Abstract
Sapindus mukorossi is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical areas of southern China; the seed kernel oil is potential biodiesel material, and the saponins extracted from fruit pericarp are very valuable efficient natural surfactants. Therefore, S. mukorossi is an ideal tree species for developing forestry bioenergy and multiple other products. In this study, 42 S. mukorossi fruits from mother trees were collected from 39 distinct locations in 12 Chinese provinces to infer fruit and seed trait responses to environmental factors. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was conducted using 21 horticultural fruit traits and 10 environmental factors that represented different climatic and geographic conditions throughout southern China. CCA revealed well-developed patterns of natural phenotypic variation, and insight into the ecological factors that are potentially important in shaping this variation. The results presented here further elucidate the natural distribution and ecological adaptations of wild S. mukorossi resources, which will be valuable for S. mukorossi cultivation by helping identify ideal planting areas. The germplasm resources with extensive morphological variation can also contribute to S. mukorossi breeding in the future by helping develop new cultivars with high saponin yield.
1. Introduction
Sapindus is distributed in tropical and subtropical areas worldwide, and includes 13 species. There are four Sapindus species in China; among them, S. mukorossi (Chinese soapberry) is the most widely distributed, and is distributed in tropical and subtropical areas of southern Qinling Mountains—Huaihe River [1]. The S. mukorossi seed kernel oil content reaches 40%, and has a high content of medium-chain monounsaturated fatty acids, which show considerable potential as resources for biodiesel production material [1,2,3,4,5]. Moreover, saponins extracted from S. mukorossi fruit pericarps are very valuable, and the content in fruit pericarp tissue ranges from 7% to 27% [6]. Saponins can serve as efficient natural surfactants and they exhibit strong pharmacological effects, including anthelmintic, antidermatophytic, antiinflammatory, antitussive, cytotoxic, hemolytic, and molluscicidal activities [1,2,7,8,9]. Therefore, S. mukorossi is an ideal tree species for developing forestry bioenergy in a sustainable and multi-production way. In particular, the wild S. mukorossi germplasm resources have recently been of great interest, because of their importance for developing new cultivars that can be commercially used in cosmetics and their potential for bioenergy and pharmacology [1,4,10].
Efforts have been made to develop Sapindus breeding programs by mostly focusing on genetic diversity, phenotypic variance, and biochemical variance analyses to identify lines that produce high seed oil yield, high saponin yield, and stronger adaptability [5,10,11,12]. Although these studies have made progress, additional research on the natural adaptive diversification of Sapindus is required. Most previous studies have focused on how a single environmental factor influenced fruit trait variation [5,10,11]. However, limited information is available on how numerous environmental factors shape morphological diversity at a large scale.
In this study, morphological variation of S. mukorossi across its entire geographical distribution in China was investigated. In total, 42 S. mukorossi mother trees were found in 12 provinces. Twenty-one horticultural fruit traits and 10 environmental factors were measured to represent morphological variation and different environmental conditions, respectively, throughout southern China. The objectives were to determine the association of morphological diversity with geographical and environmental factors so that the natural distribution and ecological adaptations of wild S. mukorossi resources could be elucidated. These findings will be valuable for S. mukorossi cultivation, because then can help identify optimal planting areas. The germplasm resources with extensive morphological variation can also contribute to S. mukorossi breeding in the future by facilitating development of new cultivars with high saponin yield.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
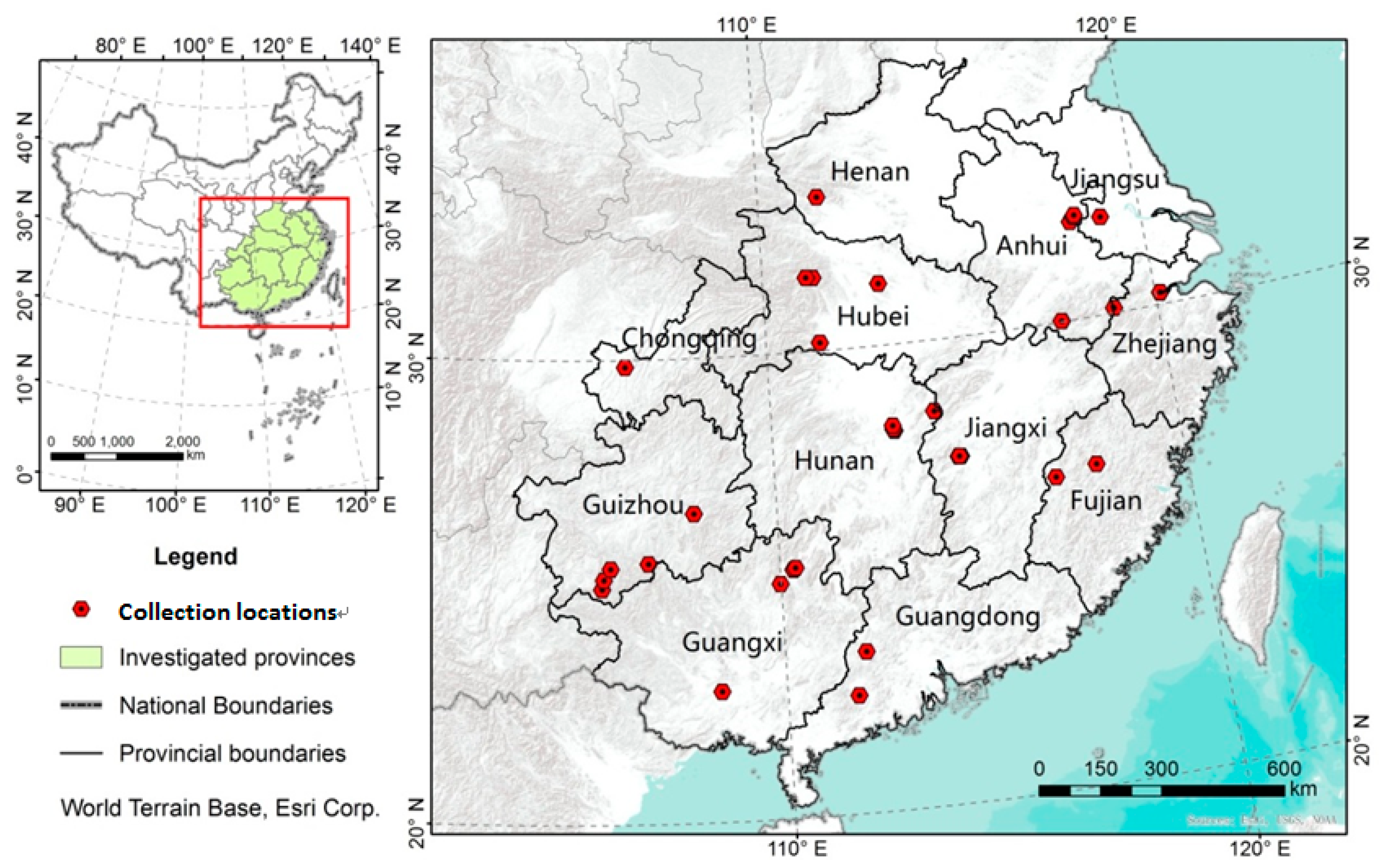
