Intensity Analysis to Communicate Detailed Detection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
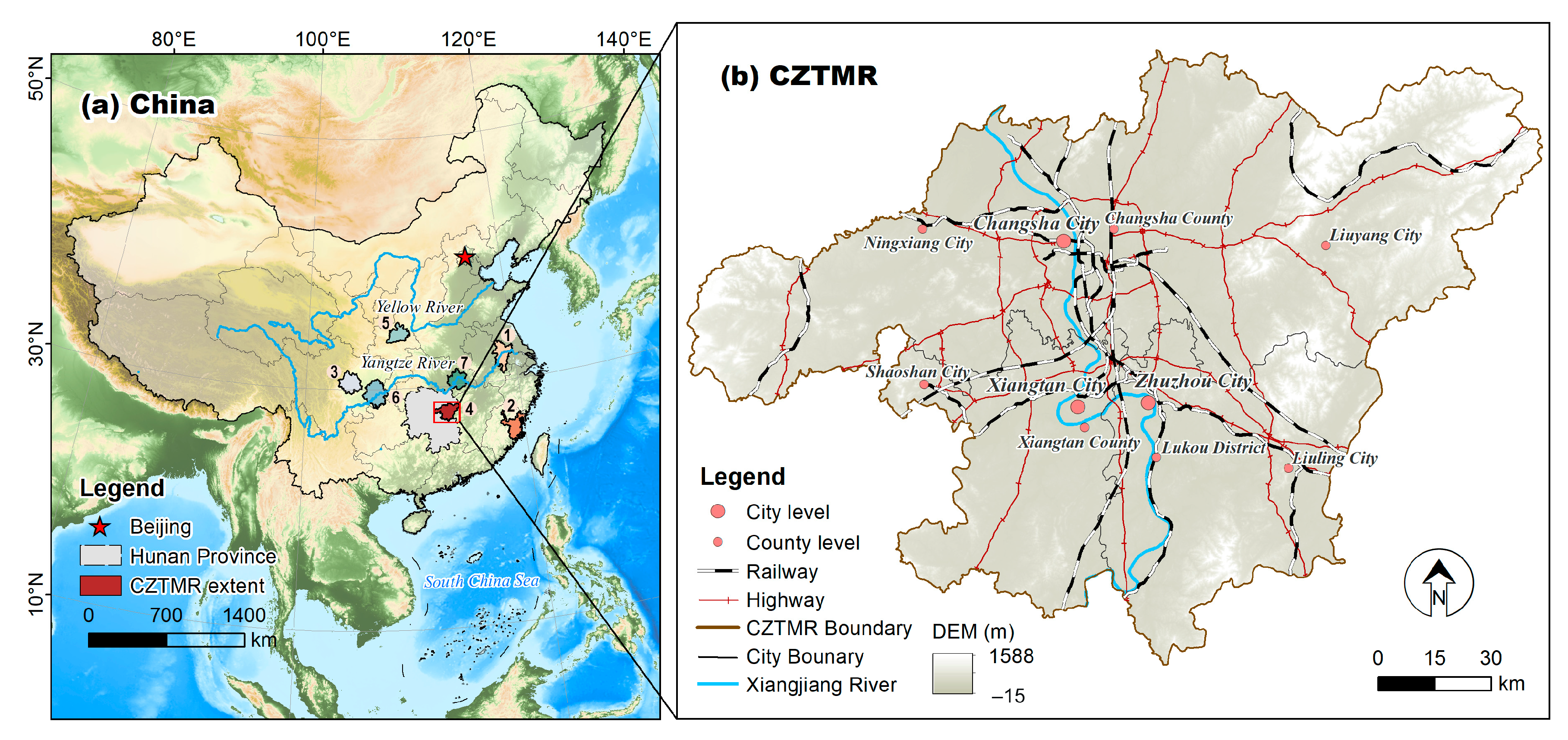
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Intensity Analysis
2.3.2. Transition Pattern
2.3.3. Spatial Mode of Landscape Expansion
2.3.4. Landscape Pattern Matrices
3. Results
3.1. LULC Structure Analysis
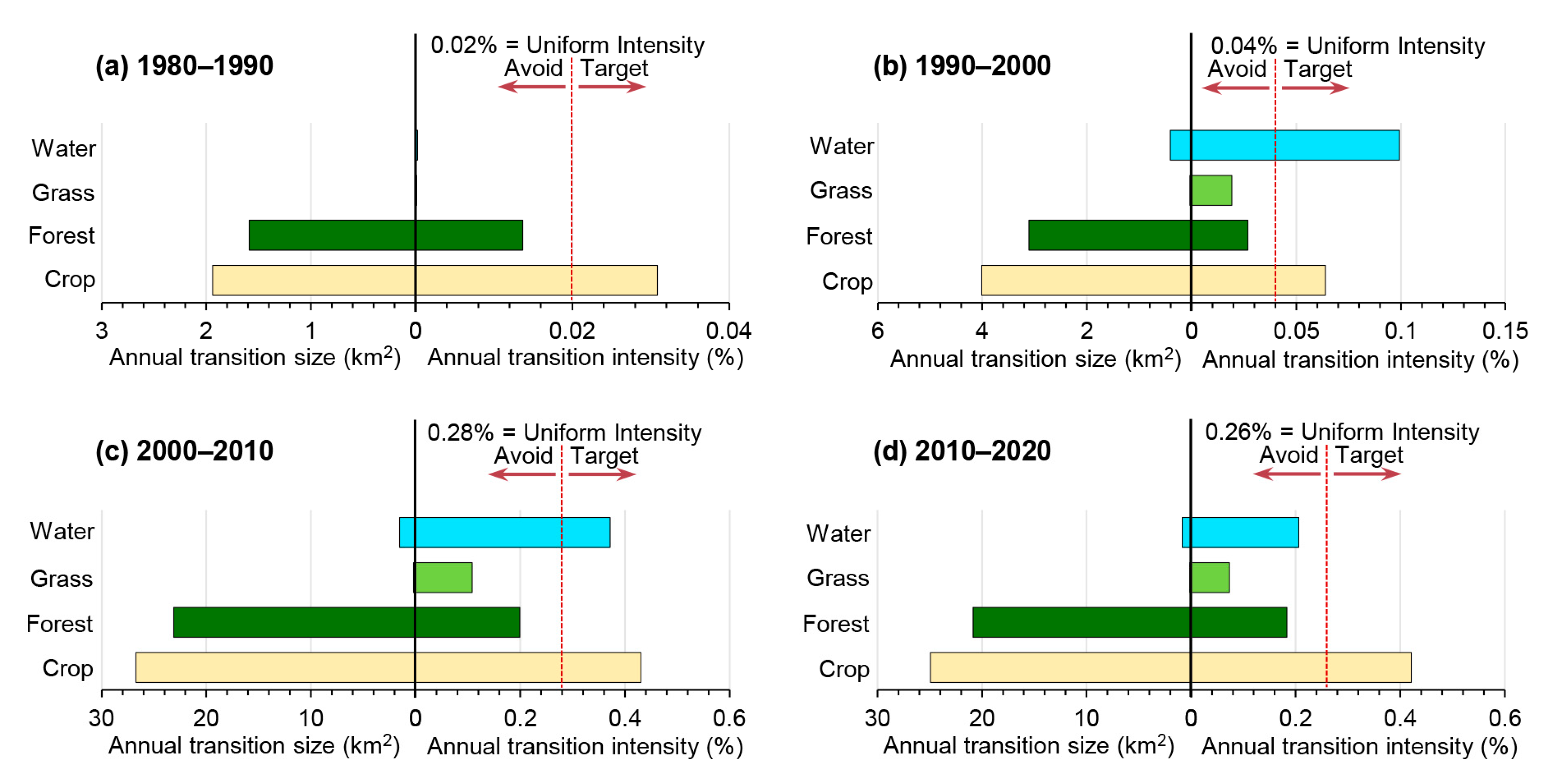
3.2. Detection of LULC Change Size and Intensity
3.2.1. Change Detection at Time Interval Level
3.2.2. Change Detection at Category Level
3.2.3. Change Detection at Transition Level
3.3. Dynamic Process of the Built Expansion
3.4. LULC Pattern Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Intensity Analysis Compared with Other Methods
- Containing information on the size and the intensity of a change rather than only evaluating the size of change;
- Distinguishing the losses and gains of land categories instead of focusing only on net change;
- Providing multiple levels of connectivity, allowing scientists to carry out any levels of land change analysis according to the needs of their study;
- Comparing and analyzing the overall change in LULC during different periods;
- Facilitating the comparison of land change patterns and processes across regions to help guide the design of regional land management policies.
