Differential Responses of Tree Species to Elevated Ozone and Increasing Air Temperature: Implications for Foliar Functional Traits, Carbon Sequestration, and Their Relationship Under Mixed Planting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
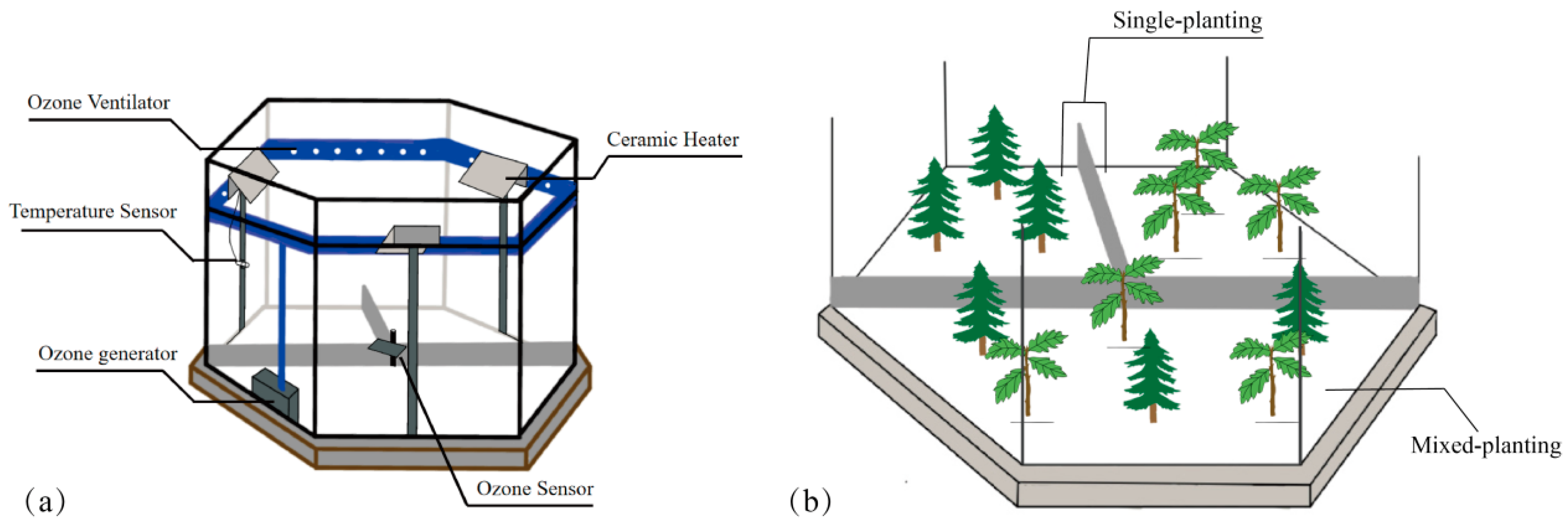
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Study Species
2.3. Leaf Functional Traits and Carbon Sequestration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
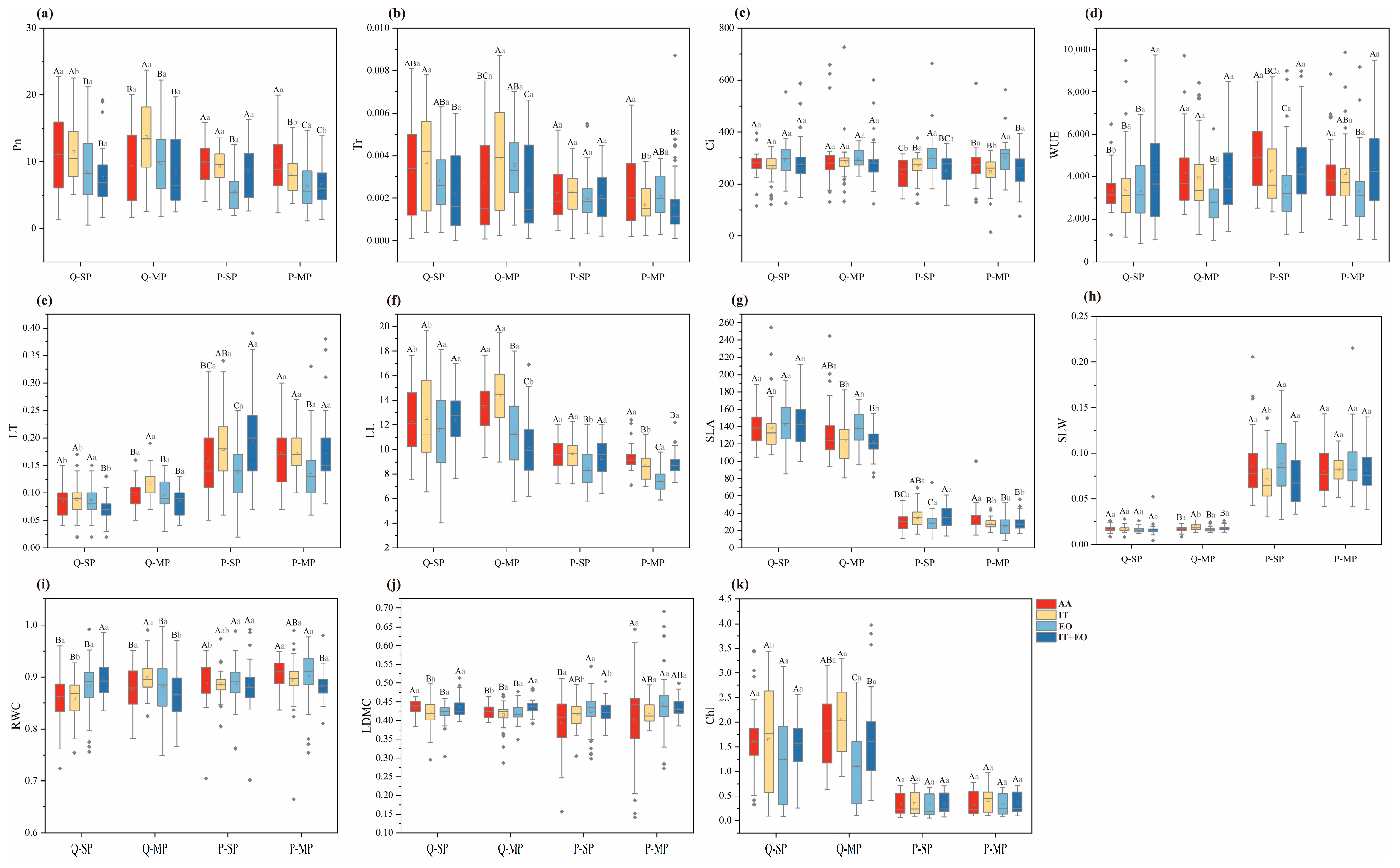
3.1. Effects of Different Planting Patterns of Tree Species on Carbon Sequestration Under Increasing Temperature and Elevated O3
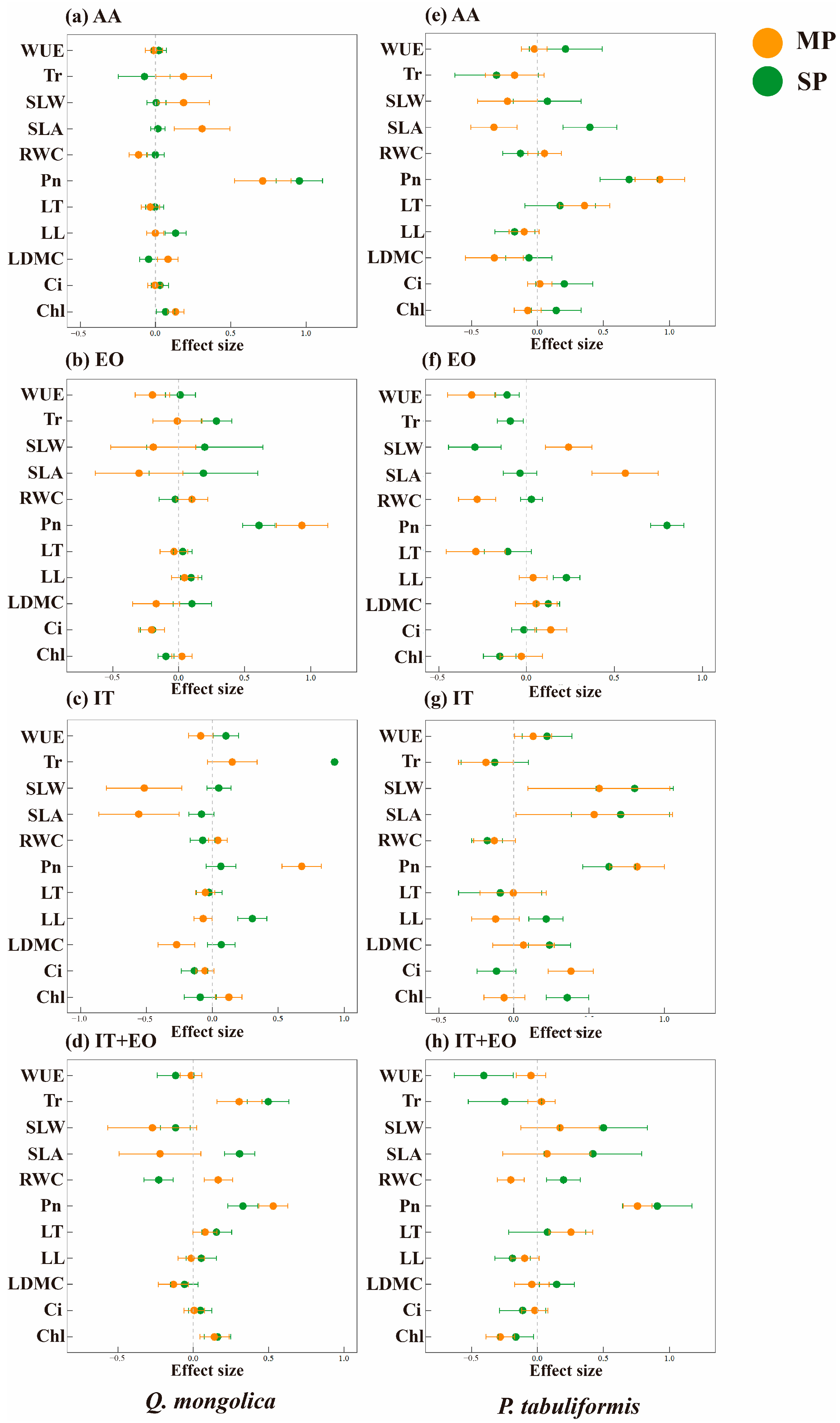
3.2. Relationship Between Plant Functional Traits and Carbon Sequestration
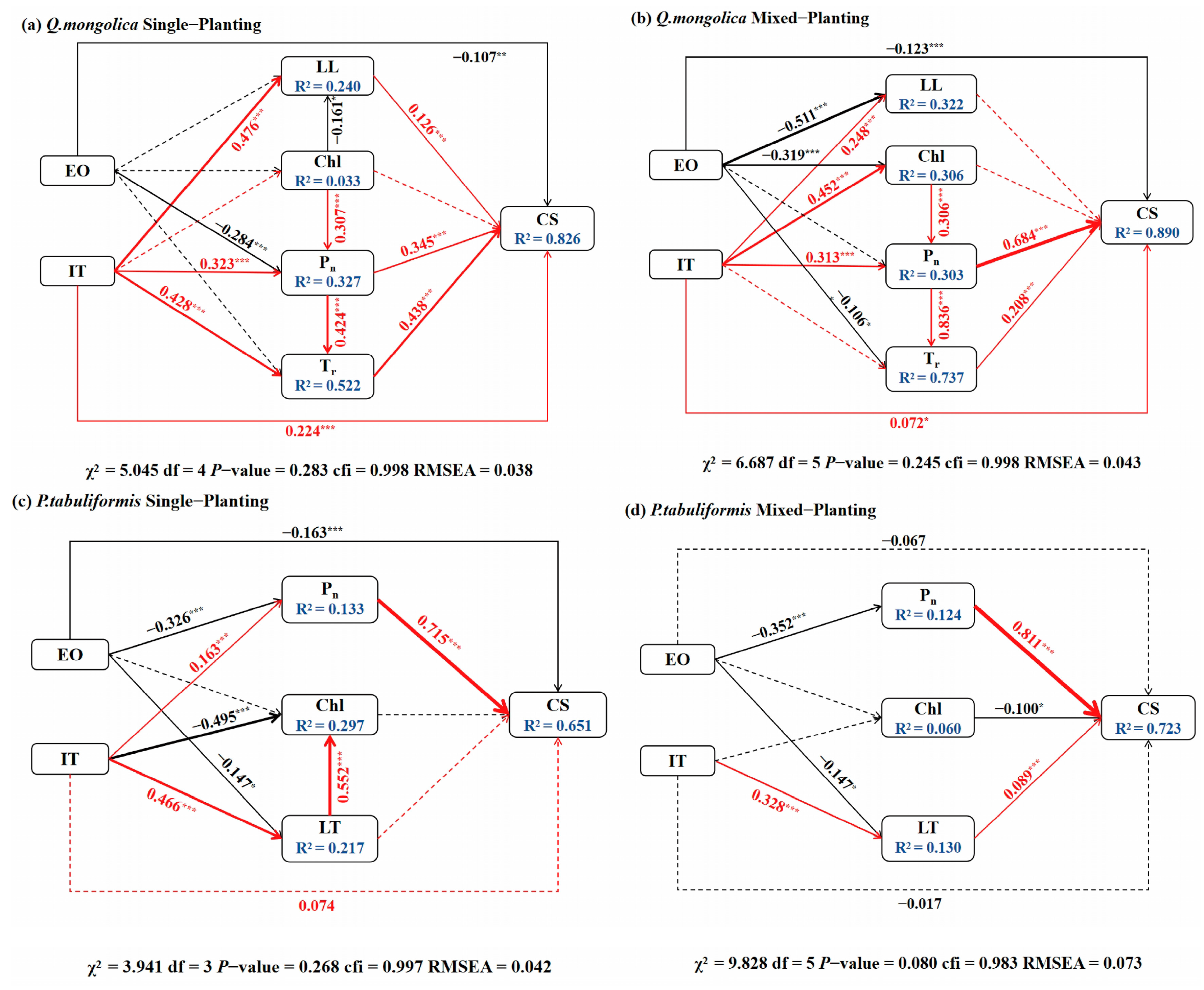
3.3. Direct and Indirect Effects Impacting Plant Carbon Sequestration
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Functional Traits of the Two Tree Species
4.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Carbon Sequestration of the Two Tree Species
4.3. Effects of Plant Functional Traits on Carbon Sequestration Under Different Treatments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.M.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chemix. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, B.; Du, Z.T.; He, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.H.; et al. Experimental warming alleviates the adverse effects from tropospheric ozone on two urban tree species. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchérif, H.; Toihir, A.M.; Mbatha, N.; Sivakumar, V.; Preez, D.J.D.; Bègue, N.; Coetzee, G.J.R. Ozone Variability and Trend Estimates from 20-Years of Ground-Based and Satellite Observations at Irene Station, South Africa. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, O.E.; Fiore, A.M.; Massman, W.J.; Baublitz, C.B.; Coyle, M. Dry Deposition of Ozone Over Land: Processes, Measurement, and Modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowroz, F.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Siddika, A.; Parvin, K.; Caparrós, P.G. Elevated tropospheric ozone and crop production: Potential negative effects and plant defense mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1244515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, I.C.; Shu, L.-S.; Chen, J.-P.; Hsieh, P.-R.; Cheng, C.-T. Projecting ozone impact on crop yield in Taiwan under climate warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.A.; Wang, X.; Shrestha, N.