + Fe).

Table 4.
Total elements’ content data for soils in the clay derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
3.2.3. Multivariate Analyses
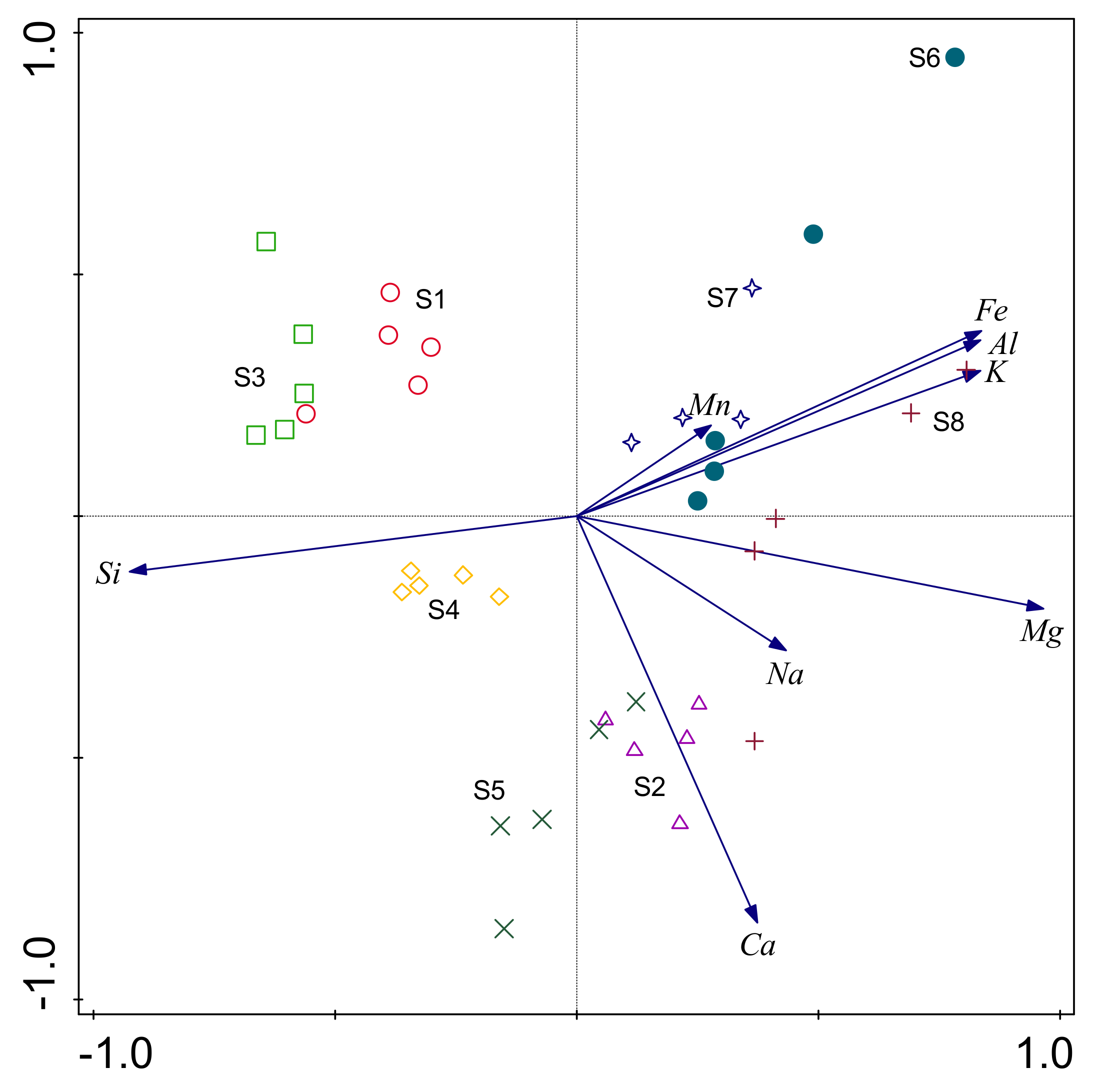
In multivariate analysis processes, the components (factors) of loading and the proportions of variance for the PCA were presented as biplots, as illustrated in Figure 3. It was found that the first two principal components explained 79.8% of the total variances. The first principal component (PC1; 62.6% of variance) was a complex multivariate parameter with component loadings ≥0.5 for Mg, Fe, Al, and K, and a loading ≤−0.5 for Si. The second principal component (PC2; 17.2% of variance) had a loading of ≤−0.5 for Ca. The first principal component appeared to represent a multivariate signal from the differences between S1, S3, and S4 and the remaining profiles, with the greatest positive loadings in PC1 from Mg, K, Al, Fe, and Na. Figure 3 illustrates the distinct differences between the soil samples obtained from each study pedon. The internal differences between the horizons of the S6 and S8 pedons were found to be large, and the differences between the horizons of the remaining pedons were generally small. Furthermore, it was determined that the S1, S3, and S4 pedons had positive loadings for Si, while the S2 and S5 pedons had positive loadings for Ca.
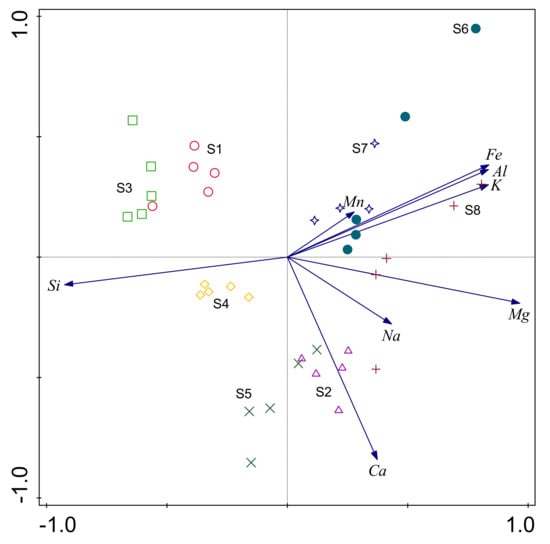
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) based on relationships between eight pedons of 39 soil samples and total elements’ content of the fine-earth fractions.
