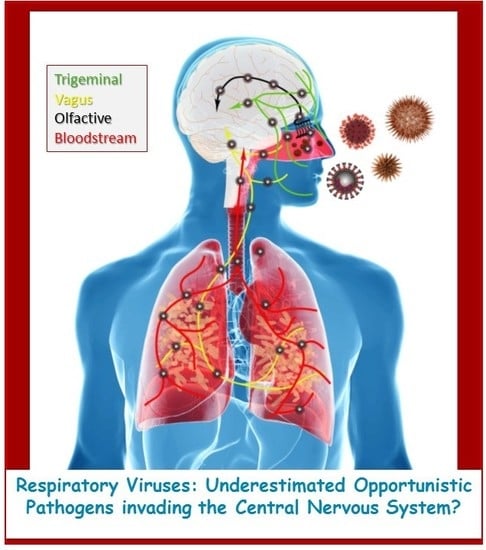
Human Coronaviruses and Other Respiratory Viruses: Underestimated Opportunistic Pathogens of the Central Nervous System?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Viruses as Plausible Etiologic Agents in Neurological Disorders
3. Respiratory Viruses with Neuroinvasive and Neurotropic Properties: Possible Associated Neuropathologies
4. Human Coronaviruses: Eclosions of Recognized Respiratory Pathogens
4.1. Human Coronaviruses: Pathogens Causing Illnesses Outside the Respiratory Tract
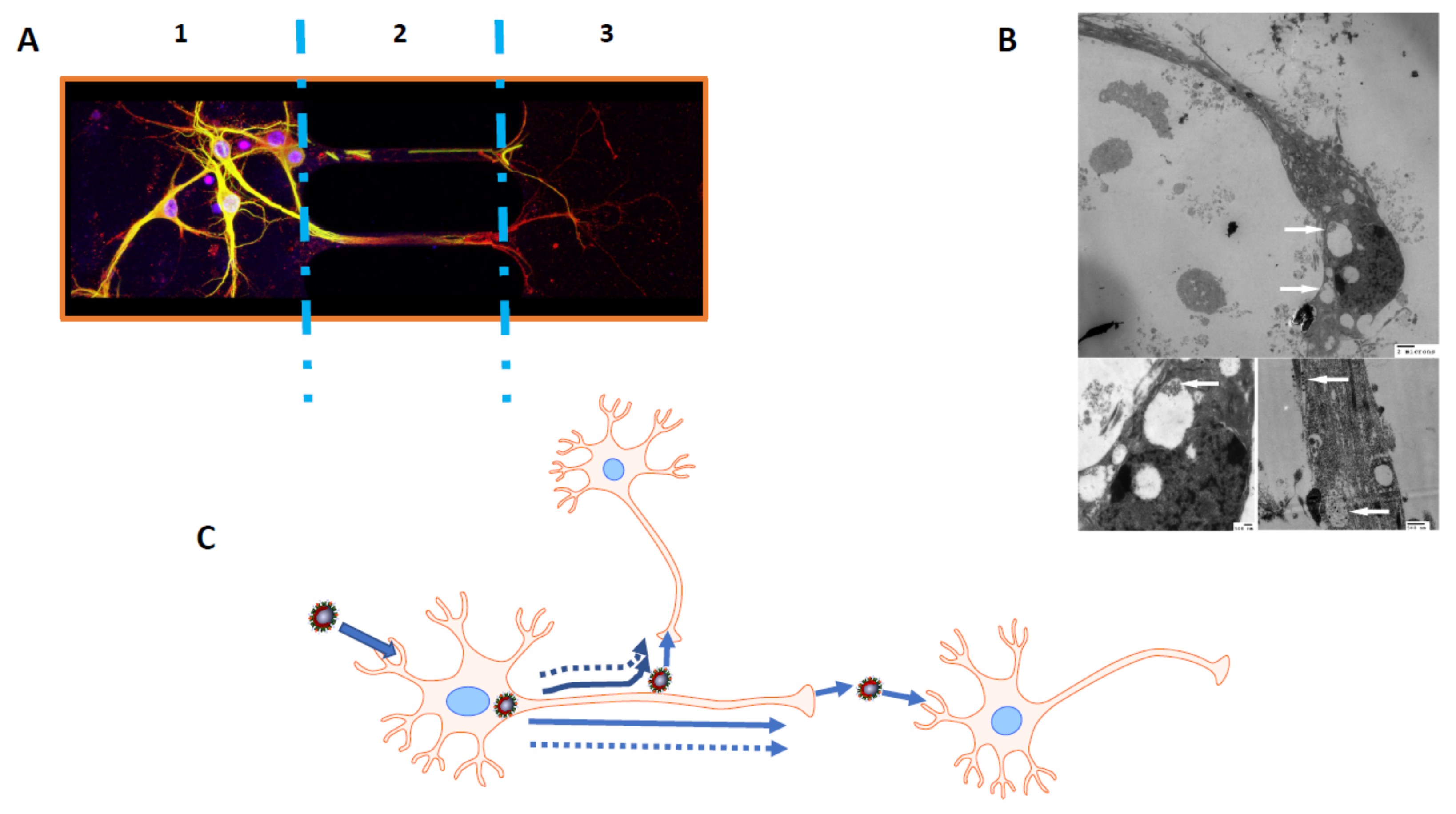
4.1.1. Possible Mechanisms of HCoV Neuroinvasiveness
4.1.2. Human Coronaviruses in the CNS: Possible Associated Neurological Pathologies
Potential Short-Term Neuropathologies
Potential Long-Term Neuropathologies and Sequelae
4.1.3. Mechanisms of HCoV-Induced Neurodegeneration: Possible Associated Neuropathologies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bale, J.F., Jr. Virus and Immune-Mediated Encephalitides: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 53, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mailles, A.; Stahl, J.P.; Bloch, K.C. Update and new insights in encephalitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Big, C.; Reineck, L.A.; Aronoff, D.M. Viral infections of the central nervous system: A case-based review. Clin. Med. Res. 2009, 7, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyler, K.L. Acute Viral Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.E. Emergence and re-emergence of viral diseases of the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, C.C.; Carabin, H.; Montano, S.M.; Bangirana, P.; Zunt, J.R.; Peterson, P.K. Global research priorities for infections that affect the nervous system. Nature 2015, 527, S178–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareille, M.; Kieninger, E.; Edwards, M.R.; Regamey, N. The airway epithelium: Soldier in the fight against respiratory viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohmwald, K.; Galvez, N.M.S.; Rios, M.; Kalergis, A.M. Neurologic Alterations Due to Respiratory Virus Infections. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesario, T.C. Viruses associated with pneumonia in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ison, M.G.; Hayden, F.G. Viral infections in immunocompromised patients: What’s new with respiratory viruses? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 15, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jartti, T.; Jartti, L.; Ruuskanen, O.; Soderlund-Venermo, M. New respiratory viral infections. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloots, T.P.; Whiley, D.M.; Lambert, S.B.; Nissen, M.D. Emerging respiratory agents: New viruses for old diseases? J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouard, J.; Vabret, A.; Nimal-Cuvillon, D.; Bach, N.; Bessiere, A.; Arion, A.; Freymuth, F. Epidemiology of acute upper and lower respiratory tract infections in children. Rev. Prat. 2007, 57, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, J.M.; Butany, J.; Poon, L.L.; Chan, K.H.; Beh, S.L.; Poutanen, S.; Peiris, J.S.; Wong, M. Time course and cellular localization of SARS-CoV nucleoprotein and RNA in lungs from fatal cases of SARS. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, H.K.; Falsey, A.R. The diagnosis of viral respiratory disease in older adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tregoning, J.S.; Schwarze, J. Respiratory viral infections in infants: Causes, clinical symptoms, virology, and immunology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 74–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pochon, C.; Voigt, S. Respiratory Virus Infections in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coverstone, A.M.; Wang, L.; Sumino, K. Beyond Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Rhinovirus in the Pathogenesis and Exacerbation of Asthma: The Role of Metapneumovirus, Bocavirus and Influenza Virus. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North. Am. 2019, 39, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, D.; Guo-Parke, H.; Coyle, P.V.; Fairley, D.; McAuley, D.F.; Taggart, C.C.; Kidney, J. Respiratory viral infection: A potential “missing link” in the pathogenesis of COPD. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, W.G.; Peck Campbell, A.J.; Boeckh, M. Respiratory viruses other than influenza virus: Impact and therapeutic advances. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kustin, T.; Ling, G.; Sharabi, S.; Ram, D.; Friedman, N.; Zuckerman, N.; Bucris, E.D.; Glatman-Freedman, A.; Stern, A.; Mandelboim, M. A method to identify respiratory virus infections in clinical samples using next-generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berry, M.; Gamieldien, J.; Fielding, B.C. Identification of new respiratory viruses in the new millennium. Viruses 2015, 7, 996–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paden, C.R.; Yusof, M.; Al Hammadi, Z.M.; Queen, K.; Tao, Y.; Eltahir, Y.M.; Elsayed, E.A.; Marzoug, B.A.; Bensalah, O.K.A.; Khalafalla, A.I.; et al. Zoonotic origin and transmission of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the UAE. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonesch, N.; Binazzi, A.; Bonafede, M.; Melis, P.; Ruggieri, A.; Iavicoli, S.; Tomao, P. Emerging zoonotic viral infections of occupational health importance. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Muth, D.; Niemeyer, D.; Drosten, C. Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses. Adv. Virus. Res. 2018, 100, 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, A.; Bottu, A.; Qaisar, M.; Mane, M.P.; Acharya, Y. Nipah virus: A narrative review of viral characteristics and epidemiological determinants. Public Health 2019, 173, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkenhagen, L.K.; Salman, M.D.; Ma, M.J.; Gray, G.C. Animal Influenza Virus Infections in Humans: A Commentary. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 88, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, J.; McArthur, J. Emerging infections of the central nervous system. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2013, 15, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza virus-related critical illness: Pathophysiology and epidemiology. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vabret, A.; Dina, J.; Brison, E.; Brouard, J.; Freymuth, F. Human coronaviruses. Pathol. Biol. 2009, 57, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, R.; Chiappe, S.; Porcella, A.; Rosatelli, D.; Fanos, V. Bronchiolitis-associated encephalopathy in critically-ill infants: An underestimated complication? J. Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 23, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desforges, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Brison, E.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Talbot, P.J. Neuroinvasive and neurotropic human respiratory coronaviruses: Potential neurovirulent agents in humans. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 807, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGavern, D.B.; Kang, S.S. Illuminating viral infections in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyuncu, O.O.; Hogue, I.B.; Enquist, L.W. Virus infections in the nervous system. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berth, S.H.; Leopold, P.L.; Morfini, G.N. Virus-induced neuronal dysfunction and degeneration. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 5239–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahm, T.; Rudolph, H.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H.; Tenenbaum, T. Neuroinvasion and Inflammation in Viral Central Nervous System Infections. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8562805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desforges, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Stodola, J.K.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronaviruses: Viral and cellular factors involved in neuroinvasiveness and neuropathogenesis. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerk, C.; Tenenbaum, T.; Kim, K.S.; Schroten, H. The choroid plexus-a multi-role player during infectious diseases of the CNS. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.K.; Corey, S.; Alvarez, X.; Williams, K. Monocyte/macrophage traffic in HIV and SIV encephalitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyris, E.G.; Acheampong, E.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Mukhtar, M.; Zhang, H. The interferon-induced expression of APOBEC3G in human blood-brain barrier exerts a potent intrinsic immunity to block HIV-1 entry to central nervous system. Virology 2007, 367, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atluri, V.S.; Hidalgo, M.; Samikkannu, T.; Kurapati, K.R.; Jayant, R.D.; Sagar, V.; Nair, M.P. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus on blood-brain barrier integrity and function: An update. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Goldstein, H. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection increases the in vivo capacity of peripheral monocytes to cross the blood-brain barrier into the brain and the in vivo sensitivity of the blood-brain barrier to disruption by lipopolysaccharide. