Sound Absorbing Properties of Selected Green Material—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
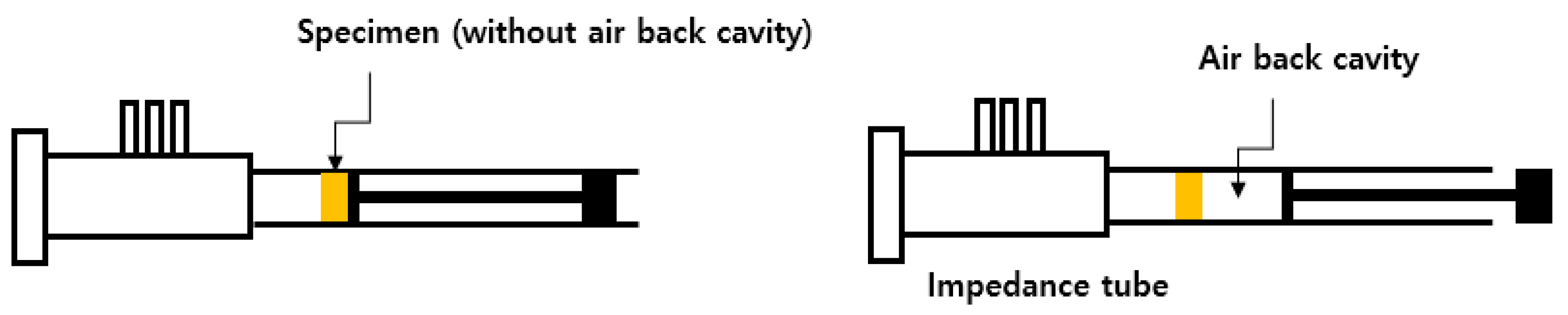
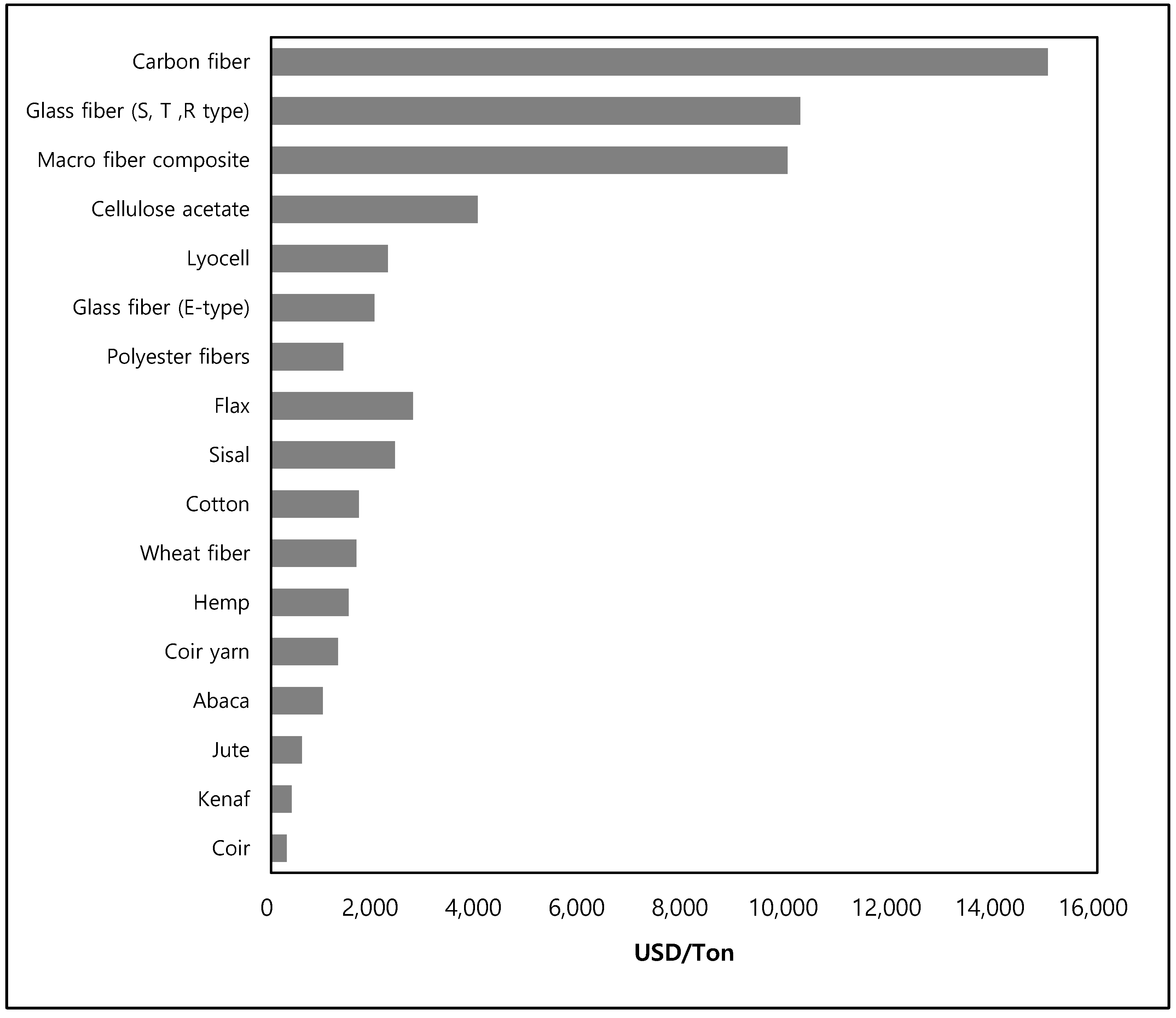
2. Sound Absorbing Green Materials
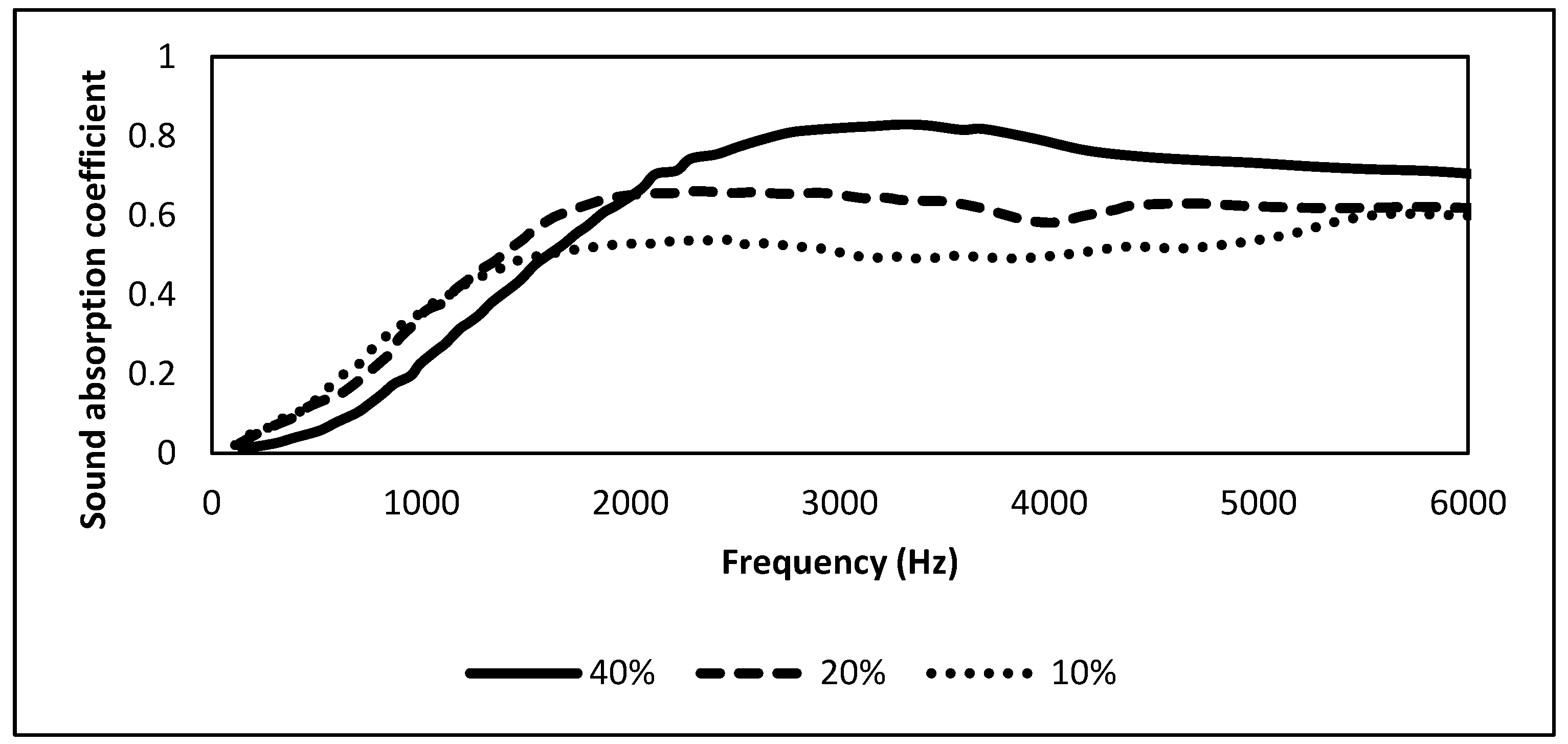
2.1. Coconut Fiber
2.2. Kenaf Fiber
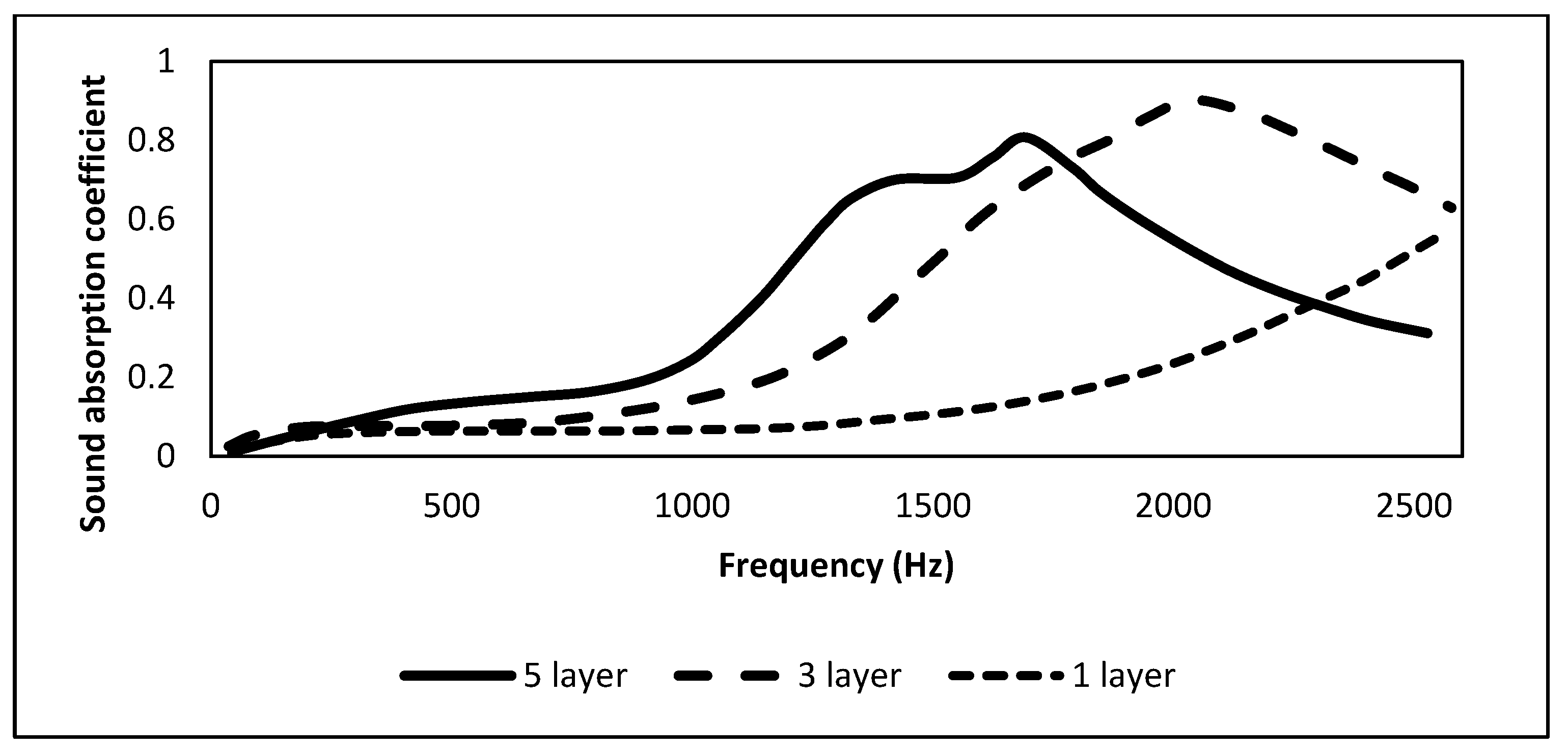
2.3. Rice Husks
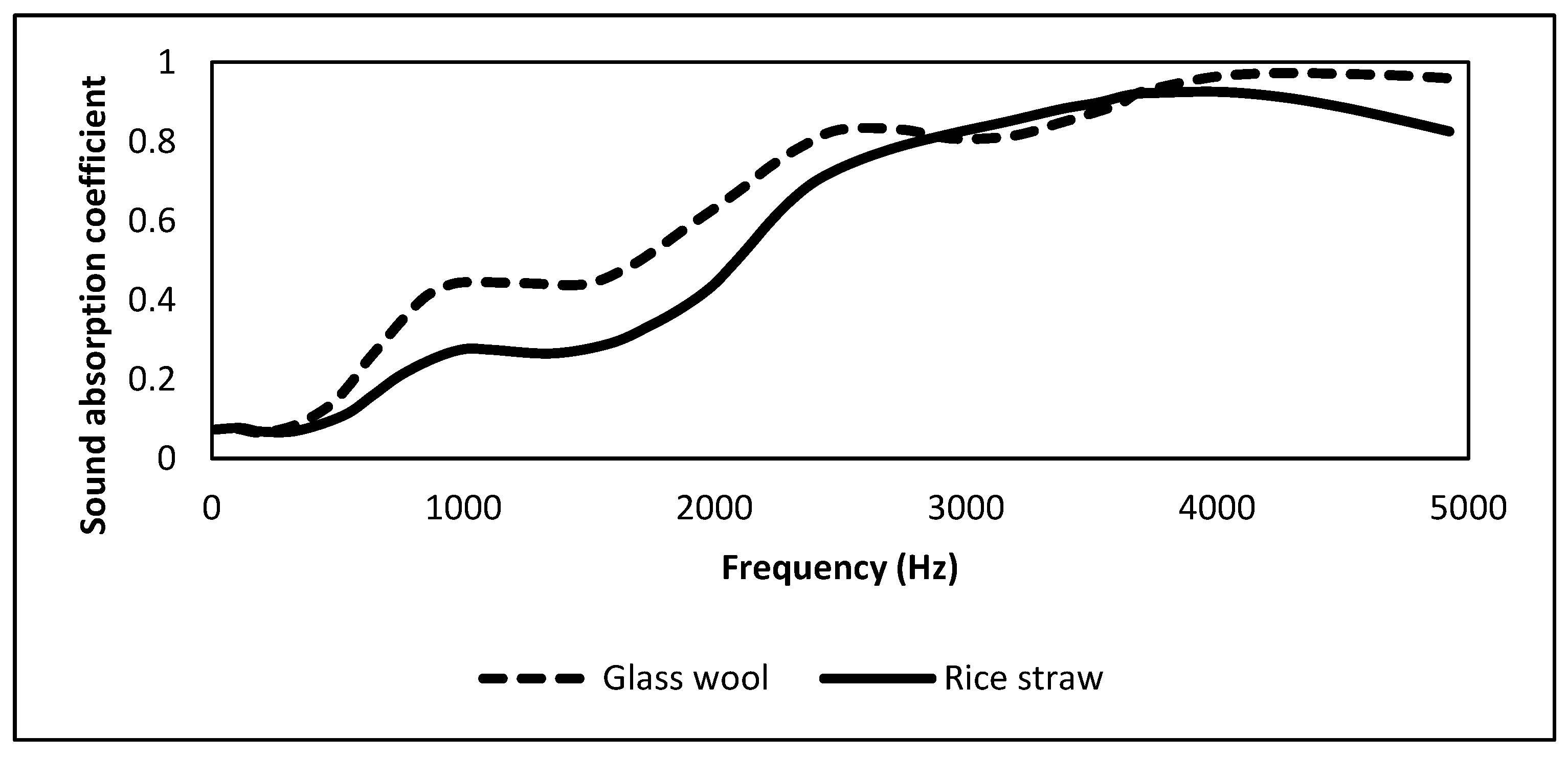
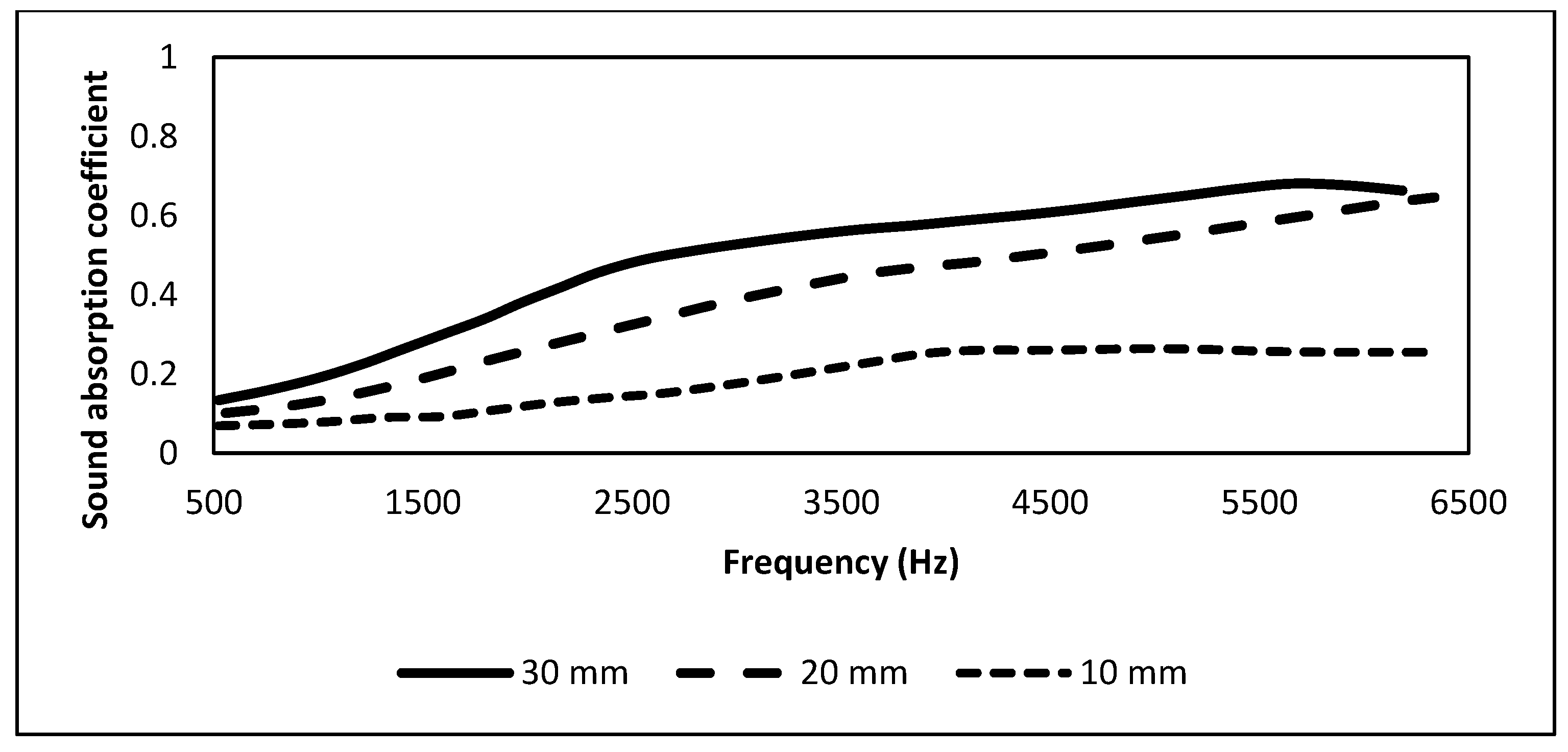
2.4. Rice Straw
2.5. Hanji (Korean Traditional Paper)
2.6. Tea-Leaf Fiber Waste
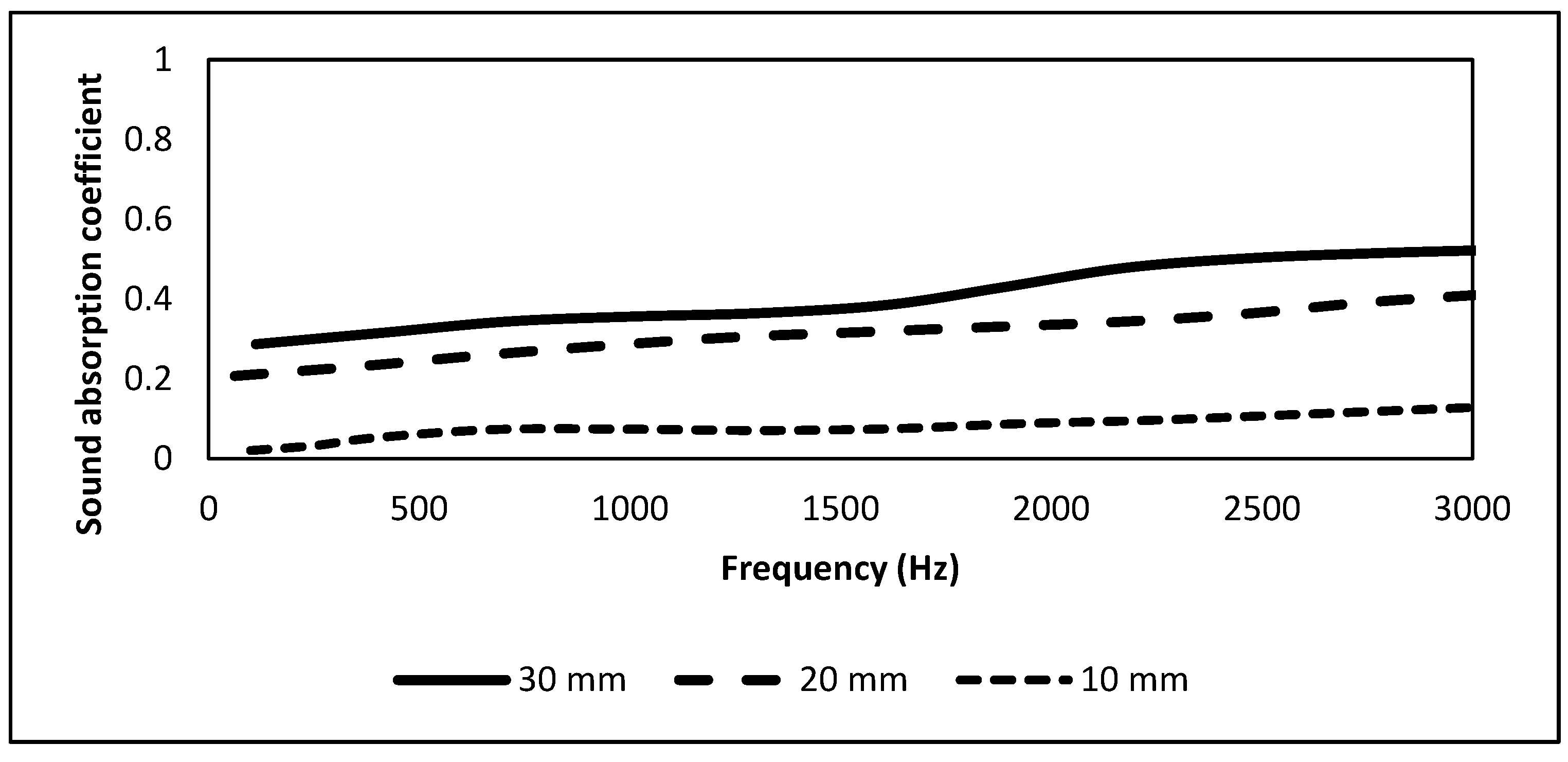
2.7. Mandarin Peel
2.8. Pineapple Leaf Fiber
2.9. Corn Husk
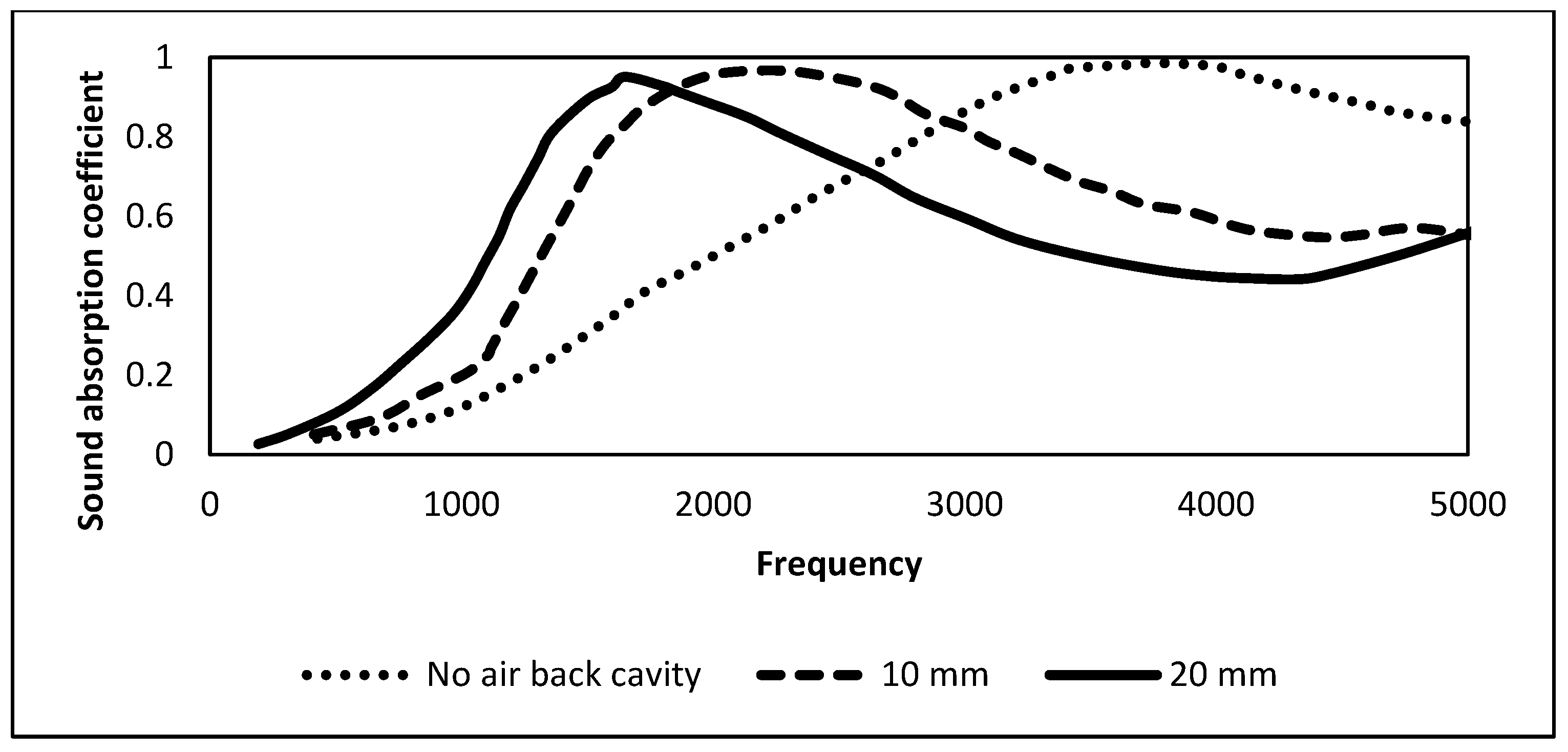
2.10. Peanut Shell
2.11. Sugar Palm Trunk Fibers
2.12. Yucca gloriosa Fiber
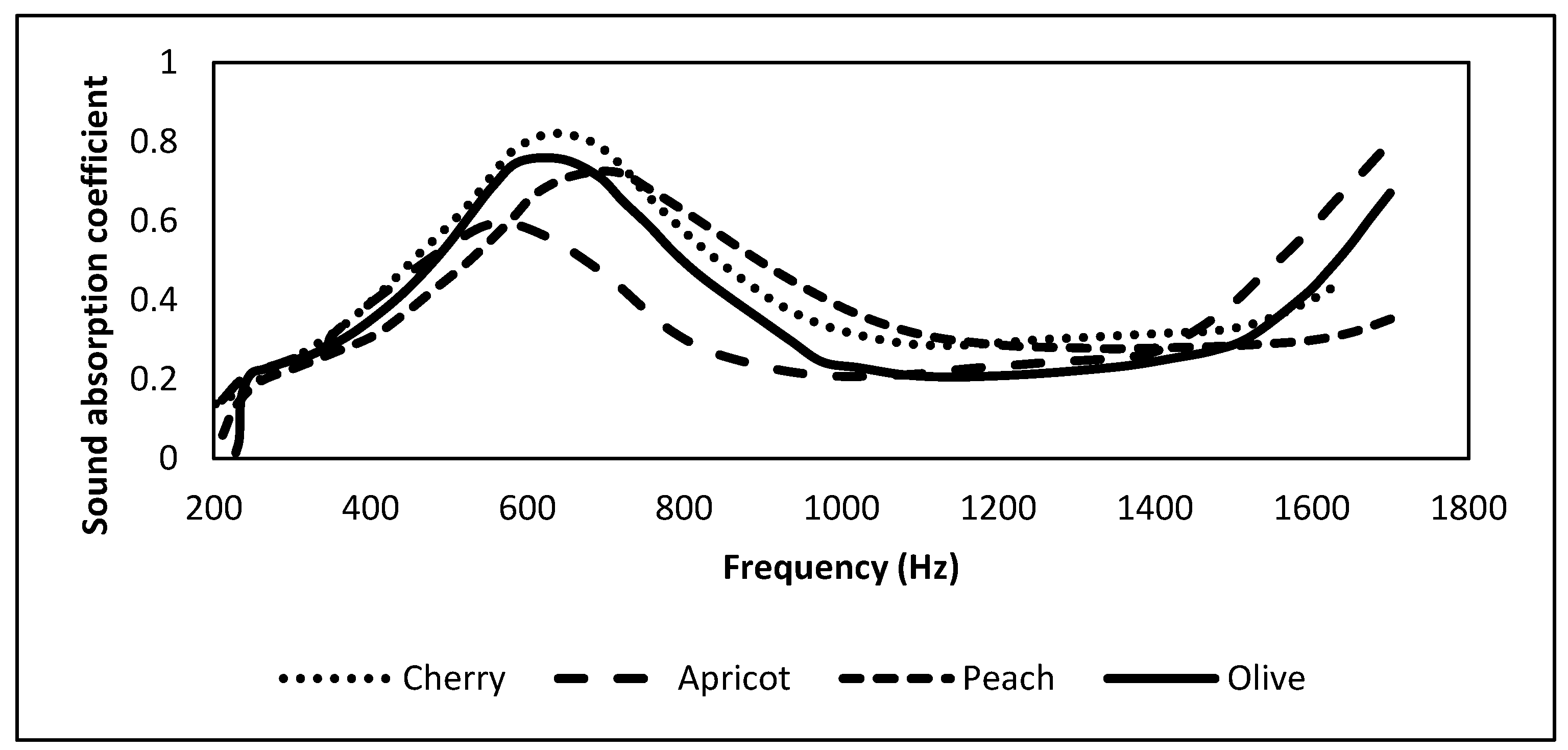
2.13. Fruit Stone Wastes (Cherry, Apricot, Peach, Olive)
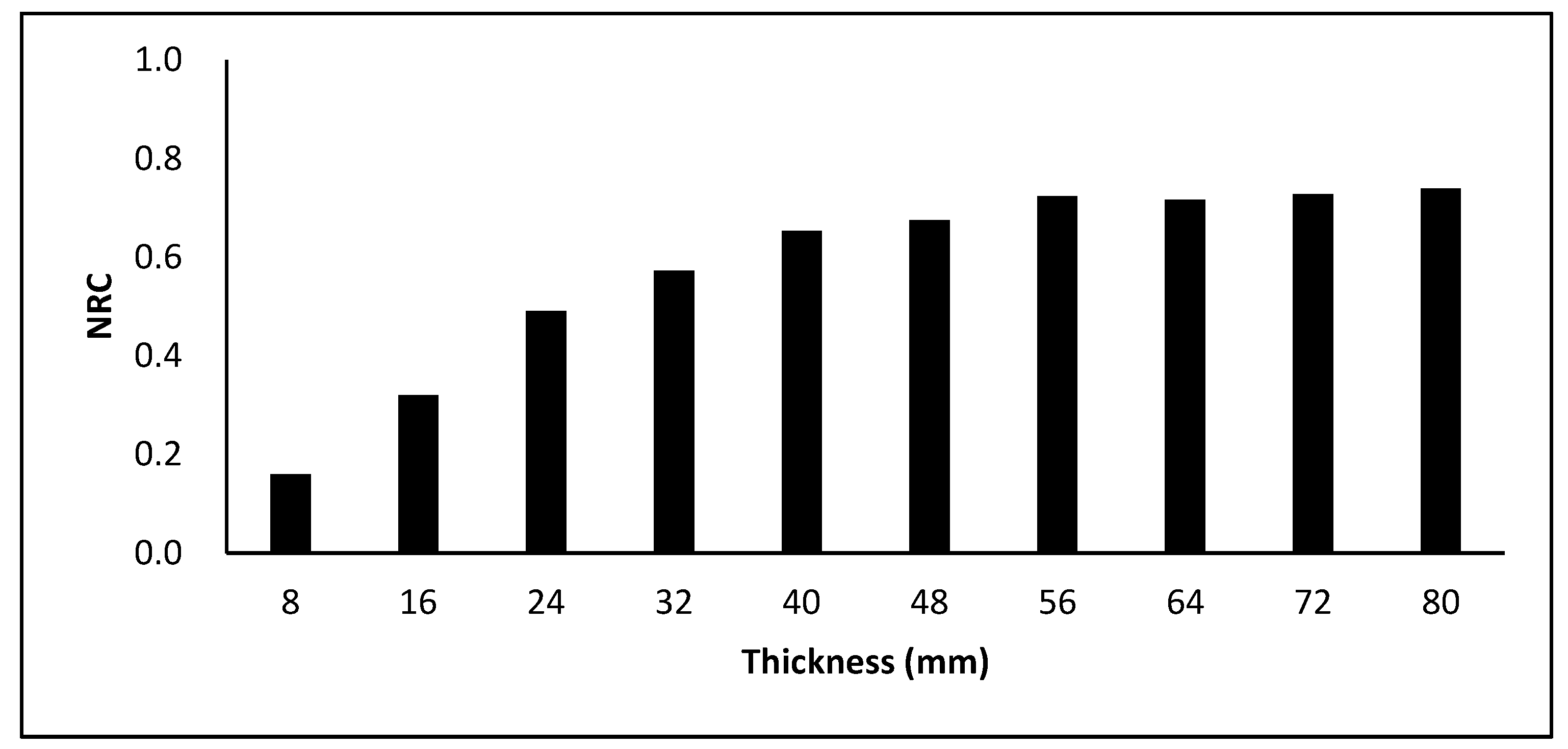
2.14. Wood Bark
2.15. Nettle Fibers
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zwolak, A.; Sarzyńska, M.; Szpyrka, E.; Stawarczyk, K. Sources of soil pollution by heavy metals and their accumulation in vegetables: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, A.K. Researches in water pollution: A review. Int. Res. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 118–142. [Google Scholar]
- Grubisic, M.; van Grunsven, R.H.; Kyba, C.C.; Manfrin, A.; Hölker, F. Insect declines and agroecosystems: Does light pollution matter? Ann. Appl. Biol. 2018, 173, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Tao, S.; Wang, X.; He, K. A review of air pollution impact on subjective well-being: Survey versus visual psychophysics. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, H.J.; Syed, H.S.; Pandya, M.J.; Gajera, Y.M. Noise Pollution & Human Health: A Review. Indoor Built Environ. 2017, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Nie, S.; Ding, H.; Hou, F.F. Environmental pollution and kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Kim, B.-J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. Recent advances in the sound insulation properties of bio-based materials. BioResources 2014, 9, 1764–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdan, N.I.; Zainulabidin, M.H.; Kassim, A.S.M. A Review on The Development of Panel and Membrane Sound Absorbers. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2021, 13, 60–74. [Google Scholar]
- Egab, L.; Wang, X.; Fard, M. Acoustical characterisation of porous sound absorbing materials: A review. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2014, 10, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.V.; Zha, X. Micro-perforated structures as sound absorbers—A review and outlook. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2006, 92, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.P.; Crocker, M.J. Recent trends in porous sound-absorbing materials. Sound Vib. 2010, 44, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, U.; Iannace, G. Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption applications. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, E.M.; Ismail, L.H.; Abdul Kadir, A. A review on physical factors influencing absorption performance offibrous sound absorption material from natural fibers. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar]