4.2. Patterns and Processes of LULC Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winkler, K.; Fuchs, R.; Rounsevell, M.; Herold, M. Global land use changes are four times greater than previously estimated. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, K.C.; Satterthwaite, D. Interactions between urbanization and global environmental change. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2010, 2, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asselen, S.; Verburg, P.H. Land cover change or land-use intensification: Simulating land system change with a global-scale land change model. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3648–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; O’Neill, B.C. Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.; Wu, S.; et al. Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China during the early 21st century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Li, Q.; Wu, G.; et al. Assessing spatiotemporal variations and predicting changes in ecosystem service values in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tong, X. Dynamic land use change simulation using cellular automata with spatially nonstationary transition rules. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 678–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, B.; Lambin, E.F. Land-cover-change trajectories in southern Cameroon. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2000, 90, 467–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Shusas, E.; McEachern, M. Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Xie, Y.; Du, T.; Wang, X. Random and systematic change analysis in land use change at the category level—A case study on Mu Us area of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 145920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z. Dynamic Evolution of Land Use/Land Cover and Its Socioeconomic Driving Forces in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zeng, Y.; Koga, M.; Vejre, H. Variations in land surface temperature and cooling efficiency of green space in rapid urbanization: The case of Fuzhou city, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Rai, P.; Mohan, K. Prediction of land use changes based on land change modeler (LCM) using remote sensing: A case study of Muzaffarpur (Bihar), India. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2014, 64, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnood Motlagh, S.; Sadoddin, A.; Haghnegahdar, A.; Razavi, S.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Ghorbani, K. Analysis and prediction of land cover changes using the land change modeler (LCM) in a semiarid river basin, Iran. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3092–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemitzi, A. Predicting land cover changes using a CA Markov model under different shared socioeconomic pathways in Greece. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. Intensity analysis to unify measurements of size and stationarity of land changes by interval, category, and transition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Quan, B. Intensity Characteristics and Multi-Scenario Projection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Hengyang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Use of Intensity Analysis to link patterns with processes of land change from 1986 to 2007 in a coastal watershed of southeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, J.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Tu, Z. Comparison of Intensity Analysis and the land use dynamic degrees to measure land changes outside versus inside the coastal zone of Longhai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, R.; Du, H.; Na, L.; Shan, Y.; He, H.S.; Wu, Z.; Zong, S.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal changes in the Aeolian desertification of Hulunbuir Grassland and its driving factors in China during 1980–2015. Catena 2019, 182, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Minaei, M.; Feng, Y.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. GlobeLand30 maps show four times larger gross than net land change from 2000 to 2010 in Asia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondwe, M.F.; Cho, M.A.; Chirwa, P.W.; Geldenhuys, C.J. Land use land cover change and the comparative impact of co-management and government-management on the forest cover in Malawi (1999–2018). J. Land Use Sci. 2020, 14, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Huang, J.; Nitivattananon, V. Enhanced Intensity Analysis to Quantify Categorical Change and to Identify Suspicious Land Transitions: A Case Study of Nanchang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. Quantifying the Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Yellow River Basin while Accounting for Data Errors Based on GlobeLand30 Maps. Land 2021, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldwaik, S.Z.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. Map errors that could account for deviations from a uniform intensity of land change. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1717–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Gao, Y.; Giner, N.; Kohyama, T.; Osaki, M.; Hirose, K. Design and Interpretation of Intensity Analysis Illustrated by Land Change in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land 2013, 2, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Intensity and spatial pattern of urban land changes in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Lei, J. Monitoring desertification in Mongolia based on Landsat images and Google Earth Engine from 1990 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinis, G.; Koutsias, N.; Arianoutsou, M. Monitoring land use/land cover transformations from 1945 to 2007 in two peri-urban mountainous areas of Athens metropolitan area, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, B.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Song, H. Intensity Analysis to communicate land change during three time intervals in two regions of Quanzhou City, China. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alo, C.A.; Pontius, R.G., Jr. Identifying Systematic Land-Cover Transitions Using Remote Sensing and GIS: The Fate of Forests inside and outside Protected Areas of Southwestern Ghana. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, Z.; Teixeira, H.; Marques, J.C. Systematic processes of land use/land cover change to identify relevant driving forces: Implications on water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, D.; Gao, G.; Lü, Y.; Xiao, F.; Fu, B. Detailed land use transition quantification matters for smart land management in drylands: An in-depth analysis in Northwest China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, R.; Odeh, I.O.A.; Pontius, R.G. Analysis of twenty years of categorical land transitions in the Lower Hunter of New South Wales, Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 135, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Linking Land Cover Change with Landscape Pattern Dynamics Induced by Damming in a Small Watershed. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Quan, B.; Deng, Z. Effects of Land Use Changes on Ecosystem Service Value in Xiangjiang River Basin, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.S.; Kanniah, K.D. Land use and land cover change and its impact on river morphology in Johor River Basin, Malaysia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; He, Q.; Zhu, X. Simulation of Impacts of Urban Agglomeration Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services Value under Multi-Scenarios: Case Study in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modelling the potential impacts of urban ecosystem changes on carbon storage under different scenarios by linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; He, B.