Fruits were collected in November 2013 from mother trees in 39 distinct locations (Figure 1) that covered the majority of the natural distribution of S. mukorossi in China [5]. With the support of local research institutions, 42 S. mukorossi fruits from mother trees were collected (Table 1) across a wide expanse of southern China (33.41–22.49° latitude, 105.76–120.12° longitude, and up to 1145 m elevation). Because they have stable fruit traits, only mature seeds were collected. The trees all reached sexual maturity and were in the full fruiting stage. To ensure that only mature seeds were obtained, yellow or red fruits with a shrunken pericarp were collected in November [12].

Figure 1.
Sample collection locations of Sapindus mukorossi fruits, southeastern China.

Table 1.
Collection locations of Sapindus mukorossi fruit and associated environmental factors.
2.2. Phenotypic Traits
To measure phenotypic traits, 30 fruits of each selected tree were arbitrarily chosen (Table 2). Fruit (seed) horizontal, vertical (from top to bottom), and lateral (from the narrowest direction) diameters, and fruit pericarp thickness were measured with a vernier caliper. Fruit (seed) index was then calculated by dividing fruit (seed) vertical diameter by fruit (seed) lateral diameter. Fruit (seed) volume index was then calculated by multiplying fruit (seed) vertical diameter by fruit (seed) lateral diameter by fruit (seed) horizontal diameter. The quarter method with three replicates was used to measure 100-fruit weight, 100-seed weight, 100-pericarp weight, and 100-seed kernel weight. Kernel content and seed content were calculated by dividing kernel weight by seed weight and seed weight by fruit weight, respectively [5].

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics of seed and fruit traits of Sapindus mukorossi.
2.3. Seed Oil Content
The seed kernel oil was extracted by a FOSS Soxhlet extraction apparatus (Soxtec 2050, Höganäs, Sweden). The four-step extraction process included heating for 30 min, condensation for 1 h, predrying for 20 min, and organic solvent recycling for 10 min. A 2-h extraction step was applied to ensure that all of the oil was extracted from the seed kernel mass. The organic solvent was petroleum ether, and each sample weighed 10–15 g. The extracted oil was dried at 80 °C for 10 min to remove residual organic solvent (Table 2) [9].
2.4. Saponin Content
To construct a standard curve for saponin content measurements, a stock solution was prepared by dissolving a 10-mg oleanolic acid standard sample (98%) in 10 mL carbinol. A 10-mL aliquot of this solution was transferred to a 100-mL volumetric flask, which was brought to volume with buffer solution. A dilution series was generated by transferring 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, and 0.7 mL of the standard solution into separate stoppered 10-mL test tubes. After heating the tubes in a water bath, 0.2 mL of glacial acetic acid mixed with 5% vanillin was added, followed by the addition of 0.8 mL perchloric acid, heating in a water bath for 15 min at 70 °C, cooling in ice water for 2 min, addition of 5 mL glacial acetic acid, and shaking. The absorbance of the standard solutions was measured at wavelengths of 400 to 800 nm with a UV spectrophotometer, which revealed a peak at 547 nm. The generated data were used to construct a standard curve.
To determine saponin content, 400 mg of Sapindus pericarp tissue was subjected to Soxhlet extraction with alcohol. The extracts were purified by ultrasonication, filtered, concentrated by rotary evaporation, dissolved in 20 mL water, extracted three times with water-saturated butanol (20, 20, and 10 mL), and reconcentrated by rotary evaporation. The residue was completely dissolved in 10 mL methyl alcohol and then refluxed with 2 mL HCl (2 mol/L) and 20 mL methyl alcohol over boiling water for 2 h. The hydrolysate was dissolved in 10 mL water and extracted three times with ethyl acetate (20, 10, and 10 mL). After concentrating the extract by rotary evaporation, the residue was dissolved in methyl alcohol in a 10-mL volumetric flask to volume.
A 0.4-mL aliquot of the solution was placed in a 10-mL test tube and heated in a water bath. Subsequently, 0.2 mL glacial acetic acid mixed with 5% vanillin was added, followed by addition of 0.8 mL perchloric acid, heating in a water bath for 15 min at 70 °C, cooling in ice water for 2 min, addition of 5 mL glacial acetic acid, and shaking. Absorbance of the solution was then recorded at 547 nm [10].