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7591–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sellner, J.; Simon, F.; Meyding-Lamade, U.; Leib, S.L. Herpes-simplex virus encephalitis is characterized by an early MMP-9 increase and collagen type IV degradation. Brain Res. 2006, 1125, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spindler, K.R.; Hsu, T.H. Viral disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bentz, G.L.; Jarquin-Pardo, M.; Chan, G.; Smith, M.S.; Sinzger, C.; Yurochko, A.D. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection of endothelial cells promotes naive monocyte extravasation and transfer of productive virus to enhance hematogenous dissemination of HCMV. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11539–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, G.; Nogalski, M.T.; Stevenson, E.V.; Yurochko, A.D. Human cytomegalovirus induction of a unique signalsome during viral entry into monocytes mediates distinct functional changes: A strategy for viral dissemination. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhoades, R.E.; Tabor-Godwin, J.M.; Tsueng, G.; Feuer, R. Enterovirus infections of the central nervous system. Virology 2011, 411, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feuer, R.; Mena, I.; Pagarigan, R.R.; Harkins, S.; Hassett, D.E.; Whitton, J.L. Coxsackievirus B3 and the neonatal CNS: The roles of stem cells, developing neurons, and apoptosis in infection, viral dissemination, and disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.W. Flaviviruses are neurotropic, but how do they invade the CNS? J. Infect. 2014, 69, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, T.; Chretien, F.; Schilte, C.; Disson, O.; Brigitte, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Touret, Y.; Barau, G.; Cayet, N.; Schuffenecker, I.; et al. A mouse model for Chikungunya: Young age and inefficient type-I interferon signaling are risk factors for severe disease. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, H.; Weber, C.E.; Schoeller, J.; Steinmann, U.; Borkowski, J.; Ishikawa, H.; Findeisen, P.; Adams, O.; Doerries, R.; Schwerk, C.; et al. Chemotaxis of T-cells after infection of human choroid plexus papilloma cells with Echovirus 30 in an in vitro model of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Virus Res. 2012, 170, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfhide, C.P.; Flanagan, B.F.; Brearey, S.P.; Hunt, J.A.; Fonceca, A.M.; McNamara, P.S.; Howarth, D.; Edwards, S.; Smyth, R.L. Respiratory syncytial virus binds and undergoes transcription in neutrophils from the blood and airways of infants with severe bronchiolitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohwedder, A.; Keminer, O.; Forster, J.; Schneider, K.; Schneider, E.; Werchau, H. Detection of respiratory syncytial virus RNA in blood of neonates by polymerase chain reaction. J. Med. Virol. 1998, 54, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Pohl, C.; Szecsi, J.; Trajkovic-Bodennec, S.; Devergnas, S.; Raoul, H.; Cosset, F.L.; Gerlier, D.; Wild, T.F.; Horvat, B. Nipah virus uses leukocytes for efficient dissemination within a host. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7863–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escaffre, O.; Borisevich, V.; Rockx, B. Pathogenesis of Hendra and Nipah virus infection in humans. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2013, 7, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Xie, H.; Campbell, A.P.; Kuypers, J.; Leisenring, W.; Boudreault, A.A.; Englund, J.A.; Corey, L.; Boeckh, M. Influenza viral RNA detection in blood as a marker to predict disease severity in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tse, H.; To, K.K.; Wen, X.; Chen, H.; Chan, K.H.; Tsoi, H.W.; Li, I.W.; Yuen, K.Y. Clinical and virological factors associated with viremia in pandemic influenza A/H1N1/2009 virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Yasui, O.; Tsuruoka, H.; Kuroda, K.; Hayashi, K.; Yamada, A.; Ishizaki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Hosaka, Y. Isolation of type B influenza virus from the blood of children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imamura, T.; Suzuki, A.; Lupisan, S.; Kamigaki, T.; Okamoto, M.; Roy, C.N.; Olveda, R.; Oshitani, H. Detection of enterovirus 68 in serum from pediatric patients with pneumonia and their clinical outcomes. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, I. Transolfactory neuroinvasion by viruses threatens the human brain. Acta Virol. 2015, 59, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryche, B.; Fretaud, M.; Saint-Albin Deliot, A.; Galloux, M.; Sedano, L.; Langevin, C.; Descamps, D.; Rameix-Welti, M.A.; Eleouet, J.F.; Le Goffic, R.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus tropism for olfactory sensory neurons in mice. J. Neurochem. 2019, e14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dups, J.; Middleton, D.; Yamada, M.; Monaghan, P.; Long, F.; Robinson, R.; Marsh, G.A.; Wang, L.F. A new model for Hendra virus encephalitis in the mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Kellohen, K.L.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Distribution of insulin in trigeminal nerve and brain after intranasal administration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Thorne, R.G. Intranasal delivery of biologics to the central nervous system. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driessen, A.K.; Farrell, M.J.; Mazzone, S.B.; McGovern, A.E. Multiple neural circuits mediating airway sensations: Recent advances in the neurobiology of the urge-to-cough. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2016, 226, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audrit, K.J.; Delventhal, L.; Aydin, O.; Nassenstein, C. The nervous system of airways and its remodeling in inflammatory lung diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Ishinaka, M.; Takada, A.; Kida, H.; Kimura, T.; Ochiai, K.; Umemura, T. The invasion routes of neurovirulent A/Hong Kong/483/97 (H5N1) influenza virus into the central nervous system after respiratory infection in mice. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Park, C.H.; Sunden, Y.; Kimura, T.; Ochiai, K.; Kida, H.; Umemura, T. The vagus nerve is one route of transneural invasion for intranasally inoculated influenza a virus in mice. Vet. Pathol. 2004, 41, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookstaver, P.B.; Mohorn, P.L.; Shah, A.; Tesh, L.D.; Quidley, A.M.; Kothari, R.; Bland, C.M.; Weissman, S. Management of Viral Central Nervous System Infections: A Primer for Clinicians. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, P.G. Viral encephalitis: Causes, differential diagnosis, and management. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, i10–i15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, P.G. Viral encephalitis. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.K.D.; Sato, D.K. Viral encephalitis: A practical review on diagnostic approach and treatment. J. Pediatr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudon, P.; Bernard, A. Inflammation in neuroviral diseases. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitley, R.J.; Gnann, J.W. Viral encephalitis: Familiar infections and emerging pathogens. Lancet 2002, 359, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskiniemi, M.; Rautonen, J.; Lehtokoski-Lehtiniemi, E.; Vaheri, A. Epidemiology of encephalitis in children: A 20-year survey. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 29, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, D.G.; Rosekrans, J.A. Overview, prevention, and treatment of rabies. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stahl, J.P.; Mailles, A. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis update. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, I.; Benninger, F. Manifestations of Herpes Virus Infections in the Nervous System. Neurol. Clin. 2018, 36, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.G.; Chaudhuri, A. Herpes simplex encephalitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 2002, 73, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurelian, L. HSV-induced apoptosis in herpes encephalitis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 289, 79–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beckham, J.D.; Tyler, K.L. Arbovirus Infections. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2015, 21, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronca, S.E.; Dineley, K.T.; Paessler, S. Neurological Sequelae Resulting from Encephalitic Alphavirus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Zika virus: An emerging flavivirus. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.M.; Martines, R.B.; Zaki, S.R. Zika Virus: Pathology from the Pandemic. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sips, G.J.; Wilschut, J.; Smit, J.M. Neuroinvasive flavivirus infections. Rev. Med. Virol. 2012, 22, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Gubler, D.J.; Petersen, L.R. Emerging flaviviruses: The spread and resurgence of Japanese encephalitis, West Nile and dengue viruses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S98–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Wimmer, E.; Cello, J. Poliovirus and poliomyelitis: A tale of guts, brains, and an accidental event. Virus Res. 2005, 111, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Haughey, N.J.; Nath, A. Cell death in HIV dementia. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, H.S.; Seth, P. Friends Turn Foe-Astrocytes Contribute to Neuronal Damage in NeuroAIDS. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcom, E.F.; Roda, W.C.; Cohen, E.A.; Li, M.Y.; Power, C. HIV-1 persistence in the central nervous system: Viral and host determinants during antiretroviral therapy. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 38, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.; Berger, J. HIV Dementia. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2004, 6, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.; Gallia, G.L.; Del Valle, L.; Amini, S.; Khalili, K. Human polyomavirus JCV and expression of myelin genes. J. Neurovirol. 2000, 6, S92–S97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weissert, R. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 231, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollebo, H.S.; White, M.K.; Gordon, J.; Berger, J.R.; Khalili, K. Persistence and pathogenesis of the neurotropic polyomavirus JC. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.E.; Osame, M.; Kubota, H.; Igata, A.; Nishitani, H.; Maeda, Y.; Khabbaz, R.F.; Janssen, R.S. The risk of development of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis among persons infected with HTLV-I. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 1990, 3, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Schoini, P.; Karampitsakos, T.; Avdikou, M.; Athanasopoulou, A.; Tsoukalas, G.; Tzouvelekis, A. Measles pneumonitis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2019, 87, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albarello, F.; Cristofaro, M.; Busi Rizzi, E.; Giancola, M.L.; Nicastri, E.; Schinina, V. Pulmonary measles disease: Old and new imaging tools. Radiol. Med. 2018, 123, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, L.A.; Rall, G.F. Blue moon neurovirology: The merits of studying rare CNS diseases of viral origin. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Ludlow, M.; Duprex, W.P. Human Paramyxoviruses and Infections of the Central Nervous System. In Neuroviral Infections. RNA Viruses and Retroviruses; Singh, S.K., Ruzek, D., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 341–372. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitch, E.C.; Jacobson, S. Viruses in chronic progressive neurologic disease. Mult. Scler. 2018, 24, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itzhaki, R.F.; Dobson, C.B.; Wozniak, M.A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 299–300, author reply 300-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludlow, M.; Kortekaas, J.; Herden, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Tappe, D.; Trebst, C.; Griffin, D.E.; Brindle, H.E.; Solomon, T.; Brown, A.S.; et al. Neurotropic virus infections as the cause of immediate and delayed neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majde, J.A. Neuroinflammation resulting from covert brain invasion by common viruses-a potential role in local and global neurodegeneration. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 75, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebov, J.F.; Brown, L.M.; MacDonald, P.D.M.; Robertson, K.; Bowman, N.M.; Hooper, S.R.; Becker-Dreps, S. Review: Evidence of Neurological Sequelae in Children With Acquired Zika Virus Infection. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 85, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherhead, J.E.; Miller, V.E.; Garcia, M.N.; Hasbun, R.; Salazar, L.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Murray, K.O. Long-term neurological outcomes in West Nile virus-infected patients: An observational study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 2015, 92, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, P.; Hasbun, R.; Nolan, M.S.; Salazar, L.; Woods, S.P.; Sheikh, K.; Murray, K.O. Long-term neuromuscular outcomes of west nile virus infection: A clinical and electromyographic evaluation of patients with a history of infection. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edridge, A.W.D.; Deijs, M.; van Zeggeren, I.E.; Kinsella, C.M.; Jebbink, M.F.; Bakker, M.; van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.C.; van der Hoek, L. Viral Metagenomics on Cerebrospinal Fluid. Genes 2019, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granerod, J.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.; Davies, N.W.; Walsh, A.L.; Ward, K.N.; Hilton, D.A.; Ambrose, H.E.; Clewley, J.P.; et al. Causality in acute encephalitis: Defining aetiologies. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granerod, J.; Tam, C.C.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Davies, N.W.; Borchert, M.; Thomas, S.L. Challenge of the unknown. A systematic review of acute encephalitis in non-outbreak situations. Neurology 2010, 75, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibler, M.; Brito, F.; Zanella, M.C.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Laubscher, F.; L’Huillier, A.G.; Ambrosioni, J.; Wagner, N.; Posfay-Barbe, K.M.; Docquier, M.; et al. Viral Sequences Detection by High-Throughput Sequencing in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Individuals with and without Central Nervous System Disease. Genes 2019, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, A.M.Q.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adams, M.J.; Dutilh, B.E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Junglen, S.; Knowles, N.J.; et al. Changes to taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2018). Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2601–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stensballe, L.G.; Devasundaram, J.K.; Simoes, E.A. Respiratory syncytial virus epidemics: The ups and downs of a seasonal virus. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, S21–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.H.; Ison, M.G. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults. BMJ 2019, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picone, S.; Mondi, V.; Di Palma, F.; Martini, L.; Paolillo, P. Neonatal Encephalopathy and SIADH during RSV Infection. Am. J. Perinatol. 2019, 36, S106–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohmwald, K.; Espinoza, J.A.; Gonzalez, P.A.; Bueno, S.M.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M. Central nervous system alterations caused by infection with the human respiratory syncytial virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morichi, S.; Kawashima, H.; Ioi, H.; Yamanaka, G.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Hoshika, A.; Nakayama, T.; Watanabe, Y. Classification of acute encephalopathy in respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Infect. Chemother. 2011, 17, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, H.; Ioi, H.; Ushio, M.; Yamanaka, G.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakayama, T. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in children with seizures from respiratory syncytial virus infection. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlateva, K.T.; Van Ranst, M. Detection of subgroup B respiratory syncytial virus in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with respiratory syncytial virus pneumonia. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2004, 23, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millichap, J.J.; Wainwright, M.S. Neurological complications of respiratory syncytial virus infection: Case series and review of literature. J. Child. Neurol. 2009, 24, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.T.; Cox, C.; Atkins, J.; Butler, I.J. Encephalopathy associated with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J. Child. Neurol. 2001, 16, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, K.; Sakazaki, H.; Murakami, S.; Yonezawa, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Seto, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hattori, H.; Matsuoka, O.; Murata, R. Sequential MRI, SPECT and PET in respiratory syncytial virus encephalitis. Pediatr. Radiol. 1999, 29, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.E.; Dinwiddie, R.; Marshall, W.C.; Matthew, D.J. Respiratory syncytial virus infection causing neurological disorder in neonates. Lancet 1981, 1, 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappel, R.; Thiry, L.; Clinet, G. Viral antibodies in the CSF after acute CNS infections. Arch. Neurol. 1975, 32, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, S.J.; Zealley, H. Neurological, electroencephalographic, and virological findings in febrile cheldren. Arch. Dis. Child. 1970, 45, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinoza, J.A.; Bohmwald, K.; Cespedes, P.F.; Gomez, R.S.; Riquelme, S.A.; Cortes, C.M.; Valenzuela, J.A.; Sandoval, R.A.; Pancetti, F.C.; Bueno, S.M.; et al. Impaired learning resulting from respiratory syncytial virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9112–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Hoogen, B.G.; de Jong, J.C.; Groen, J.; Kuiken, T.; de Groot, R.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.M.; Zhu, Y.; Griffin, M.R.; Weinberg, G.A.; Hall, C.B.; Szilagyi, P.G.; Staat, M.A.; Iwane, M.; Prill, M.M.; Williams, J.V.; et al. Burden of human metapneumovirus infection in young children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeannet, N.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Schefold, J.C.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Sommerstein, R. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in an Adult with Human Metapneumovirus-Associated Encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fok, A.; Mateevici, C.; Lin, B.; Chandra, R.V.; Chong, V.H. Encephalitis-Associated Human Metapneumovirus Pneumonia in Adult, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.L.; Wee, T.C. Adult human metapneumovirus encephalitis: A case report highlighting challenges in clinical management and functional outcome. Med. J. Malays. 2017, 72, 372–373. [Google Scholar]
