Evaluation of Landscape Soil Quality in Different Types of Pisha Sandstone Areas on Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Soil Sampling Design
2.3. Soil Property Analysis
2.4. Data Filtration and Treatment
2.4.1. Establishing Minimum Datasets
2.4.2. Scoring of Soil Indicators
2.4.3. Establish of Soil Quality Index (SQI)
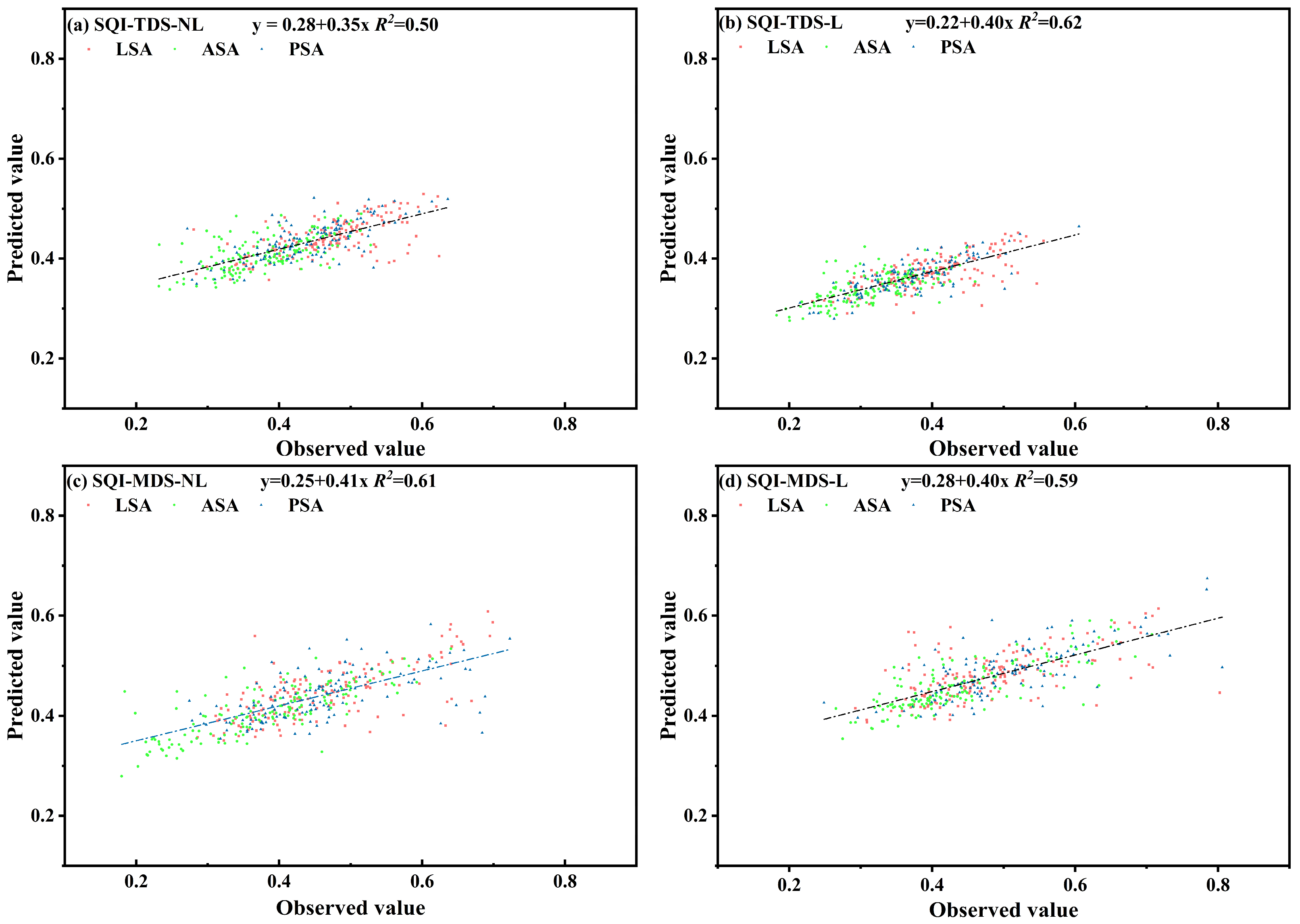
2.4.4. Soil Quality Index Predictions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
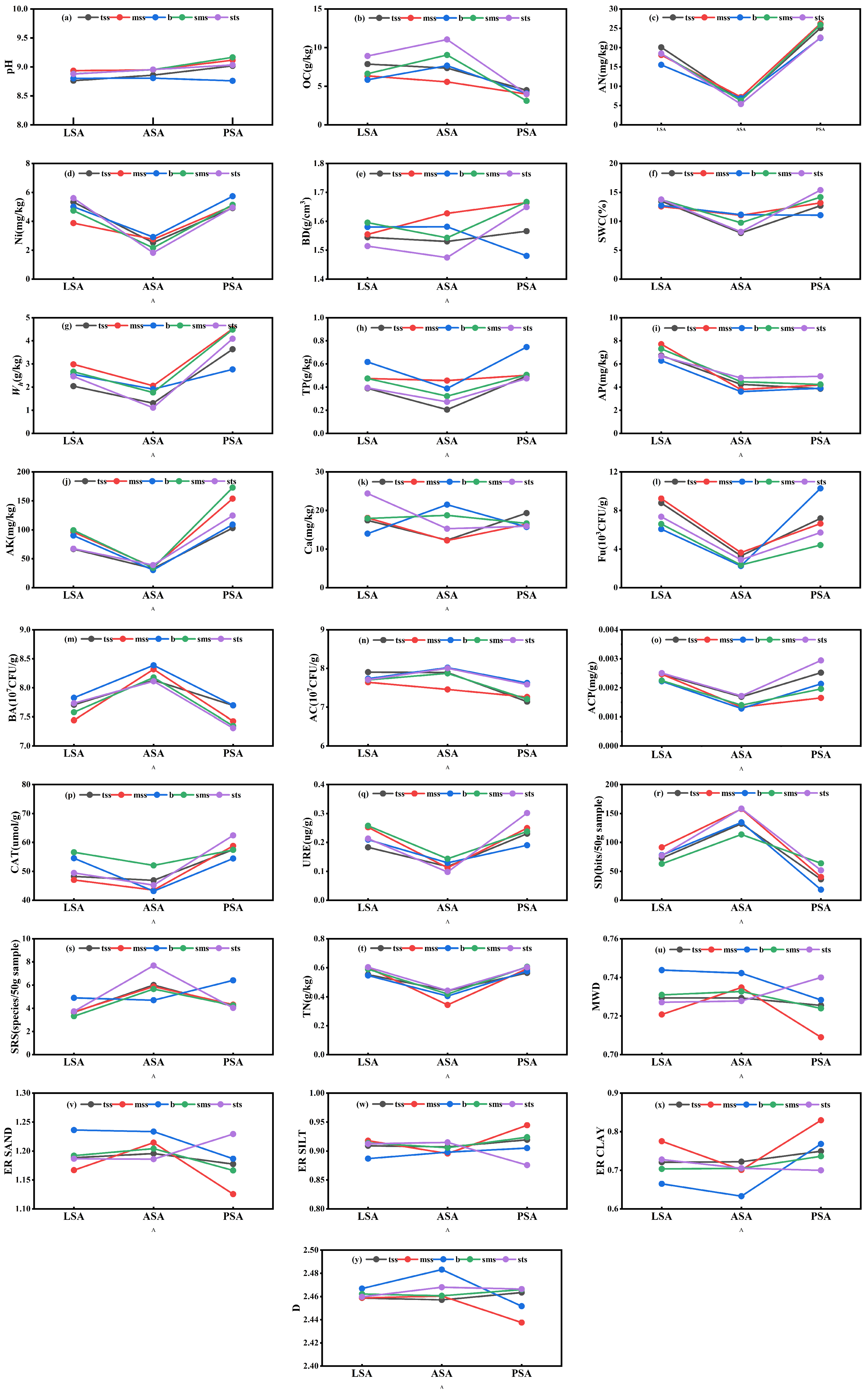
3.1. Ecological Stoichiometric Among Soil Samples
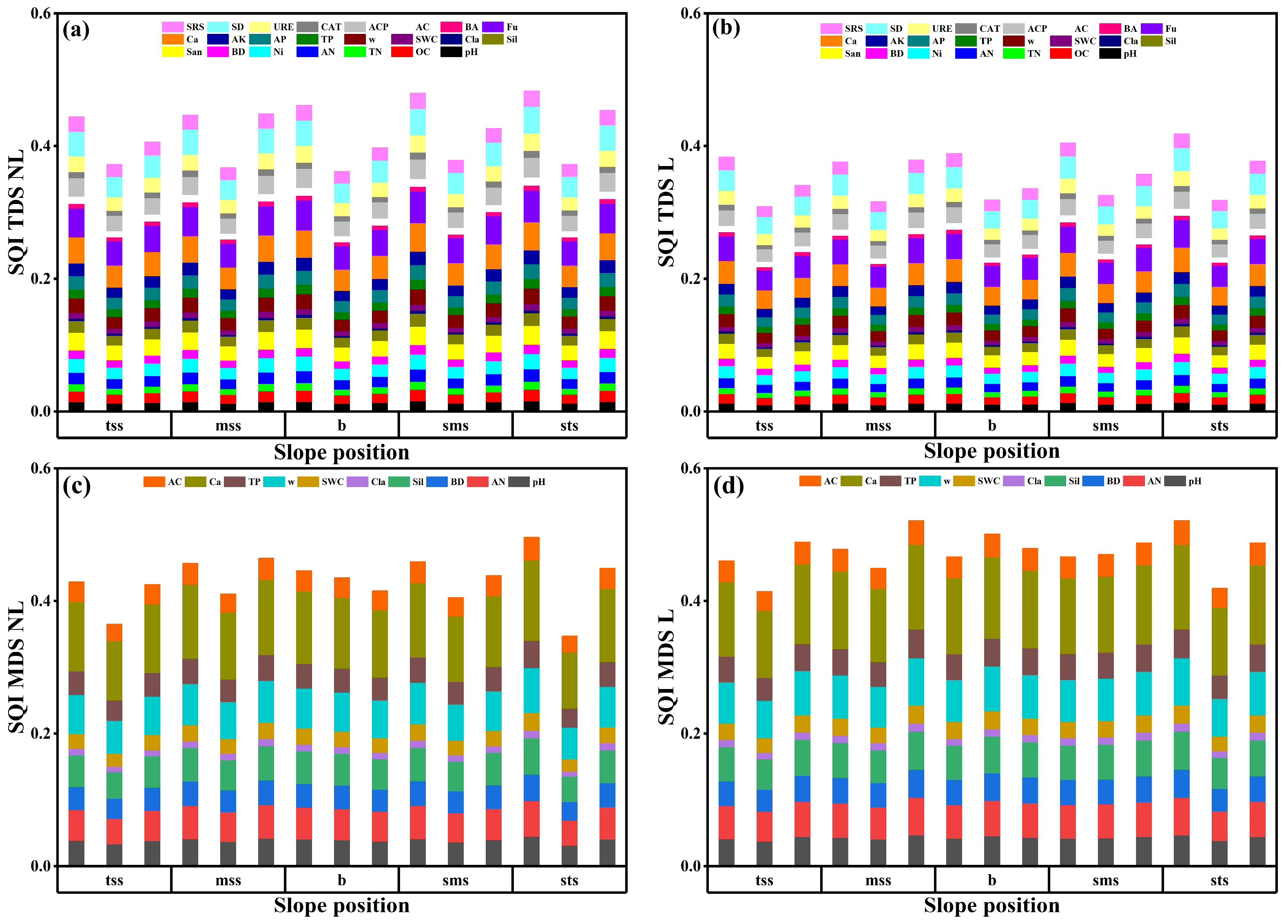
3.2. Filtration of Soil Dataset
3.3. SQI Discrepancy and Driving Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Indicators and Environmental Factors
4.2. Soil Quality Assessment Methods and Differences
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bone, J.; Head, M.; Barraclough, D.; Archer, M.; Scheib, C.; Flight, D.; Voulvoulis, N. Soil quality assessment under emerging regulatory requirements. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Chappell, A.; Eyres, M.; Scott, E. Monitor Soil Degradation or Triage for Soil Security? An Australian Challenge. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4870–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, C.; Rhee, H. Revegetation of decomposed granite roadcuts in Korea: Developing digger, evaluating cost effectiveness, and determining dimensions of drilling holes, revegetation species, and mulching treatment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Guzman, G.; Gomeza, J. Vegetation restoration dominated the attenuated soil loss rate on the Loess Plateau, China over the last 50 years. CATENA 2023, 228, 107149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anley, M.A.; Minale, A.S. Modeling the impact of land use land cover change on the estimation of soil loss and sediment export using Invest model at the Rib watershed of Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Remote Sens. Appl. 2024, 34, 101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenholtz, S.; Miegroet, H.; Burger, J. A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: Challenges and opportunities. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.G.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality: A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M.; Ci, E. Establishing a soil quality index to evaluate soil quality after afforestation in a karst region of Southwest China. CATENA 2023, 230, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F.; Kabiri, V. Identification of soil quality indicators for assessing the effect of different tillage practices through a soil quality index in a semi-arid