3.3. X-ray Diffraction
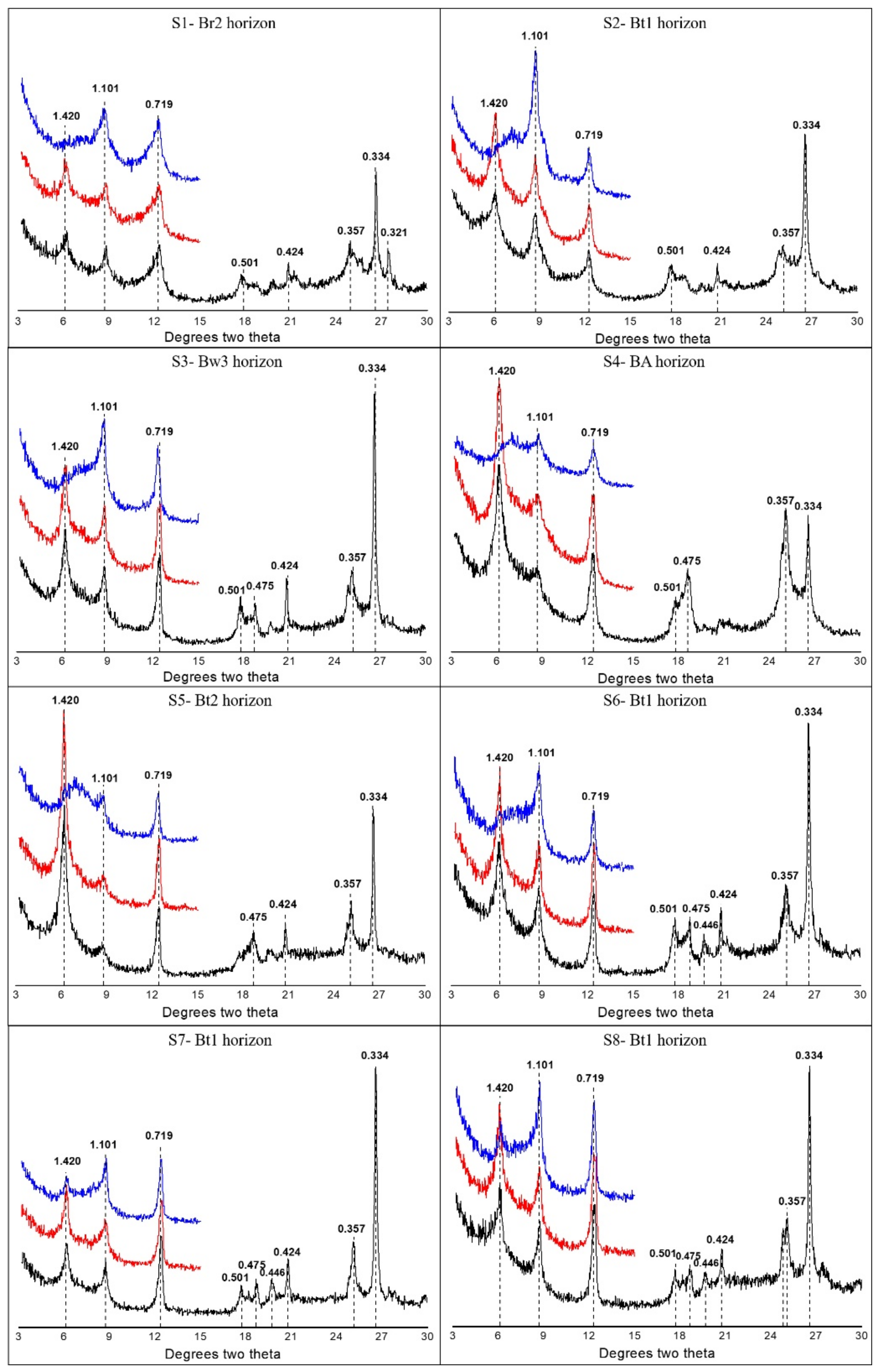
In the current research investigation, it was found that the clay fractions demonstrated variations in mineral assemblage across the elevation gradient under the conditions of a subtropical mountain climate (Figure 4). Asymmetric kaolinite peaks were evident at 0.719 nm and 0.357 nm, and collapsed after K550 treatment. It was found that kaolinite existed in all eight horizons (Figure 4). The peak intensity of the kaolinite in pedon S1 was obviously greater than that in the other pedons. The peak intensity of the kaolinite gradually decreased from pedon S1 to pedon S4, and the peak intensity gradually increased from pedon S5 to pedon S8. The eight pedons were observed to have peaks at 1.000 nm, 0.500 nm, and 0.333 nm in the EG. At 1.000 nm, the asymmetric peak was illite and the symmetrical peak was mica, which indicated that illite existed in all eight soil horizons. The peak intensity of the illite peaks gradually increased from pedon S1 to pedon S8 (with the exception of pedons S4 and S5). The vermiculite was observed to have a diffraction peak at 1.46 nm, after heating at high temperature, and the 1.46-nm diffraction peak of the K550 had weakened. These findings indicated that the eight types of soil samples contained vermiculite. The peak intensities of the vermiculite gradually increased from pedon S1 to pedon S5 and then gradually decreased from pedon S5 to pedon S8. In addition, pedons S1, S2, and S4 had illite-smectite (I–S) mixed-layered minerals (MLMs) as the dominant phase, and a progressive dominance of illite in an I–S MLMs phase prevailed toward the surface. Illite, kaolinite, vermiculite, and illite-vermiculite were found to be present in all of the pedons. Additionally, a diffractometer and all diffraction data were analyzed using JADE version 6 (Table 5). It was found that the proportions of the illite-vermiculite (I–V) MLMs gradually increased from S1 to S8. In addition, no I–S MLMs was found in S5, S6, S7 and S8, but the proportions of illite in S5, S6, S7, and S8 were higher than that in S1, S2, and S4.
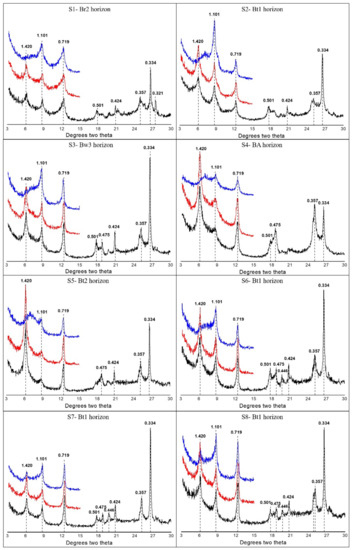
Figure 4.
