Soil Quality Evaluation and Dominant Factor Analysis of Economic Forest in Loess Area of Northern Shaanxi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Plot Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Indicators
2.4. Soil Index Evaluation Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Differences between Soil Quality Evaluation Indicators under Different Vegetation Types and Different Land Preparation Methods
3.2. Evaluation of Soil Quality
3.2.1. Characteristics of Soil Indicator Components Based on the Minimum Data Set
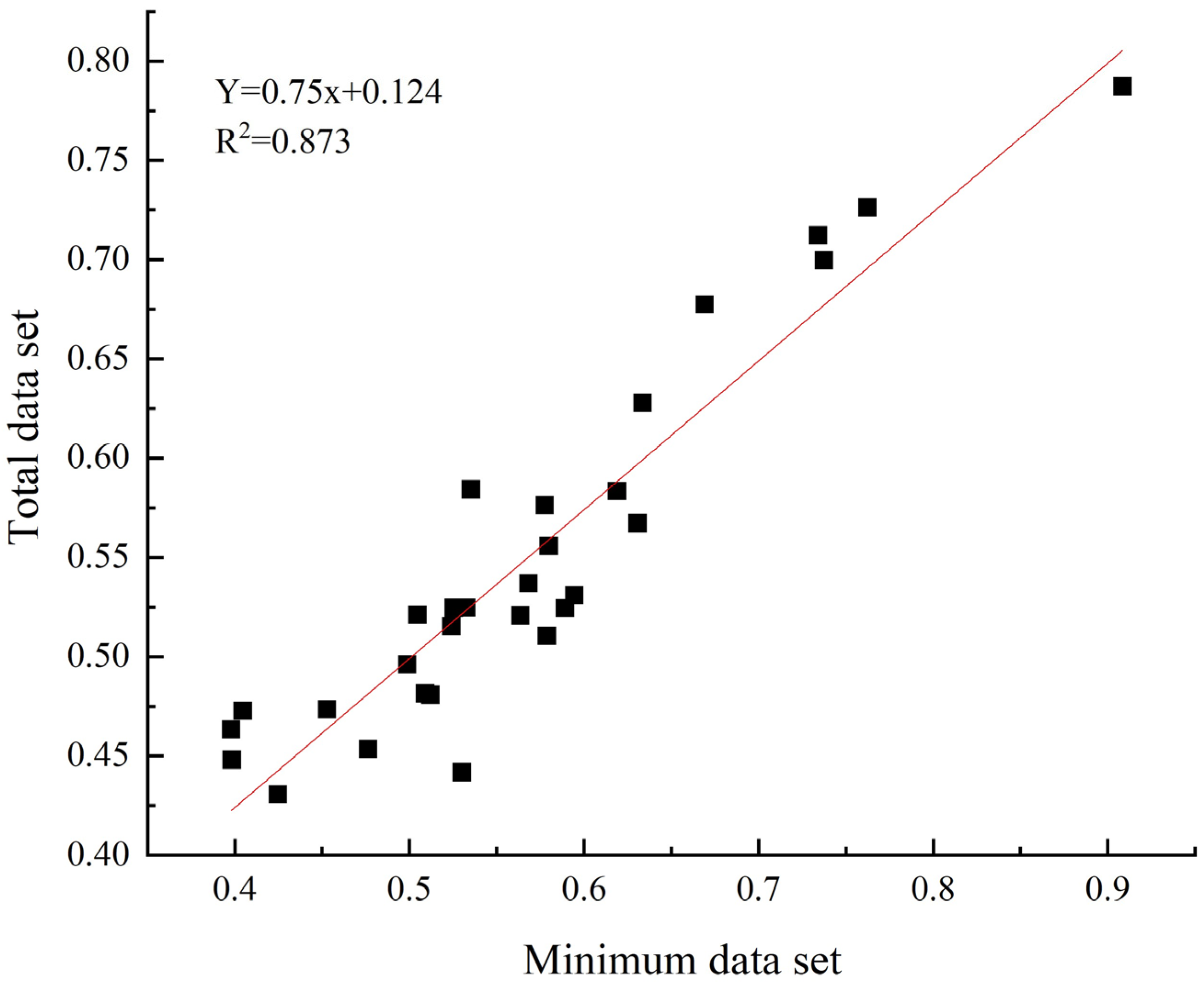
3.2.2. Soil Quality Assessment Based on a Minimum Data Set
3.3. Effects of Dominant Factors on Soil Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Difference Analysis of Soil’s Physical and Chemical Properties of Different Vegetation Types
4.2. Evaluation of Soil Quality Based on the Minimum Data Set
4.3. Effects of Dominant Factors on Soil Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Fang, K.; Wei, B.; Qin, S.; Feng, X.; Hu, T.; Ji, C.; Yang, Y. Soil carbon persistence governed by plant input and mineral protection at regional and global scales. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T. Protecting Soil Health of Cultivated Land to Promote High-Quality Development of Agriculture in China. Soils 2021, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C. Prevention and control of soil erosion in slope-type economic forestland. China Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 11, 40–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers: A review. In Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 785–811. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, G. Causes, consequences and control of wind erosion in Sahelian Africa: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, S. Research on ecological construction and green industry development planning of Yangtze River Economic Belt: A case study of Wushan county. For. Constr. 2022, 04, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and assessing soil quality. Defin. Soil Qual. Sustain. Environ. 1994, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Wang, Z. Soil quality evaluation for different forest plantation of sandy land in Yinchuan Plain, Ningxia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Yue, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of soil quality on gully region of loess plateau based on principal component analysis. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2010, 28, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sefati, Z.; Khalilimoghadam, B.; Nadian, H. Assessing urban soil quality by improving the method for soil environmental quality evaluation in a saline groundwater area of Iran. Catena 2019, 173, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valani, G.P.; Vezzani, F.M.; Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.M.V. Soil quality: Evaluation of on-farm assessments in relation to analytical index. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of Soil Quality for Different Types of Land Use Based on Minimum Dataset in the Typical Desert Steppe in Ningxia, China. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 7506189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Jin, J.; Ding, G.; Liu, X. Soil quality index evaluation model in responses to six-year fertilization practices in Mollisols. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indexing of alkaline soils under different land uses in northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, J.P.; Creamer, R.E.; Cluzeau, D.; Debeljak, M.; Gatti, F.; Henriksen, C.B.; Kuzmanovski, V.; Menta, C.; Pérès, G.; Picaud, C. Modeling of soil functions for assessing soil quality: Soil biodiversity and habitat provisioning. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, Z.; Selvalakshmi, S.; Xia, S.; Yang, X. Identification of indicators: Monitoring the impacts of rubber plantations on soil quality in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Song, M.; Liang, J. Soil quality assessment of reclaimed land in the urban-rural fringe. Catena 2023, 220, 106692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, C.; Jiménez, M.N.; Fernández-Ondoño, E.; Navarro, F.B. Effects of Afforestation on Plant Diversity and Soil Quality in Semiarid SE Spain. Forests 2021, 12, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Huang, B.; Darilek, J.L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Evaluation of soil quality in major grain-producing region of the North China Plain: Integrating minimum data set and established critical limits. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Liu, F.; Xue, S. Soil biochemical index-based assessment of the effect of drought stress on the rhizosphere soil quality in three typical grass species in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2982–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Application of soil quality index to determine the effects of different vegetation types on soil quality in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, L.C.Z.; Queiroz, H.M.; Cherubin, M.R.; Ferreira, T.O. Applying the Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF) to Assess Mangrove Soil Quality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, R.; Luo, W. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil quality in degraded karst landscapes of southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesfin, D.; Assefa, E.; Simane, B. Soil quality index under different land-use types: The case of Choke Mountain agroecosystems, upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 103, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelRahman, M.A.; Saleh, A.M.; Arafat, S.M. Assessment of land suitability using a soil-indicator-based approach in a geomatics environment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Qiang, F. Soil quality evaluation of various microtopography types at different restoration modes in the loess area of Northern Shaanxi. Catena 2021, 207, 105633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Chen, A.; Fang, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, G. Effects of vegetation restoration types on soil quality in Yuanmou dry-hot valley, China. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; He, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Yin, H. Evaluation on Ecological Benefits of the Jujube Economic Forest along the Yellow River in Loess Plateau. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Dang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, P.; Cao, X.-S.; Fan, L.-X.; Li, L. Analysis of water security risk of cash forest expansion in the Loess Plateau in terms of water footprint:A case study of apple planting. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 2750–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Ren, F. Spatial Distribution and Characteristics of Economic Forest Resources in Shaanxi Province. For. Inventory Plan. 2019, 44, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, T.; Gao, R.; Qiang, F.; Yang, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Ai, N. Coupling Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Soil Water Storage in Abandoned Economic Forests in the Loess Hilly Areas. Forests 2023, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, X.; Bu, R.; Doughty, R.; Hu, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, B. Application of the space-for-time substitution method in validating long-term biomass predictions