The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba as Examples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation and Treatment of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
2.2. Measurement Methods and Indicators
2.2.1. Determination of Growth
2.2.2. Determination of Biomass
2.2.3. Determination of Calcium Concentration in Leaves
2.2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Index
Determination of Photosynthetic Parameters
Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment
Determination of Photosynthate
2.2.5. Determination of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
2.2.6. Determination of the Stress Tolerance
Determination of Long-Term Water Use Efficiency
Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Content in Leaves of Four Tree Species Seedlings
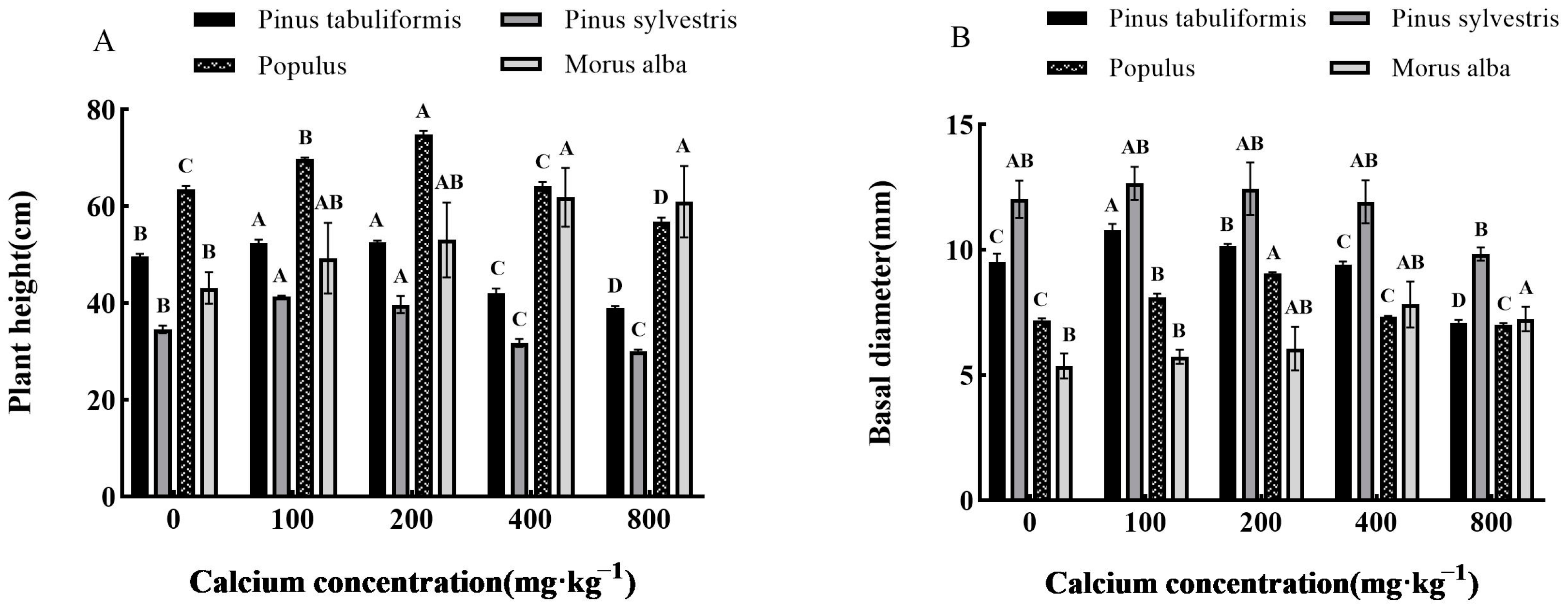
3.2. Effects of Exogenous Calcium on the Growth of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
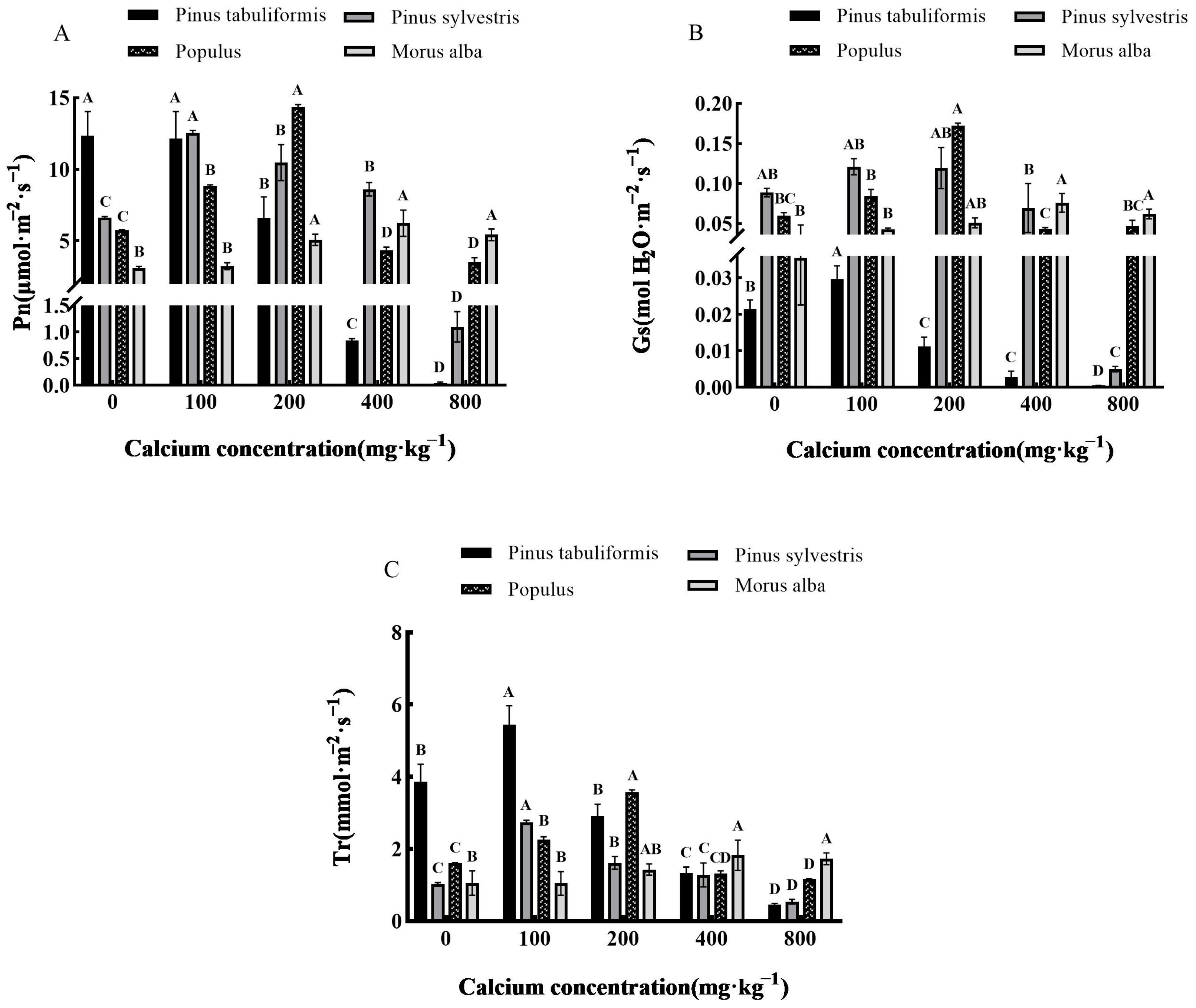
3.3. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
3.3.1. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Photosynthetic Parameters of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
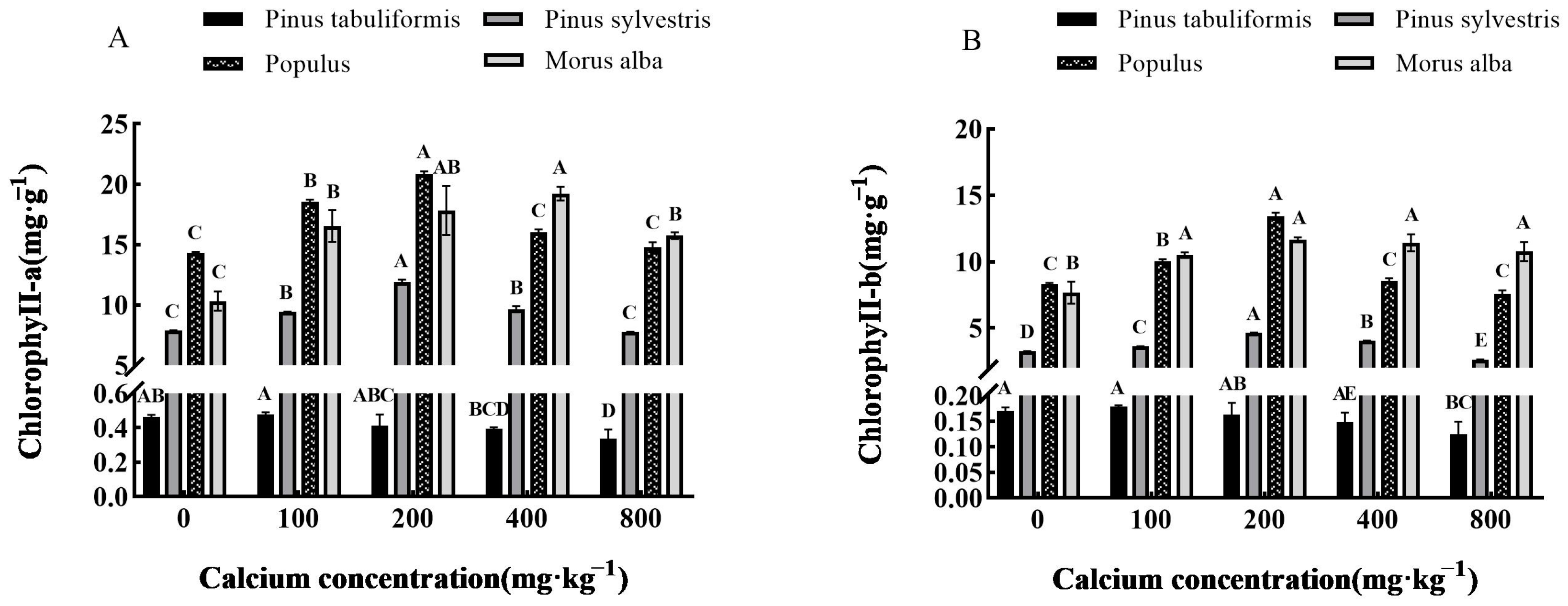
3.3.2. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Photosynthetic Pigments of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
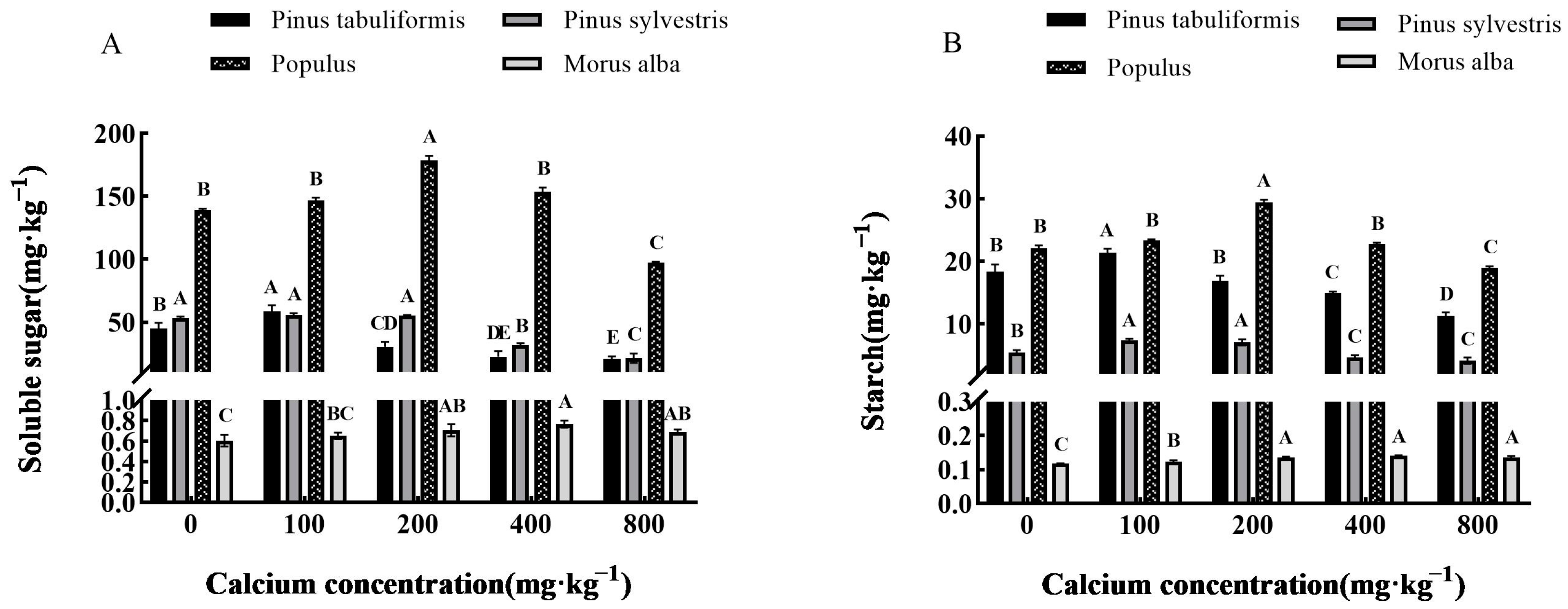
3.3.3. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Photosynthetic Products of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
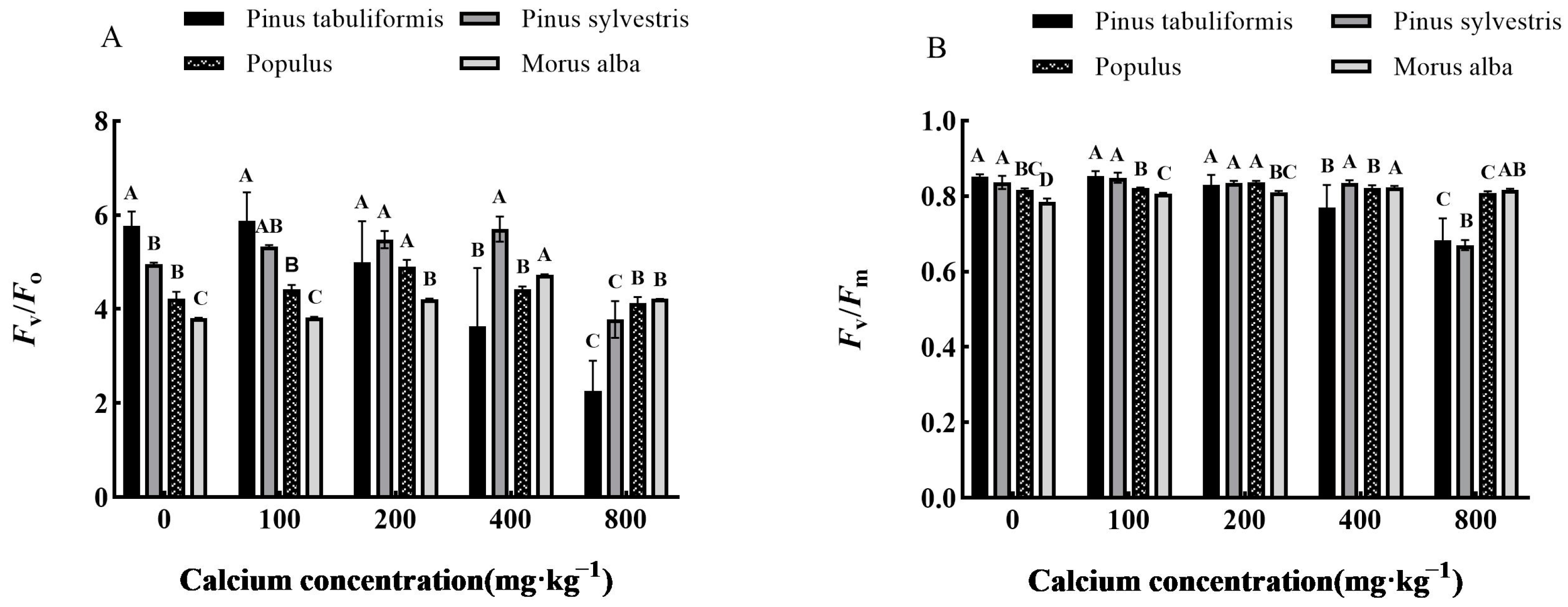
3.4. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
3.5. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on the Stress Resistance of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
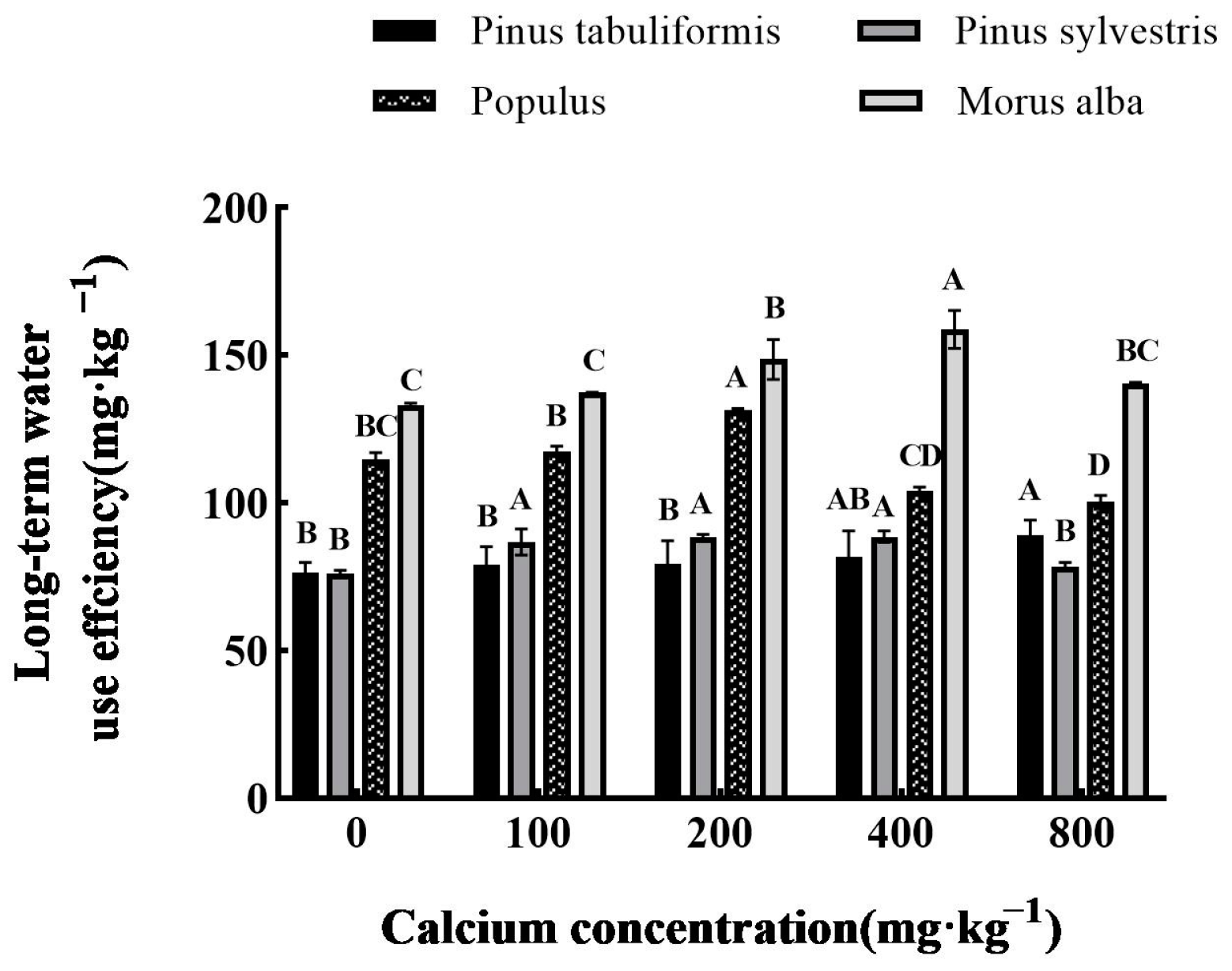
3.5.1. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Water Use Efficiency of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
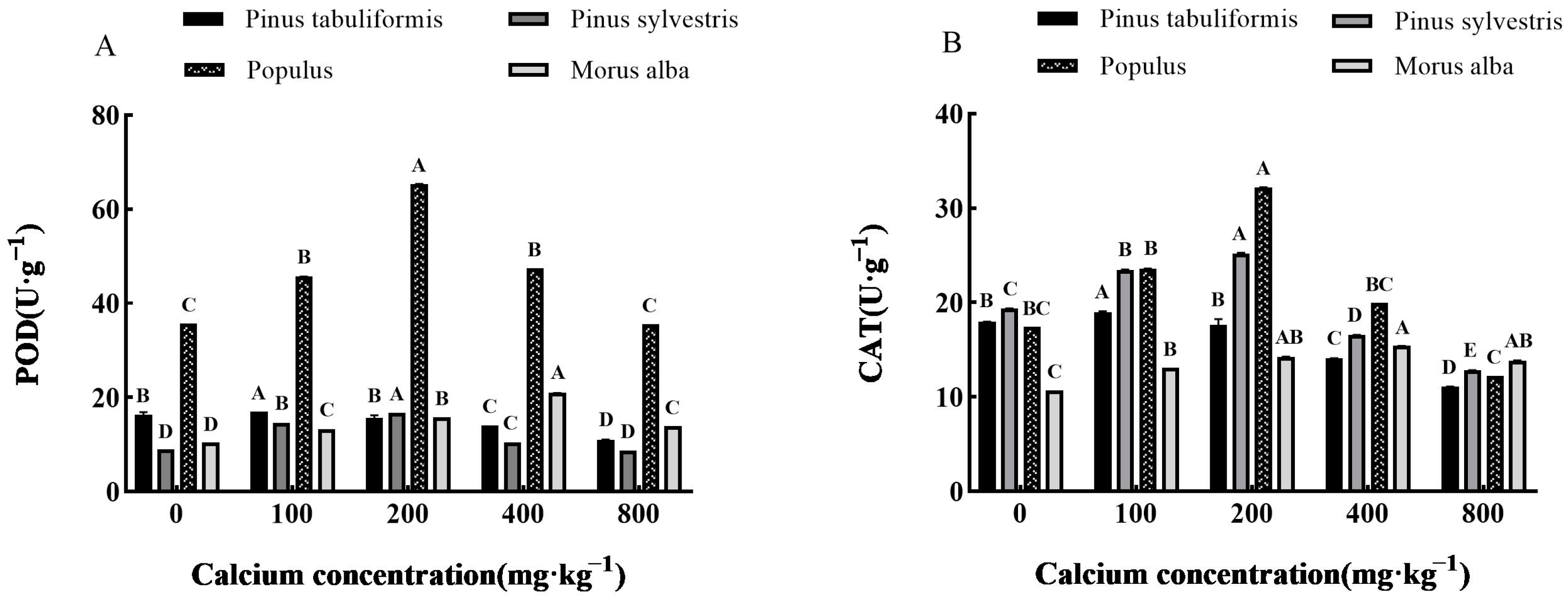
3.5.2. Effect of Exogenous Calcium on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Seedlings of Four Tree Species
4. Discussion
4.1. There Is an Optimum Calcium Concentration for Plant Growth
