Effect of Aspect-Slope on the Growth of Conifers in a Harsh Boreal Climate of Northwest Sweden
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
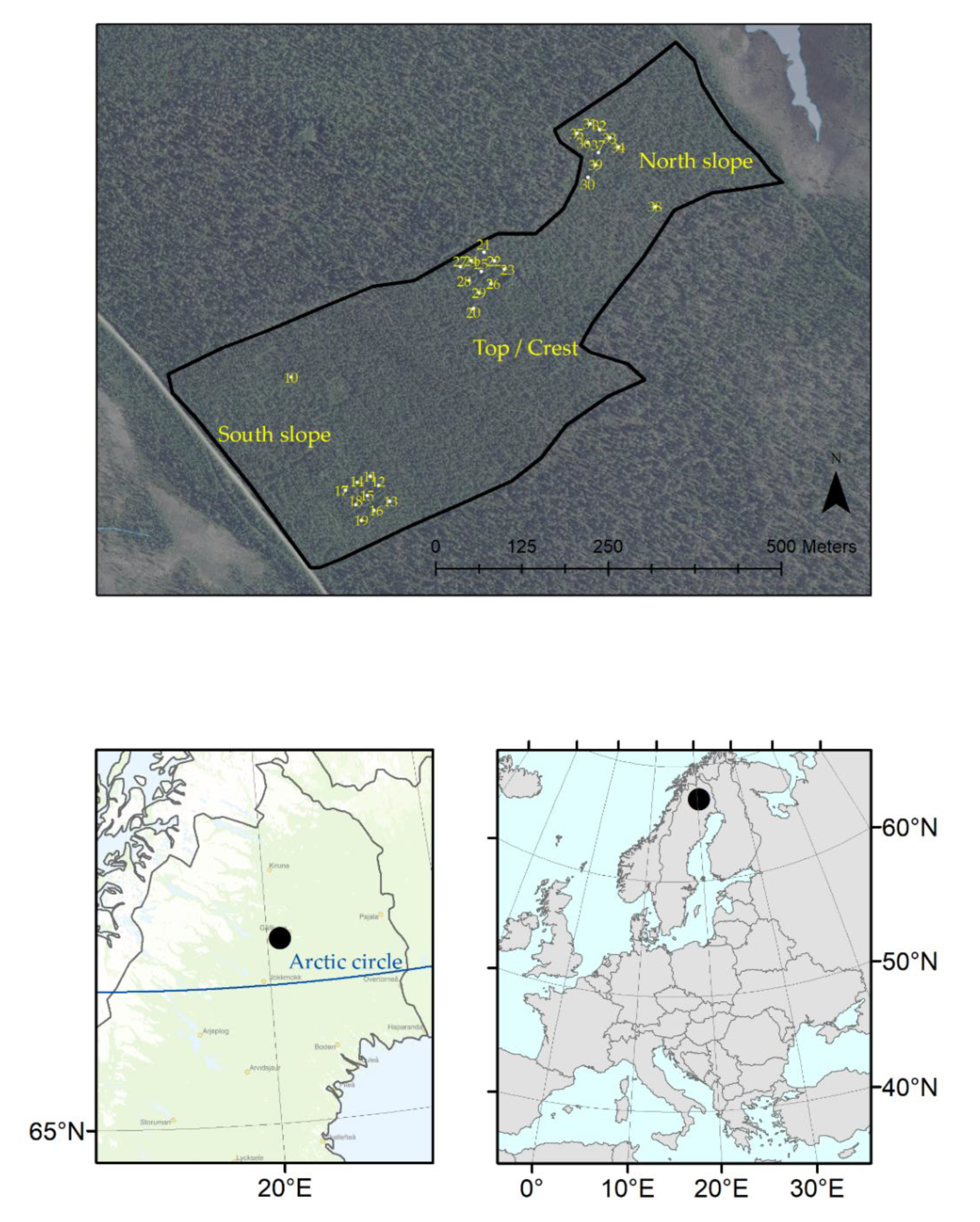
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Field Measurements
2.3. Tree Growth Reconstruction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmstrom, E.; Galnander, H.; Petersson, M. Within-site variation in seedling survival in Norway spruce plantations. Forests 2019, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, U.; Luoranen, J.; Kolström, T.; Örlander, G.; Puttonen, P. Reforestation with planting in northern Europe. Scand. J. For. Res. 2010, 25, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikström, U.; Hjelm, K.; Hanssen, K.H.; Saksa, T.; Wallertz, K. Influence of mechanical site preparation on regeneration success of planted conifers in clearcuts in fennoscandia—A review. Silva Fenn. 2020, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atanasso, J.A.; Mensah, S.; Salako, K.V.; Tohoun, R.J.; Glèlè Kakaï, R.; Assogbadjo, A.E. Factors affecting survival of seedling of Afzelia africana, a threatened tropical timber species in West Africa. Trop. Ecol. 2021, 62, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Muscarella, R.; Zimmerman, J.K. Environmental heterogeneity and biotic interactions mediate climate impacts on tropical forest regeneration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, e692–e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, I.E.; Karki, S.; Prajapati, C.; Yadav, R.K.; Shrestha, B.B. Facing north or south: Does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley? J. Arid Environ. 2015, 121, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paudel, S.; Vetaas, O.R. Effects of topography and land use on woody plant species composition and beta diversity in an arid Trans-Himalayan landscape, Nepal. