Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CesA Gene Family in Corymbia citriodora
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Identification of CesA Genes in the C. citriodora Genome
2.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Chromosome Localization, Genome Synteny, and Gene Duplication Analyses
2.4. Analysis of Ks and Ka of Homologous Genes in CcCesA Family
2.5. Motif Identification and Gene Structure
2.6. Protein Structure Analysis of CesA Family Proteins in C. citriodora
2.7. Cis-Element Analysis for CcCesA Gene Promoters
2.8. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Eaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of CcCesA Genes
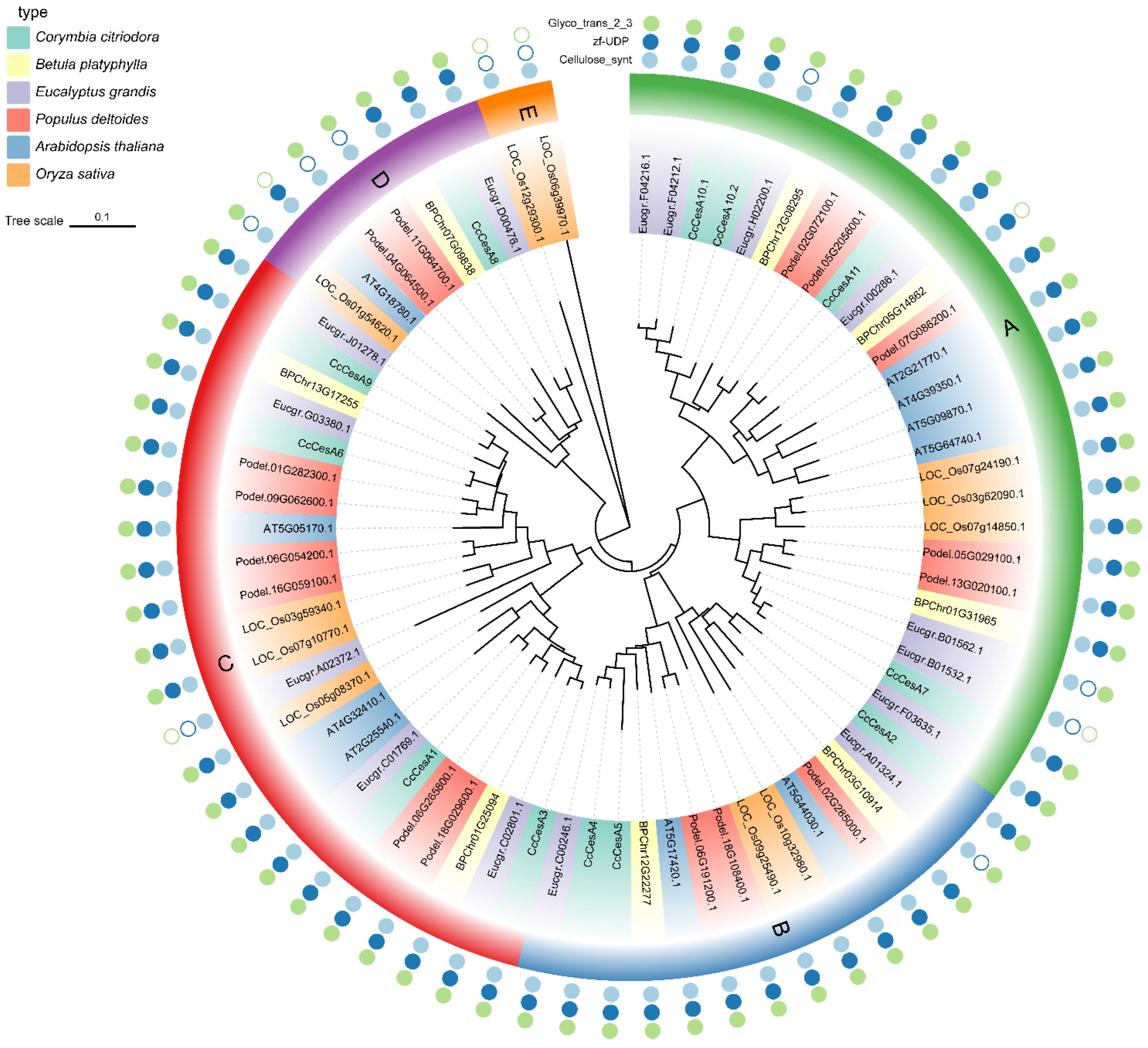
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of CesA Family
3.3. Chromosomal Localization, Gene Duplication, and Genome Synteny of CcCesAs
3.4. Motif Identification
3.5. Conserved Protein and Gene Structure Analysis of Cellulose Synthase Gene in C. citriodora
3.6. Modeling of Secondary and Tertiary Structural Homology of CcCesAs
3.7. Cis-Element Analysis of CcCesA Genes in C. citriodora
3.8. Expression Patterns of CcCesA Genes in Different DBH
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of the CcCesA Gene Family
4.2. Differences in Transmembrane Structure
4.3. The Gene Structures of CcCesAs Are Conserved
4.4. Cis-Element and Gene-Expression Patterns
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maleki, S.S.; Mohammadi, K.; Ji, K.S. Characterization of Cellulose Synthesis in Plant Cells. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 8641373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McFarlane, H.E.; Doring, A.; Persson, S. The cell biology of cellulose synthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bashline, L.; Lei, L.; Gu, Y. Cellulose synthesis and its regulation. Arab. Book 2014, 12, e0169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sunagawa, N.; Tajima, K.; Samejima, M.; Igarashi, K. Heterologous expression of cellulose synthases and trial of synthesis of cellulose in vitro to elucidate the mechanism of cellulose synthesis in nature. Kobunshi 2017, 66, 288–289. [Google Scholar]
- Somerville, C. Cellulose synthesis in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethaphong, L.; Davis, J.K.; Slabaugh, E.; Singh, A.; Haigler, C.H.; Yingling, Y.G. Prediction of the structures of the plant-specific regions of vascular plant cellulose synthases and correlated functional analysis. Cellulose 2016, 23, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelim, L.; Akiyoshi, N.; Tan, T.T.; Ihara, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hirano, K.; Matsuoka, M.; Demura, T.; Ohtani, M. Arabidopsis Group IIId ERF proteins positively regulate primary cell wall-type CESA genes. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J. Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Somssich, M.; Nakata, M.T.; Unda, F.; Atsuzawa, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Wang, T.; Bagman, A.M.; Gaudinier, A.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Complete substitution of a secondary cell wall with a primary cell wall in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Campbell, L.; Turner, S. Secondary cell walls: Biosynthesis and manipulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Dhugga, K.S.; Gill, K.; Singh, J. Novel Structural and Functional Motifs in cellulose synthase (CesA) Genes of Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pear, J.R.; Kawagoe, Y.; Schreckengost, W.E.; Delmer, D.P.; Stalker, D.M. Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12637–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, T. Higher plant cellulose synthases. Genome Biol. 2000, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.; Specht, C.D. Understanding Plant Cellulose Synthases through a Comprehensive Investigation of the Cellulose Synthase Family Sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Long, S. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies Key Cellulose Synthase Genes (CESA) and Cellulose Synthase-like Genes (CSL) in Fast Growth Period of Flax Stem (Linum usitatissimum L.). J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 10431–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Genome-wide bioinformatics analysis of Cellulose Synthase gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and the expression in the pod development. BMC Genomic Data 2022, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, J.; Chen, D.; Si, J.; Liu, C. Genome-wide identification of Cellulose-like synthase D gene family in Dendrobium catenatum. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1163–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Q.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, G.; Zuo, D. Identification of the CesA Subfamily and Functional Analysis of GhMCesA35 in Gossypium hirsutum L. Genes 2022, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Peszlen, I.; Shi, R.; Kim, H.; Katahira, R.; Kafle, K.; Xiang, Z.; Huang, X.; Min, D.; Mohamadamin, M.; et al. Involvement of CesA4, CesA7-A/B and CesA8-A/B in secondary wall formation in Populus trichocarpa wood. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Shang, X.; Wu, Z. Expression Patterns and Gene Analysis of the Cellulose Synthase Gene Superfamily in Eucalyptus grandis. Forests 2021, 12, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Song, F.; Guan, M.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C. Four novel cellulose synthase (CESA) genes from Birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.) involved in primary and secondary cell Wall biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12195–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yin, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. Cloning and analysis of cellulose synthase genes (CesA) in Acacia mangium. Tree Genet. Genomes 2018, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, A.L.; Shepherd, M.; King, G.J.; Butler, J.B.; Freeman, J.S.; Lee, D.J.; Potts, B.M.; Silva-Junior, O.B.; Baten, A.; Jenkins, J.; et al. Pests, diseases, and aridity have shaped the genome of Corymbia citriodora. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.C.d.J.A.; De Araujo, V.A.; Christoforo, A.L.; Lahr, F.A.R.; Vasconcelos, J.S. Characterization of Corymbia citriodora wood for construction. Holos 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Li, Z.; Malladi, A.; Zhang, D.; Li, M. Expression Dynamics of Two Pht1 Genes in Eucalyptus dunnii and Corymbia citriodora in Relation to Phosphate Supply. In Medicine and Biopharmaceutical: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016; pp. 1374–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.H.; Cho, J.S.; Jeon, H.W.; Sangsawang, K.; Shim, D.; Choi, Y.I.; Park, E.J.; Lee, H.; Ko, J.H. Wood Transcriptome Profiling Identifies Critical Pathway Genes of Secondary Wall Biosynthesis and Novel Regulators for Vascular Cambium Development in Populus. Genes 2019, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, H.; Shen, W.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Y. Seasonal changes in cambium activity from active to dormant stage affect the formation of secondary xylem in Pinus tabulaeformis Carr. Tree Physiol. 2022, 42, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Cavalcanti, A.; Chen, F.; Bouman, P.; Li, W. Extent of gene duplication in the genomes of Drosophila, nematode, and yeast. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Yan, B.; Hu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of rice FTIP gene family. Genomics 2020, 112, 3803–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, K.; Nath, U.K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Park, J.I.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, M.B.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, K.B.; Nou, I.S.; Chung, M.Y. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of zinc finger homeodomain (ZHD) family genes reveal likely roles in organ development and stress responses in tomato. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Tang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, C.; et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.M.; Noel, B.; Policriti, A.; Clepet, C.; Casagrande, A.; Choisne, N.; Aubourg, S.; Vitulo, N.; Jubin, C.; et al. The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 2007, 449, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vega, J.J.; Ayling, S.; Hegarty, M.; Kudrna, D.; Goicoechea, J.L.; Ergon, A.; Rognli, O.A.; Jones, C.; Swain, M.; Geurts, R.; et al. Red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) draft genome provides a platform for trait improvement. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F.; et al. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaul, S.; Koo, H.L.; Jenkins, J.; Rizzo, M.; Rooney, T.; Tallon, L.J.; Feldblyum, T.; Nierman, W.; Benito, M.-I.; Lin, X. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 2000, 408, 796–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmutz, J.; Cannon, S.B.; Schlueter, J.; Ma, J.; Mitros, T.; Nelson, W.; Hyten, D.L.; Song, Q.; Thelen, J.J.; Cheng, J.; et al. Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 2010, 463, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.H.; Ma, P.F.; Yang, G.Q.; Hu, J.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Xia, E.H.; Zhong, M.C.; Zhao, L.; Sun, G.L.; Xu, Y.X.; et al. Genome Sequences Provide Insights into the Reticulate Origin and Unique Traits of Woody Bamboos. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, Z.; Sun, W.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, C.; Chen, H. Genome-wide analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takata, N.; Taniguchi, T. Expression divergence of cellulose synthase (CesA) genes after a recent whole genome duplication event in Populus. Planta 2015, 241, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranik, M.; Myburg, A.A. Six new cellulose synthase genes from Eucalyptus are associated with primary and secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burton, R.A.; Shirley, N.J.; King, B.J.; Harvey, A.J.; Fincher, G.B. The CesA gene family of barley. Quantitative analysis of transcripts reveals two groups of co-expressed genes. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Tu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, B.; Cui, X.; Peng, L. Expression profiling and integrative analysis of the CESA/CSL superfamily in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conant, G.C.; Wolfe, K.H. Turning a hobby into a job: How duplicated genes find new functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yue, J.X.; Tian, D.; Chen, J.Q. Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2008, 280, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Landherr, L.L.; Frohlich, M.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Ma, H.; dePamphilis, C.W. Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: Evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J. 2007, 50, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worberg, A.; Quandt, D.; Barniske, A.