4.2. Different Plants Have Different Optimal Calcium Concentrations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, R.; Bai, C.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Yong, J.W.H. The significance of calcium-sensing receptor in sustaining photosynthesis and ameliorating stress responses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1019505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Guo, F.; Meng, J.; Li, X.; Wan, S. Calcium contributes to photoprotection and repair of photosystem II in peanut leaves during heat and high irradiance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, H. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of calcium uptake, transport and metabolism in plants. Bot. Bull. 2007, 6, 762–778. [Google Scholar]
- Kadota, Y.; Furuichi, T.; Ogasawara, Y.; Goh, T.; Higashi, K.; Muto, S.; Kuchitsu, K. Identification of putative voltage-dependent Ca2+-permeable channels involved in cryptogein-induced Ca2+ transients and defense responses in tobacco BY-2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aras, S.; Keles, H.; Bozkurt, E. Physiological and histological responses of peach plants grafted onto different rootstocks under calcium deficiency conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, M.R. Ca2+ signalling and control of guard-cell volume in stomatal movements. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F. The Optimum Concentration of Calcium of Quercus acutissima Carruth Seedlings and Its Effect on Growth and Physiology. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Effect of Calcium on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Fig. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Weng, X.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pei, J. The Optimum Calcium Concentration for Seedling Growth of Mongolian Pine (Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica) Under Different Soil Types in Northern Semi-Arid Areas of China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Li, H.; Weng, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y. Effect of exogenous calcium on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency of Fraxinus mandshurica. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2020, 6, 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L. Study on Leaf Functional Traits of Eight European Conifer and Broadleaved Seedlings. Master’s Thesis, China Academy of Forestry Science, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, J.; Wang, T. Economic value of mulberry tree and its application in ecological conservation. China Mark. 2017, 11, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.K.M.; Fu, Z.; Ding, C.; Jiang, L.; Han, X.; Yang, A.