Correlation between Genetic Characteristics, Cell Structure and Material Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) in Different Areas of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants Materials
2.2. Determination of Phenotypic Traits
2.3. Determination of Cell Structure
2.3.1. Frequency and Size of Vascular Bundle
2.3.2. Length and Width of Fiber and Parenchyma
2.3.3. Wall Thickness and Lumen Diameter of Fiber Cell and Parenchyma
2.3.4. Crystallinity
2.4. Material Properties
2.4.1. Physical Properties
2.4.2. Microfibril Angle
2.4.3. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Data Verification
2.5.2. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Phenotypic Traits and Correlation
3.1.1. Data Analysis of Phenotypic Traits
3.1.2. Correlation Analysis of Phenotypic Traits
3.2. Analysis of Cell Structure Traits and Correlation
3.2.1. Data Analysis of Cell Structure Traits
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis of Cell Structure Traits
3.3. Analysis of Physical Mechanic Properties and Correlation
3.3.1. Data Analysis of Physical Mechanic Properties
3.3.2. Correlation Analysis of Physical Mechanic Properties
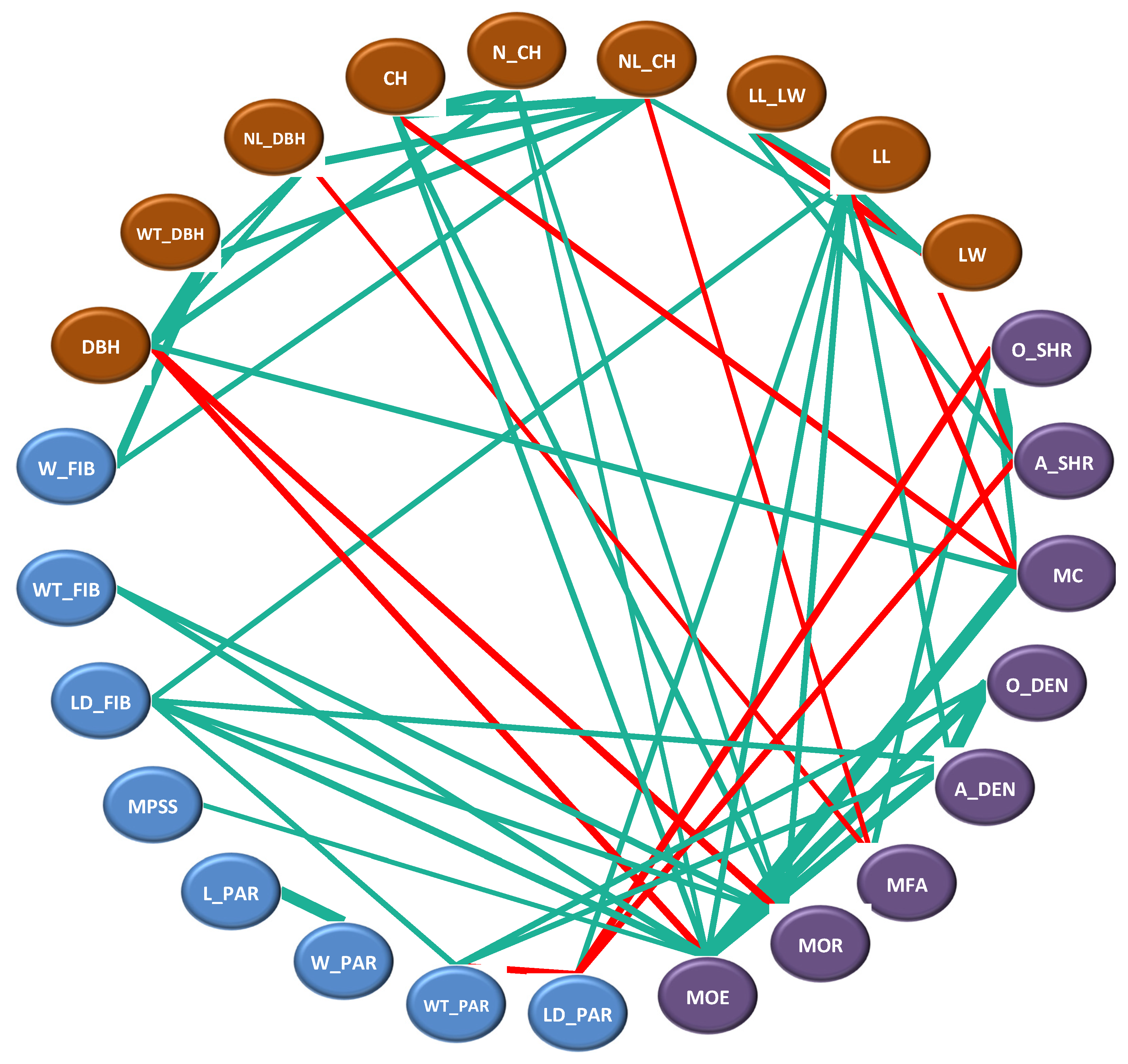
3.4. Correlation Analysis among Various Traits
3.4.1. Correlation Analysis between Phenotypic Traits and Cell Structure Properties
3.4.2. Correlation Analysis between Phenotypic Traits and Material Properties
3.4.3. Correlation Analysis between Cell Structure and Material Properties
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.X.; Guan, F.Y.; Fan, S.H.; Yan, X.R.; Huang, L.Y. Biomass Estimation, Nutrient Content, and Decomposition Rate of Shoot Sheath in Moso Bamboo Forest of Yixing Forest Farm, China. Forests 2021, 12, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.S.; Sun, S.; Ding, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Yue, X.H.; Du, X.; Wei, Q.; Fan, G.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Lou, Y.F.; et al. Analysis of 427 genomes reveals moso bamboo population structure and genetic basis of property traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsova, M.S.; Clark, L.G.; Dransfield, J.; Govaerts, R.; Baker, W.J. World Checklist of Bamboos and Rattans; International Network of Bamboo and Rattan & the Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Beijing, China; London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.H.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.B.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Gao, Z.M.; Lu, H.Y.; Hu, T.; Yao, N.; Liu, K.Y.; et al. The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.H.