environment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zong, M.; Fan, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, S.; Duan, C.; Li, H. Determining the impacts of deforestation and corn cultivation on soil quality in tropical acidic red soils using a soil quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedifar, M. Assessing alteration of soil quality, degradation, and resistance indices under different land uses through network and factor analysis. CATENA 2023, 222, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Yan, Y.; Bai, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Xin, X.; Chen, J. Conversion of croplands to shrublands does not improve soil organic carbon and nitrogen but reduces soil phosphorus in a temperate grassland of northern China. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.B.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, M.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Wu, J.Z.; Hai, X.Y.; Li, A.; Wang, K.B.; Wu, P.X.; et al. Effects of vegetation restoration types on soil nutrients and soil erodibility regulated by slope positions on the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, S.; Dengiz, O.; Demira, Ğ.; Turan, İ.; Özkan, B.; Dedeoglu, M.; Gülser, F.; Sargin, B.; Demirkaya, S.; Ay, A. An assessment of pasture soils quality based on multi-indicator weighting approaches in semi-arid ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortcliff, S. Standardization of soil quality attributes. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; Holden, N.M. Indices for quantitative evaluation of soil quality under grassland management. Geoderma 2014, 230, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Xiao, P. Ecological Comprehensive Management Theory and Technology of Pisha Sandstone Area; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2021; Chapters 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Yan, F.; Wang, Y. Vegetation Growth Status and Topographic Effects in the Pisha Sandstone Area of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chai, X.; Qu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Khan, F.; Wang, J.; Geming, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; et al. Restoration of Grassland Improves Soil Infiltration Capacity in Water-Wind Erosion Crisscross Region of China’s Loess Plateau. Land 2023, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Cai, S.; Feng, J.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Evaluating the applicability of the water erosion prediction project (WEPP) model to runoff and soil loss of sandstone reliefs in the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 11, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Tian, P.; Zhao, G.; Gómez, J.A.; Guo, J.