Spatial Distribution and Regulating Factors of Soil Nutrient Stocks in Afforested Dump of Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
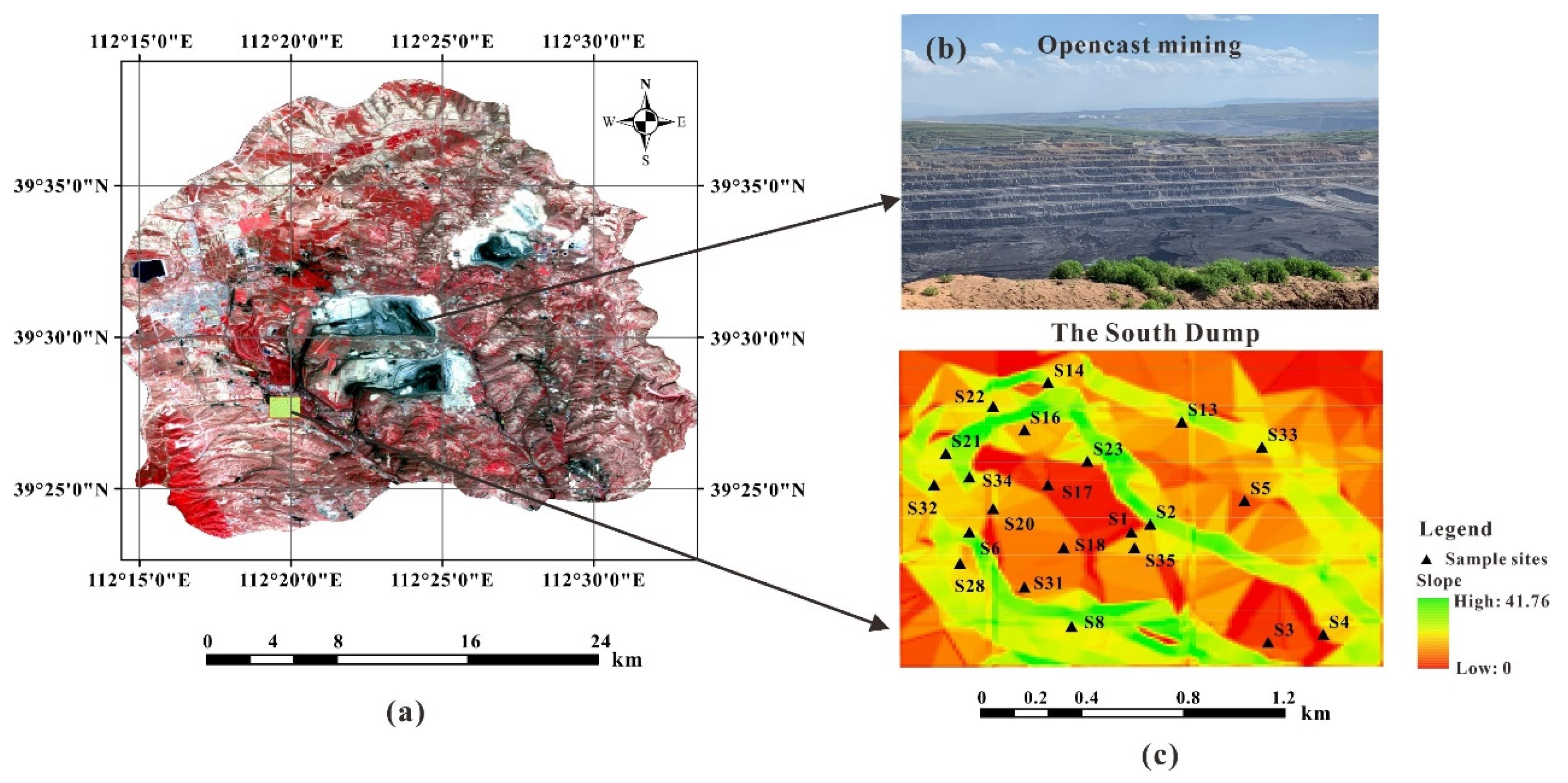
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Calculation of Reclaimed Soil Nutrient Stock
2.4. Geostatistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Measured Soil Properties, and Nutrient Stocks
3.1.1. Soil Texture, pH, and Herbaceous Biomass at Different Sample Sites
3.1.2. Statistical Characteristics of SOCD, TND, APD, and AKD in Different Soil Horizons
3.2. Geostatistical Analyses of the Calculated Nutrient Stocks
3.2.1. Semi-Variogram Analyses
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution Patterns of SOCD, TND, APD, and AKD across South Dump
3.3. Influencing Factors of SOCD, TND, APD, and AKD in Reclaimed Land
3.3.1. Afforestation
3.3.2. Soil Texture and pH
3.4. Suggestion for Nutrient Management in Reclaimed Soils of Opencast Coalmine
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Soil nutrient variations among different land use types after reclamation in the Pingshuo opencast coal mine on the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2020, 188, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Shahrour, I.; Bai, Z.K.; Fan, W.X.; Feng, L.R.; Li, H.F. Soils development in opencast coal mine spoils reclaimed for 1–13 years in the West-Northern Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 55, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.K. Ecorestoration of the Coalmine Degraded Lands; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.G.; Bai, Z.K.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, W. Rural settlement changes in compound land use areas: Characteristics and reasons of changes in a mixed mining-rural-settlement area in Shanxi Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 61, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Lv, C. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. CATENA 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, D.V.; Silva, M.L.N.; Beniaich, A.; Pio, R.; Gonzaga, M.I.S.; Avanzi, J.C.; Bispo, D.F.A.; Curi, N. Dynamics and losses of soil organic matter and nutrients by water erosion in cover crop management systems in olive groves, in tropical regions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Atkinson, K. Principle and method of soil reconstruction for coal mine land reclamation. J. China Coal Soc. 1998, 6, 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, J.A.; Currie, W.S.; Eshleman, K.N.; Kuers, K.; Monteleone, S.; Negley, T.L.; Pohlad, B.R.; Thomas, C.L. Forest to reclaimed mine land use change leads to altered ecosystem structure and function. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, D.; Singh, S.K.; Sahu, N.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P.; Duraisami, V.P.; Ramamurthy, V.; Lalitha, M.; Kalaiselvi, B. Assessment of spatial variability of soil properties using geospatial techniques for farm level nutrient management. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Xia, M.; Tang, X.; Fan, S. Spatial variability of soil nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents in Moso bamboo forests in Yong’an City, China. CATENA 2017, 150, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, K.M.; Swarup, A.; Mishra, B.; Manna, M.C.; Waniari, R.H.; Mandal, K.G.; Misra, A.K. Impact of long-term application of fertilizer, manure and lime under intensive cropping on physical properties and organic carbon content of an Alfisol. Geoderma 2008, 148, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilchano, C.; Maranon, T.; Perez-Ramos, I.M.; Noejovich, L.; Valladares, F.; Zavala, M.A. Patterns and ecological consequences of abiotic heterogeneity in managed cork oak forests of Southern Spain. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Thomas, S.C.; Tian, D.L. Forest management and soil respiration: Implications for carbon sequestration. Environ. Rev. 2008, 16, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellock, M.L.; Rafique, R.; LaPerle, C.M.; Peichl, M.; Kiely, G. Changes in ecosystem carbon stocks in a grassland ash (Fraxinus excelsior) afforestation chronosequence in Ireland. J. Plant Ecol. 2014, 7, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Xia, M.; Guan, F.; Fan, S. Spatial Distribution of Soil Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Stocks in Moso Bamboo Forests in Subtropical China. Forests 2016, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklein, A.R.; Houlton, B.Z. Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Dong, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, B.; Sun, R. Nitrogen leaching greatly impacts bacterial community and denitrifiers abundance in subsoil under long-term fertilization. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 294, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dai, Q.; Xu, F.; Yan, Y.; Peng, X. Variability in Soil Macronutrient Stocks across a Chronosequence of Masson Pine Plantations. Forests 2022, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Ma, J.W.; Xiao, C.; Li, Y.J. Effects of climate factors and soil properties on soil nutrients and elemental stoichiometry across the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin, China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1970–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, S.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Changes in soil phosphorus and its influencing factors following afforestation in Northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Zhou, W.; Bai, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics of reconstructed soil bulk density of opencast coal-mine in the loess area of China. CATENA 2021, 199, 105116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzykowski, M. Soil quality index as a tool for Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) monoculture conversion planning on afforested, reclaimed mine land. J. For. Res. 2014, 25, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.W.; Qu, Q.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.Q.; Wulan, E.; Xue, S. Stocks and Stoichiometry of Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Total Phosphorus after Vegetation Restoration in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Forests 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Z.W.; Li, L.H. Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry as affected by land-use in an agro-pastoral region of northwest China. CATENA 2017, 150, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Zhao, L.H.; Sun, P.S.; Zhao, F.Z.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Deep Soil C, N, and P Stocks and Stoichiometry in Response to Land Use Patterns in the Loess Hilly Region of China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkanç, S.Y. Effects of afforestation on soil organic carbon and other soil properties. CATENA 2014, 123, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Y.Q. Effect of environmental factors on regional soil organic carbon stocks across the Loess Plateau region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, K.; Bai, Z.K.; Cheng, H.X.; Liu, F. The development of topsoil properties under different reclaimed land uses in the Pingshuo opencast coalmine of Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 100, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, X.; Li, Y. Differentiation and mechanisms on physical properties of reconstructed soils on open-cast mine dump of loess area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6367–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, Z. Spatial distribution of soil bulk density and its relationship with slope and vegetation allocation model in rehabilitation of dumping site in loess open-pit mine area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Li, X. Comparative analysis of soil nutrients under different land-use types in the Mun River basin of Northeast Thailand. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Effects of soil pH and texture on soil carbon and nitrogen in soil profiles under different land uses in Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.L.; Li, X.Q. Contributions of soil erosion and decomposition to SOC loss during a short-term paddy land abandonment in Northeast Thailand. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 321, 107629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.A.; Allen, S.E. A wet oxidation procedure suitable for the determination of nitrogen and mineral nutrients in biological material. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Long, O.H.; Seatz, L.F. Correlation of Soil Tests for Available Phosphorus and Potassium with Crop Yield Responses to Fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1953, 17, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Romero, M.L.; Lozano-García, B.; Parras-Alcántara, L. Topography and land use change effects on the soil organic carbon stock of forest soils in Mediterranean natural areas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yu, K.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Lai, Z.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon stocks in Masson pine (Pinus massoniana) forests in subtropical China. CATENA 2019, 178, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Soil stoichiometry and carbon storage in long-term afforestation soil affected by understory vegetation diversity. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R. Quantitative spatial analysis of soil in the field. In Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marchant, B.P.; Lark, R.M. Robust estimation of the variogram by residual maximum likelihood. Geoderma 2007, 140, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlon, C.; Critto, A.; Marcomini, A.; Nathanail, P. Risk based characterisation of contaminated industrial site using multivariate and geostatistical tools. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Study on the Spatial Variability of Farmland Soil Nutrient Based on the Kriging Interpolation. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 7–8 November 2009; pp. 550–555. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, H.K.; Klik, A. Predicting the spatial distribution of soil erodibility factor using USLE nomograph in an agricultural watershed, Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Mesic, M.; Zgorelec, Z.; Jurisic, A.; Bilandzija, D. Spatial variation of soil nutrients on sandy-loam soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 144, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.K.; Lal, R. Changes in physical and chemical properties of soil after surface mining and reclamation. Geoderma 2011, 161, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juwarkar, A.A.; Mehrotraa, K.L.; Nair, R.; Wanjari, T.; Singh, S.K.; Chakrabarti, T. Carbon sequestration in reclaimed manganese mine land at Gumgaon, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bai, Z. Deciphering the origin and controlling factors of mercury in reclaimed soils: A case study in Pingshuo opencast coalmine of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Maiti, S.K. Importance of carbon fractionation for the estimation of carbon sequestration in reclaimed coalmine soils—A case study from Jharia coalfields, Jharkhand, India. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Du, H. The carbon storage in moso bamboo plantation and its spatial variation in Anji County of southeastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 14, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Novo, L.A.B.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Maiti, S.K. Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Development in Coal Mine Degraded Land by Using Integrated Mine Soil Quality Index (IMSQI): The Evidence from India. Forests 2020, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.-h.; Li, N.-n.; Zhang, B.-j.; Yang, H.-y. Soil erodibility as impacted by vegetation restoration strategies on the Loess Plateau of China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnagirytė-Kabašinskienė, I.; Žemaitis, P.; Armolaitis, K.; Stakėnas, V.; Urbaitis, G. Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Afforested Agricultural Land in Lithuanian Hemiboreal Forest Zone. Forests 2021, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwal, J.; Maiti, S.K. Development of Technosol properties and recovery of carbon stock after 16 years of revegetation on coal mine degraded lands, India. CATENA 2018, 166, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G.; Gao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, E.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors under the condition of ecological construction in a hilly-gully watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2017, 296, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Voroney, P.; Coleman, B.; Deen, B.; Gordon, A.; Thimmanagari, M.; Thevathasan, N. Quantifying soil organic carbon stocks in herbaceous biomass crops grown in Ontario, Canada. Agrofor. Syst. 2019, 93, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, F.; Gregory, A.S.; Richter, G.M. Carbon Sequestration by Perennial Energy Crops: Is the Jury Still Out? BioEnergy Res. 2015, 8, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felten, D.; Emmerling, C. Accumulation of Miscanthus-derived carbon in soils in relation to soil depth and duration of land use under commercial farming conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.R.P.; Sá, J.C.d.M.; Mishra, U.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Ferreira, L.A.; Furlan, F.J.F. Soil type and texture impacts on soil organic carbon storage in a sub-tropical agro-ecosystem. Geoderma 2017, 286, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gami, S.K.; Lauren, J.G.; Duxbury, J.M. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in Nepal long-term soil fertility experiments. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, H. Vertical patterns and controls of soil nutrients in alpine grassland: Implications for nutrient uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Huang, M.; Shao, X.M.; Mickler, R.A.; Li, K.; Ji, J.J. Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon in China. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, S200–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmitt, S.J.; Wright, D.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Jones, D.L. pH regulation of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in two agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignac, M.F.; Kogel-Knabner, I.; Michel, K.; Matzner, E.; Knicker, H. Chemistry of soil organic matter as related to C : N in Norway spruce forest (Picea abies(L.) Karst.) floors and mineral soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2002, 165, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A.; Oades, J.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Skene, T.M.; Golchin, A.; Clarke, P. Assessing the extent of decomposition of natural organic materials using solid-state C-13 NMR spectroscopy. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.X.; Han, G.L.; Liu, M.; Zeng, J.; Liang, B.; Liu, J.K.; Qu, R. Determining the Distribution and Interaction of Soil Organic Carbon, Nitrogen, pH and Texture in Soil Profiles: A Case Study in the Lancangjiang River Basin, Southwest China. Forests 2020, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.R.; Liang, G.Q.; He, P.; Liu, Z.B. Soil C/N and pH together as a comprehensive indicator for evaluating the effects of organic substitution management in subtropical paddy fields after application of high-quality amendments. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorich, E.G.; Carter, M.R.; Angers, D.A.; Monreal, C.M.; Ellert, B.H. Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic-matter quality in agricultural soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 74, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.H.; Huang, Z.Q.; He, Z.M.; Yu, Z.P.; Wang, M.H.; Davis, M.R.; Yang, Y.S. Soil C:N ratio is the major determinant of soil microbial community structure in subtropical coniferous and broadleaf forest plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 387, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.; Tsadilas, C. Phosphorus Sorption and Availability to Canola Grown in an Alfisol Amended with Various Soil Amendments. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X. Effect of annual variation in soil pH on available soil nutrients in pear orchards. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J. The effects of pH on phosphate uptake from the soil. Plant Soil 2016, 410, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Maiti, S.K.; Chaudhuri, S. Soil development in 2–21 years old coalmine reclaimed spoil with trees: A case study from Sonepur-Bazari opencast project, Raniganj Coalfield, India. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Depth (cm) | Mean | Median | Maximum | Minimum | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOCD Mg ha−1 | |||||
