Abstract
Tilia miqueliana is an endemic species belonging to the genus Tilia L. (Tiliaceae) in China, which is known for its fragrant flowers and nectar, but the dynamic changes in metabolites during its growth and development are still unclear. In this study, the metabolic profiles from T. miqueliana flowers at three developmental stages were detected by performing an ultra-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS/MS)-based widely targeted metabolomic analysis. A total of 1138 metabolites were detected, with 288 Differentially Accumulated Metabolites (DAMs) determined, flavonoids accounting for the largest proportion. The trend analysis showed that DAMs present seven distinctive patterns, and subclass 5 obtained the largest amount with continuously increased relative content during flower development. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) annotation and enrichment analysis of DAMs showed different overlap and variability in metabolic pathways, indicating different directions of flavonoids’ metabolic flux in the three developmental stages. A correlation network analysis further revealed five core metabolites that played essential roles in flavonoid biosynthesis. This research provides comprehensive insights into the exploitation and utilization of T. miqueliana as well as a scientific basis for phylogenetic studies of the genus Tilia.
1. Introduction
The linden tree (Tiliaceae) is a broadleaf deciduous tree species mainly found in the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere [1]. They are graceful and easily distinguished from other taxa by their large leafy bracts on the inflorescences. Tilia flowers, which are also known as Tiliae flos, mainly refer to the inflorescences of three species: Tilia cordata Miller, Tilia platyphyllos Scop., and Tilia × vulgaris Heyne [2]. Flavonoids, phenolic acids, and tannins are abundant in Tilia flowers, while flavonoids have been illustrated as the most important specialized metabolites [3,4]. They have been used in traditional medicine because of their medicinal properties against migraines, feverish colds, and throat irritation [5,6].
Flavonoids are one of the most important classes of specialized metabolites in plants, originating from the phenylpropanoids pathway. Generally speaking, flavonoids include flavones, flavanols, flavonols, flavanones, isoflavones, anthocyanidins, and chalcones [7]. As important signaling molecules, flavonoids have significant impacts on plant growth and development [8]. In addition, they are essential pigments that influence the colors of flowers and fruits, assist with pollination and seed dispersal [9]. They not only play crucial roles in regulating plant responses to biotic and abiotic environmental stressors [7,10], but also have antioxidant [11], anti-depression [12], anti-inflammatory activities, and anticancer effects [13], which are conducive to human health.
Previous research on flavonoids in the genus Tilia yielded many interesting results. Four flavonoid glycosides were isolated from the leaves of Tilia rubra subsp. Caucasica (Iranian Linden), and apigenin-7-O-β-d-glucoside and luteolin-7-O-β-d-glucoside were isolated in Tilia for the first time [14]. Orobol 4′-O-β-glucopyranoside, as a new isoflavone glycoside, was identified from the stems of Tilia taquetii Schneider [15]. Furthermore, five flavonol glycosides were extracted from Tilia argentea flowers, which demonstrated liver-protective (hepatoprotective) properties; kaempferol 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside was the crucial component [16]. With the widespread utilization of Tilia resources, the identification of complex specialized metabolites in different tissues has become a popular and challenging topic, leading to the development of bioactivity studies.
Tilia miqueliana Maxim. is an endemic species belonging to the genus Tilia L. (Tiliaceae), and it is an important native tree in Jiangsu province in China. It is luxuriant and fragrant; the flower has five beige petals, and the early blooming period is at the end of May in Nanjing. It is not only suitable for urban road greening and timber, but also has great potential as a nectar source [17]. However, most studies on T. miqueliana have focused on seed dormancy release [18]; at present, the metabolite composition of its flowers remains unclear. Therefore, there is great significance in investigating the metabolites in Tilia miqueliana flowers to fill the existing research gaps.
In recent years, metabolomics has become a popular method for the high-throughput exploration for the biosynthesis pathways of specialized metabolites. It can be used to analyze the metabolic compositions of different plant tissues [19] and metabolite changes during plant growth and development [20], investigate the variation of metabolites from plants in response to stress treatment [21], and explore various metabolites in plants from different provenances [22]. In this study, we obtained metabolite datasets of T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages using widely targeted metabolomics techniques, revealing the accumulation patterns of flavonoids and the mutual regulatory relationship between flavonoid biosynthesis-related metabolites. The results provide a theoretical basis for the exploitation of Tilia miqueliana flowers, especially in the optimum harvesting period for bioactivity research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Reagents
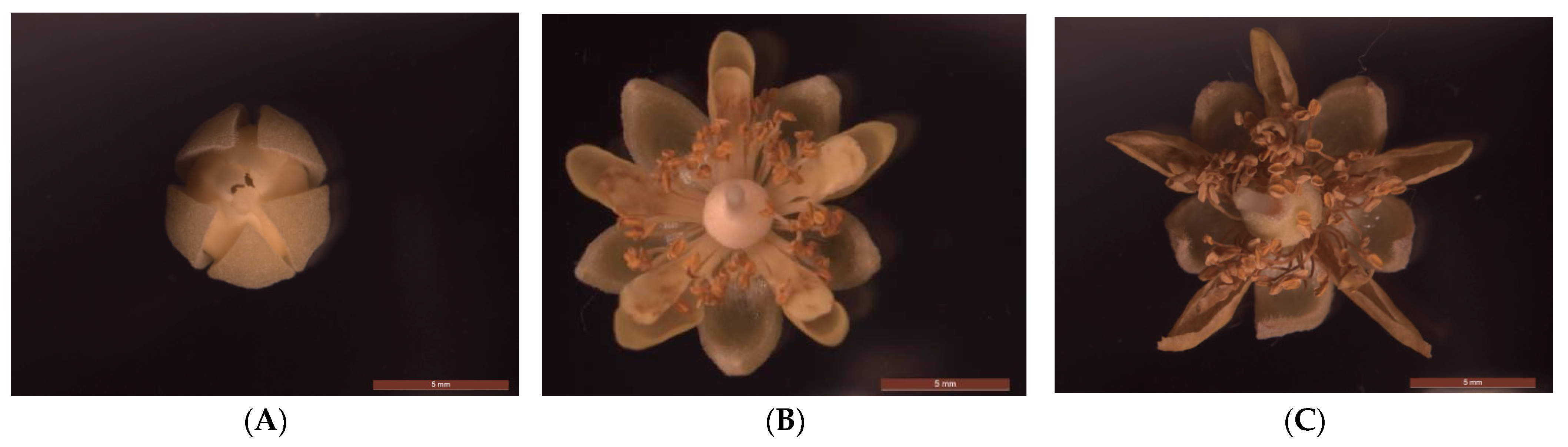
T. miqueliana flowers were collected in Tianwang town (119°12′6″ E, 31°39′29″ N), Jurong, Jiangsu Province at 9:00 am on 1 June 2022. Inflorescences were picked from 30 well-grown trees under sexual reproduction with the same provenance, and their development stages were divided as follows according to the morphology of flowers, as shown in Figure 1: Bud Stage (BS); Full-blooming Stage (FS); and Wilting Stage (WS). Samples were stored in an ultra-low-temperature freezer at −80 °C (Forma™ 900 series, Thermo Fisher Scientific (Asheville) LLC., Marietta, OH, USA) until the next analysis. HPLC-grade methanol and acetonitrile were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Hesse, Germany), and formic acid was purchased from Sigma-Aladdin (Saint Louis, MO, USA).
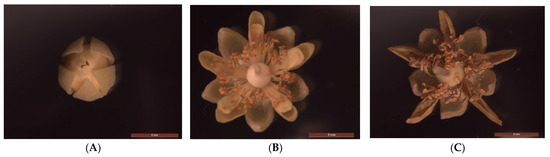
Figure 1.
Morphology of T. miqueliana flowers in different development periods. (A) Bud Stage (BS); (B) Full-blooming Stage (FS); (C) Wilting Stage (WS).
2.2. Sample Preparation
Three biological replicates of 60 fresh flowers were harvested for each development stage. Samples of BS, FS, and WS were processed by vacuum freeze-dryer (Scientz-100F, Xinzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China), ground for 1.5 min at 30 Hz with a mixer mill (MM 400, Retsch, Haan, Germany). An amount of 50 mg of lyophilized powder was dissolved with 1.2 mL of 70% methanol solution, vortexed for 30 s at the interval of 30 min, and then repeated 6 times. After centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 3 min, we obtained the extracts by passing the supernatant through a 0.22 µm pore size filter (SCAA-104, ANPEL, Shanghai, China) [23]. Equal amounts from each sample were combined to create the quality control (QC) samples.
2.3. Sample Detection and Analysis
UPLC-ESI-MS/MS system (UPLC, ExionLC™ AD, https://sciex.com.cn/ accessed on 25 July 2022; Analyst 1.6.3; MS, Applied Biosystems 4500 Q TRAP) was performed sample detection and analysis. Using an Agilent SB-C18 (1.8 µm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) column of UPLC, with a temperature of 40 °C; the mobile phase contained solvent A (0.1% formic acid with ultrapure water), and solvent B (0.1% formic acid with acetonitrile); and 4 μL was injected with the flow rate of 0.35 mL/min. Gradient programs started with 95% A, 5% B; reached to 5% A, 95% B by linear increase within 9 min and kept for 1 min; then transformed to 95% A, 5.0% B within 1.1 min, and lasted for 2.9 min.