Examples of XRD patterns in the clay fraction samples of middle horizons for each soil pedon. The sequence of treatments is represented by three different colors. Black patterns (bottom) are glycol-solvated (EG) samples. Red patterns (middle position) were analyzed as air-dried mounts’ (AD) samples. Blue patterns (top) are glycol-solvated samples heated at 550 °C (K550). All d-values assigned to peaks are in nm (10−9 m).

Table 5.
X-ray diffraction analysis data for soils in the clay derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
3.4. Soil Classification
In the present study, eight pedons were classified as two orders, three suborders in CST, and as three subgroups and four RSGs in ST and WRB, respectively. In CST, firstly, there was a horizontal wavelife or discontinuous lithic contact of carbonated rocks with its upper boundary within 125 cm of the soil surface or there were carbonate rock fragments or weathered residual lime within 125 cm of the soil surface. Secondly, there were a base saturation percentage of 50 or more and a pH value of 5.5 or more in all soil horizons. When the pedons meet the two requirements, it has the lithologic characters of carbonate rocks (L.C. of carbonate rocks) [58]. The pH value of a few or all horizons in pedons S3, S4, and S7 is less than 5.5, so they had no L.C. of carbonate rocks. The S1 and S3 pedons were not divided to the Bt horizon and were formed by weathering and soil-forming processes. There was no or almost no material illuviation and no distinct argillification took place. Therefore, those two pedons existed of a cambic horizon and were classified as Cambosols. The S1 pedon displayed L.C. of carbonate rocks and was classified as Brown Carbonati-Udic Cambosols. The S3 pedon was characterized by ferric property and was classified as Ferric Hapli-Perudic Cambosols. According to CST, the overlying eluvial horizons had 15% to 40% total clay in pedons S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 and the total clay content in the subsurface horizons was 20% or more (relative) higher than that in the eluvial horizons [58]. Additionally, argillan was observed on both the vertical and horizontal surfaces of the pedons S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8. Then, these pedons existed with argic horizons (the argic horizon is a subsurface horizon in which clay content is distinctly higher than that in the overlying horizon). Therefore, they were classified as Argosols. The soil above 800 m accounted for the perudic moisture regime, and all of the Argosols were classified as Perudic Argosols. According to the humus property, L.C. of carbonate rocks, and the soil colors, five pedons were classified as different subgroups. The S2 and S8 pedons accounted for the L.C. of carbonate rocks and were classified as Typic Carbonati-Perudic Argosols. The S5 and S6 pedons accounted for the L.C. of carbonate rocks and the humic property. Pedon S5 was classified as Humic Carbonati-Perudic Argosols and pedon S6 was classified as Humic-Brown Carbonati-Perudic Argosols. The S7 pedon accounted for the humic property and was classified as Humic Hapli-Perudic Argosols, and the S4 pedon was classified as Typic Hapli-Perudic Argosols. In ST, pedons S1 and S3 were classified as Typic Eutrudepts. The required characteristics of argillic horizon was the argillic horizon must have at least 1.2 times more clay than the eluvial horizon (the eluvial horizon has 15% to 40% total clay in the fine-earth fraction) or clay films were observed [59]. The pedons S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 existed with argillic horizon and were classified as Hapludalfs further. It was observed that pedon S7 had a base saturation (by sum of cations) of less than 60% at a depth of 125 cm below the top of the argillic horizon and was thereby classified as Ultic Hapludalfs, while the others were classified as Typic Hapludalfs. In WRB, the criteria of argic horizon were the ratio of clay in the argic horizon to that of the overlying horizons (the overlying horizons has ≥10% and <50% clay content in the fine-earth fraction) was greater than 1.4 or clay coatings’ lining ≥5% [60]. The pedons S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 could meet the criteria of argic horizon. According to the argic and cambic horizons, the principal qualifiers of Stagnic, Eutric, Xanthic, and Calcaric, and the supplementary qualifiers of Aric, Loamic, Protocalcic, Differentic, Hypereutric, Ochric, Epidystric, Profondic, Humic, and Siltic, the eight soils were classified as four RSGs (Table 6).

Table 6.
The soil classification for soils derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China.
