MART3D: A Multilayer Heterogeneous 3D Radiative Transfer Framework for Characterizing Forest Disturbances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
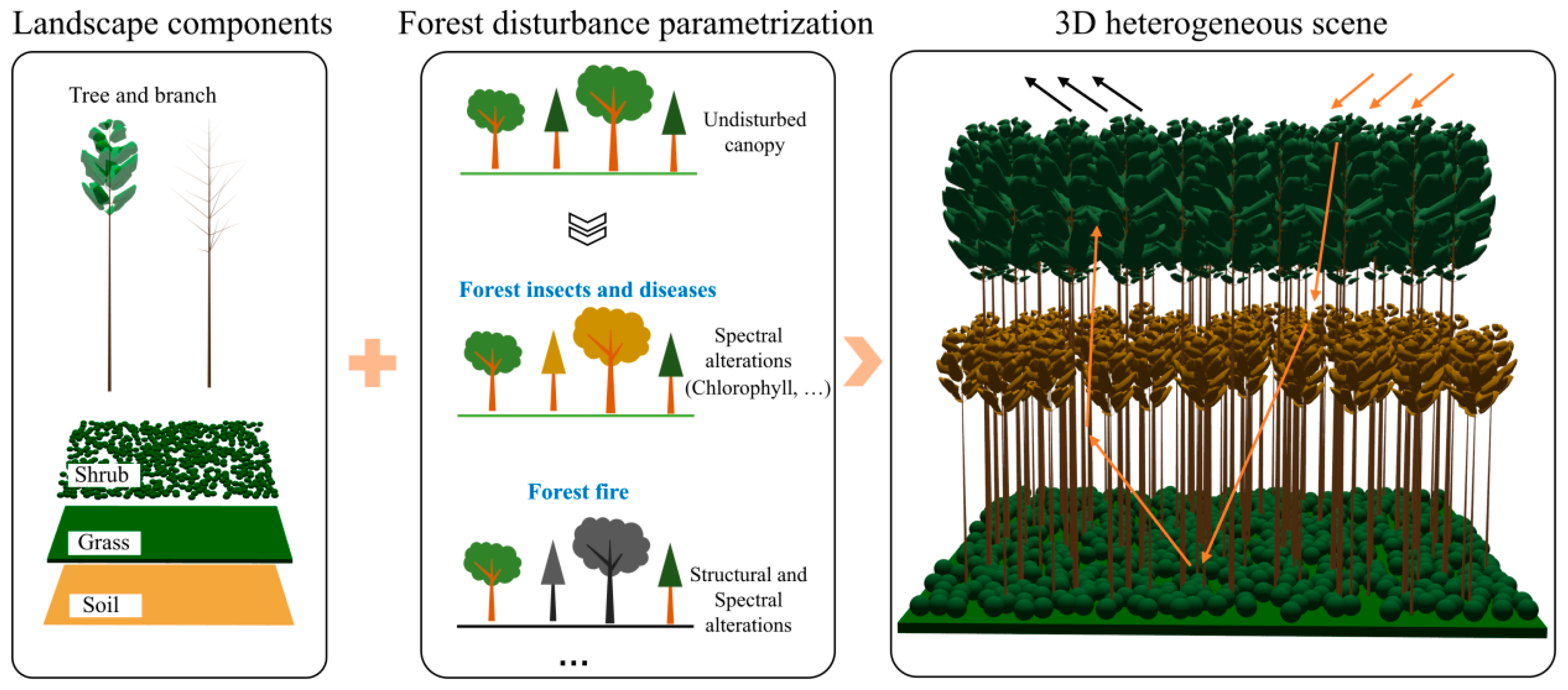
2.1. An Overview of the Framework
2.2. Structure of Landscape Components
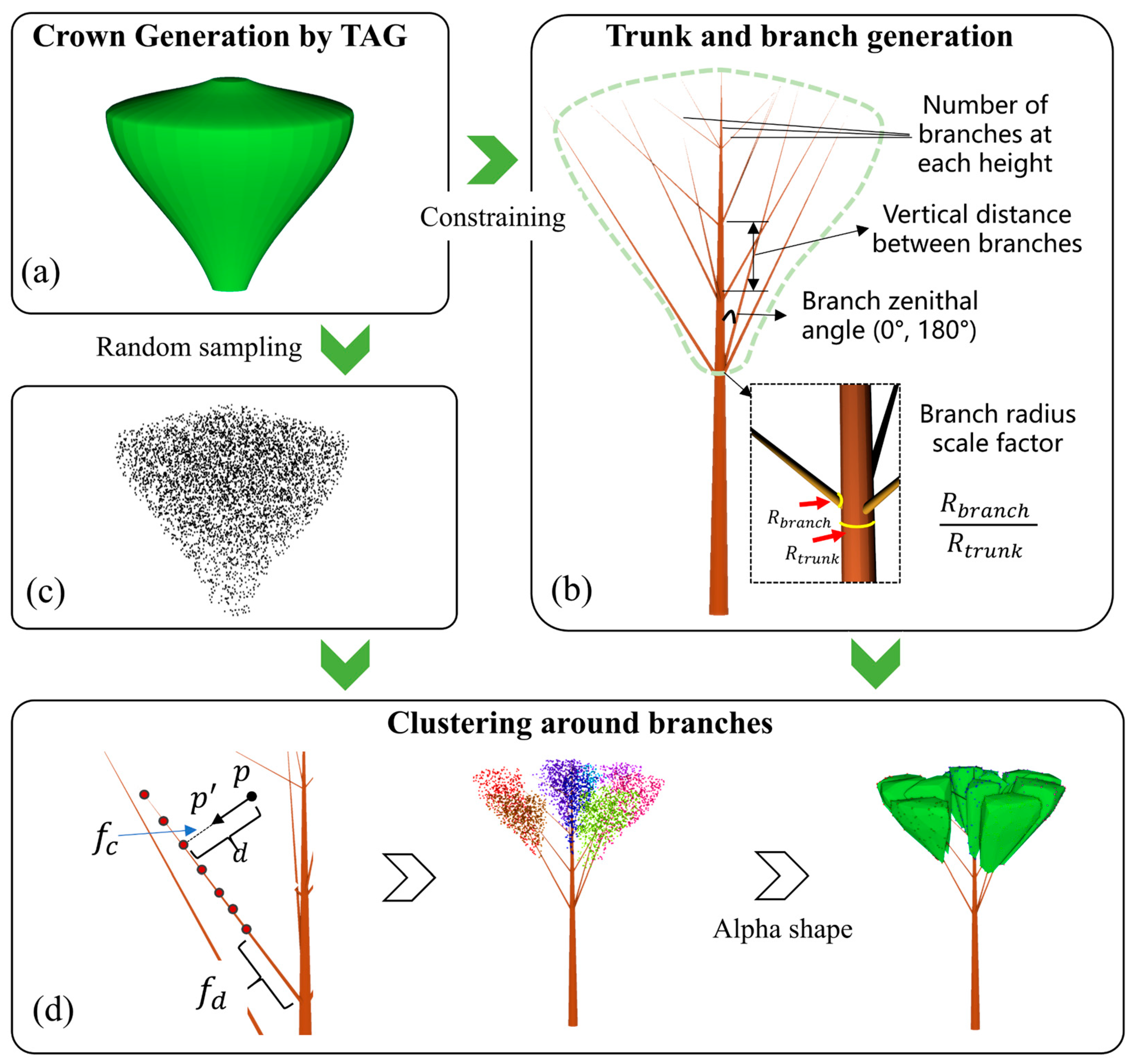
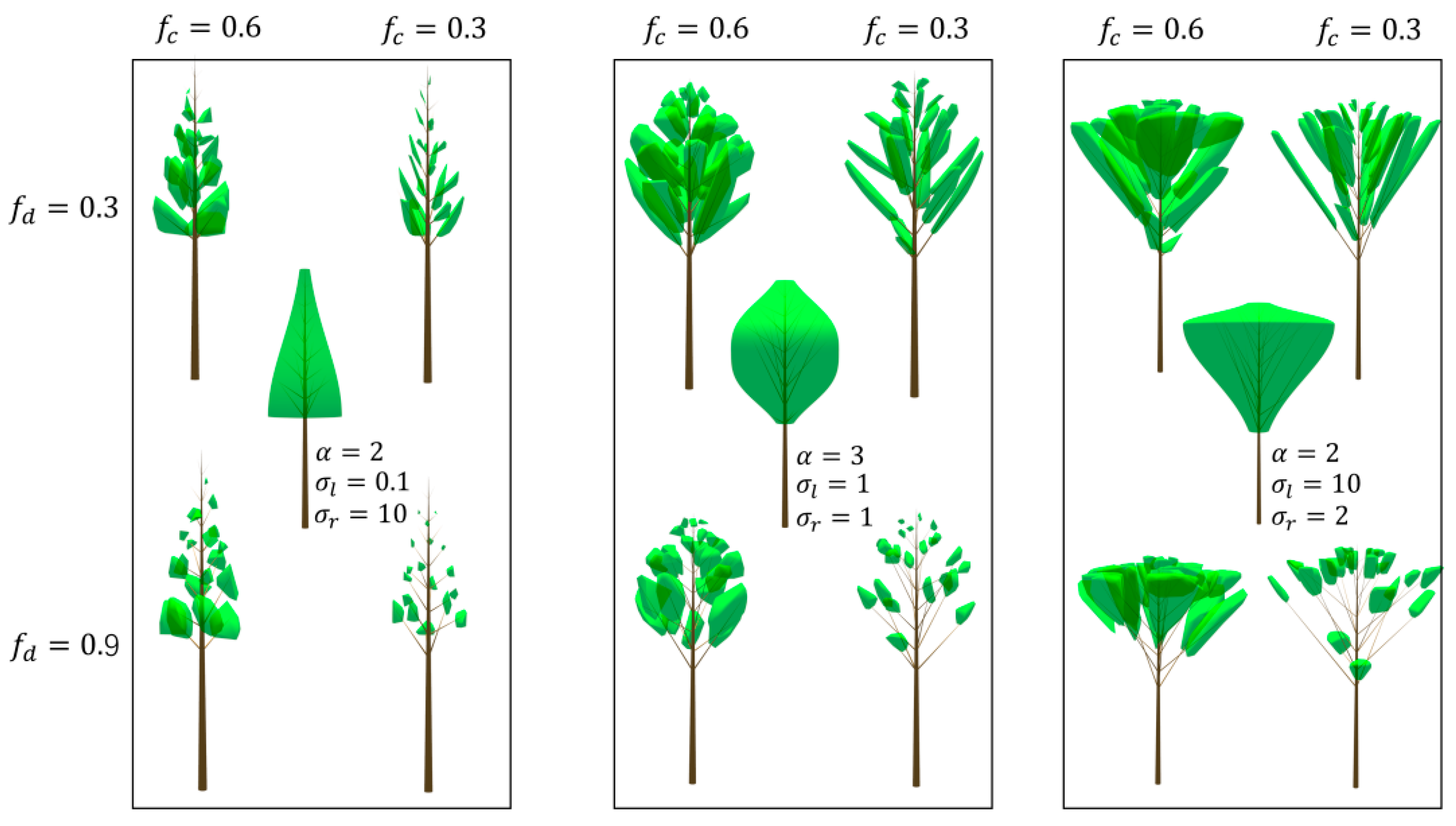
2.2.1. Modeling of Tree Crown and Branch
2.2.2. Modeling of Leaf Clumping
2.2.3. Modeling of Grass and Shrubs
2.3. Forest Disturbance Modeling
2.3.1. Forest Plot Generation
2.3.2. Disturbed Forest Plot Parametrization
2.4. Radiative Transfer Computation
3. Results
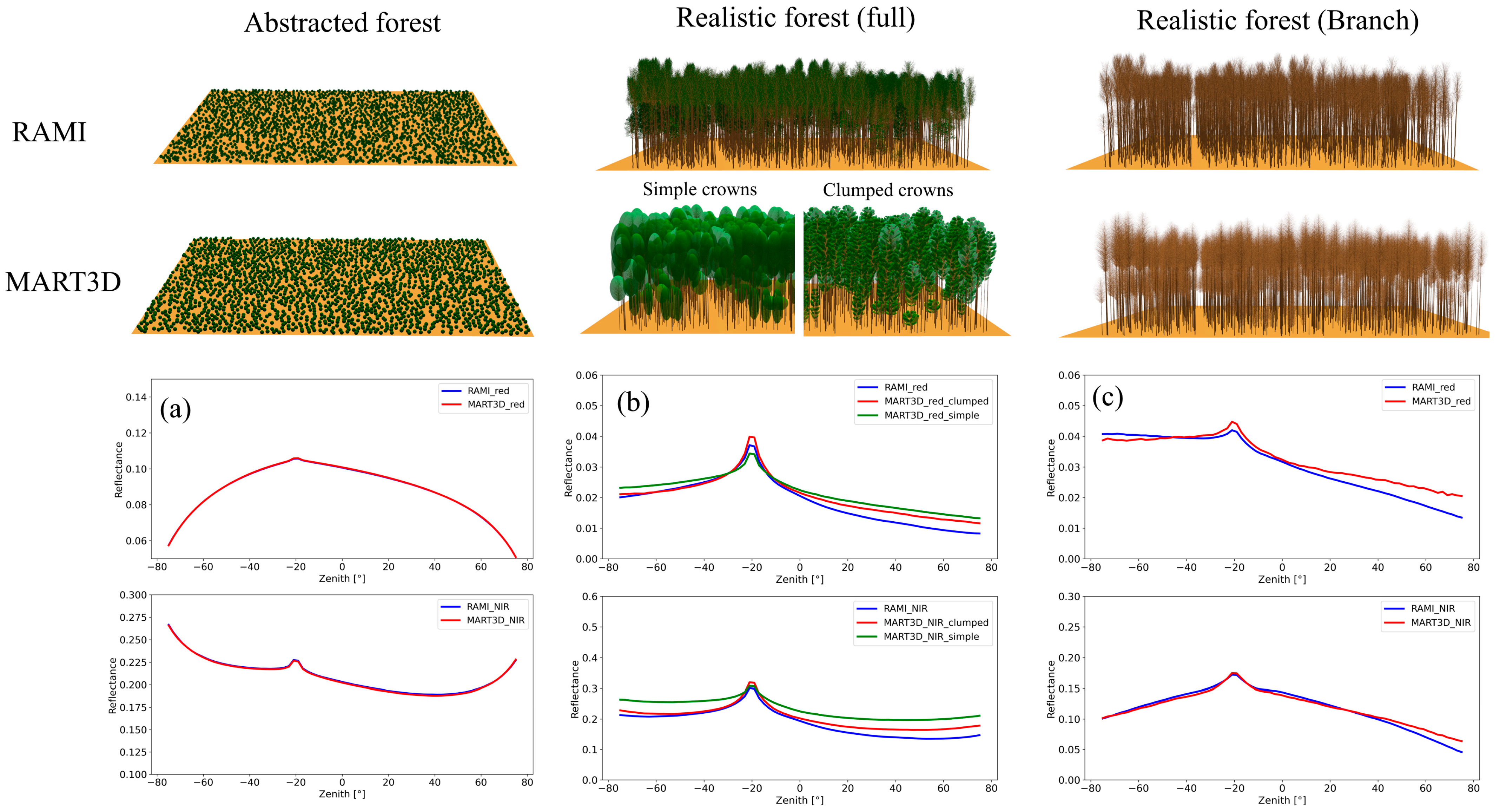
3.1. Model Accuracy Evaluation
3.2. Model Applications
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy of BRF Simulation
4.2. Innovations in Modeling Method of Individual Trees for Remote Sensing Applications
4.3. Future Applications and Limitations of MART3D
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkins, J.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Fahey, R.; Haber, L.; Stuart-Haëntjens, E.; Hardiman, B.; LaRue, E.; McNeil, B.; Orwig, D.; Stovall, A.; et al. Application of Multidimensional Structural Characterization to Detect and Describe Moderate Forest Disturbance. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montorio, R.; Pérez-Cabello, F.; Borini Alves, D.; García-Martín, A. Unitemporal Approach to Fire Severity Mapping Using Multispectral Synthetic Databases and Random Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Seidl, R.; Hostert, P. Remote Sensing of Forest Insect Disturbances: Current State and