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Mu, S.H.; Li, X.P.; Gao, J. Transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the fast growing shoots of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Chen, F.S.; Huang, J.H.; Wang, J.S.; Bruelheide, H.; Trogisch, S.; Fang, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Bu, W.S. The Bamboo Rhizome Evolution in China Is Driven by Geographical Isolation and Trait Differentiation. Forests 2021, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.S.; Yang, L.; Peng, Z.H.; Sun, H.Y.; Yue, X.H.; Lou, Y.F.; Dong, L.L.; Wang, L.L.; Gao, Z.M. Developing genome-wide microsatellite markers of bamboo and their applications on molecular marker assisted taxonomy for accessions in the genus Phyllostachys. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, P.; Hartung, J.; Bennewitz, J.; Piepho, H.P. Heritability in Plant Breeding on a Genotype-Difference Basis. Genetics 2019, 212, 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Tang, M.M.; Zhang, W.P.; Bao, X.G.; Wang, Y.; Christie, P.; Li, L. Temporal Differentiation of Crop Growth as One of the Drivers of Intercropping Yield Advantage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Guan, F.; Fan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, X. Functional Trait Responses to Strip Clearcutting in a Moso Bamboo Forest. Forests 2021, 12, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, M.I.; Che, Z.Y.; Latella, B.A. Mapping the structure, composition and mechanical properties of bamboo. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinlabi, E.T.; Anane-Fenin, K.; Akwada, D.R. Properties of Bamboo; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A.; Tochihara, S.; Sato, M.; Shima, H. Universal node distribution in three bamboo species (Phyllostachys spp.). Trees 2017, 31, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, C.Y.T.; Jye, W.K.; Ahmad, H.A.I. Mechanical properties of bamboo and bamboo composites: A Review. J. Adv. Res. Mater. Sci. 2017, 35, 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mannan, S.; Knox, J.P.; Basu, S. Correlations between axial stiffness and microstructure of a species of bamboo. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahab, R.; Mustafa, M.T.; Amini, M.H.M.; Rasat, M.S.M. Anatomy and strength properties between tropical bamboo Gigantochloa levis and G. scortechinii. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Kenaf and Allied Fibres, Selangor, Malaysia, 3–5 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petroudy, S.R.D. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Natural Fibers; Elsevier: Tehran, Iran, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grosser, D.; Liese, W. On the Anatomy of Asian Bamboos, with Special Refererce to Their Vascular Bundles. Wood Sci. Technol. 1971, 5, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Momdal, S.; Das, S.K. Bamboo-a Functionally Graded Composite-Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Strength. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5249–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Shi, P.J.; Cu, Q.; Dong, X.B.