Abstract
In northeastern China, simultaneous reconstruction of temperature and precipitation changes in the same region using tree ring data has not yet been reported, limiting our understanding of the historical climate. Using tree ring samples from the Greater Khingan Mountains, it was established that there are five standardized tree ring width chronologies of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica at five elevations. Correlation analyses revealed significant relationships between the tree ring chronologies and climate data for multiple months. Specifically, the correlation coefficient between the average minimum temperature from May to July and the composite chronologies of mid–high and mid-elevations was 0.726, whereas that between the total precipitation from August to July and the low-elevation chronology was 0.648 (p < 0.01). Based on these findings, we reconstructed two series: the average minimum temperature from May to July over the past 211 years and the total precipitation from August to July over the past 214 years. The reconstructed sequences revealed changes in the average minimum temperature from 1812 to 2022 and precipitation from 1809 to 2022 in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains. The variances explained by the reconstruction equations were 0.528 and 0.421 (adjusted R-squared: 0.520 and 0.411), with F-test values of 65.896 and 42.850, respectively, exceeding the significance level of 0.01. The reliability of the reconstructed sequences was validated by historical records of meteorological disasters and the reconstruction results in the surrounding area. The reconstructed temperature and precipitation sequences exhibited distinct patterns of temperature fluctuations, dry–wet changes, and periodic oscillations. The region experienced two warm periods (1896–1909 and 2006–2020), two cold periods (1882–1888 and 1961–1987), a wet period (1928–1938), a drought period (1912–1914), and a period prone to severe drought events (1893–1919) during the past 210 years. The temperature series showed periodicities of 2–2.5 years, 3.9 years, 5.2 years, and 68 years, while the precipitation series exhibited periodicities of 2.1 years, 2.5 years, and 2.8 years, possibly related to El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events, quasi-biennial oscillation, and Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO). Spatial correlation analysis indicated that the reconstructed temperature and precipitation sequences accurately represented the hydrothermal changes in the study area.
1. Introduction
Climate change is an important component of global change and has become a focal point of attention for countries around the world. Climate change not only affects the economic, political, and cultural aspects of human society, but also has profound impacts on the structure and functioning of natural environments, particularly in the high-latitude regions of the Northern Hemisphere, which have experienced the highest warming rates globally [1,2]. Forest ecosystems are crucial in responding to and adapting to climate change. The radial growth of trees reflects the mechanisms of forest ecosystems’ responses to climate change [3].
Due to the limited duration and uneven distribution of instrument-based meteorological data, our understanding of long-term regional temperature changes is constrained [4]. Climate proxy data provide a potential means for understanding past climate variations. Tree rings record the age of and changes in trees and the climatic and environmental variations trees experience during their growth [5,6]. Moreover, tree ring data, characterized by accurate dating, strong continuity, high resolution, good reconstruction accuracy, and wide geographical distribution, serve as important proxy data for studying the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and obtaining historical climate and environmental evolution data [7]. The long-term records generated from tree ring research can provide valuable references for regional planning and ecological conservation [8]. Temperature, precipitation, and streamflow historical sequences dating back several hundred or even thousands of years have been reconstructed worldwide using tree ring data [9,10,11,12,13]. Tree ring-based climate reconstructions have been crucial in past climate and environmental research, improving our understanding of past climate change and its mechanisms and enabling us to predict future climate change trends.
Located at the southern edge of the perennial permafrost zone of the Eurasian continent, the Greater Khingan Mountains are situated in the environmentally sensitive cold temperate region of “Northeast Asia”, and represent one of the more sensitive and vulnerable regions affected by the impacts of global climate change [14,15]. Mangui Town is located in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains, in the fragile forest–grassland transition zone in northeastern China characterized by a cold temperate continental monsoon climate with long and cold winters with a snow cover period of 160 days. Due to the combined influence of the summer monsoon and the Siberian winter monsoon from the south, the forest ecosystem in this region is affected by frequent extreme climate factors and poses a serious threat to agroforestry production [16]. Persistent high temperatures and frequent droughts also increase the risk of primitive forest fires in the northern Greater Khingan Mountains, such as the forest fire that occurred in the northern Greater Khingan Mountains on 6 May 1987, which burned for 28 d and swept more than 100 km2, originating in the Xilinji Forestry Bureau (the seat of Mohe County, which was burned to the ground throughout the county) [17]. However, there is no national (meteorological) station near the Mangui area, and the nearest meteorological station is more than 100 km away. This situation has hindered climate research and resulted in inadequate disaster response capabilities, impacts on agricultural production, and economic losses.
Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica is a kind of light-loving, cold-resistant, drought-resistant adaptable tree species, and is deep-rooted; its soil requirements are not strict, so it can grow, for example, in acidic soil, and it has weak salinity tolerance. In dry and harsh environments, and rocky exposed environments, sandy environments, on steep slopes, and in other environmentally hostile places, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica can grow well [18]. This species is often used in dendrochronological studies [9,19,20,21]. However, although tree rings have been extensively used in historical climate studies and reconstructions of past temperature and precipitation changes in northeastern China [9,22,23,24,25], current research has focused on the reconstruction of individual climate indicators, and there are no reports on the simultaneous reconstruction of temperature and precipitation changes in the same region using tree ring data, limiting our understanding of the historical climate.
Therefore, this study is conducted to fill the data gap in historical climate information in the Mangui area and aims to (1) reconstruct historical temperature and precipitation data based on the relationship between climatic factors and tree ring width, and (2) analyze the characteristics of historical climate changes based on the reconstructed temperature and precipitation sequences.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is the Beian Forest Farm in the Mangui region, located in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains. Covering the northern part of Heilongjiang Province and the northeastern part of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, the Greater Khingan Mountains are situated in the permafrost region of the Eurasian continent. This region is highly sensitive to climate change and is influenced by the Siberian winter monsoon and the summer monsoon from the south [15]. They serve as a critical ecological barrier and national forest conservation area in northeastern China. The geographical coordinates range from 43° N to 53.5° N and from 117.33° E to 126° E. The Greater Khingan Mountains cover an area of approximately 327,200 square kilometers. They have a northeast–southwest orientation, with a length of 1400 km, a width of 200 to 400 km, and an elevation ranging from 200 to 1700 m. The dominant vegetation consists of coniferous forests. Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica is the most prevalent species and grows at elevations of 400 to 1200 m. It is highly adapted to cold climates and harsh growing environments. The main soil types include brown forest, meadow, dark chestnut, dark brown, and marsh soils. This region provides an ideal setting for conducting tree ring climate research.
2.2. Tree Ring Sampling and Dendrochronology Development
The tree core samples were collected in the Beian Forest Farm area (52° N to 52.31° N and from 121.47° E to 121.98° E). The sampling was accomplished at the end of July 2022 at three elevations (700 m, 900 m, and 1150 m), and by the end of July 2023 at two elevations (800 m and 1200 m). The sampling point information is listed in Table 1. Each sampling location was centered around pristine areas in the core zone of the forest, with a focus on selecting areas with minimal human disturbance. Samples were collected from mature, old, and healthy trees. An increment borer was used to extract 2–3 tree core samples from each selected tree at breast height (1.3 m above the ground) in different directions. The diameter of the increment borer used was 10 mm.

Table 1.
Sampling site information.
The tree ring samples were naturally air-dried, sanded, and visually cross-dated according to Speer’s tree ring analysis method [26]. A LINTAB6 tree ring width measuring device (Rinntech, Heidelberg, Germany, accuracy of 0.001 mm) was used to measure the tree ring widths of the core samples. The measured tree ring widths were cross-dated using PAST5 (1995–2016 by SCIEM. All Rights Reserved. Version 5.0.600) software. The COFECHA program [27] was employed to assess the quality of the cross-dating results, and samples with low correlations were excluded from the final chronology. The following core samples were obtained in different elevation zones: high elevation (ZH)—55 cores from 24 trees; mid–high elevation (ZM-H)—57 cores from 21 trees; mid-elevation (ZM)—54 cores from 22 trees; mid–low elevation (ZM-L)—50 cores from 27 trees; and low elevation (ZL)—54 cores from 20 trees. The tree ring width chronologies were fitted and detrended using the negative exponential function detrending method of the ARSTAN program [28], and the detrended series were combined into a standardized chronology of tree ring widths using a double-weighted average.
2.3. Meteorological Data
Since there are no meteorological stations near the sampling sites, we utilized the grid data from the Climatic Research Unit time series (CRU TS) 4.04 dataset (0.5° × 0.5°) (http://climexp.knmi.nl, accessed on 26 September 2022) to analyze the relationship between the radial growth of Pinus sylvestris and the historical climate. The CRU data base is based on interpolated data from regional meteorological stations and has inhomogeneity in areas with low station density [29]. Therefore, we validated the accuracy of the CRU climate data by comparing it with the data from meteorological stations in Huzhong (52.02° N, 123.34° E), Mohe (52.58° N, 122.31° E), and Genhe (50.47° N, 121.31° E) and the average for these data. The correlation analysis revealed that the correlation between the CRU data and the weather station observations is consistently high, with a significance level of 0.01. Hence, we consider the CRU grid data for this area to be reliable.