of a forest landscape model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 94, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Soil Science; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Soil Physical Properties Determination Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; pp. 2, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Or, D. 2.4 Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, S.L.; Zhi-Yang, O.U.; Shen, W.H.; Hou, Y.R.; Huang, X.R.; Zheng, W.; Academy, G.F. Edaphic characteristics of different regeneration patterns in karst mountainous areas of Guangxi. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2016, 36, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, G.; Ai, J.; Sun, Q.; Hou, L.; Dong, Y. Soil quality assessment under different forest types in the Mount Tai, central Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Shi, D.; Lou, Y.B.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Jiang, N. Evaluation of the quality of cultivated-layer soil based on different degrees of erosion in sloping farmland with purple soil in China. CATENA 2021, 198, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, B.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, D. Difference Feature of Planted Vegetation Biomass and Litter Biomass for Three Plantations and Their Relationship with Soil Nutrients in Lvliang Mountainous Region. Bull. Bot. Res. 2016, 36, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Yawei, H.; Ruoxiu, S.; Mingshuang, S.; Zhengle, S.; Chang, L.; Qintao, X.; Junting, L.; Jianjun, Z. Effects of land use types on the stoichiometric characteristics of soil C:N:P and the physical and chemical properties of soil in western Shanxi loess region. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Ai, N.; Liu, C.; Zong, Q.; Hao, B.; Liu, J. Soil quality evaluation of main vegetation types after conversion of farmland to forest in Wuqi County. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2021, 35, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Daryanto, S.; Wang, L. Land preparation and vegetation type jointly determine soil conditions after long-term land stabilization measures in a typical hilly catchment, Loess Plateau of China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, M.D.; Van Rees, K.C. Mechanical site preparation impacts on soil properties and vegetation communities in the Northwest Territories. Can. J. For. Res. 2002, 32, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Cerdà, A.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y. Combining land preparation and vegetation restoration for optimal soil eco-hydrological services in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Daryanto, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, T. Global synthesis of the classifications, distributions, benefits and issues of terracing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Querejeta, J.I.; Rolda’n, A.; Albaladejo, J.; Castillo, V. Soil physical properties and moisture content affected by site preparation in the afforestation of a semiarid rangeland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, J.; Gao, W. Study on the benefits of slope runoff control afforestation in the loess gully area of Longdong. Soil Water Conserv. China 2018, 1, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenli, Y.; Pingzong, Z.; Jingkun, Y. Effect of Horizontal Planting Camellia oleifera on Soil Physicochemical Properties in Red Soil Slope Land. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. Soil desiccation for Loess soils on natural and regrown areas. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisaka, M.O.; Shisanya, C.; Cournac, L.; Manlay, J.R.; Gitari, H.; Muriuki, J. Integrating no-tillage with agroforestry augments soil quality indicators in kenya’s dry-land agroecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 227, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanng, P.; Jia, L.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Mu, X.; Ding, W. Improvement of soil quality by Chinese dwarf cherry cultivation in the Loess Plateau steep hill region. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2017, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Vasu, D.; Tiwari, G.; Sahoo, S.; Dash, B.; Jangir, A.; Sharma, R.P.; Naitam, R.; Tiwary, P.; Karthikeyan, K.; Chandran, P. A minimum data set of soil morphological properties for quantifying soil quality in coastal agroecosystems. Catena 2021, 198, 105042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Ai, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Soil C:N:P Stoichiometric Characteristics and Soil Quality Evaluation under Different Restoration Modes in the Loess Region of Northern Shaanxi Province. Forests 2022, 13, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiollahi, K.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R.; Moradian, S. Assessment of soil quality indices for salt-affected agricultural land in Kurdistan Province, Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 83, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Dong, C.; Huo-Yan, W.; Jian-Min, Z.; Lu, X.; Bai-Shu, Z.; Yong-Cun, Z.; Xiao-Qin, C. Minimum data set for assessing soil quality in farmland of northeast China. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 564–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xi, M.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J. Soil quality assessment of coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta of China based on the minimum data set. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Xin, Z. Effects of different ecological restoration models on deep soil organic carbon in loess remnant gully area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Han, Q.S.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Z.S.; Shangguan, Z.P. Above-ground and below-ground ecosystem biomass accumulation and carbon sequestration with Caragana korshinskii Kom plantation development. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Qiang, F.-F.; Liu, G.-Q.; Liu, C.-H.; Ai, N. Distribution characteristics of soil microbial communities and their responses to environmental factors in the sea buckthorn forest in the water-wind erosion crisscross region. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1098952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Kongsurakan, P.; Hatano, R. Assessing soil organic carbon, soil nutrients and soil erodibility under terraced paddy fields and upland rice in Northern Thailand. Agronomy 2022, 12, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Daryanto, S. Quantifying the effects of precipitation, vegetation, and land preparation techniques on runoff and soil erosion in a Loess watershed of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Liu, L.; Small, G.E.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X. The effects of land management patterns on soil carbon sequestration and C:N:P stoichiometry in sloping croplands in southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 320, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brar, S.K.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, M. Soil Quality Assessment in Diversified Long-Term Experimentation Under Different Agriculturally Based Cropping Systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wu, G.-L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. Fine roots determine soil infiltration potential than soil water content in semi-arid grassland soils. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Van Mensvoort, M. Factors affecting soil quality changes in the North China Plain: A case study of Quzhou County. Agric. Syst. 2006, 91, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.-F.; Qi, Z.-W.; Chen, J.-L.; Cui, W.-H.; Lin, W.; Gao, Z.-Q. Dynamic of Soil Porosity and Water Content under Tillage during Summer Fallow in the Dryland Wheat Fields of the Loess Plateau in China. Land 2023, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geroy, I.; Gribb, M.; Marshall, H.-P.; Chandler, D.; Benner, S.G.; McNamara, J.P. Aspect influences on soil water retention and storage. Hydrol. Processes 2011, 25, 3836–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo Montoro, J.; Alvarez Rogel, J.; Querejeta, J.; Díaz, E.; Castillo, V. Three hydro-seeding revegetation techniques for soil erosion control on anthropic steep slopes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2000, 11, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Feng, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Feng, T.; Chen, D. The effects of terracing and vegetation on soil moisture retention in a dry hilly catchment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ai, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Zong, Q.; Liu, J.; Hao, B. Soil quality characteristics of forests and grasslands returned from farmland and their responses to precipitation in the Loess Region of Northern Shaanxi, China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Sun, W.; Wu, P. Soil water effects of agroforestry in rainfed jujube (Ziziphus jujube Mill.) orchards on loess hillslopes in Northwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Number | Plot Type | Soil Type | Altitude (m) | Slope Gradient (°) | Vegetation Coverage (%) | Land Preparation Method | Tending Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JL | Loessal soil | 836 | 0 | 40 | Level bench | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| 2 | JU | Loessal soil | 860 | 25 | 43 | Undisturbed slope | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| 3 | AL | Loessal soil | 900 | 0 | 50 | Level bench | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| 4 | AU | Loessal soil | 903 | 28 | 52 | Undisturbed slope | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| 5 | GL | Loessal soil | 905 | 0 | 82 | Level bench | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| 6 | GU | Loessal soil | 904 | 30 | 80 | Undisturbed slope | Rainfed/no fertilization |
| Soil Indicator | Jujube Tree | Apple Tree | Grassland | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | |
| BD | 1.2 ± 0.09 Aa | 1.21 ± 0.08 Aa | 1.16 ± 0.07 Aa | 1.21 ± 0.04 Aa | 1.16 ± 0.04 Aa | 1.19 ± 0.04 Aa |
| SWC | 39.57 ± 3.56 Aa | 39.57 ± 1.56 Aa | 40.35 ± 1.58 Aa | 39.19 ± 1.34 Aa | 39.6 ± 0.99 Aa | 40.41 ± 1.9 Aa |
| CWHC | 33.66 ± 1.1 Bb | 33.59 ± 1.52 Bb | 35.64 ± 1.42 Aa | 33.8 ± 0.93 ABab | 34.06 ± 1.4 ABab | 34.91 ± 0.26 ABab |
| TCP | 45.9 ± 1.63 Aa | 46.98 ± 0.5 Aa | 46.87 ± 1.61 Aa | 46.83 ± 0.8 Aa | 46.01 ± 1.82 Aa | 46.5 ± 1.14 Aa |
| pH | 8.46 ± 0.01 Aa | 8.46 ± 0.03 Aa | 8.46 ± 0.06 Aa | 8.49 ± 0.07 Aa | 8.51 ± 0.01 Aa | 8.47 ± 0.1 Aa |
| EC | 72.56 ± 8.36 Bb | 69.2 ± 3.22 Bb | 73.48 ± 1.18 Ab | 74.69 ± 3.42 Bb | 92.06 ± 16.44 Aa | 73.64 ± 2.64 Bb |
| AN | 0.13 ± 0.06 Aa | 0.1 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.15 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.13 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.16 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.13 ± 0.1 Aa |
| AP | 30.44 ± 8.11 Aa | 27.1 ± 11.84 Aa | 19.5 ± 1.31 Aa | 20.28 ± 16.24 Aa | 14.29 ± 8.73 Aa | 15.5 ± 14.23 Aa |
| AK | 28.7 ± 12.16 Aa | 22.08 ± 12.08 Aa | 26.68 ± 11.12 Aa | 23.36 ± 10.48 Aa | 25.62 ± 6.48 Aa | 21.56 ± 11.91 Aa |
