Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity and Related Chemical Indexes in Woodlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
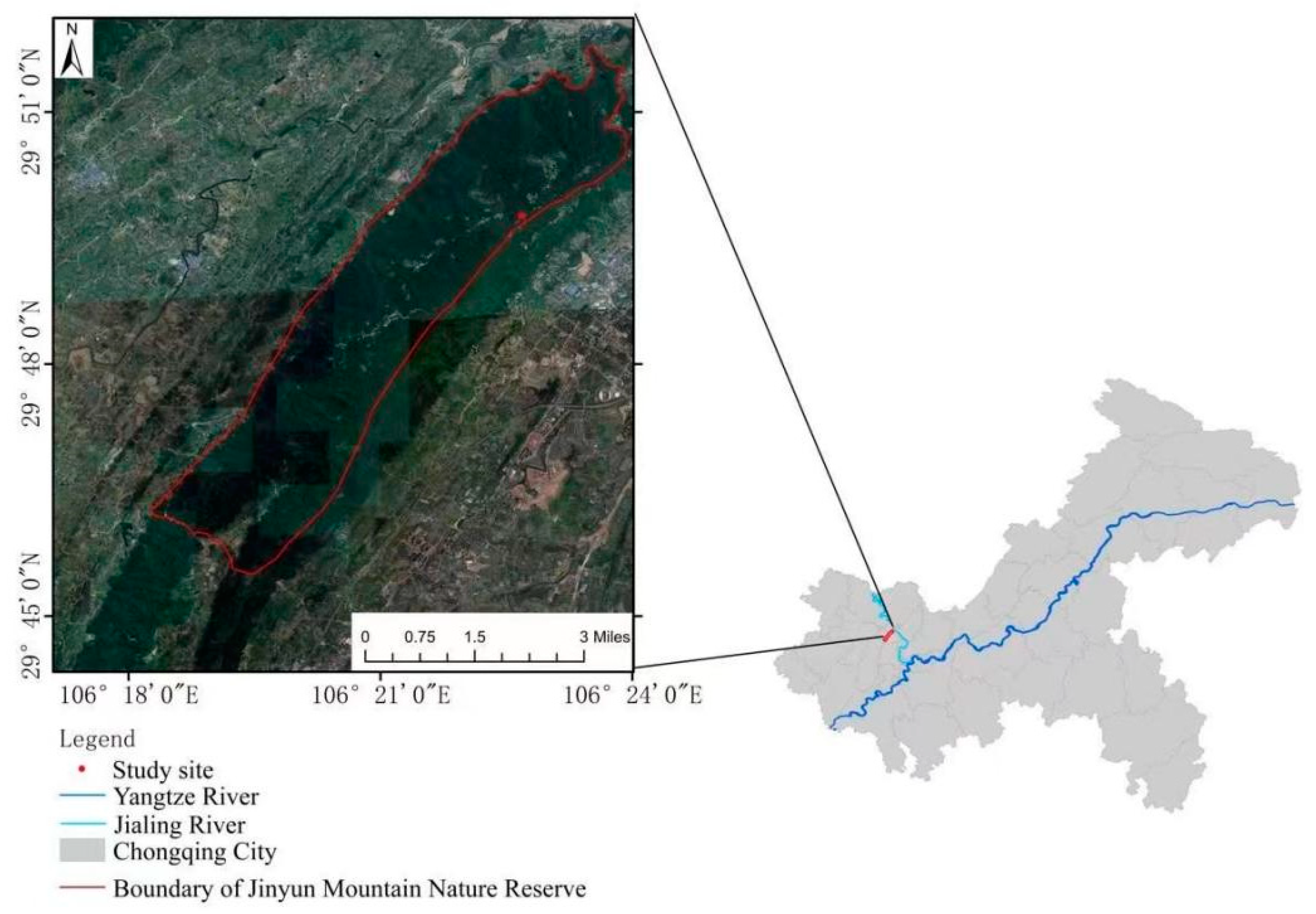
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Plot Layout and Sampling
2.3. Index Measurement and Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil pH in Two Woodland Areas
3.2. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on the Soil Main Nutrients
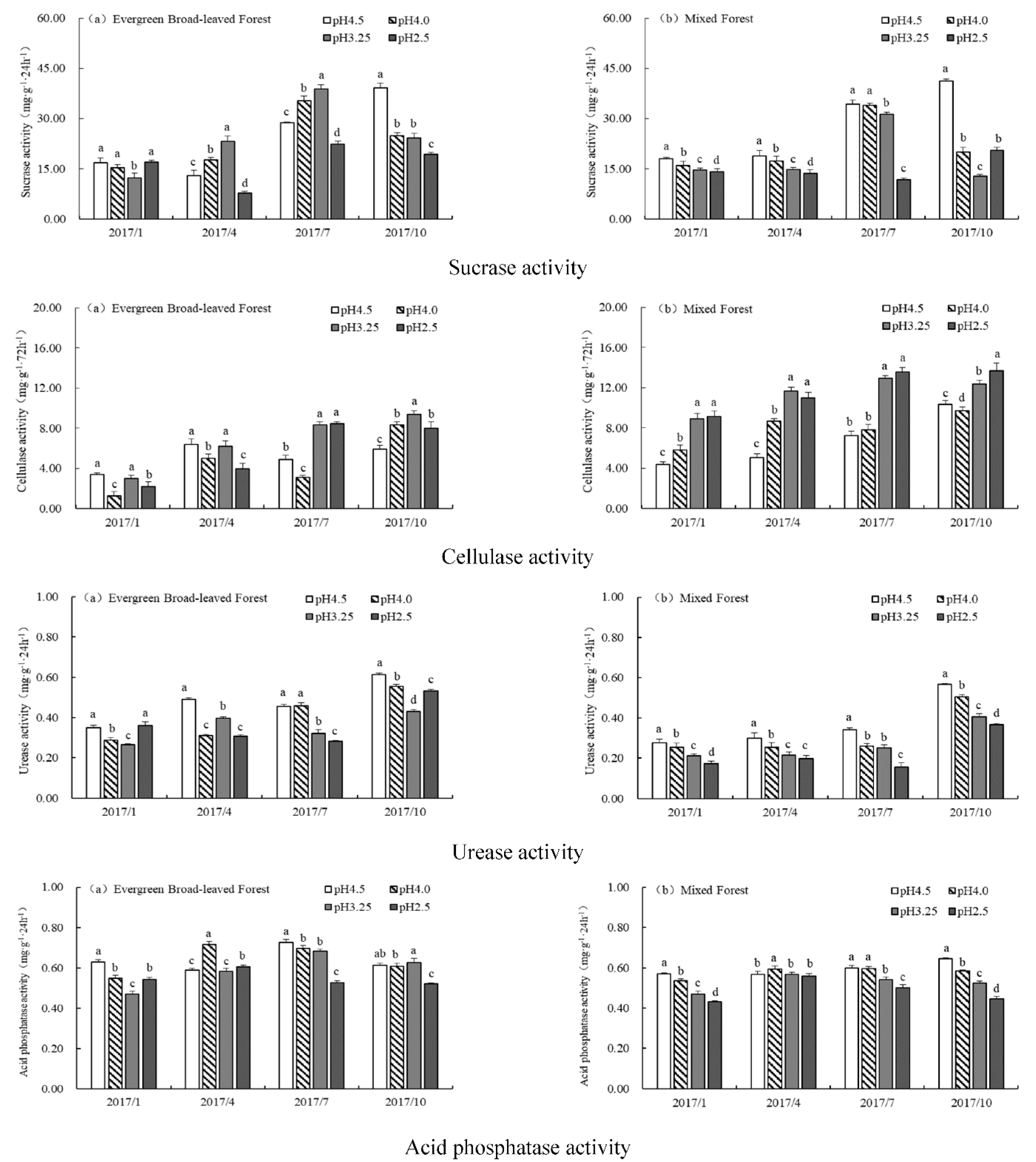
3.3. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.4. Soil Enzyme Activities during the Study Period
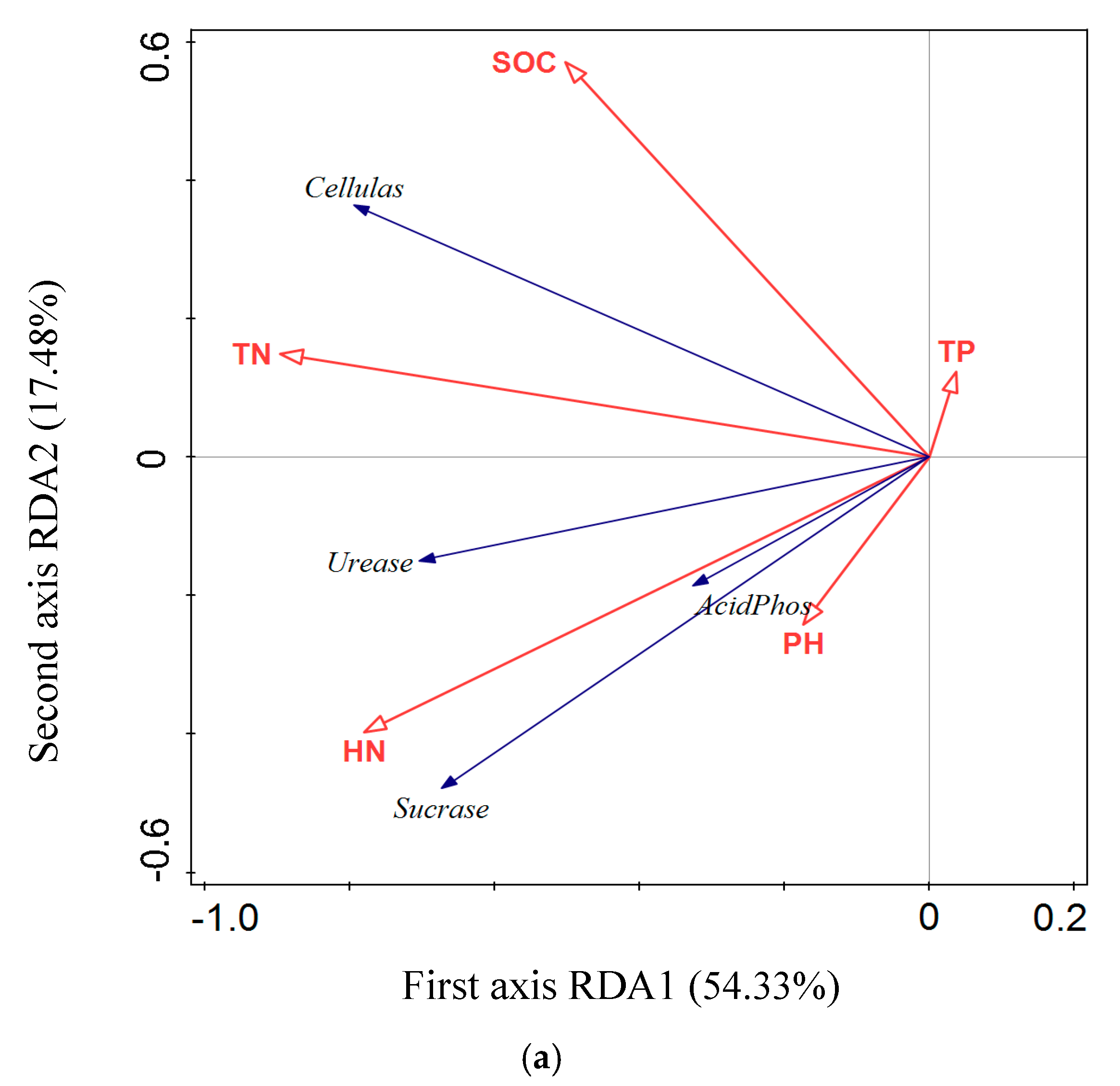
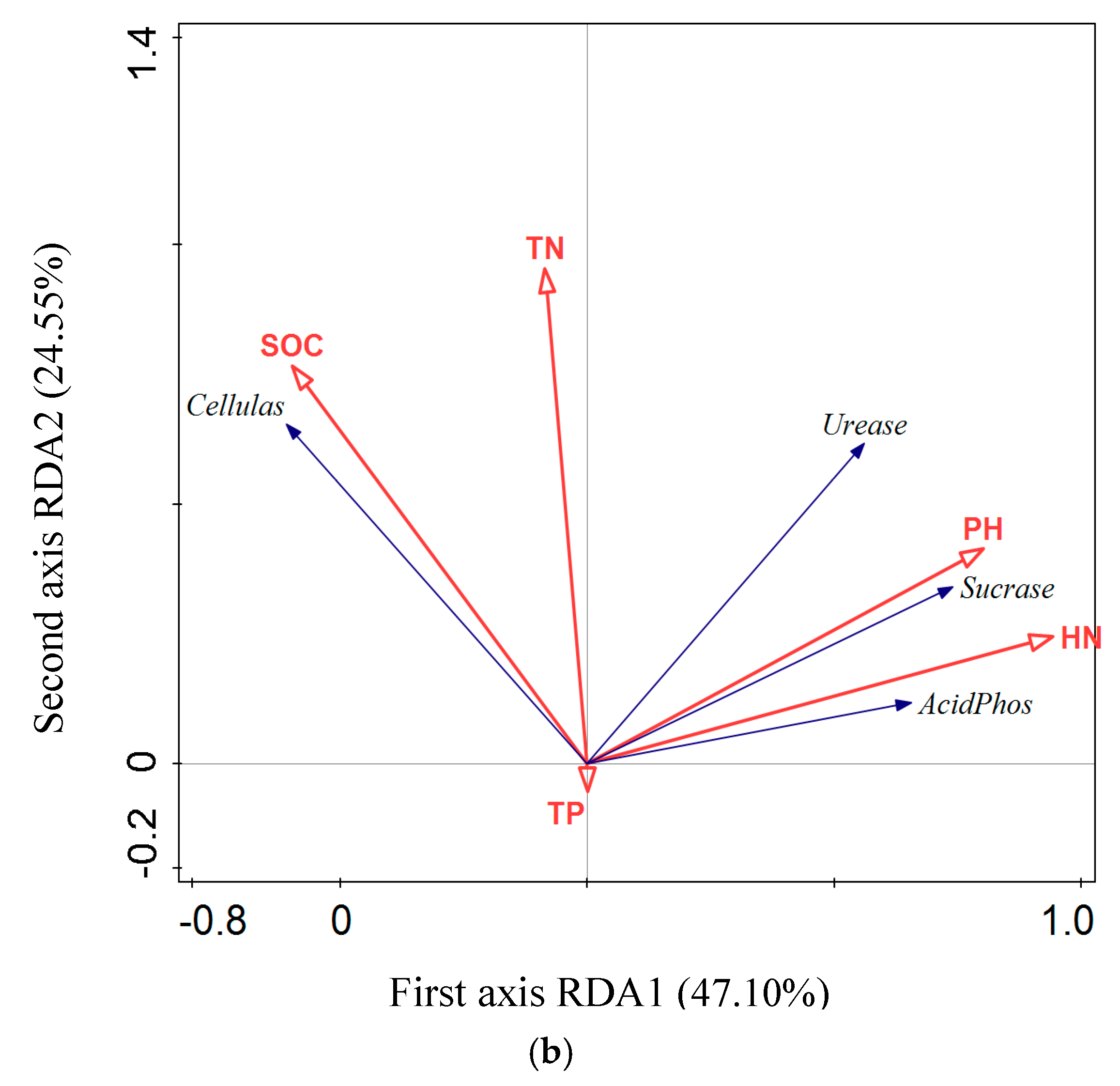
3.5. RDA Analysis of the Relationship between Soil Enzyme Activity and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation Characteristics of Soil Enzyme Activity
4.2. Relationships between Soil Nutrients and the Associated Enzymes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L. Detecting sulfuric and nitric acid rain stresses on Quercus glauca through hyperspectral responses. Sensors 2018, 18, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.R.; Meng, M.J.; Fu, Z.Y.; Xu, L.H.; Zha, Y.; Yue, J.M.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, J.C. Comparative effects of simulated acid rain of different ratios of SO42 to NO3 on fine root in subtropical plantation of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 618, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yi, X.Q.; Gao, X.Z.; Wang, M.H.; Shao, C.Y.; Lv, Z.D.; Chen, J.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Shen, C.W. Physiological and biochemical responses of tea seedlings (Camellia sinensis) to simulated acid rain conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, F.S.; Ye, S.Q.; Yu, S.Q.; Fang, X.M.; Hu, X.F. Responses of rhizosphere nitrogen and phosphorus transformations to different acid rain intensities in a hilly red soil tea plantation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Wang, R.; Wang, T. Enhancement of Germination, Seedling Growth, and Oxidative Metabolism of Barley under Simulated Acid Rain Stress by Exogenous Trehalose. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.E.; Bormann, F.H. Acid Rain: A Serious Regional Environmental Problem. Science 1974, 184, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakow, S.J.; Glenn, A. The Acid Rain Game. Sci. Act. Classr. Proj. Curric. Ideas 1982, 19, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Du, J.; Tian, X. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on litter decomposition, soil microbial biomass, and enzyme activities in subtropical forests of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Pan, Y.P.; Larssen, T.; Tang, J.; Mulder, J. Acid deposition in Asia: Emissions, deposition, and ecosystem effects. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 146, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.L.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhu, J.X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jia, Y.L.; Yu, G.R. Development of atmospheric acid deposition in China from the 1990s to the 2010s. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, Y.L.; Xiang, H.M.; Zhang, J.E.; Li, S.F.; Yang, J.Y. Soil pH Responses to Simulated Acid Rain Leaching in Three Agricultural Soils. Sustainability 2019, 12, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larssen, T.; Lydersen, E.; Tang, D. Acid Rain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habib, K.; Hamidreza, M.; Kaihua, L. Performance of Soil Cation Exchange Capacity Pedotransfer Function as Affected by the Inputs and Database Size. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700670.1–1700670.8. [Google Scholar]
- Moharami, S.; Jalali, M. Effect of acid rain on the fractionation of heavy metals and major elements in contaminated soils. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 31, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Arshad, M.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Ashraf, M.W.; Hayyat, M.U.; Mahmood, R.; Parkpian, P. Interactions Between Acidic (Al3+, Fe2+) and Basic (Ca2+, Mg2+) Cations in Oxisol and Ultisol under Acidification Induced by Simulated Acid Rain. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.S.; Wang, G.G.; Tang, C.J.; Fang, H.Y.; Duan, J.; Yu, X.F. Effects of One-Year Simulated Nitrogen and Acid Deposition on Soil Respiration in a Subtropical Plantation in China. Forests 2020, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, D.J.; Zhang, J.E.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, Q.C. Role of Simulated Acid Rain on Cations, Phosphorus, and Organic Matter Dynamics in Latosol. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Liang, G.H.; Hui, D.F.; Deng, Q.; Liu, J.X.; Chu, G.W.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhang, D.Q. Prolonged acid rain facilitates soil organic carbon accumulation in a mature forest in Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Deng, Q.; Hui, D.F.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhao, M.D.; Wang, X.; Hu, M.H.; Su, Y.X.; Zhang, H.O.; et al. Reduced Lignin Decomposition and Enhanced Soil Organic Carbon Stability by Acid Rain: Evidence from 13C Isotope and 13C NMR Analyses. Forests 2020, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, W.K.; Zhang, J.E.; Shen, H. Influence of simulated acid rain on the physiological response of flowering Chinese cabbage and variation of soil nutrients. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Ren, J.Q. Contrasting effects of long-term acid rain simulation on temperature sensitivity of soil respiration and enzymatic activities in a subtropical forest. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil respiration and its component in a mixed coniferous-broadleaved forest of the three gorges reservoir area in Southwest China. For. Ecosyst. 2019, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Meng, X.X.; Zhang, G.L. Status of acid rain pollution in Chongqing. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 11–14. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Guo, P.; Liu, C.X.; Tang, X.F.; Sun, S.Q. Acid buffering mechanism and influencing factors of forest soil in acid rain region of Jinyun Mountain, Chongqing. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 77–83. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.C.; Xiong, H.Q.; Ding, Y. Effects of acid deposition on soil and vegetation in nanshan Forest ecosystem in Chongqing. Res. Environ. Sci. 2002, 6, 8–11. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Pei, C.M. Response of soil chemical properties and enzyme activity of four species in the Three Gorges Reservoir area to simulated acid rain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.F.; Yang, Z.J.; Lin, C.F.; Liu, X.F.; Chen, G.S.; Yang, Y.S. Conversion of a natural evergreen broadleaved forest into coniferous plantations in a subtropical area: Effects on composition of soil microbial communities and soil respiration. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2016, 52, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Huang, B.; Du, N.; Guo, S.; Shu, S.; Sun, J. Effects of garlic/cucumber relay intercropping on soil enzyme activities and the microbial environment in continuous cropping. HortScience 2017, 52, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, J. Variation of soil enzyme activity and microbial biomass in poplar plantations of different genotypes and stem spacings. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yao, J.; Cai, M.; Qian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Richnow, H.H.; Blake, R.E.; Doni, S.; Ceccanti, B. Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounissamy, V.C.; Kundu, S.; Selladurai, R.; Saha, J.K.; Biswas, A.K.; Adhikari, T.; Patra, A.K. Effect of Soil Amendments on Microbial Resilience Capacity of Acid Soil Under Copper Stress. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.; Liu, L.; Xiao, X. Comparative analysis of soil organic matter determination methods. J. Hohai Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 39, 5. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.F. Comparison of soil total nitrogen determination methods. Guangzhou Environ. Sci. 2006, 21, 2. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.F.; Wu, A.Q.; Wang, F.C.; Chen, F.S. The effects of simulated acid rain on internal nutrient cycling and the ratios of Mg, Al, Ca, N, and P in tea plants of a subtropical plantation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Wang, D.; Yu, F. Effects of simulated acid rain and litter on enzyme activities in rhizosphere soil of Cryptomeria fortunei seedlings. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2014, 31, 373–379. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Deforest, J.L.; Zak, D.R.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Burton, A.J. Atmospheric Nitrate Deposition, Microbial Community Composition, and Enzyme Activity in Northern Hardwood Forests. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Bradford, M.A.; Fierer, N. Consistent effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial communities in contrasting systems. Ecology 2010, 91, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Wallenstein, M.D. Modeling the effects of temperature and moisture on soil enzyme activity: Linking laboratory assays to continuous field data. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 55, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.J.; Jiang, H.; Ma, Y.D. Effects of simulated acid rain stress on soil enzymes of Cyclobalanopsis seedlings. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 14833–14836. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yang, Y. A Review on Litter Decomposition in Forest Ecosystem. Sci. Silvae Sinicae 2006, 42, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, F.S.; Matson, P.A.; Mooney, H.A. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q.; Zhang, J.E.; Ouyang, Y.; Lin, L.; Quan, G.M.; Zhao, B.L.; Yu, J.Y. Effects of simulated acid rain on microbial characteristics in a lateritic red soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18260–18266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.H.; Shen, X.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Min, H.; Shi, Y.F. Effects of acid rain on soil microorganism and enzyme activities of Atractylodes macrocephala. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 2, 227–229. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, L.; Li, H.J.; Wang, L.F. Factors influencing soil enzyme activity in China’s forest ecosystems. Plant Ecol. 2018, 219, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Yu, L.; Liu, J. Rainfall processes and nitrogen input in three typical forests in Jinyun Mountain. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1081–1090. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.X.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Sun, L.D.; Wang, D. Effects of different rainfall on soil enzyme activities and soil microorganisms in rain-fed agricultural areas. J. South. Agric. 2015, 46, 1579–1583. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Mo, J.M.; Xue, J.H.; Fang, Y.T.; Li, J. Effects of increased nitrogen deposition on decomposition enzyme activities of forest litter. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2006, 6, 539–546. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.G.; Xiao, W.F.; Zeng, L.X.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhou, B.Z. Effects of enzyme activities in soil-litter layer on litter decomposition in Masson’s Pine forest in three Gorges Reservoir Area. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2014, 34, 2228–2237. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Kunito, T.; Isomura, I.; Sumi, H.; Park, H.D.; Toda, H.; Otsuka, S.; Nagaoka, K.; Saeki, K.; Senoo, K. Aluminum and acidity suppress microbial activity and biomass in acidic forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G. Enzyme activity in soil: Location and a possible role in microbial ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, W.A.; Cheng, L.; Wang, P. Soil acid and alkaline phosphatase activity as pH adjustment indicators. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Liu, G.S.; Xu, Z.J.; Wang, L.M.; Liu, W.P. Effects of simulated acid rain on soil acid phosphatase activity and its mechanism. China Environ. Sci. 2003, 2, 65–68. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.C.; Geng, Y.Q.; Wei, L. Studies on Soil Urease Activity of Major Forest Types in Badaling of Beijing. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2005, 23, 424. [Google Scholar]