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Soil Properties
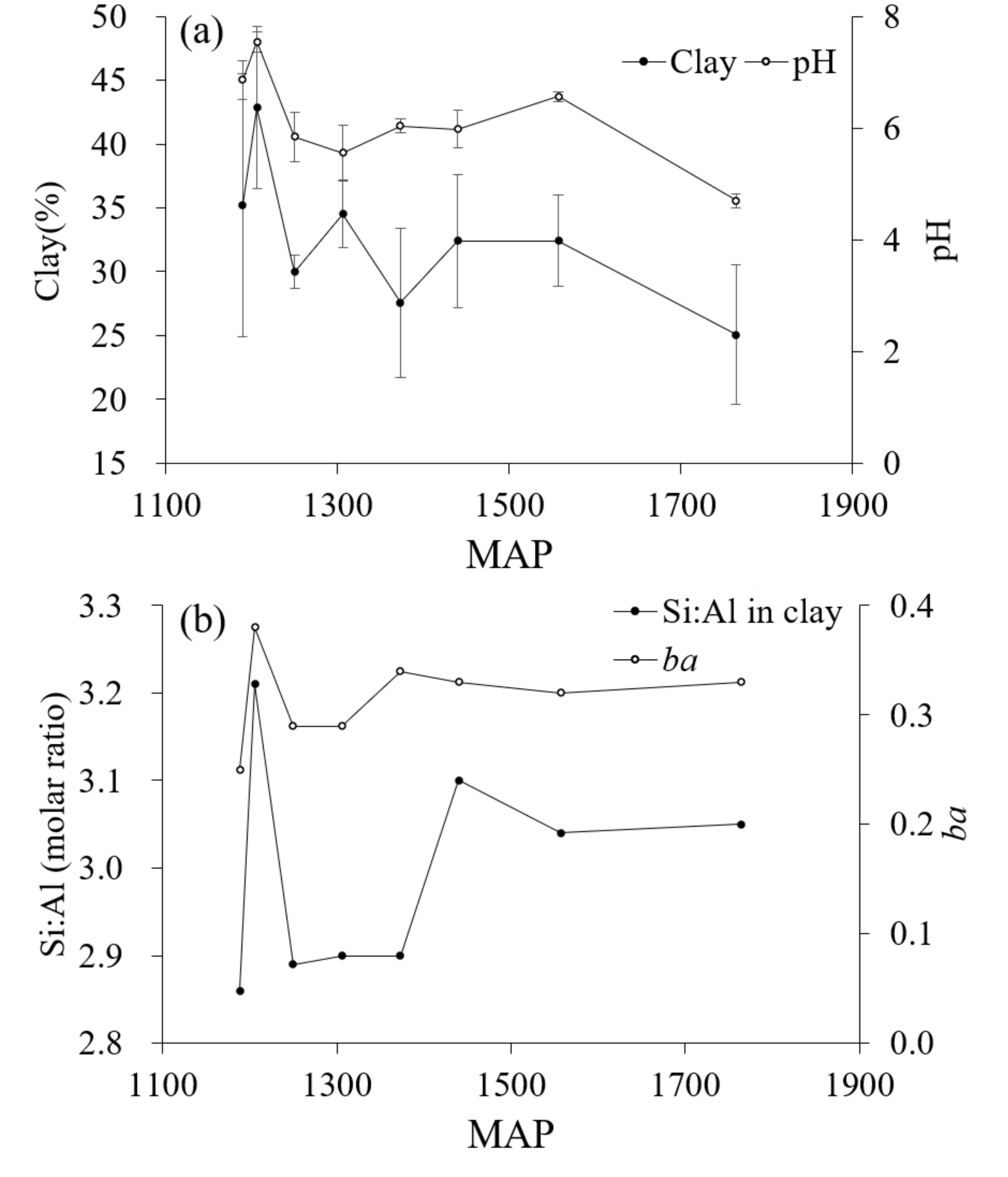
Figure 5a shows the variation trend of pH with MAP. When in a climate of MAP below 1250 mm, the soil base leaching is limited and the pH is neutral or calcareous. When the MAP is between 1250 mm and 1600 mm, the soil pH is between 5.5 and 7.0, which is stable to medium or acidic, and the change of pH trend with MAP is not obvious. When the MAP is above than 1600 mm, the soil pH is strongly acidic. In addition, in some horizons of the S1 and S2 pedons with pH levels greater 7.0, all of the bases were saturated. In regard to the remaining pedons, it was found that if the pH values of each horizon of the pedons were less than 7.0, the saturation of the bases ranged between 30.52% and 71.63%. The range of pH values reflected the limited leaching effects of the base cations for the carbonate rocks [24,25,61]. Therefore, the soil derived from the carbonate rocks at the foot of the Ta-pa Mountain Range should have carbonate rocks’ weathering and base eluviation. There are two possible reasons for the incomplete leaching of base ions in S1 and S2 pedons. One is that the leaching rate of base ions is less than the release rate due to the low MAP and the small degree of leaching [49]. The other is that S1 and S2 pedons are located at the foot of the mountain and the slope is relatively small. The slope process makes S1 and S2 pedons of base ions accumulate. Srivastava also performed micromorphological studies to indicate that carbonate rocks release Ca2+ ions and recrystallize in the process of soil formation, which will change the pH and exchangeable base of soil and can maintain the productivity of soils in India [62].
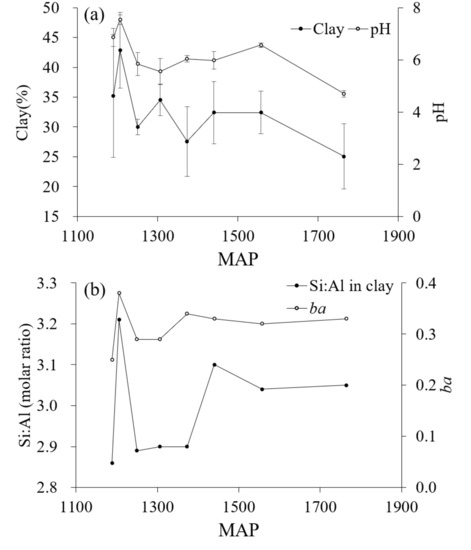
Figure 5.
(a) The average content value of clay and pH, and the error bars represent standard deviations of each pedon, (b) the Si:Al molar ratio of the clay fraction and base-alumina ratio in the stable horizon (ba; Hans,1941).
The physicochemical mechanisms of clay dispersion are the major prerequisites for clay transport [63,64,65]. Figure 5a shows the variation trend of clay content to MAP in eight tested profiles. The standard deviation of clay content is relatively large of S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 pedons, which have argic horizons. The variation trend of clay content with MAP was similar to that of pH with MAP. When the MAP is less than 1250 mm, the clay content of S1 and S2 pedons is relatively high, because of the high MAT (Table 1) and the degree of soil weathering. Therefore, the secondary clay is weathered more and the clay content is high. When the MAP is higher than 1250 mm, the clay content is lower than S1 and S2 pedons, but there is no obvious change trend with MAP. In addition, there was no obvious illuviation of clay particles in pedons S1 and S3 (Figure 2), which cannot account for the argic horizons. However, illuviation of the clay particles obviously occurred in the remaining pedons. Therefore, argic horizons can be found in the lower parts of the soil pedons where the clay content was increased or argillans can be observed. In an arid region of central Iran, the formation of an argillic horizon is due to the fact that palygorskite was trapped by pedogenic carbonate when the climate was wetter than it is today [66].
Clay illuviation had obviously occurred in the S2 site but not in the S1 site. The main reason was that the site S1 was derived from flood alluvium material and the slope was relatively gentle, as shown in Table 1. The pedon S1 is now cultivated land soil, which had low elevation and poor water conditions, with fresh parent material added frequently due to diluvial deposit. As a result, the clay particles could not be leached in the pedon. The S2 site also contained cultivated land soil with pH > 7. The slope was relatively larger than the S1 site. Although pedon S2 was composed of young soil with some fresh gravel of carbonate rocks due to the slop process, artificial activities (changes from forest land to cultivated land) essentially destroyed the soil superstructure due to destruction of vegetation. The surface soil was sandier [67] and the water-holding capacity of the soil was decreased [68,69,70]. Then, the water conditions of S2 site were better than S1 site, and an accelerable argic horizon was formed. The formation of argic horizon tends to lead to lateral infiltration of soil moisture, and soil erosion in karst areas may easily occur. Therefore, such conditions can provide a theoretical basis for prohibiting the destruction of forest vegetation in karst areas in the future.
