The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Research Method
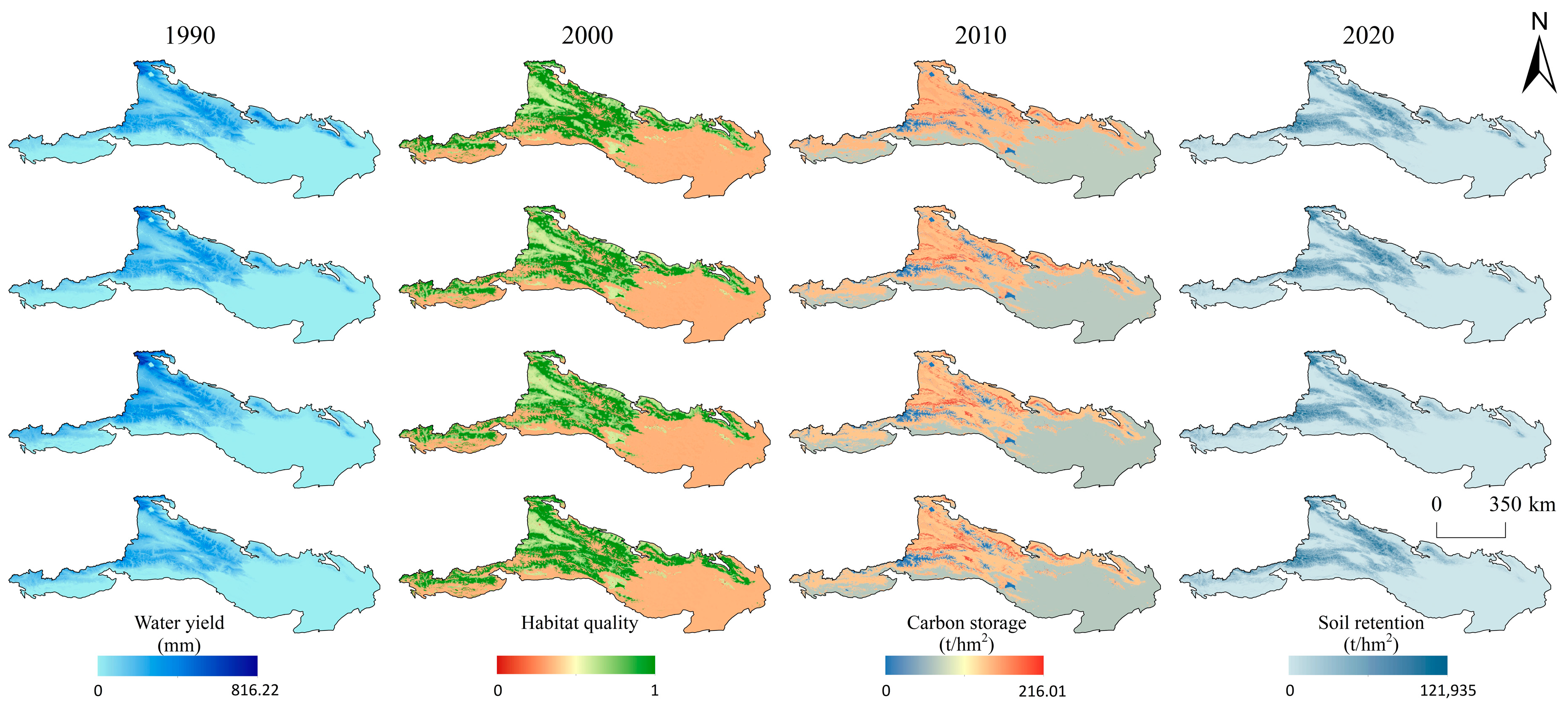
3.2.1. Ecosystem Service Assessment
Water Yield
Soil Retention
Carbon Storage
Habitat Quality
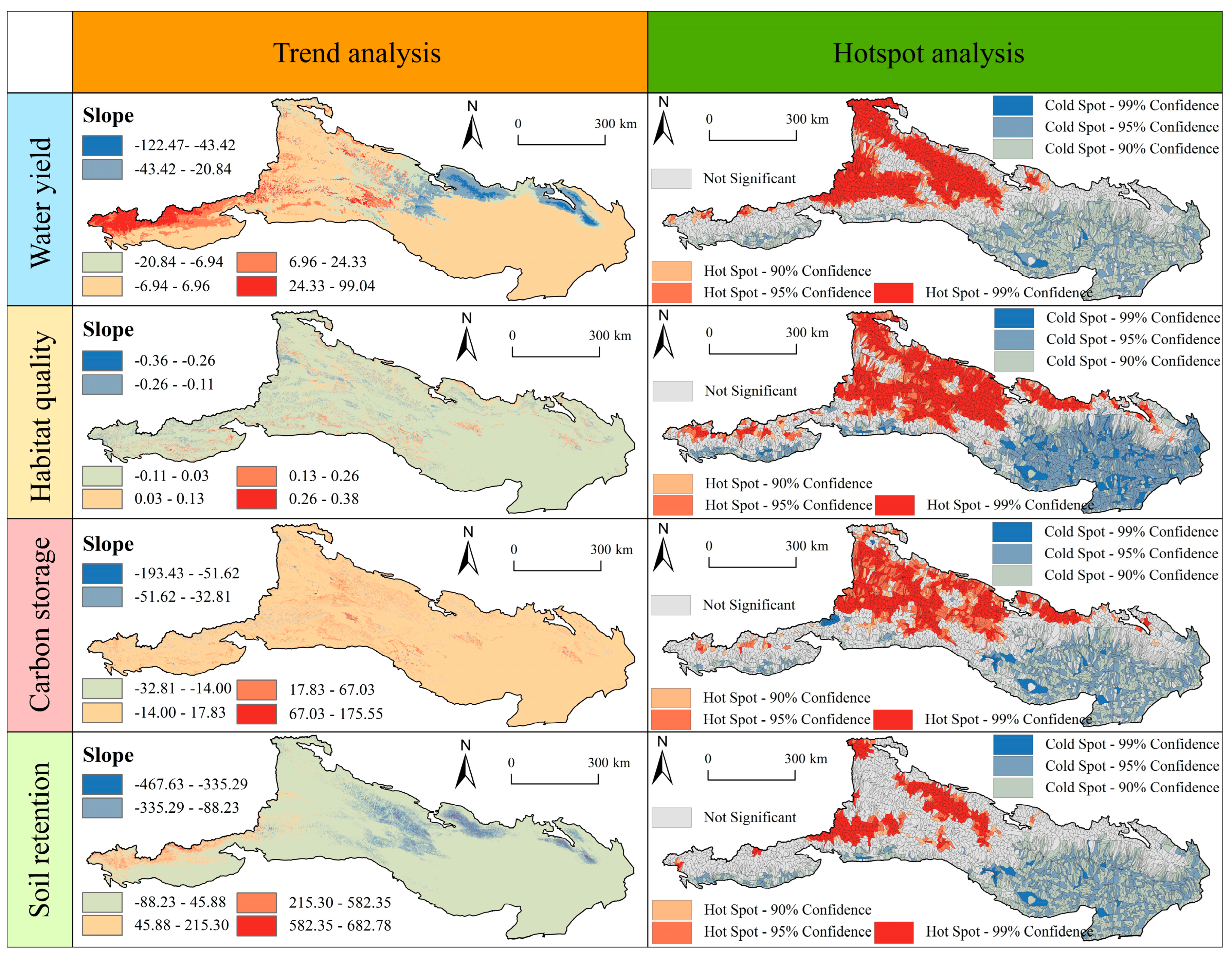
Trend Analysis
Hotspot Analysis
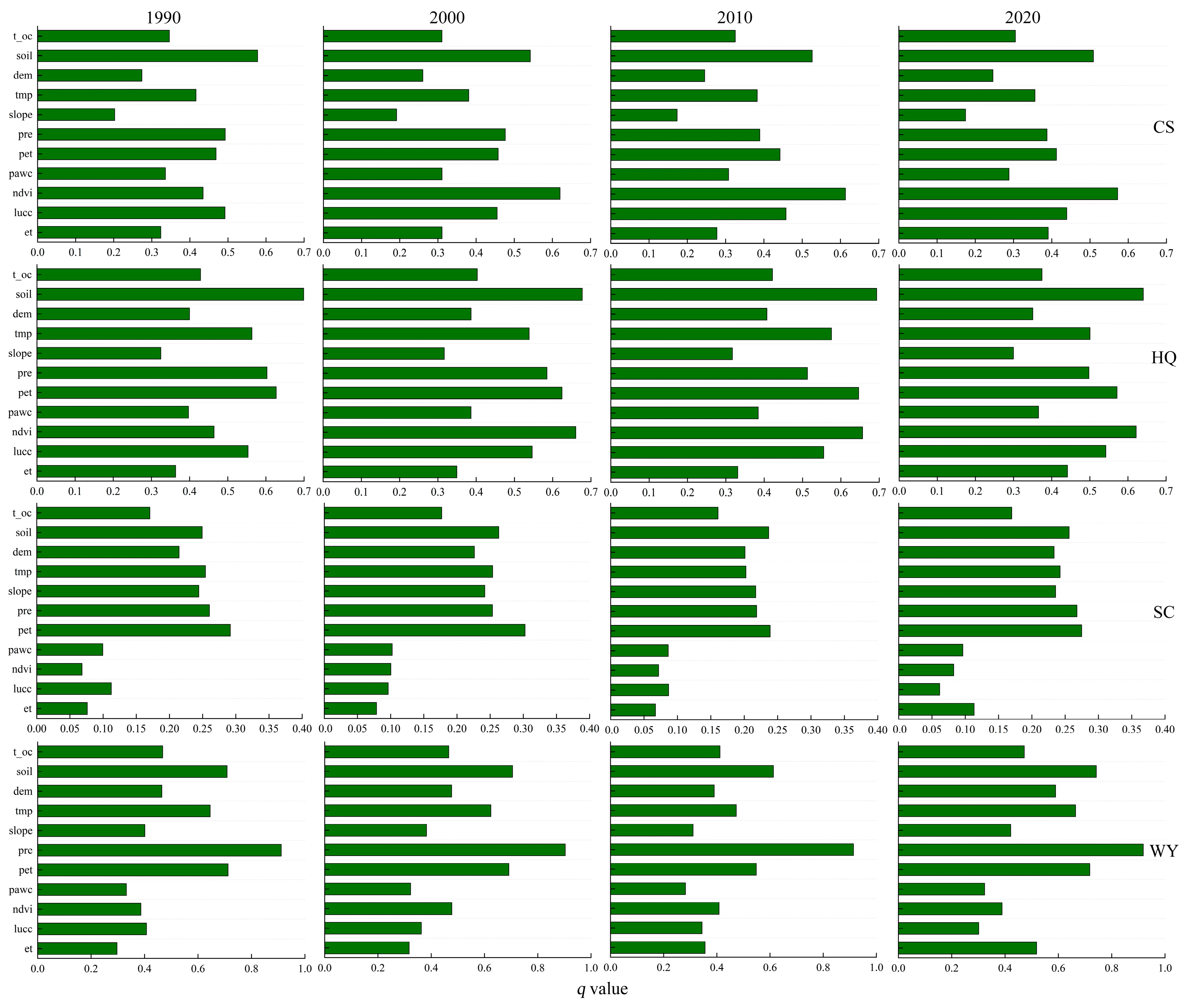
The GD Method
3.2.2. Analysis of ES Relationships
The Correlation Analysis of ES Pairs
Geographically Weighted Regression
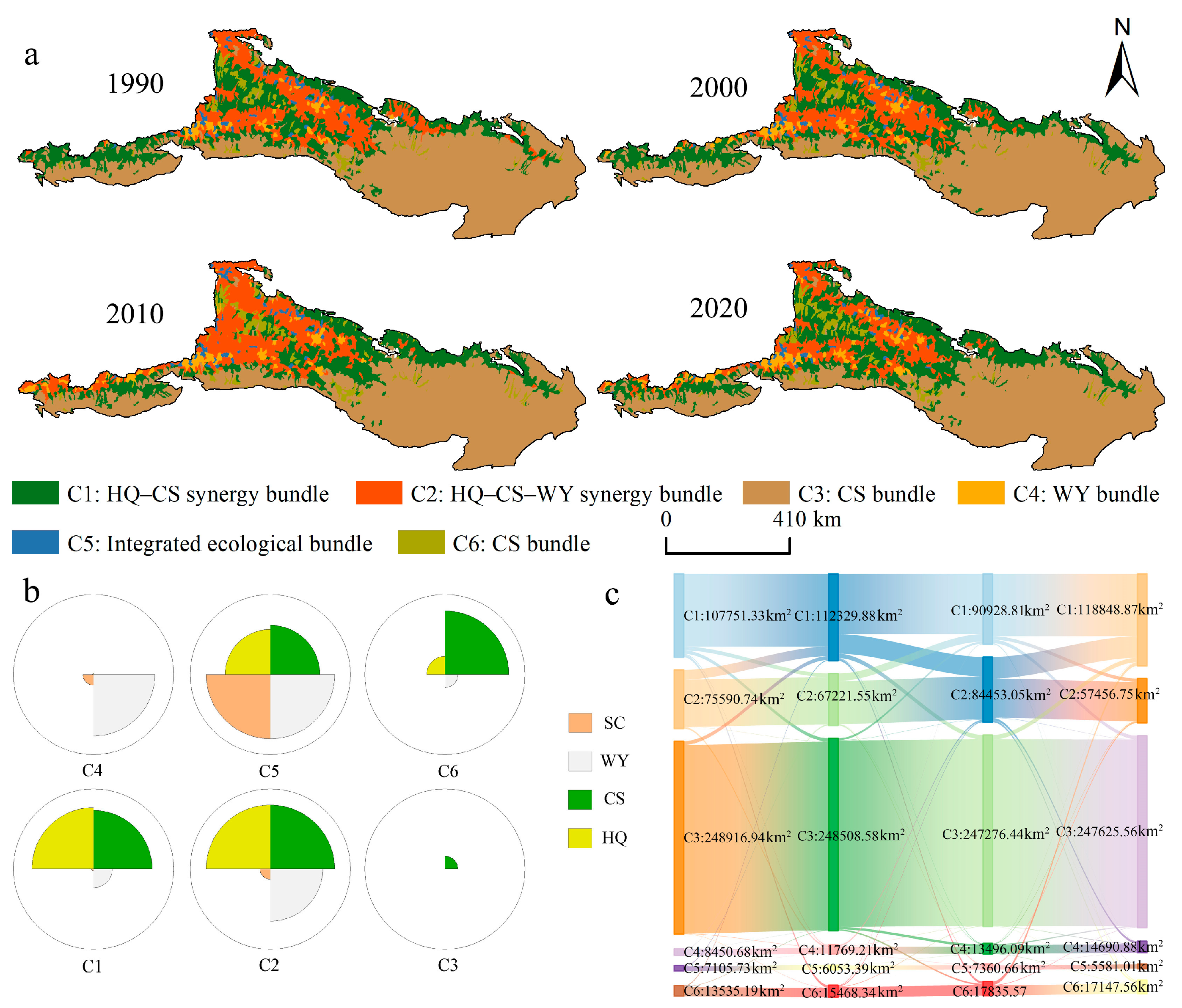
Identification of ES Bundles
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Characteristics and Driving Factors of ES Changes
4.2. Correlation Analysis
4.2.1. The Relationship between ESs
4.2.2. Spatial Pattern of the Trade-Offs and Synergies between the ESs
4.3. Distribution and Characteristics of ES Bundles
5. Discussion
5.1. The Characteristics of ES Interactions
5.2. Implications for Ecosystem Management
5.3. Limitations of This Study and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems (1997); The Future of Nature; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2013; pp. 454–464. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas-Vásquez, D.; Fürst, C.; Geneletti, D.; Almendra, O. Integration of ecosystem services in strategic environmental assessment across spatial planning scales. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, A.; Seppelt, R.; Václavík, T.; Cord, A.F. Integrating ecosystem service bundles and socio-environmental conditions—A national scale analysis from Germany. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Zuo, L.Y. Revealing ecosystem services relationships and their driving factors for five basins of Beijing. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, J.W.; May, L.; Oliver, T.H.; Hamel, P.; Sharp, R.; Bullock, J.M. National scale evaluation of the InVEST nutrient retention model in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Weiping, Z.; Hui, Z.; Yu, S. A review on principle and application of the InVEST model. Ecol. Sci. 2015, 34, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Young, C.J.; Don, L.S. Assessment of economic value of ecosystem service by using InVEST model in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2017, 8, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, M.D.; Matlock, M.D.; Cummings, E.C.; Nalley, L.L. Quantifying and mapping multiple ecosystem services change in West Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 165, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.S.; Zhang, J.T. Quantitative Assessment for the Spatiotemporal Changes of Ecosystem Services, Tradeoff-Synergy Relationships and Drivers in the Semi-Arid Regions of China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Yin, Q.