- Si, D.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Chen, L.L.; Ye, L.X.; Liu, S.L.; Li, M.Q. Soil enzyme activities of different forest types in Fengyang Mountain, Zhejiang Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 33, 258–263. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.Z.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Shen, Z.P.; You, H.M. Correlation of soil active organic carbon and its components with soil enzymes in different forest types in Lushan Mountain. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 78–82. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.P.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S.Q.; Ma, Y.D.; Dou, R.P.; Song, X.Z. Comparison of leaf litter decomposition of 6 coniferous and broadleaved species in subtropical region. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2009, 15, 655–659. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Spears, J.D.H.; Holub, S.M.; Harmon, M.E.; Lajtha, K. The influence of decomposing logs on soil biology and nutrient cycling in an old-growth mixed coniferous forest in Oregon, U.S.A. Can. J. For. Res. 2003, 33, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q. Soil microorganisms and heterotrophic respiration characteristics of typical vegetation types in loess hilly region. Ph.D. Thesis, Research Center for Soil and Water Conservation and Eco-Environment, Ministry of Education, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xianyang, China, 2017. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Feng, H.M.; Yi, Q.; Lei, S.K. Response of litter layer to acid deposition in a typical stand in southwest subtropical China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 108–113. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, M.X.; Cao, N.N.; Yan, J.H. Soil organic matter is important for acid buffering and reducing aluminum leaching from acidic forest soils. Chem. Geology. 2018, 501, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhong, X.; Xiang, H. Leaching of simulated acid rain deteriorates soil physiochemical and mechanical properties in three agricultural soils. Catena 2021, 206, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, A.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hens, L. Stakeholder Delphi-perception analysis on impacts and responses of acid rain on agricultural ecosystems in the Vietnamese upland. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4467–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, C.; Sbîrnă, S.; Ionescu, C.; Sbîrnă, L.S.; Codreşi, C. Simulated impact of acid rain on organic matter, phosphorus and other soil components. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.J.; Guo-Yi, Z.H.; Huang, Z.L.; Ju-Xiu, L.I.U.; Zhang, D.Q.; Jiong, L.I. Effect of simulated acid rain on potential carbon and nitrogen mineralization in forest soils. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.X. Theory and model application of microinterface water quality processes. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2000, 20, 8. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.L.; Staehelin, C.; Dayan, F.E.; Song, Y.Y.; Su, Y.J.; Zeng, R.S. Simulated acid rain accelerates litter decomposition and enhances the allelopathic potential of the invasive plant Wedelia trilobata (creeping daisy). Weed Sci. 2012, 60, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, S.; Li, Q.