- Schildgen, O.; Glatzel, T.; Geikowski, T.; Scheibner, B.; Matz, B.; Bindl, L.; Born, M.; Viazov, S.; Wilkesmann, A.; Knopfle, G.; et al. Human metapneumovirus RNA in encephalitis patient. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez Fernandez, I.; Rebollo Polo, M.; Munoz-Almagro, C.; Monfort Carretero, L.; Fernandez Urena, S.; Rueda Munoz, A.; Colome Roura, R.; Perez Duenas, B. Human Metapneumovirus in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of a Patient With Acute Encephalitis. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawes, B.E.; Freiberg, A.N. Henipavirus infection of the central nervous system. Pathog Dis 2019, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escaffre, O.; Borisevich, V.; Carmical, J.R.; Prusak, D.; Prescott, J.; Feldmann, H.; Rockx, B. Henipavirus pathogenesis in human respiratory epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ochani, R.K.; Batra, S.; Shaikh, A.; Asad, A. Nipah virus-the rising epidemic: A review. Infez. Med. 2019, 27, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ang, B.S.P.; Lim, T.C.C.; Wang, L. Nipah Virus Infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01875-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, K.T.; Robertson, T.; Ong, B.B.; Chong, J.W.; Yaiw, K.C.; Wang, L.F.; Ansford, A.J.; Tannenberg, A. Human Hendra virus infection causes acute and relapsing encephalitis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2009, 35, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Shieh, W.J.; Kumar, S.; Norain, K.; Abdullah, W.; Guarner, J.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Chua, K.B.; Lam, S.K.; Tan, C.T.; et al. Nipah virus infection: Pathology and pathogenesis of an emerging paramyxoviral zoonosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 2153–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Hossain, J.; Saha, S.K.; Gurley, E.S.; Banu, S.; Hamadani, J.D.; Faiz, M.A.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mohammad, Q.D.; Mollah, A.H.; et al. Long-term neurological and functional outcome in Nipah virus infection. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.Y.; Lim, C.C.; Yeoh, A.; Lee, W.L. Neuropsychiatric sequelae of Nipah virus encephalitis. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.T.; Tan, C.T. Clinical and pathological manifestations of human henipavirus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 359, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munster, V.J.; Prescott, J.B.; Bushmaker, T.; Long, D.; Rosenke, R.; Thomas, T.; Scott, D.; Fischer, E.R.; Feldmann, H.; de Wit, E. Rapid Nipah virus entry into the central nervous system of hamsters via the olfactory route. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Coffin, K.M.; Johnston, S.C.; Babka, A.M.; Bell, T.M.; Long, S.Y.; Honko, A.N.; Kuhn, J.H.; Zeng, X. Nipah virus persists in the brains of nonhuman primate survivors. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.T.; Goh, K.J.; Wong, K.T.; Sarji, S.A.; Chua, K.B.; Chew, N.K.; Murugasu, P.; Loh, Y.L.; Chong, H.T.; Tan, K.S.; et al. Relapsed and late-onset Nipah encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 51, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, T.; Riteau, B.; Fouchier, R.A.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Pathogenesis of influenza virus infections: The good, the bad and the ugly. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, K.; Kumar, B. Emerging Influenza D Virus Threat: What We Know so Far! J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, K.G.; Wood, J.M.; Zambon, M. Influenza. Lancet 2003, 362, 1733–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.P.; Florescu, S.A.; Lupulescu, E.; Zaharia, M.; Tardei, G.; Lazar, M.; Ceausu, E.; Ruta, S.M. Neurologic Complications of Influenza B Virus Infection in Adults, Romania. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Boltz, D.; Sturm-Ramirez, K.; Shepherd, K.R.; Jiao, Y.; Webster, R.; Smeyne, R.J. Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14063–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuiken, T.; Taubenberger, J.K. Pathology of human influenza revisited. Vaccine 2008, 26, D59–D66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sivadon-Tardy, V.; Orlikowski, D.; Porcher, R.; Sharshar, T.; Durand, M.C.; Enouf, V.; Rozenberg, F.; Caudie, C.; Annane, D.; van der Werf, S.; et al. Guillain-Barre syndrome and influenza virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millichap, J.G.; Millichap, J.J. Role of viral infections in the etiology of febrile seizures. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 35, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkale, Y.; Erol, I.; Ozkale, M.; Demir, S.; Alehan, F. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis associated with influenza A H1N1 infection. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 47, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toovey, S. Influenza-associated central nervous system dysfunction: A literature review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2008, 6, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Li, W.; Li, K. Acute encephalopathy and encephalitis caused by influenza virus infection. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Quinet, S.; Huang, W.; Gan, Y.; Han, C.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. Clinical and MRI features of neurological complications after influenza A (H1N1) infection in critically ill children. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinya, K.; Makino, A.; Hatta, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hatta, Y.; Gao, P.; Ozawa, M.; Le, Q.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Subclinical brain injury caused by H5N1 influenza virus infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5202–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.; Wilk, E.; Michaelsen-Preusse, K.; Gerhauser, I.; Baumgartner, W.; Geffers, R.; Schughart, K.; Korte, M. Long-Term Neuroinflammation Induced by Influenza A Virus Infection and the Impact on Hippocampal Neuron Morphology and Function. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3060–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beraki, S.; Aronsson, F.; Karlsson, H.; Ogren, S.O.; Kristensson, K. Influenza A virus infection causes alterations in expression of synaptic regulatory genes combined with changes in cognitive and emotional behaviors in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurgens, H.A.; Amancherla, K.; Johnson, R.W. Influenza infection induces neuroinflammation, alters hippocampal neuron morphology, and impairs cognition in adult mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, A.; Ni, K.; Xiang, Z.; Wen, K.; Tu, W. Influenza virus infection exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis disease by promoting type I T cells infiltration into central nervous system. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonen, M.; Laaksonen, M.; Aalto, V.; Ilonen, J.; Salonen, R.; Eralinna, J.P.; Panelius, M.; Salmi, A. Temporal relationship between environmental influenza A and Epstein-Barr viral infections and high multiple sclerosis relapse occurrence. Mult. Scler. 2011, 17, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, S.; Zvartau, M.; Clarke, H.; Irving, W.; Blumhardt, L.D. Clinical relapses and disease activity on magnetic resonance imaging associated with viral upper respiratory tract infections in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998, 64, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, C.; Vila, J.; Gimferrer, L.; Pinana, M.; Esperalba, J.; Codina, M.G.; Barnes, M.; Martin, M.C.; Fuentes, F.; Rubio, S.; et al. Surveillance of enteroviruses from paediatric patients attended at a tertiary hospital in Catalonia from 2014 to 2017. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 110, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Messacar, K.; Torok, M.R.; Rick, A.M.; Holzberg, J.; Montano, A.; Bagdure, D.; Curtis, D.J.; Oberste, M.S.; Nix, W.A.; et al. Enterovirus D68 in Critically Ill Children: A Comparison With Pandemic H1N1 Influenza. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 17, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J. Innate Immunity Evasion by Enteroviruses: Insights into Virus-Host Interaction. Viruses 2016, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebruegge, M.; Curtis, N. Enterovirus infections in neonates. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009, 14, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazama, K.; Shiihara, T.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Matsushige, T.; Dowa, Y.; Watanabe, M. Rhinovirus-associated acute encephalitis/encephalopathy and cerebellitis. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasina, M.; Domanska, A.; Palm, K.; Butcher, S. Human picornaviruses associated with neurological diseases and their neutralization by antibodies. J. Gen. Virol 2017, 98, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, J.; Knoester, M.; Van Leer-Buter, C.C.; Neuteboom, R.F.; Meiners, L.C.; Niesters, H.G.; Brouwer, O.F. Acute flaccid myelitis and enterovirus D68: Lessons from the past and present. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christy, A.; Messacar, K. Acute Flaccid Myelitis Associated With Enterovirus D68: A Review. J. Child. Neurol. 2019, 34, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F. Enterovirus D68: Acute respiratory illness and the 2014 outbreak. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 33, e19–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons-Salort, M.; Parker, E.P.; Grassly, N.C. The epidemiology of non-polio enteroviruses: Recent advances and outstanding questions. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 28, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brian, D.A.; Baric, R.S. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 287, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Greig, A.S.; Mitchell, D.; Corner, A.H.; Bannister, G.L.; Meads, E.B.; Julian, R.J. A Hemagglutinating Virus Producing Encephalomyelitis in Baby Pigs. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1962, 26, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.E.; Lapointe, J.M.; Koblik, P.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C. Diagnostic features of clinical neurologic feline infectious peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.E.; Rand, C.; Leutenegger, C. Inflammation and changes in cytokine levels in neurological feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2003, 5, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, P.W.; Sims, J.K.; Kniazeff, A.J. Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1973, 24, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, S.J.; Weiss, S.R. Pathogenesis of murine coronavirus in the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowley, T.J.; Weiss, S.R. Murine coronavirus neuropathogenesis: Determinants of virulence. J. Neurovirology 2010, 16, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, M.P.; Lane, T.E. The pathogenesis of murine coronavirus infection of the central nervous system. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 30, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, S.H. Human Coronavirus Infections. In The Coronaviridae; Siddell, S.G., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 389–401. [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell, D.A.; Bynoe, M.L. Cultivation of a Novel Type of Common-Cold Virus in Organ Cultures. Br. Med. J. 1965, 1, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamre, D.; Procknow, J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.; Becker, W.B.; Chanock, R.M. Growth in suckling-mouse brain of “IBV-like” viruses from patients with upper respiratory tract disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 58, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drosten, C.; Gunther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Kuiken, T.; Schutten, M.; van Amerongen, G.; van Doornum, G.J.; van den Hoogen, B.G.; Peiris, M.; Lim, W.; Stohr, K.; Osterhaus, A.D. Aetiology: Koch’s postulates fulfilled for SARS virus. Nature 2003, 423, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Vermeulen-Oost, W.; Berkhout, R.J.; Wolthers, K.C.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; Kaandorp, J.; Spaargaren, J.; Berkhout, B. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Chu, C.M.; Chan, K.H.; Tsoi, H.W.; Huang, Y.; Wong, B.H.; Poon, R.W.; Cai, J.J.; Luk, W.K.; et al. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabeca, T.K.; Granato, C.; Bellei, N. Epidemiological and clinical features of human coronavirus infections among different subsets of patients. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and clinical presentations of the four human coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 detected over 3 years using a novel multiplex real-time PCR method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larson, H.E.; Reed, S.E.; Tyrrell, D.A. Isolation of rhinoviruses and coronaviruses from 38 colds in adults. J. Med. Virol. 1980, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.S.; Chan, K.H.; Chu, K.W.; Kwan, S.W.; Guan, Y.; Poon, L.L.; Peiris, J.S. Human coronavirus NL63 infection and other coronavirus infections in children hospitalized with acute respiratory disease in Hong Kong, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E.; Speicher, D.J.; O’Neil, N.T.; McErlean, P.K.; Greer, R.M.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. Co-circulation of four human coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland children with acute respiratory tract illnesses in 2004. Viruses 2012, 4, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theamboonlers, A.; Samransamruajkit, R.; Thongme, C.; Amonsin, A.; Chongsrisawat, V.; Poovorawan, Y. Human coronavirus infection among children with acute lower respiratory tract infection in Thailand. Intervirology 2007, 50, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oong, X.Y.; Ng, K.T.; Takebe, Y.; Ng, L.J.; Chan, K.G.; Chook, J.B.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Tee, K.K. Identification and evolutionary dynamics of two novel human coronavirus OC43 genotypes associated with acute respiratory infections: Phylogenetic, spatiotemporal and transmission network analyses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Paranhos-Baccala, G.; Ren, L.; Wang, J. Genotype shift in human coronavirus OC43 and emergence of a novel genotype by natural recombination. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez, S.R.; Sims, G.E.; Wentworth, D.E.; Halpin, R.A.; Robinson, C.C.; Town, C.D.; Holmes, K.V. Genomic analysis of 16 Colorado human NL63 coronaviruses identifies a new genotype, high sequence diversity in the N-terminal domain of the spike gene and evidence of recombination. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2387–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerna, G.; Campanini, G.; Rovida, F.; Percivalle, E.; Sarasini, A.; Marchi, A.; Baldanti, F. Genetic variability of human coronavirus OC43-, 229E-, and NL63-like strains and their association with lower respiratory tract infections of hospitalized infants and immunocompromised patients. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Lee, P.; Tsang, A.K.; Yip, C.C.; Tse, H.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.Y.; Lau, Y.L.; Chan, K.H.; Woo, P.C.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of human coronavirus OC43 reveals evolution of different genotypes over time and recent emergence of a novel genotype due to natural recombination. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11325–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vabret, A.; Dina, J.; Mourez, T.; Gouarin, S.; Petitjean, J.; van der Werf, S.; Freymuth, F. Inter- and intra-variant genetic heterogeneity of human coronavirus OC43 strains in France. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3349–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijgen, L.; Lemey, P.; Keyaerts, E.; Van Ranst, M. Genetic variability of human respiratory coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3223–3224, author reply 3224–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Yip, C.C.; Huang, Y.; Tsoi, H.W.; Chan, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Comparative analysis of 22 coronavirus HKU1 genomes reveals a novel genotype and evidence of natural recombination in coronavirus HKU1. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7136–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, P.J.; Jacomy, H.; Desforges, M. Pathogenesis of Human Coronaviruses other than Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. In Nidoviruses; Perlman, S., Gallagher, T., Snijder, E.J., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, S.B. Update on Human Rhinovirus and Coronavirus Infections. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Storch, G.A. Characterization of human coronavirus OC43 and human coronavirus NL63 infections among hospitalized children <5 years of age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 814–820. [Google Scholar]
