Yield and Survival of 19 Cultivars of Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops over Eight Rotations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
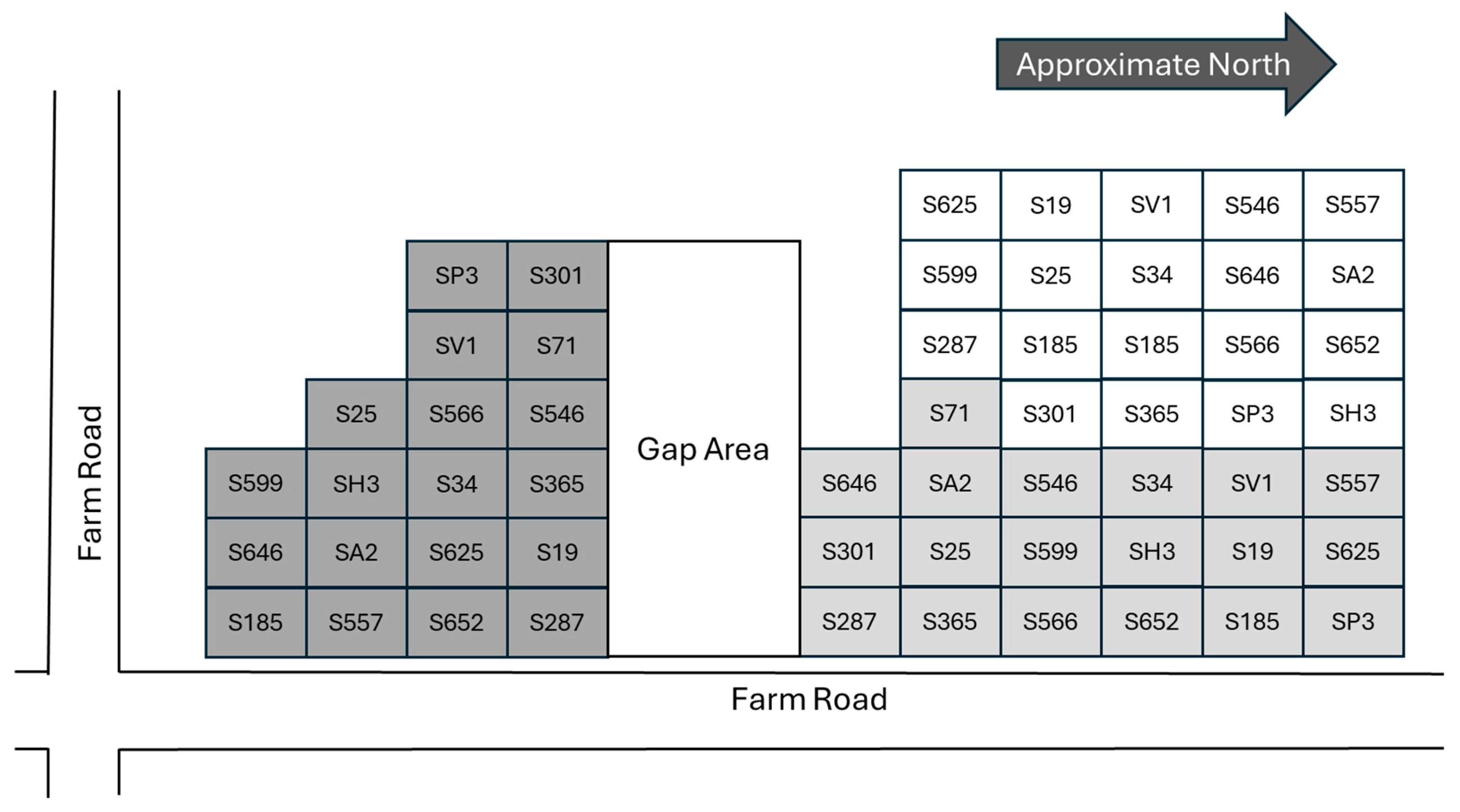
2.1. Trial Description
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
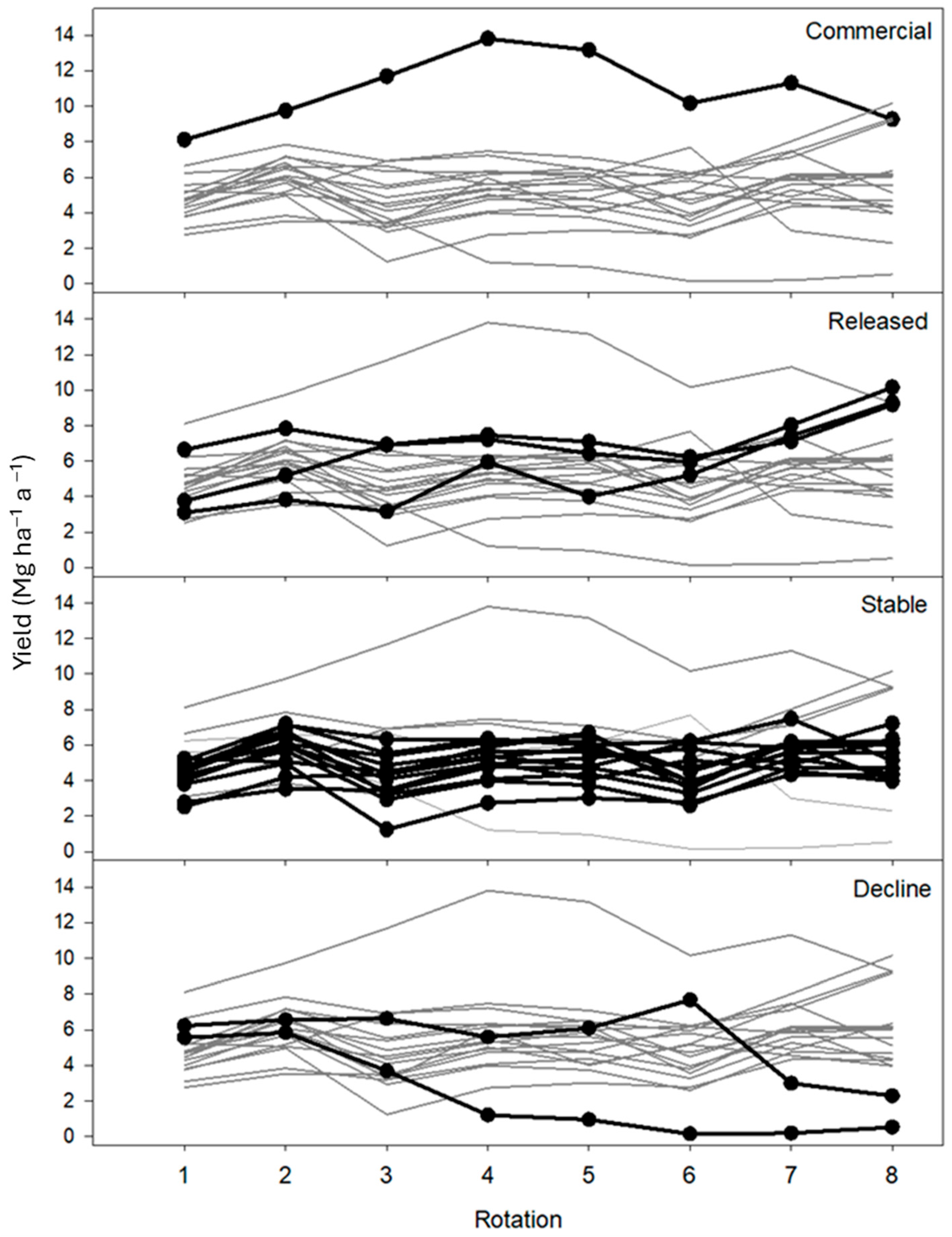
3.1. Biomass Yield and Climate Data over Eight Rotations
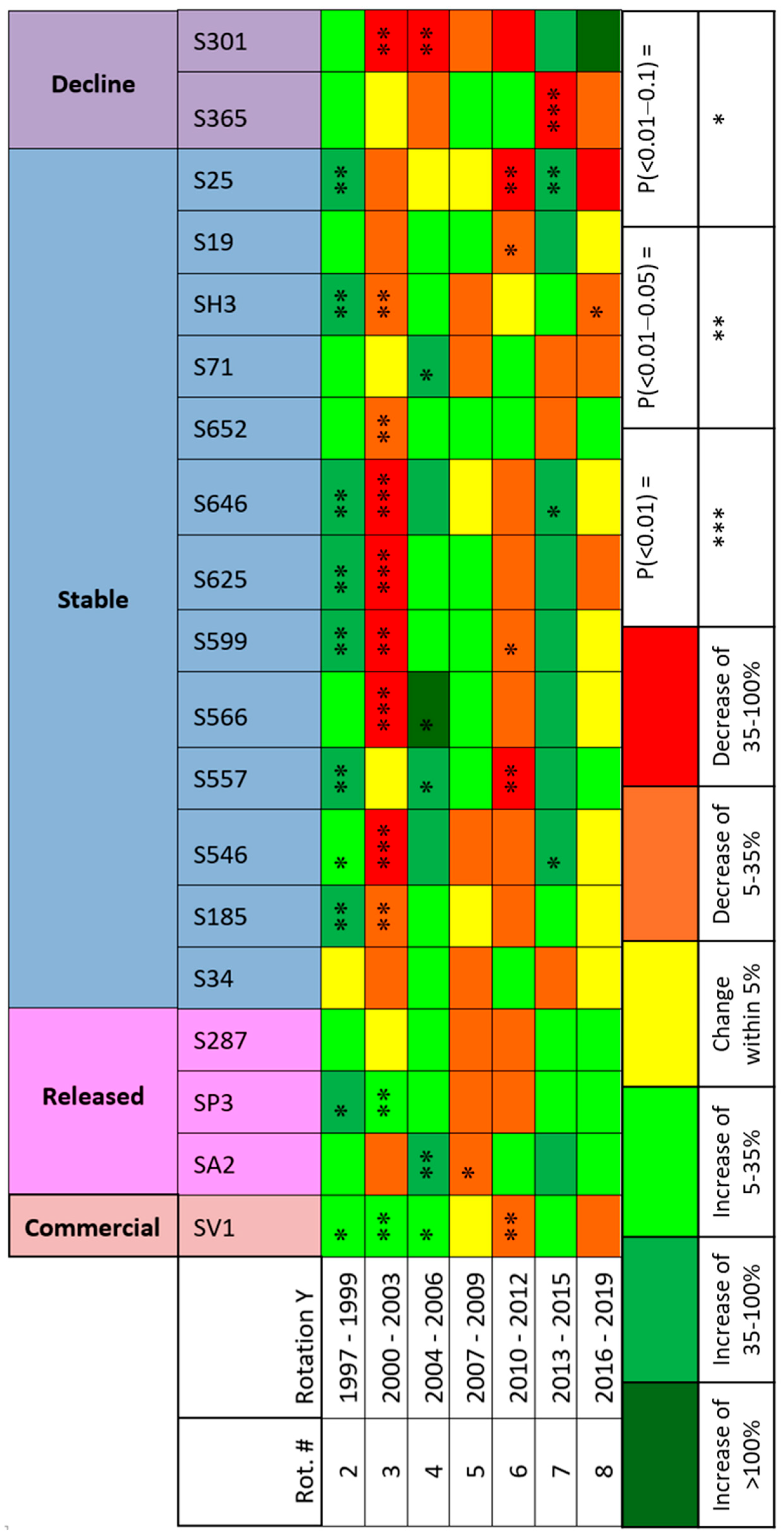
3.2. Relative Biomass
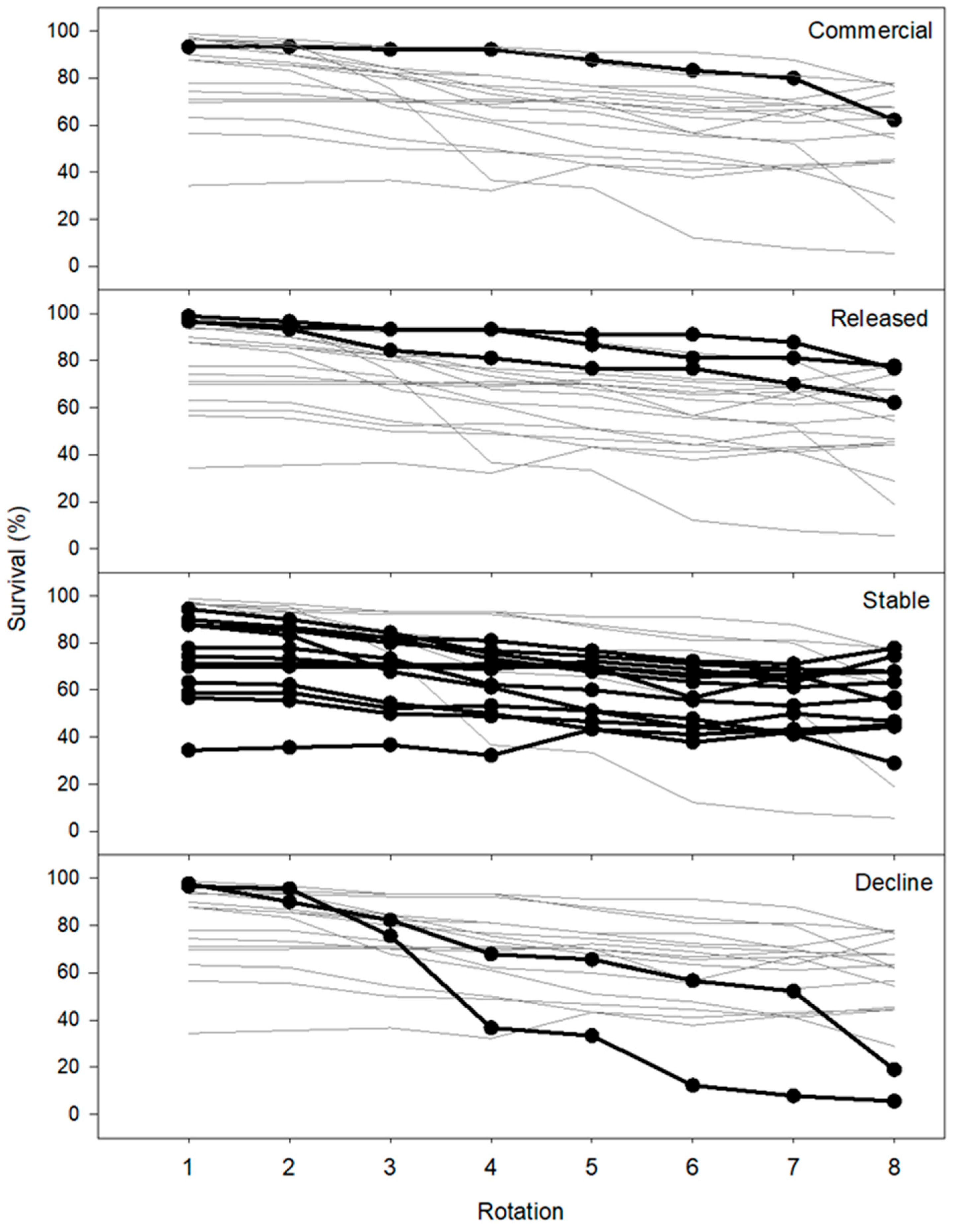
3.3. Willow Survival
3.4. Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Cohort | Cultivars | N | Yield | Relative Yield 2–8 | Survival | First Rotation with <80% Survival | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd–8th | Average | 95% CI | 1st | Mean | 8th | ||||
| Mg ha−1 a−1 | Proportion | Percent | ||||||||
| All cultivars | All | 456 | 5.16 | 5.91 | 1.233 | ±0.048 | 80.9 | 67.4 | 54.9 | 2 |
| Commercial | SV1 | 24 | 8.93 | 12.16 | 1.360 | ±0.096 | 93.3 | 85.5 | 62.0 | 8 |
| Release | S287 | 24 | 7.32 | 8.00 | 1.167 | ±0.142 | 96.7 | 80.1 | 62.3 | 5 |
| SP3 | 24 | 4.14 | 7.51 | 1.978 | ±0.297 | 99.0 | 88.5 | 77.7 | 8 | |
| SA2 | 24 | 3.42 | 5.88 | 1.759 | ±0.292 | 96.7 | 90.5 | 76.3 | 8 | |
| Stable | SH3 | 24 | 4.89 | 6.73 | 1.394 | ±0.122 | 87.7 | 58.5 | 29.0 | 3 |
| S19 | 24 | 5.25 | 6.27 | 1.241 | ±0.160 | 87.7 | 76.5 | 67.7 | 4 | |
| S185 | 24 | 5.14 | 6.17 | 1.245 | ±0.141 | 90.0 | 73.5 | 63.3 | 4 | |
| S25 | 24 | 5.63 | 6.09 | 1.120 | ±0.135 | 94.7 | 74.1 | 54.7 | 4 | |
| S652 | 24 | 5.29 | 5.71 | 1.153 | ±0.173 | 88.0 | 79.3 | 78.0 | 5 | |
| S557 | 24 | 2.78 | 5.78 | 2.079 | ±0.225 | 56.7 | 48.4 | 44.3 | 1 | |
| S34 | 24 | 5.77 | 5.77 | 1.066 | ±0.134 | 74.3 | 69.6 | 67.7 | 1 | |
| S599 | 24 | 4.91 | 5.70 | 1.224 | ±0.136 | 70.3 | 69.6 | 74.3 | 1 | |
| S646 | 24 | 4.39 | 5.30 | 1.226 | ±0.128 | 63.7 | 50.4 | 44.7 | 1 | |
| S625 | 24 | 5.26 | 4.81 | 0.939 | ±0.115 | 71.0 | 69.6 | 68.0 | 1 | |
| S71 | 24 | 3.04 | 4.57 | 1.498 | ±0.160 | 36.7 | 38 | 45.7 | 1 | |
| S546 | 24 | 4.72 | 4.33 | 0.940 | ±0.145 | 77.7 | 64.6 | 56.7 | 1 | |
| S566 | 24 | 4.20 | 3.56 | 0.843 | ±0.122 | 59.0 | 51.0 | 46.7 | 1 | |
| Decline | S365 | 24 | 6.87 | 5.91 | 1.233 | ±0.049 | 98.0 | 66.5 | 19.0 | 2 |
| S301 | 24 | 6.12 | 1.97 | 0.327 | ±0.144 | 97.0 | 45.5 | 5.3 | 3 | |

References