Future Directions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2017, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bempah, A.N.; Kyereh, B.; Ansong, M.; Asante, W. The Impacts of Invasive Trees on the Structure and Composition of Tropical Forests Show Some Consistent Patterns but Many Are Context Dependent. Biol. Invasions 2021, 23, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaeva, T.; Andreychev, A.; Kiyaykina, O.; Balčiauskas, L. Taxonomic and Ecological Composition of Forest Stands Inhabited by Forest Dormouse Dryomys Nitedula (Rodentia: Gliridae) in the Middle Volga. Biologia 2021, 76, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Rammer, W.; Verkerk, P.J. Increasing Forest Disturbances in Europe and Their Impact on Carbon Storage. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E.; Vaughan, P.J. Short-Term Assessment of Burn Severity Using the Inversion of PROSPECT and GeoSail Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana-Soto, A.; Okujeni, A.; Pflugmacher, D.; García, M.; Aguado, I.; Hostert, P. Quantifying Post-Fire Shifts in Woody-Vegetation Cover Composition in Mediterranean Pine Forests Using Landsat Time Series and Regression-Based Unmixing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 281, 113239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X. Forest Fire Spread Monitoring and Vegetation Dynamics Detection Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleniou, M.; Koutsias, N. Sensitivity of Spectral Reflectance Values to Different Burn and Vegetation Ratios: A Multi-Scale Approach Applied in a Fire Affected Area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Pu, R.