The effluent was alternatively connected to an ESI-triple-quadrupole–linear ion trap (QTRAP)-MS. The electrospray ionization (ESI) temperature was set to 550 °C, the ion spray voltage (IS), 5500 V (positive ion mode)/−4500 V (negative ion mode); ion source gas I (GSI), gas II (GSII), and curtain gas (CUR) were set at 50, 60, and 25 psi, respectively, with high collision-activated dissociation (CAD). Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode was used to acquire QQQ scans, with the collision gas (nitrogen) set at medium.
2.4. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Metabolites
Qualitative analysis of metabolites was conducted by using the secondary spectrum information, based on the self-built metware database MWDB (Metware Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) [24]. During the analysis, the isotopic signal, duplicated signal from other fragments of larger molecular weight compounds, and repetitive signal containing K+, Na+, and NH4+ ions were eliminated [24]. Triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) analysis was used to quantify the metabolites. Following the acquisition of the metabolic mass spectrometry data from samples, the peak area integral was carried out for each chromatographic peak of the substances, and the mass spectrum peak of the same metabolite in various samples was integrally adjusted [25].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Metabolites data was processed and filtered by R software (www.r-project.org/) to conduct statistical analysis: principal component analysis (PCA) through R (base package) Version 3.5.1; orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) via R (MetaboAnalystR) Version 1.0.1; hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) via R (ComplexHeatmap) Version 2.8.0; pearson correlation coefficients (PCC) by R (base package, Hmisc) Version 3.5.1, 4.4.0. PCA was performed to preliminary test the overall metabolite differences between samples (including QC samples) of each group and the variability within the groups. Pairwise comparisons was conducted by OPLS-DA for screening differential variables based on the variable importance projection (VIP) threshold of 1 [24]. HCA was used for visualizing the accumulation patterns of metabolites for samples in each group. To filtrate DAMs, VIP ≥ 1 and fold change ≥2 or ≤0.5 were set as the selection criteria [26]. The KEGG Compound database (http://www.kegg.jp/eg/compound/ accessed on 30 June 2023) was performed to annotate and classify the DAMs, and then mapped to the KEGG pathway database (http://www.kegg.jp/eg/pathway.html accessed on 30 June 2023) to display metabolic pathways for DAMs enrichment, significant enrichment was identified by p-value < 0.05. Based on PCC, constructed the correlation networks of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs filtered with a threshold of correlation coefficient |cor| > 0.8 and p-value < 0.05, visualized by Cytoscape Version 3.7.1.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Quality Evaluation and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
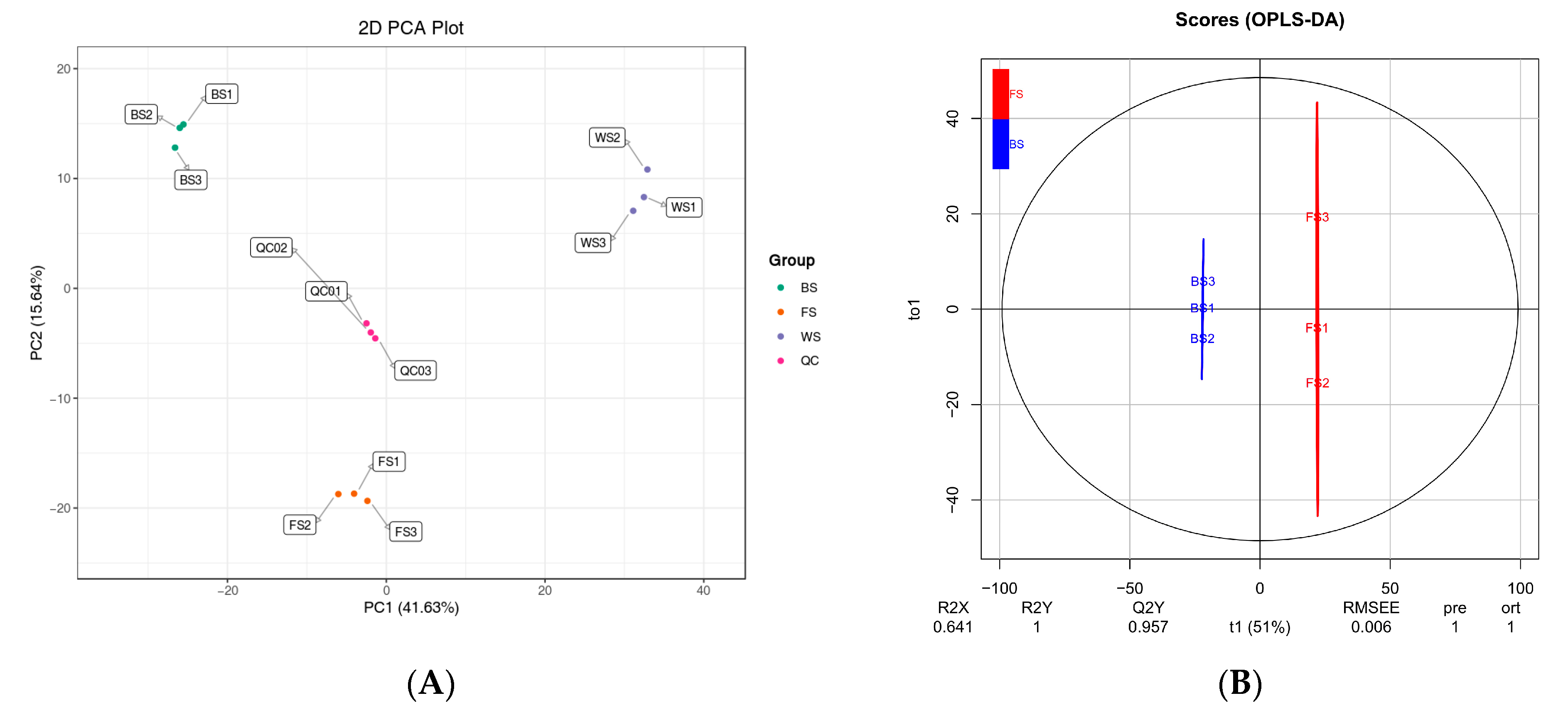
Based on UPLC-ESI-MS/MS, a widely targeted metabolomics method was used to determine the metabolite composition of T. miqueliana flowers at three development stages. Quality control (QC) samples were used for testing the reproducibility of metabolite extraction and detection. In addition, the Pearson correlation coefficient analysis demonstrated good homogeneity with an R2 close to 1 for all samples within groups (Figure S1a,b).
After quality control, PCA was conducted to acquire the overall degree of variation among different groups, as well as samples within groups. In the PCA score plot, the principal components PC1, and PC2 explained 41.63% and 15.64% of the variation, respectively (Figure 2A). Three biological replicates of each group clustered together, and different groups were distinctly separated within a 95% confidence interval. It indicated that samples had good reproducibility in biological replicates, while significant differences in metabolites were observed during the flower development.
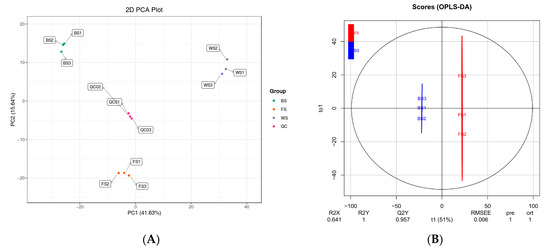

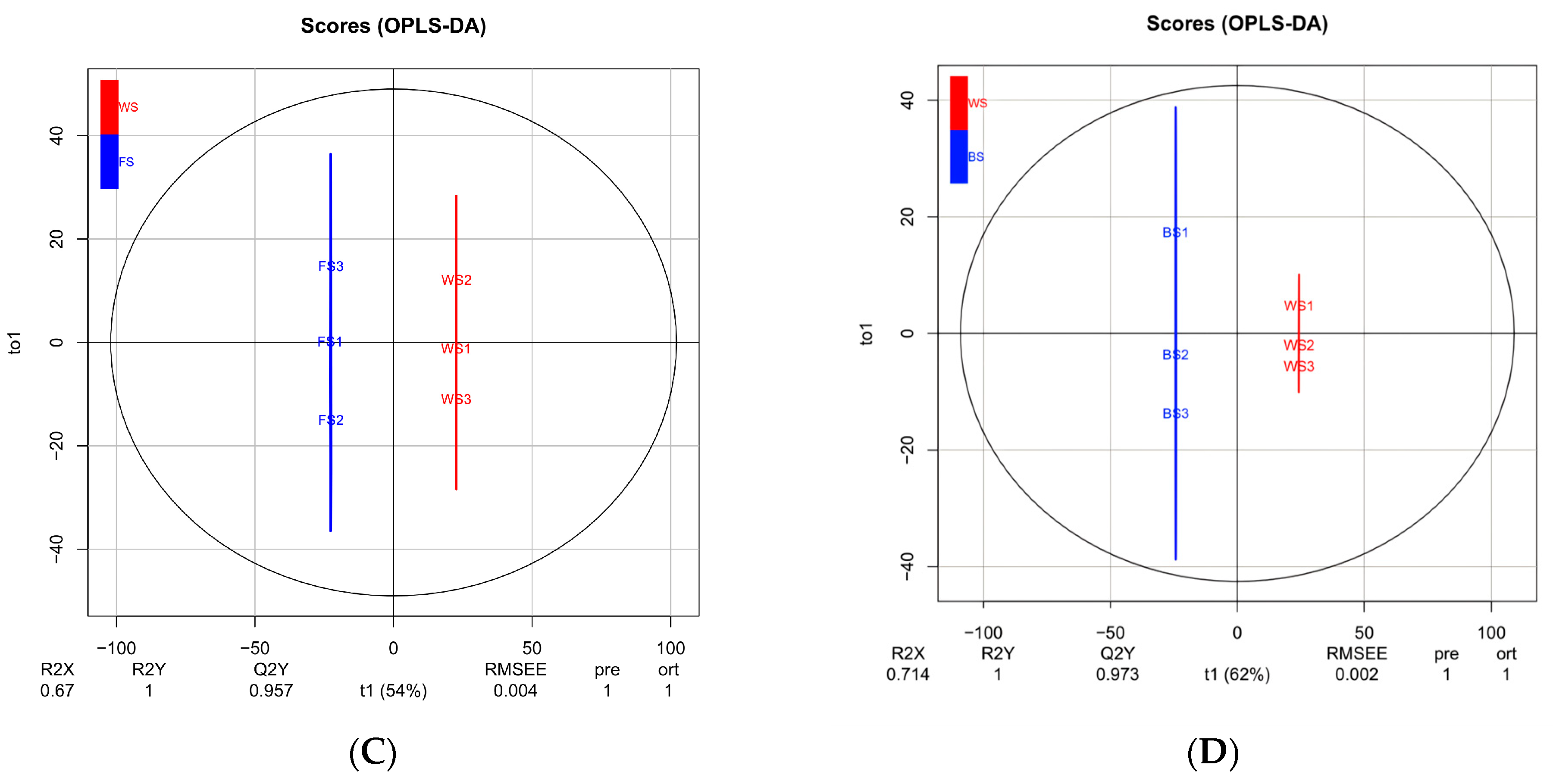
Figure 2.