Soil mineralogy plays an important role in soil genesis [19,71,72]. In soils, irregularly stacked MLMs are usually present as a result of the transitions between one clay mineral and another [72]. Consequently, I–V MLMs, I–S MLMs, kaolinite-smectite (K–S) MLMs [73,74,75], and kaolinite-illite (K–I) MLMs [76,77,78] could potentially result from mineral transformations in those zones. In the S1, S2, and S4 sites, it was determined that the mineral suite <2-μm size fractions was dominated by MLMs in different compositional ranges. These findings suggested that progressive transformations from one clay mineral into another via mixed-layering reactions occurred. In the aforementioned horizons, MLMs rich in illite horizons were the main observed mineral phases, which were replaced by MLMs rich in smectite layers toward the surface [71]. The illite had been gradually converted to I–S MLMs at low elevations in the Ta-pa Mountain Range. It was found that as the elevation and MAP increased and the MAT decreased, the proportions of the I–V MLMs gradually increased, as detailed in Table 5 [79]. It is known that, at pH 6, Al is insoluble and, in contrast, Si is highly soluble [19]. In addition, illite will form montmorillonite with Mg under alkaline conditions and form vermiculite in soil with less weathering and better drainage to leach K+. Therefore, it was concluded that the decisive factors were the climate conditions (precipitation and temperature), which indicated that it had been easier for the illite to transform to vermiculite with the increasing elevations of the Ta-pa Mountains. Therefore, the effects of temperature on soil mineral transformation gradually weakened with the increases in elevation. Rasmussen et al. also found that weathering and mineralogical transformations were limited by temperature. Then, the degree weathering and mineral assemblage of soil derived from basalt exhibited a clear threshold at around 1200 m in the Cascade Range of California [18].
4.2. Weathering and Leaching Intensity
Previous researchers have confirmed that soil weathering is an important indicator of soil pedogenesis and evolution [71,80,81,82,83]. In the present study, the soil pedogenesis and weathering intensities tended to vary significantly along a climosequence and were characterized by substantial variations in the depths to bedrock, clay content (17% to 53%), relative cation leaching and aluminum accumulation (ba 0.25 to 0.40), and mineral assemblage (illite to kaolinite).
The molar ratio of Si:Al of sites S1 and S2 was observed to gradually increase with the increases in the profile depths. Meanwhile, the molar ratio of Si:Al of the other pedons gradually decreased with the increases in the profile depths. This may have been due to the fact that there were higher accumulations of soil temperature in the upper pedons of the soil below 900 m above sea level when compared with the other pedons. Furthermore, the allitization of the S1 and S2 sites was stronger than others. Additionally, the soil temperature accumulations became gradually smaller with the increasing elevation, which impacted the soil-weathering processes. Therefore, this study concluded that the climatic condition determined the molar ratio of Si:Al in the soil, which gradually increased from the S1 climate to the S3 climate and then varied little from the S3 climate to the S8 climate.
In addition, ba value is a main symbolic indicator of weathering and leaching processes [45,84]. As shown in Figure 5b, the regularity of ba and Si:Al ratio in clay was similar and they all had a relationship with MAP. It was found that, with the exception of the ba values for the S2 pedon, which ranged between 0.36 and 0.38, the ba values of pedons S1, S3, and S4 (which were below 1300 m of elevation, 1310 mm of MAP, and above 11.5 °C of MAT) were lower than 0.30 and the ba values of sites S6, S7, and S8 (which were above 1600 m of elevation, 1380 mm of MAP, and below 10.5 °C of MAT) were above 0.30. These findings indicated that the soil weathering and leaching below S4 climate was stronger than that of the soil higher than S5 climate.
The molar ratio of Si:Al and Si:(Al + Fe) in the clay of the soil can potentially reflect the degrees of the allitization [85]. The order of the molar ratios of Si:Al and Si:(Al + Fe) in the clay of the test pedons were observed to be similar (Table 4). The results indicated that the S2 pedon had the highest degree of allitization, which confirmed this study’s speculation that the S2 was a young pedon. However, the molar ratios of Si:Al in the clay of the other pedons displayed good trends with the elevation gradient. Moreover, the molar ratios of Si:Al in the clay of pedons S1, S3, S4, and S5 (below 1600 m of elevation, 1380 mm of MAP, and above 10 °C of MAT) were all below 2.90. The temperature values were determined to have led to strong allitization in those particular soil pedons. In regard to the S6, S7, and S8 pedons, below 1600 m of elevation, 1380 mm of MAP, and above 10 °C of MAT, only minor differences in the molar ratios of Si:Al in the clay were observed. This indicated that the allitization had been weakly affected by climate. According to Figure 3, the greatest negative loadings in PC1 were for Si, elements which were speculated to be the most easily weathered during weathering processes. Therefore, the PC1 may also be considered to represent a weathering intensity variable. It was observed that principal component 2 had strong loadings for Ca and most likely represented the variability in the data caused by the loss of Ca during chemical weathering processes. In the negative direction, PC2 was observed to be significantly influenced by variances in the Ca. The Cambosols of sites S1 and S3 displayed positive loadings for Si, resulting in the desilicification, allitization, and ferritization degrees being higher (Figure 2). In the Chinese Soil Genetic Classification, the yellow soil was a kind of zonal soil group with allitization and yellowing features. The typical yellow soil was mainly distributed below 1300 m and was an important soil resource in Chongqing Municipality. The molar ratio of Si:Al in the clay of typical yellow soil was between 2.00 and 2.50. Then the minimum molar ratio of Si:Al in the clay of pedon S1 was 2.86, which was greater than that of the typical yellow soil in China. Therefore, it was suggested that the climatic conditions of the Ta-pa Mountain area restricted the soil from having strong enough desilicification, allitization, and ferritization degrees to form yellow soil [86].