-M.; Löhne, C.; Hilu, K.W.; Borsch, T. Phylogeny of basal eudicots: Insights from non-coding and rapidly evolving DNA. Org. Divers. Evol. 2007, 7, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Imtiaz, M.; Rehman, H.M.; Ali, M.A.; Baloch, F.S.; Atif, R.M.; Yang, S.H.; Chung, G. Characterization of Cellulose Synthase A (CESA) Gene Family in Eudicots. Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 248–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S.H. Evolution of Gene Duplication in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, I.; Law, R.; Kileeg, Z.; Stronghill, P.; Northey, J.G.B.; Strap, J.L.; Bonetta, D.T. Alleles Causing Resistance to Isoxaben and Flupoxam Highlight the Significance of Transmembrane Domains for CESA Protein Function. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, A. Genomic surveys and expression analysis of bZIP gene family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). Planta 2014, 239, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.W.; Penny, D. A very high fraction of unique intron positions in the intron-rich diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana indicates widespread intron gain. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.C.; Ko, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Bae, H.J.; Han, K.H. MYB46 directly regulates the gene expression of secondary wall-associated cellulose synthases in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 73, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, J.S.; Lachance, D.; Duval, I.; Nguyen, T.T.A.; Stewart, D.; Mackay, J.; Seguin, A. Functional Analysis of the PgCesA3 White Spruce Cellulose Synthase Gene Promoter in Secondary Xylem. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Sheng, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, L.; Hu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, F.; Hu, Z.; Diao, Y.; Jin, S. Differential expression patterns reveal the roles of cellulose synthase genes (CesAs) in primary and secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Miscanthus × giganteus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokshina, N.; Gorshkova, T.; Deyholos, M.K. Chitinase-like (CTL) and cellulose synthase (CESA) gene expression in gelatinous-type cellulosic walls of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) bast fibers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganguly, A.; Zhu, C.; Chen, W.; Dixit, R. FRA1 Kinesin Modulates the Lateral Stability of Cortical Microtubules through Cellulose Synthase-Microtubule Uncoupling Proteins. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2508–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.; Gill, T.; Zahoor, I.; Ahuja, P.S.; Sreenivasulu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.K. Ectopic expression of SOD and APX genes in Arabidopsis alters metabolic pools and genes related to secondary cell wall cellulose biosynthesis and improve salt tolerance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1985–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhen, Z.; Ge, Q.; Fan, S.; Liu, A.; Gong, W.; Li, J.; Gong, J.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the evolution and expression patterns of the cellulose synthase gene superfamily in Gossypium species. Gene 2018, 646, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Gene Number | Forward Primer Sequences | Reverse Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Cocit.F0728.1.v2.1 | CCTATATGGTATGGTTACAGTGGGA | GTGCAATAAGCAATCAGAGGGA |
| Cocit.A0286.1.v2.1 | CCAGGTTTATTTGGGAAGTGCT | GCCTTCTTGTGGTGCTGGTAA |
| Cocit.C1849.1.v2.1 | TATGACGCAGATGCCAAACAA | TAATCAACCGAAGGATAATCACAAC |
| Cocit.C0102.1.v2.1 | GATGCCTTCTTCCCTTCACAA | TCCACCCTCCCTCTTTCTTTT |
| Cocit.C0101.1.v2.1 | TGGTATGGTTACAAAGCAGGGA | GTAGGCGATGAGTGGTAAAGAGG |