Multivariate statistical analysis of metabolites in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages. (A) PCA score plot of 3 comparison groups and quality control (QC) samples; (B–D) score plots of the OPLS-DA model for BS vs. FS, FS vs. WS, BS vs. WS, respectively. BS: Bud Stage; FS: Full-blooming Stage; WS: Wilting Stage.
OPLS-DA models were performed to determine metabolite characteristics for pairwise comparisons (Figure 2B–D). R2X and R2Y denote the rate of explanation of the X and Y matrices, respectively; Q2Y denotes the predictive ability of the model: BS vs. FS (R2X = 0.641, R2Y = 1, Q2Y = 0.957; Figure 2B), FS vs. WS (R2X = 0.67, R2Y = 1, Q2Y = 0.957; Figure 2C), BS vs. WS (R2X = 0.714, R2Y = 1, Q2Y = 0.973; Figure 2D). The values of R2X and R2Y were close to 1, and Q2Y exceeded 0.95 in all pairwise comparisons. Simultaneously, random permutation tests of OPLS-DA models were conducted 200 times, and p values from R2Y and Q2 were all less than 0.005 in each pairwise comparison. It suggested the results were stable and reliable, possessed great predictability.
3.2. Metabolites Profiling Analysis of T. miqueliana Flowers
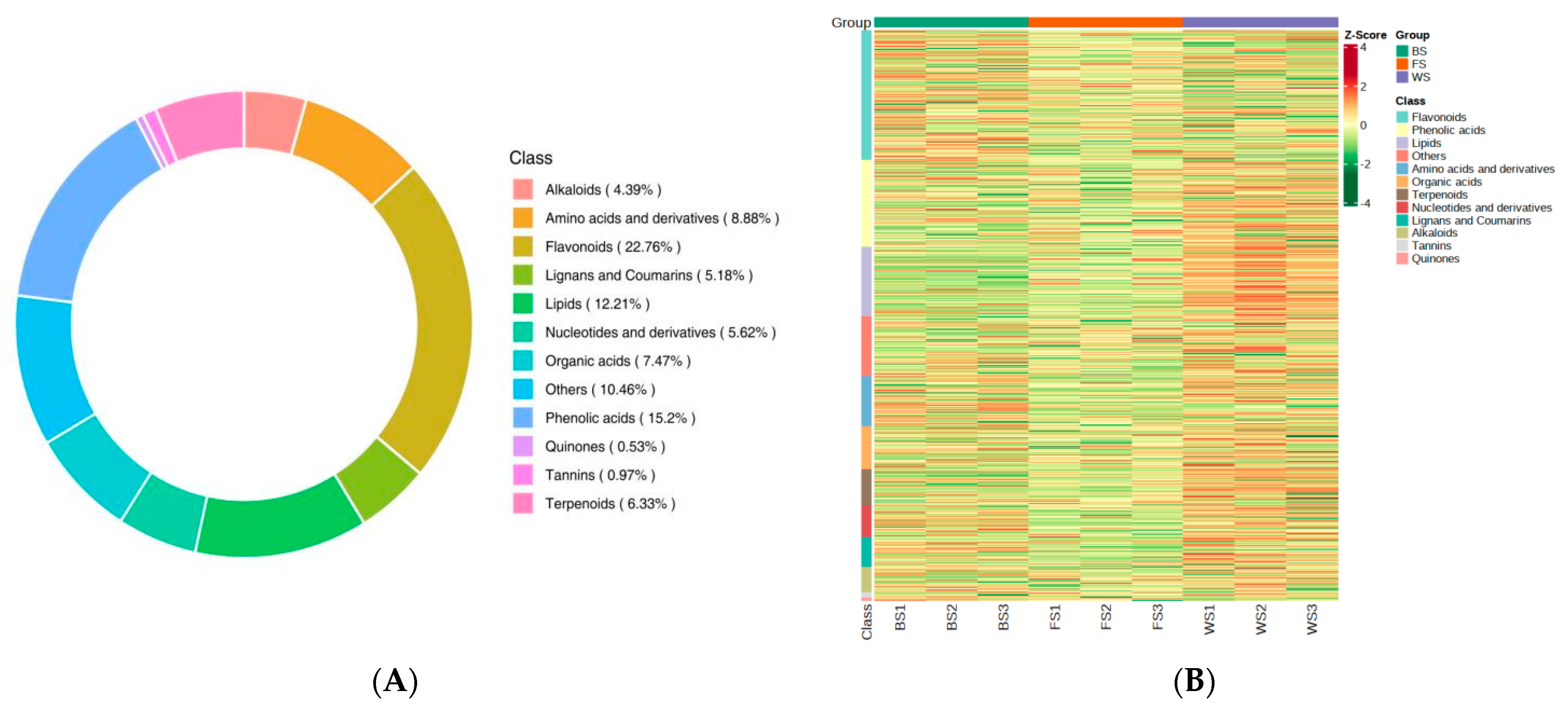
A total of 1138 metabolites were identified in the three developmental stages of T. miqueliana flowers. They were classified into 12 categories with the following distribution: 259 flavonoids, 173 phenolic acids, 139 lipids, 101 amino acids and derivatives, 85 organic acids, 72 terpenoids, 64 nucleotides and derivatives, 59 lignans and coumarins, 50 alkaloids, 11 tannins, 6 quinones, and 119 other compounds (Table S1 and Figure 3A). The accumulation patterns of metabolites in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages were visualized by HCA (Figure 3B). This analysis showed significant differences in metabolite composition and relative content. It was observed that the relative contents of lipids, phenolic acids, and terpenoids in WS were obviously higher than in BS and FS, possibly due to their biosynthesis and decomposition being regulated by the development period of the flowers.
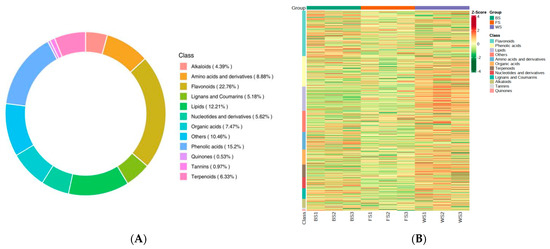
Figure 3.
Metabolites analysis of T. miqueliana flowers. (A) Classification of the 1138 metabolites; (B) hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) of all metabolites in different developmental stages of T. miqueliana flowers samples.