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Sediment source tracing during flood events in the Huangfu River basin in the northern Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Qin, F.; Che, Z. Geochemical indicators to constrain weathering, provenance and tectonic setting of the Pisha Sandstone (Early-Middle Triassic) in Northeast Ordos Basin, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, J. Mixture-proportioning design of cement soil containing Pisha sandstone for mine filling. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2024, 20, e02904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yang, K.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of Hydrophilic Polyurethane on Interfacial Shear Strength of Pisha Sandstone Consolidation under Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Polymers 2023, 15, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Du, W.; Liu, Z.; Hu, F. Effects of Pisha sandstone additions on microstructural stability of sandy soil in Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Soil Till. Res. 2025, 248, 106437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X. Microbially induced calcite precipitation and synergistic mineralization cementation mechanism of Pisha sandstone components. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A. United Arab Emirates Keys to Soil Taxonomy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D.W. Selecting the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indexing of alkaline soils under different land uses in northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamehpour, N.; Rezapour, S.; Ghaemian, N. Quantitative assessment of soil quality indices for urban croplands in a calcareous semi-arid ecosystem. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis & Description of Soil Profiles; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Analysis Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Elsas, J.D.V. Methods of soil analysis. Part 2—Microbiological and biochemical properties. Sci. Hortic. 1995, 63, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdemann, J.W.; Nicolson, T.H.; Gerdemann, J.W.; Nicolson, T.H. Spores of mycorrhizal Endogone extracted from soil by wet sieving and decanting. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc. 1963, 46, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A. The Soil Management Assessment Framework: A Quantitative Soil Quality Evaluation Method. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Tormena, C.A.; Karlen, D.L. Soil quality evaluation using the soil management assessment framework (SMAF) in Brazilian Oxi-sols with contrasting texture. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2017, 41, e0160148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lal, R. The biochar dilemma. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, J.M.; Xing, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, X.Q. Minimum Data Set for Assessing Soil Quality in Farmland of Northeast China. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Shi, H.; Yan, Y.; Pu, J.; Dai, Q.; Gou, J.; Fan, Y. Soil quality assessment of karst trough valley under different bedrock strata dip and land-use types, based on a minimum data set. CATENA 2024, 241, 108048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, K.B.; Wu, J. Soil quality should be accurate evaluated at the beginning of lifecycle after land consolidation for eco-sustainable development on the Loess Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, B.; Bulmer, C.E.; Schmidt, M.G. Predictive soil parent material mapping at a regional-scale: A Random Forest approach. Geoderma 2014, 214–215, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Nabiollahi, K.; Kerry, R. Digital mapping of soil organic carbon at multiple depths using different data mining techniques in Baneh region, Iran. Geoderma 2016, 266, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Schmidt, K.; Amirian-Chakan, A.; Rentschler, T.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Sarmadian, F.; Valavi, R.; Davatgar, N.; Behrens, T.; Scholten, T. Improving the Spatial Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Two Contrasting Climatic Regions by Stacking Machine Learning Models and Rescanning Covariate Space. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Vu, N.H.; Zhen, S.; Zhu, H.; Fei, Z.; Zhong, Z. Characteristics of bulk and rhizosphere soil microbial community in an ancient Platycladus orientalis forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 132, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, G.T.; Ktterer, T.; Munkholm, L.J.; Parvage, M.M.; Kirchmann, H. Short-term effects of loosening and incorporation of straw slurry into the upper subsoil on soil physical properties and crop yield. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 184, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negis, H.; Eker, C.S.; Erci, V.; Gumus, I. Establishment of a minimum dataset and soil quality assessment for multiple reclaimed areas on a wind-eroded region. CATENA 2023, 229, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; et al. Complex vegetation patterns improve soil nutrients and maintain stoichiometric balance of terrace wall aggregates over long periods of vegetation recovery. CATENA 2023, 227, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Finn, D.R.; Brunotte, J.; Tebbe, C.C. Distinct seasonal and annual variability of prokaryotes, fungi and protists in cropland soil under different tillage systems and soil texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 203, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of 