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yao, S.; Li, J.H.; Hou, Q.Q.; Hu, W.G.; Ran, J.Z.; et al. Variations and driving factors of leaf functional traits in the dominant desert plant species along an environmental gradient in the drylands of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suding, K.N.; Lavorel, S.; Chapin, F.S.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Dlaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Goldberg, D.E.; Hooper, D.U.; Jackson, S.T.; Navas, M.L. Scaling environmental change through the community-level: A trait-based response-and-effect framework for plants. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, S.; Grigulis, K. How fundamental plant functional trait relationships scale-up to trade-offs and synergies in ecosystem services. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kannaujia, R.; Narayan, S.; Tewari, A.; Shirke, P.A.; Pandey, V. Impact of chronic elevated ozone exposure on photosynthetic traits and anti-oxidative defense responses of Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de wit tree under field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Vitale, M.; Popa, I.; Anav, A.; Badea, O.; Silaghi, D.; Leca, S.; Screpanti, A.; Paoletti, E. Ozone exposure affects tree defoliation in a continental climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, J.M.; Moraes, R.M. Gas exchange, antioxidants and foliar injuries in saplings of a tropical woody species exposed to ozone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.; Burkey, K.; Taggart, M.; Rufty, T. Leaf Traits That Contribute to Differential Ozone Response in Ozone-Tolerant and Sensitive Soybean Genotypes. Plants 2019, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutomi, Y.; Kinose, Y.; Takimoto, T.; Yonekura, T.; Oue, H.; Kobayashi, K. Ozone changes the linear relationship between photosynthesis and stomatal conductance and decreases water use efficiency in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, B.; Feng, Z.; Li, P.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Y.; Calatayud, V. Ozone exposure- and flux-based response relationships with photosynthesis, leaf morphology and biomass in two poplar clones. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tosens, T.; Harley, P.C.; Jiang, Y.; Kanagendran, A.; Grosberg, M.; Jaamets, K.; Niinemets, Ü. Glandular trichomes as a barrier against atmospheric oxidative stress: Relationships with ozone uptake, leaf damage, and emission of LOX products across a diverse set of species. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Shang, B.; Dai, L.; Uddling, J.; Tarvainen, L. Mesophyll conductance limitation of photosynthesis in poplar under elevated ozone. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinose, Y.; Fukamachi, Y.; Okabe, S.; Hiroshima, H.; Watanabe, M.; Izuta, T. Toward an impact assessment of ozone on plant carbon fixation using a process-based plant growth model: A case study of Fagus crenata grown under different soil nutrient levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didion-Gency, M.; Gessler, A.; Buchmann, N.; Gisler, J.; Schaub, M.; Grossiord, C. Impact of warmer and drier conditions on tree photosynthetic properties and the role of species interactions. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, W.S.; Fujimori, M.; Tase, K.; Sugiyama, S. Heat tolerance and suppression of oxidative stress: Comparative analysis of 25 cultivars of the C3 grass Lolium perenne. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 78, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lie, Z.Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, C.M.; Liu, S.Z. Effect of warming on nutrient content and stoichiometry of four tree species in a South Asian tropical mixed forest. J. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 28, 890. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Guo, J. Effects of Drought and Warming on Biomass, Nutrient Allocation, and Oxidative Stress in Abies fabri in Eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 32, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.A.; Gonzalez, N.M.; Stinson, K.A. Red hot maples: Acer rubrum first-year phenology and growth responses to soil warming. Can. J. For. Res. 2017, 47, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, G.; Molau, U.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M. Community and species-specific responses of plant traits to 23 years of experimental warming across subarctic tundra plant communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.M.G.; Henry, G.H.R.; Cornwell, W.K. Taller and larger: Shifts in Arctic tundra leaf traits after 16 years of experimental warming. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q.; Yao, J.; Xu, C.Y. Effect of simulated warming on leaf functional traits of urban greening plants. Bmc Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, H.; Hua, L.; Luo, Q.; Lin, Y.; He, P.C.; Feng, S.W.; Liu, J.X.; Yr, Q. Differential Responses of Stomata and Photosynthesis to Elevated Temperature in Two Co-occurring Subtropical Forest Tree Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhelm, A.F.