4.3. Classification and Evolution Determinations
The soils derived from different parent materials had different evolution directions in different climo-toposequences. Rasmussen et al. also found that with increasing elevation soil rived from basalt development followed Alfisols, Ultisols, Andisols, and Entisols in the Cascade Range of California [18]. Abdenna performed a transect study along a toposequence in Didessa watershed. It was found that Ultisols were developed on tertiary basalt at midland, Alfisols were developed on tertiary basalts and granitic gneisses at midland and highland, and Vertisols were developed on alluvium and colluvium at lowland [49]. The changes in clay content are important indicators of soil classification [29,31]. In the CST, the S1 and S3 pedons were classified as Cambosols and the S2, S4, S5, S6, S7, and S8 pedons were classified as Argosols (S2 due to human activities). Therefore, it was considered possible that the soil had carried out obvious clay particle migration to form Argosols above 1100–1200 m of elevation, 1250–1300 mm of MAP, and 11.5–13.5 °C of MAT range under the natural vegetation environmental conditions in the Ta-pa Mountains. In the present study, sites S1, S2, S5, S6, and S8 accounted for the L.C. of carbonate rocks. Compared to the sites at higher elevation, sites S3 and S4 had higher air temperatures, which were more suitable for the growth of Pinus massoniana Lamb. The roots of Pinus massoniana Lamb could exudate a variety of organic acids, which was conducive to the leaching of base ions in the soils. Under the higher temperature, the forest litter and topsoil organic matter of sites S3 and S4 were easy to decompose [87,88], a thinner (about 1–2 cm) O horizon was found in pedons S3 and S4, and the SOC content in surface horizon was also obviously lower in the two pedons than that in other forest soils at higher elevation (Table 2). The decomposition of these organic matters made more CO2 dissolve in the soil water, which could accelerate the corrosion of limestone fragments and the leaching of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the soils. Therefore, the lower pH values (<5.5) were found in the topsoil for pedons S3 and S4 (Table 2). Therefore, those particular sites could not account for the L.C. of carbonate rocks. In addition, site S7 was affected by topography, due to its location on a gentle slope of a small, flat dam in the mountains or in the foothills of the inner mountain slope. It also could not account for the L.C. of carbonate rocks. Therefore, it was determined in this study that, under subtropical climate condition, the soil formed from carbonate rocks cannot account for the L.C. of carbonate rocks due to the influencing effects of topography and vegetation. The soil sites located between 1300 m and 2100 m above sea level had accounted for the humus properties, while those with elevations above 2100 m (S8) could not have. This may have been due to the fact that the accumulation and leaching processes of the organic carbon were limited due to the effects of vegetation. In summary, in the Ta-pa Mountain area, the L.C. of carbonate rocks were affected by the vegetation and local topography, and the soil between 1300 m and 2100 m above sea level was able to accumulate organic carbon; thus, these areas accounted for the humus property. In addition, the soil below 1100–1200 m of elevation, 1250–1300 mm of MAP, and 11.5–13.5 °C of MAT could be divided into Cambosols (Inceptisols in ST, Cambisols in WRB) or Argosols (Alfisols in ST, Luvisols or Alisols in WRB) under the influences of artificial activities. In the soil above1100–1200 m of elevation, 1250–1300 mm of MAP, and 11.5–13.5 °C of MAT, which was not affected by artificial activities, the environmental conditions were beneficial for the soil to evolve to Argosols.
5. Conclusions
In the current research investigation, the quantification of the pedogenesis of soil derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in the Ta-pa Mountains indicated that, under the subtropical mountain climatic conditions, the illite had been transformed into illite-smectite below 1300–1500 m of elevation, 1300–1370 mm of MAP, and above 10.5–11.5 °C of MAT, and to vermiculite above this climate. Thus, the temperature levels were the main controlling factors that determined the weathering of clay minerals at low elevation sites, resulting in the illite transforming into I–S MLMs. However, the effects of temperature on soil mineral transformation gradually weakened with the increases in elevation, resulting in the illite transforming into vermiculite. Furthermore, it was determined that changes from forest land to cultivated land (due to destruction of vegetation) could potentially accelerate the formation of argic horizons from carbonate rocks in subtropical mountain. These findings provided a theoretical basis for carbonate rocks’ weathering and ecological problems in karst areas. When the soils reached approximately 1100–1200 m of elevation, 1250–1300 mm of MAP, and 11.5–13.5 °C of MAT, the argic horizons of the soil could be accounted for. It was concluded that the soil in the study area evolved from the Cambosols in the CST (Inceptisols in ST, Cambisols in WRB) to the Argosols in the CST (Alfisols in ST, Luvisols or Alisols in WRB) under the conditions of the natural vegetation environment. Therefore, the conclusions obtained in this study provide support for the future determination of the soil-type boundaries along a climosequence in subtropical mountain climates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.C. and J.H.; methodology, E.C., J.H., and S.Z.; software, J.H. and S.L.; investigation, J.H., E.C., S.L., and M.L.; data curation, J.H., S.L., and M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, E.C., J.H., and S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41977002), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. XDJK2020B069), and the Chongqing Postgraduate Research and Innovation Project (CYS19124).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
MAP, mean annual precipitation; MAT, mean annual temperature; XRD, X-ray diffraction; CST, Chinese Soil Taxonomy; ST, Soil Taxonomy; WRB, World Reference Base for Soil Resources; SOC, soil organic carbon; Fed, free iron oxide; RF, rock fragments; BD, bulk density; CEC7, cation exchange capacity at pH 7.0; CCE, calcium carbonate equivalent; ECa2+, exchange Ca2+; BS, base saturation; EG, glycol solvated; AD, air-dried mounts; K550, glycol-solvated samples heated at 550 °C; ba, base-alumina ratio; PCA, principal component analysis; MLMs, mixed-layered minerals; L.C. of carbonate rocks, lithologic characters of carbonate rocks.