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, G.Z.; Ke, Q.J.; Guo, Q. Analysis of Ecosystem Service Contribution and Identification of Trade-Off/Synergy Relationship for Ecosystem Regulation in the Dabie Mountains of Western Anhui Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, N.; Spray, C. Ecosystem services bundles: Challenges and opportunities for implementation and further research. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chen, S.G.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.R. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Trade-Offs/Synergies among Ecosystem Services in Beijing from 2000 to 2020. Forests 2023, 14, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.; Yu, J.X.; Yue, D.P.; Yang, L.Z.; Mao, X.Q.; Hu, Y.H.; Long, Q.Q. The Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Ecosystem Service Synergy/Trade-Offs Based on Ecological Units. Forests 2021, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.P.; Skinner, D. Ecosystem services in changing land use. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Odgaard, M.V.; Bocher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Svenning, J.C. Bundling ecosystem services in Denmark: Trade-offs and synergies in a cultural landscape. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.F.; Ge, Y.; Xue, H.; Yang, W.; Shi, Y.; Peng, C.H.; Du, Y.Y.; Fan, X.; Ren, Y.; Chang, J. Using ecosystem service bundles to detect trade-offs and synergies across urban-rural complexes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 136, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; He, X.Y.; Chen, W.; Ye, Y.; Guo, R.C.; Yu, L.Z. A local-scale spatial analysis of ecosystem services and ecosystem service bundles in the upper Hun River catchment, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 22, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.M.; Feng, J.L.; Jia, X.H.; Li, J.J. Spatial correlations among ecosystem services and their socio-ecological driving factors: A case study in the city belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.S.; Li, X.B.; Li, S.K.; Dang, D.L.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, S.Y. Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.M.; Li, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, N.; La, L.M.; Liu, C.F.; Xiao, W.F. Identifying and analyzing ecosystem service bundles and their socioecological drivers in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.R.; Chen, T.Q.; Wu, J.S. Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing?Tianjin?Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Understanding the importance of landscape configuration on ecosystem service bundles at a high resolution in urban landscapes in the UK. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2007–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.Y.; Gao, J.B. Investigating the compounding effects of environmental factors on ecosystem services relationships for Ecological Conservation Red Line areas. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4609–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Hao, S.; Xu, W.J.; Lv, L.T.; Yu, S. Spatial -temporal variation and tradeoffs/synergies analysis on multiple ecosystem services: A case study in the Three -River Headwaters region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; García-Llorente, M.; Norström, A.; Meacham, M.; Peterson, G.; Castro, A.J. Integrating supply and demand in ecosystem service bundles characterization across Mediterranean transformed landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.Y.; Ding, Q.; Zhou, T.; Kong, L.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, W. Ecosystem service bundle index construction, spatiotemporal dynamic display, and driving force analysis. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1843972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcun, L.; Keqin, J.; Kui, Z.; Yan, L.; Tianding, H.; Yu, Z. The response of precipitation to global climate change in the Tianshan Mountains, China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 748–759. [Google Scholar]
- Yayan, L.; Xiaoliang, X.; Jicai, L.; Xiaohua, F.; Luyuan, L. Research on the spatio-temporal variation of carbon storage in the Xinjiang Tianshan Mountains based on the InVEST model. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.H.; Hu, Z.C.; Xi, C.; Ming, C.W. The new methodology of geomorphologic zonalization in Xinjiang based on geographical grid. Geogr. Res. 2008, 27, 481–492+725–726. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groombridge, B.; Jenkins, M. Global Biodiversity: Earth’s Living Resources in the 21st Century; World Conservation Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Liang, D.; Xia, J.; Song, J.X.; Cheng, D.D.; Wu, J.T.; Cao, Y.L.; Sun, H.T.; Li, Q. Evaluation of water conservation function of Danjiang River Basin in Qinling Mountains, China based on InVEST model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Mamat, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xing, L.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H. Analysis of spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of soil erosion in the Jiangnan Hills red soil zone, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.L.; Liu, X.H.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.P.; Xing, L.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.H. Assessment of Spatial-Temporal Variations of Soil Erosion in Hulunbuir Plateau from 2000 to 2050. Land 2023, 12, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N. InVEST+ VERSION+ User’s Guide. Nat. Cap. Proj. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Du, Y.Y.; Meersmans, J.; Qiu, S.J. Linking ecosystem services and circuit theory to identify ecological security patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Fan, F.F. Identification of the geographical factors influencing the relationships between ecosystem services in the Belt and Road region from 2010 to 2030. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 124153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.C.; Wang, X.F.; Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Chen, Y.Z. A Comparison of SSEBop-Model-Based Evapotranspiration with Eight Evapotranspiration Products in the Yellow River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, W.; Zhang, S.Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, Y. Impacts of urbanization on ecosystem services in the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration: Changes and trade-offs. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, C.C. How to optimize ecological compensation to alleviate environmental injustice in different cities in the Yellow River Basin? A case of integrating ecosystem service supply, demand and flow. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfu, D.; Yahui, W. Spatial heterogeneity and driving mechanisms of water yield service in the Hengduan Mountain region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 607–619. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-F.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Liu, X.T.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.H. Variations in Ecosystem Service Value and Its Driving Factors in the Nanjing Metropolitan Area of China. Forests 2023, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C. Measuring Spatial Variations in Relationships with Geographically Weighted Regression. In Recent Developments in Spatial Analysis: Spatial Statistics, Behavioural Modelling, and Computational Intelligence; Fischer, M.M., Getis, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 60–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollini, I.; Lu, B.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C.; Harris, P. GWmodel: An R package for exploring spatial heterogeneity using geographically weighted models. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.0413. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H.; Ma, Y. A Framework for Assessing Trade-Offs and Synergies in Green Space System Services Based on Ecosystem Services Bundles. Forests 2023, 14, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, R.; Buydens, L.M. Self-and super-organizing maps in R: The Kohonen package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Kairui, Z. Effects of NDVI/Land-Use on Evapotranspiration in the Loess Plateau. Yellow River 2021, 43, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangzhu, L.; Qing, L.; Ting, Z. Spatial scale enhancement and spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration based on the relationship between K_c and NDVI. South–North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.F.