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Kubiske, M.E.; Zak, D.R.; Campany, C.E.; Burton, A.J.; Dickson, R.E.; Hendrey, G.R.; Isebrands, J.G.; Isebrands, J.G.; et al. Elevated carbon dioxide and ozone alter productivity and ecosystem carbon content in northern temperate forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Jian, J.; Abulimiti, M.; Yuan, P. Warming promotes accumulation of microbial- and plant-derived carbon in terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Guo, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.X.; Burkey, K.O.; Shew, H.D.; Zobel, R.W.; et al. Warming and elevated ozone induce tradeoffs between fine roots and mycorrhizal fungi and stimulate organic carbon decomposition. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; He, X.; Chen, W. Responses of growth, photosynthesis and related physiological characteristics in leaves of Acer ginnala Maxim. to increasing air temperature and/or elevated O3. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäenpää, M.; Sutinen, S.; Valolahti, H.; Haikio, E.; Riikonen, J.; Kasurinen, A.; Ghimire, R.P.; Holopaninen, J.K.; Holopainen, T. Warming and elevated ozone differently modify needle anatomy of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris). Can. J. For. Res. 2017, 47, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartikainen, K.; Kivimäenpää, M.; Nerg, A.M.; Mäenpää, M.; Oksanen, E.; Rousi, M.; Holopainen, T. Elevated temperature and ozone modify structural characteristics of silver birch (Betula pendula) leaves. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Niu, J. Responses of native broadleaved woody species to elevated ozone in subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Buker, P.; Pleijel, H.; Emberson, L.; Karlsson, P.E.; Uddling, J. A unifying explanation for variation in ozone sensitivity among woody plants. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plas, F.; Schroeder-Georgi, T.; Weigelt, A.; Barry, K.; Meyer, S.; Alzate, A.; Barnard, R.L.; Buchmann, N.; Kroon, H.D.; Ebeling, A.; et al. Plant traits alone are poor predictors of ecosystem properties and long-term ecosystem functioning. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S. Soil abiotic properties and plant functional diversity co-regulate the impacts of nitrogen addition on ecosystem multifunctionality in an alpine meadow. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshika, Y.; Paoletti, E.; Centritto, M.; Gomes, M.T.G.; Puertolas, J.; Haworth, M. Species-specific variation of photosynthesis and mesophyll conductance to ozone and drought in three Mediterranean oaks. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; del Rio, M.; Pretzsch, H.; Jactel, H.; Bielak, K.; Bravo, F.; Brazaitis, G.; Defossez, E.; Engel, M.; Godvod, K.; et al. The greater resilience of mixed forests to drought mainly depends on their composition: Analysis along a climate gradient across Europe. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 481, 118687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Song, M.; Wang, N.; Fan, P.; Wu, P.; Cui, K.N.; Zheng, P.M.; Du, N.; Wang, H.; et al. Physiological Responses of Robinia pseudoacacia and Quercus acutissima Seedlings to Repeated Drought-Rewatering Under Different Planting Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 760510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, B.; Li, P.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.J. Soil high Cd exacerbates the adverse impact of elevated O3 on Populus alba ‘Berolinensis’ L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Lavorel, S.; Garnier, E.; Díaz, S.; Buchmann, N.; Gurvich, D.E.; Reich, P.B.; Steege, H.; Morgan, H.D.; Heijden, M.G.A.; et al. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2003, 51, 335–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhou, J.P.; Shang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pei, J. Comparative Study on Several Determination Methods of Chlorophyll Content in Plants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 730, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, H.L. 2024. Carbon Fixation and Oxygen Release Capacity of Typical Riparian Plants in Wuhan City and Its Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, S.; Kattge, J.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Wright, I.J.; Lavorel, S.; Dray, S.; Reu, B.; Kleyer, M.; Wirth, C.; Prentice, I.C.; et al. The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature 2016, 529, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, L.G.; Courbet, G.; Ourry, A.; Ainsworth, E.A. Elevated Ozone Concentration Reduces Photosynthetic Carbon Gain but Does Not Alter Leaf Structural Traits, Nutrient Composition or Biomass in Switchgrass. Plants 2019, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xy, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.T.; Chen, W.; He, X.Y.; Hayes, F.; Li, M.H. Individual and interactive effects of air warming and elevated O3 on carbon fixation and allocation in two urban tree species. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 345, 109856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, C. Having the right neighbors: How tree species diversity modulates drought impacts on forests. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.Q.; Han, Y.Z.; Cheng, X.R. Mixing planting proportions in a plantation affects functional traits and biomass allocation of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Phoebe bournei seedlings. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lan, Y.H.; Jiang, C.Y.; Cui, Y.H.; He, Y.Q. Leaf Traits Explain the Growth Variation and Nitrogen Response of Eucalyptus urophylla × Eucalyptus grandis and Dalbergia odorifera in Mixed Culture. Plants 2024, 13, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Mei, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G. Growing in Mixed Stands Increased Leaf Photosynthesis and Physiological Stress Resistance in Moso Bamboo and Mature Chinese Fir Plantations. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 649204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Cisse, E.M.; Li, D.D.; Guo, L.Y.; Xiang, L.S.; Miao, L.F. Competitive Relationship Between Cleistocalyx operculatus and Syzygium jambos Under Well-Watered Conditions Transforms into a Mutualistic Relationship Under Waterlogging Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 869418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.T.; Li, X.X.; Ren, P.; Chai, C.H.; Camarero, J.J.; Leavitt, S.W.; Rossi, S.; Liang, E.Y. Lengthening height-growth duration in Smith fir as onset becomes more synchronous across elevations under climate warming scenarios. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 326, 109193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Montenegro, L.; Lopez-Fernandez, M.; Giménez, E. Worldwide Research on the Ozone Influence in Plants. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xu, S.; Li, B.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; He, X.Y.; Wang, N. Responses of spring leaf phenological and functional traits of two urban tree species to air warming and/or elevated ozone. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 179, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Woo, S.Y.; Kwak, M.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.D.; Lin, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, K.A. Effects of Elevated Temperature and Ozone in Brassica juncea L.: Growth, Physiology, and ROS Accumulation. Forests 2020, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, S.; Montgomery, R.A.; Cavender-Bares, J. Physiological responses to light explain competition and facilitation in a tree diversity experiment. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 2000–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, M.; Piedallu, C.; Baudry, J.; Morin, X. Tree diversity and the temporal stability of mountain forest productivity: Testing the effect of species composition, through asynchrony and overyielding. Eur. J. For. Res. 2020, 140, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatsu, K.; Kondoh, M. Density-dependent interspecific interactions and the complexity-stability relationship. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, J.; Castagneyrol, B.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Ghazoul, J.; Kattge, J.; Koricheva, J.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Morath, D.; Jactel, H. Contrasting effects of tree diversity on young tree growth and resistance to insect herbivores across three biodiversity experiments. Oikos 2015, 124, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, T.E.; Matyssek, R. Limitations and perspectives about scaling ozone impacts in trees. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 115, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yin, R.B.; Zhou, H.M.; Xu, S.; Zhu, F. Functional traits of poplar leaves and fine roots responses to ozone pollution under soil nitrogen addition. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 113, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.K.; Singer, G.A.; Kainz, M.J.; Lennon, J.T. Evidence for a temperature acclimation mechanism in bacteria: An empirical test of a membrane-mediated trade-off. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, G.; Xu, S.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, G.X.; Yan, J.H.; Ma, K.P.; et al. Patterns and controlling factors of plant nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across China’s forests. Biogeochemistry 2019, 143, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, D.-D.; Jiao, F.; Yao, J.; Du, H.-T. The Latitudinal Patterns of Leaf and Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry in the Loess Plateau of China. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Q.; Cao, J.; Biswas, A.; Su, H.; Liu, W.; Qin, Y.P.; Zhu, M. Response of leaf stoichiometry of Potentilla anserina to elevation in China’s Qilian Mountains. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 941357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Kozovits, A.R.; Grams, T.E. Competition modifies effects of enhanced ozone/carbon dioxide concentrations on carbohydrate and biomass accumulation in juvenile Norway spruce and European beech. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Long, J.R.; Jackson, B.G.; Wilknson, A.; Pritchard, W.J.; Oakley, S.; Mason, K.E.; Stephan, J.G.; Ostle, N.J.; Johnson, D.; Badds, E.M.; et al. Relationships between plant traits, soil properties and carbon fluxes differ between monocultures and mixed communities in temperate grassland. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudjoe, E.; Bravo, F.; Ruiz-peinaso, R. Allometry and biomass dynamics in temperate mixed and monospecific stands: Contrasting response of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and sessile oak (Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl.). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Carbon Sequestration | |