2.5. Environmental Factors
Location data including longitude, latitude, and elevation were obtained at each collection point with a GPS (JUNO® SCSD, Trimble, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Climate data, including annual average relative humidity, annual minimum and maximum temperatures, annual average temperature, average annual precipitation, annual minimum relative humidity, and mean annual sunshine duration, were obtained from the National Meteorological Data of China (http://www.escience.gov.cn/metdata/page/index.html) [9].
2.6. Statistical Analyses
Mean and standard deviation of each fruit trait were calculated. The analyses were conducted using the statistical package STATISTICA 6.0 (StatSoft Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). Correlation analyses of environmental variables and fruit trait variables were performed separately to independently examine the correlations between fruit traits and environmental factors.
Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was conducted to detect environmental influence on fruit trait variation; the fruit trait variables were the response variables and environmental factors were the explanatory variables [9]. A potential analytical problem is redundancy of environmental factors (including geographical factors) that may be correlated with each other or show strong co-linearity. Consequently, the CCA model was simplified to avoid co-linearity issues when selecting key environmental factors. In addition, the geographical factors and climate factors that strongly affected fruit trait variation were separately analyzed in the simplified CCA models. Subsequently, data were also subjected to ANOVA to test the significance of each variable in the CCA model, and to test the significance of the coupled CCA principal components to the model. All ordination analyses were performed with the package vegan v. 1.8-5 and gclus v. 1.3.1 in the R v. 3.4.1 statistical environment [9,13,14].
3. Results
3.1. Geographic Distribution
In total, 42 S. mukorossi trees in 39 distinct geographical locations were found in our field surveys throughout the entire S. mukorossi distribution in inland China (Table 1; Figure 1). The extensive geographic distribution ranges from the Funiu Mountains to southern China and from the southeast coast of the East China Sea to the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, which borders on the geographical distribution of S. delavayi. Our survey data further showed that S. mukorossi appears to have a wide range of adaptations to different habitat conditions. There are three preferential habitats for S. mukorossi growth: (1) scattered in weed tree forests in hilly areas, (2) isolated trees beside stream banks or village edges, and (3) scattered in weed tree forests in flat areas (Figure 1).
The geographical variables and habitat traits of all surveyed locations are listed in Table 1. The average elevation of S. mukorossi locations was 338 m, and ranged from 20 m (Zhejiang) to 1145 m (Guizhou). The mean annual rainfall of the collection locations ranged from 639.5 mm (Henan) to 1810.4 mm (Guangxi), with an average of 1332.8 mm, and the annual mean temperature ranged from 16.0 °C (Jiangsu) to 22.2 °C (Guangdong), with an average of 18.3 °C. The annual minimum temperature ranged from −8.6 °C (Anhui) to 2.7 °C (Guangdong), with an average of 3.5 °C. The annual maximum temperature ranged from 33.4 °C (Guizhou) to 41.8 °C (Zhejiang), with an average of 39.0 °C. Annual sunshine duration ranged from 1353 h (Guizhou) to 4827 h (Guangdong), with an average of 1900 h. The annual average relative humidity ranged from 64% (Henan) to 82.77% (Guangdong), with an average of 78%. The annual minimum relative humidity ranged from 5% (Henan) to 23% (Congqing), with an average of 13%.
3.2. Fruit Traits
Because this study was broadly focused on economic utilization, we analyzed key traits that are related to the continued selection of germplasm resources, such as seed oil production, saponin content, and fruit quality. As shown in Table 2, we observed that coefficients of variation of seed and fruit traits had wide variation that ranged from 0.04 to 0.43, with a mean value of 0.23. Among them, the maximum value belonged to 100-fruit saponin (7.1 g to 53.4 g), and the minimum value belonged to fruit index (0.82 to 1.02). Alternatively, the coefficients of variation were lower than the mean values for 100-seed kernel weight (16 g to 67.9 g), seed content in fruit (33.43% to 64.39%), fruit coat thickness (0.99 mm to 2.75 mm), seed index (0.26 to 1.18), seed kernel oil content (28.34% to 44.69%), fruit horizontal diameter (16.37 mm to 25.28 mm), fruit vertical diameter (16.75 mm to 22.7 mm), seed lateral diameter (9.58 mm to 14.69 mm), seed vertical diameter (11.59 mm to 16.7 mm), and fruit index (0.82 to 1.02). This means that S. mukorossi fruits have less variation in seed kernel oil, fruit shape, and seed shape. However, coefficients of variation were greater than 0.23 for 11 fruit traits, including 100-fruit saponin (7.1 g to 53.4 g), seed horizontal diameter (9.8 mm to 49.77 mm), seed volume index (0.11 to 0.73), 100-kernel oil (4.8 g to 25.8 g), fruit coat saponin content (7.67% to 27.04%), 100-fruit coat weight (80.39 g to 448.07 g), 100-seed kernel weight (16 g to 67.9 g), fruit volume index (0.38 to 1.66), fruit lateral diameter (13.87 mm to 42.5 mm), 100-fruit weight (166.58 g to 686.5 g), and 100-seed weight (81.87 g to 238.52 g). Among them, the coefficient of variation for 100-fruit saponin (7.1 g to 53.4 g) was 0.43, which was the largest value. These traits are important economic traits, and these findings indicate that economic traits had greater variation than other traits, which was caused by the interaction between environment and genotypes.