| SOC | 7.36 ± 0.81 Aa | 7.27 ± 0.84 Aa | 4.08 ± 1.27 Ab | 3.21 ± 1.41 BCbc | 2.56 ± 1.04 BCbc | 2.39 ± 0.54 Cc |
| NWC | 12.25 ± 1.08 Aa | 11.94 ± 1.5 aBb | 10.58 ± 0.86 BCbc | 10.16 ± 1.21 Cc | 8.37 ± 0.86 Dd | 5.84 ± 0.25 Ee |
| NCP | 6.06 ± 2.61 Aa | 6.3 ± 1.37 Aa | 5.35 ± 1.55 Aa | 5.96 ± 1.15 Aa | 6.41 ± 1.1 Aa | 6.35 ± 1.71 Aa |
| CP | 39.84 ± 1.46 Aa | 40.68 ± 1.47 Aa | 41.48 ± 3.02 Aa | 40.91 ± 1.2 Aa | 39.6 ± 2.33 Aa | 40.15 ± 0.61 Aa |
| TP | 543.88 ± 21.21 ABab | 404.18 ± 29.37 Cc | 523.24 ± 32.19 ABab | 562.33 ± 76.92 Aa | 510.16 ± 112.13 ABab | 451.9 ± 22.26 BCbc |
| Clay | 4.13 ± 0.37 CDcd | 4.69 ± 0.09 ABab | 4.42 ± 0.32 BCbc | 4.29 ± 0.14 CDcd | 3.94 ± 0.22 Dd | 4.79 ± 0.14 Aa |
| Silt | 74.29 ± 1.11 Bb | 79.12 ± 1.26 Aa | 75.82 ± 0.78 Bb | 75.08 ± 2.04 Bb | 75.65 ± 0.93 Bb | 76.21 ± 0.94 Bb |
| Sand | 21.57 ± 1.35 Aa | 16.18 ± 1.2 Cc | 19.76 ± 1.1 Bb | 16.03 ± 0.98 Cc | 20.4 ± 0.96 ABab | 18.99 ± 0.91 Bb |
| Soil Indicator | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | Classing | Norm | Communality | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD | −0.923 | −0.190 | 0.042 | 0.074 | −0.121 | 1 | 1.715 | 0.823 | 0.181 |
| SWC | 0.894 | −0.005 | 0.011 | 0.361 | 0.106 | 1 | 1.660 | 0.919 | 0.202 |
| NCP | 0.870 | −0.135 | 0.196 | −0.085 | 0.258 | 1 | 1.616 | ||
| Silt | −0.083 | −0.896 | −0.038 | −0.004 | −0.250 | 2 | 1.545 | 0.590 | 0.130 |
| Sand | 0.115 | 0.773 | 0.030 | −0.027 | 0.021 | 2 | 1.333 | ||
| Clay | 0.210 | −0.769 | −0.020 | 0.108 | 0.318 | 2 | 1.326 | ||
| TP | 0.032 | 0.716 | 0.087 | −0.267 | 0.175 | 2 | 1.235 | ||
| SOC | 0.055 | −0.100 | 0.927 | −0.016 | 0.115 | 3 | 1.529 | 0.929 | 0.205 |
| NWC | −0.070 | 0.042 | 0.872 | 0.053 | 0.110 | 3 | 1.438 | ||
| AP | 0.180 | 0.252 | 0.782 | −0.079 | 0.114 | 3 | 1.289 | ||
| TCP | 0.125 | −0.210 | 0.031 | 0.844 | 0.039 | 4 | 1.284 | 0.702 | 0.155 |
| CWHC | 0.478 | 0.145 | −0.371 | 0.684 | −0.125 | 4 | 1.040 | ||
| CP | −0.663 | −0.033 | −0.148 | 0.676 | −0.194 | 4 | 1.028 | ||
| EC | 0.301 | 0.377 | −0.293 | −0.610 | −0.081 | 4 | 0.928 | ||
| AN | 0.228 | 0.189 | −0.057 | −0.214 | 0.826 | 5 | 1.209 | 0.576 | 0.127 |
| AK | 0.334 | 0.276 | 0.372 | −0.017 | 0.737 | 5 | 1.079 | ||
| pH | −0.029 | 0.128 | −0.222 | −0.143 | −0.730 | 5 | 1.069 | ||
| Eigenvalue variance (%) | 3.452 | 2.972 | 2.719 | 2.313 | 2.145 | ||||
| contribution rate (%) | 20.306 | 17.483 | 15.993 | 13.606 | 12.615 | ||||
| Accumulative contribution rate (%) | 20.306 | 37.790 | 53.782 | 67.388 | 80.003 |
| Vegetation Type | Jujube Tree | Apple Tree | Grassland | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | Level Bench | Undisturbed Slope | |
| SQI-MDS | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, T.; Qiang, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Ai, N. Soil Quality Evaluation and Dominant Factor Analysis of Economic Forest in Loess Area of Northern Shaanxi. Forests 2023, 14, 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061179
Xiang T, Qiang F, Liu G, Liu C, Ai N. Soil Quality Evaluation and Dominant Factor Analysis of Economic Forest in Loess Area of Northern Shaanxi. Forests. 2023; 14(6):1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061179
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Ting, Fangfang Qiang, Guangquan Liu, Changhai Liu, and Ning Ai. 2023. "Soil Quality Evaluation and Dominant Factor Analysis of Economic Forest in Loess Area of Northern Shaanxi" Forests 14, no. 6: 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061179
APA StyleXiang, T., Qiang, F., Liu, G., Liu, C., & Ai, N. (2023). Soil Quality Evaluation and Dominant Factor Analysis of Economic Forest in Loess Area of Northern Shaanxi. Forests, 14(6), 1179. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14061179