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, G.G.; Hui, C. Does the Size-Density Relationship Developed for Bamboo Species Conform to the Self-Thinning Rule? For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 361, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amom, T.; Tikendra, L.; Rahaman, H.; Potshangbam, A.; Nongdam, P. Evaluation of genetic relationship between 15 bamboo species of North-East India based on ISSR marker analysis. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2018, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mohmod, A.L. Effects of age and height of three bamboo species on their machining properties. J. Trop. For. Sci. 1992, 5, 528–535. [Google Scholar]
- Kelemwork, S. Effects of some anatomical characteristics of Ethiopian lowland bamboo (Oxytenanthera abyssinica) on physical and mechanical properties. J. Bamboo Ratt. 2009, 8, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Parameswaran, N.; Liese, W. On the fine structure of bamboo fibres. Wood Sci. Technol. 1976, 10, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Penellum, M.; Sharma, B.; Shah, D.U.; Foster, R.M.; Ramage, M.H. Relationship of structure and stiffness in laminated bamboo composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmod, A.L.; Mustafa, M.T. Variation in anatomical properties of three Malaysian bamboos from natural stands. J. Trop. For. Sci. 1992, 5, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Omobowale, M.O.; Gedengbe, O.K. Trends in fiber characteristics of Nigerian grown bamboo and its effect on its impact and tensile strengths. J. Am. Bamboo Soc. 2008, 21, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.M.; Liese, W.; Kumar, A.; Rao, I.V.R.; Sastry, C. Moisture Content of Two Malaysian Bamboos in Relation to Age, Culm Height, Site and Harvesting Month. In Bamboo for Sustainable Development; Kumar, A., Ramanuja Rao, I.V., Sastry, C., Eds.; Brill Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2002; Available online: https://brill.com/view/book/9789004473911/B9789004473911_s024.xml (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Wangaard, F.F.; Woodson, G.E. Fiber length strength interrelationship for slash pine and its effect on pulp-sheet properties. Wood Sci. 1973, 5, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiku, N.A.; Oluyege, A.O.; Ajayi, B. Fibre dimension and chemical characterisation of naturally grown Bambusa vulgaris for pulp and paper production. J. Bamboo Ratt. 2016, 15, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Mao, F.; Du, H.; Zhou, G.; Xing, L.; Liu, T.; Han, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal evolution and impacts of climate change on bamboo distribution in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, W.; Janshah, M.; Hashim, W.S.; Shirley, B. Morphological and anatomical characteristics of managed natural bamboo stands—Gigantochloa scortechinii. J. Bamboo Ratt. 2007, 6, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, R.; Mohamed, A.; Mustafa, M.T.; Hassan, A. Physical Characteristics and Anatomical Properties of Cultivated Bamboo (Bambusa vulgaris Schrad.) Culms. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 9, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamizi, M.; Mu, S.; Wahab, R.; Sudin, M.; Khalid, I. Anatomical and microstructures features of tropical bamboo Gigantochloa brang, G. levis, G. scotechinii and G. wrayi. Int. J. For. Soil Eros. 2011, 1, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Research and utilization status of natural bamboo fiber. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 159, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, B.; Gao, Z.; Jin, W.; Liu, Z. Biological, Anatomical, and Chemical Characteristics of Bamboo. In Secondary Xylem Biology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Saha, S.K.; Bose, A.K.; Islam, M.N. Effects of age and height on physical and mechanical properties of bamboo. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2008, 20, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Cave, I.D. Theory of X-ray measurement of microfibril angle in wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.H. Growth and Quality of Indigenous Bamboo Species in the Mountainous Regions of Northern Vietnam. Ph.D. Thesis, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Yu, Y.L.; Yu, W.J. Effect of thermal treatment on the physical and mechanical properties of Phyllostachys pubescen bamboo. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2013, 71, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Yang, H.X.; Ivković, M.; Gapare, W.J.; Matheson, C.A.; Wu, H.X. Effect of genotype by spacing interaction on radiata pine genetic parameters for height and diameter growth. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 304, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, A.; Cullis, B.; Welham, S.; Gogel, B.; Thompson, R. An efficient computing strategy for prediction in mixed linear models. Adv. Mater. Res. 2004, 44, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fei, B.H.; Tian, G.L.; Yue, X.H.; Jiang, Z.H. Comparative Study on Growth and Phenotypic Traits of Phyllostachys edulis in Different Areas. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2019, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fei, B.H.; Hu, T.; Ma, Y.J.; Chang, Y.T.; Xia, M.S.; Fan, K.K.; Jiang, Z.H. Comparative Study on Cell Structure Traits of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) in Different Areas. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 38, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fei, B.H.; Tian, G.L.; Hu, T.; Yue, X.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Jiang, Z.H. Comparative study on physical mechanic properties of Phyllostachys edulis in different latitudes. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2019, 41, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lakkad, S.C.; Patel, J.M. Mechanical properties of bamboo, a natural composite. Fibre Sci. Technol. 1981, 14, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fang, C.H.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.X.; Fei, B.H. Hygroscopic swelling of moso bamboo cells. Cellulose 2020, 27, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaut, J.M.; Fracheboud, Y.; Monneveux, P.; Banziger, M.; Vargas, M.; Jiang, C.J. Quantitative trait loci for yield and correlated traits under high and low soil nitrogen conditions in tropical maize. Mol. Breed. 2007, 20, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, R.F.; South, S.; Johnson, W.; Iacono, W. The Heritability of Personality Is Not Always 50%: Gene-Environment Interactions and Correlations Between Personality and Parenting. J. Personal. 2008, 76, 1485–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.G.; Shen, Z.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Shen, X.G.; Chen, Y.J. A Study on the Stalk Factor and Fiber Traits and Their Correlation of Phyllostachys edulis ‘Pachyloen’. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2021, 42, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.L.; Qi, J.Q.; Hu, T.X.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Hoop, C.F.D.; Huang, X.Y. Anatomical characteristics and physical–mechanical properties of Neosinocalamus affinis from Southwest China. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, P.; Aguiar, C.; Labbe, N.; Commandre, J.M. Enhancing the combustible properties of bamboo by torrefaction. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8225–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Fang, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Fei, B.H. Observing bamboo dimensional change caused by humidity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 124988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.P.; Kyanka, G.H.; Thorpe, J.L. S2 fibril angle elastic modulus relationship of TMP Scotch pine fibers. Woodence 1977, 10, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cave, I.D.; Walker, J. Stiffness of wood in fast-grown plantation softwoods: The influence of microfibril angle. For. Prod. J. 1994, 44, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shupe, T.F.; Choong, E.T.; Stokke, D.; Gibson, M.D. Variation in cell dimensions and fibril angle for two fertilized even-aged loblolly pine plantations. Wood Fiberence 1996, 28, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Elspeth, M.; Jason, H. A review of the effects of silviculture on timber quality of Sitka spruce. Forestry 2002, 75, 107–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, H.K.; Lu, F.; Tian, G.L.; Lin, J.G. Bamboo fibers for composite applications: A mechanical and morphological investigation. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Fei, B.H. Comparison of the mechanical characteristics of fibers and cell walls from moso bamboo and wood. BioResours 2017, 12, 8230–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okahisa, Y.; Kojiro, K.; Kiryu, T.; Oki, T.; Furuta, Y.; Hongo, C. Nanostructural changes in bamboo cell walls with aging and their possible effects on mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroudy, S.R.D. 3-Physical and mechanical properties of natural fibers. In Advanced High Strength Natural Fibre Composites in Construction; Woodhead Publishing: Mazandaran, Iran, 2017. [Google Scholar]
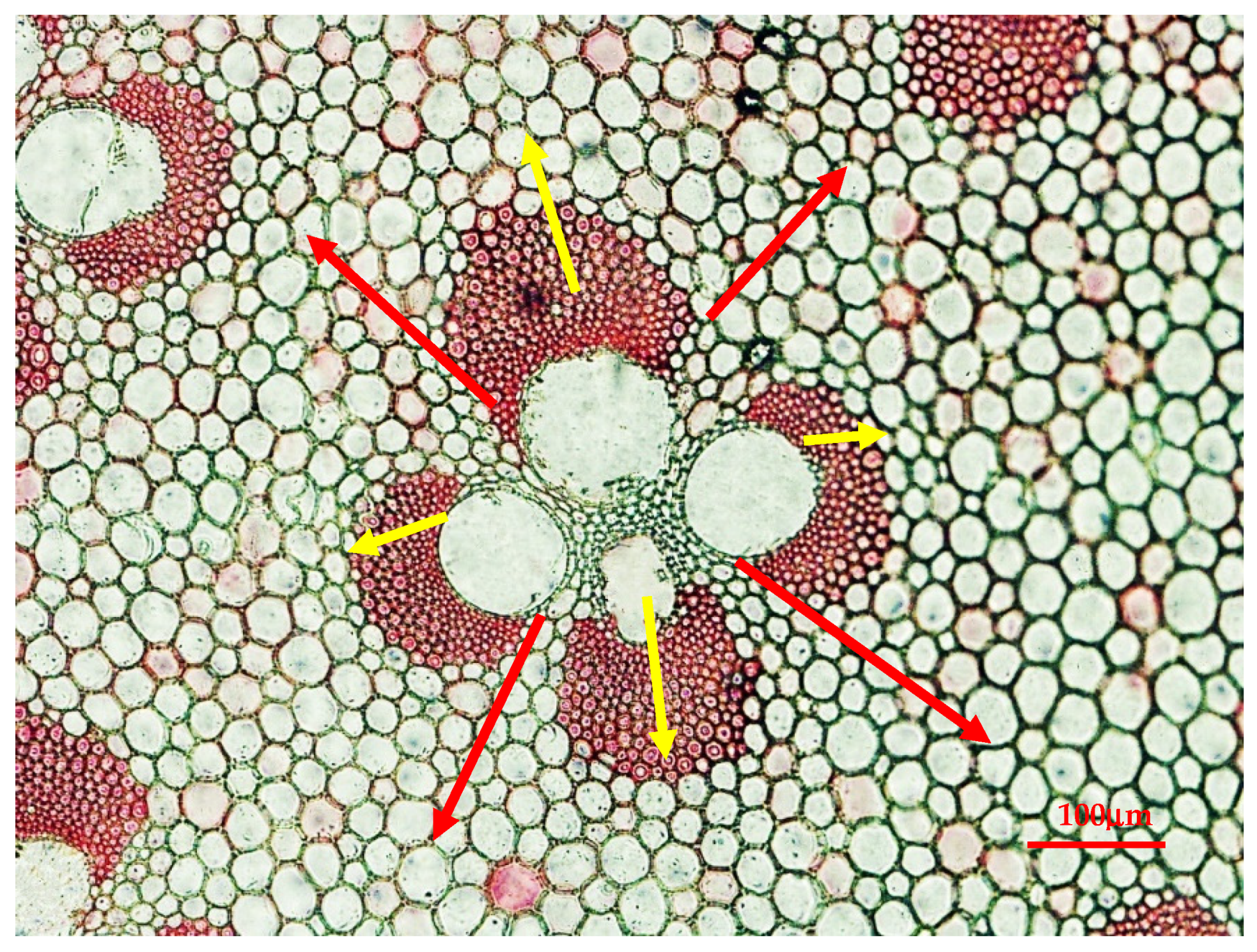
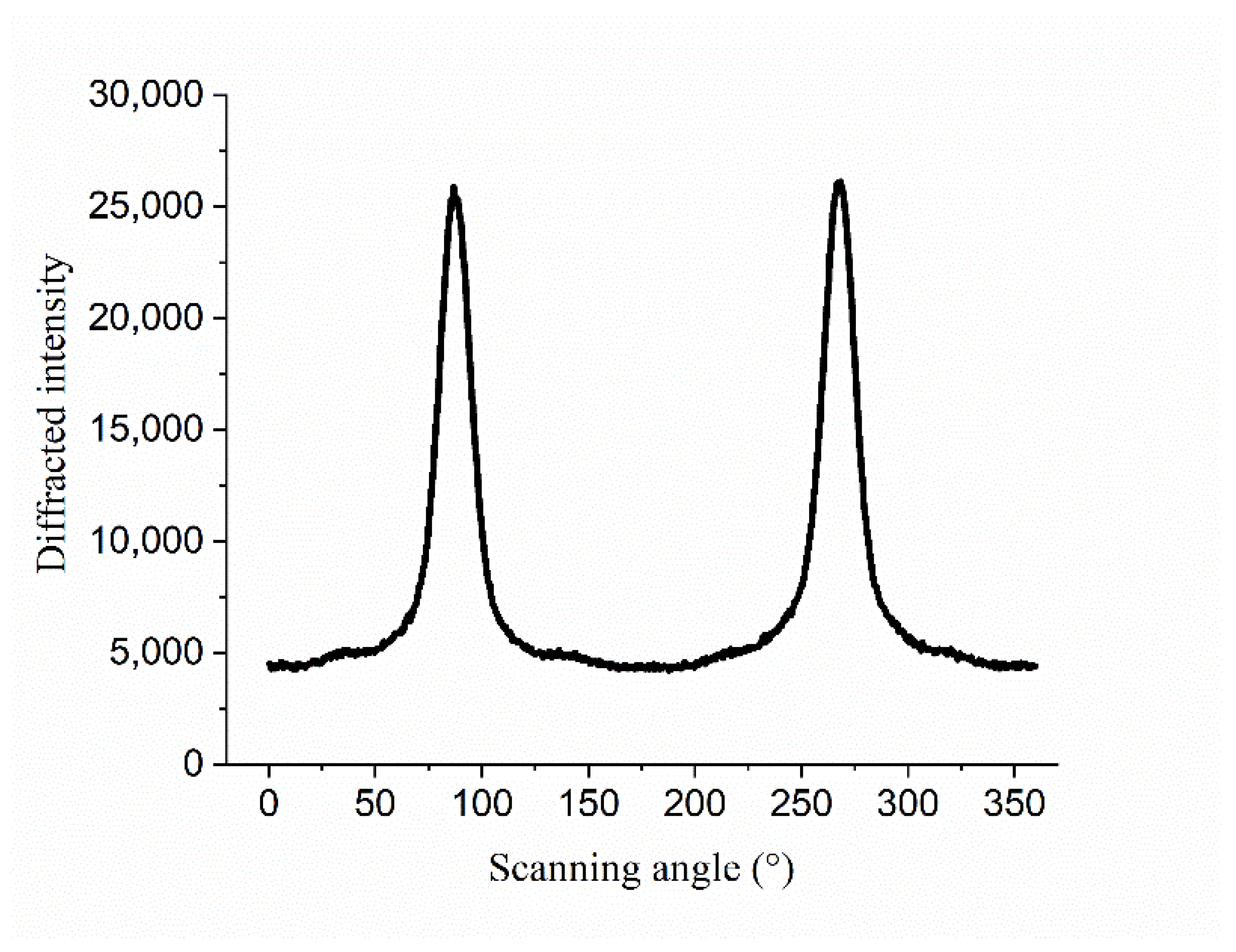
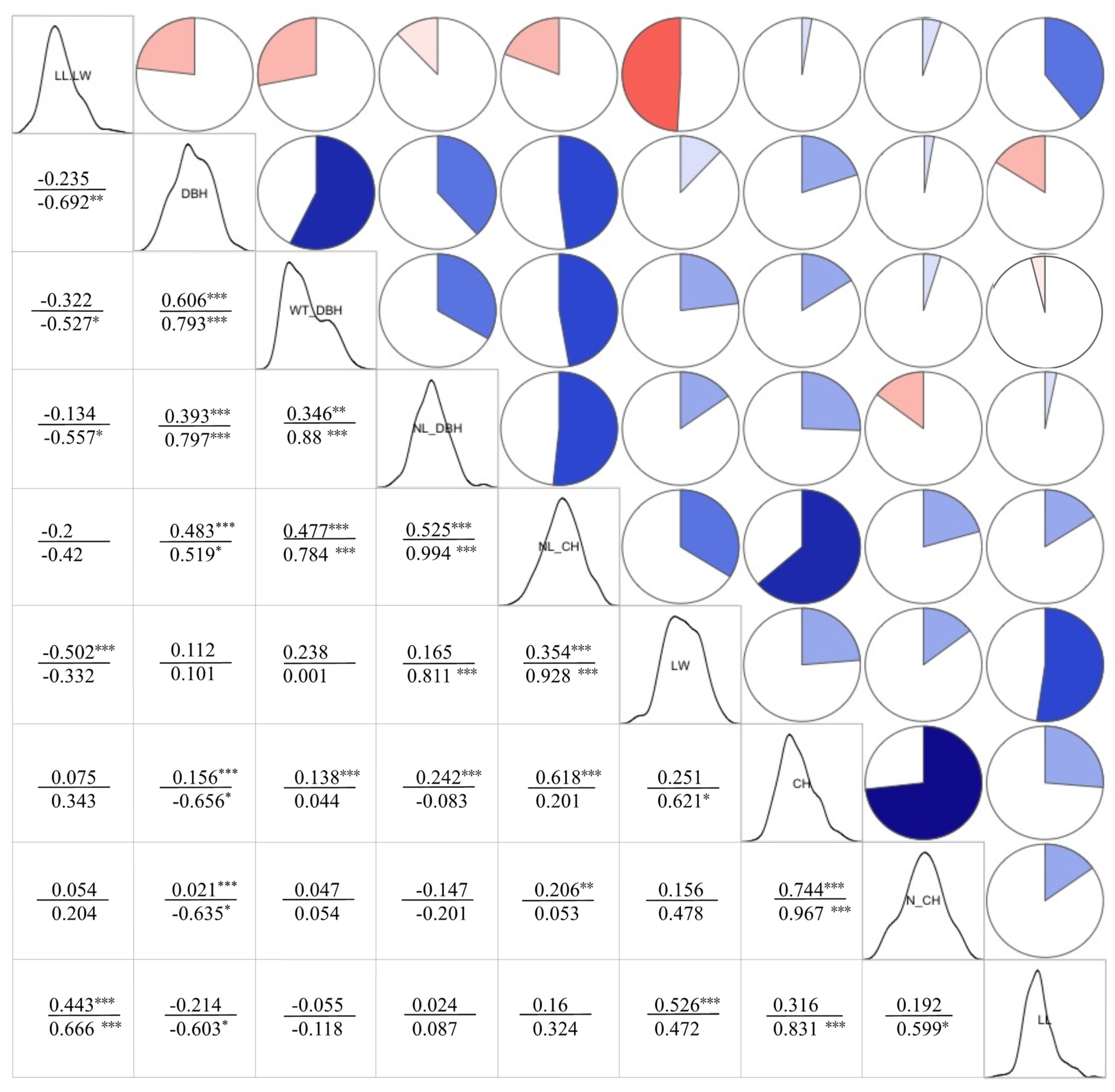
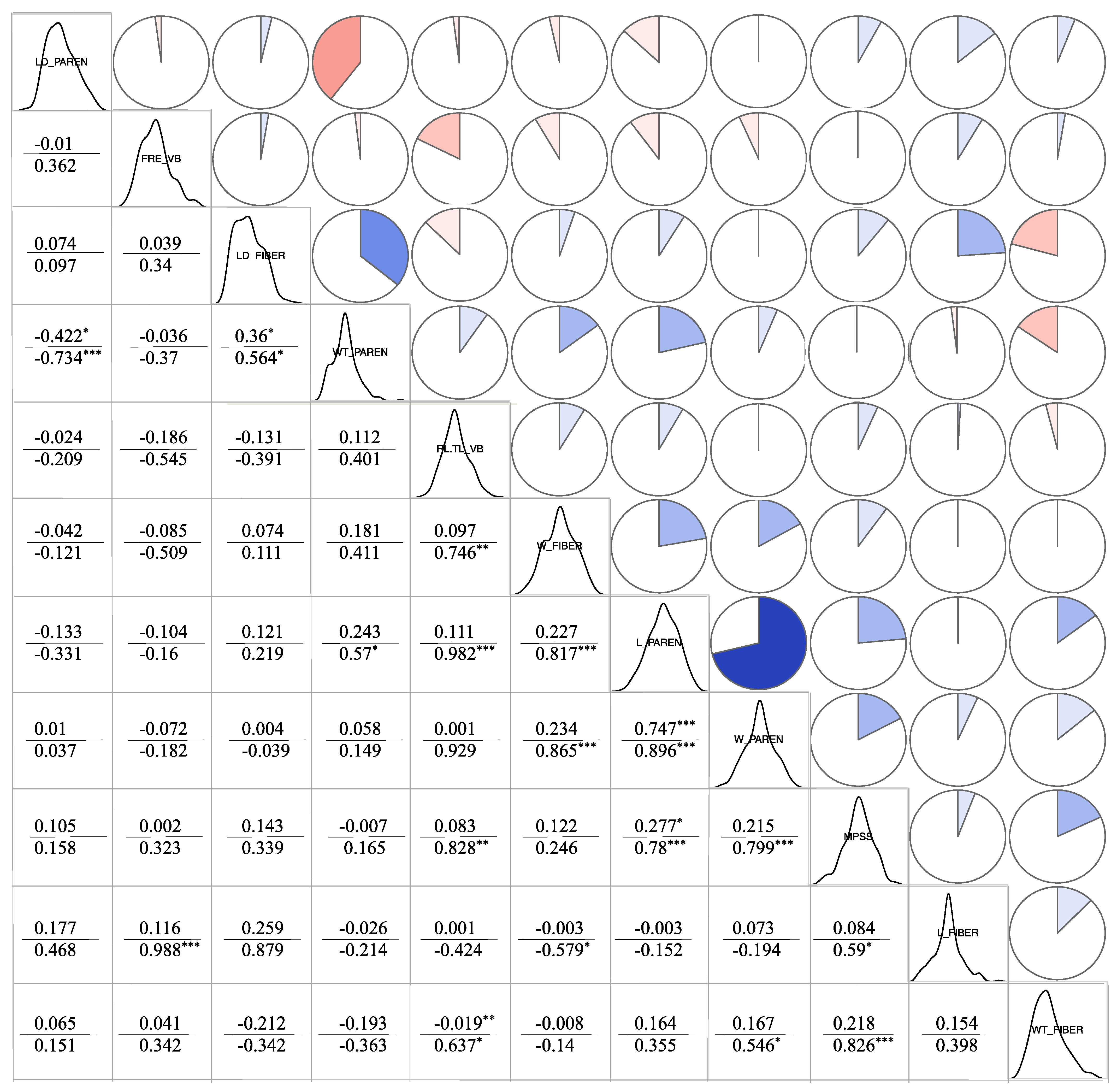

| Area | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude/m | Collected Time | Simple NO. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huoshan, Anhui Province | 116°21′32″ E | 31°18′38.5″ N | 335 | 15–17 October 2016 | 70 |
| Guanyang, Guangxi Province | 110°49′13.4″ E | 25°12′24.8″ N | 519 | 5–7 November 2016 | 69 |
| Anji, Zhejiang Province | 119°36′37.6″ E | 30°33′3.6″ N | 135 | 27–29 October 2016 | 70 |
| Trait | DBH | NL_DBH | WT_DBH | CH | NL_CH | N_CH | LL | LW | LL.LW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotypic Correlation Coefficient | FRE_VB | −0.269 ** | −0.06 | −0.287 *** | −0.053 | −0.161 | 0.007 | −0.008 | −0.035 | −0.004 |
| RL.TL_VB | 0.088 | −0.069 | 0.219 | 0.099 | 0.103 | 0.123 | 0.113 | 0.096 | 0.017 | |
| L_FIBER | −0.188 | −0.022 | −0.33 | 0.259 * | 0.047 | 0.222 | 0.204 | 0.009 | 0.157 | |
| W_FIBER | 0.266 | 0.281 * | 0.592 ** | 0.215 | 0.377 ** | 0.129 | 0.053 | 0.229 | −0.215 | |
| WT_FIBER | −0.155 | −0.038 | −0.114 | 0.107 | −0.05 | 0.034 * | 0.214 | −0.007 | 0.188 | |
| LD_FIBER | −0.311 | −0.024 | −0.144 | 0.305 | 0.028 | 0.274 | 0.361 ** | 0.172 | 0.17 | |
| MPSS | −0.155 | 0.045 | 0.007 | 0.199 * | 0.04 | 0.162 * | 0.146 | 0.108 | 0.048 | |
| L_PAREN | 0.056 | 0.074 | 0.296 | 0.244 | 0.15 | 0.269 | 0.044 | 0.138 | −0.091 | |
| W_PAREN | 0.074 | 0.075 | 0.285 | 0.193 | 0.179 | 0.173 | 0.022 | 0.05 | −0.072 | |
| WT_PAREN | 0.026 | −0.025 | 0.183 | 0.231 | 0.071 * | 0.272 | 0.001 | 0.082 | −0.052 | |
| LD_PAREN | −0.045 | 0.119 | −0.129 | 0.096 | 0.208 | −0.034 | 0.361 ** | 0.205 | 0.14 | |
| Genetic Correlation Coefficient | FRE_VB | −0.615 * | −0.413 | −0.697 * | 0.3 | −0.176 | 0.297 | 0.09 | 0.33 | −0.242 |
| RL.TL_VB | 0.103 | 0.173 | 0.669 * | 0.574 * | 0.222 | 0.646 * | 0.163 | 0.179 | −0.013 | |
| L_FIBER | −0.992 *** | −0.645 * | −0.84 *** | 0.53 * | −0.398 | 0.468 | 0.569 * | 0.122 | 0.469 | |
| W_FIBER | 0.537 * | 0.833 *** | 0.953 *** | 0.406 | 0.854 *** | 0.404 | 0.15 | 0.764 *** | −0.457 | |
| WT_FIBER | −0.446 | −0.387 | −0.205 | 0.393 | −0.218 | 0.378 | 0.268 | −0.066 | 0.254 | |
| LD_FIBER | −0.577 * | −0.145 | −0.207 | 0.694 ** | 0.061 | 0.687 ** | 0.567 * | 0.427 | 0.279 | |