- Volk, T.A.; Heavey, J.P.; Eisenbies, M.H. Advances in Shrub-Willow Crops for Bioenergy, Renewable Products, and Environmental Benefits. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therasme, O.; Volk, T.A.; Eisenbies, M.H.; Amidon, T.E.; Fortier, M.-O. Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Ethanol Produced via Fermentation of Sugars Derived from Shrub Willow (Salix ssp.) Hot Water Extraction in the Northeast United States. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullerdiek, N.; Neuling, U.; Kaltschmitt, M. A GHG Reduction Obligation for Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) in the EU and in Germany. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2021, 92, 102020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, H. Sustainable Aviation Fuel: Agencies Should Track Progress toward Ambitious Federal Goals; Government Accounting Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Energy. 2023 Billion-Ton Report 2024: An Assessment of U.S. Renewable Carbon Resources; ORNL/SPR-2024/3103; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, E.S.; Volk, T.A.; Miller, R.O.; Serapiglia, M.J.; Kemanian, A.R.; Montes, F.; Kuzovkina, Y.A.; Kling, G.J.; Smart, L.B. Contributions of Environment and Genotype to Variation in Shrub Willow Biomass Composition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Energy. 2016 Billion-Ton Report: Advancing Domestic Resources for a Thriving Bioeconomy, Volume 1: Economic Availability of Feedstocks; ORNL/TM-2016/160; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.R.; Brown, T.R.; Volk, T.A.; Heavey, J.P.; Malmsheimer, R.W. A Stochastic Techno-Economic Analysis of Shrub Willow Production Using EcoWillow 3.0S. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2018, 12, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.; Therasme, O.; Volk, T.A.; Brown, T.; Malmsheimer, R.W.; Fortier, M.-O.; Eisenbies, M.H.; Ha, H.; Heavey, J. Integrated Stochastic Life Cycle Assessment and Techno-Economic Analysis for Shrub Willow Production in the Northeastern United States. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Volk, T.; Fortier, M.-O. Willow Biomass Crops Are a Carbon Negative or Low-Carbon Feedstock Depending on Prior Land Use and Transportation Distances to End Users. Energies 2020, 13, 4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, J.; Balogh, S.B.; Volk, T.A.; Johnson, L.; Puettmann, M.; Lippke, B.; Oneil, E. Incorporating Uncertainty into a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Model