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X. Growth and wood properties of a 38-year-old Populus simonii × P. nigra plantation established with different densities in semi-arid areas of northeastern China. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. An analysis of the causes and definition criteria of forest degradation in the Three Northern Protected Forests in Liaoning Province. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Problems and countermeasures of the Three Northern Protective Forests in Liaoning Province. Mod. Agric. 2021, 1, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, Y.; Fu, A. Climate change may accelerate the decline of desert riparian forest in the lower Tarim River, Northwestern China: Evidence from tree-rings of Populus euphratica. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Gao, G.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y. Drivers of Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Community Structure Associated with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Differ at Regional vs. Local Spatial Scales in Northern China. Forests 2020, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, L.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, D.; Chen, Z. Warming-drying climate intensifies the restriction of moisture on radial growth of Pinus tabuli-formis plantation in semi-arid area of Northeast China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3459–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zou, X. From matching site with trees towards matching calcium with trees. J. Nanjing For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. Soil and Plant Nutrition Experiments; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Huang, S.; Ren, C.; Weng, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pei, J. Optimal exogenous calcium alleviates the damage of Snow-melting agent to Salix matsudana seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 928092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Li, H.; Ren, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. Calcium Regulates Growth and Nutrient Absorption in Poplar Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 887098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.J. The Experimental Guide for Plant Physiology, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, S. Plant Physiology Experiment; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 2–63. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, M.; Yu, G. Comparison of intrinsic water use efficiency between different aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica wide windbreaks in semiarid sandy land of northern China. Agrofor. Syst. 2015, 89, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S.; Saeed, M.; Parveen, A.; Javed, M.; Zafar, S.; Iqbal, N. Modulation of growth and key physiobiochemical attributes after foliar application of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under cadmium (Cd) stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Sun, X.; Mo, C.; Hao, M.; Wei, X.; Ma, A. Relationship between antioxidant enzymes and sclerotial formation of Pleurotus tuber-regium under abiotic stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Sun, L.; Hao, F. Roles and mechanisms of Ca2+ in regulating primary root growth of plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1748283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. The effect of calcium chloride on growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant responses of Zoysia japonica under drought conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lan, Z.; Tian, L.; Li, J.; Yang, G.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X. Change of Physiological Properties and Ion Distribution by Synergistic Effect of Ca2+ and Grafting under Salt Stress on Cucumber Seedlings. Agronomy 2021, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Zhan, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Chen, X. Regulation of Calcium on Peanut Photosynthesis Under Low Night Temperature Stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Pang, J.; Yong, J.; Chen, Y.; Bai, C.; Lambers, H. Supplementary Calcium Restores Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Growth and Photosynthetic Capacity Under Low Nocturnal Temperature. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correia, S.; Queirós, F.; Ribeiro, C.; Vilela, A.; Aires, A.; Barros, A. Effects of calcium and growth regulators on sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) quality and sensory attributes at harvest. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 248, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Zhu, C.; Wu, F.