3.3. Correlation Analysis
As shown in Table 3, correlation analysis between S. mukorossi fruit traits, and three geographical factors and seven climate factors revealed a substantial amount of significant correlations, especially with elevation, temperature factors, latitude, and longitude. Elevation was significantly positively correlated with nine morphological and oil-related traits, of which 100-seed weight (R = 0.568, p < 0.01) was the most strongly correlated. Whereas annual maximum temperature was significantly negatively correlated with 12 morphological, oil-related, and saponin-related traits, the most strongly correlated fruit trait was coat thickness (R = −0.575, p < 0.01). Annual average temperature was significantly positively correlated with four saponin-related traits, of which the most strongly correlated trait was 100-fruit saponin (R = 0.624, p < 0.01). Annual lowest temperature was significantly correlated with seven saponin-related traits, of which the most strongly correlated trait was 100-fruit saponin (R = 0.712, p < 0.01). Latitude was significantly correlated with seven traits, of which the most strongly correlated was 100-fruit saponin (R = −0.552, p < 0.01). Longitude was significantly correlated with 11 traits, of which the strongest was 100-fruit saponin (R = −0.539, p < 0.01).

Table 3.
Correlation analysis results between environmental factors, and seed and fruit traits of Sapindus mukorossi.
Overall, key traits of seed oil, including 100-seed weight, 100-seed kernel weight, and 100-kernel oil, were significantly positively correlated with elevation, but negatively correlated with annual maximum temperature and annual precipitation. Alternatively, key traits of saponin, including 100-fruit coat weight, fruit coat saponin content, and 100-fruit saponin, were significantly positively correlated with annual average temperature, annual lowest temperature, and minimum relative humidity, but negatively correlated with latitude and longitude.
3.4. CCA
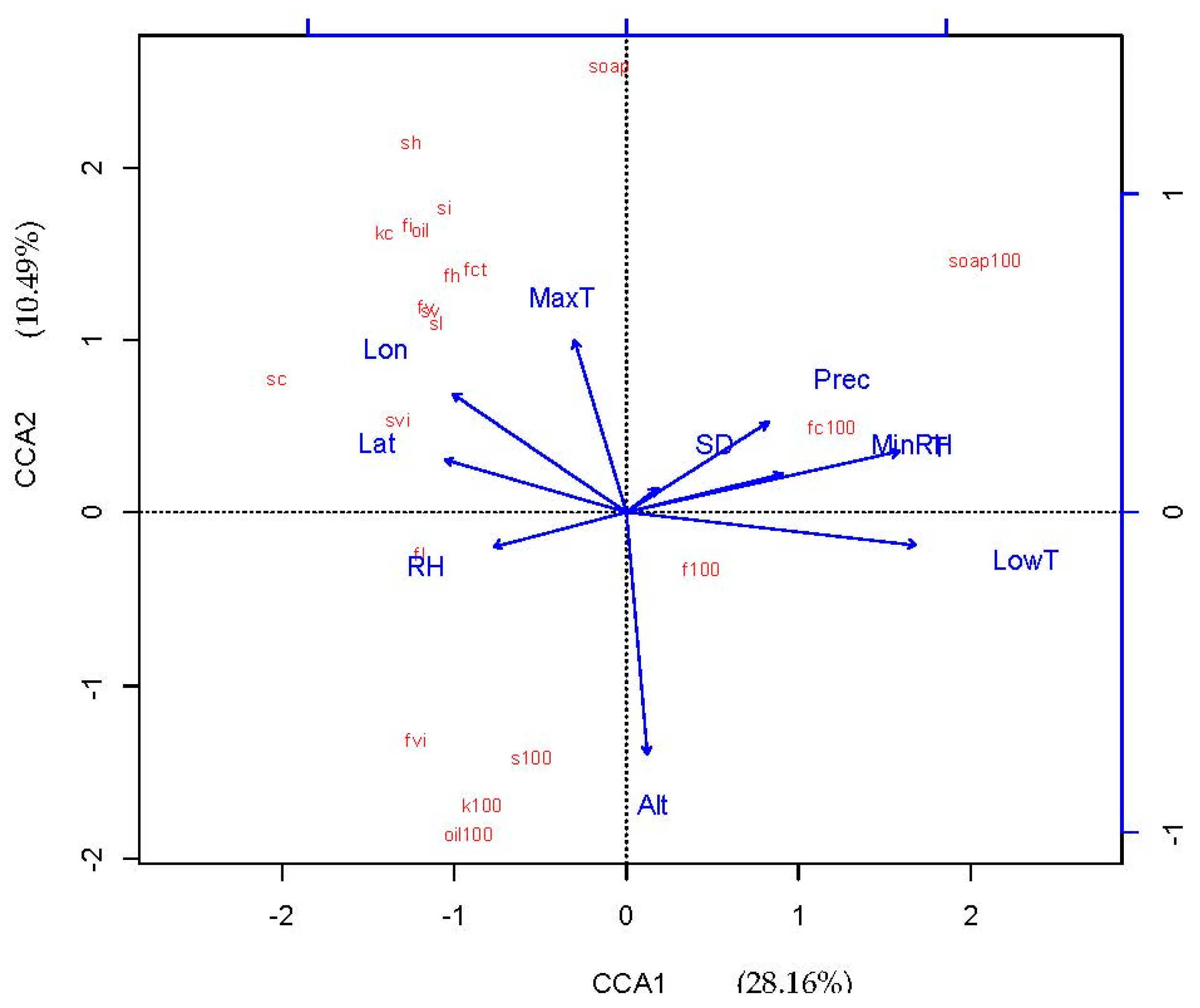
Table 4 summarizes the CCA results for all environmental factors. The canonical axes explained 47.22% of the total variation in fruit traits. The first two canonical axes explained a large proportion (38.65%) of the total variance (47.22%). In the CCA model, the first two axes were both significant (p < 0.001), and 28.16% of the variation was explained by CCA1 and 10.49% was explained by CCA2. Based on the correlation coefficients, the first CCA axis was predominantly associated with annual average temperature (0.86) and annual lowest temperature (0.91), and inversely associated with latitude (−0.57) and longitude (−0.55). The second axis was predominantly associated with annual maximum temperature (0.54) and inversely associated with altitude (−0.75).