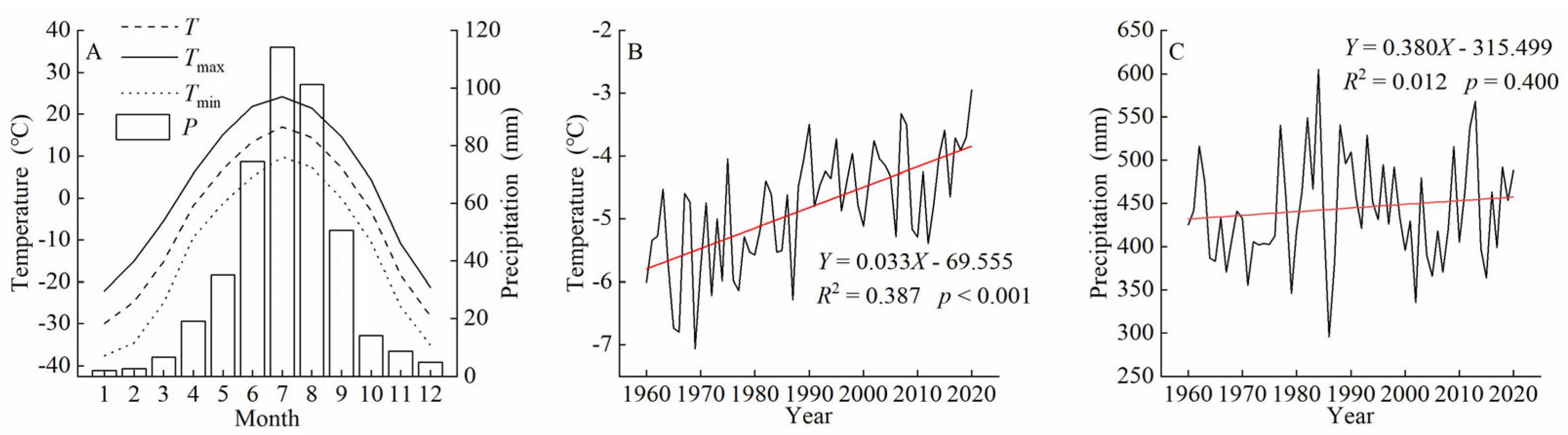
Since the coverage of the five sampling points spanned two grid cells, we selected the 0.5° × 0.5° CRU climate grid data in the ranges of 52.00–52.50° N, 121.00–121.50° E and 52.00–52.50° N, 121.50–122.00° E [30]. The average values from these two grid cells were used to represent the climatic background of the study area. The selected climate variables included mean temperature (T), maximum temperature (Tmax), minimum temperature (Tmin), and precipitation (P). The period ranged from 1960 to 2020. Figure 1A shows the monthly variations in precipitation and temperature in the study area. The monthly precipitation and mean temperature exhibited a unimodal distribution throughout the year, with peak values occurring in July. There were distinct wet and dry seasons, as well as concurrent rainy and hot periods. The maximum precipitation was 117.59 mm, representing 26.69% of the annual precipitation, and the highest mean temperature was 16.84 °C. The interannual climate variability (Figure 1B,C) indicated a significant increasing trend in annual mean temperature (Y = 0.033X − 69.555, R2 = 0.397, p < 0.001) from 1960 to the present year. However, there was no significant trend in annual precipitation during the same period (Y = 0.380X − 315.499, R2 = 0.012, p = 0.400).
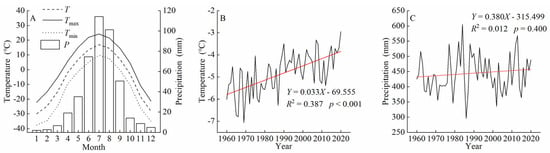
Figure 1.
Climatic characteristics of the northern Greater Khingan Mountains from 1960 to 2020. (A) Changes in mean monthly temperature and total monthly precipitation. (B) Changes in annual mean temperature. (C) Changes in annual precipitation. P, precipitation; T, mean temperature; Tmax, mean maximum temperature; Tmin, mean minimum temperature.
2.4. Research Methods
We investigated the chronology of tree ring widths of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica at different elevations using Pearson’s correlation analysis to correlate with precipitation and the mean, maximum, and minimum air temperatures at five elevations. Monthly data from October of the previous year to September of the current year were chosen for the correlation analysis because of the lagging effect of climatic factors on the radial growth of trees.
3. Results
3.1. Chronological Characteristics
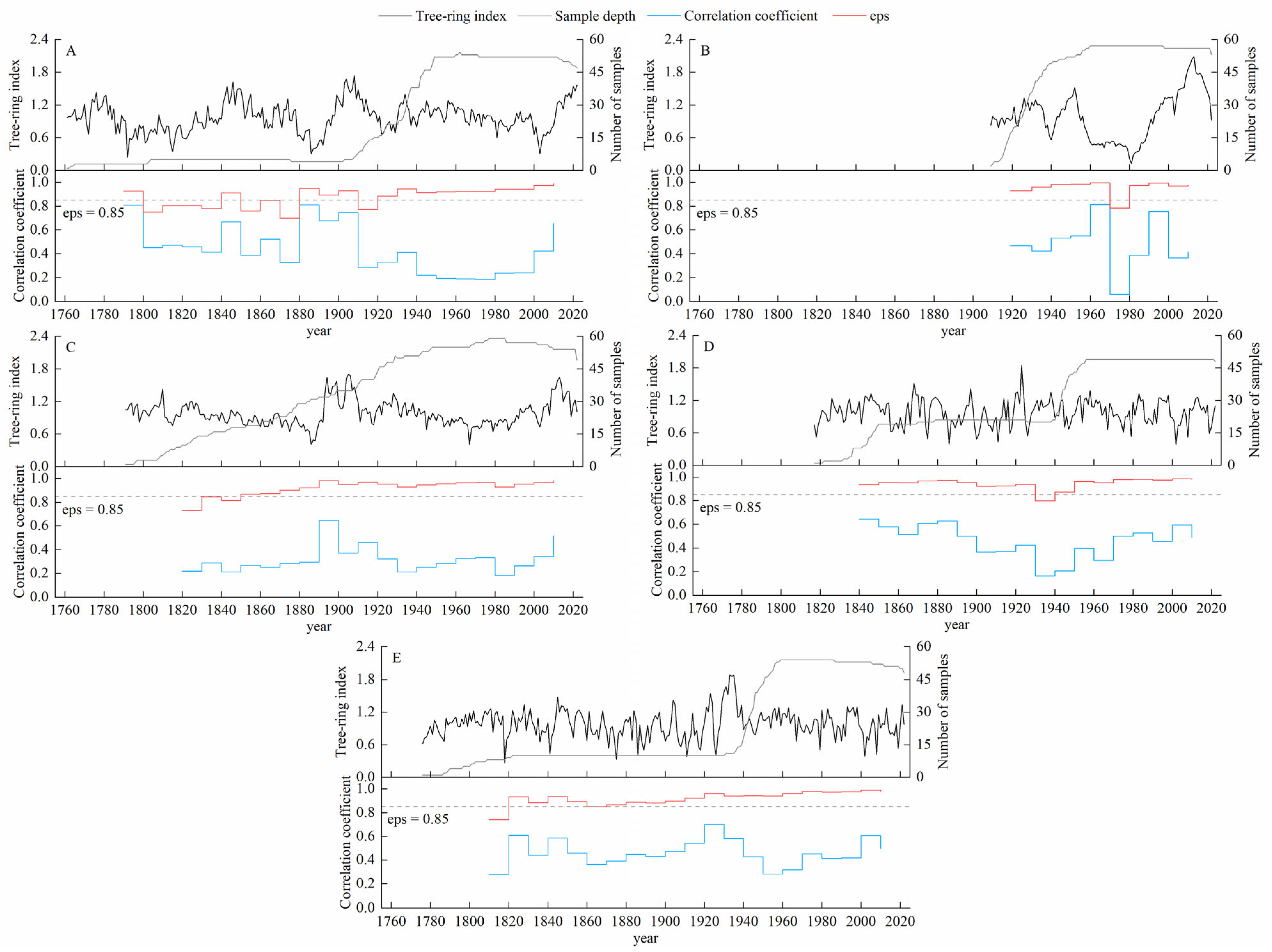
We established standardized tree ring width chronologies for Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica for the five elevations (Figure 2) and analyzed the characteristic parameters to retain the low-frequency climate information in the chronologies. As shown in Table 2, the values of most parameters (signal-to-noise ratio, inter-series correlation, inter-sample correlation, inter-tree correlation, first-order autocorrelation, and sample variance explained) were generally higher for the ZM-H chronology than the values for the other chronologies. This result indicates that the quality was higher for the ZM-H chronology. However, the ZM-H chronology was the shortest, spanning only 112 years. All five elevation chronologies exhibited high expressed population signal (EPS) values, indicating that they were suitable for dendroclimatic analysis.
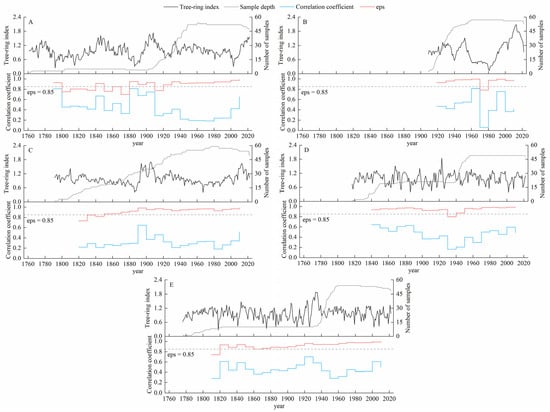
Figure 2.
Standardized chronology, sample depth, expressed population signal, and mean inter-series correlation at different elevations. (A) High elevation. (B) Medium–high elevation. (C) Medium elevation. (D) Medium–low elevation. (E) Low elevation.

Table 2.
Main characteristic parameters of tree ring width standardized chronology.