| MPSS | −0.699 ** | −0.288 | −0.052 | 0.985 *** | 0.04 | 0.996 *** | 0.746 ** | 0.389 | 0.41 | |
| L_PAREN | −0.003 | 0.229 | 0.622 * | 0.755 *** | 0.389 | 0.85 *** | 0.262 | 0.547 * | −0.212 | |
| W_PAREN | 0.122 | 0.507 | 0.704 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.641 * | 0.658 * | 0.403 | 0.708 ** | −0.202 | |
| WT_PAREN | −0.059 | −0.183 | 0.28 | 0.364 | −0.129 | 0.593 * | −0.072 | 0.007 | −0.054 | |
| LD_PAREN | −0.24 | 0.378 | −0.211 | 0.216 | 0.455 | −0.118 | 0.687 ** | 0.47 | 0.338 |
| Trait | DBH | NL_DBH | WT_DBH | CH | NL_CH | N_CH | LL | LW | LL.LW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotypic Correlation Coefficient | O_SHRINK | −0.198 * | −0.218 | −0.211 * | −0.104 | −0.303 | 0.014 | −0.122 ** | −0.175 | 0.029 |
| A_SHRINK | −0.208 | −0.21 | −0.215 | −0.046 | −0.3 | 0.079 | −0.021 | −0.323 * | 0.371 *** | |
| MC | 0.402 * | 0.056 | 0.207 | −0.405 * | −0.033 | −0.311 | −0.429 *** | −0.104 | −0.342 | |
| O_DENSITY | −0.26 | −0.044 | 0.011 | 0.302 | 0.061 | 0.249 *** | 0.289 ** | 0.267 ** | −0.013 | |
| A_DENSITY | −0.151 | −0.014 | 0.079 | 0.22 ** | 0.105 | −0.081 | 0.334 ** | 0.267 ** | 0.05 | |
| MFA | −0.262 | −0.324 ** | −0.38 | 0.076 | −0.316 * | 0.246 | −0.163 | −0.155 | 0.004 | |
| MOR | −0.484 ** | −0.131 | −0.29 | 0.379 * | −0.066 | 0.313 *** | 0.392 * | 0.166 | 0.201 | |
| MOE | −0.466 ** | −0.076 | −0.264 | 0.405 * | −0.027 | 0.309 *** | 0.414 * | 0.171 | 0.214 | |
| Genetic Correlation Coefficient | O_SHRINK | −0.198 | −0.849 *** | −0.267 | −0.152 | −0.84 *** | 0.174 | −0.585 * | −0.703 ** | −0.049 |
| A_SHRINK | −0.316 | −0.737 ** | −0.268 | 0.007 | −0.728 ** | 0.183 | −0.097 | −0.714 ** | 0.515 * | |
| MC | 0.787 *** | 0.171 | 0.261 | −0.932 *** | −0.122 | −0.782 *** | −0.973 *** | −0.456 | −0.652 ** | |
| O_DENSITY | −0.554 * | −0.305 | 0.024 | 0.889 *** | −0.046 | 0.994 *** | 0.363 | 0.389 | 0.027 | |
| A_DENSITY | −0.59 * | −0.185 | 0.105 | 0.991 *** | 0.088 | 0.984 | 0.65 * | 0.44 | 0.311 | |
| MFA | −0.655 ** | −0.963 *** | −0.588 * | 0.194 | −0.831 *** | 0.443 | −0.213 | −0.446 | 0.103 | |
| MOR | −0.879 *** | −0.551 * | −0.372 | 0.892 *** | −0.236 | 0.933 *** | 0.609 * | 0.234 | 0.405 | |
| MOE | −0.857 *** | −0.503 | −0.329 | 0.913 *** | −0.183 | 0.945 *** | 0.633 * | 0.279 | 0.392 |
| Trait | O_SHRINK | A_SHRINK | MC | O_DENSITY | A_DENSITY | MFA | MOR | MOE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotypic Correlation Coefficient | FRE_VB | 0.099 | 0.05 * | −0.008 | 0.085 | −0.021 | 0.078 | 0.168 | 0.154 |
| RL.TL_VB | 0.043 | 0.023 | −0.027 | 0.153 | 0.163 | 0.077 | 0.111 | 0.109 | |
| L_FIBER | −0.035 | 0.009 | −0.035 | 0.148 | 0.157 | 0.137 | 0.327 | 0.035 | |
| W_FIBER | −0.159 | −0.157 | −0.002 | 0.204 | 0.173 | −0.148 | 0.014 | 0.029 | |
| WT_FIBER | 0.043 | −0.099 | −0.179 | 0.284 *** | 0.213 * | 0.092 | 0.423 * | 0.44 * | |