of Short-Rotation Willow Biomass (Salix spp.) Crops. BioEnergy Res. 2013, 7, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.A.; Berguson, B.; Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.D.; Miller, R.; Rials, T.G.; Abrahamson, L.P.; Buchman, D.; Buford, M.; Cunningham, M.W.; et al. Poplar and Shrub Willow Energy Crops in the United States: Field Trial Results from the Multiyear Regional Feedstock Partnership and Yield Potential Maps Based on the PRISM-ELM Model. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, N.J.; Volk, T.A. Recently Bred Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops Show Stable Yield Trends Over Three Rotations at Two Sites. BioEnergy Res. 2016, 9, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, N.J.; Volk, T.A.; Johnson, G.A.; Eisenbies, M.H.; Shi, S.; Fabio, E.S.; Pooler, P.S. Change in Yield Between First and Second Rotations in Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops Is Strongly Related to the Level of First Rotation Yield. BioEnergy Res. 2016, 9, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi Nissim, W.; Pitre, F.E.; Teodorescu, T.I.; Labrecque, M. Long-Term Biomass Productivity of Willow Bioenergy Plantations Maintained in Southern Quebec, Canada. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 56, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.U.; Jørgensen, U.; Kjeldsen, J.B.; Lærke, P.E. Long-Term Yield Effects of Establishment Method and Weed Control in Willow for Short Rotation Coppice (SRC). Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Mola-Yudego, B.; Dimitriou, I.; Aronsson, P.; Murphy, R. Environmental Assessment of Energy Production Based on Long Term Commercial Willow Plantations in Sweden. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarski, M.J.; Szczukowski, S.; Tworkowski, J.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Załuski, D. Willow Production during 12 Consecutive Years—The Effects of Harvest Rotation, Planting Density and Cultivar on Biomass Yield. GCB Bioenergy 2019, 11, 635–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzovkina, Y.A.; Schulthess, C.P.; Zheng, D. Influence of Soil Chemical and Physical Characteristics on Willow Yield in Connecticut. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayama, H.; Uemura, A.; Utsugi, H.; Han, Q.; Kitao, M.; Maruyama, Y. The Effects of Weather, Harvest Frequency, and Rotation Number on Yield of Short Rotation Coppice Willow over 10 Years in Northern Japan. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njakou Djomo, S.; Ac, A.; Zenone, T.; De Groote, T.; Bergante, S.; Facciotto, G.; Sixto, H.; Ciria Ciria, P.; Weger, J.; Ceulemans, R. Energy Performances of Intensive and Extensive Short Rotation Cropping Systems for Woody Biomass Production in the EU. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talagai, N.; Marcu, M.V.; Zimbalatti, G.; Proto, A.R.; Borz, S.A. Productivity in Partly Mechanized Planting Operations of Willow Short Rotation Coppice. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 138, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrochers, V.; Frenette-Dussault, C.; Guidi Nissim, W.; Brisson, J.; Labrecque, M. Using Willow Microcuttings for Ecological Restoration: An Alternative Method for Establishing Dense Plantations. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 151, 105859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, D.R.; Goldsworthy, M.; Smith, P. Are Biomass Feedstocks Sustainable? A Systematic Review of Three Key Sustainability Metrics. GCB Bioenergy 2024, 16, e13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, B.; Volk, T.; Tharakan, P.; Nowak, C.; Phillipon, S.; Abrahamson, L.; White, E. Clone Site Testing and Selections for Scale up Plantings: Final Report to US Department of Energy; SUNY-ESF: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA Climate Data Online. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/cdo-web/ (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- NDMC; USDA; NOAA. US Drought Monitor. Available online: https://www.drought.gov/data-maps-tools/us-drought-monitor (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Jochner, M.; Bugmann, H.; Nötzli, M.; Bigler, C. Tree Growth Responses to Changing Temperatures across Space and Time: A Fine-Scale Analysis at the Treeline in the Swiss Alps. Trees 2018, 32, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.G. Temperature and Tree Growth. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climate Smart Farming. CSF Growing Degree Day Calculator. Available online: http://climatesmartfarming.org/tools/csf-growing-degree-day-calculator/ (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Yankee Publishing Company. Almanac. Available online: https://www.almanac.com/gardening/planting-calendar/NY/Tully (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- McCracken, A.R.; Walsh, L.; Moore, P.J.; Lynch, M.; Cowan, P.; Dawson, M.; Watson, S. Yield of Willow (Salix spp.) Grown in Short Rotation Coppice Mixtures in a Long-Term Trial. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2011, 159, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, A.R.; Dawson, W.M.; Bowden, G. Yield Responses of Willow (Salix) Grown in Mixtures in Short Rotation Coppice (SRC). Biomass Bioenergy 2001, 21, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarski, M.J.; Szczukowski, S.; Tworkowski, J.; Krzyżaniak, M.; Załuski, D. Willow Biomass and Cuttings’ Production Potential over Ten Successive Annual Harvests. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 105, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberacki, D.; Kocięcka, J.; Stachowski, P.; Rolbiecki, R.; Rolbiecki, S.; Sadan, H.A.; Figas, A.; Jagosz, B.; Wichrowska, D.; Ptach, W.; et al. Water Needs of Willow (Salix L.) in Western Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.F.; Abrahamson, L.P.; White, E.H.; Volk, T.A.; Nowak, C.A.; Fillhart, R.C. Willow Biomass Production during Ten Successive Annual Harvests. Biomass Bioenergy 2001, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willebrand, E.; Ledin, S.; Verwijst, T. Willow Coppice Systems in Short Rotation Forestry: Effects of Plant Spacing, Rotation Length and Clonal Composition on Biomass Production. Biomass Bioenergy 1993, 4, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Takeda, F.; Kramer, E.A.; Ashrafi, H.; Hunter, J. 3D Point Cloud Data to Quantitatively Characterize Size and Shape of Shrub Crops. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, G. Determinants of Forest Stand Productivity. In Proceedings—A Symposium on Principles of Maintaining Productivity on Prepared Sites; USDA Forest Service: Starkville, MS, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J. Cumulative Effects of Silvicultural Technology on Sustained Forest Productivity. In Assessing the Effects of Silvicultural Practices on Sustained Productivity, Proceedings of the e IEA/BE Workshop ‘93, Fredericton, NB, Canada, 16–22 May 1993; Canadian Forest Service—Maritimes Region, Natural Resources Canada: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1994; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Skovsgaard, J.P.; Vanclay, J.K. Forest Site Productivity: A