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroter, D.; Cramer, W.; Leemans, R.; Prentice, I.C.; Araujo, M.B.; Arnell, N.W.; Bondeau, A.; Bugmann, H.; Carter, T.R.; Gracia, C.A.; et al. Ecology: Ecosystem service supply and vulnerability to global change in Europe. Science 2005, 310, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moren, A.-S.; Perttu, K.L. Regional Temperature and Radiation Indices and Their Adjustment to Horizontal and Inclined Forest Land; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 1994; Volume 19, ISBN 91-576-4915-4. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-García, E.; Miettinen, H.; Rubio, E.; García-Morote, F.A.; Andrés-Abellán, M.; López-Serrano, F.R. Effects of post-fire management practices and slope-aspect on medium-term Spanish black pine regeneration: Implications of using a direct seeding strategy in burnt areas. Eur. J. For. Res. 2018, 137, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ma, J.; Shugart, H.H.; Yan, X. Evaluating the impacts of slope aspect on forest dynamic succession in Northwest China based on FAREAST model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 34027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Alcón, S.; Coll, L. Unraveling the relative importance of factors driving post-fire regeneration trajectories in non-serotinous Pinus nigra forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 361, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fries, C. Aspects of Forest Regeneration in a Harsh Boreal Climate; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Umeå, Sweden, 1991; ISBN 91-576-4470-5. [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist, C.; Wallertz, K.; Johansson, U. Survival, early growth and impact of damage by late-spring frost and winter desiccation on Douglas-fir seedlings in southern Sweden. New For. 2018, 49, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swedish Forest Agency. Statistical Database of Forestry. 2019. Available online: https://www.skogsstyrelsen.se/en/statistics/statistical-database/ (accessed on 7 February 2022). (In Swedish).