2-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade Barbosa, M.; de Sousa Ferraz, R.L.; Coutinho, E.L.M.; Coutinho Neto, A.M.; da Silva, M.S.; Fernandes, C.; Rigobelo, E.C. Multivariate analysis and modeling of soil quality indicators in long-term management systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Long, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Effects of disturbance to moss biocrusts on soil nutrients, enzyme activities, and microbial communities in degraded karst landscapes in southwest China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 152, 108065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yang, J.; Hussain, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cui, D. Stable isotopes reveal the formation diversity of humic substances derived from different cotton straw-based materials. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.X.; Lu, S.X.; He, M.; Yang, L.M.; Hu, M.F.; Yang, Z.J.; Liu, X.F.; Hui, D.F.; Guo, J.F.; Yang, Y.S. Long-term throughfall exclusion decreases soil organic phosphorus associated with reduced plant roots and soil microbial biomass in a subtropical forest. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, S. Mechanism of sand cementation with an efficient method of microbial-induced calcite precipitation. Materials 2021, 14, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Qi, Y.B.; Chang, Q.R. Impacts of revegetation management modes on soil properties and vegetation ecological restoration in degraded sandy grassland in farming-pastoral ecotone. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and Assessing Soil Quality; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.; Xie, Y.; Jia, X.; Su, T.; Li, J.; Shen, Y. Assessment of soil quality indexes for different land use types in typical steppe in the loess hilly area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheshiulo, E.M.A.; Larney, F.J.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; St. Luce, M.; Chau, H.W.; Liu, K. Quantitative evaluation of soil health based on a minimum dataset under various short-term crop rotations on the Canadian prairies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, G.; Das, B.; Morajkar, S.; Desai, A.; Murgaokar, D.; Kulkarni, R.; Sale, R.; Patel, K. Soil quality assessment of coastal salt-affected acid soils of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26221–26238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiollahi, K.; Golmohamadi, F.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R.; Davari, M. Assessing the effects of slope gradient and land use change on soil quality degradation through digital mapping of soil quality indices and soil loss rate. Geoderma 2018, 318, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius, B.N.; van Es, H.M.; Schindelbeck, R.R.; Idowu, O.J.; Clune, D.J.; Thies, J.E. Evaluation of laboratory-measured soil properties as indicators of soil physical quality. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Lopez-Vicente, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.L. A nature-based solution to reduce soil water vertical leakage in arid sandy land. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Plots Location | Plot Classification | Longitude and Latitude | Number of Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nuanshui | Typical Pisha Sandstone area (PSA) | 39°47′15″ N 110°35′54″ E | 34 |
| Tetong Gully | 39°47′19″ N 110°36′4″ E | 12 | |
| Shibu Ertai Gully | 39°59′58″ N 109°53′36″ E | 80 | |
| Er Laohu Gully | Loess soil area (LSA) | 39°47′40″ N 110°36′7″ E | 164 |
| Tela Gully | Aeolian soil area (ASA) | 39°34′6″ N 110°57′34″ E | 72 |
| Ada Freeway | 39°27′50″ N 109°56′59″ E | 20 | |
| Huojitu | 39°14′12″ N 110°10′13″ E | 20 | |
| Hala Gully | 39°31′68″ N 110°21′6″ E | 20 | |
| Shigetai Gully | 39°41′45″ N 110°8′12″ E | 20 |
| Categories of Indicator | Indicators and Abbreviation | Test Method and Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Soil water content (SWC), hygroscopic water content (Wh), bulk density (BD), soil particle composition | Drying–weighing method |
| Chemical | pH | Mettler–Toledo testing |
| Organic carbon (OC) | Potassium dichromate-concentrated sulfuric acid external heating | |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | Elementar vario MACROCUBE elemental analyzer | |
| Ammonia nitrogen, available (AN) available phosphorus (AP), available potassium (AK) | Top-cloud TPY-6PC soil nutrient rapid measurement | |
| Total phosphorus (TP) | NaOH melt-molybdenum reaction colorimetric | |
| Soluble calcium (Ca) | Atomic absorption spectroscopy | |
| Nitrate (Ni) | Reduction distillation | |
| Total potassium (TK) | Alkali fusion | |
| Biological | Culturable fungi (Fu), culturable bacteria (Ba), and culturable actinomycetes (AC) | Microbial medium and pipetting |
| Activities of alkaline phosphatase (AKP), acid phosphatase (ACP), neutral phosphatase (NP) | 0.5% phenylene disodium phosphate | |
| Activities of urease (URE), invertase (SC), and catalase (CAT) | Modified indophenol blue colorimetric method, phthalic acid buffer method, and potassium permanganate titration method | |
| Spore density (SD), spore richness (SRS), Shannon–Wiener index (SWI), and Simpson index (SI) | Wet sieve pour and sucrose centrifugation (50 g of soil as the standard sample size) |
| Type | Scoring Function (Linear) | Scoring Function (Non-Linear) |
|---|---|---|
| More is better | ||
| Less is better | ||
| Optimal value | Combine “more is better” with “less is better” in increasing and decreasing part of the function |