- Zulkifli, R.; Nor, M.M.; Tahir, M.M.; Ismail, A.; Nuawi, M. Acoustic properties of multi-layer coir fibres sound absorption panel. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 8, 3709–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metintas, S.; Ak, G.; Metintas, M. A review of the cohorts with environmental and occupational mineral fiber exposure. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2019, 74, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojola, W.H.; Moran, J.B. Commentary: Exposure Limits for Man-Made Mineral Fibers. Position of the Building and Construction Trades Department, AFL-CIO. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1992, 7, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carel, R.; Olsson, A.C.; Zaridze, D.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Rudnai, P.; Lissowska, J.; Fabianova, E.; Cassidy, A.; Mates, D.; Bencko, V. Occupational exposure to asbestos and man-made vitreous fibres and risk of lung cancer: A multicentre case-control study in Europe. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007, 64, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.S. Occupational cancer update. Korean J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 23, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątkowska, B.; Szeszenia-Dąbrowska, N. Spirometry: A predictor of lung cancer among asbestos workers. Inhal. Toxicol. 2017, 29, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; Carbone, I.; Nagy, J. Green building materials: A review of state of the art studies of innovative materials. J. Green Build. 2017, 12, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Y.; Putra, A.; Efendy, H.; Farid, W.; Ayob, M. Investigation on sound absorption coefficient of natural paddy fibers. Int. J. Renew. Energy Resour. 2013, 3, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jayamani, E.; Hamdan, S. Sound absorption coefficients natural fibre reinforced composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 701, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A. Natural fiber textile reinforced bio-based composites: Mechanical properties, creep, and environmental impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.-J.; Sohn, J.-Y. Variations of Indoor Air Quality by Application of Environmentally Friendly and Absorbent Materials. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2008, 24, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X. Indoor Microbial Volatile Organic Compound (MVOC) Levels and Associations with Respiratory Health, Sick Building Syndrome (SBS), and Allergy. In Environmental Mycology in Public Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.; Park, J.H.; Wi, S.; Yang, S.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S. Latent heat storage biocomposites of phase change material-biochar as feasible eco-friendly building materials. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, J.-O.; Kim, K.-W.; Yang, K.-S.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, M.-J. Physical properties of cellulose sound absorbers produced using recycled paper. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Fatima, S. Noise control using green materials. Sound Vib. 2015, 49, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mamtaz, H.; Fouladi, M.H.; Al-Atabi, M.; Narayana Namasivayam, S. Acoustic absorption of natural fiber composites. J. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5836107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salva, J.K.C., Jr.; Yu, B.A.L. Coconut Coir Based Sound Absorber Board for Noise Pollution Control. APEC Youth Sci. J. 2017, 9, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, C.; Bonet Aracil, M.; Gisbert-Payá, J.; Liuzzi, S.; Stefanizzi, P.; Zamorano Cantó, M.; Martellotta, F. Composite eco-friendly sound absorbing materials made of recycled textile waste and biopolymers. Materials 2019, 12, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santhanam, S.; Temesgen, S.; Atalie, D.; Ashagre, G. Recycling of cotton and polyester fibers to produce nonwoven fabric for functional sound absorption material. J. Nat. Fibers 2019, 16, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.H.; Luu, T.P.; Thai, Q.B.; Le, D.K.; Chau, N.D.Q.; Nguyen, S.T.; Le, P.K.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Heat and sound insulation applications of pineapple aerogels from pineapple waste. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.H.; Ghassem, M.; Ayub, M.; Jailani, M.; Nor, M. Implementation of coir fiber as acoustic absorber material. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2011, 42, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, J.; Stern, T.; Schoggl, J.; Ree, R.; Corato, U.; Bari, I.; Bell, G.; Stichnothe, H. Natural Fibers and Fiber-Based Materials in Biorefineries: Status Report 2018; IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peças, P.; Carvalho, H.; Salman, H.; Leite, M. Natural fibre composites and their applications: A review. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalauni, K.; Pawar, S. A review on the taxonomy, factors associated with sound absorption and theoretical modeling of porous sound absorbing materials. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1795–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, M.; Levi, E.; Cuerva, E.; Pardo-Bosch, F.; Zabaleta, A.G.; Pujadas, P. Sound absorbing and insulating low-cost panels from end-of-life household materials for the development of vulnerable contexts in circular economy perspective. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.M.; Cascone, S.; Vitale, M. Building insulating materials from agricultural by-products: A review. In Sustainability in Energy and Buildings; Littlewood, J., Howlett, R., Capozzoli, A., Jain, L., Eds.; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, E.M.; Dettendorfer, A.; Kain, G.; Barbu, M.C.; Réh, R.; Krišťák, Ľ. Sound-absorption coefficient of bark-based insulation panels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahani, F.; Soltani, P.; Zarrebini, M. The analysis of acoustical characteristics and sound absorption coefficient of woven fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 875–882. [Google Scholar]