- Swedish Forest Agency. Forest Management in SWEDEN Current Practice and Historical Background; The Swedish Forest Agency: Jönköping, Sweden, 2020. Available online: https://www.skogsstyrelsen.se/globalassets/om-oss/rapporter/rapporter-2021202020192018/rapport-2020-4-forest-management-in-sweden.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Esseen, P.-A.; Ehnström, B.; Ericson, L.; Sjöberg, K. Boreal Forests. Ecol. Bull. 1997, 46, 16–47. [Google Scholar]
- Saucier, J.P.; Baldwin, K.; Krestov, P.; Jorgenson, T. Boreal forests. In Routledge Handbook of Forest Ecology; Peh, K.S.-H., Corlett, R.T., Bergeron, Y., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 23. ISBN 9781315818290. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, P.; Karlman, M. Survival, height and health status of 20-year-old pinus sylvestris and pinus contorta after different scarification treatments in a harsh boreal climate. Scand. J. For. Res. 1997, 12, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlman, M.; Hansson, P.; Witzell, J. Scleroderris canker on lodgepole pine introduced in northern Sweden. Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 1948–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, O.; Hjelm, K.; Nilsson, U. Early growth of planted Norway spruce and Scots pine after site preparation in Sweden. Scand. J. For. Res. 2019, 34, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, U.; Elfving, B.; Karlsson, K. Productivity of Norway spruce compared to scots pine in the interior of Northern Sweden. Silva Fenn. 2012, 46, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SMHI Yearly and Monthly Statistics. Available online: http://www.smhi.se/klimatdata/meteorologi/temperatur/2.1240 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Nilsson, P.; Roberge, C.; Fridman, J. Forest Statistics 2021; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Umea, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, L.-Å. CDendro. 2020. Available online: http://www.cybis.se/forfun/dendro/index.php (accessed on 3 December 2021).
- Heym, M.; Bielak, K.; Wellhausen, K.; Uhl, E.; Biber, P.; Perkins, D.; Steckel, M.; Andreas Thurm, E.; Rais, A.; Pretzsch, H. A New Method to Reconstruct Recent Tree and Stand Attributes of Temporary Research Plots: New Opportunity to Analyse Mixed Forest Stands. In Conifers; Gonçalves, A.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 21. ISBN 978-1-78984-801-4. [Google Scholar]
- Petterson, H. Barrskogens volymproduktion. Medd. Fran Statens Skogsforskningsinstitut 1955, 45, 391. [Google Scholar]
- Pretzsch, H. Forest Dynamics, Growth and Yield; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Freising, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-540-88306-7. [Google Scholar]
- Holmström, E.; Goude, M.; Nilsson, O.; Nordin, A.; Lundmark, T.; Nilsson, U. Productivity of Scots pine and Norway spruce in central Sweden and competitive release in mixtures of the two species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 429, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidman, F.D.; Holmström, E.; Lundmark, T.; Fahlvik, N. Management of spontaneously regenerated mixed stands of birch and Norway spruce in Sweden. Silva Fenn. 2021, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Alvarez-Uria, P.; Körner, C. Low temperature limits of root growth in deciduous and evergreen temperate tree species. Funct. Ecol. 2007, 21, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orangeville, L.; Houle, D.; Duchesne, L.; Phillips, R.P.; Bergeron, Y.; Kneeshaw, D. Beneficial effects of climate warming on boreal tree growth may be transitory. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omary, A. Al Effects of aspect and slope position on growth and nutritional status of planted Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis Mill.) in a degraded land semi-arid areas of Jordan. New For. 2011, 42, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salekin, S.; Mason, E.G.; Morgenroth, J.; Bloomberg, M.; Meason, D.F. Hybrid height growth and survival model for juvenile Eucalyptus globoidea (Blakely) and E. bosistoana (F. Muell) in New Zealand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 490, 119074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Brueck, H.; Giese, K.M.; Zhang, L.; Sattelmacher, B.; Lin, S. Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotzer, T.; Biber, P.; Moser, A.; Schäfer, C.; Pretzsch, H. Stem and root diameter growth of European beech and Norway spruce under extreme drought. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 406, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.; Macalady, A.K.; Chenchouni, H.; Bachelet, D.; McDowell, N.; Vennetier, M.; Kitzberger, T.; Rigling, A.; Breshears, D.D.; Hogg, E.H.; et al. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 660–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigler, C.; Bräker, O.U.; Bugmann, H.; Dobbertin, M.; Rigling, A. Drought as an inciting mortality factor in scots pine stands of the Valais, Switzerland. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camarero, J.J.; Gazol, A.; Sangüesa-Barreda, G.; Oliva, J.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. To die or not to die: Early warnings of tree dieback in response to a severe drought. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, B.J.; Liu, S.L.; Ma, K.M.; Zhu, Y.G. Relationships between soil characteristics, topography and plant diversity in a heterogeneous deciduous broad-leaved forest near Beijing, China. Plant Soil 2004, 261, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidari, M.; Ronzello, G.; Vecchio, G.; Muscolo, A. Influence of slope aspects on soil chemical and biochemical properties in a Pinus laricio forest ecosystem of Aspromonte (Southern Italy). Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2008, 44, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odin, H.; Löfvenius, M.; Aman, K. Klimatstudier pa ett Nordligt Högläge; Stencil 12: Uppsala, Sweden, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Aldea, J.; Ruiz-Peinado, R.; del Río, M.; Pretzsch, H.; Heym, M.; Brazaitis, G.; Jansons, A.; Metslaid, M.; Barbeito, I.; Bielak, K.; et al. Species stratification and weather conditions drive tree growth in Scots pine and Norway spruce mixed stands along Europe. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, H. Genetic diversity reduces competition and increases tree growth on a Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] KARST.) provenance mixing experiment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 497, 119498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, E.; Carlström, T.; Goude, M.; Lidman, F.D.; Felton, A. Keeping mixtures of Norway spruce and birch in production forests: Insights from survey data. Scand. J. For. Res. 2021, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboite, F.O.; Comeau, P.G. Climate sensitive growth models for predicting diameter growth of western Canadian boreal tree species. For. An Int. J. For. Res. 2021, 94, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacek, Z.; Prokupkova, A.; Vacek, S.; Bulusek, D.; Simunek, V.; Hajek, V.; Kralicek, I. Mixed vs. monospecific mountain forests in response to climate change: Structural and growth perspectives of Norway spruce and European beech. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 488, 119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, J.G.; Liang, H.; Rossi, S.; Bergeron, Y.; Shishov, V.V.; Jiang, S.; Kang, J.; Zhu, H.; Dong, Z. Radial growth of Larix sibirica was more sensitive to climate at low than high altitudes in the Altai Mountains, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 304–305, 108392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Blanco, N.E.; Hermida-Carrera, C.; Lehotai, N.; Hurry, V.; Strand, Å. Two dominant boreal conifers use contrasting mechanisms to reactivate photosynthesis in the spring. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavankar, F.; Lo Monaco, A.; Nikooy, M.; Venanzi, R.; Bonyad, A.; Picchio, R. Snow damages on trees of an uneven age in mixed broadleaf forests: Effects of topographical conditions and tree characteristics. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | SW | Top | NE |
|---|---|---|---|
| BS | 89 ± 3.8 a | 84 ± 3.7 ab | 86 ± 3.1 ab |
| LP | 72 ± 5.1 a | 41 ± 5.0 b | 43 ± 2.6 b |
| NS | 38 ± 3.7 a | 51 ± 3.4 b | 40 ± 3.8 a |
| SL | 84 ± 2.7 a | 71 ± 3.8 a | 77 ± 5.2 a |
| SP | 36 ± 3.2 a | 30 ± 3.5 a | 22 ± 2.9 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogana, F.N.; Sjödin, F.; Holmström, E.; Fries, C.; Nilsson, U. Effect of Aspect-Slope on the Growth of Conifers in a Harsh Boreal Climate of Northwest Sweden. Forests 2022, 13, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020301
Ogana FN, Sjödin F, Holmström E, Fries C, Nilsson U. Effect of Aspect-Slope on the Growth of Conifers in a Harsh Boreal Climate of Northwest Sweden. Forests. 2022; 13(2):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020301
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgana, Friday N., Fredrik Sjödin, Emma Holmström, Clas Fries, and Urban Nilsson. 2022. "Effect of Aspect-Slope on the Growth of Conifers in a Harsh Boreal Climate of Northwest Sweden" Forests 13, no. 2: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020301
APA StyleOgana, F. N., Sjödin, F., Holmström, E., Fries, C., & Nilsson, U. (2022). Effect of Aspect-Slope on the Growth of Conifers in a Harsh Boreal Climate of Northwest Sweden. Forests, 13(2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020301