|---|---|
| PP | 0.104 |
| TS | <0.001 *** |
| IT | 0.152 |
| EO | <0.001 *** |
| PP ∗ TS | 0.405 |
| PP ∗ IT | 0.436 |
| PP ∗ EO | 0.727 |
| TS ∗ IT | 0.683 |
| TS ∗ EO | 0.606 |
| IT ∗ EO | 0.680 |
| PP ∗ TS ∗ IT | 0.02 * |
| PP ∗ TS ∗ EO | 0.604 |
| PP ∗ IT ∗ EO | 0.021 * |
| TS ∗ IT ∗ EO | <0.001 *** |
| PP ∗ TS ∗ IT ∗ EO | 0.137 |
| Q. mongolica | P. tabuliformis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Planting | Mixed Planting | Single Planting | Mixed Planting | |
| Chl | −0.054 | 0.075 * | −0.003 | −0.126 ** |
| LT | 0.032 | −0.013 | −0.063 | 0.149 * |
| LL | 0.208 *** | 0.086 ** | 0.085 | −0.026 |
| RWC | −0.076 * | −0.029 | −0.014 | −0.094 |
| LDMC | 0.013 | −0.002 | −0.005 | −0.015 |
| SLW | 0.018 | 0.081 | −0.007 | 0.044 |
| SLA | −0.017 | 0.072 | 0.139 | 0.003 |
| Pn | 0.273 *** | 0.697 *** | 0.846 *** | 0.805 *** |
| Tr | 0.660 *** | 0.219 ** | −0.137 | 0.070 |
| Ci | −0.103 ** | −0.024 | −0.120 * | 0.074 |
| WUE | 0.089 * | 0.012 | −0.129 | 0.055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Xu, S.; Ping, Q.; Li, K.; Gao, K.; He, X. Differential Responses of Tree Species to Elevated Ozone and Increasing Air Temperature: Implications for Foliar Functional Traits, Carbon Sequestration, and Their Relationship Under Mixed Planting. Forests 2024, 15, 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122183
Wang R, Xu S, Ping Q, Li K, Gao K, He X. Differential Responses of Tree Species to Elevated Ozone and Increasing Air Temperature: Implications for Foliar Functional Traits, Carbon Sequestration, and Their Relationship Under Mixed Planting. Forests. 2024; 15(12):2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122183
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruiting, Sheng Xu, Qin Ping, Kexin Li, Kexin Gao, and Xingyuan He. 2024. "Differential Responses of Tree Species to Elevated Ozone and Increasing Air Temperature: Implications for Foliar Functional Traits, Carbon Sequestration, and Their Relationship Under Mixed Planting" Forests 15, no. 12: 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122183
APA StyleWang, R., Xu, S., Ping, Q., Li, K., Gao, K., & He, X. (2024). Differential Responses of Tree Species to Elevated Ozone and Increasing Air Temperature: Implications for Foliar Functional Traits, Carbon Sequestration, and Their Relationship Under Mixed Planting. Forests, 15(12), 2183. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15122183