Table 4.
CCA results for seed and fruit traits of Sapindus mukorossi with environmental factors.
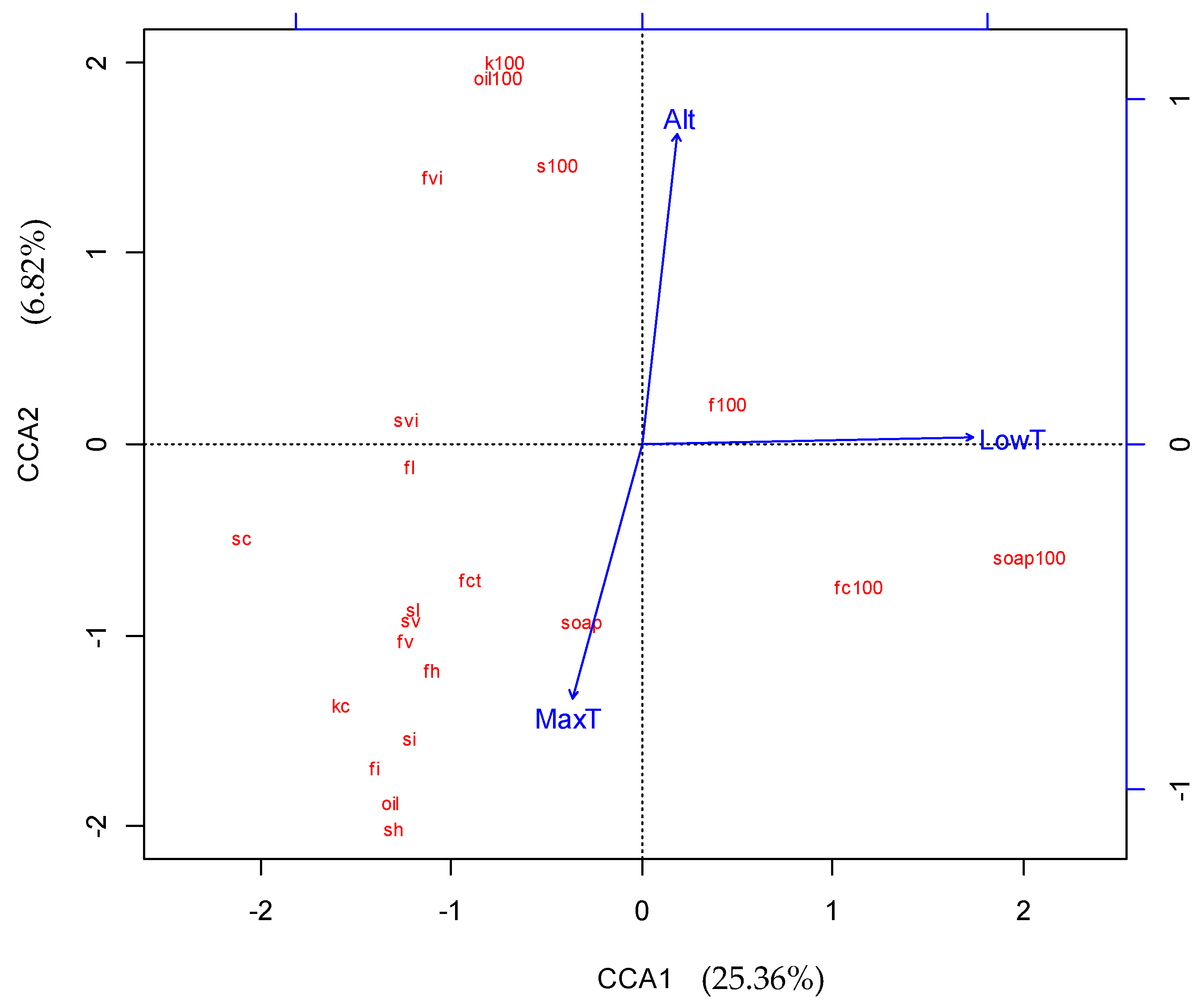
To solve the problem of redundancy from using multi-dimensional data, the model was simplified (Table 5). In the simplified model, elevation, annual maximum temperature, and annual lowest temperature were selected, because they significantly affect S. mukorossi fruit traits, and explained 34.11% of the variance (total variance, 47.22%). For further analysis, a ‘climate factors’ CCA model was made, which explained 38.94% of the total variance in fatty acid composition; this model determined that annual maximum temperature and annual lowest temperature explained 29.33% of the total variance. Additionally, a ‘geographical factors’ CCA model was constructed, which explained 22.32% of the total variance in fatty acid composition; this model determined that elevation and latitude explained 17.71% of the total variance. Then, proportion of variation explained by each environmental factor was used for further analysis. Among them, annual lowest temperature had the highest explanation of 23.56%, and annual average temperature had the second highest of 21.20%. However, the variation explained by other variables was less than 10%, except for latitude (11.35%) and longitude (10.50%).

Table 5.
ANOVA of key factors in CCA models.
Based on CCA analysis, we constructed two triplots that depicted the relationship between fruit trait variation and environmental factors. As shown in Figure 2, there were relationships between fruit traits and most environmental factors, although the relationship between fruit traits and geographical variation was not clear because of the influence of multi-dimensional factors. As shown in Figure 3, to obtain the most economically important information, the CCA model was simplified by selecting annual extreme temperature and elevation as key factors. We found that the fruit traits were divided into three groups: pericarp soap yield-related traits (100-fruit weight, 100-fruit coat weight, and 100-fruit saponin), seed oil yield-related traits (100-seed oil, 100-kernel weight, and 100-seed weight), and morphological fruit traits (seed kernel oil content, fruit coat saponin content, seed kernel content, seed content in fruit, fruit horizontal diameter, fruit vertical diameter, fruit lateral diameter, fruit coat thickness, seed horizontal diameter, seed vertical diameter, seed lateral diameter, fruit index, fruit volume index, seed index, and seed volume index). For the pericarp soap yield-related traits, we found that annual minimum temperature was the most important factor. However, for the seed oil yield-related traits, elevation and annual maximum temperature were the most important factors but had opposite correlation patterns. For the morphological fruit traits, annual maximum temperature, elevation, and annual lowest temperature all had some effect.