3.2. Climate Response Analysis
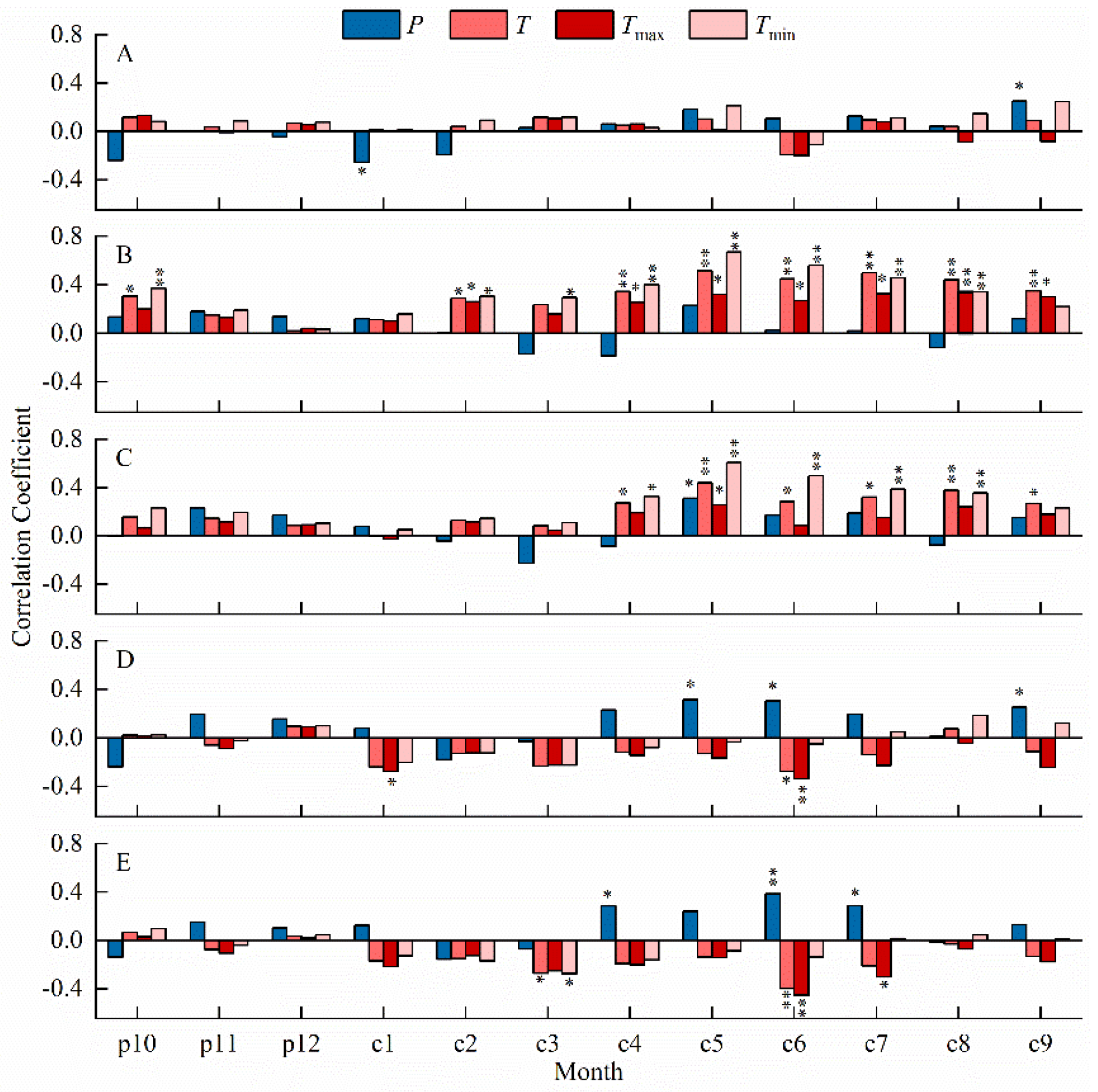
The monthly correlation analysis between the chronologies at the five elevations and the climate factors (Figure 3) shows that the ZH chronology is significantly negatively correlated with one-month precipitation and significantly positively correlated with one-month precipitation. The ZM-H chronology shows a significant positive correlation with nine-month temperature. The ZM chronology is significantly positively correlated with six-month temperature and one-month precipitation. The ZM-L chronology exhibits a significant negative correlation with two-month temperature and a significant positive correlation with three-month precipitation. The ZL chronology demonstrates a significant negative correlation with three-month temperature and a significant positive correlation with three-month precipitation. The ZM-H chronology has the strongest response to climate factors, particularly temperature, despite its shorter length. To increase the length of the reconstruction sequence, we performed a correlation analysis of the chronologies at all elevations. We found that the ZM-H and ZM chronologies had very high correlation values. Therefore, we integrated the data into a composite chronology (ZS). The combined correlation analysis revealed that the ZS chronology exhibited the highest correlation coefficient with the average minimum temperature from May to July (r = 0.726, p < 0.001, n = 61). The ZL chronology displayed the highest correlation coefficient with precipitation from August to July (r = 0.649, p < 0.001, n = 61).
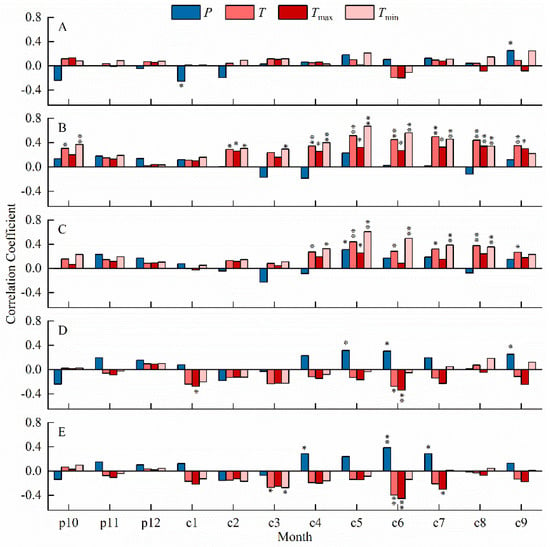
Figure 3.
Pearson correlation between climate data and chronology. (A) High elevation. (B) Medium–high elevation. (C) Medium elevation. (D) Medium–low elevation. (E) Low elevation. p, previous year; c, current year. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
3.3. Reconstruction and Verification
We used the reliability of the reconstruction equation, the magnitude of variance explained, and the physiological significance of Pinus sylvestris as criteria. Based on the results of the correlation analysis, we reconstructed the average minimum temperature from May to July, and the cumulative precipitation from August to July, to validate the results. Linear regression analysis was employed to establish the reconstruction equation as follows:
where and represent the reconstructed values of the average minimum temperature from May to July of the current year and the cumulative precipitation from the previous August to the current July in the study area, while and represent the annual tree ring sequences of ZS and ZL at the sampling points. The complex correlation coefficients of this transformation function are 0.726 and 0.649, respectively, and the values of variance explained are 0.528 and 0.421 (adjusted R-squared 0.520 and 0.411) for the two variables. The F-test values are 65.896 and 42.850, both exceeding the significance level of 0.01. We used this equation and considered a sample signal strength (SSS) > 0.85 to establish relationships between the standardized tree ring width chronologies and the average minimum temperature from May to July for 1814–2022 A.D. and the cumulative precipitation from August to July for 1809–2022 A.D. in the Greater Khingan Mountains.
(n = 61, r = 0.726, R2 = 0.528, R2adj = 0.520, SE = 0.592, F = 65.90)
(n = 61, r = 0.649, R2 = 0.421, R2adj = 0.411, SE = 50.993, F = 42.85)
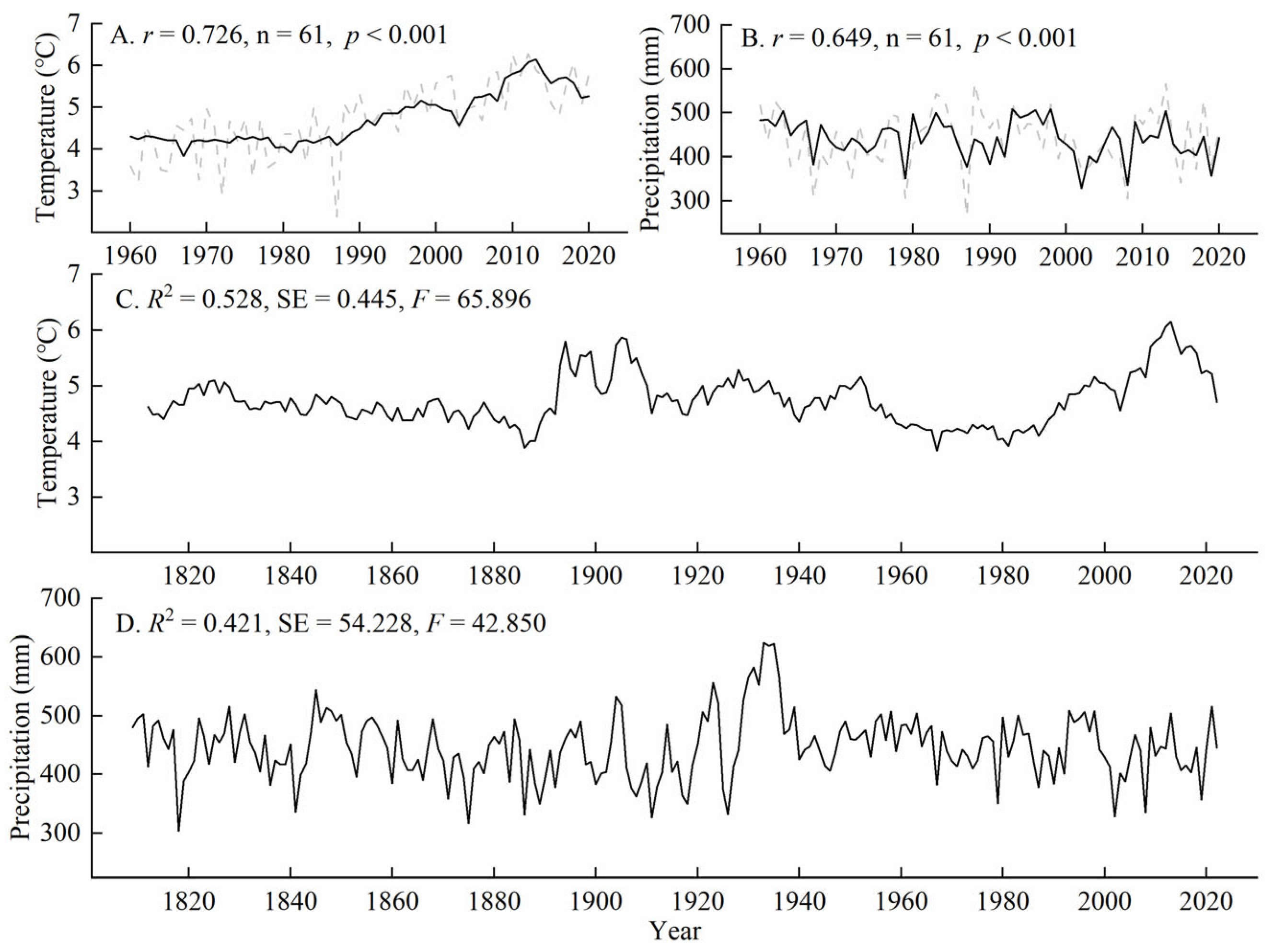
The reconstructed temperature and precipitation series accurately captured the variations in the sequences during the reconstruction period (1960–2020). Both variables exhibited good consistency in their temporal trends. Figure 4A,B show the reconstructed temperature and precipitation series. We conducted a split-period test by dividing the series into 1960–1990 and 1991–2020 to validate the reliability of the reconstruction equation. These two periods served as independent verification and calibration periods. The verification results of the reconstruction equation are presented in Table 3. The results indicate that the reduction in the error (RE) and the coefficient of efficiency (CE) values were positive, and the sign test (S) for the original values reached a significance level of 0.05 during the verification period. All statistical parameters confirmed the reliability of the reconstruction equation. Therefore, it can be concluded that the reconstruction equation is stable, and the reconstructed sequences of average minimum temperature and precipitation are reliable.