Review of Spatial and Temporal Variability in Natural Site Conditions. Forestry 2013, 86, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsgaard, J.P.; Vanclay, J.K. Forest Site Productivity: A Review of the Evolution of Dendrometric Concepts for Even-Aged Stands. Forestry 2008, 81, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, L.; Volk, T.; Lin, J.; Kopp, R.; Phillips, I.; Cameron, K.; White, R.; Abrahamson, L. Genetic Improvement of Shrub Willow (Salix spp.) Crops for Bioenergy, Bioproducts, and Environmental Applications. Unasylva 2005, 56, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbies, M.H.; Volk, T.A.; Espinoza, J.; Gantz, C.; Himes, A.; Posselius, J.; Shuren, R.; Stanton, B.; Summers, B. Biomass, Spacing and Planting Design Influence Cut-and-Chip Harvesting in Hybrid Poplar. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 106, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.A.; Spinelli, R.; Eisenbies, M.; Clark, R.; Emerson, R.; Frank, J.; Hallen, K.; Therasme, O.; Webb, E. Harvesting Systems for Short Rotation Coppice Crops Influence Cost, Performance, and Biomass Quality. In Handbook of Biorefinery Research and Technology; Bisaria, V., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–31. ISBN 978-94-007-6724-9. [Google Scholar]

| Cultivar | Species | Origin 1 |
|---|---|---|
| SV1 | S. dasyclados | OMNR |
| SA2 | S. alba | OMNR |
| SP3 | S. pupurea | OMNR |
| S287 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S34 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S185 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S546 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S557 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S566 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S599 | S. eriocephala x petiolaris | U of T |
| S625 | S. eriocephala x interior | U of T |
| S646 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S652 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S71 | S. petiolaris x eriocephala | U of T |
| SH3 | S. pupurea | OMNR |
| S19 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S25 | S. eriocephala | U of T |
| S365 | S. discolor | U of T |
| S301 | S. interior x eriocephala | U of T |