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Loinaz, G.; Alday, J.G.; Onaindia, M. Multiple ecosystem services landscape index: A tool for multifunctional landscapes conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wu, H.Q.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.F.; Wan, W. Exploring the interrelations and driving factors among typical ecosystem services in the Yangtze river economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.S.; Li, S.C.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.B.; Li, D.L.; Wu, S.Y. Exploring the heterogeneity and nonlinearity of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services bundles in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, P.; Lei, G.C. Mapping the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in Ningxia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.K.; Li, X.B.; Dou, H.S.; Dang, D.L.; Gong, J.R. Integrating constraint effects among ecosystem services and drivers on seasonal scales into management practices. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.X.; Zuo, L.Y.; Gao, J.B.; Jiang, Y.; Du, F.J.; Zhang, Y.B. Exploring the driving factors of trade-offs and synergies among ecological functional zones based on ecosystem service bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.X. Scale effect on spatial patterns of ecosystem services and associations among them in semi-arid area: A case study in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Han, F. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Mountainous Ecosystem Services in an Arid Region and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of the Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang. Land 2022, 11, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.T.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.X.; Xi, H.Y.; Yang, L.S.; Chang, X.G. Precipitation changes and its interaction with terrestrial water storage determine water yield variability in the world’s water towers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.Z.; Yin, X.X.; Shao, M. Natural and anthropogenic factors on China’s ecosystem services: Comparison and spillover effect perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, C.A.R.; Bustos, S.L.H.; Moreno, C.A.P. Modeling interactions among multiple ecosystem services. A critical review. Ecol. Model. 2020, 429, 109103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L. Carbon storage, spatial distribution and the influence factors in Tianshan forests. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 40, 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, W. Spatiotemporal variation and multiscenario simulation of carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems in the Turpan-Hami Basin based on PLUS-InVEST model. Arid Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, H.; Wu, F.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, X. Study on the spatial differentiation pattern and driving force of ecosystem services in Qinghai Lake Basin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Song, Q. InVEST model-based spatiotemporal analysis of water supply services in the Zhangcheng District. Forests 2021, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.X.; Carpenter, S.R.; Booth, E.G.; Motew, M.; Zipper, S.C.; Kucharik, C.J.; Loheide, S.P.; Turner, A.G. Understanding relationships among ecosystem services across spatial scales and over time. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 054020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, L.J.; Wu, T. Coordinating ecosystem service trade-offs to achieve win-win outcomes: A review of the approaches. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 82, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, Z. Accounting of value of ecosystem services in the desert: An example of the Kubuqi Desert ecosystem. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 11, 1247367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Z.; Du, H.; Hasi, E.; Lu, X. Changes in land use and ecosystem service value in desert areas of China after reform and opening up. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1251605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Derksen, C.; Fletcher, C.G.; Hall, A. Snow and climate: Feedbacks, drivers, and indices of change. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2019, 5, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.K.; Pretis, F. An empirical estimate for the snow albedo feedback effect. Clim. Chang. 2023, 176, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Tu, K.; Ye, S.; Tang, H.; Hu, Y.; Xie, C. Land use and land cover classification meets deep learning: A review. Sensors 2023, 23, 8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Guo, W.; He, J.; Sun, M.; Chai, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Topography, diversity, and forest structure attributes drive aboveground carbon storage in different forest types in Northeast China. Forests 2022, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data | Description | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Land-use type data in 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 | The spatial resolution is 30 m. | https://zenodo.org (accessed on 23 October 2023) |