3.3. Identification and Characteristics Analysis of DAMs
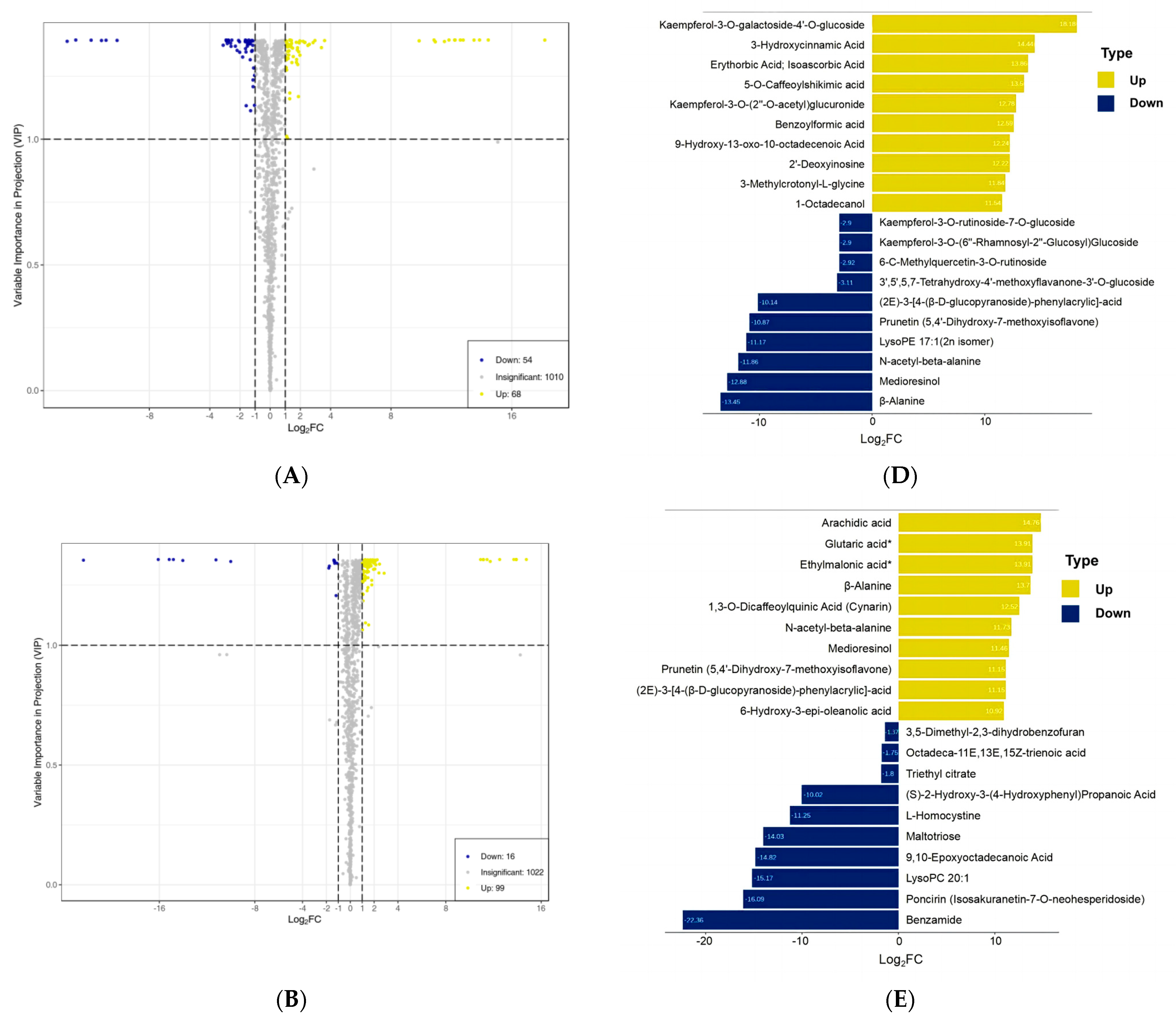
As we can see, 288 DAMs were identified in T. miqueliana flowers and showed specificity and overlap in pairwise comparisons (Table S2). The amount of DAMs in pairwise comparisons were visualized by volcano plots: 68 up-regulated and 54 down-regulated in BS vs. FS (Figure 4A); 99 up-regulated and 16 down-regulated in FS vs. WS (Figure 4B); 184 up-regulated and 59 down-regulated in BS vs. WS (Figure 4C). The amount of up-regulated DAMs was always higher than down-regulated, implying that some physiological and metabolic activities were gradually activated with the development of T. miqueliana flowers.
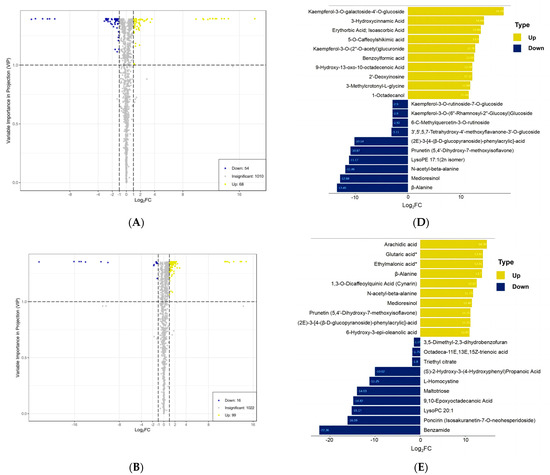
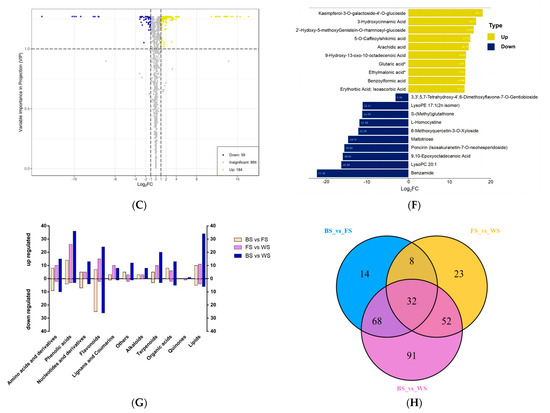
Figure 4.
Analysis of DAMs in flowers of T. miqueliana at different developmental periods. (A–C) Volcano plots present DAM expression levels in BS vs. FS, FS vs. WS, BS vs. WS, respectively; yellow and dark blue dots indicate up-regulated and down-regulated DAMs, gray means metabolites were detected but not significantly different. (D–F) Yellow and dark blue denote the top 10 of up-regulated and down-regulated DAMs in BS vs. FS, FS vs. WS, BS vs. WS, respectively. BS: Bud Stage; FS: Full-blooming Stage; WS: Wilting Stage. Note: compounds with “*” means isomers. (G) Categories composition and variation of DAMs in pairwise comparisons. (H) Venn diagram shows the quantitative distribution of 288 DAMs in pairwise comparisons.
The top and bottom 10 DAMs of each pairwise comparison along with the highest significant variation in Log2FC values were present, with a range of 11.54 to 18.18 in Log2FC value for up-regulated and −13.45 to −2.9 for down-regulated in BS vs. FS (Figure 4D); 10.92 to 14.76 for up-regulated and −22.36 to −1.37 for down-regulated in FS vs. WS (Figure 4E); 13.72 to 18.17 for up-regulated and −22.35 to −3.15 for down-regulated in BS vs. WS (Figure 4F). The most significant up-regulated DAM is Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside-4′-O-glucoside (Xmyp005599) in BS vs. FS and BS vs. WS, with the Log2FC values of 18.18 and 18.17, respectively.
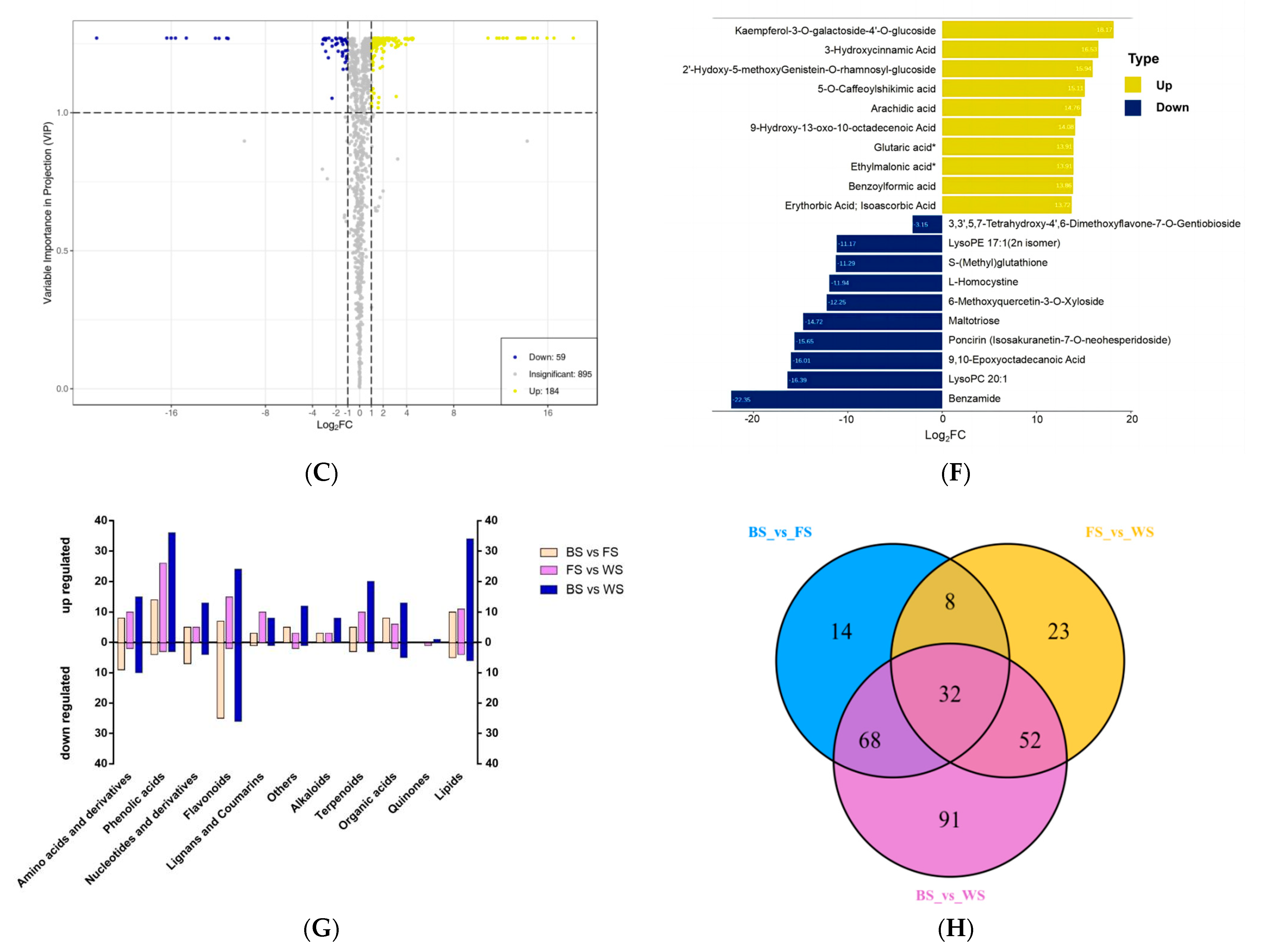
The DAMs from these pairwise comparisons were further classified and divided into 11 categories, mainly concentrated in flavonoids, lipids, phenolic acids, amino acids, and their derivatives (Figure 4G). The Venn diagrams revealed the amount of unique and common DAMs between the developmental stages (Figure 4H). The 32 DAMs that were found in all stages were considered essential metabolites in response to the development events of T. miqueliana flowers and provided a train to further explore potential biomarkers.