| Growing Degree Days (Base 10 °C) a | Recorded Droughts b | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotation Number | Rotation Length (Years) | Mean Seasonal GDD (18 May–30 September) | Seasonal GDD Relative to the 30-Year Average (%) | Mean Early Season GDD (18 May–30 June) | Early Season GDD Relative to the 30-Year Average (%) | Early Growing Season Droughts | Early Season Drought Length | Growing Season Droughts | Drought Length (Months) | % Cultivar Increased Production |
| 1 | 3 | 1017 | 98.1 | 306 | 104.7 | 1 (1995) | full early season | 1 (1995) | April to October (7 months) | N/A |
| 2 | 3 | 1043 | 100.5 | 302 | 103.5 | 1 (1999) | full early season | 1 (1999) | mid-May to September (4.5 months) | 95% |
| 3 | 4 | 994 | 95.9 | 257 | 88.2 | 1 (2001) | mid-May to early June | 1 (2001) | mid-May to early June (1.5 months) | 21% |
| 4 | 3 | 1064 | 102.7 | 287 | 98.5 | 0 | N/A | 0 | N/A | 84% |
| 5 | 3 | 987 | 95.2 | 287 | 98.2 | 0 | N/A | 1 (2007) | late August to mid-September (<1 month) | 84% |
| 6 | 3 | 1173 | 113.1 | 354 | 121.3 | 0 | N/A | 2 (2011, 2012) | Late July to September (2011), Early July to October (2012) (6 months combined) | 32% |
| 7 | 3 | 1059 | 102.2 | 304 | 104.2 | 0 | N/A | 0 | N/A | 79% |
| 8 | 4 | 1089 | 105.0 | 287 | 98.3 | 1 (2016) | late June | 1 (2016) | Late June to October (4 months) | 47% |
| Scenarios | Cultivars | N | Yield | Relative Yield 2–8 | Survival | First Rotation with <80% Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd–8th | Mean | 95% CI | 1st | Mean | 8th | |||||
| Mg ha−1 a−1 | Proportion | ||||||||||
| All | All cultivars combined | 19 cultivars | 456 | 5.16 (0.23) | 5.91 (0.13) | 1.233 (0.030) | ±0.048 * | 80.9 (2.6) | 67.4 (1.0) | 54.9 (2.9) | 2 |
| Patterns | Commercial | SV1 | 24 | 8.93 A (0.11) | 12.16 A (0.51) | 1.360 B (0.056) | ±0.096 * | 93.3 A (3.8) | 85.5 A (2.5) | 62.0 AB (4.9) | 8 |
| Released | S287, SA2, SP3 | 72 | 4.96 CD (0.73) | 7.13 B (0.25) | 1.635 A (0.094) | ±0.157 * | 97.4 A (1.0) | 86.4 A (1.4) | 72.1 A (3.7) | 7 | |
| Stable > 80 sur | 5 cultivars | 120 | 5.24 C (0.28) | 6.19 C (0.15) | 1.231 B (0.038) | ±0.064 * | 89.6 A (1.7) | 72.4 B (1.5) | 58.5 AB (5.1) | 3 | |
| Stable < 80 sur | 8 cultivars | 192 | 4.38 D (0.29) | 4.98 D (0.13) | 1.227 B (0.042) | ±0.069 * | 63.5 B (3.9) | 57.6 C (1.3) | 56.0 B (3.3) | 1 | |
| Decline | S365, S301 | 48 | 6.50 B (0.36) | 3.92 E (0.50) | 0.595 C (0.074) | ±0.124 * | 97.5 A (0.5) | 56.0 C (4.8) | 12.2 C (5.9) | 3 | |
| a priori | Top 3 Initial Yield | SV1, S287, S365 | 72 | 7.71 (0.50) | 8.68 (0.44) | 1.130 (0.051) | ±0.085 * | 96.0 (1.4) | 77.4 (2.4) | 47.8 (8.2) | 5 |