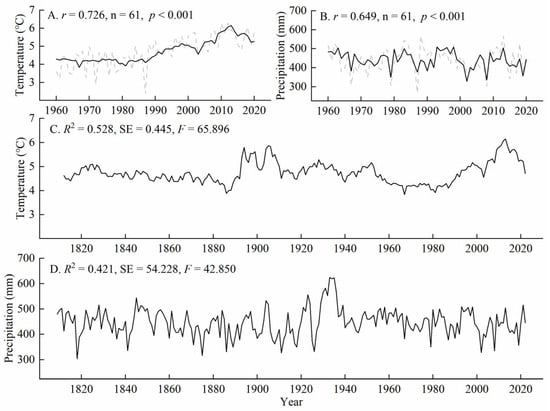
Figure 4.
Comparison of reconstructed and measured values. ((A) minimum temperature; (B) precipitation) and reconstructed sequence ((C) minimum temperature; (D) precipitation).

Table 3.
Statistical tests for reconstruction equations.
3.4. Fluctuation Characteristics of the Reconstructed Sequence
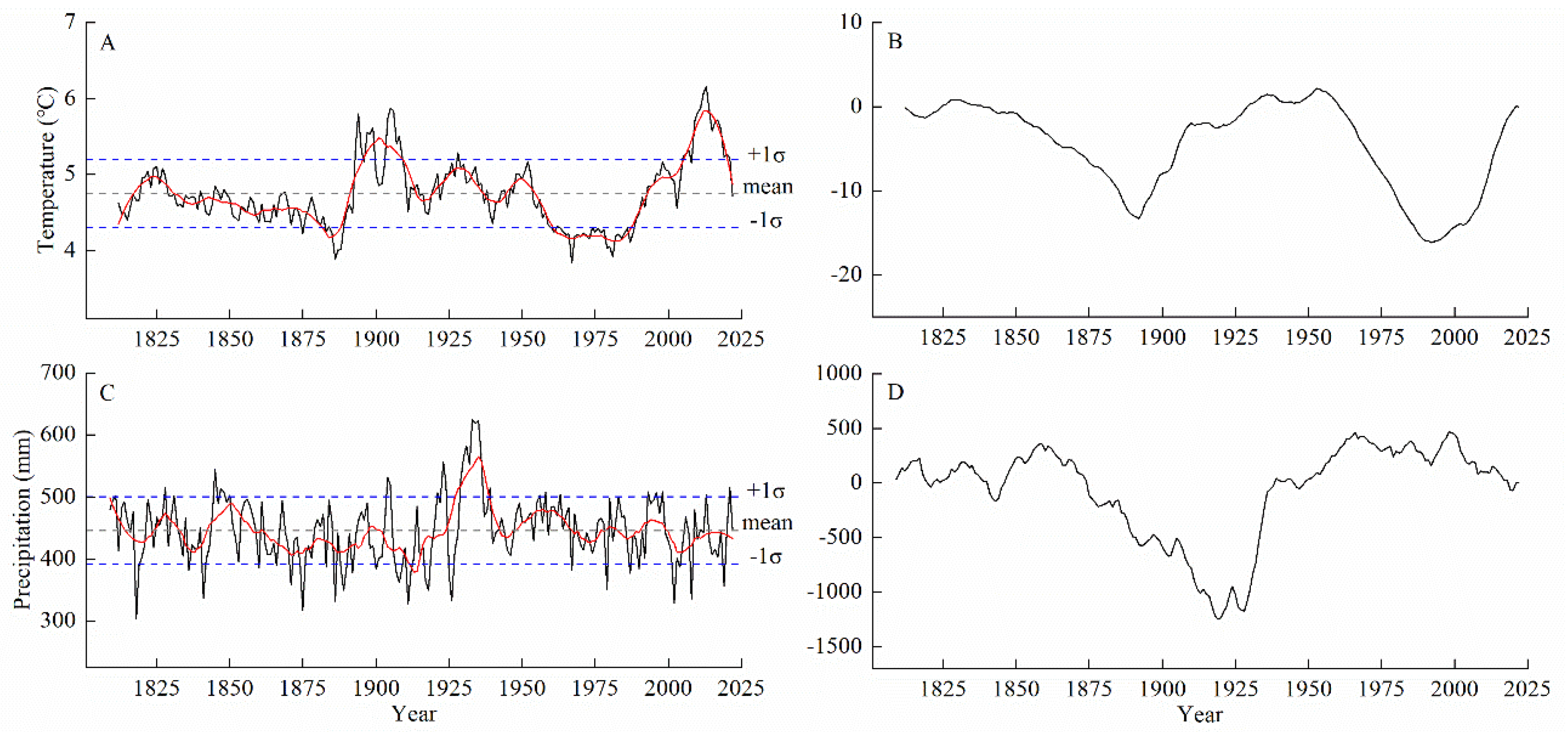
Figure 5A,C depict the historical variations in the average minimum temperature from May to July since 1812 and cumulative precipitation from August to July since 1809 in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains. A 21-year low-pass filter was applied to the series to determine the low-frequency trends in temperature and precipitation. The average value of the reconstructed temperature series was 4.75 °C, with a standard deviation of 0.44 °C. The average value of the precipitation series was 446.16 mm, with a standard deviation of 54.22 mm. Years in which the average temperature exceeded ±1–2 standard deviations were defined as warm (cold) years, and years in which the average temperatures exceeded ±2 standard deviations were defined as extremely warm (cold) years. Years in which the average precipitation exceeded ±1–2 standard deviations were defined as wet (dry) years, and years in which the average precipitation exceeded ±2 standard deviations were defined as extremely wet (dry) years. There were 12 years with extremely warm conditions and 1 year with extremely cold conditions in the past 211 years (Table 4). Two warm periods (1896–1909 and 2006–2020) and two cold periods (1882–1888 and 1961–1987) were identified. There were 7 years with extremely wet conditions and 8 years with extremely dry conditions in the past 214 years (Table 4). Additionally, a wet period was observed from 1928 to 1938, and a dry period occurred from 1912 to 1914.
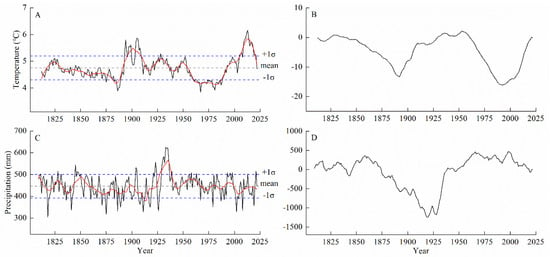
Figure 5.
Reconstruction of the mean minimum temperature and precipitation series and the 210-year sliding average (A,C) and the cumulative distance horizon (B,D).

Table 4.
Reconstruction of the extremes of the mean minimum temperature and precipitation series.
The cumulative distance horizon curves (Figure 5B,D) indicate low temperature and precipitation variations during different historical periods. The reconstructed curve of the summer low-temperature anomalies had a “W” shape, which was divided into four periods: from 1812 to 1892, the cumulative anomaly curve decreased, indicating cool summers; from 1893 to 1953, the cumulative anomaly curve increased, indicating hot summers; from 1954 to 1992, the cumulative anomaly curve decreased, entering another cool summer period; from 1993 to 2022, the cumulative anomaly curve increased, entering another hot summer period. The reconstructed curve of the precipitation anomalies had one valley. From 1858 to 1919, the cumulative anomaly curve decreased, indicating a dry period; from 1920 to 1966, the cumulative anomaly curve increased, indicating wet conditions. From 1809 to 1857 and from 1967 to 2022, the precipitation anomaly values fluctuated around zero (the average precipitation value), indicating a relatively stable period. Figure 5B,D show that the study area experienced hot summers and water shortages from 1893 to 1919, making it highly susceptible to severe drought events.