| 0–10 | 15.60 | 9.24 | 58.19 | 3.45 | 99.14 |
| 10–20 | 10.13 | 4.22 | 74.88 | 2.54 | 169.89 |
| 20–30 | 26.56 | 3.91 | 304.63 | 1.76 | 259.21 |
| 30–40 | 31.20 | 3.21 | 496.49 | 1.90 | 339.75 |
| 40–50 | 31.37 | 2.82 | 559.12 | 1.46 | 378.31 |
| 50–60 | 26.72 | 3.42 | 397.62 | 1.81 | 323.00 |
| TND Mg ha−1 | |||||
| 0–10 | 0.79 | 0.58 | 1.97 | 0.35 | 57.74 |
| 10–20 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 68.78 |
| 20–30 | 0.73 | 0.39 | 5.11 | 0.19 | 147.68 |
| 30–40 | 0.81 | 0.32 | 8.65 | 0.18 | 219.75 |
| 40–50 | 0.83 | 0.34 | 9.92 | 0.17 | 247.51 |
| 50–60 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 6.67 | 0.20 | 192.11 |
| APD Mg ha−1 | |||||
| 0–10 | 0.0056 | 0.0050 | 0.0116 | 0.0026 | 39.83 |
| 10–20 | 0.0053 | 0.0042 | 0.0149 | 0.0004 | 63.30 |
| 20–30 | 0.0062 | 0.0047 | 0.0149 | 0.0004 | 63.83 |
| 30–40 | 0.0074 | 0.0061 | 0.0165 | 0.0018 | 63.69 |
| 40–50 | 0.0091 | 0.0072 | 0.0255 | 0.0005 | 60.17 |
| 50–60 | 0.0097 | 0.0086 | 0.0303 | 0.0010 | 62.42 |
| AKD Mg ha−1 | |||||
| 0–10 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 52.12 |
| 10–20 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 41.63 |
| 20–30 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 41.98 |
| 30–40 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 47.09 |
| 40–50 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 44.37 |
| 50–60 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 48.10 |
| Soil nutrient Stocks | Optimal Model | C0/(C + C0) % a | R2 b | RSS c | A0/m d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOCD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | 17.05 | 0.58 | 2.65 × 10−2 | 971.68 |
| TND (Mg ha−1) | Spherical | 25.60 | 0.82 | 1.06 × 10−2 | 242.00 |
| APD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | 0.20 | 0.66 | 8.28 × 10−8 | 171.47 |
| AKD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | 0.14 | 0.74 | 9.33 × 10−4 | 280.59 |
| Soil nutrient Stocks | Optimal Model | ME | AME | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOCD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | −2.56 × 100 | 1.05 × 101 | 1.47 × 101 |
| TND (Mg ha−1) | Spherical | −1.38 × 100 | 2.69 × 100 | 5.92 × 100 |
| APD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | −1.07 × 10−3 | 1.83 × 10−2 | 2.25 × 10−2 |
| AKD (Mg ha−1) | Gaussian | −1.21 × 10−2 | 1.81 × 10−1 | 2.69 × 10−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Qian, M.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Cao, Y. Spatial Distribution and Regulating Factors of Soil Nutrient Stocks in Afforested Dump of Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China. Forests 2022, 13, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020345
Zhou W, Qian M, Wang S, Li S, Cao Y. Spatial Distribution and Regulating Factors of Soil Nutrient Stocks in Afforested Dump of Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China. Forests. 2022; 13(2):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020345
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wenxiang, Mingjie Qian, Shufei Wang, Shengpeng Li, and Yingui Cao. 2022. "Spatial Distribution and Regulating Factors of Soil Nutrient Stocks in Afforested Dump of Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China" Forests 13, no. 2: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020345
APA StyleZhou, W., Qian, M., Wang, S., Li, S., & Cao, Y. (2022). Spatial Distribution and Regulating Factors of Soil Nutrient Stocks in Afforested Dump of Pingshuo Opencast Coalmine, China. Forests, 13(2), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020345





