Spatial Heterogeneity of Mountain Greenness and Greening in the Tibetan Plateau: From a Remote Sensing Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
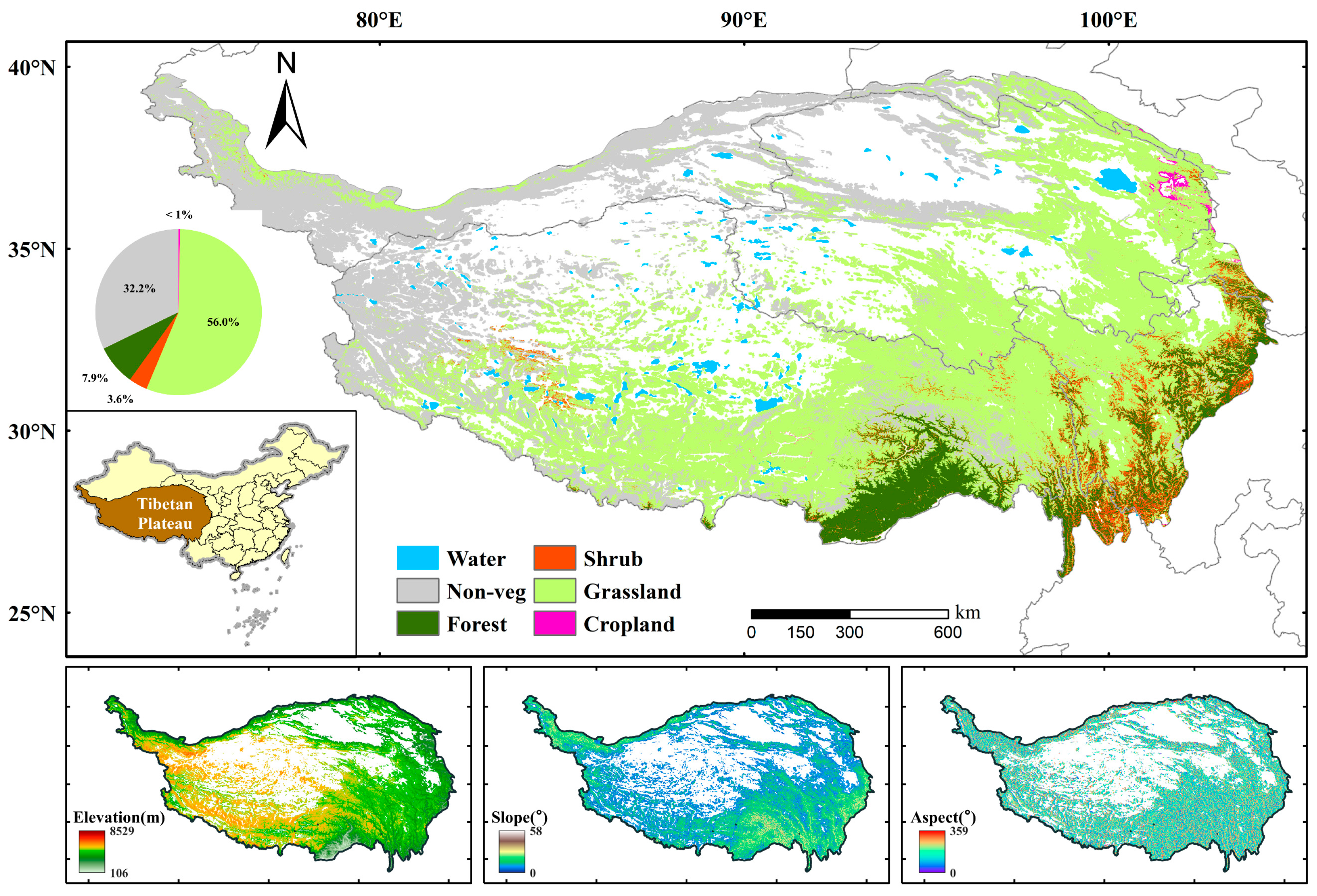
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. LAI Datasets
2.2.2. Land Cover Data
2.2.3. Mountain Range Identifier Data
2.2.4. Digital Elevation Model Data
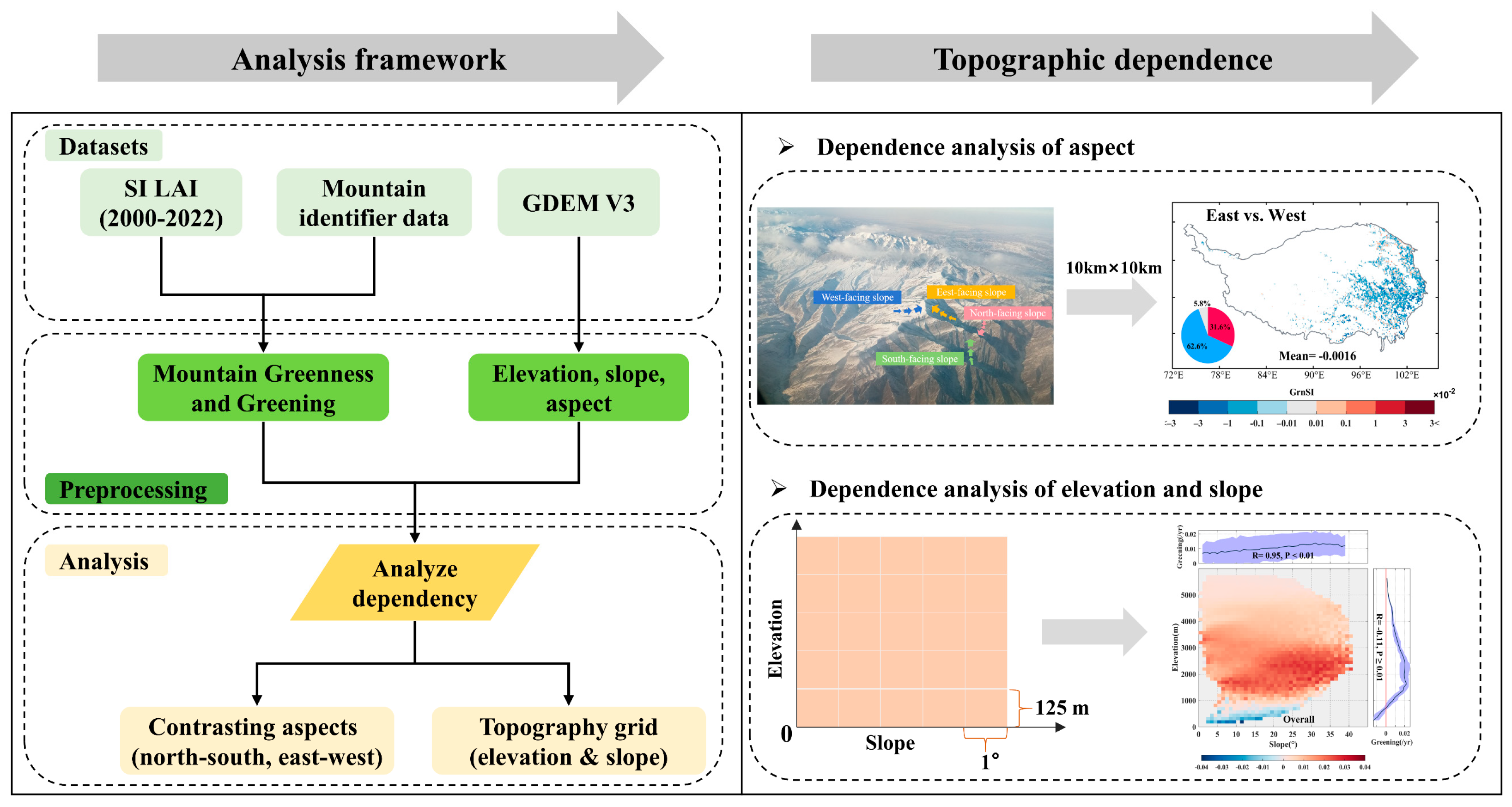
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Extraction of Greenness and Greening
2.3.2. Dependence Analysis on Topographic Factors
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Patterns of Greenness
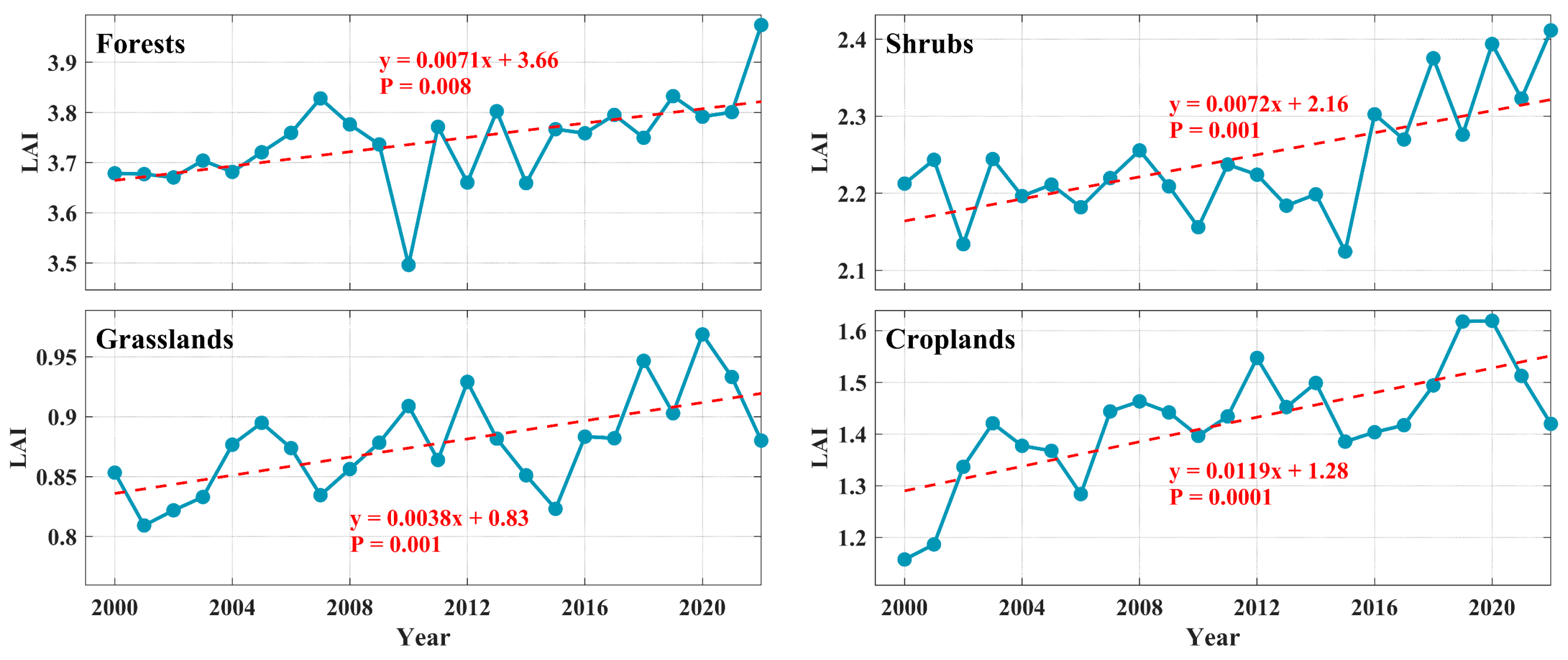
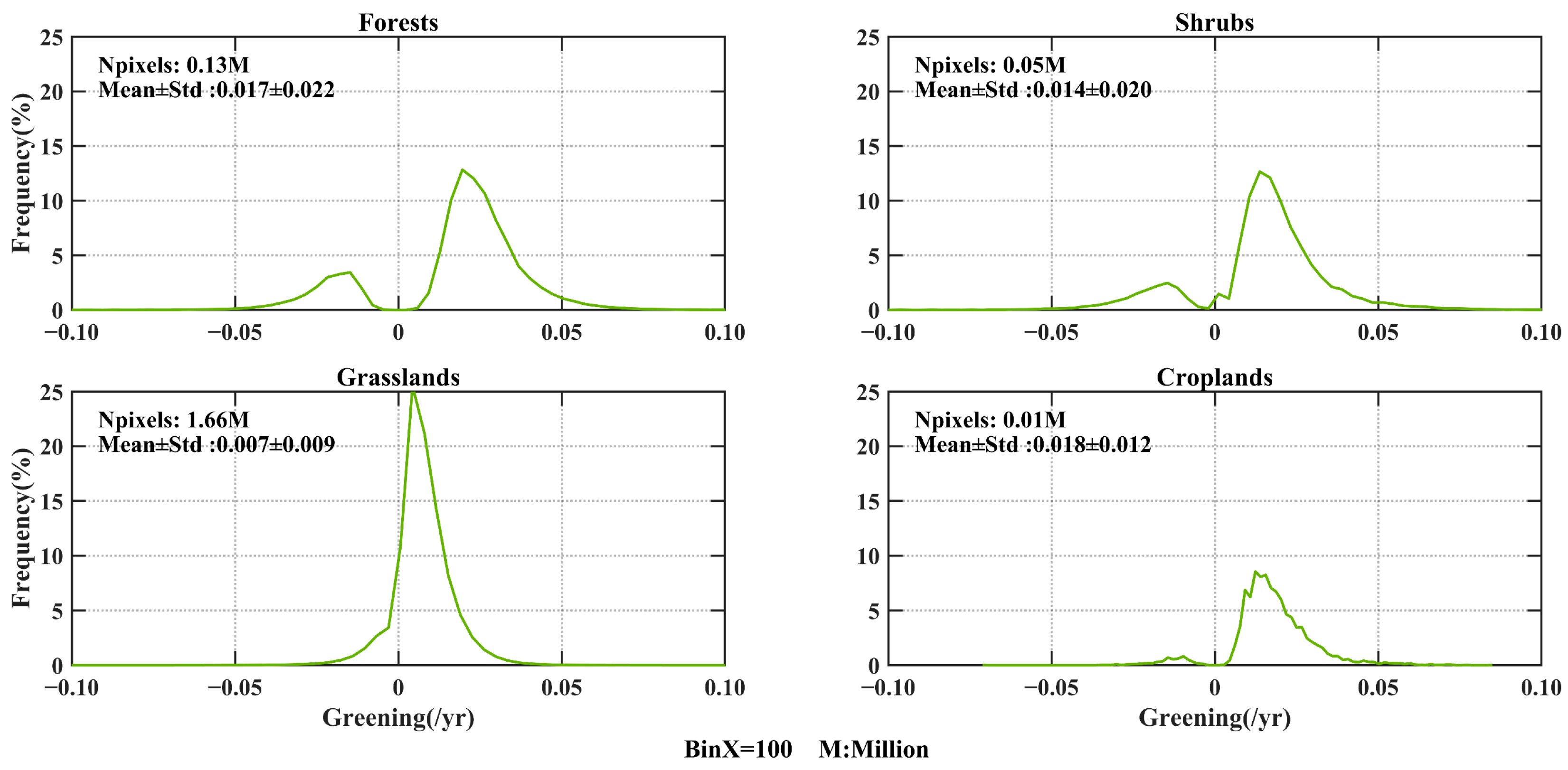
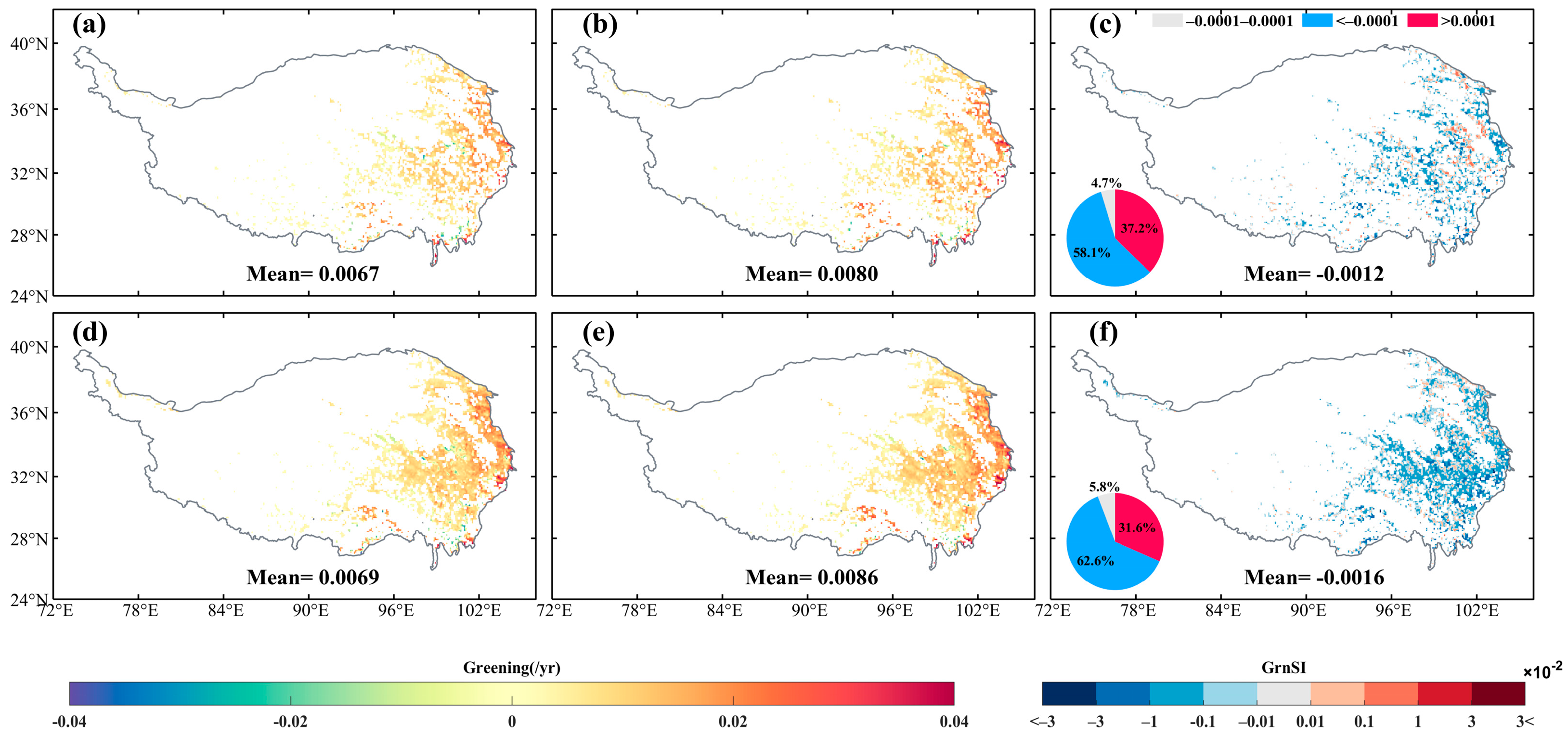
3.2. Spatial Patterns of Greening
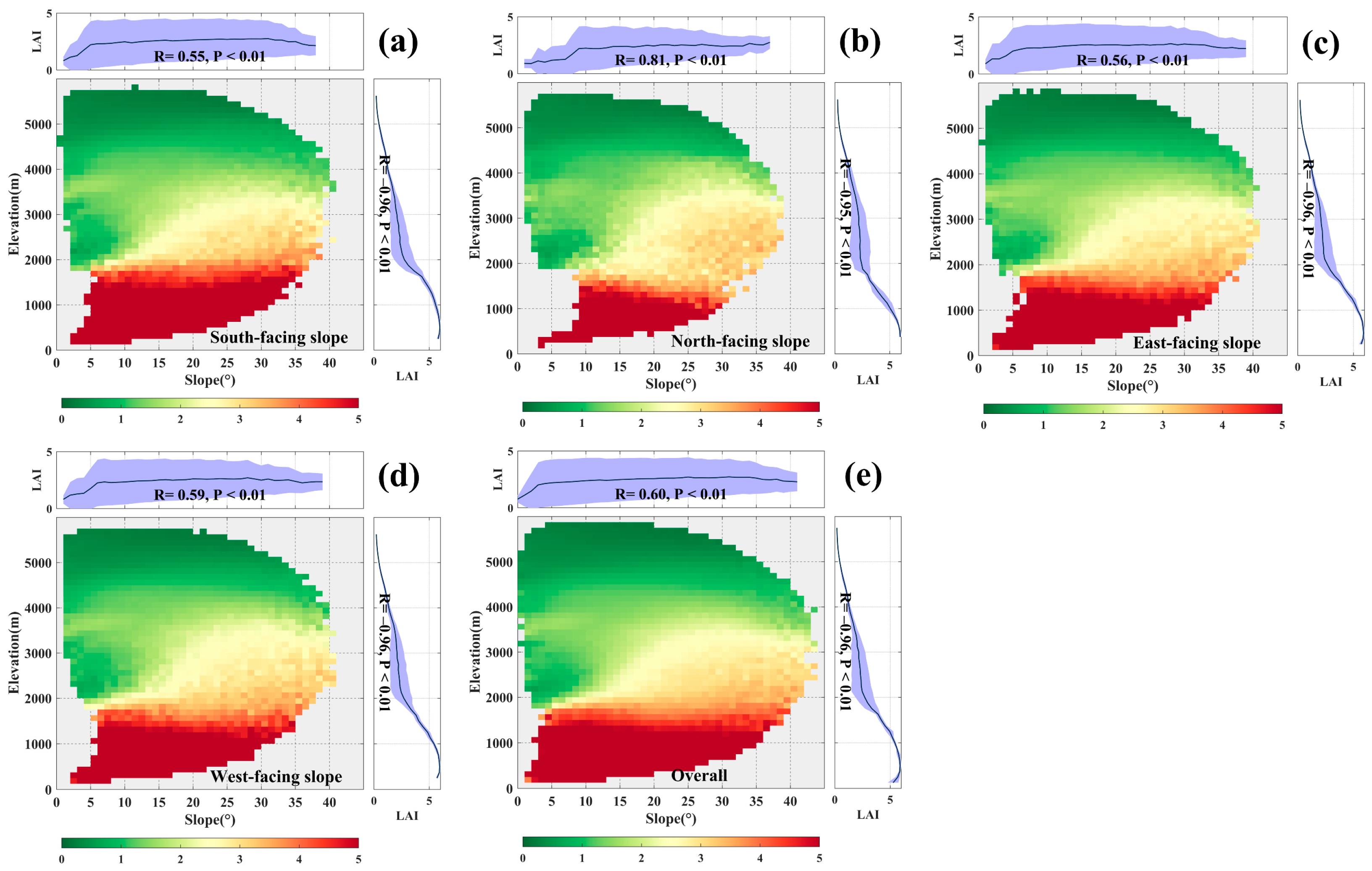
3.3. Dependence of Vegetation Greenness on Topography
3.4. Dependence of Vegetation Greening on Topography
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Greenness and Greening
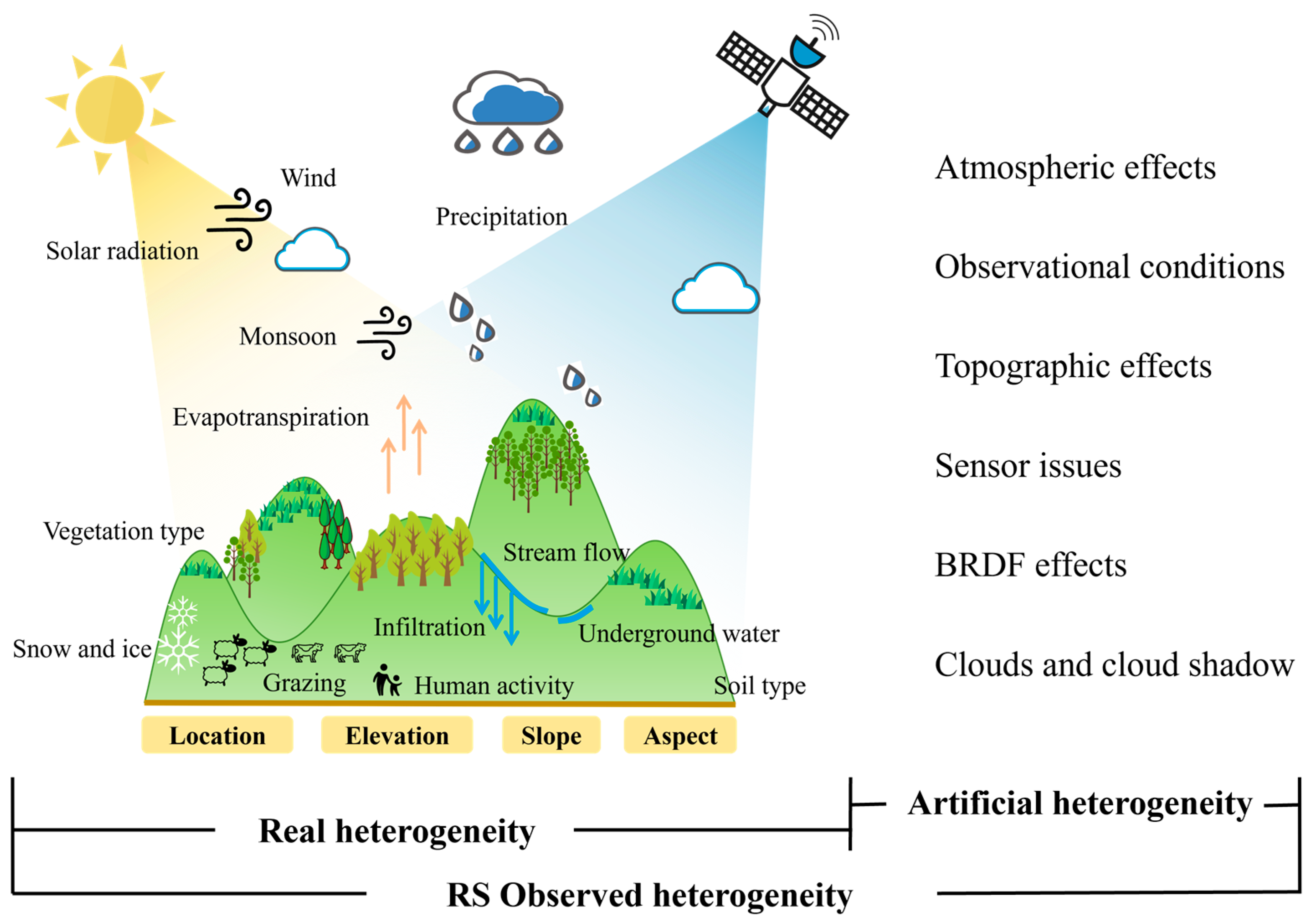
4.2. Dominant Factors Contributing to the Spatial Heterogeneity of Vegetation Greenness and Greening
4.3. Uncertainty and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonan, G.B.; Pollard, D.; Thompson, S.L. Effects of boreal forest vegetation on global climate. Nature 1992, 359, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Salama, M.S.; Su, Z. Assessment of vegetation dynamics and their response to variations in precipitation and temperature in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Change 2010, 103, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, B.; Ives, J.D. Mountains of the World: A Global Priority; Parthenon Publishing Group: Carnforth, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schröter, D.; Cramer, W.; Leemans, R.; Prentice, I.C.; Araújo, M.B.; Arnell, N.W.; Bondeau, A.; Bugmann, H.; Carter, T.R.; Gracia, C.A. Ecosystem service supply and vulnerability to global change in Europe. Science 2005, 310, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity: Ecological and Economic Foundations; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, Y.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-C. Terrain gradient variations in ecosystem services of different vegetation types in mountainous regions: Vegetation resource conservation and sustainable development. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 482, 118856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, J.; Soares-Filho, B.; Costa, M.H.; Oliveira, U.; Ribeiro, S.C.; Pires, G.F.; Oliveira, A.; Rajão, R.; May, P.; Van Der Hoff, R. Spatially explicit valuation of the Brazilian Amazon forest’s ecosystem services. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Onaindia, M.; de Manuel, B.F.; Madariaga, I.; Rodríguez-Loinaz, G. Co-benefits and trade-offs between biodiversity, carbon storage and water flow regulation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 289, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rogora, M.; Frate, L.; Carranza, M.L.; Freppaz, M.; Stanisci, A.; Bertani, I.; Bottarin, R.; Brambilla, A.; Canullo, R.; Carbognani, M. Assessment of climate change effects on mountain ecosystems through a cross-site analysis in the Alps and Apennines. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Xi, G.; Ji, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, Y. Spatial and temporal variation in vegetation cover and its response to topography in the selinco region of the qinghai-tibet plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Zhu, X.; Shen, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Tang, Y. Mismatch in elevational shifts between satellite observed vegetation greenness and temperature isolines during 2000–2016 on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 5411–5425. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.; Ciais, P.; Tømmervik, H. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, M.; Gentine, P.; Nemani, R.R.; Myneni, R.B. Biophysical impacts of Earth greening largely controlled by aerodynamic resistance. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb1981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zou, B. A greening world enhances the surface-air temperature difference. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Walther, S.; Duveiller, G.; Cescatti, A.; Mahecha, M.D.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; García-Haro, F.J.; Guanter, L. A unified vegetation index for quantifying the terrestrial biosphere. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Yan, K.; Liu, J.; Pu, J.; Zou, D.; Qi, J.; Mu, X.; Yan, G. Assessment of remote-sensed vegetation indices for estimating forest chlorophyll concentration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112001. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, N.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, F.; Pan, S. Increasing global vegetation browning hidden in overall vegetation greening: Insights from time-varying trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.X.; Zhou, L.; Ciais, P.