3.5. Periodicity in the Reconstruction Sequence
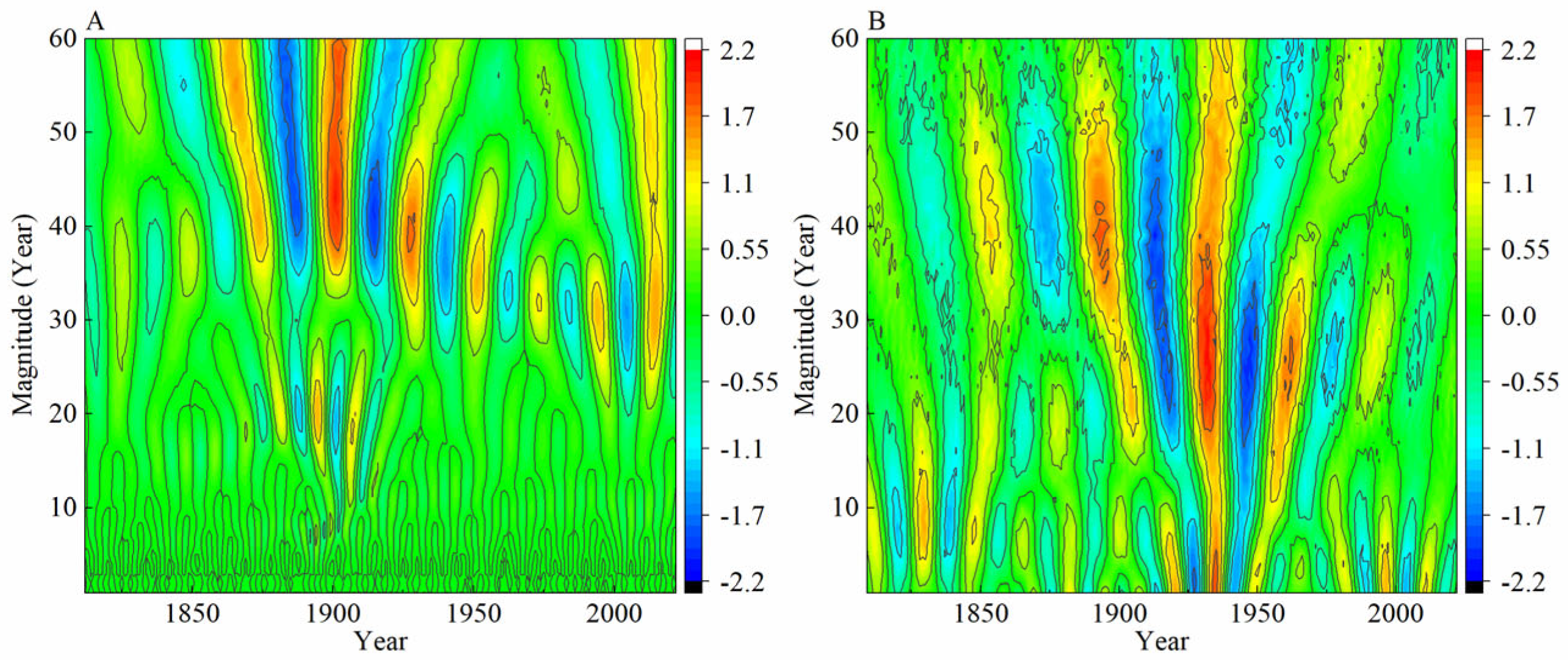
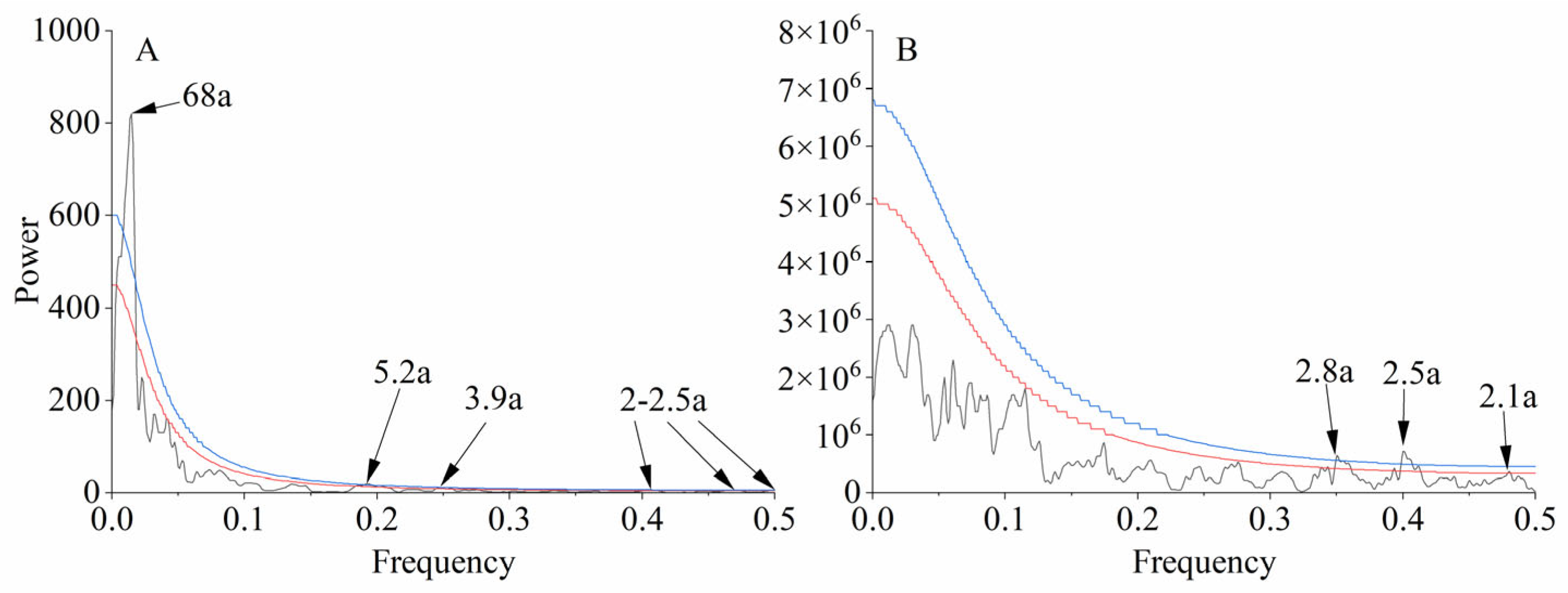
The results of wavelet analysis (Figure 6) and multi-window spectrum analysis (Figure 7) indicate that the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains over the past 210 years exhibited multiple interannual and decadal variations. The average minimum temperature series shows various periodicities (95% confidence interval) at scales of 2–2.5, 3.9, 5.2, and 68 years. The precipitation series also exhibits multiple periodicities (95% confidence interval) at scales of 2.1, 2.5, and 2.8 years, and most of the periodic variations are significant (99% confidence interval).
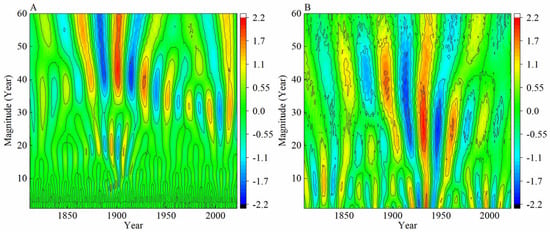
Figure 6.
Reconstruction of wavelet analysis of mean minimum temperature (A) and precipitation (B).
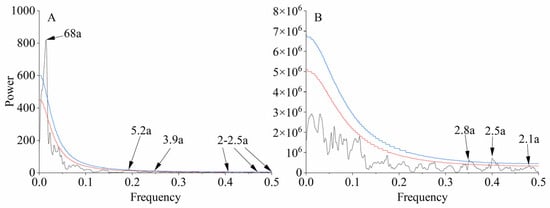
Figure 7.
Multi-window spectral analysis for reconstruction of mean minimum temperature (A) and precipitation (B). — (red line), p < 0.05; — (blue line), p < 0.01.
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of Tree Radial Growth in Response to Climatic Factors
The average minimum temperature exceeded 5 °C (5.07 °C) in May, coinciding with the physiological minimum temperature for tree growth [31]. The trees are in the early growth stage, and the temperature increase accelerates snow melting, raising soil water content and soil temperatures, thereby promoting early xylem cell division and growth [11,32]. Thus, the dormancy of trees occurred earlier. Higher temperatures in the spring encourage earlier skeleton activity, extending the tree’s growth period and making the annual rings wider [33,34,35]. Higher temperatures during the growing season increase the rate of photosynthesis, promote cell division, accelerate radial growth, increase the speed of growth, and make the annual rings wider [11,34,35,36]. Summertime is the peak growth period for trees, with relatively high temperatures favoring photosynthesis, allowing for the buildup of photosynthesis to promote tree growth [37]. The precipitation from August to July is a crucial weather variable, affecting soil moisture availability and tree growth [9]. July is the growing season for trees and also for cell growth and division for conifers. Adequate water supply during the growing season ensures adequate physiological activities and the accumulation of photosynthetic products in trees. Moreover, sufficient precipitation at this time compensates for water loss caused by high-temperature evaporation at high temperatures and facilitates cell division and stretching, leading to larger cells and slimmer cell walls, which is conducive to tree growth [38,39,40]. Therefore, the analysis of tree ring width in response to climatic factors in this study is reasonable.
4.2. Comparison with Historical Events and Other Reconstruction Results
In contrast to the elaborate historical record of southern China, the vicinity of our study area has few and fragmented meteorological disaster records due to the historical nomadic lifestyles, warfare, and relatively low population density. These finite historical accounts do not adequately characterize past climatic changes, but can be used to validate the accuracy of climate sequences rebuilt using tree ring chronologies. The northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains is located in Heilongjiang Province and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Therefore, we used the records of droughts and floods in the “China Meteorological Disasters Encyclopedia—Heilongjiang Volume” and “China Meteorological Disasters Encyclopedia—Inner Mongolia Volume” to validate the reconstructed series. During the wet period of the reconstructed precipitation series (1928–1938), heavy rainfall events and floods occurred in the Greater Khingan Mountains. From 1933 to 1935, severe flood disasters occurred for three consecutive years. This was described as the “Heilongjiang water level showing a rapid rise”, “Heilongjiang flooding with the highest flood peak of 99.36 m”, and “excessive rainfall in Hailar in autumn and summer”. Similarly, records of drought periods and extreme drought years were observed in the reconstructed series. For example, the Dongmeng region experienced drought in the summer of 1899; the rivers were dry, and the grass withered. In 1909, drought occurred in Buteha and Zalantun, and the entire region of the Nenjiang Prefecture suffered from summer drought, resulting in only 30%–40% of the normal harvest. In June of 1914, the Hohhot and Zalantun regions experienced drought, and in 1918, Buta Banner (Zalantun) received only 56.9 mm of rainfall in July and August, which was nearly 80% below the normal level, causing severe drought. These records confirm that the study area experienced hot summers and water shortages from 1893 to 1919, making it highly susceptible to severe drought events.