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of sulfuric, nitric, and mixed acid rain on the decomposition of fine root litter in Southern China. Ecol. Processes 2021, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, J.; Oulehle, F.; Krám, P.; Hruška, J. Loss of nutrients due to litter raking compared to the effect of acidic deposition in two spruce stands, Czech Republic. Biogeochemistry 2008, 88, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, S.P.; Yanai, R.D.; Arthur, M.A.; Blum, J.D.; Siccama, T.G. Biotic control of calcium cycling in northern hardwood forests: Acid rain and aging forests. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C. Effects of simulated acid rain on dissolution and transformation of aluminum in acid soils of south China. J. Soil Environ. Sci. 2001, 10, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Tie, L.; Zhang, S.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Huang, C. Responses of soil C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios to N and S additions in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Geoderma 2020, 379, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, K.J.; Fuchslueger, L.; Hoosbeek, M.R.; Hofhansl, F.; Martins, L.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.J.; Hartley, I.P.; Lugli, L.F.; Quesada, C.A. Litter inputs and phosphatase activity control the temporal variability of organic phosphorus in a tropical forest soil in the Central Amazon. J. Plant Soil. 2021, 469, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lin, Y.H.; He, X.B.; Han, G.M. Acid rain decelerates the decomposition of Cunninghamia lanceolata needle and Cinnamomum camphora leaf litters in a karst region in China. J. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Guo, P.; Han, G.M.; Feng, X.G.; Zhang, P.; Tian, X.J. Effect of simulated acid rain on the litter decomposition of Quercus acutissima and Pinus massoniana in forest soil microcosms and the relationship with soil enzyme activities. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Cui, X.H.; Bai, X.L.; Xia, L.F.; Li, J.N. Hydrological dynamics of mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests and evergreen broad-leaved forests in Dagang Mountain. J. Forest Res. 2002, 1, 13–20. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
| Forest Type | Chemical Element Content (mg·g−1) | Acid Rain Treatment Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.5 | pH 4.0 | pH 3.25 | pH 2.5 | ||
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SOC | 16.03 ± 0.27 d | 18.02 ± 0.14 c | 20.19 ± 0.16 b | 21.04 ± 0.13 a |
| TN | 1.07 ± 0.09 a | 1.12 ± 0.10 a | 1.05 ± 0.13 a | 1.06 ± 0.07 a | |
| TP | 0.56 ± 0.02 a | 0.72 ± 0.06 a | 0.61 ± 0.05 a | 0.59 ± 0.04 a | |
| HN | 0.19 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.00 b | 0.17 ± 0.00 c | |
| Soil pH | 3.71 ± 0.03 a | 3.66 ± 0.01 b | 3.53 ± 0.03 c | 3.48 ± 0.03 c | |
| Mixed Forest | SOC | 13.11 ± 0.41 b | 15.36 ± 0.29 ab | 16.02 ± 0.43 ab | 18.02 ± 0.21 a |
| TN | 0.86 ± 0.17 a | 0.95 ± 0.21 a | 1.08 ± 0.22 a | 1.01 ± 0.25 a | |
| TP | 0.39 ± 0.04 a | 0.45 ± 0.04 a | 0.47 ± 0.02 a | 0.38 ± 0.08 a | |
| HN | 0.17 ± 0.00 a | 0.17 ± 0.00 a | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | 0.14 ± 0.00 c | |
| Soil pH | 3.46 ± 0.05 a | 3.42 ± 0.02 a | 3.31 ± 0.04 b | 3.26 ± 0.04 c | |