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, H. Exogenous calcium regulates the growth and development of Pinus massoniana detecting by physiological, proteomic, and calcium-related genes expression analysis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 196, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Guan, G.; Yao, F.; Zhou, G.; Liu, G. Effect of calcium and magnesium deficiency on growth and mineral nutrient uptake distribution of navel orange seedlings. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2023, 4, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X. Role of calcium as a possible regulator of growth and nitrate nitrogen metabolism in apple dwarf rootstock seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 276, 109740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Činčerová, A. Effect of calcium deficiency on L-lysine-α-ketoglutarate aminotransferase in wheat plants. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 1976, 80, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Riaz, M.; Yan, L.; Zeng, Y.; Cuncang, J. Boron and calcium deficiency disturbing the growth of trifoliate rootstock seedlings (Poncirus trifoliate L.) by changing root architecture and cell wall. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Papadopoulos, A. Effects of calcium and magnesium on plant growth, biomass partitioning, and fruit yield of winter greenhouse tomato. HortScience 2004, 39, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z. Effect and Mechanism of High Calcium on Seedlings and Fruits in Fragaria vesca. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guizhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, S.; Gilliham, M.; Athman, A.; Schreiber, A.; Baumann, U.; Moller, I. Cell-specific vacuolar calcium storage mediated by CAX1 regulates apoplastic calcium concentration, gas exchange, and plant productivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cybulska, J.; Zdunek, A.; Konstankiewicz, K. Calcium effect on mechanical properties of model cell walls and apple tissue. J. Food Eng. 2011, 102, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Pereira, R.; Martins, M.; Tamagnini, P.; Serôdio, J.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Fidalgo, F. Glyphosate-dependent effects on photosynthesis of Solanum lycopersicum L.