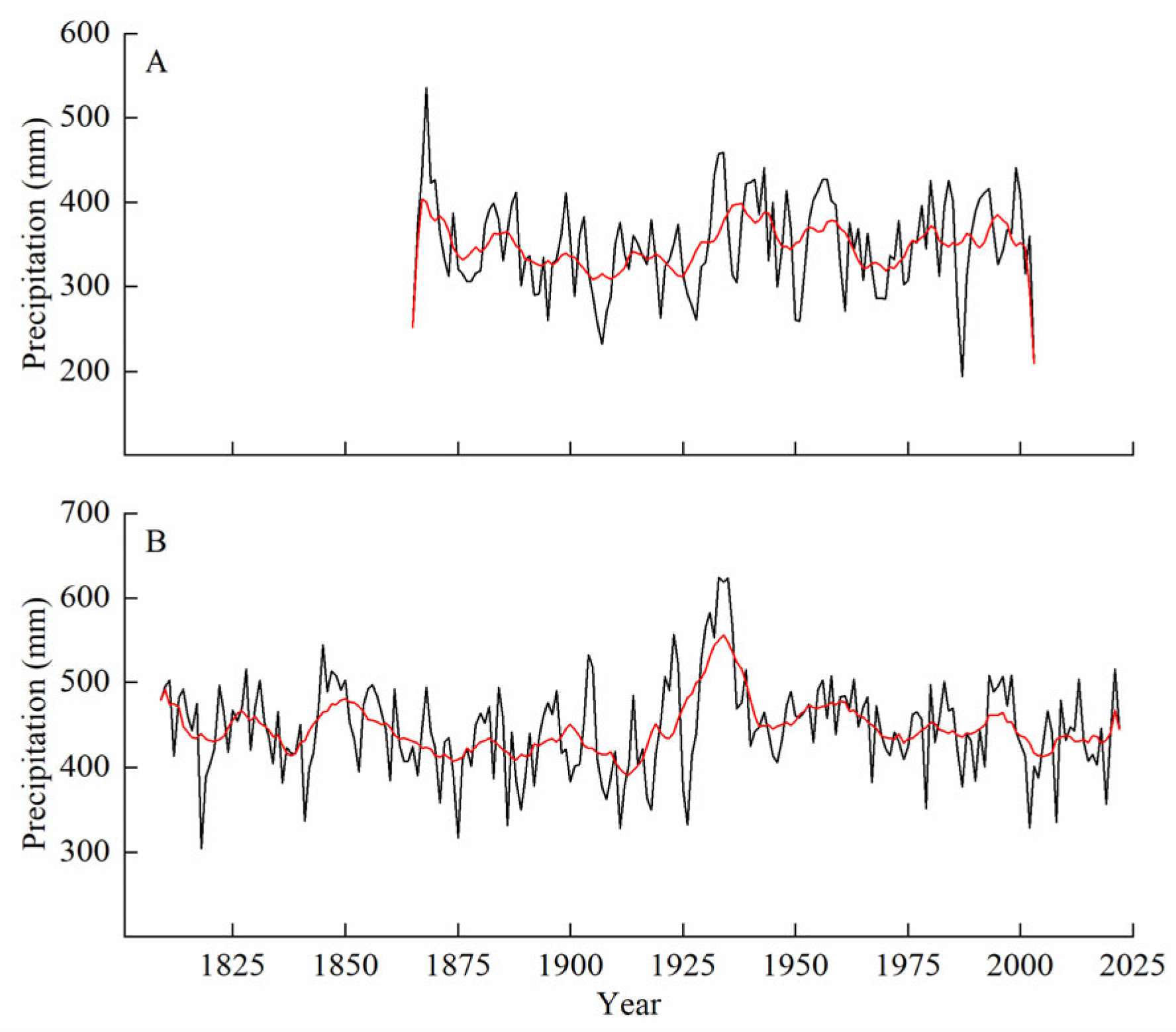
We compared the reconstructed temperature and precipitation sequences with other nearby chronologies in the study area to confirm the accuracy of the reconstructed series. We found that the reconstructed climatic periods of warmth and dryness were consistent with those of the other chronologies, with good matches in most cases. However, some differences between the series were observed and were attributed to different regions in the study area, tree species, chronologies, and reconstruction seasons [41]. Additionally, the differences in the standardization of tree ring data could also have caused mismatches in dry and wet periods [41]. The warm periods recorded in the reconstructed minimum temperature series (1896–1909 and 2006–2020) were also observed in the temperature series reconstructed by Chen et al. [42] in northern Inner Mongolia. Furthermore, the continued warming in the 21st century is a widely recognized phenomenon. The wet period (1928–1938) and drought period (1912–1914) recorded in the reconstructed precipitation series are consistent with the findings of Liu et al. [43] in the Kalaqin region of Inner Mongolia, Zhang et al. [44] in the Mohe area, and Chen et al. [45] in the forest-steppe ecotone of northern Inner Mongolia, who reconstructed precipitation series in their respective studies. Our reconstructed precipitation series showed a highly similar trend to that in Hailar, Inner Mongolia (1865–2003) (r = 0.252, p < 0.01, n = 139) (Figure 8), reconstructed by Liu et al. [9], where nearly all precipitation peaks and troughs matched. Although the tree species were the same in these studies, the straight-line distance between the two study areas exceeded 350 km. Additionally, the most severe drought in the reconstruction period occurred from 1893 to 1919, with precipitation consistently below average levels and the opposite for temperature. This drought period was also widespread in the arid and semi-arid regions of Northern China, leading to widespread famine and significant loss of life [46]. These results confirm the reliability of the reconstructed average minimum temperature and precipitation series in revealing the characteristics of climate change in this region.
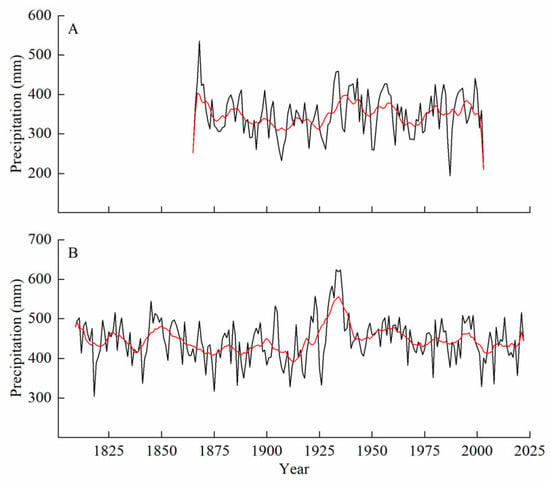
Figure 8.
Comparison of reconstructed precipitation sequences with neighboring sequences in this paper: (A) reconstruction of minimum temperature in Hailar; (B) reconstruction of minimum temperature in the Mangui area (this study).
4.3. Drivers of Climate Change
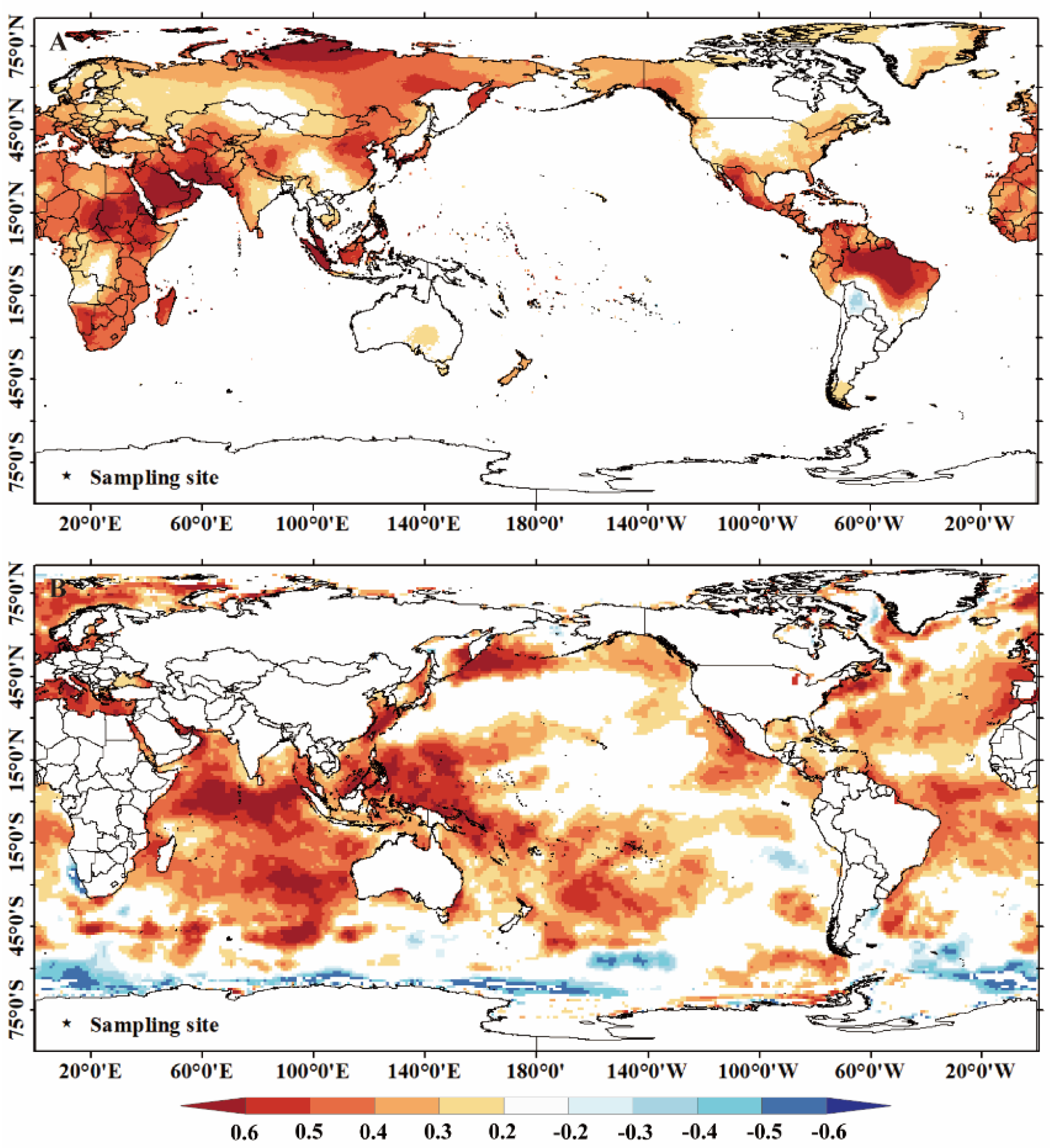
Local, regional climate and larger-scale climate variations influence tree growth in Northern China [47,48]. Wavelet analysis revealed that the reconstructed mean minimum temperature series had period variations of 2–2.5, 3.9, 5.2, and 68 years, and the precipitation series had period variations of 2.1, 2.5, and 2.8 years, respectively. The widely accepted El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle is 2–7 years [49,50,51], and the periods of 2–2.5, 2.8, 3.9, and 5.2 years coincide with this cycle, indicating a possible relationship between temperature and precipitation changes in the region and ENSO activity [52,53]. Additionally, the widespread 2-year period may be associated with the quasi-biennial oscillation. Previous studies have shown that quasi-biennial oscillations have a wide range of influence and may be related to coupled oscillations between the ocean and the atmosphere [54]. Furthermore, another crucial period observed in this study was the 68-year period of the mean minimum temperature series, which may be related to the PDO because it coincides with the 50–70-year cycle of the PDO [55]. This is strongly supported by the significant positive correlation between the reconstructed average minimum temperature series and the Pacific sea surface temperatures (SSTs) (Figure 9). The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) period/signal is widely reflected in most tree ring-based temperature and precipitation reconstructions [20,56]. It has a crucial influence on droughts in the northern part of the Greater Khingan Mountains because it modulates the ocean–atmosphere–land surface interactions and other large-scale circulation patterns [21,57]. These periodic variations indicate that the hydrothermal changes in the Manzhouli area reflect the fluctuations in the East Asian summer monsoon and indicate large-scale ocean–land coupling. However, the complex atmospheric circulations and limited understanding of their potential interactions make it difficult to distinguish their individual impacts. Further research is needed to understand the underlying physical mechanisms.