| Categories Contained in Datasets for SQI | Indicators (Abbr.) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | BD | Less is better |
| Sand | Less is better | |
| Silt and Clay | More is better | |
| SWC | More is better | |
| Wh | More is better | |
| Chemical | pH | Optimal value |
| OC | More is better | |
| TN | More is better | |
| AN | More is better | |
| Ni | More is better | |
| TP | More is better | |
| AP | More is better | |
| AK | More is better | |
| Ca | Optimal value | |
| Biological | Fungi | More is better |
| Bacteria | More is better | |
| AC | More is better | |
| ACP | More is better | |
| CAT | More is better | |
| URE | More is better | |
| SD | More is better | |
| SRS | More is better |
| Indicators | Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Norm | Group | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | PC8 | PC9 | |||
| Eigenvalues | 3.883 | 2.562 | 2.231 | 1.937 | 1.508 | 1.267 | 1.172 | 1.067 | 1.003 | ||
| Variance contribution/% | 16.881 | 11.139 | 9.699 | 8.421 | 6.555 | 5.510 | 5.097 | 4.639 | 4.359 | ||
| Cumulative contribution/% | 16.881 | 28.020 | 37.719 | 46.141 | 52.696 | 58.206 | 63.303 | 67.942 | 72.301 | ||
| pH | −0.171 | 0.303 | 0.068 | 0.331 | −0.573 | 0.193 | 0.165 | 0.258 | −0.088 | 1.11 | 5 |
| OC | −0.252 | 0.029 | 0.702 | 0.019 | 0.058 | 0.104 | −0.115 | 0.265 | 0.220 | 1.23 | 3 |
| TN | 0.665 | 0.261 | 0.274 | 0.129 | −0.130 | 0.031 | −0.151 | −0.118 | 0.138 | 1.48 | 1 |
| AN | 0.714 | −0.252 | −0.009 | −0.275 | −0.084 | 0.201 | −0.020 | 0.110 | −0.143 | 1.54 | 1 |
| Ni | 0.477 | −0.407 | −0.223 | 0.042 | 0.101 | −0.145 | 0.265 | −0.187 | 0.079 | 1.26 | 1 |
| BD | 0.213 | 0.014 | −0.468 | 0.010 | 0.501 | 0.372 | 0.116 | 0.255 | −0.194 | 1.16 | 5 |
| Sand | 0.061 | 0.639 | −0.243 | −0.662 | −0.091 | 0.163 | −0.057 | −0.118 | 0.136 | 1.46 | 4 |
| Silt | −0.028 | −0.691 | 0.166 | 0.629 | 0.149 | −0.205 | −0.061 | 0.060 | −0.043 | 1.47 | 2 |
| Clay | −0.140 | 0.217 | 0.323 | 0.140 | −0.246 | 0.179 | 0.494 | 0.244 | −0.394 | 1.05 | 7 |
| SWC | 0.363 | 0.074 | −0.017 | 0.264 | 0.344 | 0.398 | 0.237 | −0.114 | 0.265 | 1.09 | 6 |
| Wh | 0.742 | 0.375 | 0.089 | 0.140 | 0.125 | −0.031 | 0.192 | 0.260 | −0.020 | 1.64 | 1 |
| TP | 0.236 | −0.181 | −0.361 | −0.061 | −0.275 | −0.319 | 0.439 | 0.176 | 0.361 | 1.11 | 7 |
| AP | 0.471 | −0.382 | 0.255 | −0.271 | −0.029 | 0.265 | −0.312 | 0.136 | 0.096 | 1.33 | 1 |
| AK | 0.682 | 0.319 | −0.204 | 0.255 | −0.202 | −0.065 | −0.111 | 0.126 | 0.158 | 1.55 | 1 |
| Ca | −0.226 | 0.085 | 0.634 | −0.201 | 0.376 | 0.134 | 0.200 | 0.141 | 0.303 | 1.26 | 3 |
| Fu | −0.018 | −0.563 | −0.109 | −0.056 | 0.024 | 0.420 | 0.108 | 0.096 | 0.040 | 1.05 | 2 |
| BA | −0.640 | −0.057 | −0.286 | 0.084 | −0.095 | 0.392 | 0.122 | −0.314 | −0.019 | 1.46 | 1 |
