Live Cell Microscopy of Murine Polyomavirus Subnuclear Replication Centers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. Stable Cell Line Generation
2.3. Plasmids
2.4. Viruses and Infections
2.5. Microscopy
2.5.1. Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy
2.5.2. High-Throughput Widefield Microscopy
2.5.3. Spinning Disc Confocal Microscopy
2.6. Immunofluorescence Antibodies
2.7. Image Processing
2.8. Image Analysis
2.8.1. Line Scan Analysis
2.8.2. Infectibility Assay
2.8.3. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Live Cell Microscopy
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. GFP-RPA32 Relocalizes to Cellular DNA Damage Foci
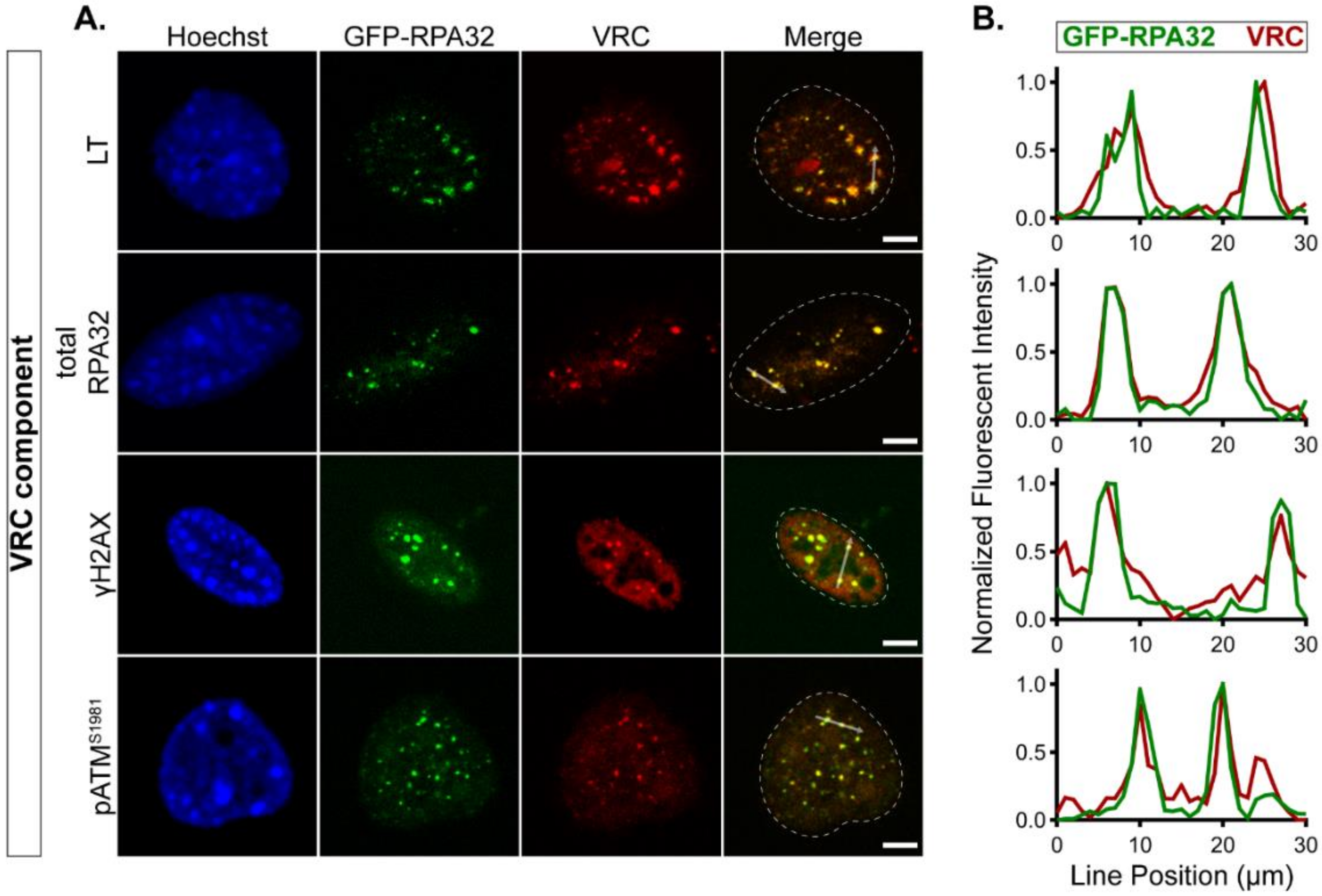
3.2. GFP-RPA32 Localizes to VRCs in MuPyV-Infected Cells
3.3. GFP-RPA32 Relocalizes to VRCs Over Time in MuPyV-Infected Cells
3.4. Kinetics of VRC Formation Depend on Multiplicity of Infection
3.5. Small T-Antigen Is Required for VRC Expansion
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández de Castro, I.; Tenorio, R.; Risco, C. Virus Factories. In Reference Module in Life Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128096338. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.; Speiseder, T.; Dobner, T.; Gonzalez, R.A. DNA Virus Replication Compartments. J. Virol. 2013, 88, 1404–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weitzman, M.D.; Fradet-Turcotte, A. Virus DNA Replication and the Host DNA Damage Response. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charman, M.; Weitzman, M.D. Replication Compartments of DNA Viruses in the Nucleus: Location, Location, Location. Viruses 2020, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erickson, K.D.; Bouchet-Marquis, C.; Heiser, K.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E.; Mishra, R.; Lamothe, B.; Hoenger, A.; Garcea, R.L. Virion Assembly Factories in the Nucleus of Polyomavirus-Infected Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiser, K.; Nicholas, C.; Garcea, R.L. Activation of DNA damage repair pathways by murine polyomavirus. Virology 2016, 497, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, D.K.; Garcea, R.L. Murine polyomavirus DNA transitions through spatially distinct nuclear replication subdomains during infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlie, B.B.; Krauss, M.R.; Buckler-White, A.J.; Benbow, R.M.; Pigiet, V. Polyoma virus minichromosomes: A soluble in vitro replication system. J. Virol. 1981, 38, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krauss, M.R.; Benbow, R.M. Polyoma virus minichromosomes: Associated DNA molecules. J. Virol. 1981, 38, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, P.; Robles, M.T.S.; Pipas, J.M. Large T Antigens of Polyomaviruses: Amazing Molecular Machines. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.Y.; Ichaso, N.; Adamarek, A.; Zila, V.; Forstová, J.; Dibb, N.J.; Dilworth, S.M. Polyomavirus Middle T-Antigen Is a Transmembrane Protein That Binds Signaling Proteins in Discrete Subcellular Membrane Sites. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3046–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrabi, S.; Hwang, J.H.; Choe, J.K.; Roberts, T.M.; Schaffhausen, B.S. Comparisons between Murine Polyomavirus and Simian Virus 40 Show Significant Differences in Small T Antigen Function. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10649–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borowiec, J.A.; Dean, F.B.; Bullock, P.A.; Hurwitz, J. Binding and unwinding—How T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell 1990, 60, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, E.; Zhao, K. SV40 DNA replication: From the A gene to a nanomachine. Virology 2009, 384, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Courtneidge, S.A.; Smith, A.E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature 1983, 303, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluck, M.; Schaffhausen, B.S. Lessons in Signaling and Tumorigenesis from Polyomavirus Middle T Antigen. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 542–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallas, D.C.; Shahrik, L.K.; Martin, B.L.; Jaspers, S.; Miller, T.B.; Brautigan, D.L.; Roberts, T.M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell 1990, 60, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Hahn, W.C. Involvement of PP2A in viral and cellular transformation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7746–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrabi, S.; Gjoerup, O.V.; Kean, J.A.; Roberts, T.M.; Schaffhausen, B.S. Protein phosphatase 2A regulates life and death decisions via Akt in a context-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19011–19016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, T.L. Host Range Mutants of Polyoma Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcea, R.L.; Talmage, D.A.; Harmatz, A.; Freund, R.; Benjamin, T.L. Separation of host range from transformation functions of the hr-t gene of polyomavirus. Virology 1989, 168, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J.; Carmichael, G.G.; Benjamin, T.L. A polyoma mutant that encodes small T antigen but not middle T antigen demonstrates uncoupling of cell surface and cytoskeletal changes associated with cell transformation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1984, 4, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahl, J.; You, J.; Benjamin, T.L. Induction and Utilization of an ATM Signaling Pathway by Polyomavirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13007–13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pancholi, N.J.; Price, A.M.; Weitzman, M.D. Take your PIKK: Tumour viruses and DNA damage response pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sowd, G.A.; Li, N.Y.; Fanning, E. ATM and ATR Activities Maintain Replication Fork Integrity during SV40 Chromatin Replication. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowd, G.A.; Fanning, E. A Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing: SV40 Co-opts Host Genome Maintenance Proteins to Replicate Viral DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, A.; Zou, L. RPA-coated single-stranded DNA as a platform for post-translational modifications in the DNA damage response. Cell Res. 2014, 25, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanning, E.; Klimovich, V.; Nager, A.R. A dynamic model for replication protein A (RPA) function in DNA processing pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4126–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, P.; de Jesus, R.; Gjoerup, O.; Schaffhausen, B.S. Viral Interference with DNA Repair by Targeting of the Single-Stranded DNA Binding Protein RPA. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornreiter, I.; Erdile, L.; Gilbert, I.; von Winkler, D.; Kelly, T.; Fanning, E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshart, K.; Taneja, P.; Fanning, E. The Replication Protein A Binding Site in Simian Virus 40 (SV40) T Antigen and Its Role in the Initial Steps of SV40 DNA Replication. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9771–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arunkumar, A.I.; Klimovich, V.; Jiang, X.; Ott, R.D.; Mizoue, L.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into hRPA32 C-terminal domain–mediated assembly of the simian virus 40 replisome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feunteun, J.; Sompayrac, L.; Fluck, M.; Benjamin, T. Localization of gene functions in polyoma virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 4169–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, G.G.; Benjamin, T.L. Identification of DNA sequence changes leading to loss of transforming ability in polyoma virus. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Garcea, R.L.; Benjamin, T.L. Host range transforming gene of polyoma virus plays a role in virus assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3613–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephan, H.; Concannon, C.; Kremmer, E.; Carty, M.P.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Ionizing radiation-dependent and independent phosphorylation of the 32-kDa subunit of replication protein A during mitosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 6028–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montross, L.; Watkins, S.; Moreland, R.B.; Mamon, H.; Caspar, D.L.; Garcea, R.L. Nuclear assembly of polyomavirus capsids in insect cells expressing the major capsid protein VP1. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4991–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vassin, V.M.; Wold, M.S.; Borowiec, J.A. Replication Protein A (RPA) Phosphorylation Prevents RPA Association with Replication Centers. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1930–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bancaud, A.; Huet, S.; Daigle, N.; Mozziconacci, J.; Beaudouin, J.; Ellenberg, J. Molecular crowding affects diffusion and binding of nuclear proteins in heterochromatin and reveals the fractal organization of chromatin. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3785–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.-P. UV-induced DNA damage and repair: A review. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Xu, Y.-J. The Cell Killing Mechanisms of Hydroxyurea. Genes 2016, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercilla, A.; Feu, S.; Aranda, S.; Llopis, A.; Brynjólfsdóttir, S.H.; Sørensen, C.S.; Toledo, L.I.; Agell, N. Acute hydroxyurea-induced replication blockade results in replisome components disengagement from nascent DNA without causing fork collapse. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 77, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, E.; May, P.; Weil, R. Analysis of the Events Leading to SV40-Induced Chromosome Replication and Mitosis in Primary Mouse Kidney Cell Cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braet, C.; Stephan, H.; Dobbie, I.M.; Togashi, D.M.; Ryder, A.G.; Földes-Papp, Z.; Lowndes, N.; Nasheuer, H.-P. Mobility and distribution of replication protein A in living cells using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakakibara, N.; Chen, D.; Jang, M.K.; Kang, D.W.; Luecke, H.F.; Wu, S.-Y.; Chiang, C.-M.; McBride, A.A. Brd4 Is Displaced from HPV Replication Factories as They Expand and Amplify Viral DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, J.L.; Verhalen, B.; Jiang, M. Polyomavirus interaction with the DNA damage response. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A. Machine learning applications in cell image analysis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffié, J.; Shannon, M.; Bromley, C.L.; Boelen, L.; Burn, G.L.; Williamson, D.J.; Heard, N.A.; Cope, A.P.; Owen, D.M.; Rubin-Delanchy, P. A Bayesian cluster analysis method for single-molecule localization microscopy data. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2499–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zila, V.; Difato, F.; Klimova, L.; Huérfano, S.; Forstová, J. Involvement of Microtubular Network and Its Motors in Productive Endocytic Trafficking of Mouse Polyomavirus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stubdal, H.; Zalvide, J.; Campbell, K.S.; Schweitzer, C.; Roberts, T.M.; de Caprio, J.A. Inactivation of pRB-related proteins p130 and p107 mediated by the J domain of simian virus 40 large T antigen. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 4979–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewers, H.; Smith, A.E.; Sbalzarini, I.F.; Lilie, H.; Koumoutsakos, P.; Helenius, A. Single-particle tracking of murine polyoma virus-like particles on live cells and artificial membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15110–15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, G.K.; Dickson, M. Development of Cell Cycle Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2009, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Türler, H.; Salomon, C. Small and middle T antigens contribute to lytic and abortive polyomavirus infection. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, U.-S.; Morrone, S.; Sablina, A.A.; Arroyo, J.D.; Hahn, W.C.; Xu, W. Structural Basis of PP2A Inhibition by Small t Antigen. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Bao, Q.; Xing, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Stock, J.B.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structural and biochemical insights into the regulation of protein phosphatase 2A by small t antigen of SV40. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Viciana, P.; Collins, C.; Fried, M. Polyoma and SV40 proteins differentially regulate PP2A to activate distinct cellular signaling pathways involved in growth control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19290–19295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sontag, E.; Fedorov, S.; Kamibayashi, C.; Robbins, D.; Cobb, M.H.; Mumby, M. The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell 1993, 75, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.; Chen, H.I.; George, M.; Benjamin, T.L. Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Controls Viral Chromatin Modifications through Effects on Kinetics of Virus Growth and Cell Cycle Progression. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10064–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellman, M.; Bikel, I.; Figge, J.; Roberts, T.; Schlossman, R.; Livingston, D.M. Localization of the simian virus 40 small t antigen in the nucleus and cytoplasm of monkey and mouse cells. J. Virol. 1984, 50, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsang, S.H.; Wang, R.; Nakamaru-Ogiso, E.; Knight, S.A.B.; Buck, C.B.; You, J. The Oncogenic Small Tumor Antigen of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Is an Iron-Sulfur Cluster Protein That Enhances Viral DNA Replication. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.H.; Narayanan, D.; Limmer, A.L.; Simonette, R.A.; Rady, P.L.; Tyring, S.K. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Induces DNA Damage Response. Intervirology 2019, 62, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, A.T.P.; Andrabi, S.; Cizmecioglu, O.; Zhu, C.; Livingston, D.M.; Higgins, J.M.G.; Schaffhausen, B.S.; Roberts, T.M. Polyoma small T antigen triggers cell death via mitotic catastrophe. Oncogene 2014, 34, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Veldman, G.M.; Cowie, A.; Carr, A.; Schaffhausen, B.; Kamen, R. Construction and functional characterization of polyomavirus genomes that separately encode the three early proteins. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erickson, K.D.; Garcea, R.L. Viral replication centers and the DNA damage response in JC virus-infected cells. Virology 2019, 528, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSwiggen, D.T.; Hansen, A.S.; Teves, S.S.; Marie-Nelly, H.; Hao, Y.; Heckert, A.; Umemoto, K.K.; Darzacq, C.D.; Tjian, R.; Darzacq, X. Evidence for DNA-mediated nuclear compartmentalization distinct from phase separation. eLife 2019, 8, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peters, D.K.; Erickson, K.D.; Garcea, R.L. Live Cell Microscopy of Murine Polyomavirus Subnuclear Replication Centers. Viruses 2020, 12, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101123
Peters DK, Erickson KD, Garcea RL. Live Cell Microscopy of Murine Polyomavirus Subnuclear Replication Centers. Viruses. 2020; 12(10):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101123
Chicago/Turabian StylePeters, Douglas K., Kimberly D. Erickson, and Robert L. Garcea. 2020. "Live Cell Microscopy of Murine Polyomavirus Subnuclear Replication Centers" Viruses 12, no. 10: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101123