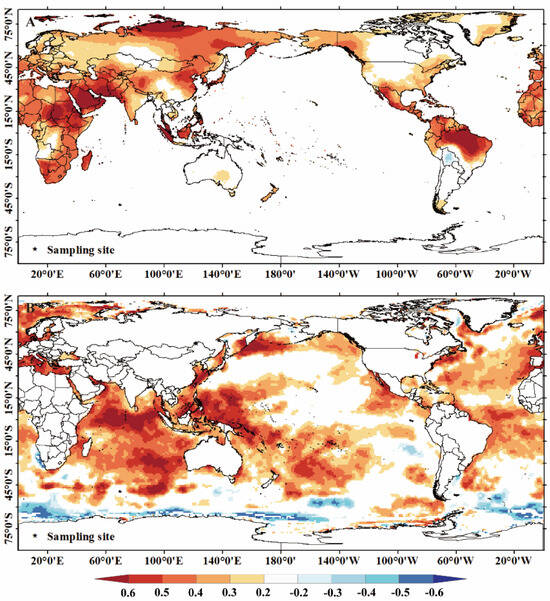
Figure 9.
Reconstruction of spatial correlation between mean minimum temperature and land (A) and sea (B) temperatures.
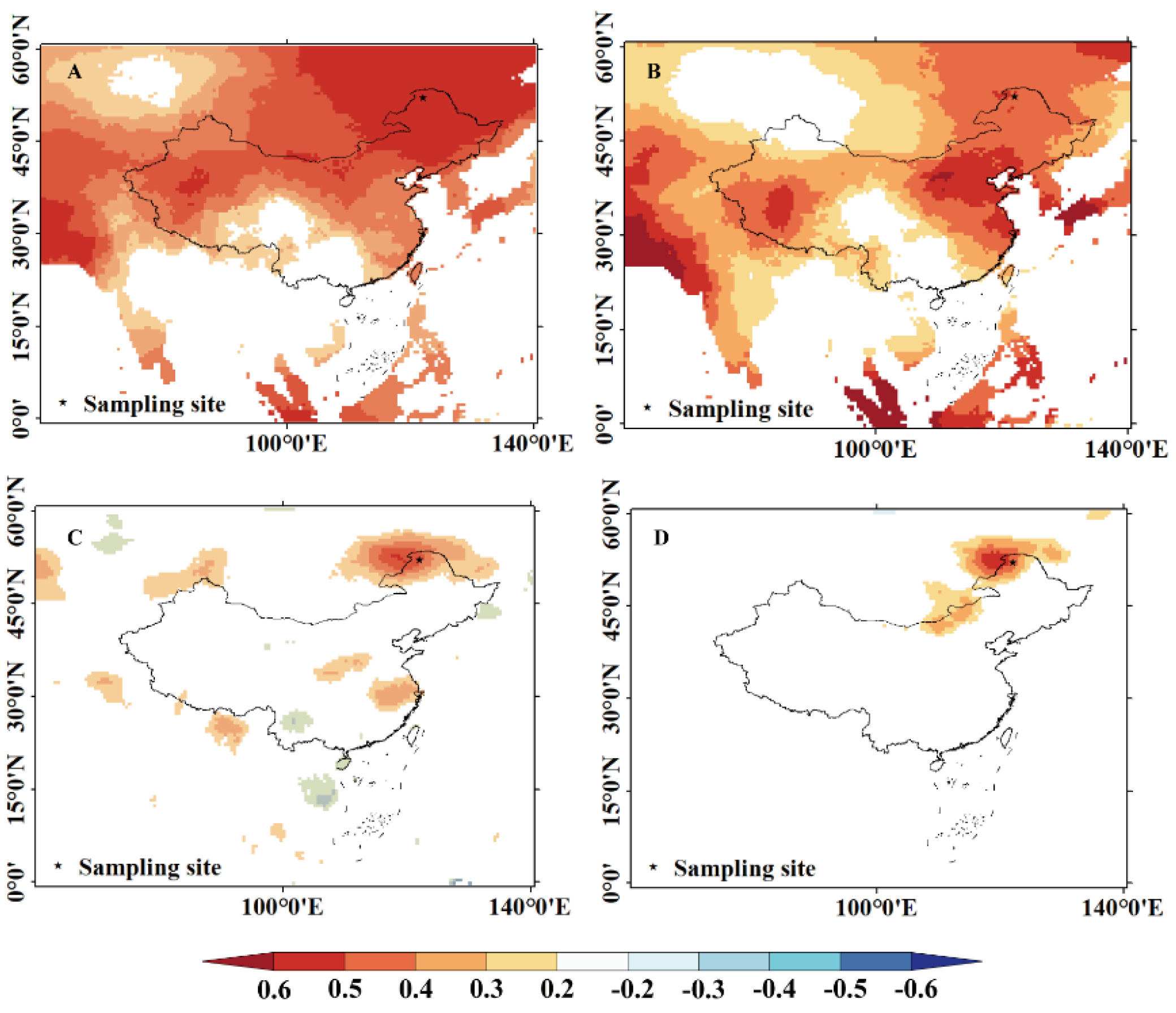
We conducted a spatial correlation analysis between the CRU TS 4.07 gridded observational dataset and the observed and reconstructed average minimum temperature and annual precipitation series (1901–2020) to assess the spatial representativeness of the re-constructed temperature and precipitation series. The results (Figure 10) indicate that both series exhibited good spatial consistency. Significant (p < 0.05) correlations were observed in a large area, but areas with highly significant correlations were relatively small. This finding suggests that the reconstructed series captured large-scale interannual temperature variations in the high-frequency domain surrounding the northern Greater Khingan Mountains. Additionally, we analyzed the spatial correlation between the reconstructed temperature series and global SSTs. Figure 9 shows that the reconstructed temperature series has high correlation coefficients with land temperatures in northern Siberia and near the equator and with SSTs in the Western and Northern Pacific, Indian Ocean, and central Atlantic. This result indicates that temperature variations in these regions influence radial tree growth in the northern Greater Khingan Mountains. Therefore, the summer monsoon and the Siberian winter monsoon from the south affect forest ecosystems in the Greater Khingan Mountains.
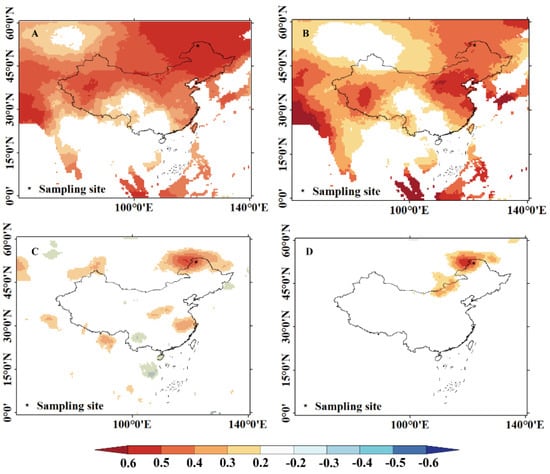
Figure 10.
Spatial correlation analysis of measured and reconstructed mean minimum temperature and precipitation series with grid point data. (A) measured mean minimum temperature; (B) reconstructed mean minimum temperature; (C) measured precipitation; (D) reconstructed precipitation.
