Potential Factors behind the Decline of Pinus pinea Nut Production in Mediterranean Pine Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigated Areas and Data Collection
2.2. Post Harvesting Phase and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pine Production 2008–2017
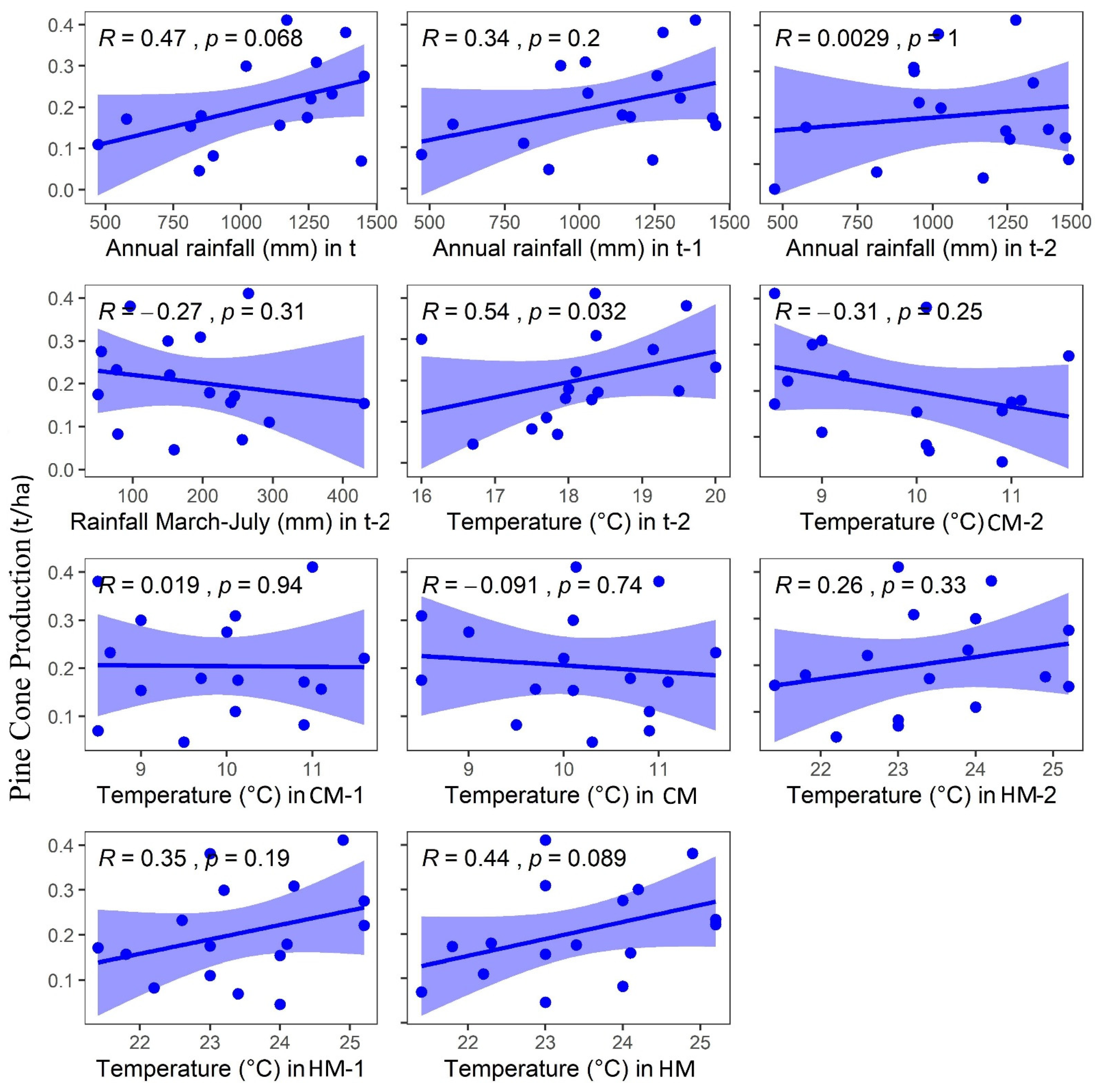
3.2. Climatic Variables Effect
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbero, M.; Loisel, R.; Quezel, P.; Richardson, D.M.; Romane, F. Pines of the mediterranean basin. In Ecology and Biogeography of Pinus; Richardson, D.M., Rundel, P.W., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 153–170. [Google Scholar]
- Mutke, S.; Gordo, J.; Gil, L. Variability of Mediterranean Stone pine cone production: Yield loss as response to climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 132, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R.; González-Martínez, S.C.; Montero, G.; Gordo, F.J.; Bono, D.; Gil, L. Mediterranean stone pine: Botany and horticulture. Hortic. Rev. 2012, 39, 153–201. [Google Scholar]
- Calama, R.; Gordo, J.; Madrigal, G.; Mutke, S.; Conde, M.; Montero, G.; Pardos, M. Enhanced tools for predicting annual stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) cone production at tree and forest scale in Inner Spain. For. Syst. 2016, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamade, K.; FAO. Non-Wood Forest Product Value Chains in Lebanon. 2016. Available online: www.fao.org/publications (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Ovando, P.; Campos, P.; Calama, R.; Montero, G. Landowner net benefit from stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) afforestation of dry-land cereal fields in Valladolid, Spain. J. For. Econ. 2010, 16, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, H.U.M.; Pettenella, D. Pine nuts: A review of recent sanitary conditions and market development. Forests 2017, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarascia-Mugnozza, G.; Oswald, H.; Piussi, P.; Radoglou, K. Forests of the Mediterranean region: Gaps in knowledge and research needs. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 132, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe-Muñoz, V.; Delard, C. Effect of irrigation in growth and fruit production in stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) in Chile. In Proceedings of the XXIX International Horticultural Congress on Horticulture: Sustaining Lives, Livelihoods and Landscapes (IHC2014), Brisbane, Australia, 17 August 2014; 1130, pp. 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Valdiviesso, T.; Pimpao, M.; Trindade, C.S.; Varela, M.C. Reproductive phenology of Pinus pinea. Méditerranéennes Série A Séminaires Méditerranéens 2017, 122, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.; Prieto, A.; Calama, R.; Diaz-Balteiro, L. Optimal management in Pinus pinea L. stands combining silvicultural schedules for timber and cone production. Silva Fenn. 2015, 49, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemer, N.; FAO. Report on Insect Pests Associated with Conelet Losses and Their Management in Pinus Pinea Forests in Lebanon. Lebanon. 2015. Available online: www.researchgate.net/publication/313471959_Report_on_insect_pests_associated_with_conelet_losses_and_their_management_in_Pinus_pinea_forests_in_Lebanon (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- FAO. National Forest and Tree Assessment and Inventory TCP/LEB/2903 Final Report. 2005. Available online: www.fao.org/forestry/15565-0f921641e230ef06f11d15b8856f2ff07.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- FAO. Country Report Lebanon. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010. 2010. Available online: www.fao.org/3/i1757e/i1757e.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Nakhoul, J.; Fernandez, C.; Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Nemer, N.; Abboud, J.; Prévosto, B. Vegetation dynamics and regeneration of Pinus pinea forests in Mount Lebanon: Towards the progressive disappearance of pine. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 152, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrieri, L.; Cecchini, C. Antichi Mestieri Rurali Nel Territorio Del Parco; Felici Editore: Italy, 2010; 157p. [Google Scholar]