| Temperature (°C) | Monthly average temperature data with a 1 km resolution. | National Tibetan Plateau Scientific Data Center https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 8 May 2023) |
| Precipitation (mm) | Monthly average precipitation data with a 1 km resolution. | |
| Evapotranspiration (mm) | Annual evapotranspiration data with a 1 km resolution. | |
| Potential evapotranspiration (mm) | Annual potential evapotranspiration data with a 1 km resolution. | |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | The spatial resolution is 1 km. | |
| Soil data | Used to calculate the plant available water capacity (PAWC) and soil erodibility factor. | |
| Soil type | The spatial resolution is 1 km. | |
| Rainfall erosivity factor | Reflects the rainfall intensity and time in the study area. | Obtained by calculating the rainfall data |
| Carbon density (t/hm2) | Used to calculate the CS. | Based on relevant literature |
| Digital elevation model (DEM) (m) | Used to calculate the slope direction and slope, terrain fluctuation, with a spatial resolution of 30 m. | Geospatial Data Cloud https://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 19 May 2023) |
| Gross domestic product (GDP) | The GDP value of the county-level unit with a 1 km resolution. | Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 18 May 2023) |
| Population gridded dataset (POP) | The population value of the county-level unit with a 1 km resolution. | |
| Road data | Used to calculate the distance to the road. | OpenStreetMap Data extract https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 24 April 2023) |
| River network data | Used to calculate the distance to the river channel. | |
| The location of the government | Used to calculate the distance to the government. | National Geographic Information Resources Catalog Service System https://www.webmap.cn (accessed on 11 April 2023) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y. The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains. Forests 2024, 15, 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091678
Chen W, Wang R, Liu X, Lin T, Hao Z, Zhang Y, Zheng Y. The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains. Forests. 2024; 15(9):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091678
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wudi, Ran Wang, Xiaohuang Liu, Tao Lin, Zhe Hao, Yukun Zhang, and Yu Zheng. 2024. "The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains" Forests 15, no. 9: 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091678
APA StyleChen, W., Wang, R., Liu, X., Lin, T., Hao, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2024). The Interrelationships and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Functions in the Tianshan Mountains. Forests, 15(9), 1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091678