| LD_FIBER | −0.034 | 0.135 | −0.482 | 0.41 | 0.347 * | 0.113 | 0.36 * | 0.474 ** | |
| MPSS | −0.022 | −0.104 | −0.201 | 0.244 | 0.197 | 0.071 | 0.286 * | 0.305 * | |
| L_PAREN | 0.001 | −0.041 | −0.171 | 0.293 | 0.179 | 0.023 | 0.261 | 0.281 | |
| W_PAREN | −0.151 | −0.123 | −0.138 | 0.161 | 0.136 | −0.128 | 0.161 | 0.197 | |
| WT_PAREN | 0.232 | 0.32 | −0.048 | 0.395 * | 0.367 *** | 0.18 | 0.209 | 0.199 | |
| LD_PAREN | −0.484 * | −0.417 * | −0.328 | −0.156 | −0.065 | −0.307 | 0.024 | 0.05 | |
| Genetic Correlation Coefficient | FRE_VB | 0.012 | −0.501 | −0.334 | 0.397 | 0.09 | 0.626 * | 0.619 * | 0.603 * |
| RL.TL_VB | 0.2 | 0.114 | −0.195 | 0.571 * | 0.669 * | 0.012 | 0.384 | 0.423 | |
| L_FIBER | −0.024 | −0.052 | −0.905 | 0.66 | 0.659 | 0.551 * | 0.812 *** | 0.946 | |
| W_FIBER | −0.318 | −0.298 | −0.06 | 0.345 | 0.449 | −0.487 | −0.05 | −0.004 | |
| WT_FIBER | 0.108 | −0.176 | −0.325 | 0.31 | 0.266 | 0.358 | 0.597 * | 0.614 * | |
| LD_FIBER | −0.045 | 0.272 | −0.706 ** | 0.631 * | 0.724 ** | 0.231 | 0.559 * | 0.546 * | |
| MPSS | 0.011 | −0.001 | −0.859 *** | 0.862 *** | 0.966 *** | 0.362 | 0.982 *** | 0.992 *** | |
| L_PAREN | 0.127 | −0.015 | −0.333 | 0.814 *** | 0.86 *** | 0.136 | 0.52 * | 0.552 * | |
| W_PAREN | −0.242 | −0.378 | −0.349 | 0.562 * | 0.652 * | −0.175 | 0.403 | 0.455 | |
| WT_PAREN | 0.564 * | 0.673 ** | −0.101 | 0.651 ** | 0.654 * | 0.385 | 0.254 | 0.238 | |
| LD_PAREN | −0.901 *** | −0.628 * | −0.51 * | −0.295 | −0.116 | −0.552 * | 0.076 | 0.103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Hu, T.; Chang, Y.; Fei, B.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xia, M.; Fan, K.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z. Correlation between Genetic Characteristics, Cell Structure and Material Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) in Different Areas of China. Forests 2022, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010107
Zhang W, Hu T, Chang Y, Fei B, Ma Y, Deng Y, Xia M, Fan K, Zhang X, Jiang Z. Correlation between Genetic Characteristics, Cell Structure and Material Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) in Different Areas of China. Forests. 2022; 13(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenbo, Tao Hu, Yanting Chang, Benhua Fei, Yanjun Ma, Yayun Deng, Mengsi Xia, Keke Fan, Xue Zhang, and Zehui Jiang. 2022. "Correlation between Genetic Characteristics, Cell Structure and Material Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) in Different Areas of China" Forests 13, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010107
APA StyleZhang, W., Hu, T., Chang, Y., Fei, B., Ma, Y., Deng, Y., Xia, M., Fan, K., Zhang, X., & Jiang, Z. (2022). Correlation between Genetic Characteristics, Cell Structure and Material Properties of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) in Different Areas of China. Forests, 13(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010107