| >80% Initial Survival | See below | 264 | 5.73 (0.31) | 6.58 (0.19) | 1.237 (0.041) | ±0.068 * | 93.5 (1.1) | 74.4 (1.4) | 54.1 (4.5) | 6 | |
| Top 3 Initial Survival | SP3, S365, S301 | 72 | 5.71 (0.51) | 5.12 (0.41) | 1.056 (0.112) | ±0.186 NS | 98.0 (0.5) | 66.8 (3.7) | 34.0 (11.6) | 4 | |
| a posteriori | Top 3 Mean Yield | SV1, S287, SP3 | 72 | 6.80 (0.82) | 9.22 (0.35) | 1.502 (0.079) | ±0.131 * | 96.3 (1.5) | 84.7 (1.6) | 67.3 (3.5) | 7 |
| Top 3 Mean Survival | SA2, SP3, SV1 | 72 | 5.50 (0.90) | 8.52 (0.43) | 1.799 (0.088) | ±0.146 * | 96.3 (1.5) | 88.2 (1.1) | 72.0 (3.5) | 8 | |
| Top 3 Ending Survival | S652, SP3, SA2 | 72 | 4.28 (0.42) | 6.37 (0.24) | 1.630 (0.097) | ±0.161 * | 94.6 (2.5) | 86.1 (1.1) | 77.3 (2.1) | 8 | |
| Single Cultivars | SP3 | SP3 | 24 | 4.14 (0.76) | 7.51 (0.34) | 1.978 (0.172) | ±0.297 * | 99.0 (1.0) | 88.5 (1.7) | 77.7 (2.3) | 8 |
| S365 | S365 | 24 | 6.87 (0.53) | 5.91 (0.13) | 0.863 (0.090) | ±0.156 NS | 98.0 (1.0) | 66.5 (5.1) | 19.0 (10.7) | 2 | |
| S301 | S301 | 24 | 6.12 (0.50) | 1.97 (0.50) | 0.327 (0.084) | ±0.144 * | 97.0 (0.0) | 45.5 (7.7) | 5.3 (3.9) | 3 | |
| Stable > 80 | S652, S185, S19, SH3, S25 | ||||||||||
| Stable < 80 | S557, S646, S34, S599, S546, S625, S566, S71 | ||||||||||
| Survival > 80 | SP3, S365, S301, SA2, S287, S25, SV1, S185, S652, SH3, S19 | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santucci, S.; Eisenbies, M.; Volk, T. Yield and Survival of 19 Cultivars of Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops over Eight Rotations. Forests 2024, 15, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15112041
Santucci S, Eisenbies M, Volk T. Yield and Survival of 19 Cultivars of Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops over Eight Rotations. Forests. 2024; 15(11):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15112041
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantucci, Shane, Mark Eisenbies, and Timothy Volk. 2024. "Yield and Survival of 19 Cultivars of Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops over Eight Rotations" Forests 15, no. 11: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15112041
APA StyleSantucci, S., Eisenbies, M., & Volk, T. (2024). Yield and Survival of 19 Cultivars of Willow (Salix spp.) Biomass Crops over Eight Rotations. Forests, 15(11), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15112041