- Roversi, P.F.; Strong, W.B.; Caleca, V.; Maltese, M.; Peverieri, G.S.; Marianelli, L.; Marziali, L.; Strangi, A. Introduction into Italy of Gryon pennsylvanicum (Ashmead), an egg parasitoid of the alien invasive bug Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann. EPPO Bull. 2011, 41, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roversi, P.F. Adattamento di specie neo-introdotte, Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann. In Insetti Esotici e Tutela Ambientale; Arti Grafiche Maspero Fontana and C: Cermenate, Italy, 2009; pp. 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, M.Á.; Costas, M.; Outerelo, R.; Melero-Alcíbar, R. Una chinche invasora en la Comunidad de Madrid: Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae). Heteropterus Rev. Entomol. 2009, 9, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bracalani, M.; Benedettelli, S.; Croci, F.; Terreni, P.; Tiberi, R.; Panzavolta, T. Cone and seed pests of Pinus pinea: Assessment and characterization of damage. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, S. An invasive species: Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heidemann) how does it affect forestry activities? Kast. Univ. J. For. Fac. 2017, 17, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, A.O.; Branco, M.; Pereira, M.F.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Maurício, A.; Yart, A.; Guerreiro, V.; Sousa, E.M.R.; Roques, A. Micro X-ray computed tomography suggests cooperative feeding among adult invasive bugs Leptoglossus occidentalis on mature seeds of stone pine Pinus pinea: Consumption of P. pinea seeds by L. occidentalis. Agric. For. Entomol. 2018, 20, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemer, N.; El Khoury, Y.; Noujeim, E.; Zgheib, Y.; Tarasco, E.; Van Der Heyden, T. First records of the invasive species Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Hemiptera: Coreidae) on different coniferous species including the cedars of Lebanon. Rev. Chil. Entomol. 2019, 45, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calama, R.; Mutke, S.; Tomé, J.; Gordo, J.; Montero, G.; Tomé, M. Modelling spatial and temporal variability in a zero-inflated variable: The case of Stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) cone production. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, A.C.O.; Silva, J.E.P.; Correia, A.C.; Sousa, E.M.R.; Roques, A.; Branco, M. Is Leptoglossus occidentalis entirely responsible for the high damage observed on cones and seeds of Pinus pinea? Results from a fertirrigation trial in Portugal. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 429, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, Y.; Binazzi, F.; Nemer, N.; Noujeim, E.; Tarasco, E.; Roversi, P.F.; Pennachio, F. Bark beetles (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae) associated with Pinus pinea in Lebanon: New records with remarks on their ecology, distribution and potential threat for forest stands. Redia 2019, 102, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchi, N.; Mancini, V.; Feducci, M.; Santini, A.; Capretti, P. Leptoglossus occidentalis and Diplodia pinea: A new insect-fungus association in Mediterranean forests. For. Pathol. 2012, 42, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, O. New species of Leptoglossus from North America. Proc. Entomol. Soc. 1910, 12, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Koerber, T.W. Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera, Coreidae), a Newly Discovered Pest of Coniferous Seed. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1963, 56, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.L.; Strong, W.B.; Borden, J.H. Abortion and seed set in lodgepole and western white pine conelets following feeding by Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae). Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.B.; Bates, S.L.; Stoehr, M.U. Feeding by Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: Coreidae) reduces seed set in lodgepole pine (Pinaceae). Can. Entomol. 2001, 133, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.B. Seasonal changes in seed reduction in lodgepole pine cones caused by feeding of Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: Coreidae). Can. Entomol. 2006, 138, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutke, S.; Martinez, J.; Gordo, J.; Nicolas, J.L.; Herrero, N.; Pastor, A.; Calama, R. Severe seed yield loss in Mediterranean stone pine cones (Pinus pinea). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mediterranean Pines (MedPine5), Solsona, Spain, 26 September 2014; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Calama, R.; Manso, R.; Barbeito, I.; Madrigal, G.; Garriga, E.; Gordo, F.J.; Montero, G.; Cañellas, I.; Pardos, M. Do inter-specific differences in seed size determine natural regeneration traits in Pinus pinea and Pinus sylvestris? Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W. Lodgepole pine seedset increase by mesh bagging is due to exclusion of Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: Coreidae). J. Entomol. Soc. Br. Columbia 2015, 12, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tescari, G. Leptoglossus occidentalis, coreide neartico rinvenuto in Italia (Heteroptera, Coreidae). Lav. Soc. Veneziana Sci. Nat. 2001, 26, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, L. La cimice americana delle conifere Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera, Coreidae) e fruttificazione del pino domestic. Georgofili 2009, 6, 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ribes, J.; Escolà, O. Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910, a Nearctic bug (Hemiptera, Heteroptera, Coreidae) found in Catalonia, Spain. Sess. Conjucta d’Entomologia 2005, 43, 47–50, ICHN-SCL 13,47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pagola-Carte, S. Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera, Coreidae), chinche invasora en la cornisa cantábrica ibérica. Heteropterus Rev. Entomol. 2009, 9, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Valvárcel, J.P.; Portillo, P. NOTA BREVE Primer registro de Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera, Coreidae) para Murcia (S.E. de la Península Ibérica). Arq. Entomolóxicos 2009, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Valvárcel, J.P.; Prieto Pilona, F. Primeros registros de Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hem., Coreidae) para Galicia (N.O. Península Ibérica). Arq. Entomolóxicos 2010, 4, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso-Silva, J.M. The north american western conifer seed bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis Geidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera, Coreidae), new to Portugal. Arq. Entomoloxicos 2010, 4, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, E.; Naves, P. The western conifer seed bug Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Portugal. Boletín Sanid. Veg. Plagas 2011, 37, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fent, M.; Kment, P. First record of the invasive western conifer seed bug Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Turkey. North-West. J. Zool. 2011, 7, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur, V.; Yart, A.; Guilbon, S.; Lorme, P.; Auger-rozenberg, M.A.; Roques, A. The invasive Leptoglossus seed bug, a threat for commercial seed crops, but for conifer diversity? Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1833–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R.; Montero, G.; Gordo, J. Pine nut production from forests and agroforestry systems around the Mediterranean- a short overview. In Proceedings of the COST Action FP1203 Workshop and MC Meeting, Zagreb, Croatia, 18–20 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur, V.; Lombaert, E.; Guillemaud, T.; Courtial, B.; Strong, W.; Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.A. The rapid spread of Leptoglossus occidentalis in Europe: A bridgehead invasion. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgen, İ.; Dioli, P.; Çelik, V. New and Interesting record of western conifer seed bug: Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heidemann, 1910) (Heteroptera: Coreıdae) in Eastern Turkey. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 830–833. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kikuhara, Y. Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Hemiptera: Coreidae), a presumable recent invader to Japan. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 12, 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.B. Exotic coreid bugs introduced into China. In Proceedings of the 4th Meeting of the International Heteropterist’s Society, Nankai University, Tianjin, China, 12–17 July 2010; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, S.J.; Son, D.; Choo, H.Y.; Park, C.G. The first record on Leptoglossus occidentalis (Hemiptera: Coreidae) in Korea, a potential pest of the pinaceous tree species. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2013, 16, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaa, M.L.B.; Mejri, M.; Naves, P.; Sousa, E. Detection of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Tunisia. Afr. Entomol. 2013, 21, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapon, D.A. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Morocco. Heteropterus Rev. Entomol. 2015, 15, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae: Coreinae: Anisoscelini) has reached the Greek island of Crete. Arq. Entomolóxicos 2017, 18, 185–187. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae: Coreinae: Anisoscelini) in the Golan Heights. Rev. Gaditana Entomol. 2018, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. Summarized data on the European distribution of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera: Coreidae: Coreinae: Anisoscelini). Rev. Chil. Entomol. 2019, 45, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heyden, T. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae: Coreinae: Anisoscelini) in Algeria. Rev. Gaditana Entomol. 2019, 10, 159–161. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T.; Zettel, H. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae) from Cyprus. Z. Arb. Osterr. Entomol. 2019, 71, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. First records of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera: Coreidae: Coreinae: Anisoscelini) in Finland. Rev. Chil. Entomol. 2020, 46, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Coreidae) in Andorra. Arq. Entomolóxicos 2020, 22, 377–378. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. First record of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 in Guatemala (Hemiptera, Heteroptera, Coreidae). Bol. Asoc. Esp. de Entomol. 2020, 44, 213–214. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T.; Faúndez, E. First records of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Brazil and South Africa. Boletín Mus. Nac. Hist. Nat. Parag. 2020, 24, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- van der Heyden, T. First records of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Estonia and Belarus. Heteroptera Pol. Acta Faun. 2021, 15, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: http://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Dutang, C. fitdistrplus: An R Package for Fitting Distributions. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 64, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peruzzi, A.; Cherubini, P.; Gorreri, L.; Cavalli, S. Le pinete e la produzione dei pinoli dal passato ai giorni nostri, nel territorio del parco di Migliarino, S. Rossore, Massaciuccoli; Pisa: Ento Parco Regionale Migliarino, San rossore, Massaciuccoli, 1998; 134p. [Google Scholar]