| AC | −0.362 | 0.001 | 0.024 | 0.280 | −0.278 | 0.276 | 0.058 | −0.195 | 0.443 | 1.06 | 9 |
| ACP | 0.199 | −0.129 | 0.024 | 0.142 | −0.271 | 0.287 | −0.399 | −0.016 | −0.242 | 0.83 | 7 |
| CAT | 0.162 | 0.285 | 0.471 | −0.041 | 0.258 | −0.140 | 0.226 | −0.442 | −0.306 | 1.14 | 3 |
| URE | 0.592 | 0.048 | 0.294 | 0.342 | −0.165 | 0.127 | 0.029 | −0.415 | 0.026 | 1.43 | 1 |
| SD | −0.015 | 0.449 | −0.369 | 0.514 | 0.309 | 0.134 | −0.125 | −0.026 | 0.003 | 1.23 | 4 |
| SRS | −0.329 | 0.427 | −0.105 | 0.340 | 0.240 | −0.149 | −0.288 | 0.216 | 0.092 | 1.19 | 2 |
| SQI Scoring Method | SQI TDS NL | SQI TDS L | SQI MDS NL | SQI MDS L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ntree | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| mtry | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Increased node purity (IncNodePurity) | MWD | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.33 |
| ERsand | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.61 | 0.57 | |
| ERsilt | 0.37 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.59 | |
| ERclay | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.76 | 0.65 | |
| D | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.45 | |
| Increased mean squared error (IncMSE) | MWD | 6.33 | 4.19 | 4.93 | 4.77 |
| ERsand | 7.15 | 8.01 | 7.57 | 8.07 | |
| ERsilt | 5.07 | 4.80 | 7.86 | 8.31 | |
| ERclay | 4.87 | 5.41 | 5.79 | 5.12 | |
| D | 3.48 | 0.61 | 5.85 | 4.21 | |
| Fitting effect on training data | RMSE | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| R2 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.78 | |
| MAE | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | |
| Fitting effect on testing data | RMSE | 0.09 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.011 |
| R2 | 2 × 10−3 | 5.4 × 10−8 | 9 × 10−5 | 1 × 10−3 | |
| MAE | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Rao, L. Evaluation of Landscape Soil Quality in Different Types of Pisha Sandstone Areas on Loess Plateau. Forests 2025, 16, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040699
Huang L, Rao L. Evaluation of Landscape Soil Quality in Different Types of Pisha Sandstone Areas on Loess Plateau. Forests. 2025; 16(4):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040699
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lei, and Liangyi Rao. 2025. "Evaluation of Landscape Soil Quality in Different Types of Pisha Sandstone Areas on Loess Plateau" Forests 16, no. 4: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040699
APA StyleHuang, L., & Rao, L. (2025). Evaluation of Landscape Soil Quality in Different Types of Pisha Sandstone Areas on Loess Plateau. Forests, 16(4), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16040699