3.4. Variation Trends Analysis of DAMs
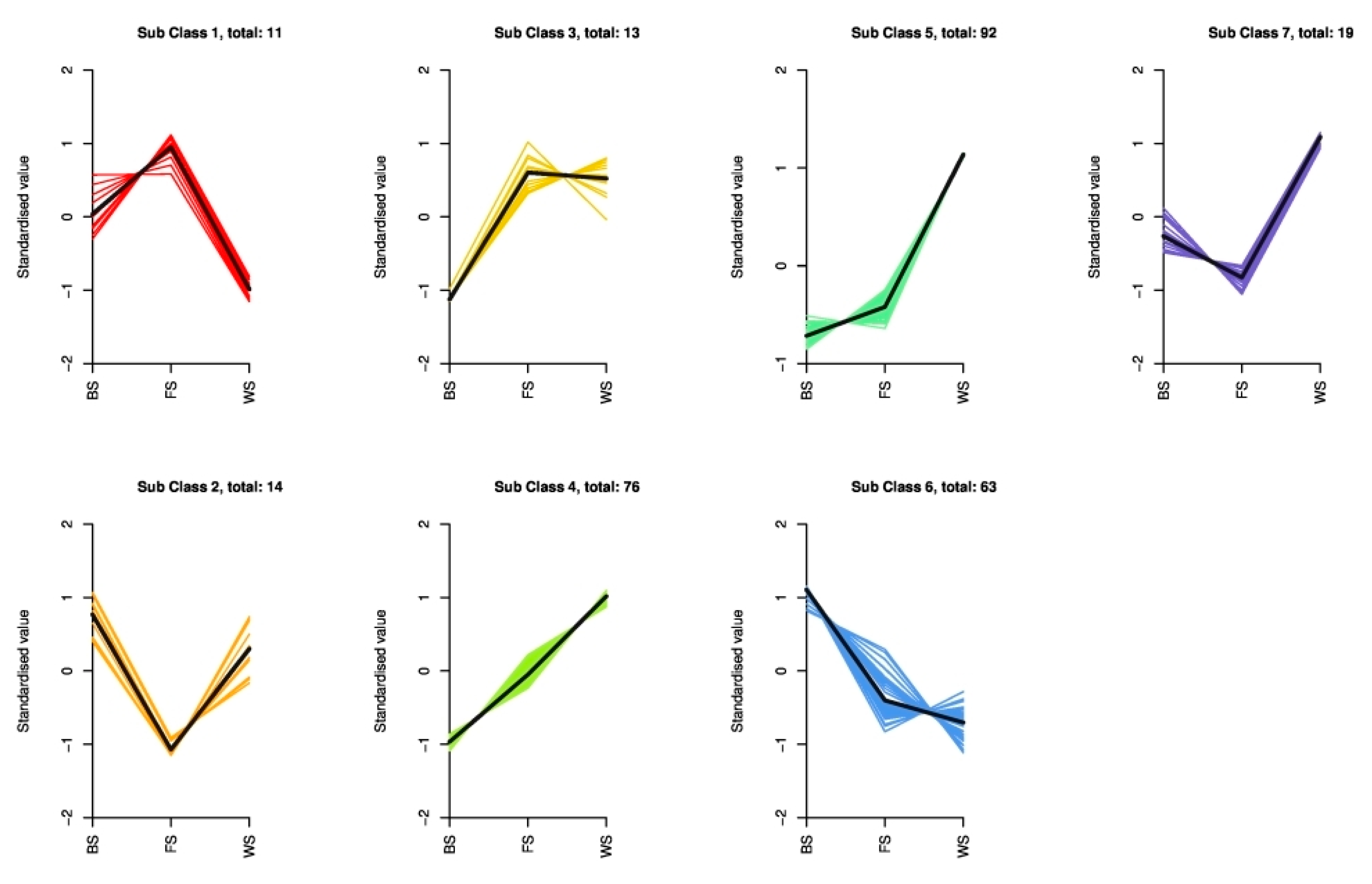
To explore the variation trends of DAMs in T. miqueliana flowers during development, we classified and visualized them through metabolites abundance at different stages. The DAMs were subjected to unit variance scaling and K-means clustering analysis, where DAMs with similar accumulation patterns were grouped together in a cluster [27]. The variation trends of 288 DAMs were divided into 7 clusters, from Subclass 1 to Subclass 7, which contained 11, 14, 13, 76, 92, 63, and 19 metabolites, respectively (Figure 5). The overall variations of DAMs can be roughly separated into four categories: continuous up-regulated (Subclass 4 and Subclass 5); continuous down-regulated (Subclass 6); down-regulated followed by up-regulated (Subclass 2 and Subclass 7), and up-regulated followed by down-regulated (Subclass 1). Subclass 4, 5, and 6 contained most of the DAMs, more than half of them increased continuously during the three developmental stages.
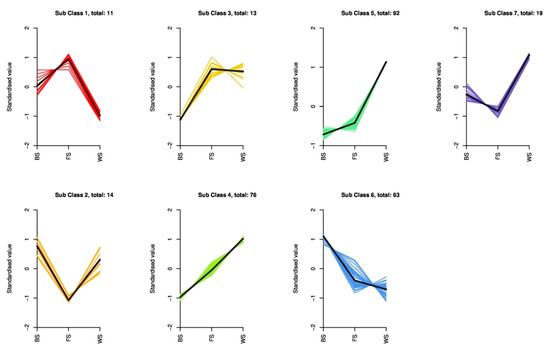
Figure 5.
Variation trends in DAMs of T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental periods.
3.5. KEGG Enrichment and Biosynthesis Pathway Analysis for DAMs
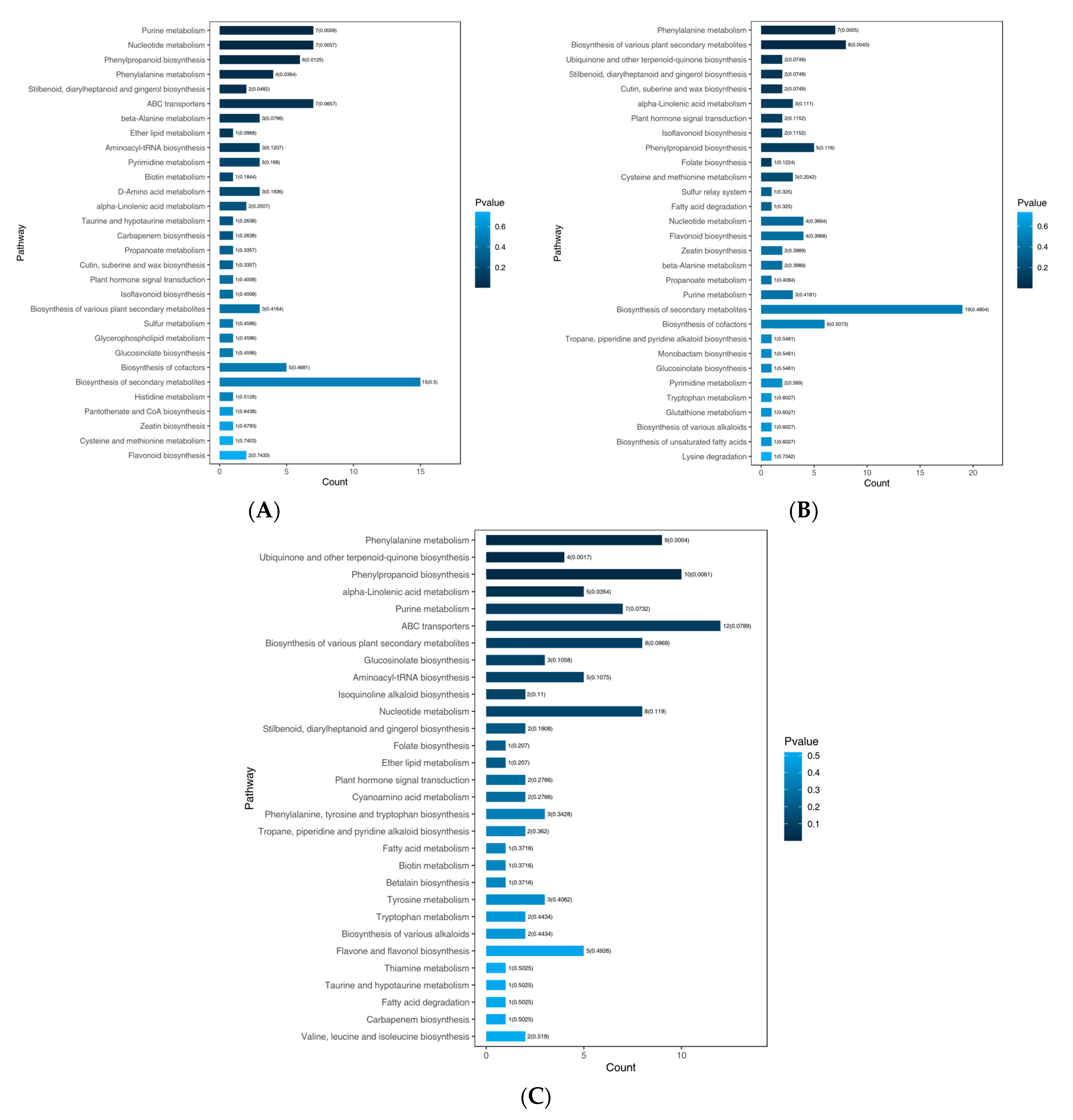
All DAMs of T. miqueliana flowers were annotated in the KEGG pathway database and subjected to enrichment analysis. There were 34, 41, and 65 pathways in BS vs. FS, FS vs. WS, and BS vs. WS, respectively (Table S3), the top 30 pathways in terms of p-value were displayed in Figure 6. The most common enrichments were metabolic pathways (ko01100) (the cluster frequency: 23/33, 69.70%, in BS vs. FS; 25/42, 59.52%, in FS vs. WS; 43/71, 60.56%, in BS vs. WS) and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites (ko01110) (the cluster frequency: 15/33, 45.45%, in BS vs. FS; 19/42, 45.24%, in FS vs. WS; 30/71,42.25%, in BS vs. WS) (Table S3).