- Calama, R.; Gordo, J.; Conde, M.; Madrigal, G.; Mutke, S.; Pardos, M.; Garriga, E.; Montero, G.; Finat, L.; Martín, R.; et al. Pérdidas de rendimiento de piña y piñón en las masas de Pinus pinea. Jorn. Presentación Proy. PROPINEA 2014, 21, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Loewe-Muñoz, V.; Balzarini, M.; Delard, C.; Álvarez, A. Variability of stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) fruit traits impacting pine nut yield. Ann. For. Sci. 2019, 76, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calama, R.; Gordo, J.; Mutke, S.; Conde, M.; Madrigal, G.; Garriga, E.; Arias, M.; Pique, M.; Gandía, R.; Montero, G.; et al. Decline in commercial pine nut and kernel yield in Mediterranean stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) in Spain. iForest-Biogeosciences For. 2020, 13, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, S.E.; Borden, J.H. Distribution and impact of Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Hemiptera: Coreidae) in seed orchards in British Columbia. Can. Entomol. 1996, 128, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.L.; Lait, C.G.; Borden, J.H.; Kermode, A.R. Effect of feeding by the western conifer seed bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis, on the major storage reserves of developing seeds and on seedling vigor of Douglas-fir. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, S.L.; Borden, J.H. Life table for Leptoglossus occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera: Coreidae) and prediction of damage in lodgepole pine seed orchards. Agric. For. Entomol. 2005, 7, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcella, F. Ovulate cone production in pinyon: Negative exponential relationship with late summer temperature. Ecology 1981, 62, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, M.D.; Forcella, F.; Barger, N.N. Declines in pinyon pine cone production associated with regional warming. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.R.; Roques, A.; Hulme, P.E.; Sykes, M.T.; Pysek, P.; Kuhn, I.; Zobel, M.; Bacher, S.; Botta-Dukat, Z.; Bugmann, H.; et al. Alien species in a warmer world: Risks and opportunities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loewe-Muñoz, V.; Balzarini, M.; Álvarez-Contreras, A.; Delard-Rodríguez, C.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M. Fruit productivity of Stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) along a climatic gradient in Chile. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, W.; Schmidt, G.; Schönrock, S. Modelling and mapping of plant phenological stages as bio-meteorological indicators for climate change. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Khoury, Y.; Noujeim, E.; Bubici, G.; Tarasco, E.; Al Khoury, C.; Nemer, N. Potential Factors behind the Decline of Pinus pinea Nut Production in Mediterranean Pine Forests. Forests 2021, 12, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091167
El Khoury Y, Noujeim E, Bubici G, Tarasco E, Al Khoury C, Nemer N. Potential Factors behind the Decline of Pinus pinea Nut Production in Mediterranean Pine Forests. Forests. 2021; 12(9):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091167
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Khoury, Yara, Elise Noujeim, Giovanni Bubici, Eustachio Tarasco, Charbel Al Khoury, and Nabil Nemer. 2021. "Potential Factors behind the Decline of Pinus pinea Nut Production in Mediterranean Pine Forests" Forests 12, no. 9: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091167
APA StyleEl Khoury, Y., Noujeim, E., Bubici, G., Tarasco, E., Al Khoury, C., & Nemer, N. (2021). Potential Factors behind the Decline of Pinus pinea Nut Production in Mediterranean Pine Forests. Forests, 12(9), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091167








