Effect of Environmental Humidity on the Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
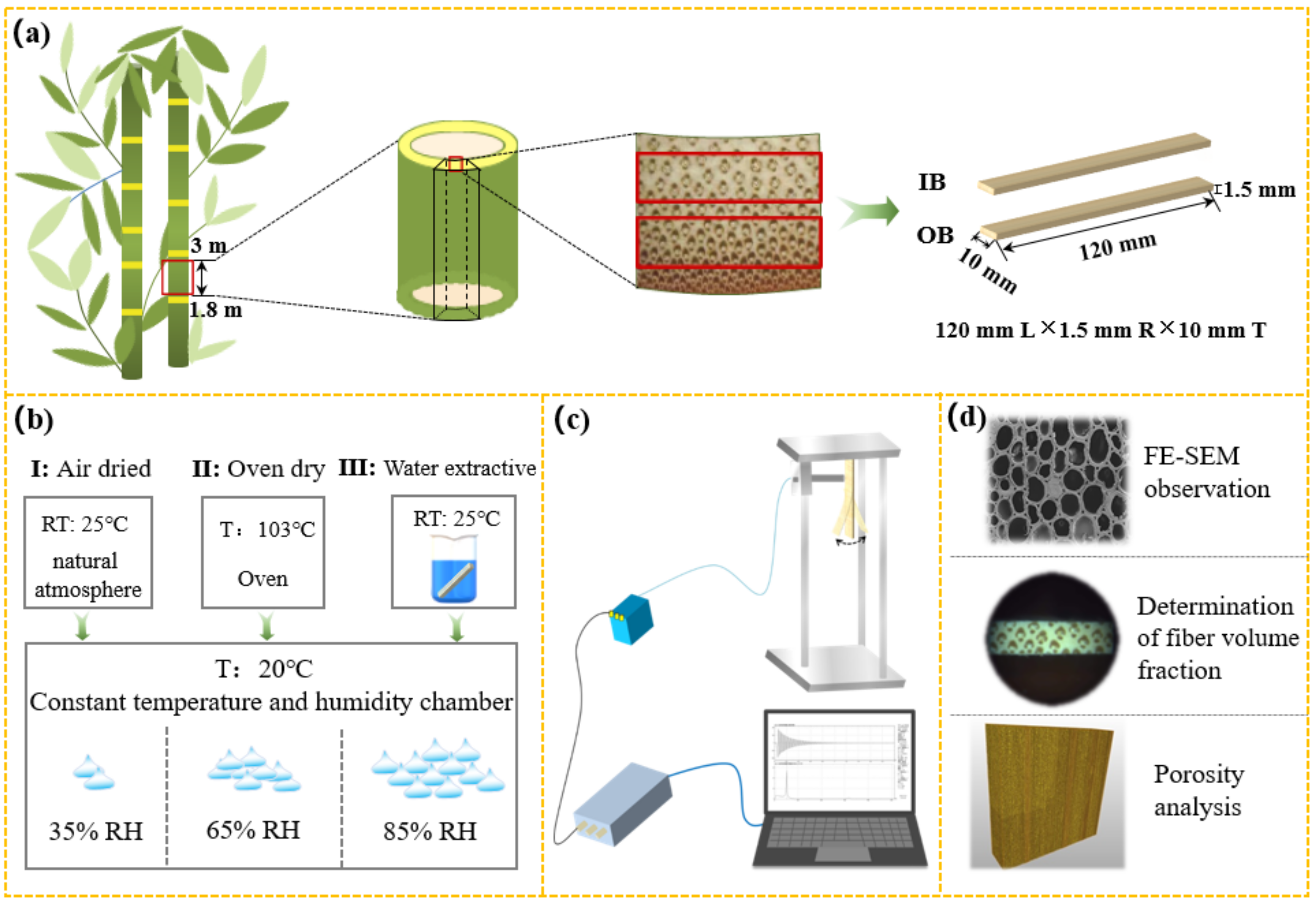
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Adjusting for Constant Relative Humidity (Status I)
2.1.2. Adjusting for Changeable Relative Humidity (Status II)
2.1.3. Water Extraction (Status III)
2.2. Characterization
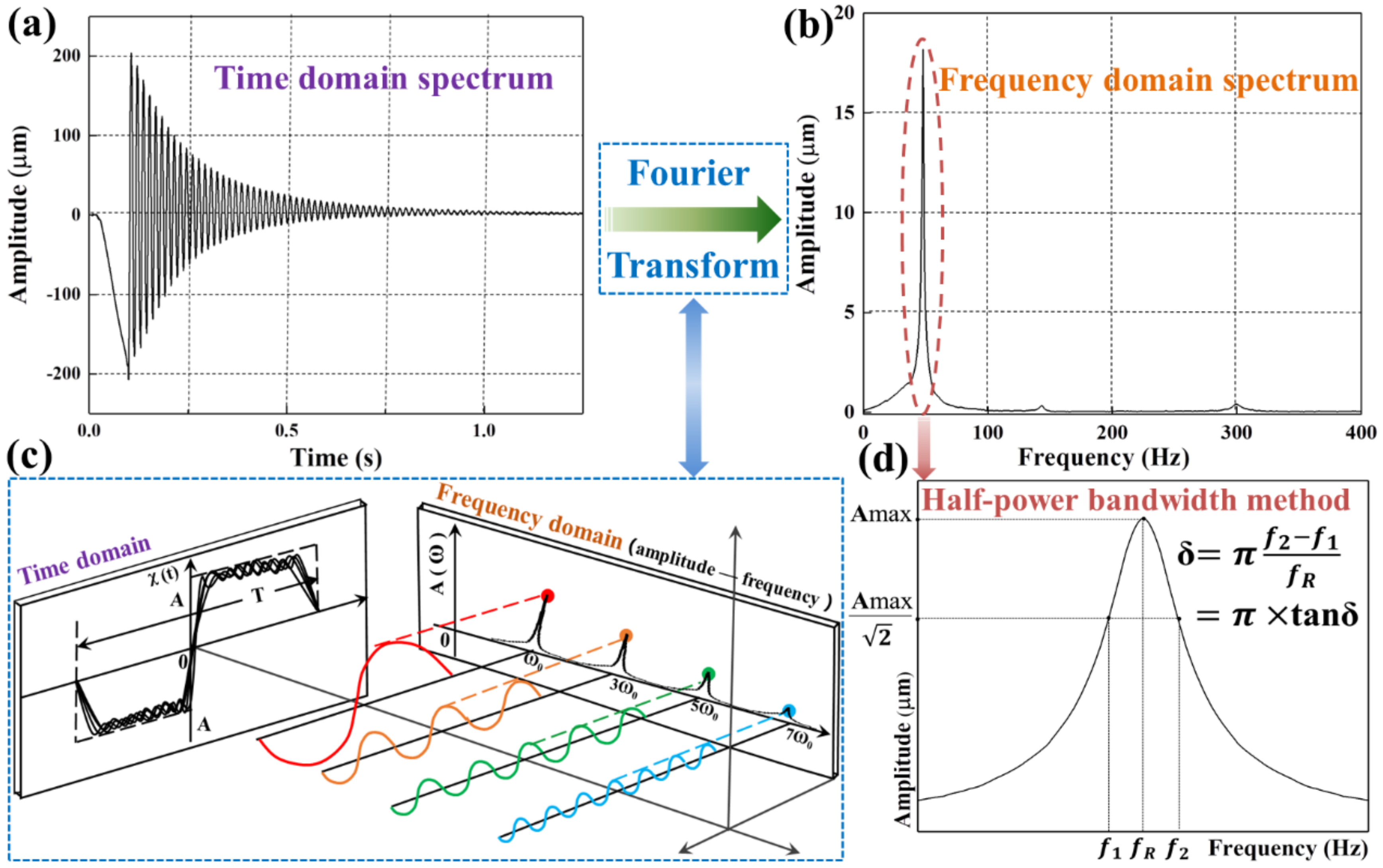
2.2.1. Acoustic Vibration Characteristics
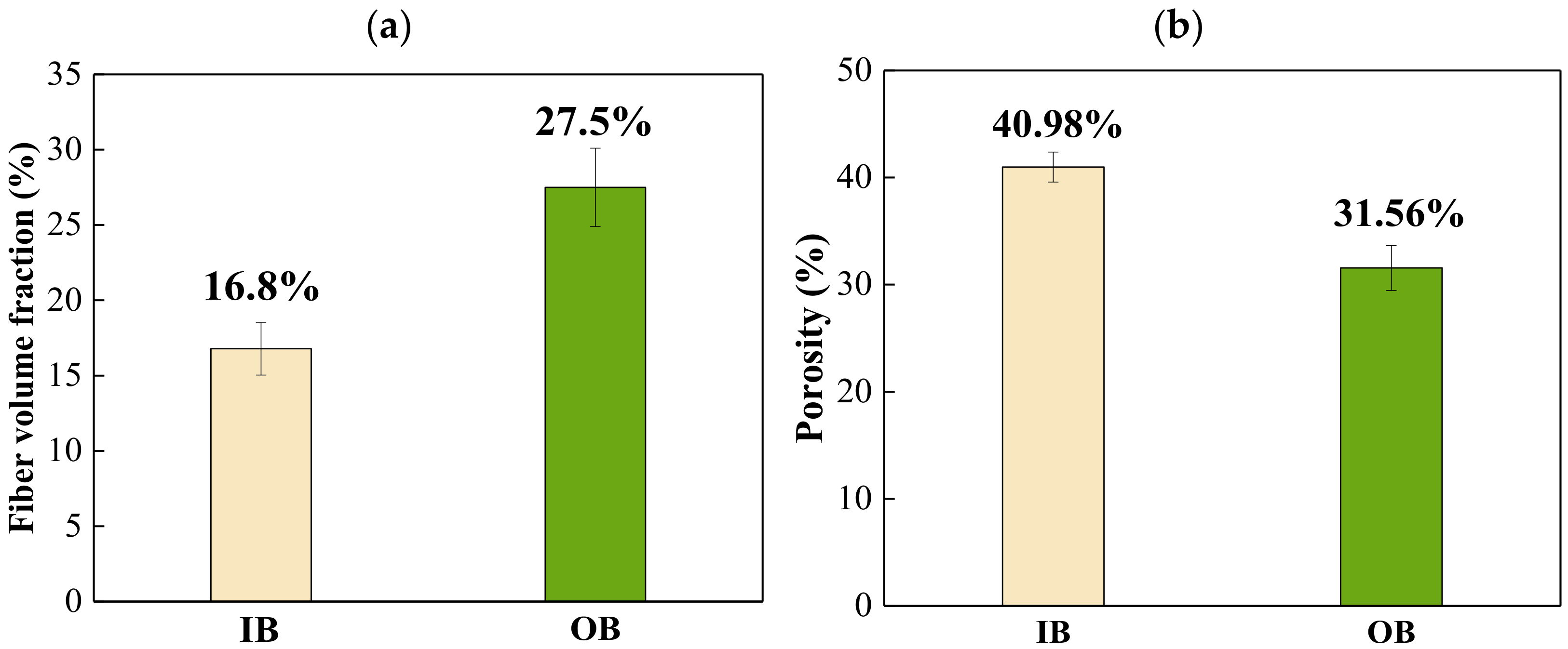
2.2.2. Determination of Fiber Volume Fraction
2.2.3. X-ray Micro-CT
3. Results and Discussion
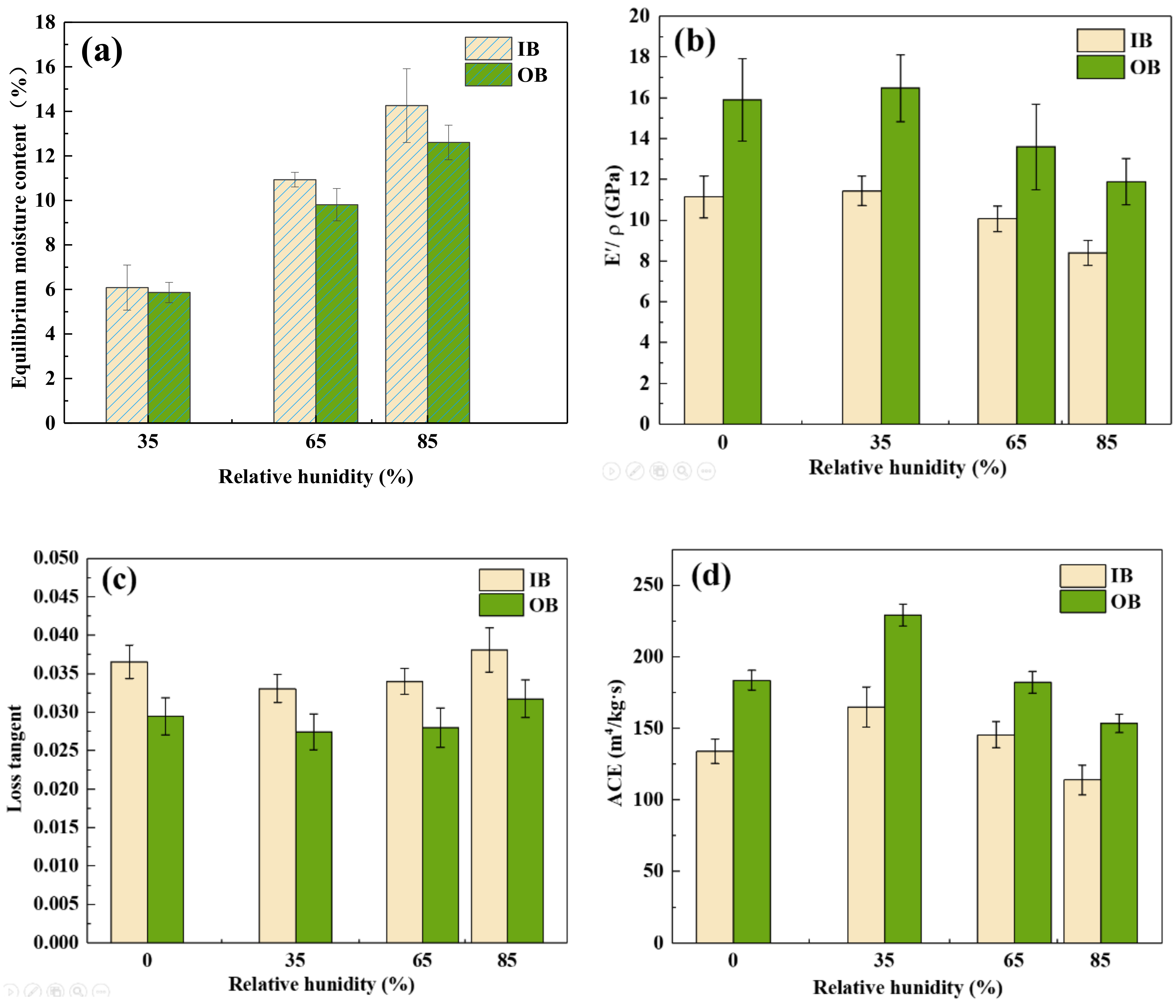
3.1. Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo under Constant Relative Humidity (Status I)
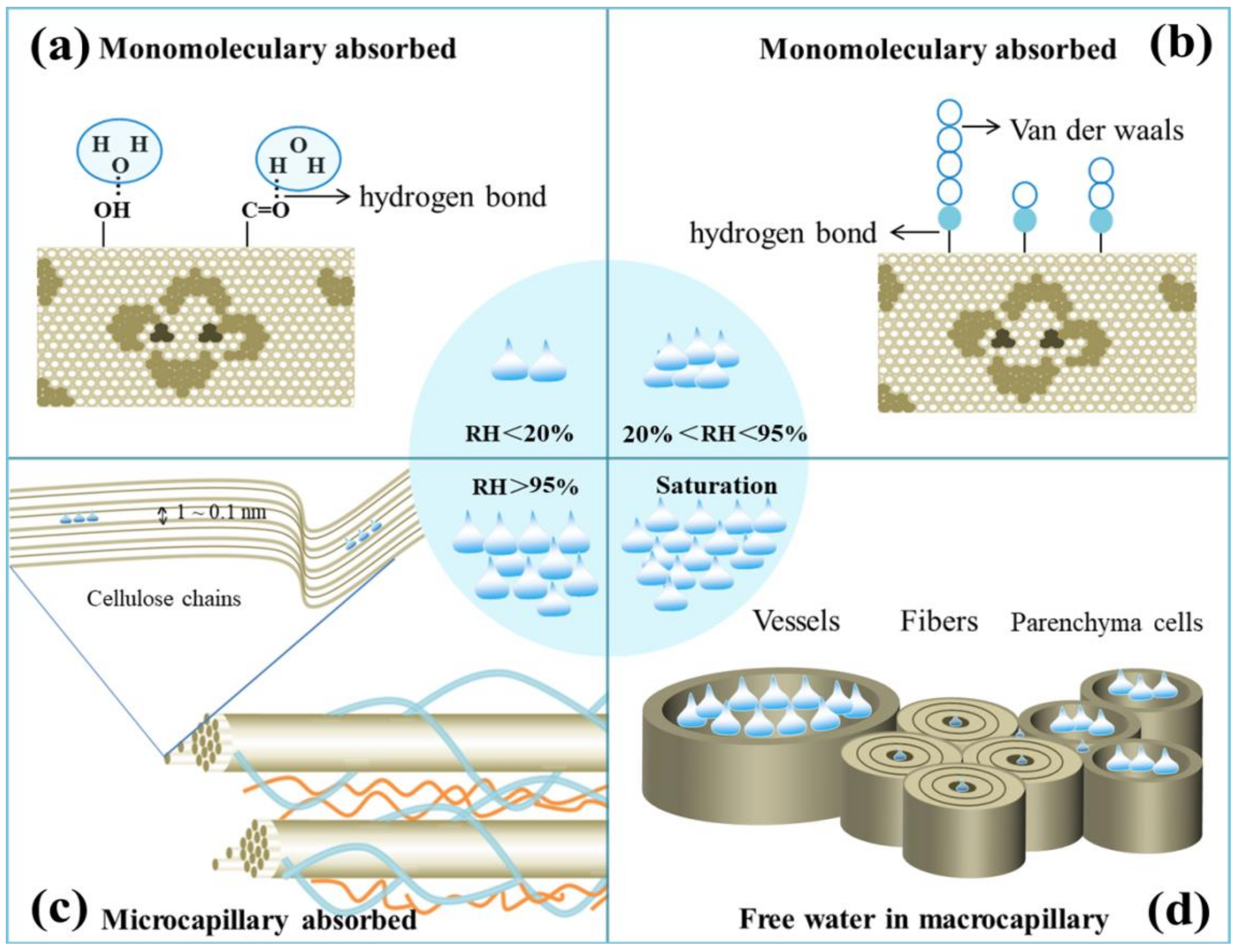
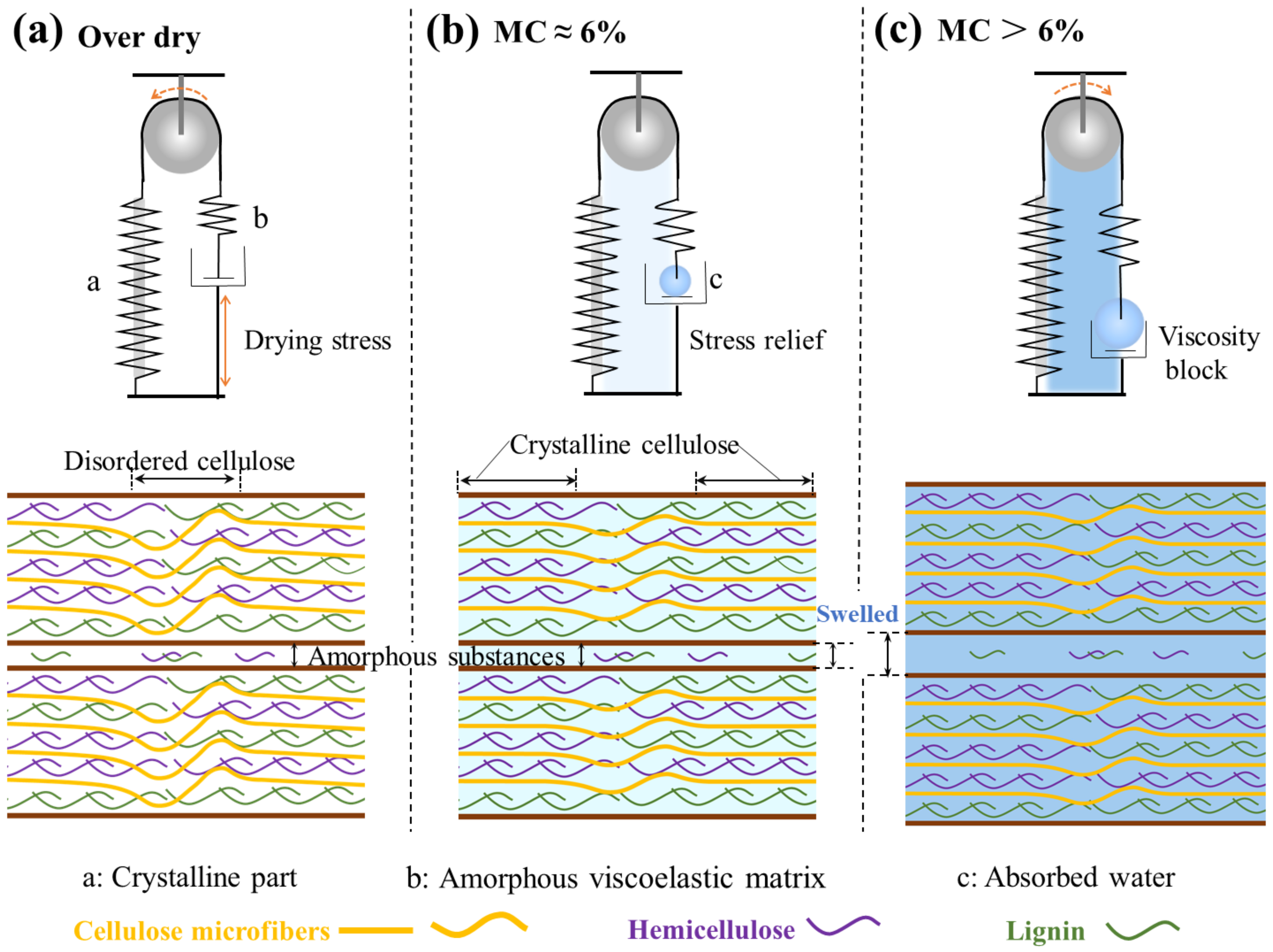
3.2. Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo under Changeable Relative Humidity (Status II)
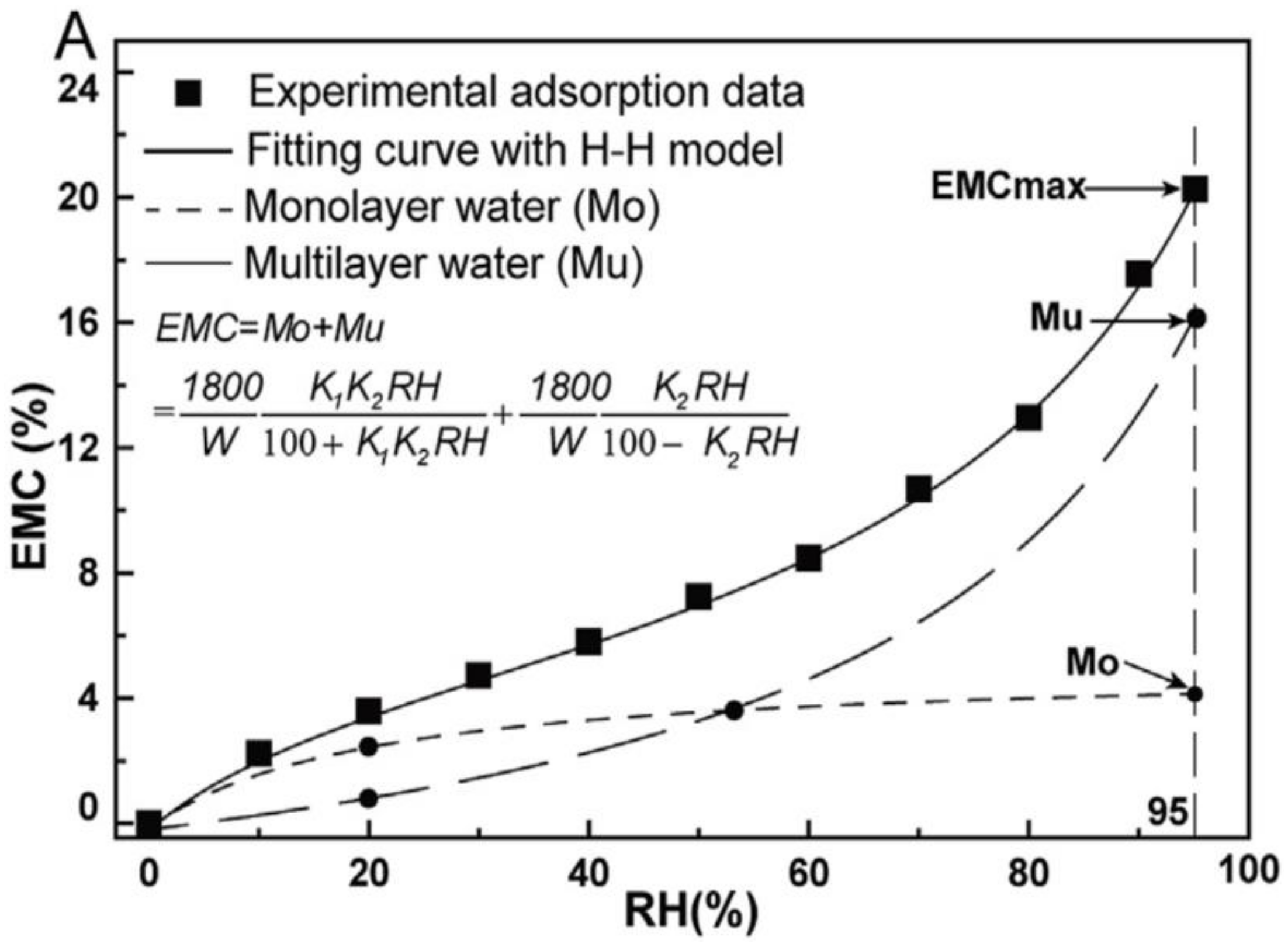
3.3. Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo Subjected to Water Extraction (Status III)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wegst, U. Wood for sound. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U. Bamboo and wood in musical instruments. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 323–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obataya, E.; Ono, T.; Norimoto, M. Vibrational properties of wood along the grain. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancheriau, L.; Baillères, H.; Détienne, P.; Gril, J.; Kronland, R. Key signal and wood anatomy parameters related to the acoustic quality of wood for xylophone-type percussion instruments. J. Wood Sci. 2006, 52, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. Study on relationships between Picea Species structures and Vibration properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, G.; Tian, G.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y. Sensitivity of several selected mechanical properties of Moso bamboo to moisture content change under the fiber saturation point. BioResources 2012, 7, 5048–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakchaure, M.R.; Kute, S.Y. Effect of moisture content on physical and mechanical properties of bamboo. Asian J. Civ. Eng 2012, 13, 753–763. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ren, D.; Yu, Y. Effects of Moisture Content on the Mechanical Properties of Moso Bamboo at the Macroscopic and Cellular Levels. BioResources 2013, 8, 5475–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Low, I.M.; Che Latella, B.A. Mapping the structure, composition and mechanical properties of bamboo. J. Mater. 2006, 28, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H. Investigating the water vapor sorption behavior of bamboo with two sorption models. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 8241–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liese, W. Research on bamboo. Wood Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, Y. Lignocellulosic Chemistry; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.; Walters, M.C.; Paulino, G.H. Modeling bamboo as a functionally graded material: Lessons for the analysis of affordable materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 6991–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.K.; Samaei, A.T.; Gheshlaghi, B.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y. Asymmetric flexural behavior from bamboo’s functionally graded hierarchical structure: Underlying mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2015, 16, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W. An in-depth study of molecular and supramolecular structures of bamboo cellulose upon heat treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.; Margem, F.; Braga, F.; Luz, F.; Simonassi, T. Weibull analysis of the tensile strength dependence with fiber diameter of giant bamboo. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Sahu, J.K.; Sharma, G.D. Moisture sorption isotherms, heat of sorption and properties of sorbed water of raw bamboo (Dendrocalamus longispathus) shoots. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, R.; Lian, C.; Luo, J.; Fei, B. Intercellular pathways in internodal metaxylem vessels of moso bamboo Phyllostachys edulis. IAWA J. 2019, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, G. Wood-Based Materials Science; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Luo, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, S. Water effects on the deformation and fracture behaviors of the multi-scaled cellular fibrous bamboo. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obataya, E. Effects of natural and artificial ageing on the physical and acoustic properties of wood in musical instruments. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 27, S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z. Vibration Characteristics of Wood for Resonance Board and Acoustic Quality of National Instruments; China Science Publishing & Media: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Farvardin, F.; Roohnia, M.; Lashgari, A. The effect of extractives on acoustical properties of Persian silk wood (Albizia julibrissin). Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2015, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Deng, L.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Chen, F. Measuring the damping performance of gradient-structured bamboo using the resonance method. Forests 2021, 12, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, G.; Smith, L.M.; Jiang, H. The hygroscopicity of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) with a gradient fiber structure. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4309–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Hill, C.A.S. The sorption of water vapour by anhydride modified softwood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann, F.; Krech, H. Dynamic measurement of damping capacity and elastic properties of wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 1960, 18, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M. The effects of water-sorption and temperature on dynamic Young’s modulus and logarithmic decrement of wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 1962, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fukada, E. The vibrational properties of wood. II. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1951, 6, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obataya, E.; Norimoto, M.; Gril, J. The effects of adsorbed water on dynamic mechanical properties of wood. Polymer 1998, 39, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhards, C.C. Effect of moisture content and temperature on the mechanical properties of wood: An analysis of immediate effects. Wood Fiber 1982, 14, 4–36. [Google Scholar]
- Guitard, D.; ElAmri, F. Modèles prévisionnels de comportement élastique tridimensionnel pour les bois feuillus et les bois résineux. Ann. Sci. For. 1987, 44, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brémaud, I.; Gril, J. Moisture content dependence of anisotropic vibrational properties of wood at quasi equilibrium: Analytical review and multi-trajectories experiments. Holzforschung 2020, 75, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.G.; Gril, J. Evidence of a physical ageing phenomenon in wood. J. Mater. Sci. Let. 1996, 15, 1580–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, E. The vibrational properties of wood I. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1950, 5, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.L. Effect of temperature and moisture content on internal friction and speed of sound in Douglas-fir. For. Prod. J. 1961, 11, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Brémaud, I.; Gril, J. Transient destabilisation in anisotropic vibrational properties of wood when changing humidity. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gril, J. Une Modélisation Du Comportement Hygro-Rhéologique Du Bois À Partir De Sa Microstructure. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnic School, University of Paris VI, Paris, France, 1988; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Norimoto, M.; Yamada, T.; Rowell, R.M. Effect of moisture on the acoustical properties of wood. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 1988, 34, 794–803. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Dlouha, J.; Gril, J.; Clair, B.; Almeras, T. Evidence and modelling of physical aging in green wood. Rheol. Acta 2009, 48, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Struik, L.C.E. Physical aging in amorphous polymers and other materials. Dr. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1977, 279, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, M.; Goli, G.; Carlson, B. Viscoelastic and mechano-sorptive studies applied to the conservation of historical violins: A case study of the Guarneri “del Gesù” violin (1743) known as the “Cannone”. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, G.; Fioravanti, M.; Busoni, S.; Carlson, B.; Mazzanti, P. Measurement and modelling of mass and dimensional variations of historic violins subjected to thermo-hygrometric variations: The case study of the Guarneri “del Gesù” violin (1743) known as the “Cannone”. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, S154–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, M.J.; Borland, M.J. The Effect of Humidity and Moisture Content on the Tone of Musical Instruments. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2014; p. 161. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10012/8253 (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Torres, J.A.; de Icaza-Herrera, M.; Castaño, V.M. Guitar acoustics quality: Shift by humidity variations. Acta Acust. Unit. Acust. 2014, 100, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.J. Surface Performance Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo; Chinese Academy of Forestry: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, M.; Sakai, K.; Kamitakahara, H.; Minato, K.; Nakatsubo, F. Vibrational property changes of spruce wood by impregnation with water-soluble extractives of Pernambuco (Guilandina echinata Spreng.) II. Structural analysis of extractive components. J. Wood Sci. 2000, 46, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, M.; Obataya, E.; Minato, K.; Nakatsubo, F. Working mechanism of adsorbed water on the vibrational properties of wood impregnated with extractives of Pernambuco (Guilandina echinata Spreng.). J. Wood Sci. 2000, 46, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpayegani, A.; Brémaud, I.; Gril, J.; Thevenon, M.F.; Pourtahmasi, K. Effect of extractions on dynamic mechanical properties of white mulberry (Morus alba). J. Wood Sci. 2012, 58, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.S.; Longui, E.L.; Amano, E. Pernambuco wood (Caesalpinia echinata) used in the manufacture of bows for string instruments. IAWA J. 2008, 29, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obataya, N. Acoustic properties of a reed (Arundo donax L.) used for the vibrating plate of a clarinet. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuchi, Y.; Fushitani, M.; Kubo, T.; Sato, K. Effects of water extractives on the moisture-content dependence of vibrational properties of Bamboo. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 1999, 45, 77–84. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z. Effect of Environmental Humidity on the Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo. Forests 2022, 13, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020329
Deng L, Chen X, Chen F, Liu X, Jiang Z. Effect of Environmental Humidity on the Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo. Forests. 2022; 13(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Liping, Xiaoyi Chen, Fuming Chen, Xing’e Liu, and Zehui Jiang. 2022. "Effect of Environmental Humidity on the Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo" Forests 13, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020329
APA StyleDeng, L., Chen, X., Chen, F., Liu, X., & Jiang, Z. (2022). Effect of Environmental Humidity on the Acoustic Vibration Characteristics of Bamboo. Forests, 13(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020329