Figure 2.
CCA ordination diagram of Sapindus mukorossi seed and fruit traits, and environmental factors. Abbreviations: MaxT: Annual Maximum Temperature, T: Annual Average Temperature, LowT: Annual Lowest Temperature, Prec: Average Annual Precipitation, SD: Sunshine Duration, RH: Relative Humidity, MinRH: Minimum Relative Humidity, Lat: Latitude, Lon: Longitude, Alt: Altitude, Oilc: Seed kernel oil content, sopc: Fruit coat saponin content, 100f: 100-fruit weight, s100: 100-seed weight, 100fc: 100-fruit coat weight, kc: Seed kernel content, sc: Seed content in fruit, fh: Fruit horizontal diameter, fv: Fruit vertical diameter, fl: Fruit lateral diameter, fct: Fruit coat thickness, sh: Seed horizontal diameter, sv: Seed vertical diameter, sl: Seed lateral diameter, 100k: 100-kernel weight, 100oil: 100-seed oil, 100soap: 100-fruit saponin, fi: Fruit index, fvi: Fruit volume index, si: Seed index, svi: Seed volume index.
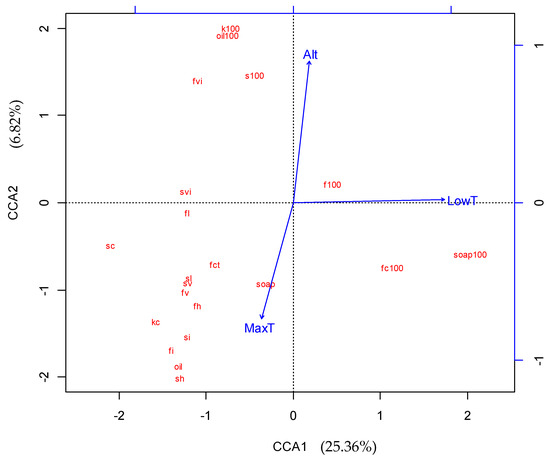
Figure 3.
Simplified CCA ordination diagram of Sapindus mukorossi seed and fruit traits, and environmental factors.
4. Discussion
The genus Sapindus, which has a broad global distribution, includes 13 species that inhabit tropical to subtropical areas. Of the species present in China, S. mukorossi is the most widely distributed across southern China but is scarce [1]. Other Sapindus species (S. delavayi, S. tomentosus, S. rarak, and S. rarak var. velutinus) have distributions with relatively narrower elevation and climate ranges than S. mukorossi [1,5,15]. Generally, Sapindus species in China except S. mukorossi mainly occur in Yunnan and Sichuan Provinces at relatively higher elevations (500–2600 m). However, S. mukorossi has a much wider distribution, including Henan, Guizhou, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Guangdong, Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Anhui, Hunan, Hubei, and Chongqing Provinces, which are at relatively lower elevations (0–1200 m).
For tree breeding, natural biodiversity is an underexploited sustainable resource that can enrich genetic pools to improve productivity, quality, and adaptation. Research on phenotypic variation of genetic resources provides a basis for analyzing natural genetic resources [16,17,18]. In this study, 42 S. mukorossi mother trees showed extensive variation in fruit traits. Such a wide range of variation and rich germplasm resources provides potential for S. mukorossi cultivar improvement. From a commercial perspective, the trees with high seed oil yield and high fruit saponin yield could be selected as potential new cultivars for production. Other trees with unique fruit characteristics, such as very large seed and fruit sizes, could be good choices for developing breeding targets that can be used to make artware and process activated carbon [1,9,19,20].
In this research, 100-fruit coat, fruit coat saponin content, and 100-fruit saponin were all significantly positively correlated with annual average temperature and annual minimum temperature, and were significantly negatively correlated with annual maximum temperature. CCA revealed that annual minimum temperature was the key factor that influences saponin variation, because it had the highest correlation coefficient (0.77, p < 0.01). Therefore, it can be inferred that annual minimum temperature played an important role in S. mukorossi saponin variation. This finding is consistent with the prior finding that S. mukorossi trees with higher saponin yield were more likely to be found in areas with higher temperatures [10]. Additionally, Jiao found that moderately high temperatures are beneficial for triterpenoid saponin synthesis in plants [21]. Moreover, in this study, high precipitation levels were found to inhibit saponin synthesis based on correlation analysis (R = −0.380, p < 0.05). This finding was not surprising, because moderate drought stress promotes triterpenoid saponin synthesis and accumulation in plants [21,22].
Genetic factors, abiotic factors such as environmental factors and soil conditions, and their interaction are known to affect the fatty acid composition of plant seed oils [23,24,25,26,27]. In this research, S. mukorossi seed oil-related variables including 100-seed weight, 100-kernel weight, and 100-oil weight were significantly negatively correlated with annual maximum temperature and annual precipitation. However, kernel oil content was not significantly correlated with environmental factors, which was consistent with the findings of Shao [11]. Comparatively, 100-seed oil weight was highly correlated with elevation (R = 0.424, p < 0.01) and annual maximum temperature (R = −0.363, p < 0.05). Combined with CCA, the 100-seed oil weight, which was the most valuable seed oil-related trait, showed continuous variation with elevation and annual maximum temperature. Moreover, although the correlation was not strong, seed oil yield tended to be influenced by elevation. Trees from Guizhou and Hubei Provinces had higher seed oil yield than from other provinces. This conclusion was partly consistent with the findings of Fan [28], who found that oil output capacity of S. mukorossi trees showed a high degree of association with annual average temperature and elevation. However, in this research, the oil output capacity of S. mukorossi trees varied much more at the seed kernel level than the kernel oil content. However, the fatty acid composition seemed stable despite the wide distribution of S. mukorossi, which is ideal for industrial use of these oils [9,29].