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.; Yuan, L.; Wu, K.; Huang, W. Monitoring Plant Diseases and Pests through Remote Sensing Technology: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, J. Detection of Shoot Beetle Stress on Yunnan Pine Forest Using a Coupled LIBERTY2-INFORM Simulation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Ritger, H.; Pearce, C.; Eickwort, J.; Hulcr, J. Ability of Remote Sensing Systems to Detect Bark Beetle Spots in the Southeastern US. Forests 2020, 11, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, E.; Yun, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y. Quantification of One-Year Gypsy Moth Defoliation Extent in Wonju, Korea, Using Landsat Satellite Images. Forests 2021, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, S.; Näsi, R.; Koivumaki, N.; Imangholiloo, M.; Saarinen, N.; Raisio, J.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, H.; Hyyppä, J.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; et al. Multispectral Imagery Provides Benefits for Mapping Spruce Tree Decline Due to Bark Beetle Infestation When Acquired Late in the Season. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Tong, T.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Hou, T.; Su, Y.; Lv, X.; Fu, W.; et al. Integrating Multi-Scale Remote-Sensing Data to Monitor Severe Forest Infestation in Response to Pine Wilt Disease. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordache, M.; Mantas, V.; Baltazar, E.; Pauly, K.; Lewyckyj, N. A Machine Learning Approach to Detecting Pine Wilt Disease Using Airborne Spectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migas-Mazur, R.; Kycko, M.; Zwijacz-Kozica, T.; Zagajewski, B. Assessment of Sentinel-2 Images, Support Vector Machines and Change Detection Algorithms for Bark Beetle Outbreaks Mapping in the Tatra Mountains. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Gang, B.; Bao, Y.; Dashzebeg, G.; Nanzad, T.; Dorjsuren, A.; Enkhnasan, D.; Ariunaa, M. Detection of Larch Forest Stress from Jas’s Larch Inchworm (Erannis Jacobsoni Djak) Attack Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Lao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhou, H. Pine Pest Detection Using Remote Sensing Satellite Images Combined with a Multi-Scale Attention-UNet Model. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Skidmore, A.K.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Wang, T. Estimation of Forest Leaf Water Content through Inversion of a Radiative Transfer Model from LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 74, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shabanov, N.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H. Modeling Solar-Induced Fluorescence of Forest with Heterogeneous Distribution of Damaged Foliage by Extending the Stochastic Radiative Transfer Theory. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E. GeoCBI: A Modified Version of the Composite Burn Index for the Initial Assessment of the Short-Term Burn Severity from Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E. Burn Severity Estimation from Remotely Sensed Data: Performance of Simulation versus Empirical Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Calvo, L. Radiative Transfer Modeling to Measure Fire Impact and Forest Engineering Resilience at Short-Term. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 176, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Suárez-Seoane, S.; Quintano, C.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Calvo, L. Comparison of Physical-Based Models to Measure Forest Resilience to Fire as a Function of Burn Severity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Verrelst, J.; Calvo, L.; Suárez-Seoane, S. Hybrid Inversion of Radiative Transfer Models Based on High Spatial Resolution Satellite Reflectance Data Improves Fractional Vegetation Cover Retrieval in Heterogeneous Ecological Systems after Fire. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, H.; Shabanov, N.; Chen, L.; Yan, K.; Shi, J. Extending the Stochastic Radiative Transfer Theory to Simulate BRF over Forests with Heterogeneous Distribution of Damaged Foliage inside of Tree Crowns. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Du, H.; Zhou, G. Early Detection of Pine Shoot Beetle Attack Using Vertical Profile of Plant Traits through UAV-Based Hyperspectral, Thermal, and Lidar Data Fusion. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 125, 103549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y. Using the 3D Model RAPID to Invert the Shoot Dieback Ratio of Vertically Heterogeneous Yunnan Pine Forests to Detect Beetle Damage. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT+SAIL Models: A Review of Use for Vegetation Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xie, D.; Yin, T.; Yan, G.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Mu, X.; Norford, L.K. LESS: LargE-Scale Remote Sensing Data and Image Simulation Framework over Heterogeneous 3D Scenes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kallel, A.; Yang, X.; Regaieg, O.; Lauret, N.; Guilleux, J.; Chavanon, E.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P. DART-Lux: An Unbiased and Rapid Monte Carlo Radiative Transfer Method for Simulating Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 112973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Xie, D.; Jiang, J.; Huang, H. 3D Radiative Transfer Modeling of Structurally Complex Forest Canopies through a Lightweight Boundary-Based Description of Leaf Clusters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 283, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qiu, J. Exploring the Potential of GEDI in Characterizing Tree Height Composition Based on Advanced Radiative Transfer Model Simulations. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 4, 0132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape Assessment (LA). 2006. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/research/treesearch/24066 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Widlowski, J.-L.; Taberner, M.; Pinty, B.; Bruniquel-Pinel, V.; Disney, M.; Fernandes, R.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P.; Gobron, N.; Kuusk, A.; Lavergne, T.; et al. Third Radiation Transfer Model Intercomparison (RAMI) Exercise: Documenting Progress in Canopy Reflectance Models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D09111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xie, D.; Zhou, K.; Yan, G.; Mu, X. Analysis of the Directional Characteristics of the Clumping Index (CI) Based on RAMI-V Canopy Scenes. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 4, 0133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, F.; Chen, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Tu, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; et al. Evaluation of GOFP over Four Forest Plots Using RAMI and UAV Measurements. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1433–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Tao, S.; Su, Y. VBRT: A Novel Voxel-Based Radiative Transfer Model for Heterogeneous Three-Dimensional Forest scenesVBRT. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.A.; Skowronski, N.S.; Gallagher, M.R. High Spatial Resolution Burn Severity Mapping of the New Jersey Pine Barrens with WorldView-3 near-Infrared and Shortwave Infrared Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favorskaya, M.N.; Jain, L.C. Tree Modelling in Virtual Reality Environment. In Handbook on Advances in Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems: Paradigms and Applications in Forest Landscape Modeling; Favorskaya, M.N., Jain, L.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 141–179. ISBN 978-3-319-52308-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Yang, H.; Qi, J.; Han, S.; Sun, Z.; Feng, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Yang, G. Evaluation of the Effect of Leaf Spatial Aggregation on Chlorophyll Content Retrieval in Open-Canopy Apple Orchards. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 121, 103367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
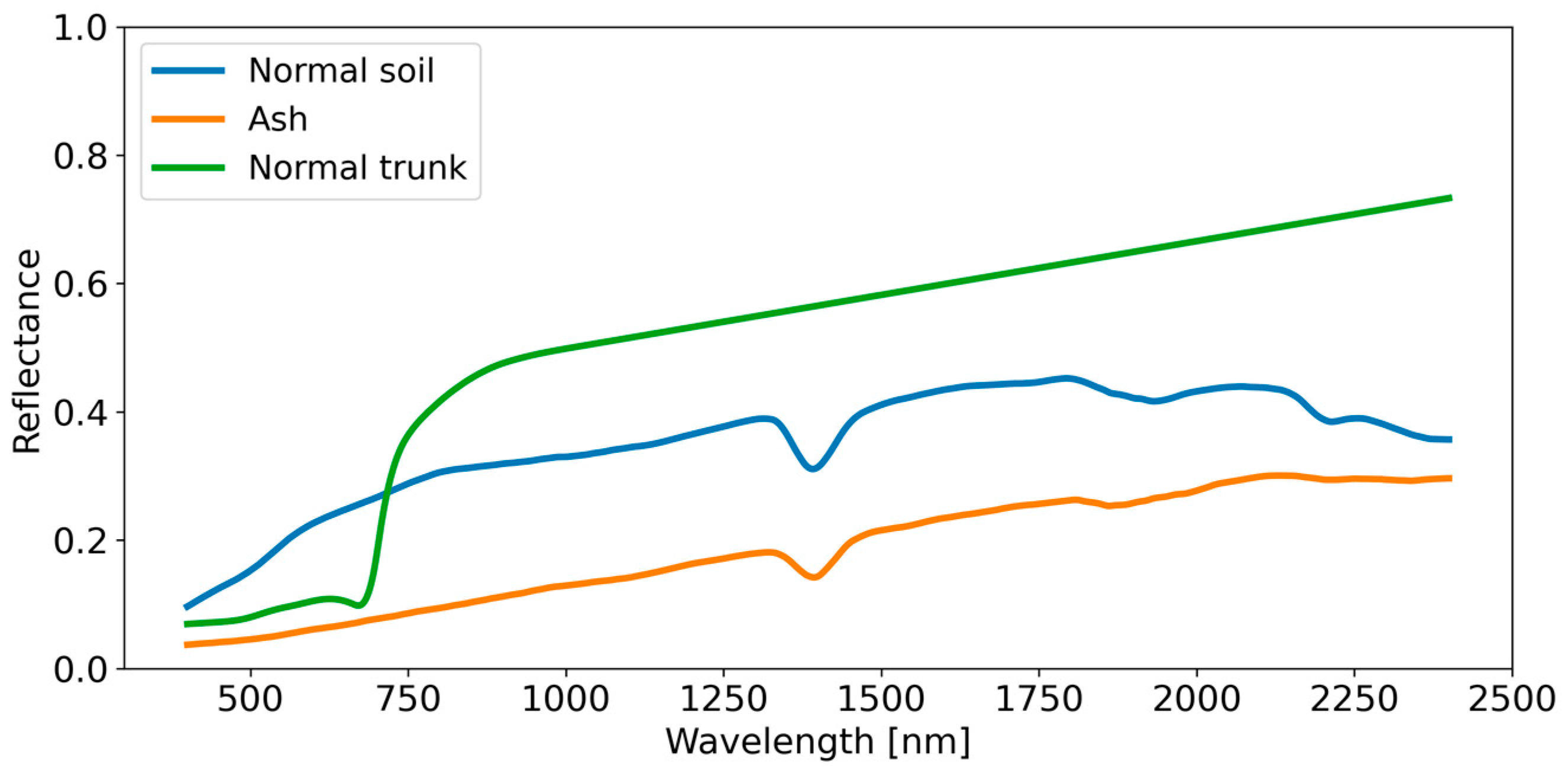
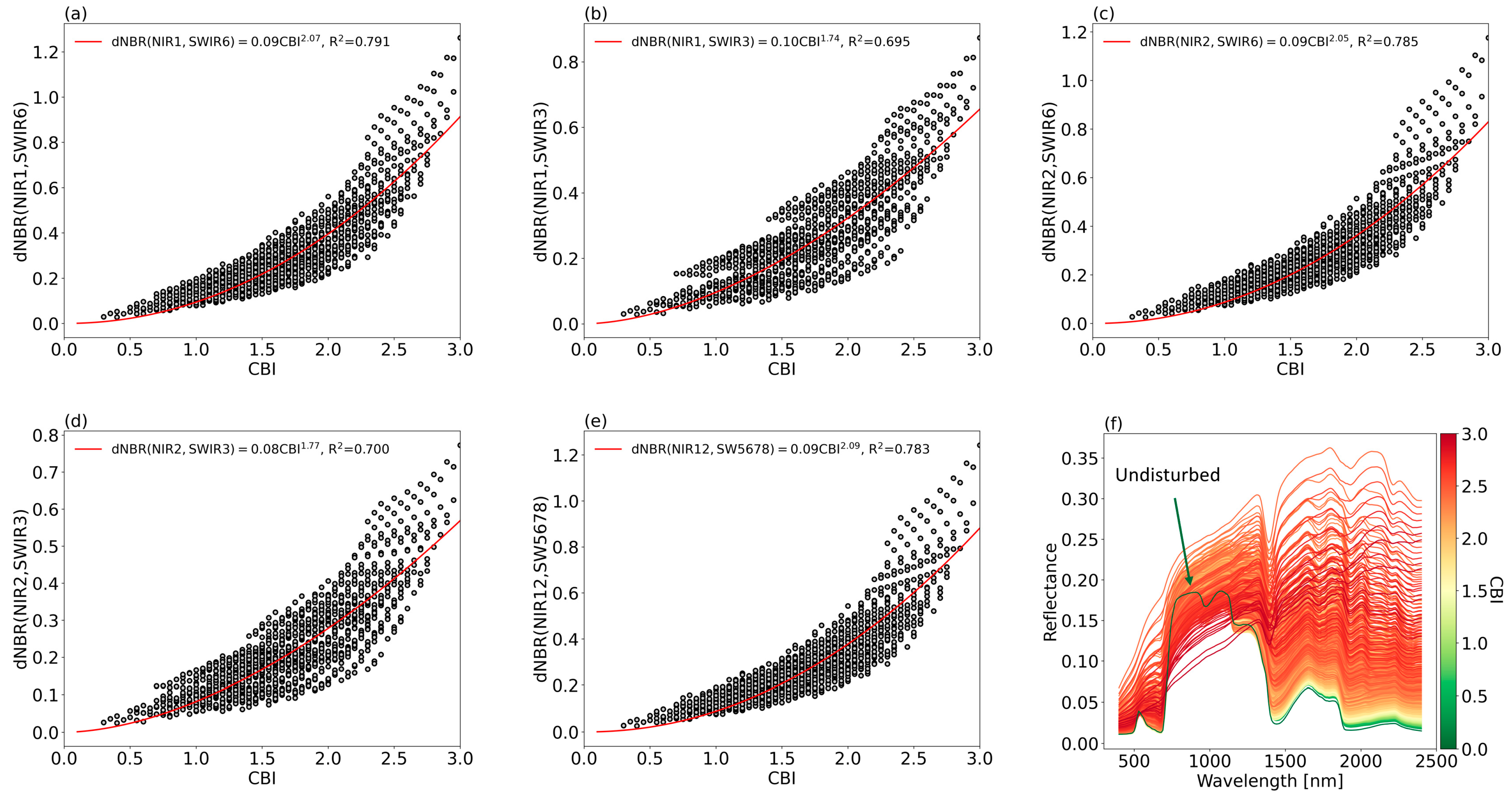
| Layer | LAI | FCC | Leaf Parameters (N, Car, BP, Cm, Cab, Anth, Cw) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass | 1.0 | --- | Green leaf: 2.5, 8.0, 0.2, 0.035, 70, 0.0, 0.048 Brown leaf: 2.5, 8.0, 1.5, 0.035, 20, 0.0, 0.0008 |
| Shrub | 1.0 | 0.5 | |
| Mediate tree | 1.5 | 0.3 | |
| Upper tree | 2.5 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, L.; Qi, J.; Wang, Q.; Jia, K.; Cao, B.; Zhao, W. MART3D: A Multilayer Heterogeneous 3D Radiative Transfer Framework for Characterizing Forest Disturbances. Forests 2024, 15, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050824
Ouyang L, Qi J, Wang Q, Jia K, Cao B, Zhao W. MART3D: A Multilayer Heterogeneous 3D Radiative Transfer Framework for Characterizing Forest Disturbances. Forests. 2024; 15(5):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050824
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Lingjing, Jianbo Qi, Qiao Wang, Kun Jia, Biao Cao, and Wenzhi Zhao. 2024. "MART3D: A Multilayer Heterogeneous 3D Radiative Transfer Framework for Characterizing Forest Disturbances" Forests 15, no. 5: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050824
APA StyleOuyang, L., Qi, J., Wang, Q., Jia, K., Cao, B., & Zhao, W. (2024). MART3D: A Multilayer Heterogeneous 3D Radiative Transfer Framework for Characterizing Forest Disturbances. Forests, 15(5), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15050824