- Self, W.H.; Williams, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Ampofo, K.; Pavia, A.T.; Chappell, J.D.; Hymas, W.C.; Stockmann, C.; Bramley, A.M.; Schneider, E.; et al. Respiratory Viral Detection in Children and Adults: Comparing Asymptomatic Controls and Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogimi, C.; Englund, J.A.; Bradford, M.C.; Qin, X.; Boeckh, M.; Waghmare, A. Characteristics and Outcomes of Coronavirus Infection in Children: The Role of Viral Factors and an Immunocompromised State. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2019, 8, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogimi, C.; Greninger, A.L.; Waghmare, A.A.; Kuypers, J.M.; Shean, R.C.; Xie, H.; Leisenring, W.M.; Stevens-Ayers, T.L.; Jerome, K.R.; Englund, J.A.; et al. Prolonged Shedding of Human Coronavirus in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients: Risk Factors and Viral Genome Evolution. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogimi, C.; Waghmare, A.A.; Kuypers, J.M.; Xie, H.; Yeung, C.C.; Leisenring, W.M.; Seo, S.; Choi, S.M.; Jerome, K.R.; Englund, J.A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Human Coronavirus in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples From Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients and Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Cheung, C.L.; Luo, S.W.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Guan, Y.J.; et al. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braden, C.R.; Dowell, S.F.; Jernigan, D.B.; Hughes, J.M. Progress in global surveillance and response capacity 10 years after severe acute respiratory syndrome. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.D. The chronology of the 2002-2003 SARS mini pandemic. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2004, 5, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, J.D.; Krogstad, P. SARS: The first pandemic of the 21st century. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Brand, J.M.; Haagmans, B.L.; van Riel, D.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Kuiken, T. The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Experimental Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome and Influenza in Animal Models. J. Comp. Pathol. 2014, 151, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Gong, E.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; Xie, Z.; et al. Multiple organ infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.S.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A.; Haagmans, B.L. MERS: Emergence of a novel human coronavirus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 5, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, C.M.; Frieman, M.B. Emergence of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Groot, R.J.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; Brown, C.S.; Drosten, C.; Enjuanes, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; Galiano, M.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Memish, Z.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV); Announcement of the Coronavirus Study Group. J. Virol. 2013, 5, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotten, M.; Watson, S.J.; Kellam, P.; Al-Rabeeah, A.A.; Makhdoom, H.Q.; Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Alhakeem, R.F.; Madani, H.; AlRabiah, F.A.; et al. Transmission and evolution of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Saudi Arabia: A descriptive genomic study. Lancet 2013, 382, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotten, M.; Watson, S.J.; Zumla, A.I.; Makhdoom, H.Q.; Palser, A.L.; Ong, S.H.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; Alhakeem, R.F.; Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; et al. Spread, circulation, and evolution of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. mBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memish, Z.A.; Cotten, M.; Watson, S.J.; Kellam, P.; Zumla, A.; Alhakeem, R.F.; Assiri, A.; Rabeeah, A.A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A. Community case clusters of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Hafr Al-Batin, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: A descriptive genomic study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 23, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Assiri, A.; Memish, Z.A. Middle East respiratory syndrome novel corona MERS-CoV infection. Epidemiology and outcome update. Saudi. Med. J. 2013, 34, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Al-Rabeeah, A.A.; Al-Rabiah, F.A.; Al-Hajjar, S.; Al-Barrak, A.; Flemban, H.; Al-Nassir, W.N.; Balkhy, H.H.; Al-Hakeem, R.F.; et al. Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assiri, A.; McGeer, A.; Perl, T.M.; Price, C.S.; Al Rabeeah, A.A.; Cummings, D.A.; Alabdullatif, Z.N.; Assad, M.; Almulhim, A.; Makhdoom, H.; et al. Hospital outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haagmans, B.L.; Osterhaus, A.D. Neutralizing the MERS coronavirus threat. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 235fs19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kang, J.M.; Ha, Y.E.; Park, G.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kang, C.I.; Jo, I.J.; et al. MERS-CoV outbreak following a single patient exposure in an emergency room in South Korea: An epidemiological outbreak study. Lancet 2016, 388, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Ryu, Y.W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Yi, S.J. Epidemiological investigation of MERS-CoV spread in a single hospital in South Korea, May to June 2015. Euro Surveill 2015, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemida, M.G. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus and the One Health concept. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Omari, A.; Rabaan, A.A.; Salih, S.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Memish, Z.A. MERS coronavirus outbreak: Implications for emerging viral infections. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E. An Opportunistic Pathogen Afforded Ample Opportunities: Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Viruses 2017, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hui, D.S.; Memish, Z.A.; Zumla, A. Severe acute respiratory syndrome vs. the Middle East respiratory syndrome. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2014, 20, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peiris, J.S.; Guan, Y.; Yuen, K.Y. Severe acute respiratory syndrome. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S88–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jevsnik, M.; Steyer, A.; Pokorn, M.; Mrvic, T.; Grosek, S.; Strle, F.; Lusa, L.; Petrovec, M. The Role of Human Coronaviruses in Children Hospitalized for Acute Bronchiolitis, Acute Gastroenteritis, and Febrile Seizures: A 2-Year Prospective Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riski, H.; Hovi, T. Coronavirus infections of man associated with diseases other than the common cold. J. Med. Virol. 1980, 6, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerna, G.; Passarani, N.; Battaglia, M.; Rondanelli, E.G. Human enteric coronaviruses: Antigenic relatedness to human coronavirus OC43 and possible etiologic role in viral gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resta, S.; Luby, J.P.; Rosenfeld, C.R.; Siegel, J.D. Isolation and propagation of a human enteric coronavirus. Science 1985, 229, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esper, F.; Ou, Z.; Huang, Y.T. Human coronaviruses are uncommon in patients with gastrointestinal illness. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risku, M.; Lappalainen, S.; Rasanen, S.; Vesikari, T. Detection of human coronaviruses in children with acute gastroenteritis. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfopoulou, S.; Brown, J.R.; Davies, E.G.; Anderson, G.; Virasami, A.; Qasim, W.; Chong, W.K.; Hubank, M.; Plagnol, V.; Desforges, M.; et al. Human Coronavirus OC43 Associated with Fatal Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbour, N.; Day, R.; Newcombe, J.; Talbot, P.J. Neuroinvasion by human respiratory coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8913–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristallo, A.; Gambaro, F.; Biamonti, G.; Ferrante, P.; Battaglia, M.; Cereda, P.M. Human coronavirus polyadenylated RNA sequences in cerebrospinal fluid from multiple sclerosis patients. New Microbiol. 1997, 20, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fazzini, E.; Fleming, J.; Fahn, S. Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to coronavirus in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 1992, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.N.; Mounir, S.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus gene expression in the brains of multiple sclerosis patients. Virology 1992, 191, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.A.; Collins, A.; Cohen, M.E.; Duffner, P.K.; Faden, H. Detection of coronavirus in the central nervous system of a child with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Pediatrics 2004, 113, e73–e76. [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers, M.A.; McKean, M.; Rutman, A.; Myint, B.S.; Silverman, M.; O’Callaghan, C. The effects of coronavirus on human nasal ciliated respiratory epithelium. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Koekkoek, S.M.; Deijs, M.; Jonsdottir, H.R.; Molenkamp, R.; Ieven, M.; Goossens, H.; Thiel, V.; van der Hoek, L. Isolation and characterization of current human coronavirus strains in primary human epithelial cell cultures reveal differences in target cell tropism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6081–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desforges, M.; Miletti, T.C.; Gagnon, M.; Talbot, P.J. Activation of human monocytes after infection by human coronavirus 229E. Virus Res. 2007, 130, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R. In vitro detection of apoptosis in monocytes/macrophages infected with human coronavirus. Clin. Diagn Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesel-Lemoine, M.; Millet, J.; Vidalain, P.O.; Law, H.; Vabret, A.; Lorin, V.; Escriou, N.; Albert, M.L.; Nal, B.; Tangy, F. A human coronavirus responsible for the common cold massively kills dendritic cells but not monocytes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wentworth, D.E.; Tresnan, D.B.; Turner, B.C.; Lerman, I.R.; Bullis, B.; Hemmila, E.M.; Levis, R.; Shapiro, L.H.; Holmes, K.V. Cells of human aminopeptidase N (CD13) transgenic mice are infected by human coronavirus-229E in vitro, but not in vivo. Virology 2005, 335, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, M.; Weber, F. Inhibition of cytokine gene expression and induction of chemokine genes in non-lymphatic cells infected with SARS coronavirus. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reuter, J.D.; Gomez, D.L.; Wilson, J.H.; Van Den Pol, A.N. Systemic immune deficiency necessary for cytomegalovirus invasion of the mature brain. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1473–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lassnig, C.; Sanchez, C.M.; Egerbacher, M.; Walter, I.; Majer, S.; Kolbe, T.; Pallares, P.; Enjuanes, L.; Muller, M. Development of a transgenic mouse model susceptible to human coronavirus 229E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8275–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, I.; Nishiyama, Y.; Yokochi, T.; Kimura, Y. Olfactory transmission of neurotropic viruses. J. Neurovirology 2005, 11, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, D.M.; Ghosh, S.; Klein, R.S. The Olfactory Bulb: An Immunosensory Effector Organ during Neurotropic Viral Infections. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacomy, H.; Talbot, P.J. Vacuolating encephalitis in mice infected by human coronavirus OC43. Virology 2003, 315, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCray, P.B., Jr.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, N.; Pewe, L.; Trandem, K.; Perlman, S. Murine encephalitis caused by HCoV-OC43, a human coronavirus with broad species specificity, is partly immune-mediated. Virology 2006, 347, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- St-Jean, J.R.; Jacomy, H.; Desforges, M.; Vabret, A.; Freymuth, F.; Talbot, P.J. Human respiratory coronavirus OC43: Genetic stability and neuroinvasion. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8824–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Netland, J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Moore, S.; Cassell, M.; Perlman, S. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection causes neuronal death in the absence of encephalitis in mice transgenic for human ACE2. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7264–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Coupanec, A.; Desforges, M.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Dube, M.; Day, R.; Seidah, N.G.; Talbot, P.J. Cleavage of a Neuroinvasive Human Respiratory Virus Spike Glycoprotein by Proprotein Convertases Modulates Neurovirulence and Virus Spread within the Central Nervous System. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacomy, H.; St-Jean, J.R.; Brison, E.; Marceau, G.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Mutations in the spike glycoprotein of human coronavirus OC43 modulate disease in BALB/c mice from encephalitis to flaccid paralysis and demyelination. J. Neurovirology 2010, 16, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brison, E.; Jacomy, H.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Glutamate excitotoxicity is involved in the induction of paralysis in mice after infection by a human coronavirus with a single point mutation in its spike protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12464–12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dube, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Wong, A.H.M.; Rini, J.M.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Axonal Transport Enables Neuron-to-Neuron Propagation of Human Coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Deng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, N.; et al. Detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the brain: Potential role of the chemokine mig in pathogenesis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgay, C.; Emine, T.; Ozlem, K.; Muhammet, S.P.; Haydar, A.T. A rare cause of acute flaccid paralysis: Human coronaviruses. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2015, 10, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, K.K.; Yu, W.C.; Chu, C.M.; Lau, S.T.; Sheng, B.; Yuen, K.Y. Possible central nervous system infection by SARS coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Tengsupakul, S.; Sanchez, O.; Phaltas, R.; Maertens, P. Guillain-Barre syndrome with unilateral peripheral facial and bulbar palsy in a child: A case report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Principi, N.; Bosis, S.; Esposito, S. Effects of coronavirus infections in children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.K.; Hsieh, S.T.; Chang, Y.C. Neurological manifestations in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Acta Neurol. Taiwan 2005, 14, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Algahtani, H.; Subahi, A.; Shirah, B. Neurological Complications of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: A Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Neurol. Med. 2016, 2016, 3502683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Harthi, A.; Hussein, J.; Bouchama, A.; Johani, S.; Hajeer, A.H.; Saeed, B.T.; Wahbi, A.; Saedy, A.; AlDabbagh, T.; et al. Severe neurologic syndrome associated with Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus (MERS-CoV). Infection 2015, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Tandi, T.E.; Choi, J.W.; Moon, J.M.; Kim, M.S. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) outbreak in South Korea, 2015: Epidemiology, characteristics and public health implications. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 95, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, R.; Wen, B.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X.; et al. Coronavirus Infections in the Central Nervous System and Respiratory Tract Show Distinct Features in Hospitalized Children. Intervirology 2016, 59, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.S.; Brown, B.; Brian, D.; Cabirac, G.F. Detection of coronavirus RNA and antigen in multiple sclerosis brain. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 31, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, W.A.; Bamford, C.R.; Clark, K. Clinical viral infections and multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1985, 1, 1313–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Lussenburg, C.M.; Zheng, Q. Coronavirus and multiple sclerosis: Results of a case/control longitudinal serological study. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1987, 218, 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, S.S. SARS, avian flu, bioterror: Infection control awareness for the optometrist. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2007, 90, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severance, E.G.; Dickerson, F.B.; Viscidi, R.P.; Bossis, I.; Stallings, C.R.; Origoni, A.E.; Sullens, A.; Yolken, R.H. Coronavirus immunoreactivity in individuals with a recent onset of psychotic symptoms. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, A.; Quach, C.; Yung, A.; Semret, M. Severity and outcome associated with human coronavirus OC43 infections among children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, H.; Fragoso, G.; Almazan, G.; Mushynski, W.E.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus OC43 infection induces chronic encephalitis leading to disabilities in BALB/C mice. Virology 2006, 349, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Carmo, S.; Jacomy, H.; Talbot, P.J.; Rassart, E. Neuroprotective effect of apolipoprotein D against human coronavirus OC43-induced encephalitis in mice. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10330–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brison, E.; Jacomy, H.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Novel treatment with neuroprotective and antiviral properties against a neuroinvasive human respiratory virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1548–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Heo, J.H.; Kim, H.O.; Song, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Park, T.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Choi, J.P. Neurological Complications during Treatment of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. J. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 13, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomishima, M.J.; Enquist, L.W. In vivo egress of an alphaherpesvirus from axons. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8310–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Yang, Y.; Ye, F.; Liu, G.