- ISO11654; Acoustics—Sound Absorbers for Use in Buildings—Rating of Sound Absorption. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S. Sound absorption performance of noise barrier according to single number rating methods. Trans. Korean Soc. Noise Vib. Eng. 2017, 27, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W. Investigation on the Malysian Duabanga Moluccana cross section as sound absorbing functional materials. Wood Res. 2022, 67, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.; Muftakhidinov, B.; Winchen, T.; Jedrzejewski-Szmek, Z. Engauge Digitizer Software. Available online: https://markummitchell.github.io/engauge-digitizer/ (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Nor, M.J.M.; Jamaludin, N.; Tamiri, F.M. A preliminary study of sound absorption using multi-layer coconut coir fibers. Electron. J. Tech. Acoust. 2004, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Panyakaew, S.; Fotios, S. New thermal insulation boards made from coconut husk and bagasse. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozli, Z.; Zulkarnain, Z. Noise control using coconut coir fiber sound absorber with porous layer backing and perforated panel. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S. Peanut Shells as an Environmentally Beneficial Sound-Absorbing Material. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, R.; Hanana, M.; Mzid, R.; Hamrouni, L.; Khouja, M.l.; Salhi Hanachi, A. Hibiscus cannabinus L.—Kenaf: A review paper. J. Nat. Fibers 2017, 14, 466–484. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Hakeem, K.; Paridah, M.; Khalina, A.; Alothman, O. Potential of bioenergy production from industrial kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) based on Malaysian perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, H.; Omar, M.; Mazuki, A.M.; Safiee, S.; Ishak, Z.M.; Bakar, A.A. Kenaf fiber reinforced composites: A review. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.; Putra, A.; Nor, M.; Yaakob, M. Sound absorption performance of natural kenaf fibres. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 130, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, L.; Ghazali, M.I.; Mahzan, S.; Zaidi, A.A. Sound absorption of Arenga pinnata natural fiber. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 67, 804–806. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, T.; Tsujiuchi, N.; Adachi, A. The development of sound absorbing materials using natural bamboo fibers. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2002, 59, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, S.N.H.; Abdul Razak, N.A.; Abdul Rashid, A.H.; Yahya, M.N.B.; Zamri Tan, N.Z.; Shaari, M.F.; Mahmood, S.; Marsi, N.; Mohamad Isa, H.M. Development of Kenaf Nonwoven as Automotive Noise Absorption. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2019, 892, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Yang, J.E.; Chung, L. Sensory characteristics of rice confections by descriptive analysis. J. Korean Soc. Food Cult. 2016, 31, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- António, J.; Tadeu, A.; Marques, B.; Almeida, J.A.; Pinto, V. Application of rice husk in the development of new composite boards. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, T. Rice husk, Rice husk ash and their applications. In Rice Bran and Rice Bran Oil; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 207–246. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiaoping, C. Rice consumption in China: Can China change rice consumption from quantity to quality. In Rice Is Life: Scientific Perspectives for the 21st Century; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2005; pp. 497–499. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.; Cho, H.; Yeo, Y. Rice biotechnology and current development. J. Korean Soc. Int. Agric. 2016, 1, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-H.; Hong, S.-G. Feasibility of Korean Rice Husk Ash as Admixture for High Strength Concrete: Particle Size Distribution, Chemical Composition and Absorption Capacity Depending on Calcination Temperature and Milling Process. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2017, 18, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Chabannes, M.; Bénézet, J.-C.; Clerc, L.; Garcia-Diaz, E. Use of raw rice husk as natural aggregate in a lightweight insulating concrete: An innovative application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, T. Recycling of raw rice husk to manufacture magnesium oxysulfate cement based lightweight building materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, C.; Belloni, E.; Lascaro, E.; Merli, F.; Ricciardi, P. Rice husk panels for building applications: Thermal, acoustic and environmental characterization and comparison with other innovative recycled waste materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzan, S.; Ahmad Zaidi, A.M.; Ghazali, M.I.; Yahya, M.N.; Ismail, M. Investigation on sound absorption of rice-husk reinforced composite. In Proceedings of the MUCEET 2009, Malaysian Technical Universities Conference on Engineering and Technology, Kuantan, Malaysia, 20–22 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Ren, L.; Yu, H.; Galland, M.A.; Ichchou, M. Acoustic characteristics parameters of polyurethane/rice husk composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, B.; Tadeu, A.; António, J.; Almeida, J.; de Brito, J. Mechanical, thermal and acoustic behaviour of polymer-based composite materials produced with rice husk and expanded cork by-products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRRI. Rice Straw Management. Available online: https://www.irri.org/rice-straw-management (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- USDA. Rice Straw Market in Japan; JA2020-0078; USDA Foreign Agricultural Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- KOSIS. Statistics on Rice Straw Production in Korea. Available online: https://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1ET0032 (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Romasanta, R.; Sander, B.; Gaihre, Y.; Alberto, M.; Gummert, M.; Quilty, J.; Nguyen, V.; Castalone, A.; Balingbing, C.; Sandro, J. How does rice straw burning compare with other straw management practices in terms of on-field CH4 and N2O emissions? A comparative field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 239, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Z.; Ashour, T.; Khalil, M.; Bahnasawy, A.; Ali, S.; Hollands, J.; Korjenic, A. Rice Straw and Flax Fiber Particleboards as a Product of Agricultural Waste: An Evaluation of Technical Properties. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sander, B.O.; Quilty, J.; Balingbing, C.; Castalone, A.G.; Romasanta, R.; Alberto, M.C.R.; Sandro, J.M.; Jamieson, C.; Gummert, M. An assessment of irrigated rice production energy efficiency and environmental footprint with in-field and off-field rice straw management practices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16887. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, J.