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Lian, X.U.; Wood, E.F.; Friedlingstein, P. Climate mitigation from vegetation biophysical feedbacks during the past three decades. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Zhou, T.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Accelerated urban expansion in lhasa city and the implications for sustainable development in a Plateau City. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Changes in alpine wetland ecosystems of the Qinghai–Tibetan plateau from 1967 to 2004. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 180, 189–199. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Esper, J.; Büntgen, U.; Li, L.; Xoplaki, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Luterbacher, J. Weakening of annual temperature cycle over the Tibetan Plateau since the 1870s. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14008. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, D.; Yan, K.; Pu, J.; Gao, S.; Li, W.; Mu, X.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Revisit the performance of MODIS and VIIRS leaf area index products from the perspective of time-series stability. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8958–8973. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, M. Using the NDVI to identify variations in, and responses of, vegetation to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2012. Quat. Int. 2017, 444, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Montenegro, A.; Zhu, X. NDVI and vegetation phenology dynamics under the influence of sunshine duration on the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 687–698. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Qin, X. Precipitation and temperature regulate the seasonal changes of NDVI across the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 291. [Google Scholar]
- Palombo, C.; Marchetti, M.; Tognetti, R. Mountain vegetation at risk: Current perspectives and research reeds. Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2014, 148, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Xie, J.; Ma, D.; Xie, Q.; Verger, A.; Descals, A.; Filella, I.; Peñuelas, J. Aspect matters: Unraveling microclimate impacts on mountain greenness and greening. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105879. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Zeng, J. Terrain gradient variations in the ecosystem services value of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02008. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, D.M.; Barnard, H.R.; Molotch, N.P. Topoclimate effects on growing season length and montane conifer growth in complex terrain. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064003. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, D.; Das, P.K.; Paul, S.; Sharma, J.R.; Dadhwal, V.K. Assessment of ecological disturbance in the mangrove forest of Sundarbans caused by cyclones using MODIS time-series data (2001–2011). Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 775–790. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Yan, F. Vegetation growth status and topographic effects in frozen soil regions on the qinghai–Tibet plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hao, D.; Huete, A.; Dechant, B.; Berry, J.; Chen, J.M.; Joiner, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Ryu, Y. Optical vegetation indices for monitoring terrestrial ecosystems globally. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhong, R.; Yan, K.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Pu, J.; Gao, S.; Qi, J.; Yin, G.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluating the saturation effect of vegetation indices in forests using 3D radiative transfer simulations and satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Baret, F.; Plummer, S.; Schaepman-Strub, G. An overview of global leaf area index (LAI): Methods, products, validation, and applications. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 739–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Park, T.; Yan, G.; Chen, C.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.; Nemani, R.R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluation of MODIS LAI/FPAR product collection 6. Part 1: Consistency and improvements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Scurlock, J.M.; Hicke, J.A. Global synthesis of leaf area index observations: Implications for ecological and remote sensing studies. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zou, D.; Yan, G.; Fang, H.; Weiss, M.; Rautiainen, M.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. A Bibliometric Visualization Review of the MODIS LAI/FPAR Products from 1995 to 2020. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 7410921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Popescu, S. Lidar-based mapping of leaf area index and its use for validating GLOBCARBON satellite LAI product in a temperate forest of the southern USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1628–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.B.; Hoffman, S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Glassy, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, G.R. Global products of vegetation leaf area and fraction absorbed PAR from year one of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Pu, J.; Park, T.; Xu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, G.; Weiss, M.