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J.; Tan, W. Safe and Sensitive Antiviral Screening Platform Based on Recombinant Human Coronavirus OC43 Expressing the Luciferase Reporter Gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5492–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Niu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Zhu, N.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, F.; Cen, S.; et al. High-Throughput Screening and Identification of Potent Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, J.; Shen, L.; Huang, B.; Ye, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tan, W. Non-invasive bioluminescence imaging of HCoV-OC43 infection and therapy in the central nervous system of live mice. Antivir. Res. 2020, 173, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, M.; Desjardins, J.; Zhang, C.; Talbot, P.J. The acetyl-esterase activity of the hemagglutinin-esterase protein of human coronavirus OC43 strongly enhances the production of infectious virus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stodola, J.K.; Dubois, G.; Le Coupanec, A.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. The OC43 human coronavirus envelope protein is critical for infectious virus production and propagation in neuronal cells and is a determinant of neurovirulence and CNS pathology. Virology 2018, 515, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbour, N.; Cote, G.; Lachance, C.; Tardieu, M.; Cashman, N.R.; Talbot, P.J. Acute and persistent infection of human neural cell lines by human coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3338–3350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arbour, N.; Ekande, S.; Cote, G.; Lachance, C.; Chagnon, F.; Tardieu, M.; Cashman, N.R.; Talbot, P.J. Persistent infection of human oligodendrocytic and neuroglial cell lines by human coronavirus 229E. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasek, M.J.; Garber, C.; Dorsey, D.; Durrant, D.M.; Bollman, B.; Soung, A.; Yu, J.; Perez-Torres, C.; Frouin, A.; Wilton, D.K.; et al. A complement-microglial axis drives synapse loss during virus-induced memory impairment. Nature 2016, 534, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agner, S.C.; Klein, R.S. Viruses have multiple paths to central nervous system pathology. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Epidemiologic evidence for multiple sclerosis as an infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 382–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusick, M.F.; Libbey, J.E.; Fujinami, R.S. Multiple sclerosis: Autoimmunity and viruses. Curr. Opin. Rheumato 2013, 25, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilden, D.H. Infectious causes of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakalacheva, K.; Munz, C.; Lunemann, J.D. Viral triggers of multiple sclerosis. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2011, 1812, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saberi, A.; Akhondzadeh, S.; Kazemi, S. Infectious agents and different course of multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 118, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smatti, M.K.; Cyprian, F.S.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al Thani, A.A.; Almishal, R.O.; Yassine, H.M. Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses 2019, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desforges, M.; Favreau, D.J.; Brison, E.; Desjardins, J.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Jacomy, H.; Talbot, P.J. Human Coronaviruses. Respiratory Pathogens Revisited as Infectious Neuroinvasive, Neurtropic, and Neurovirulent Agents. In Neuroviral Infections. RNA Viruses and Retroviruses; Singh, S.K., Ruzek, D., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 93–121. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, A.; Desforges, M.; Duquette, P.; Talbot, P.J. Long-term human coronavirus-myelin cross-reactive T-cell clones derived from multiple sclerosis patients. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 123, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, P.J.; Paquette, J.S.; Ciurli, C.; Antel, J.P.; Ouellet, F. Myelin basic protein and human coronavirus 229E cross-reactive T cells in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Puentes, F.; Baker, D.; van der Valk, P. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2010, 129, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, J.; Rothstein, J.D.; Kerr, D.A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates glutamate transport in the CNS and is a critical determinant of outcome from viral encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2009, 1263, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Favreau, D.J.; Desforges, M.; St-Jean, J.R.; Talbot, P.J. A human coronavirus OC43 variant harboring persistence-associated mutations in the S glycoprotein differentially induces the unfolded protein response in human neurons as compared to wild-type virus. Virology 2009, 395, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favreau, D.J.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus-induced neuronal programmed cell death is cyclophilin d dependent and potentially caspase dispensable. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meessen-Pinard, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Pivotal Role of Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 and Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like in Neuronal Cell Death Induced by the Human Neuroinvasive Coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Abrams, J.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Fulda, S.; et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.L.; Sola, I.; Becares, M.; Alberca, B.; Plana, J.; Enjuanes, L.; Zuniga, S. Coronavirus gene 7 counteracts host defenses and modulates virus virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Birdwell, L.D.; Wu, A.; Elliott, R.; Rose, K.M.; Phillips, J.M.; Li, Y.; Grinspan, J.; Silverman, R.H.; Weiss, S.R. Cell-type-specific activation of the oligoadenylate synthetase-RNase L pathway by a murine coronavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 8408–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Jha, B.K.; Wu, A.; Elliott, R.; Ziebuhr, J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Silverman, R.H.; Weiss, S.R. Antagonism of the interferon-induced OAS-RNase L pathway by murine coronavirus ns2 protein is required for virus replication and liver pathology. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Rose, K.M.; Elliott, R.; Van Rooijen, N.; Weiss, S.R. Cell-type-specific type I interferon antagonism influences organ tropism of murine coronavirus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10058–10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talbot, P.J.; Desforges, M.; Brison, E.; Jacomy, H. Coronaviruses as Encephalitis-inducing infectious agents. In Non-Flavirus Encephalitis; Tkachev, S., Ed.; In-Tech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.R.; Sample, H.A.; Zorn, K.C.; Arevalo, S.; Yu, G.; Neuhaus, J.; Federman, S.; Stryke, D.; Briggs, B.; Langelier, C.; et al. Clinical Metagenomic Sequencing for Diagnosis of Meningitis and Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2327–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.D.C.; Blawid, R.; Silva, J.M.F.; Nagata, T. Human virome in nasopharynx and tracheal secretion samples. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2019, 114, e190198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R. The Aetiology of Tuberculosis (Translation of Die Aetiologie der Tuberculose (1882); Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Fredericks, D.N.; Relman, D.A. Sequence-based identification of microbial pathogens: A reconsideration of Koch’s postulates. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. The Environment and Disease: Association or Causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovannoni, G.; Cutter, G.R.; Lunemann, J.; Martin, R.; Munz, C.; Sriram, S.; Steiner, I.; Hammerschlag, M.R.; Gaydos, C.A. Infectious causes of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desforges, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Dubeau, P.; Bourgouin, A.; Lajoie, L.; Dubé, M.; Talbot, P.J. Human Coronaviruses and Other Respiratory Viruses: Underestimated Opportunistic Pathogens of the Central Nervous System? Viruses 2020, 12, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010014
Desforges M, Le Coupanec A, Dubeau P, Bourgouin A, Lajoie L, Dubé M, Talbot PJ. Human Coronaviruses and Other Respiratory Viruses: Underestimated Opportunistic Pathogens of the Central Nervous System? Viruses. 2020; 12(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesforges, Marc, Alain Le Coupanec, Philippe Dubeau, Andréanne Bourgouin, Louise Lajoie, Mathieu Dubé, and Pierre J. Talbot. 2020. "Human Coronaviruses and Other Respiratory Viruses: Underestimated Opportunistic Pathogens of the Central Nervous System?" Viruses 12, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010014
APA StyleDesforges, M., Le Coupanec, A., Dubeau, P., Bourgouin, A., Lajoie, L., Dubé, M., & Talbot, P. J. (2020). Human Coronaviruses and Other Respiratory Viruses: Underestimated Opportunistic Pathogens of the Central Nervous System? Viruses, 12(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12010014