| Forest Type | Chemical Element Content (mg·g−1) | Acid Rain Treatment Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.5 | pH 4.0 | pH 3.25 | pH 2.5 | ||
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SOC | 18.11 ± 0.22 d | 20.27 ± 0.18 c | 23.19 ± 0.14 b | 25.43 ± 0.20 a |
| TN | 1.30 ± 0.04 a | 1.42 ± 0.23 a | 1.35 ± 0.06 a | 1.35 ± 0.12 a | |
| TP | 0.48 ± 0.03 b | 0.73 ± 0.04 a | 0.67 ± 0.04 a | 0.71 ± 0.03 a | |
| HN | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.00 b | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.18 ± 0.00 c | |
| Soil pH | 3.93 ± 0.04 a | 3.82 ± 0.04 b | 3.68 ± 0.03 c | 3.61 ± 0.04 d | |
| Mixed Forest | SOC | 16.52 ± 0.31 b | 16.61 ± 0.24 b | 21.19 ± 0.43 a | 21.33 ± 0.38 a |
| TN | 1.17 ± 0.15 a | 1.11 ± 0.15 a | 1.11 ± 0.12 a | 1.07 ± 0.05 a | |
| TP | 0.43 ± 0.05 a | 0.45 ± 0.07 a | 0.43 ± 0.08 a | 0.38 ± 0.02 a | |
| HN | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | |
| Soil pH | 3.55 ± 0.04 a | 3.51 ± 0.06 a | 3.41 ± 0.03 b | 3.33 ± 0.04 c | |
| Forest Type | Chemical Element Content (mg·g−1) | Acid Rain Treatment Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.5 | pH 4.0 | pH 3.25 | pH 2.5 | ||
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SOC | 19.02 ± 0.05 c | 19.03 ± 0.22 c | 25.81 ± 0.04 b | 27.13 ± 0.18 a |
| TN | 1.45 ± 0.13 a | 1.36 ± 0.19 a | 1.50 ± 0.23 a | 1.48 ± 0.16 a | |
| TP | 0.57 ± 0.02 b | 0.51 ± 0.01 b | 0.67 ± 0.02 a | 0.70 ± 0.01 a | |
| HN | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | 0.22 ± 0.06 b | 0.21 ± 0.05 c | 0.19 ± 0.04 d | |
| Soil pH | 4.02 ± 0.04 a | 3.81 ± 0.02 b | 3.63 ± 0.03 c | 3.51 ± 0.05 d | |
| Mixed Forest | SOC | 16.98 ± 0.19 b | 17.13 ± 0.59 b | 25.27 ± 0.15 a | 26.37 ± 0.46 a |
| TN | 1.26 ± 0.03 b | 1.18 ± 0.04 c | 1.49 ± 0.05 a | 1.35 ± 0.06 a,b | |
| TP | 0.35 ± 0.01 c | 0.45 ± 0.02 a | 0.40 ± 0.02 b,c | 0.42 ± 0.01 b | |
| HN | 0.20 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.00 b | 0.16 ± 0.00 c | 0.15 ± 0.01 d | |
| Soil pH | 3.69 ± 0.04 a | 3.61 ± 0.02 b | 3.47 ± 0.03 c | 3.41 ± 0.04 d | |
| Forest Type | Chemical Element Content (mg·g−1) | Acid Rain Treatment Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4.5 | pH 4.0 | pH 3.25 | pH 2.5 | ||
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SOC | 23.03 ± 0.16 d | 25.16 ± 0.16 c | 27.31 ± 0.11 b | 30.03 ± 0.08 a |
| TN | 1.86 ± 0.03 a | 1.74 ± 0.04 ab | 1.65 ± 0.04 b | 1.83 ± 0.03 a | |
| TP | 0.70 ± 0.02 a | 0.56 ± 0.09 a | 0.63 ± 0.02 a | 0.67 ± 0.13 a | |
| HN | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.00 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 c | 0.21 ± 0.00 d | |
| Soil pH | 3.72 ± 0.04 a | 3.65 ± 0.04 b | 3.62 ± 0.02 b | 3.52 ± 0.05 c | |
| Mixed Forest | SOC | 18.17 ± 0.12 b | 21.91 ± 0.18 b | 25.99 ± 0.56 a | 29.12 ± 0.16 a |
| TN | 1.46 ± 0.21 a | 1.54 ± 0.20 a | 1.65 ± 0.18 a | 1.70 ± 0.17 a | |
| TP | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 0.35 ± 0.02 b | 0.41 ± 0.02 a | 0.42 ± 0.02 a | |
| HN | 0.21 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | 0.15 ± 0.00 c | |
| Soil pH | 3.77 ± 0.02 a | 3.61 ± 0.05 b | 3.42 ± 0.02 c | 3.38 ± 0.03 c | |
| Forest Type | Source | SS | df | MS | F-Ratio | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SAR | 694.693 | 3.00 | 231.564 | 173.207 | <0.01 |