There is a complex interplay between genes and environments that can influence the fruit traits of plants [30,31,32,33]. The CCA results indicated that environmental factors play important roles in determining S. mukorossi fruit trait variation. This information is valuable for S. mukorossi cultivation, because it can be used to identify optimal areas for planting S. mukorossi. Annual minimum temperature was determined to be a limiting climate factor for fruit trait variation that restricts further extension of possible planting areas. Because of high economic benefits, S. mukorossi have been planted in China, but many problems have been raised when the geographic adaptation of S. mukorossi has been ignored [1,9].
Based on the results of several CCA analysis models, we determined that a substantial amount of fruit trait variation was explained by environmental factors (47.22%). The simplified ‘climate factors’ CCA explained 38.94% of the 47.22%, whereas the ‘geographic factors’ CCA explained 22.32%. Therefore, it can be inferred that there is 14.04% overlap between climate and geographic factors, which means that the geographic factors only explained 8.28% of net proportion. Therefore, it was clear that climate factors explained more of the fruit trait variation. Among the climate variables, fruit trait variation was most explained by annual minimum temperature (23.56%) and annual average temperature (21.20%). The high sensitivity of S. mukorossi to temperature may be attributed to factors that affect growth, especially the frail thin bark.
For further analysis, the simplified ‘all factors’ CCA model determined that annual maximum temperature, annual minimum temperature, and altitude explained 34.11% of the total morphological variance. Comparatively, the simplified ‘climate factors’ CCA model determined that annual maximum temperature and annual minimum temperature explained 29.33% of the total variance, and the ‘geographical factors’ CCA model determined that altitude and latitude explained 17.71% of the total variance. Three key factors (annual maximum temperature, annual minimum temperature, and altitude) were found in the simplified ‘all factors’ CCA model, but did not include latitude. Therefore, it can be inferred that the variance explained by latitude substantially overlapped with that explained by annual maximum temperature and annual minimum temperature. However, annual maximum temperature, annual minimum temperature, and altitude were the key factors that explained fruit trait variation. When considering the ‘geographical factors’ alone, altitude and latitude had the greatest impact. When considering ‘climate factors’ alone, annual maximum temperature and annual minimum temperature had the greatest impact.
Many of these environmental factors appear to be very important in shaping natural species distributions. In particular, precipitation, temperature, and vegetation cover are important [34,35], which indicates that relatively few environmental conditions might be predominantly influential in determining S. mukorossi habitat preferences. In addition to S. mukorossi, other Sapindus species or varieties, such as S. delavayi, S. tomentosus, S. rarak, and S. rarak var. velutinus, are found in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau [1,9,36]. Among them, S. delavayi and S. mukorossi are naturally sympatric in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, and there may be inter- or intra-hybridization among different Sapindus species, which could account for the unique morphological characters of local germplasm resources. In the present study, all wild S. mukorossi genotypes distributed in Guizhou Province are potential hybrids, which was also suggested in previous studies [5,36,37]. Therefore, the origin of S. mukorossi fruit traits could be related to natural hybridization or divergent ecological adaptations, such as inter- or intra-hybridization between S. delavayi and S. mukorossi, which could have greatly enhanced morphological and genetic variation.
5. Conclusions
Our research elucidated geographical variation of S. mukorossi fruit traits in China and characterized this variation relative to environmental factors for the first time. The natural distribution and geographic variation models will be useful for S. mukorossi germplasm resources collection and utilization. The key environmental factors that shape fruit trait variation could provide a reference for S. mukorossi cultivation. Further research should be conducted to explore the genetic diversity and soil conditions associated with S. mukorossi fruit traits. These studies will help identify environmental and genetic interactions underlying phenotypic variation of this economically important species.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015ZCQ-LX-02).