| Cocit.G2461.1.v2.1 | GGATCAGTTTCCGAAGTGGTTT | CAGTATTTGCCGTCACAAGAGG |
| Cocit.H0683.1.v2.1 | TGTGGTTTCTGTCGCTTTTCAT | CGAGACTCCTCCAATGACCC |
| Cocit.D0255.1.v2.1 | CCGCTCTTTGGCAAAGTCTT | ACAATGGTCGGAGTCCTGTTCT |
| Cocit.J0893.1.v2.1 | GCCAGAACCGCACTCCTACT | TCAATCCTCACCCACAACAAAG |
| Cocit.L2008.1.v2.1 | AATACAGATGATTTGGAGCGTGAG | AAAGTTAAGGCGAGTGGACAGC |
| Cocit.L2008.2.v2.1 | GGGTCTCATCTCACCTGTTTGC | TTGGACGTGACCATGAAGTTTG |
| Cocit.I0213.1.v2.1 | GAAAGAAGCCATTCAAGTCATCAG | ATCCTCAGTCACCGAACCGTAT |
| Actin | TCAGGATAAGTCTTGGCGAGTG | TCCGTCCTTGTAGGCTCTGG |
| Gene Name | Accession Number | Protein (AA) | MW (kDa) | pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY | Loc | TMHs | Identity with AtCesA1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcCesA1 | Cocit.F0728.1.v2.1 | 1082 | 121.83 | 6.66 | 38.77 | 85.50 | −0.225 | plas | 6 | 87.47 |
| CcCesA2 | Cocit.A0286.1.v2.1 | 1045 | 117.91 | 7.41 | 37.21 | 81.89 | −0.238 | plas | 8 | 64.29 |
| CcCesA3 | Cocit.C1849.1.v2.1 | 1085 | 122.15 | 6.34 | 42.75 | 84.00 | −0.247 | plas | 6 | 87.19 |
| CcCesA4 | Cocit.C0102.1.v2.1 | 1040 | 117.81 | 6.18 | 41.60 | 82.39 | −0.218 | plas | 8 | 66.17 |
| CcCesA5 | Cocit.C0101.1.v2.1 | 1041 | 117.35 | 6.41 | 41.79 | 83.63 | −0.224 | plas | 6 | 62.00 |
| CcCesA6 | Cocit.G2461.1.v2.1 | 1080 | 121.33 | 6.61 | 38.52 | 85.81 | −0.198 | plas | 8 | 70.20 |
| CcCesA7 | Cocit.H0683.1.v2.1 | 1096 | 123.42 | 6.68 | 39.03 | 84.68 | −0.201 | plas | 8 | 67.46 |
| CcCesA8 | Cocit.D0255.1.v2.1 | 978 | 110.02 | 6.33 | 39.01 | 85.72 | −0.087 | plas | 6 | 63.43 |
| CcCesA9 | Cocit.J0893.1.v2.1 | 1079 | 121.05 | 7.00 | 41.02 | 85.26 | −0.184 | plas | 8 | 69.89 |
| CcCesA10.1 | Cocit.L2008.1.v2.1 | 1092 | 123.76 | 6.50 | 40.24 | 87.72 | −0.174 | plas | 8 | 64.50 |
| CcCesA10.2 | Cocit.L2008.2.v2.1 | 1021 | 115.46 | 6.38 | 41.29 | 88.38 | −0.169 | plas | 8 | 67.30 |
| CcCesA11 | Cocit.I0213.1.v2.1 | 1092 | 123.51 | 6.52 | 40.70 | 85.12 | −0.246 | plas | 8 | 64.65 |
| Gene | Alpha Helix (%) | Beta Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) | Extended Strand (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CcCesA1 | 31.89 | 4.53 | 47.78 | 15.80 |
| CcCesA2 | 32.44 | 4.88 | 47.65 | 14.93 |
| CcCesA3 | 32.26 | 4.61 | 47.47 | 15.67 |
| CcCesA4 | 33.46 | 5.00 | 45.77 | 15.77 |
| CcCesA5 | 32.56 | 5.00 | 47.07 | 15.37 |
| CcCesA6 | 31.57 | 4.35 | 49.54 | 14.54 |
| CcCesA7 | 31.57 | 6.20 | 44.71 | 17.52 |
| CcCesA8 | 33.54 | 3.89 | 48.06 | 14.52 |
| CcCesA9 | 31.70 | 4.36 | 49.77 | 14.18 |
| CcCesA10.1 | 32.14 | 5.04 | 47.53 | 15.29 |
| CcCesA10.2 | 33.69 | 3.72 | 46.23 | 16.36 |
| CcCesA11 | 31.68 | 4.03 | 49.73 | 14.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Huang, A.; He, W.; Ou, Y.; Lu, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, P.; Luo, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CesA Gene Family in Corymbia citriodora. Forests 2023, 14, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030618
Wang C, Huang A, He W, Ou Y, Lu W, Lin Y, Wang P, Luo J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CesA Gene Family in Corymbia citriodora. Forests. 2023; 14(3):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030618
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chubiao, Anying Huang, Wenliang He, Yuduan Ou, Wanhong Lu, Yan Lin, Peng Wang, and Jianzhong Luo. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CesA Gene Family in Corymbia citriodora" Forests 14, no. 3: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030618
APA StyleWang, C., Huang, A., He, W., Ou, Y., Lu, W., Lin, Y., Wang, P., & Luo, J. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CesA Gene Family in Corymbia citriodora. Forests, 14(3), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14030618