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Y. Simulation of urban agglomeration ecosystem spatial distributions under different scenarios: A case study of the Changsha–Zhuzhou–Xiangtan urban agglomeration. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lei, X.; Jia, K.; Wu, Y. Simulating urban land use change by incorporating an autologistic regression model into a CLUE-S model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, X. Exploring Smart Growth Boundaries of Urban Agglomeration with Land Use Spatial Optimization: A Case Study of Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan City Group, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, X. Path analysis and mediating effects of influencing factors of land use carbon emissions in Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 188, 122268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunan Province Bureau of Statistics. Hunan Province Statistical Yearbook 2021; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Kuang, W.; Zhang, S.; Du, G.; Yan, C.; Wu, S.; Li, R.; Lu, D.; Pan, T.; Ning, J.; Guo, C. Remotely sensed mapping and analysis of spatio-temporal patterns of land use change across China in 2015–2020. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Du, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr. Metrics That Make a Difference; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, B.; Ren, H.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Liu, P. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns concerning land change in Changsha, China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 14, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, S.; Ai, B. A new landscape index for quantifying urban expansion using multi-temporal remotely sensed data. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. The spatial granularity effect, changing landscape patterns, and suitable landscape metrics in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, 1995–2015. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fan, Z.; Gao, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Cover and Their Driving Forces in the Yellow River Basin since 1990. Land 2022, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, R.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y. Dynamic characteristics and responses of ecosystem services under land use/land cover change scenarios in the Huangshui River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiong, P.; Li, C.; Quan, B. Spatial Pattern Simulation of Land Use Based on FLUS Model under Ecological Protection: A Case Study of Hengyang City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmy, M.W.A.; Gessler, P.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Salem, B.B. Land use/land cover change detection and prediction in the north-western coastal desert of Egypt using Markov-CA. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abijith, D.; Saravanan, S. Assessment of land use and land cover change detection and prediction using remote sensing and CA Markov in the northern coastal districts of Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 86055–86067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, X.; Xie, X. Dynamic change of land use/land cover patterns and driving factors of Nansihu Lake Basin in Shandong Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr. Component intensities to relate difference by category with difference overall. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 77, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, M. Analysis of the Evolution of Land-Use Types in the Qilian Mountains from 1980 to 2020. Land 2023, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Huang, J.; Jiang, W.; Khallaghi, S.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Quan, B.; Ye, S. Rules to write mathematics to clarify metrics such as the land use dynamic degrees. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, F.O.; Pontius, R.G., Jr.; Braimoh, A.K. Land change dynamics: Insights from Intensity Analysis applied to an African emerging city. J. Spat. Sci. 2017, 62, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mwangi, H.; Lariu, P.; Julich, S.; Patil, S.; McDonald, M.; Feger, K.-H. Characterizing the Intensity and Dynamics of Land-Use Change in the Mara River Basin, East Africa. Forests 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekumah, B.; Armah, F.A.; Afrifa, E.K.A.; Aheto, D.W.; Odoi, J.O.; Afitiri, A.-R. Assessing land use and land cover change in coastal urban wetlands of international importance in Ghana using Intensity Analysis. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 28, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Systematicity and Stability Analysis of Land Use Change—Taking Jinan, China, as an Example. Land 2022, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, G. Impact of LUCC on ecosystem services values in the Yili River Basin based on an intensity analysis model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fahad, S.; Li, W.; Lashari, A.H.; Islam, A.; Khattak, L.H.; Rasool, U. Evaluation of land use and land cover Spatio-temporal change during rapid Urban sprawl from Lahore, Pakistan. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Bao, G.; Rong, A.; Huang, X.; Bao, Y.; Bao, Y. Comparison of the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Use Changes in Four Municipalities of China Based on Intensity Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Glendinning, A.; Xu, Y. Land-use changes and land policies evolution in China’s urbanization processes. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Hu, Q.; van Vliet, J.; Verburg, P.H.; Wu, W. GlobeLand30 shows little cropland area loss but greater fragmentation in China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xie, B.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Xiao, J.; Liu, C. Impacts of landscape pattern on ecological network evolution in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meimei, W.; Zizhen, J.; Tengbiao, L.; Yongchun, Y.; Zhuo, J. Analysis on absolute conflict and relative conflict of land use in Xining metropolitan area under different scenarios in 2030 by PLUS and PFCI. Cities 2023, 137, 104314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Quan, B. Intensity Analysis to Communicate Detailed Detection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Region, China. Forests 2023, 14, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050939
Deng Z, Quan B. Intensity Analysis to Communicate Detailed Detection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Region, China. Forests. 2023; 14(5):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050939
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhiwei, and Bin Quan. 2023. "Intensity Analysis to Communicate Detailed Detection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Region, China" Forests 14, no. 5: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050939
APA StyleDeng, Z., & Quan, B. (2023). Intensity Analysis to Communicate Detailed Detection of Land Use and Land Cover Change in Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Region, China. Forests, 14(5), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050939