—An ecophysiological, ultrastructural and molecular approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Deng, P.; Zhou, X.; Huang, S. Effect of salt stress on growth and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of seedlings of Luo Han Guo. Fruit Trees South China 2021, 2, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Phonenasay, S. Effects of nitrogen application rate on the photosynthetic pigment, leaf fluorescence characteristics, and yield of indica hybrid rice and their interrelations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.; Zhang, C.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, Z. The effects of different water and nitrogen methods on fluorescence characteristic and growth of rice in black soil region on Songnen plain, northeast China. Agric. Res. 2021, 10, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Nan, F.; Liu, Q.; Lv, J.; Feng, J.; Xie, S. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Tolerance to High Concentrations of Calcium Chloride Stress in Parachlorella kessleri. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Huo, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of exogenous calcium on the growth and physiological characteristics of sandy camphor pine seedlings. Soil Bull. 2021, 5, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R. Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiao, J.; Kou, M.; Yin, Q.; Xu, H. The antioxidation-related functional structure of plant communities: Understanding antioxidation at the plant community level. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Tang, Q.; Hua, X. Arabidopsis brassinosteroid mutants det2-1 and bin2-1 display altered salt tolerance. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 29, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melorose, J.; Perroy, R.; Careas, S. Brassinosteriods: A Class of Plant Hormone. Statewide Agricultural Land Use Baseline; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhuo, Z.; Luo, Q. Seasonal variation in carbon isotope composition and WUEi correspond with weather factors for five cultivars of Chinese jujube in Xinjiang. J. Fruit Trees 2012, 1, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Han, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Su, B. Foliar δ13C Within Temperate Deciduous Forest: Its Spatial Change and Interspecies Variation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1998, 40, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Gao, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, J. Photosynthesis, transpiration, and water use efficiency of Caragana microphylla, C. intermedia, and C. korshinskii. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Gao, T.; Fang, X.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Mu, J. Calcium alleviates decreases in photosynthesis under salt stress by enhancing antioxidant metabolism and adjusting solute accumulation in Calligonum mongolicum. Conserv. Physiol. 2017, 5, cox060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Yan, R.; Chen, F. Effects of different storage temperatures and times on germination and antioxidant responses of Jatropha curcas seeds. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Glusac, J.; Morina, F.; Veljovic-Jovanovic, S.; Boroja, M.; Kukavica, B. Changes in the antioxidative metabolism induced by drought and Cd excess in the leaves of houseleek (Sempervivum tectorum L.). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, F.S., III. The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1980, 11, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westoby, M.; Wright, I. Land-plant ecology on the basis of functional traits. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.B. The world-wide ‘fast–slow’ plant economics spectrum: A traits manifesto. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Fang, J. Latitudinal pattern and the driving factors of leaf functional traits in 185 shrub species across eastern China. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Study on the Effect of Calcium on the Growth and Development of Ginseng. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Effect of calcium excess on photosynthetic properties and chloroplast ultrastructure of tea plants. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2010, 2, 432–438. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, P.; Ellsworth, D.; Walters, M.; Vose, J.; Gresham, C.; Volin, J. Generality of Leaf Trait Relationships: A Test across Six Biomes. Ecology 1999, 80, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salguero-Gómez, R. Applications of the fast–slow continuum and reproductive strategy framework of plant life histories. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, J. Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes Vegetation Processes; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Craine, J. Resource strategies of wild plants. In Resource Strategies of Wild Plants; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damián, X.; Ochoa-López, S.; Gaxiola, A.; Fornoni, J.; Domínguez, C.; Boege, K. Natural selection acting on integrated phenotypes: Covariance among functional leaf traits increases plant fitness. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gul, Z.; Guo, X. Effects of exogenous calcium on adaptive growth, photosynthesis, ion homeostasis and phenolics of Gleditsia sinensis Lam. plants under salt stress. Agriculture 2021, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Effect of exogenous calcium on physiological characteristics of iron holly seedlings at high temperature. Green Technol. 2022, 19, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Calcium Concentration/mg·kg−1 | Pinus tabuliformis Seedlings | Pinus sylvestris Var. mongolica Seedlings | Populus Seedlings | Morus alba Seedlings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 59.17 ± 0.35 B | 69.68 ± 0.70 C | 28.59 ± 0.08 C | 23.99 ± 0.82 D |
| 100 | 65.34 ± 0.72 A | 81.73 ± 0.04 A | 30.27 ± 0.17 B | 27.44 ± 0.40 BD |
| 200 | 53.74 ± 1.41 C | 75.21 ± 0.44 B | 33.54 ± 0.23 A | 30.26 ± 2.93 C |
| 400 | 45.07 ± 0.80 D | 45.38 ± 0.40 D | 28.46 ± 0.10 C | 46.75 ± 1.13 A |
| 800 | 39.96 ± 0.63 E | 27.49 ± 0.38 E | 25.15 ± 0.29 D | 35.15 ± 8.38 B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Weng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pei, J. The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba as Examples. Forests 2023, 14, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071437
Li H, Zhao Y, Weng X, Zhou Y, Zhang S, Liu L, Pei J. The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba as Examples. Forests. 2023; 14(7):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071437
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Yaoyao Zhao, Xiaohang Weng, Yongbin Zhou, Songzhu Zhang, Liying Liu, and Jiubo Pei. 2023. "The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba as Examples" Forests 14, no. 7: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071437
APA StyleLi, H., Zhao, Y., Weng, X., Zhou, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, L., & Pei, J. (2023). The Most Suitable Calcium Concentration for Growth Varies among Different Tree Species—Taking Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba as Examples. Forests, 14(7), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071437