-Y.; Kang, C.-W. Possibility of using waste tire composites reinforced with rice straw as construction materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Lv, C.; Chen, M.; Zhou, X.; Dai, Z.; Shen, D. Development and performance evaluation of a new thermal insulation material from rice straw using high frequency hot-pressing. Energy Build. 2015, 87, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez-Garcia, C.C.; Garcia-Ortuño, T.; Ferrandez-Garcia, M.T.; Ferrandez-Villena, M.; García, C.E.F. Fire-resistance, physical, and mechanical characterization of binderless rice straw particleboards. BioResources 2017, 12, 8539–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, P.; Wu, Y. Construction of compatible interface of straw/magnesia lightweight materials by alkali treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-W.; Jang, E.-S.; Jang, S.-S.; Kang, H.-Y. Comparison of transfer function method and reverberation room method in measuring the sound absorption coefficient of rice straw particle mat. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Kim, H.-J. Rice straw–wood particle composite for sound absorbing wooden construction materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H. A study on the present situation of Hanji costume design and production. J. Korean Soc. Knit Des. 2007, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, Y.B.; Kim, K.H.; Lim, H.A. A study on the properties of Jumchi Hanji for application as shroud materials. J. Korean Soc. Cloth. Text. 2014, 38, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lim, J. The experimental study on the efficiency of ventilation of Korean paper (hanji). Korean J. Air-Cond. Refrig. Eng. 2004, 16, 482–489. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, H. A Study on the performance of controlling indoor humidity and air quality of the traditional Korean paper (Hanji) as building materials. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2007, 23, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.Y.; Lee, S.G. A study on coarse Hanji yarn manufacturing and properties of the Hanji fabric. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W.; Kang, H.-Y.; Jang, S.-S. Sound Absorption Property of Traditional Korean Natural Wallpaper (Hanji). J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, N.; Kim, M. Evaluation on the sound absorption of mulberry paper (Hanji) backed by an air cavity and porous material. J. Korean Soc. Living Environ. Syst. 2008, 15, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.-H.; Kim, K.-J.; Park, S.-B.; Eom, T.-J. Comparison of the functional properties of Hanji depending on the different manufacturing process. J. Korea Tech. Assoc. Pulp Pap. Ind. 2009, 41, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Rahman, N.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Abdul Rahman, N. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from tea leaf waste fibers. Polymers 2017, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ersoy, S.; Küçük, H. Investigation of industrial tea-leaf-fibre waste material for its sound absorption properties. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-U.; Ko, S.-B. A Study on the Ordinance in Connection with the Production and Distribution of Citrus in Jeju Special Self-Governing Province. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2022, 23, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Jeoung, S.-H.; Gim, S.-B.; Choi, H.-J.; Kim, D.-H. Study of Anti-microbe Activity of Essential oil (Unshiu oil) purified from Citrus unshiu S. Marcov. J. Haehwa Med. 2012, 20, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.; Jin, T.; Kang, H.-Y. Effect of Flame Resistant Treatment on the Sound Absorption Capability of Sawdust-mandarin Peel Composite Particleboard. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kengkhetkit, N.; Amornsakchai, T. Utilisation of pineapple leaf waste for plastic reinforcement: 1. A novel extraction method for short pineapple leaf fiber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, A.; Or, K.H.; Selamat, M.Z.; Nor, M.J.M.; Hassan, M.H.; Prasetiyo, I. Sound absorption of extracted pineapple-leaf fibres. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 136, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanklevska, N.; Petrenko, V.; Karnaushenko, A.; Melnykova, K. World corn market: Analysis, trends and prospects of its deep processing. Agric. Resour. Econ. Int. Sci. E-J. 2020, 6, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhansanj, S.; Turhollow, A.; Cushman, J.; Cundiff, J. Engineering aspects of collecting corn stover for bioenergy. Biomass Bioenergy 2002, 23, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Sapuan, S.; Zainudin, E.; Zuhri, M. Potential of using multiscale corn husk fiber as reinforcing filler in cornstarch-based biocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Yan, X. Corn husk for noise reduction: Robust acoustic absorption and reduced thickness. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 134, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorita, G.D.; Leimann, F.V.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Biorefinery approach: Is it an upgrade opportunity for peanut by-products? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Laila, U.-E.; Bareen, F.-E.; Hameed, E.; Shafiq, M. Sustainable management of peanut shell through biochar and its application as soil ameliorant. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawade, U.A.; Jadhav, M.G. Investigation of Peanut Shell as Alternative Sound Absorbing Material. Am. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2019, 3, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilyas, R.; Sapuan, S.; Atiqah, A.; Asyraf, M.; Nurazzi, N.; Norrrahim, M.N.; Jenol, M.A.; Harussani, M.; Ibrahim, R.; Atikah, M. Thermal Properties of Sugar Palm Fiber-Based Hybrid Composites. In Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Thermal Properties and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyang, M.L.; Sapuan, S.; Jawaid, M.; Ishak, M.; Sahari, J. Recent developments in sugar palm (Arenga pinnata) based biocomposites and their potential industrial applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imraan, M.; Ilyas, R.; Norfarhana, A.; Bangar, S.P.; Knight, V.F.; Norrrahim, M. Sugar Palm (Arenga pinnata) Fibers: New Emerging Natural Fibre and its Relevant Properties, Treatments and Potential Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 4551–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, A.E.; Diharjo, K.; Prasetiyo, I. Sound Absorption Performance of Sugar Palm Trunk Fibers. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 130, 01003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, P.; Taban, E.; Faridan, M.; Samaei, S.E.; Amininasab, S. Experimental and computational investigation of sound absorption performance of sustainable porous material: Yucca Gloriosa fiber. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 157, 106999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, S.E.; Asilian Mahabadi, H.; Mousavi, S.M.; Khavanin, A.; Faridan, M. Effect of Alkali treatment on diameter and tensile properties of Yucca Gloriosa fiber using response surface methodology. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, N.H.; Kumar, J.; Mazari, S.A.; Ahmed, S.; Fatima, N.; Mubarak, N.M. Development of fruit waste derived bio-adsorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, J.G.; Sanchis, E.J.; Alcaraz, J.S.; Belda, I.M. Sustainable sound absorbers from fruit stones waste. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 161, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W. The pore structure and sound absorption capabilities of Homalium (Homalium foetidum) and Jelutong (Dyera costulata). Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W. Why the sound-absorbing performance of heartwood and sapwood differs in yellow poplar (liriodendron tulipifera) cross-sections? Wood Res. 2022, 67, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W. Investigation of the pore structure and sound-absorbing capability of the Chinese parasol tree (Firmiana simplex (L.) W. Wight) and Chinese tulip poplar (Liriodendron chinense) transverse sections as eco-friendly, porous, sound-absorbing materials. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W. Effect of porous traits of hardwoods cross-section on sound absorption performance—Focus on 6 species of Korean hardwoods. Wood Fiber Sci. 2021, 53, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Song, B. Sound absorption properties of wooden perforated plates. Wood Res. 2018, 63, 559–572. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.-W.; Jang, E.-S.; Jang, S.-S.; Kang, H.-Y.; Kang, S.-G.; Oh, S.-C. Sound Absorption Rate and Sound Transmission Loss of Wood Bark Particle. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P.K.; Meena, D.; Vatsa, S.; Singh, I. Tensile behavior of nettle fiber composites exposed to various environments. J. Nat. Fibers 2013, 10, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Fatima, S.; Tandon, N. An experimental and theoretical study on environment-friendly sound absorber sourced from nettle fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, E.-S. Sound Absorbing Properties of Selected Green Material—A Review. Forests 2023, 14, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071366
Jang E-S. Sound Absorbing Properties of Selected Green Material—A Review. Forests. 2023; 14(7):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071366
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Eun-Suk. 2023. "Sound Absorbing Properties of Selected Green Material—A Review" Forests 14, no. 7: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071366
APA StyleJang, E.-S. (2023). Sound Absorbing Properties of Selected Green Material—A Review. Forests, 14(7), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071366