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Performance stability of the MODIS and VIIRS LAI algorithms inferred from analysis of long time series of products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 260, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, K.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Pu, J.; Yan, G.; Heiskanen, J.; Zhu, P.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. An Insight into The Internal Consistency of MODIS Global Leaf Area Index Products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4411716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, J.; Peng, R.; Yang, K.; Chen, X.; Yin, G.; Dong, J.; Weiss, M.; Pu, J.; Myneni, R.B. HiQ-LAI: A high-quality reprocessed MODIS LAI dataset with better spatio-temporal consistency from 2000 to 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1601–1622. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.; Yan, K.; Roy, S.; Zhu, Z.; Rautiainen, M.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Sensor-independent LAI/FPAR CDR: Reconstructing a global sensor-independent climate data record of MODIS and VIIRS LAI/FPAR from 2000 to 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2023, 2023, 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V. Recent third pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: Multidisciplinary approach with observations, modeling, and analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, S. Climate change and its impacts on vegetation distribution and net primary productivity of the alpine ecosystem in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniwaer, N.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Hong, S. Shifts in the trends of vegetation greenness and photosynthesis in different parts of Tibetan Plateau over the past two decades. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 345, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tang, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Yang, J.; Ye, T.; Wang, J.a.; Liang, S. Factors contributing to spatial–temporal variations of observed oxygen concentration over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, T.; Piao, S. Increasingly important role of atmospheric aridity on Tibetan alpine grasslands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 2852–2859. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, X.; Jiao, J.J. Review on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau during the last half century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3979–4007. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MODIS/Terra+ Aqua land cover type yearly L3 global 500m SIN grid V061. NASA EOSDIS Land Process. DAAC. 2022. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mcd12q1v061/ (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Snethlage, M.A.; Geschke, J.; Ranipeta, A.; Jetz, W.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Körner, C.; Spehn, E.M.; Fischer, M.; Urbach, D. A hierarchical inventory of the world’s mountains for global comparative mountain science. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Yao, Y.; Pereira, P. The rising human footprint in the Tibetan Plateau threatens the effectiveness of ecological restoration on vegetation growth. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119963. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. Dual influence of climate change and anthropogenic activities on the spatiotemporal vegetation dynamics over the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau from 1981 to 2015. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M. Assessment of irrigation system sustainability using the Theil–Sen estimator of slope of time series. Sustain. Sci. 2014, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhong, G.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Z. Modified Mann-Kendall trend test for hydrological time series under the scaling hypothesis and its application. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2419–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Naudiyal, N.; Wu, N.; Cui, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Q. Multiple effects of topographic factors on Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation patterns in the three parallel rivers region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhai, L.; Sang, H.; Cheng, S.; Li, H. Effects of hydrothermal factors and human activities on the vegetation coverage of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, Z. Precipitation drives the NDVI distribution on the Tibetan Plateau while high warming rates may intensify its ecological droughts. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, J.; Cheng, G.; Jiang, H. Effect of altitude and latitude on surface air temperature across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2011, 8, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y. Spatial patterns of wet season precipitation vertical gradients on the Tibetan Plateau and the surroundings. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5057. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, D. Vertical differentiation of land cover in the central Himalayas. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 969–987. [Google Scholar]
- Måren, I.E.; Karki, S.; Prajapati, C.; Yadav, R.K.; Shrestha, B.B. Facing north or south: Does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley? J. Arid. Environ. 2015, 121, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Shen, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, W.; Yu, L.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Li, X. Contrasting effects of temperature and precipitation on vegetation greenness along elevation gradients of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Huete, A.R.; Shen, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; He, G.; Yu, L.; Xu, X. Characteristics of greening along altitudinal gradients on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau based on time-series Landsat images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Nan, H.; Huntingford, C.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S.; Peng, S.; Ahlström, A.; Canadell, J.G.; Cong, N. Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Innes, J.L.; Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Myneni, R.B. Changes in vegetation growth dynamics and relations with climate over China’s landmass from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3263–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Li, R.; Tang, Y.; Du, M. Causes for the unimodal pattern of biomass and productivity in alpine grasslands along a large altitudinal gradient in semi-arid regions. J. Veg. Sci. 2013, 24, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevéy, J.; Vellend, M.; Rüger, N.; Hollister, R.D.; Bjorkman, A.D.; Myers-Smith, I.H.; Elmendorf, S.C.; Clark, K.; Cooper, E.J.; Elberling, B.O. Greater temperature sensitivity of plant phenology at colder sites: Implications for convergence across northern latitudes. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Jia, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, S. Vegetation change and its relationship with climate factors and elevation on the Tibetan plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z.; Che, Y.; Qiang, F.; Qu, D. Decrease in snowfall/rainfall ratio in the Tibetan Plateau from 1961 to 2013. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, D. Does summer precipitation trend over and around the Tibetan Plateau depend on elevation? Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafitlhile, T.M.; Liu, Y. Temperature contributes more than precipitation to the greening of the Tibetan Plateau during 1982–2019. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 1471–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.M.; Quade, J. Long-term east-west asymmetry in monsoon rainfall on the Tibetan Plateau. Geology 2013, 41, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, C. A revival of Indian summer monsoon rainfall since 2002. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Niu, B.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Weakening summer westerly circulation actuates greening of the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2023, 221, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, P.; Ma, D.; Li, M. Land system evolution of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under various development strategies. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 104, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Cost-benefit analysis of ecological restoration based on land use scenario simulation and ecosystem service on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Sun, J.; Cao, R.; Ling, X.; Fang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X. Plant phenology changes and drivers on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, P.; Liu, J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Mountain Greenness and Greening in the Tibetan Plateau: From a Remote Sensing Perspective. Forests 2025, 16, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040576
Liu Z, Zhang X, Zhao S, Liu P, Liu J. Spatial Heterogeneity of Mountain Greenness and Greening in the Tibetan Plateau: From a Remote Sensing Perspective. Forests. 2025; 16(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhao, Xingjian Zhang, Shuang Zhao, Panpan Liu, and Jinxiu Liu. 2025. "Spatial Heterogeneity of Mountain Greenness and Greening in the Tibetan Plateau: From a Remote Sensing Perspective" Forests 16, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040576
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhang, X., Zhao, S., Liu, P., & Liu, J. (2025). Spatial Heterogeneity of Mountain Greenness and Greening in the Tibetan Plateau: From a Remote Sensing Perspective. Forests, 16(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040576