5. Conclusions
We reconstructed the average minimum temperature series for May to July from 1812 to 2022 and the annual precipitation series from August to July from 1809 to 2022 using Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in the Mangui region of Inner Mongolia. The reconstructed average minimum temperature series explained 52.8% (adjusted for degrees of freedom, 52.0%) of the variance in the observed data from 1960 to 2020, and the reconstructed precipitation series explained 42.1% (adjusted for degrees of freedom, 41.1%) of the variance in the observed data from 1960 to 2020. Two warm periods (1896–1909 and 2006–2020) and two cold periods (1882–1888 and 1961–1987) occurred during the past 211 years. One wet period (1928–1938) and one dry period (1912–1914) were observed over the past 214 years. Moreover, the study area experienced hot summers and dry spells from 1893 to 1919, making it highly susceptible to severe drought events. The warm, cold, wet, and dry periods in the reconstructed sequence showed high consistency with temperature and precipitation series in surrounding areas. The reconstructed average minimum temperature series exhibited periodic variations of 2–2.5, 3.9, 5.2, and 68 years, whereas the precipitation series exhibited periodic variations of 2.1, 2.5, and 2.8 years. ENSO events, quasi-biennial oscillation, and PDO affected the climatic periodic variations in the study area. These results suggest that the tree ring chronology series accurately reflected the climate in the study area for two centuries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W. and D.Z.; methodology, Z.W. and K.S.; software, Z.W., X.L. and K.S.; validation, D.Z. and T.Z.; formal analysis, Z.W.; investigation, Z.W.; resources, D.Z.; data curation, X.W., S.Z., X.L., T.L. and Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.W.; writing—review and editing, Z.W., D.Z. and T.Z.; project administration, Z.W. and D.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41671064), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (No. TD2023D005) and the Academic Innovation Project of Harbin Normal University (HSDBSCX 2022-102).
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank researcher Yu Liu for providing the reconstructed data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known financial interests or personal relationships that might influence the work reported here.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Fu, B. Effects of global climate change on forest ecosystems. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; He, X.; Chen, Z. Tree-ring growth responses of Mongolian oak (Quercus mongolica) to climate change in southern Northeast: A case study in Qianshan Mountains. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Variability of mean temperature since 1808 A.D. in Shennongjia Mountain area inferred from tree ring. Quat. Sci. 2021, 41, 334–345. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Mao, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, X.; Huang, W.; Liu, R.; Li, Y. Response of radial growth of Pinus koraiensis in broad-leaved Korean pine forests with different latitudes to climatic factors. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Liu, R.; Jiahan, S.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of growth characteristics and climate responses in four coniferous tree species of southern Luoxiao Mountains. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, K.; Osborn, T.; Schweingruber, F. Large-scale temperature inferences from tree rings: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2004, 40, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Cui, J.; Peng, M.; Huo, J.; Yang, L. A Tree-Ring-Based Assessment of Pinus armandii Adaptability to Climate Using Two Statistical Methods in Mt. Yao, Central China during 1961–2016. Forests 2021, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bao, G.; Song, H.; Cai, Q.; Sun, J. Precipitation reconstruction from Hailar pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) tree rings in the Hailar region, Inner Mongolia, China back to 1865 AD. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2009, 282, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, M.; Fang, K.; Gao, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, F. Tree ring based streamflow reconstruction for the Upper Yellow River over the past 1234 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 3236–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cook, E.; Li, J.; Lu, H. Unprecedented January–July warming recorded in a 178-year tree-ring width chronology in the Dabie Mountains, southeastern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2013, 381, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Fan, Y.; Shang, H.; Jiang, S.; Qin, L.; Zhang, H. Tree-ring width based streamflow reconstruction for the Kaidu River originating from the central Tianshan Mountains since AD 1700. Dendrochronologia 2020, 61, 125700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, T.; Shang, H.; Fan, Y.; Yu, S.; Jiang, S.; Mao, W.; Liu, X. Total Streamflow Variation for the Upper Catchment of Bosten Lake Basin in China Inferred from Tree-Ring Width Records. Forests 2023, 14, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Bu, R.; Xiong, Z.; Hu, Y. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation in Northeastern China from 1961 to 2005. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Yue, Y.; Xue, J.; Shi, L. How permafrost degradation threatens boreal forest growth on its southern margin? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; He, X.; Chen, Z.; Cui, M.; Li, N. Responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica radial growth to climate warming in Great Xingan Mountins: A case study in Mangui. Chin. J. Appl. Eeology 2011, 12, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J. Influence of forest fire disaster on forest ecosystem in Great Xing’anling. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2002, 24, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W. Chinese Tree Journal; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.; Luo, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Mao, H. Responses of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica tree ring width to climate factors at different elevations in the northern Greater Khingan Mountains. Dendrochronologia 2024, 83, 126166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Meng, S.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, B.; Liu, Q. April to July preipitation reeonstmction based on tree-ring width for the past 242 years in the norhem Greater Khingan Mountains, Northeast China. Quat. Sci. 2024, 44, 895–907. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Yao, Q.; Cooper, D.; Han, S.; Wang, X. Response of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica to water change and drought history reconstruction in the past 260 years, Northeast China. Clim. Past 2018, 14, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Duan, J. Reconstructing mean maximum temperatures of May–August from tree-ring maximum density in North Da Hinggan Mountains, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Guo, P.; Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Yu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, F. Reconstruction of the October mean temperature since 1796 from tree ring data at Wuying of Xiaoxinganling Mountains. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2009, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Fang, X.; Shao, X.; Yin, Z. Tree ring-based February–April temperature reconstruction for Changbai Mountain in Northeast China and its implication for East Asian winter monsoon. Clim. Past 2009, 5, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudureheman, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, D. A 219-year reconstruction of April–June mean minimum temperature from the tree-ring earlywood density on the Changbai Mountains, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 6150–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.H. Fundamentals of Tree-Ring Research; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, R.L. Computer-Assisted Quality Control in Tree-Ring Dating and Measurement; Tree-Ring Society: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.R.; Krusic, P.J. Program ARSTAN: A Tree-Ring Standardization Program Based on Detrending and Autoregressive Time Series Modeling, with Interactive Graphics; Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University: Palisades, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McAfee, S.; Guentchev, G.; Eischeid, J. Reconciling precipitation trends in Alaska: 2. Gridded data analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13820–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.; Osborn, T.; Lister, D. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations–the CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaganov, E.; Hughes, M.; Shashkin, A. Growth Dynamics of Conifer Tree Rings: Images of Past and Future Environments; Ecological Studies: Millbrook, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 183. [Google Scholar]
- Måren, I.; Karki, S.; Prajapati, C.; Yadav, R.; Shrestha, B. Facing north or south: Does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley? J. Arid Environ. 2015, 121, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Deslauriers, A.; Anfodillo, T.; Carraro, V. Evidence of threshold temperatures for xylogenesis in conifers at high altitudes. Oecologia 2007, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujansuu, J.; Yasue, K.; Koike, T.; Abaimov, A.; Kajimoto, T.; Takeda, T.; Tokumoto, M.; Matsuura, Y. Climatic responses of tree-ring widths of Larix gmelinii on contrasting north-facing and south-facing slopes in central Siberia. J. Wood Sci. 2007, 53, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.; Revuelto, J.; Gilaberte, M.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Pons, M.; Jover, E.; Esteban, P.; García, C.; Pomeroy, J. The effect of slope aspect on the response of snowpack to climate warming in the Pyrenees. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Kudo, K.; Rahman, M.; Nakaba, S.; Yamagishi, Y.; Nabeshima, E.; Nugroho, W.; Oribe, Y.; Kitin, P.; Jin, H.; et al. Climate change and the regulation of wood formation in trees by temperature. Trees 2018, 32, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, G.; Dai, L.; Wang, Q. Dendroclimatic analysis of Betula ermanii forests at their upper limit of distribution in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 240, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Peng, J.; Huo, J.; Chen, L. Temperature variation and influence mechanism of Pinus tabulaeformis ring width recorded since 1801 at Yao Mountain, He’nan Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bonan, G.; Sirois, L. Air temperature, tree growth, and the northern and southern range limits to Picea mariana. J. Veg. Sci. 1992, 3, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, K. Characteristics of ring-growth chronologies of Picea crassifolia and their responses to climate at different elevations in the Anyemaqen Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2007, 27, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; You, X. Dendrohydrology Research and Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Davi, N.; Cui, M.; Peng, J. Extension of summer (June–August) temperature records for northern Inner Mongolia (1715–2008), China using tree rings. Quat. Int. 2013, 283, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Hao, W.; Song, H.; Cai, Q.; Tian, H.; Sun, B.; Linderholm, H. Tree-ring-based annual precipitation reconstruction in Kalaqin, Inner Mongolia for the last 238 years. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, W.; Yu, S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, F.; Shang, H.; Qin, L. A tree-ring based precipitation reconstruction for the Mohe region in the northern Greater Higgnan Mountains, China, since AD 1724. Quat. Res. 2014, 82, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cui, M.; He, X.; Ding, W. Tree-ring based precipitation reconstruction for the forest-steppe ecotone in northern Inner Mongolia, China and its linkages to the Pacific Ocean variability. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 86, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, N.; Fang, X. The 1920s droughtrecorded by tree rings and historical documents in the semi-aridand arid areas of Northern China. Clim. Change 2006, 79, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Liu, Y. Temperature Variability since 1776 Inferr ed from Tree-rings of Pinus tabulaeformis in Mt. Helan. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Qin, J. Reconstruction of precipitation history in Taibai Mountain of Qinling Mountains based on tree-ring width and meteorological data in recent 160 years. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S. Changes of mean minimum temperature in June—July since 1798 in central Altay Mountain recorded by tree rings. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1944–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Rittenour, T.; Brigham-Grette, J.; Mann, M. El Niño–Like Climate Teleconnections in New England During the Late Pleistcene. Science 2000, 288, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Caballero, R. Eocene El Niño: Evidence for Robust Tropical Dynamics in the “Hothouse”. Science 2003, 299, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Shah, S.; Zhou, G.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Q. Tree-ring-recorded drought variability in the northern Daxinganling Mountains of Northeastern Chinaj. Forests 2018, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G. A general survey of the studies on El NiÃo and LaNi ña in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2000, 20, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Meehl, G.; Arblaster, J. The Tropospheric biennial oscillation and Indian Monsoon rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G.; Case, R. Variations in the Pacific Decadal Oscillation over the past millennium. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Application of tree ring analysis to the study on environment variation. Quat. Sci. 1990, 2, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Q. Tree-ring based summer temperature regime reconstruction in XiaoXingAnling Mountains, northeastem China since 1772 CE. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocli Matology Palaeoecol. 2018, 495, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).