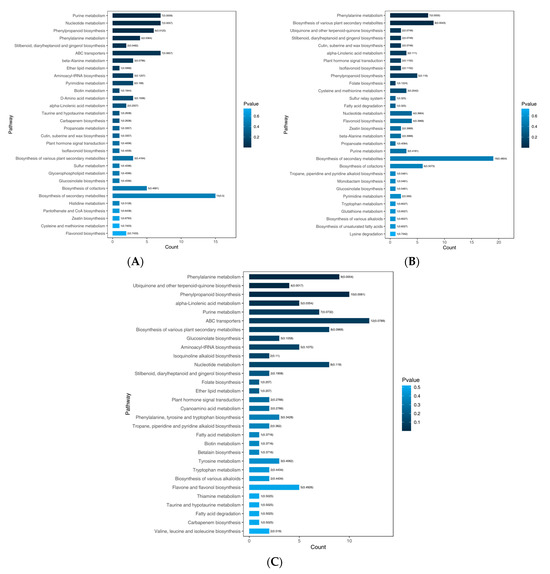
Figure 6.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of DAMs in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental periods. (A) BS vs. FS; (B) FS vs. WS; (C) BS vs. WS. BS: Bud Stage; FS: Full-blooming Stage; WS: Wilting Stage.
For BS vs. FS, the purine metabolism (ko00230), nucleotide metabolism (ko01232), phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (ko00940), phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360), stilbenoid, diarylheptanoid, and gingerol biosynthesis (ko00945) were significantly enriched (p < 0.05). In FS vs. WS, phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360) and biosynthesis of various plant secondary metabolites (ko00999) were significantly enriched (p < 0.05). And in BS vs. WS, phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360), ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis (ko00130), phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (ko00940), and alpha-linolenic acid metabolism (ko00592) were significantly enriched (p < 0.05).
It was worth noting that phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360) was significantly enriched (p < 0.05) in all pairwise comparisons, and showed extremely significant enrichment (p < 0.01) in FS vs. WS and BS vs. WS. L-phenylalanine (pme0021), as a precursor for the synthesis of phenylpropanoids in plants, leads to the biosynthesis of flavonoids and lignin. Flavonoid biosynthesis (ko00941) and isoflavonoid biosynthesis (ko00943)-enriched in the three pairwise comparisons. However, the flavone and flavonol biosynthesis (ko00944) was enriched in FS vs. WS and BS vs. WS, but not enriched in BS vs. FS, it might according to the regulation of flavonoid metabolic flux redirection during the developmental stages of T. miqueliana flowers.
3.6. Analysis of DAMs in Flavonoid Biosynthesis-Related Pathway
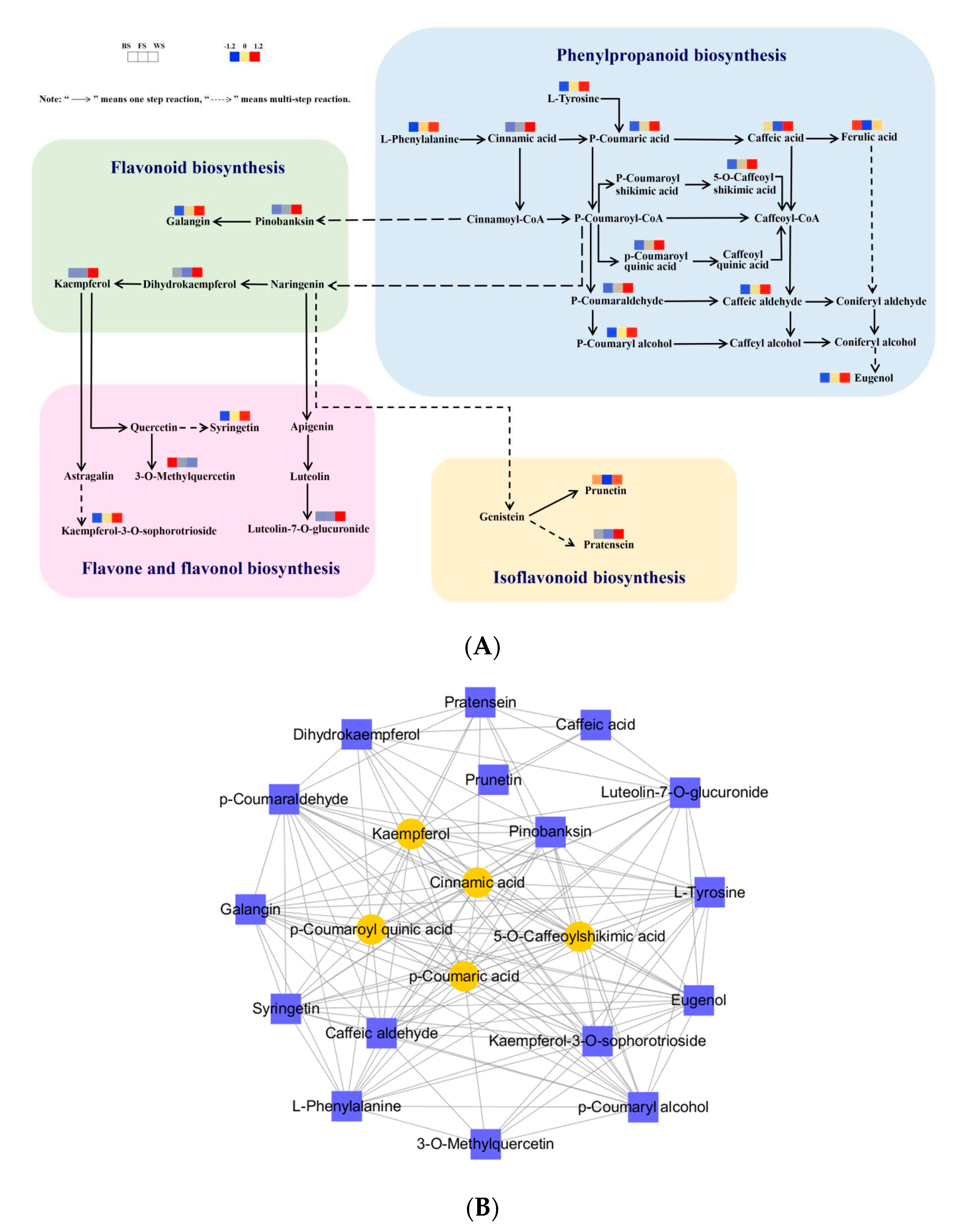
In this research, 22 DAMs of flavonoid biosynthesis-related pathways in pairwise comparisons were filtrated with enrichments and annotations in the KEGG pathway database. Flavonoid biosynthesis-related pathways of T. miqueliana flowers included phenylpropanoid biosynthesis (ko00940), flavonoid biosynthesis (ko00941), flavone and flavonol biosynthesis (ko00944), and isoflavonoid biosynthesis (ko00943).