| Times | 3181.478 | 3.00 | 1060.493 | 793.233 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 1406.392 | 9.00 | 156.266 | 116.885 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 64.172 | 48.00 | 1.337 | |||
| Mixed Forest | SAR | 1688.466 | 3.00 | 562.822 | 463.743 | <0.01 |
| Times | 1505.531 | 3.00 | 501.844 | 413.499 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 1813.012 | 9.00 | 201.446 | 165.983 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 58.255 | 48.00 | 1.214 |
| Forest type | Source | SS | df | MS | F-Ratio | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SAR | 45.290 | 3.00 | 15.097 | 62.857 | <0.01 |
| Times | 250.647 | 3.00 | 83.549 | 347.864 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 90.237 | 9.00 | 10.026 | 41.746 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 11.528 | 48.00 | 0.240 | |||
| Mixed Forest | SAR | 34.165 | 3.00 | 11.388 | 475.412 | <0.01 |
| Times | 19.653 | 3.00 | 6.551 | 273.479 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 4.372 | 9.00 | 0.486 | 20.277 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 1.150 | 48.00 | 0.024 |
| Forest Type | Source | SS | df | MS | F-Ratio | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SAR | 0.144 | 3.00 | 0.048 | 223.286 | <0.01 |
| Times | 0.407 | 3.00 | 0.136 | 629.647 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 0.141 | 9.00 | 0.016 | 72.988 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 0.010 | 48.00 | 0.000 | |||
| Mixed Forest | SAR | 0.194 | 3.00 | 0.065 | 315.100 | <0.01 |
| Times | 0.581 | 3.00 | 0.194 | 946.308 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 0.027 | 9.00 | 0.003 | 14.392 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 0.010 | 48.00 | 0.000 |
| Forest Type | Source | SS | df | MS | F-Ratio | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest | SAR | 0.094 | 3.00 | 0.031 | 170.315 | <0.01 |
| Times | 0.105 | 3.00 | 0.035 | 190.243 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 0.127 | 9.00 | 0.014 | 76.728 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 0.009 | 48.00 | 0.000 | |||
| Mixed Forest | SAR | 0.122 | 3.00 | 0.041 | 165.524 | <0.01 |
| Times | 0.044 | 3.00 | 0.015 | 60.103 | <0.01 | |
| Times × SAR | 0.040 | 9.00 | 0.004 | 18.252 | <0.01 | |
| Error | 0.012 | 48.00 | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity and Related Chemical Indexes in Woodlands. Forests 2022, 13, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060860
Zheng Y, Wang Y, Zheng Y, Li Y. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity and Related Chemical Indexes in Woodlands. Forests. 2022; 13(6):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060860
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yifan, Yunqi Wang, Yonglin Zheng, and Yifan Li. 2022. "Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity and Related Chemical Indexes in Woodlands" Forests 13, no. 6: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060860
APA StyleZheng, Y., Wang, Y., Zheng, Y., & Li, Y. (2022). Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Enzyme Activity and Related Chemical Indexes in Woodlands. Forests, 13(6), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060860