References
- Braithwaite, C.J.R. Carbonate rocks. Nature 1967, 216, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.T.; Luo, Y. Measurement of carbonated rocks distribution area in China. Carsologica Sin. 1983, 02, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Ji, H. Determining CO2 consumption from elemental change in soil profiles developed on carbonate and silicate rocks. Acta Geochim. 2015, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clow, D.W.; Mast, M.A. Mechanisms for chemostatic behavior in catchments: Implications for CO2 consumption by mineral weathering. Chem. Geol. 2010, 269, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J. Study on the Character Diagnostic Characteristic of Calcareous Soil in Kaster Ecological Environment of Guizhou Province. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guizhong, China, 2009. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lv, M.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Cai, Y.L. General Review of Soil Erosion in the Karst Area of Southwest China. Prog. Geogr. 2007, 26, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Weng, Q. The impact of land use and land cover changes on land surface temperature in a karst area of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, W.R.; Romero, R.E.; de Souza Júnior, V.S.; Cooper, M.; Sartor, L.R.; de Moya Partiti, C.S.; Jorge, F.D.O.; Cohen, R.; de Jesus, S.L.; Ferreira, T.O. Effects of slope orientation on pedogenesis of altimontane soils from the Brazilian semi-arid region (Baturité massif, Ceará). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3731–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campodonico, V.A.; Pasquini, A.I.; Lecomte, K.L.; García, M.G.; Depetris, P.J. Chemical weathering in subtropical basalt-derived laterites: A mass balance interpretation (Misiones, NE Argentina). Catena 2019, 173, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Tseng, K.; Hsia, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, J. Soil respiration in a subtropical montane cloud forest in Taiwan. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Z.; Zehetner, F.; Fujii, K.; Watanabe, T.; Nakao, A. Geochemical fractionation of chromium and nickel in serpentine soil profiles along a temperate to tropical climate gradient. Geoderma 2018, 327, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierczak, J.; Neel, C.; Bril, H.; Puziewicz, J. Effect of mineralogy and pedoclimatic variations on Ni and Cr distribution in serpentine soils under temperate climate. Geoderma 2007, 142, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Óskarsson, B.V.; Riishuus, M.S.; Arnalds, Ó. Climate-dependent chemical weathering of volcanic soils in Iceland. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.G.; Lambert, J.; Nanzyo, M.; Dahlgren, R.A. Soil genesis and mineralogy across a volcanic lithosequence. Geoderma 2017, 285, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.L. Weathering and Pedogenesis of Karst Catchments, Behavior of Mineral. Elements and Environmental Quality; State Key Laboratory of Environment Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science: Guizhou, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, M.; Merkli, C.; Sartori, G.; Mirabella, A. and Plötze, M. Weathering, mineralogical evolution and soil organic matter along a Holocene soil toposequence developed on carbonate-rich materials. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 675–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattar, B.I.; Taimeh, A.Y.; Ziadat, F.M. Variation in soil chemical properties along toposequences in an arid region of the Levant. Catena 2010, 83, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Southard, R.J. Basalt weathering and pedogenesis across an environmental gradient in the southern Cascade Range, California, USA. Geoderma 2010, 154, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Matsuyama, N.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Southard, R.J.; Brauer, N. Soil Genesis and Mineral Transformation Across an Environmental Gradient on Andesitic Lahar. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsui, C.; Chen, Z.; Hsieh, C. Relationships between soil properties and slope position in a lowland rain forest of southern Taiwan. Geoderma 2004, 123, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Long, X. Effects of elevation and lithology on clay mineral composition of soils derived from limestone. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 535–542. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Mao, X.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, L. Genetic characteristics and taxonomic classification of vertical soils in the fanjingshan mountain. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 49, 757–766. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, E.; Ottner, F.; Lundström, U.S. Pedogenesis in the Alnö carbonatite complex, Sweden. Geoderma 2007, 142, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owliaie, H.R.; Abtahi, A.; Heck, R.J. Pedogenesis and clay mineralogical investigation of soils formed on gypsiferous and calcareous materials, on a transect, southwestern Iran. Geoderma 2006, 134, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rate, A.W.; Sheikh-Abdullah, S.M. The geochemistry of calcareous forest soils in Sulaimani Governorate, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Geoderma 2017, 289, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Yao, Y.C.; Qiu, Z.T.; Mao, X.L.; Yang, L.Y. Pedogenetic characteristics and taxonomic classification of soils developed from carbonate rocks in the south of China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2019, 45, 54–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, Y.J. Pronblem related to weathering and pedogenesis of carbonate rock in karst area. J. Guangxi Teach. Educ. Univ. 2019, 36, 94–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.C.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xu, A.N.; Li, D.H.; Cui, Y. Structure styles and their deformation mechanisms of dabashan foreland thrust belt in the North of Sichuan Basin. Geoscience 2006, 20, 429–435. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.H. Tectonic Geomorphology of the Qinling-Daba Mountains and its Geodynamic Implications. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest University, Shaanxi, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- National Soil Survey Center, Natural Resources Conservation Service. Field Book for Describing and Sampling Soils, Version 3.0; Government Printing Office: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2013.
- United States Department of Agriculture. Soil Survey Manual; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Liu, Y. The Research on the Flood Disaster and the Prevention and Reduction System of the Disaster in Chongqing. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2009. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Baillie, I.C. Soil survey staff 1999, soil taxonomy. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 17, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, E. Soil Series of China, Chongqing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. Study on Genetic Characteristics and Taxonomy of Limestone Soils in Chongqing. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Burt, R. Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Lu, R.K. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil; China Agricultural Scientech Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Gong, Z.T. Soil Survey Laboratory Methods; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Munsell Color. Munsell Soil Color Charts; Gretag MacBeth: New Windsor, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Whittig, L.D.; Allardice, W.R. X-ray diffraction techniques. In Methods of Soil Analysis—Part I. Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, H.D. Cation exchange capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2.; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, J.P.; Jackson, M.L. Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite–citrate–bicarbonate system buffered with bicarbonate sodium. Clays Clay Miner. 1960, 7, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis Part. 3. Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; Amer Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Camobell, G.S.; Horton, R.; Jury, W.A.; Nielsen, D.R.; van Es, H.M.; Wierenga, P.J.; Dane, J.H.; Topp, G.C. (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part. 4. Physical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; Amer Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hans, J. Factors of Soil Formation—A System of Quantitative Pedology; Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Lepš, B.J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data using CANOCO 5; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Villas-Boas, P.R.; Franco, M.A.; Martin-Neto, L.; Gollany, H.T.; Milori, D.M.B.P. Applications of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for soil characterization, part II: Review of elemental analysis and soil classification. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockheim, J.G.; Hartemink, A.E. Distribution and classification of soils with clay-enriched horizons in the USA. Geoderma 2013, 209–210, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deressa, A.; Yli-Halla, M.; Mohamed, M.; Wogi, L. Soil classification of humid Western Ethiopia: A transect study along a toposequence in Didessa watershed. Catena 2018, 163, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Maroto, J.M.; Alonso-Azcárate, J. What is clay? A new definition of “clay” based on plasticity and its impact on the most widespread soil classification systems. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2018, 161, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, N.; Ríos, M. Soil classification maps: A valuable tool for learning, interpreting and transferring soil knowledge. Catena 2019, 180, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Circelli, L.; Lorenzetti, R.; Costantini, E.A.C.; Egendorf, S.P.; Colombo, C. Estimation of andic properties from Vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for volcanic soil classification. Catena 2019, 182, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiarpour, I.; Salehi, M.H.; Karimi, A.; Kamali, A. Correlation between Soil Taxonomy and World Reference Base for Soil Resources in classifying calcareous soils: (A case study of arid and semi-arid regions of Iran). Geoderma 2013, 197–198, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J. Revisiting the definitions of gypsic and petrogypsic horizons in soil taxonomy and world reference base for soil resources. Geoderma 2004, 120, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachtergaele, F.O.; Spaargaren, O.; Deckers, J.A.; Ahrens, B. New developments in soil classification: World reference base for soil resources. Geoderma 2000, 96, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Wu, K.N.; Zhang, G.L.; Rossiter, D.G.; Li, L. Characterization of Some calcareous soils from henan and their proposed classification in chinese soil taxonomy. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Rossiter, D.G.; Zhang, G.L. How compatible are numerical classifications based on whole-profile vis–NIR spectra and the Chinese Soil Taxonomy? Eur. J. Soilence 2019, 70, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinese Soil Taxonomy Research Group, I.O.S.S. Keys to Chinese Soil Taxonomy, 3rd ed.; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Hefei, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Staff, S.S. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014: International soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Zaleski, T.; Józefowska, A.; Mazurek, R. Soil formation on calcium carbonate-rich parent material in the outer Carpathian Mountains—A case study. Catena 2019, 174, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Pal, D.K. Significance of the formation of calcium carbonate minerals in the pedogenesis and management of cracking Clay soils (Vertisols) of India. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.N.; Dultz, S.; Tran, T.T.T.; Bui, A.T.K. Effect of anions on dispersion of a kaolinitic soil clay: A combined study of dynamic light scattering and test tube experiments. Geoderma 2013, 209–210, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, D.K.; Srivastava, P.; Bhattacharyya, T. Clay illuviation in calcareous soils of the semiarid part of the Indo-Gangetic Plains, India. Geoderma 2003, 115, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, K.; Pustovoytov, K.; Kuzyakov, Y. Cation exchange retards shell carbonate recrystallization: Consequences for dating and paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Catena 2016, 142, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, H.; Mermut, A.R. Submicroscopy and stable isotope geochemistry of carbonates and associated palygorskite in Iranian Aridisols. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 50, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Bai, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y. Land use effect on soil aggregates in the karst hilly areas—A case study in Qianjiang Chongqing China. Carsologica Sin. 2011, 30, 72–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H. Comparative Research of Soil Micromorphological Characters on Typical Crop Land and Artificial Ecological-Forest Eastern Guanzhong Areas, Shaanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Shaanxi Normal University, Shaanxi, China, 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Heathman, G.C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C. Fractal features of soil particle-size distribution as affected by plant communities in the forested region of Mountain Yimeng, China. Geoderma 2009, 154, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Xiang, N.; Lv, S.; Zhang, G. Fractal characterization of soil particle-size distribution under different land-use patterns in the Yellow River Delta Wetland in China. J. Soil. Sediment. 2014, 14, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.R.P.; Azevedo, A.C.D.; Lepchak, J.K.; Assis, T.C. Weathering of Permian sedimentary rocks and soil clay minerals transformations under subtropical climate, southern Brazil (Paraná State). Geoderma 2019, 336, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J. Weathering of the primary rock-forming minerals: Processes, products and rates. Clay Min. 2004, 39, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Pernes, M.; Tessier, D. Interestratificado caulinita-esmectita em um argissolo desenvolvido a partir de rocha sedimentar do Sul do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2007, 31, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.L.; Churchman, G.J.; Gu, Y.S.; Yin, K.; Wang, C.W. Kaolinite–smectite mixed-layer clays in the Jiujiang red soils and their climate significance. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P.C.; Huertas, F.J. The temporal evolution of pedogenic Fe–smectite to Fe–kaolin via interstratified kaolin–smectite in a moist tropical soil chronosequence. Geoderma 2009, 151, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, F.; Caner, L.; Meunier, A.; Lanson, B. Advances in characterization of soil clay mineralogy using X-ray diffraction: From decomposition to profile fitting. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2009, 60, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubert, F.; Caner, L.; Meunier, A.; Ferrage, E. Unraveling complex <2 μm clay mineralogy from soils using X-ray diffraction profile modeling on particle-size sub-fractions: Implications for soil pedogenesis and reactivity. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viennet, J.C.; Hubert, F.; Ferrage, E.; Tertre, E.; Legout, A.; Turpault, M.P. Investigation of clay mineralogy in a temperate acidic soil of a forest using X-ray diffraction profile modeling: Beyond the HIS and HIV description. Geoderma 2014, 241–242, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khormali, F.; Abtahi, A. Origin and distribution of clay minerals in calcareous arid and semi-arid soils of Fars Province, southern Iran. Clay Min. 2003, 38, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangari, A.C.; Scarciglia, F.; Piluso, E.; Marinangeli, L.; Pompilio, L. Role of weathering of pillow basalt, pyroclastic input and geomorphic processes on the genesis of the Monte Cerviero upland soils. Catena 2018, 171, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Amistadi, M.K.; Chadwick, O.A.; Chorover, J. Fractionation of yttrium and holmium during basaltic soil weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 2013, 119, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torrent, J.; Cabedo, A. Sources of iron oxides in reddish brown soil profiles from calcarenites in Southern Spain. Geoderma 1986, 37, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, A.; Cardace, D.; Tibbett, M.; Echevarria, G. Ecological implications of pedogenesis and geochemistry of ultramafic soils in Kinabalu Park. Catena 2018, 160, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, J. The Soil Resource-Origin and Behavior; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zanelli, R.; Egli, M.; Mirabella, A.; Giaccai, D.; Abdelmoula, M. Vegetation effects on pedogenetic forms of Fe, Al and Si and on clay minerals in soils in southern Switzerland and northern Italy. Geoderma 2007, 141, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.L.; Ci, E.; Li, S.; Lian, M.S.; Chen, L. Pedogenetic Process and Taxonomy of Yellow Soil in Chongqing, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 3, 579–589. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, K.; Kong, X.; Yuan, L.; Lin, H.; He, Z.; Yao, B.; Ji, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, S.; Tian, X. Priming effect of litter mineralization: The role of root exudate depends on its interactions with litter quality and soil condition. Plant Soil 2019, 440, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Shen, P.P.; Zhou, C.L.; Wanga, L.S. Biochemical responses of the mycorrhizae in Pinus massoniana to combined e ects of Al, Ca and low pH. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).