Author Contributions
L.J. conceived and designed the experiments; C.S. and G.Z. performed the experiments; C.S. and J.W. analyzed the data; C.S., J.D., X.W. and L.J. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; C.S. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jia, L.M.; Sun, C.W. Research progress of biodiesel tree Sapindus mukorossi. J. China Agric. Univ. 2012, 17, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Dobhal, U.; Bisht, N.S.; Bhandari, S.L. Traditional values of Sapindus mukorossi gaertn. vern. Ritha: A review. Plant Arch. 2007, 7, 485–486. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chiang, T.H.; Chen, J.H. Properties of soapnut (Sapindus mukorossi) oil biodiesel and its blends with diesel. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 52, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Baruah, D.C. Production and characterization of biodiesel obtained from Sapindus mukorossi kernel oil. Energy 2013, 60, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.W.; Jia, L.M.; Ye, H.L.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, C.Y.; Weng, X.H. Geographic variation evaluating and correlation with fatty acid composition of economic characters of Sapindus spp. fruits. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.C.; Wu, M.D.; Tsai, W.J.; Liao, S.C.; Liaw, C.C.; Hsu, L.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H. Triterpenoid saponins from the fruits and galls of Sapindus mukorossi. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, M.F.; Lopez-Avila, A. Effect of extracts from Sapindus saponaria on the glasshouse whitefly Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 2009, 35, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, J.C.; Ho, M.L.; Lin, R.J.; Chang, J.S.; Wang, H.M. Tyrosinase inhibition, free radical scavenging, anti-microorganism and anticancer proliferation activities of Sapindus mukorossi extracts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2010, 41, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.W.; Jia, L.M.; Xi, B.Y.; Wang, L.C.; Weng, X.H. Natural variation in fatty acid composition of Sapindus spp. seed oil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 102, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.H.; Yao, X.M.; Zhang, T.Y.; Lin, X.Q.; Tang, X.H.; Ma, L.Z. The selection of high-saponin-yield plus tree of Sapinsndus mukorossi. J. For. Sci. Technol. 2013, 40, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.H.; Diao, S.F.; Dong, R.X.; Jiang, J.M.; Yue, H.F. Study on Geographic Variation of Morphology and Economic Character of Fruit and Seed of Sapindus mukorossi. For. Res. 2013, 26, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, S.F.; Shao, W.H.; Jiang, J.M.; Dong, R.X.; Li, Y.J. Phenotypic traits of Sapindus mukorossi seedling population for association analysis. Bull. Bot. Res. 2014, 34, 458–464. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, K.; Fujino, H.; Kasai, R.; Tanaka, O.; Zhou, J. Saponins of pericarps of Chinese Sapindus delavayi (Pyi-shiau-tzu), a source of natural surfactants. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.F.; Su, J.R.; Liu, W.D.; Lang, X.D.; Zhang, Z.J.; Su, L.; Jia, C.; Xin, Z.; Yang, H.J. Phenotypic variations in cones and seeds of natural Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis populations. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.H.; Zhu, X.F.; Yu, C.L.; Dai, Y.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Huang, J.Q.; Liu, Li. Variability of phenotypic characters and fatty acid composition of endemichickory nuts (Carya dabieshanensis) from different geographical provenances. J. Fruit Sci. 2014, 31, 370–377. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.S.; Lv, F.D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.A.; Wang, S.; Li, F.S.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, L.L. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of nut quality indexes of alternative superior individuals in Juglansregia. Nonwood For. Res. 2015, 33, 7–32. [Google Scholar]
- Flechas, C.; Henry, A.; Aragón, D.; Morales, C.; Jiménez, N.B.; Jiménez, G.P.; John, A. Study and development of three jaboncillo (Sapindus saponaria L.) products as grounding in its industrialization. Rev. Colomb. For. 2009, 12, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Xie, Y.; Asao, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Yamashita, C.; Muraoka, O.; Matsuda, H.; Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Yuan, D.; Yoshikawa, M. Oleanane-typetriterpene oligoglycosides with pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity from thepericarps of Sapindus rarak. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.L.; Gao, W.W. Advances in studies on influence of environmental factors on triterpenoid saponin synthesis in medicinal plants. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Guo, L.P.; Yang, G.; Chen, B.D.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, L.Q. Effect of environmental ecological factors on saponins of medicinal plant. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2012, 18, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Geleta, M.; Stymne, S.; Bryngelsson, T. Variation and inheritance of oil content and fatty acid composition in niger (Guizoti aabyssinica). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, K.; Heidari, G.; Javaheri, M.; Rokhzadi, A.; Nezhad, M.T.K.; Sohrabi, Y.; Talebi, R. Fertilization affects the agronomic traits of high oleic sunflower hybrid in different tillage systems. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 44, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunvald, A.K.; de Carvalho, C.G.P.; Leite, R.S.; Mandarino, J.M.G.; Andrade, C.A.D.; Amabile, R.F.; Godinho, V.D.C. Influence of temperature on the fatty acid composition of the oil from sunflower genotypes grown in tropical regions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Merwe, R.; Labuschagne, M.T.; Herselman, L.; Hugo, A. Stability of seed oil quality traits in high and mid-oleic acid sunflower hybrids. Euphytica 2013, 193, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, Y.O.; Canavar, O.; Yorulmaz, A.; Erekul, O. Influence of nitrogen level and water scarcity during seed filling period on seed yield and fatty acid compositions of corn. Philipp. J. Crop Sci. 2015, 40, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yao, X.M.; Lin, X.Q.; Tang, X.H.; Ma, L.Z. Selection of superior individuals of Sapindus mukorossi for high yield of oil. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2014, 34, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lovato, L.; Pelegrini, B.L.; Rodrigues, J.; de Oliveira, A.J.B.; Ferreira, I.C.P. Seed oil of Sapindus saponaria L. (Sapindaceae) as potential C16 to C22 fatty acids resource. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 60, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestili, S.; Giardini, A.; Ficcadenti, N. Genetic diversity among Italian melon inodorus (Cucumis melo L.) germplasm revealed by ISSR analysis and agronomic traits. Acta Hortic. 2011, 9, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, K.S.; Rana, T.S.; Ranade, S.A.; Meena, B. Genetic variability and population structure in Sapindus emarginatus Vahl from India. Gene 2011, 485, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, L.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhong, C.H.; Huang, H.W. Geographical distribution and morphological diversity of red-fleshed kiwifruit germplasm (Actinidia chinensis Planchon) in China. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2013, 60, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek, M.; Seker, M.; Ipek, A.; Gul, M.K. Identification of molecular markers associated with fruit traits in olive and assessment of olive core collection with AFLP markers and fruit traits. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 2762–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisichelli, N.A.; Frelich, L.E.; Reich, P.B. Climate and interrelated tree regeneration drivers in mixed temperate-boreal forests. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.L.; Pan, F.J.; Yang, S.; Shu, S.Y. Factors controlling accumulation of soil organic carbon along vegetation succession in a typical karst region in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, K.S.; Rana, T.S.; Ranade, S.A. Molecular analyses of genetic variability in soap nut (Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011, 34, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, K.S.; Rana, T.S.; Ranade, S.A.; Pande, V.; Palni, L.M.S. Estimation of genetic variability and population structure in Sapindus trifoliatus L.; using DNA fingerprinting methods. Trees 2013, 27, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).