In Figure 7A, L-Phenylalanine (pme0021) is the initial metabolite and can generate Cinnamic acid (mws2213), which can be hydroxylated and methylated several times to synthesize phenylpropanoids such as p-Coumaric acid (pme1439), Caffeic acid (mws2212), Ferulic acid (mws0014, isomer), and Eugenol (Lhhp120814). P-Coumaric acid (pme1439) can be converted to p-Coumaroyl-CoA, which is a central precursor of many flavonoids. Subsequently, in these pathways, further modifications lead to the synthesis of pinobanksin (mws0914) and naringenin (MWSHY0017, isomer) as part of the flavonoid biosynthesis. In addition, naringenin is an important metabolic shunt hub in flavonoid metabolism, as it divides the metabolic pathway into the following three branches: to generate Kaempferol (mws1068) after synthesizing Dihydrokaempferol (mws1094) in the flavonoid biosynthesis; to generate luteolin-7-O-glucuronide (mws4167) after synthesizing apigenin, which thus flows into the flavone and flavonol biosynthesis; and to enter the Isoflavonoid biosynthesis with the generation of Prunetin (mws0918) and Pratensein (pmp000548, isomer) after synthesizing Genistein.
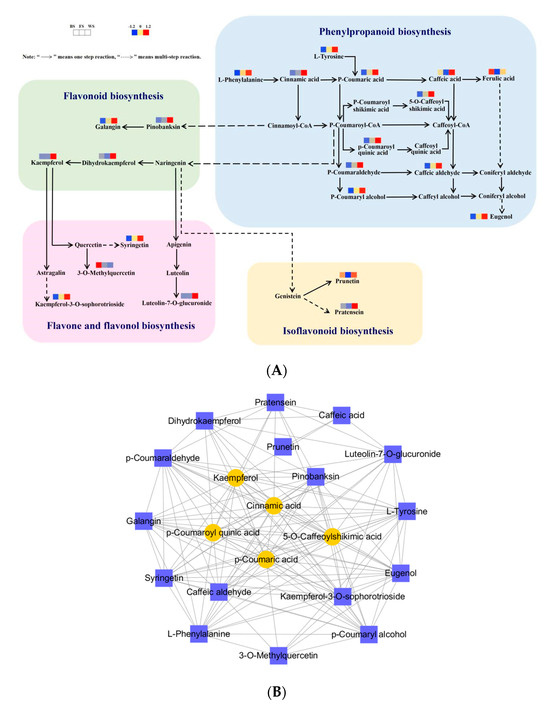
Figure 7.
DAMs analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis-related pathway in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages. (A) Metabolic pathways analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs; (B) correlation network diagram of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs, the core regulatory metabolites are represented by yellow ovals and other metabolites by purple squares.
To further visualize the synergistic regulatory relationships among the 22 flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs, a correlation network diagram was constructed based on the Pearson correlations (Figure 7B). Ferulic acid (mws0014, isomer) did not match the screening criteria and was filtered out. There were 134 pairs of positive correlations (cor > 0.8 and p < 0.05) and 7 pairs of negative correlations (cor < −0.8 and p < 0.05) were screened (Table S4). In the correlation network diagram, nodes represent metabolite (meta), and the highest connectivity was considered as the core regulatory metabolite (coremeta). In terms of the degree of correlations, Kaempferol (mws1068), Cinnamic acid (mws2213), p-Coumaric acid (pme1439), p-Coumaroyl quinic acid (pmb3074, isomer), and 5-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid (Hmln002806) had the highest degree of correlations with the other metabolites (degree = 17) (Table S5), so that could be defined as core metabolites that played essential roles in flavonoid biosynthesis in T. miqueliana flowers.
4. Discussion
Previous studies on metabolites of Tilia have mostly used traditional phytochemical methods to analyze specific primary or secondary metabolites in different species or tissues, such as sugars, terpenoids, alkaloids, flavonoids, and straight-chain alkanes [28]. Few metabolomics approaches have been carried out to explore the similarities and differences of metabolites in Tilia flowers during the development stages. Here, we utilized a widely targeted metabolomics technique to analyze metabolites in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages. This revealed the accumulation patterns and metabolic network involved in flavonoid biosynthesis, so as to lay a scientific foundation for the exploitation of T. miqueliana resources.
Phenylpropanoid metabolism generates more than 8000 aromatic compounds from phenylalanine, which is one of the end products of the shikimate pathway [29]. They are not only crucial mediators of plant pest resistance and play a significant role in how plants react to both biotic and abiotic stimuli, but also serve as indicators of how plants respond to changes in stress in the environment [30]. In this study, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis was significantly enriched during the development of T. miqueliana flowers. The contents of metabolites involved in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, such as p-Coumaric acid and Caffeic acid, increased significantly during flower development and reached the highest relative content at the Wilting Stage.
Flavonoids present specificity in plant tissues, development, and environmental factors in plant metabolism, participate in plant ecological defense, and serve as messengers in the reproductive process [31]. It has been proved that the developmental stage is one of the primary variables affecting the accumulation of secondary metabolism [32,33]. Research on Abelmoschus manihot flower showed that the total flavonoid content was significantly enriched during flower developmental stages and reached the peak at the Full-blooming Stage [34]. Our research showed that some flavonoids continuously increased in terms of relative content during the development of T. miqueliana flower. It might be attributed to the antioxidant properties of flavonoids that reduce oxidative damage brought by reactive oxygen species (ROS) during plant growth and development.
Furthermore, flavonoid accumulation in plants is also influenced by genetic regulation. Previous research focuses on key structural genes in flavonoid biosynthetic pathways in two cultivated species of Chimonanthus praecox (L.) Link flowers, showing that gene expression levels of CHS1, F3H1, FLS1, UFGT1 significantly affected the content of total flavonoids at three development stages [35]. Therefore, the variation of flavonoid content in T. miqueliana flowers at different development stages could be caused by the expression of flavonoid synthesis-related genes and the corresponding enzyme activities. In addition, the biosynthesis and accumulation of flavonoids are also closely related to relevant transcription factors, such as MYB [36], bHLH [37], WKRY [38], and WD40 [39].
Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis are important branches derived from the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. They originate from the reaction of p-coumaryl-CoA and three molecules of malonyl-CoA catalyzed by chalcone synthase (CHS) to generate naringenin chalcone [7,40]. After this, naringenin chalcone is converted to naringenin by chalcone isomerase (CHI), and naringenin as the common precursor can be further catalyzed to form flavones and flavonols [7]. We found that flavonols accounted for nearly half of the flavonoid compounds, while many flavonol DAMs present down-regulated in the BS vs. FS and BS vs. WS, suggesting that flavonol degradation occurs with the development of T. miqueliana flower. Similar phenomena have also been observed in other flowering plants. Flavonol content in sepals of Helleborus niger flowers decreased significantly during flower development and reached the lowest in non-pollinated and senescent pollinated flowers [41]. The content of total flavonols in the petals of the Rosa chinensis ‘Sun City’ increased from the unopened Bud Stage, reached a maximum at the semi-opened stage, and then continuously declined with the development of flowers [42]. Flavonol can affect pollen fertility, attract pollinators, as well as defend against pathogens and herbivores [43]. Therefore, flavonol content would be significantly higher in young floral organs with non-pollinated than in senescent floral organs that were pollinated.
In natural plants, flavonoids usually exist with their glycosides, such as glucoside, galactoside, arabinoside, rhamnoside, and rutinoside, flavonols with O-glycosides are one of the most common forms [44,45]. Herein, Kaempferol- and Quercetin-derived substances were the most abundant in flavonols of T. miqueliana flowers, frequently modified by different glycosidic bonds with glycosylation occurring, mainly at the positions of 3-O and 7-O. Our research results consistent with the previous studies confirmed that flavonoids such as Kaempferol, Quercetin, and their glycosides are the major components in flowers and leaves of some Tilia species [3,46,47,48]. Glycosylation contributes to the structural diversity and complexity of flavonoids, as well as the improvement of water solubility and stability [49], further altering bioactivity and bioavailability in vivo [50]. For instance, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside possesses anti-neuroinflammatory activity and could be considered a natural agent for treating neurodegenerative diseases [51]. Quercetin-3-O-arabinoside has a pronounced effect on α-glucosidase inhibitory that could be used for exploiting hypoglycemic nutraceuticals [52]. Thus, abundant flavonoids identified in T. miqueliana flowers will be an essential reference for the isolation of distinctive flavonoids in Tilia, together with physiological functions and biological activities research.
5. Conclusions
In this research, metabolites of T. miqueliana flowers at three developmental periods were explored for the first time through a widely targeted metabolomic technique. The metabolite profiles contained 1138 metabolites, and 288 DAMs were identified, flavonoids accounted for the largest proportion. KEGG enrichment analysis of DAMs showed different overlap and variability in metabolic pathways, contributing to the variability of metabolite profiles at different development stages. Based on the directions of flavonoid metabolic flux, we visualized the metabolic pathways of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs, further revealed regulatory relationships among them, and confirmed five core metabolites. Herein, the diversity and characteristics of metabolites along with the accumulation pattern of flavonoids were revealed, providing new insights into the scientific basis for the targeted exploitation of T. miqueliana. Nevertheless, the molecular mechanism of flavonoid biosynthesis and the biological functions of these metabolites during the development of T. miqueliana flowers need to be further researched.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f15101795/s1, Figure S1-a: Correlation of T. miqueliana flower samples; Figure S1-b: Correlation of QC samples; Table S1: 1138 metabolites detected in T. miqueliana flowers at different developmental stages; Table S2: DAMs in pairwise comparisons; Table S3: KEGG pathway enrichment of DAMs in pairwise comparisons; Table S4: Correlation analysis of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs with filtered threshold; Table S5: Connectivity degree of flavonoid biosynthesis-related DAMs with filtered threshold.
Author Contributions
W.B.: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Data Curation, and Writing—Original Draft. Y.S.: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—Review and Editing, and Funding Acquisition. J.C.V.: Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the “Jiangsu Provincial Agricultural Science and Technology Independent Innovation Fund” (CX(23)3142), from Jiangsu Provincial Department of Finance.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Radoglou, K.; Dobrowolska, D.; Spyroglou, G.; Nicolescu, V.N. A Review on the Ecology and Silviculture of Limes (Tilia cordata Mill., Tilia platyphyllos Scop. and Tilia tomentosa Moench.) in Europe. Romania. 2008. 29p. Available online: http://www.valbro.uni-freiburg.de/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Karioti, A.; Chiarabini, L.; Alachkar, A.; Chehna, M.F.; Vincieri, F.; Bilia, A. HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI-MS analyses of Tiliae flos and its preparations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Hernández, E.; González-Trujano, M.E.; Martínez, A.L.; Moreno, J.; Kite, G.; Terrazas, T.; Soto-Hernández, M. HPLC/MS analysis and anxiolytic-like effect of quercetin and kaempferol flavonoids from Tilia americana var. mexicana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosakowska, O.K.; Bączek, K.; Przybył, J.L.; Ejdys, M.; Kuźma, P.; Obiedziński, M.; Węglarz, Z. Intraspecific variability in the content of phenolic compounds, essential oil and mucilage of small-leaved lime (Tilia cordata Mill.) from Poland. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 78, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szucs, Z.; Cziaky, Z.; Kiss-Szikszai, A.; Sinka, L.; Vasas, G.; Gonda, S. Comparative metabolomics of Tilia platyphyllos Scop. bracts during phenological development. Phytochemistry 2019, 167, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, A.; Granica, S.; Popowski, D.; Malinowska, N.; Piwowarski, J.P. Tiliae flos metabolites and their beneficial influence on human gut microbiota biodiversity ex vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Rahman, S.U.; Bilal, M.; Huang, D. Role of flavonoids in plant interactions with the environment and against human pathogens—A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbach, R.J. Biochemistry and genetics of flower color. Plant Breed. Rev. 2005, 25, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaravarathan, S.; Kannaiyan, S. Role of plant flavonoids as signal molecules to Rhizobium. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 144–164. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, H.; Arici, A.; Simsek, O. Simsek, Flavonoids in Our Foods: A Short Review. J. Basic Clin. Health Sci. 2019, 3, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Gidaro, M.C.; Petzer, A.; Costa, G.; Guglielmi, P.; Chimenti, P.; Alcaro, S.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase: Biological and Molecular Modeling Studies on Selected Natural Flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9004–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, D.; Fornai, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Colucci, R.; Blandizzi, C.; Antonioli, L. Dietary flavonoids as a potential intervention to improve redox balance in obesity and related co-morbidities: A review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delnavazi, M.R.; \Shahabi, M.; Yassa, N. Flavonoids from the leaves of Iranian Linden; Tilia rubra subsp. caucasica. Res. J. Pharmacogn. 2015, 2, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.-M.; Lee, N.-H. A New Isoflavone Glycoside from the Stems of Tilia taquetii Schneider. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsuda, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Shimoda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Hepatoprotective principles from the flowers of Tilia argentea (Linden): Structure requirements of tiliroside and mechanisms of action. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Huang, X.; Yue, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, H. Analyses on diversity and variation of phenotypic traits of natural populations of Tilia miqueliana. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2021, 30, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, W.H.; Peng, C.Y.; Shen, Y.B.; Visscher, A.M.; Pritchard, H.W.; Gao, Q.; Sun, X.R.; Wang, M.Z.; Deng, Z. Effects of H2SO4, GA3, and cold stratification on the water content, coat composition, and dormancy release of Tilia miqueliana seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1240028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, H.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X. Analysis of flavonoid metabolism during the process of petal discoloration in three Malus Crabapple Cultivars. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 37304–37314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Liao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, R.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules 2020, 25, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Fan, L. Widely target metabolomics analysis of the differences in metabolites of licorice under drought stress. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 117071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hao, S.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, C.; Jia, G.; Chen, H. Widely targeted metabolomics analysis reveals the major metabolites in the hemp seeds from the longevity village of Bama, China. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 206, 117661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Gu, C.; He, S.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Widely targeted metabolomics analysis reveals new biomarkers and mechanistic insights on chestnut (Castanea mollissima Bl.) calcification process. Food Res Int. 2021, 141, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; Sun, W.; Yang, W.; He, R.; Wahab, A.-T.; et al. Metabolomics analysis reveals the accumulation patterns of flavonoids and phenolic acids in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) grains of different colors. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Duan, Y. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis of the Petals of Osmanthus fragrans ‘Yanzhi Hong’ in Different Developmental Phases. J. Northwest. Univ. 2022, 37, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, T.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; HUAng, H.; Xu, W.; Wei, H.; Gong, J.; Ni, S. Overview of Pharmacological Research on Tilia L. J. Anhui Agric. Sci 2014, 36, 12912–12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.-J. Multifaceted regulations of gateway enzyme phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Nagel, C.; Taylor, L.P. Biochemical complementation of chalcone synthase mutants defines a role for flavonols in functional pollen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7213–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Bonfill, M.; Fattahi, B.; Torras-Claveria, L.; Sefidkon, F.; Cusido, R.M.; Palazon, J. Secondary metabolites profiling of Dracocephalum kotschyi Boiss at three phenological stages using uni- and multivariate methods. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2016, 3, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Liu, X.-T.; Feng, W.-T.; Chen, S.-S.; Xu, L.-F.; Wang, Z.-G.; Zhang, J.-L.; Li, P.-M.; Ma, F.-W. Different biosynthesis patterns among flavonoid 3-glycosides with distinct effects on accumulation of other flavonoid metabolites in pears (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ye, G.-Y.; Liu, H.-L.; Wang, Z.-H. New insights on Abelmoschus manihot flower development: Dynamic changes of flavonoids based on a metabolomic approach. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Aslam, M.Z.; Yu, L.; Chen, L. Comprehensive analysis of wintersweet flower reveals key structural genes involved in flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Gene 2018, 676, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.-J.; Song, A.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. Comparative transcriptome analysis and flavonoid profiling of floral mutants reveals CmMYB11 regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in chrysanthemum. Plant Sci. 2023, 336, 111837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.-S.; Ni, R.; Wang, P.-Y.; Gao, S.; Lou, H.-X.; Cheng, A.-X. Functional characterization of a liverworts bHLH transcription factor involved in the regulation of bisbibenzyls and flavonoids biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunewald, W.; de Smet, I.; Lewis, D.R.; Löfke, C.; Jansen, L.; Goeminne, G.; Vanden Bossche, R.; Karimi, M.; de Rybel, B.; Vanholme, B.; et al. Transcription factor WRKY23 assists auxin distribution patterns during Arabidopsis root development through local control on flavonol biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H. Functional Characterization of One CsWD40 Gene Involved in Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Tea Plants. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Le Roy, J.; Huss, B.; Creach, A.; Hawkins, S.; Neutelings, G. Neutelings, Glycosylation Is a Major Regulator of Phenylpropanoid Availability and Biological Activity in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitzer, V.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Stampar, F. Sepal phenolic profile during Helleborus niger flower development. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Ahmad, S.; Tang, A.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Q. Flavonols and Carotenoids in Yellow Petals of Rose Cultivar (Rosa ‘Sun City’): A Possible Rich Source of Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.Q.; Lin, H.X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veitch, N.C.; Grayer, R.J. Flavonoids and their glycosides, including anthocyanins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 1626–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Muzashvili, T.S.; Georgiev, M.I. Advances in the biotechnological glycosylation of valuable flavonoids. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, G.; Santi, D.; Tabach, R. Flavonol glycosides found in hydroethanolic extracts from Tilia cordata, a species utilized as anxiolytics. Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2013, 15, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P.; Mauri, P.; Bruno, A.; Zini, L. High-performance liquid chromatography and micellar electrokinetic chromatography of flavonol glycosides from Tilia. J. Chromatogr. A 1993, 638, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaja, M.; Pawłowska, K.A.; Józefczyk, K.; Pruś, A.; Stefańska, J.; Granica, S. UHPLC-DAD-MS/MS analysis of extracts from linden flowers (Tiliae flos): Differences in the chemical composition between five Tilia species growing in Europe. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 154, 112691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Pozzo, T.; Liu, J.; Ara, K.Z.G.; Turner, C.; Karlsson, E.N. Substituent Effects on in Vitro Antioxidizing Properties, Stability, and Solubility in Flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Jiang, Y. New insights on bioactivities and biosynthesis of flavonoid glycosides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, D.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; et al. Bioactive Phenols as Potential Neuroinflammation Inhibitors from the Leaves of Xanthoceras Sorbifolia Bunge. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5018–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashchenko, N.I.; Olennikov, D.N.; Chirikova, N.K. Metabolites of Geum aleppicum and Sibbaldianthe bifurca: Diversity and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Potential. Metabolites 2023, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).