A Cell-Based Capture Assay for Rapid Virus Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Viruses
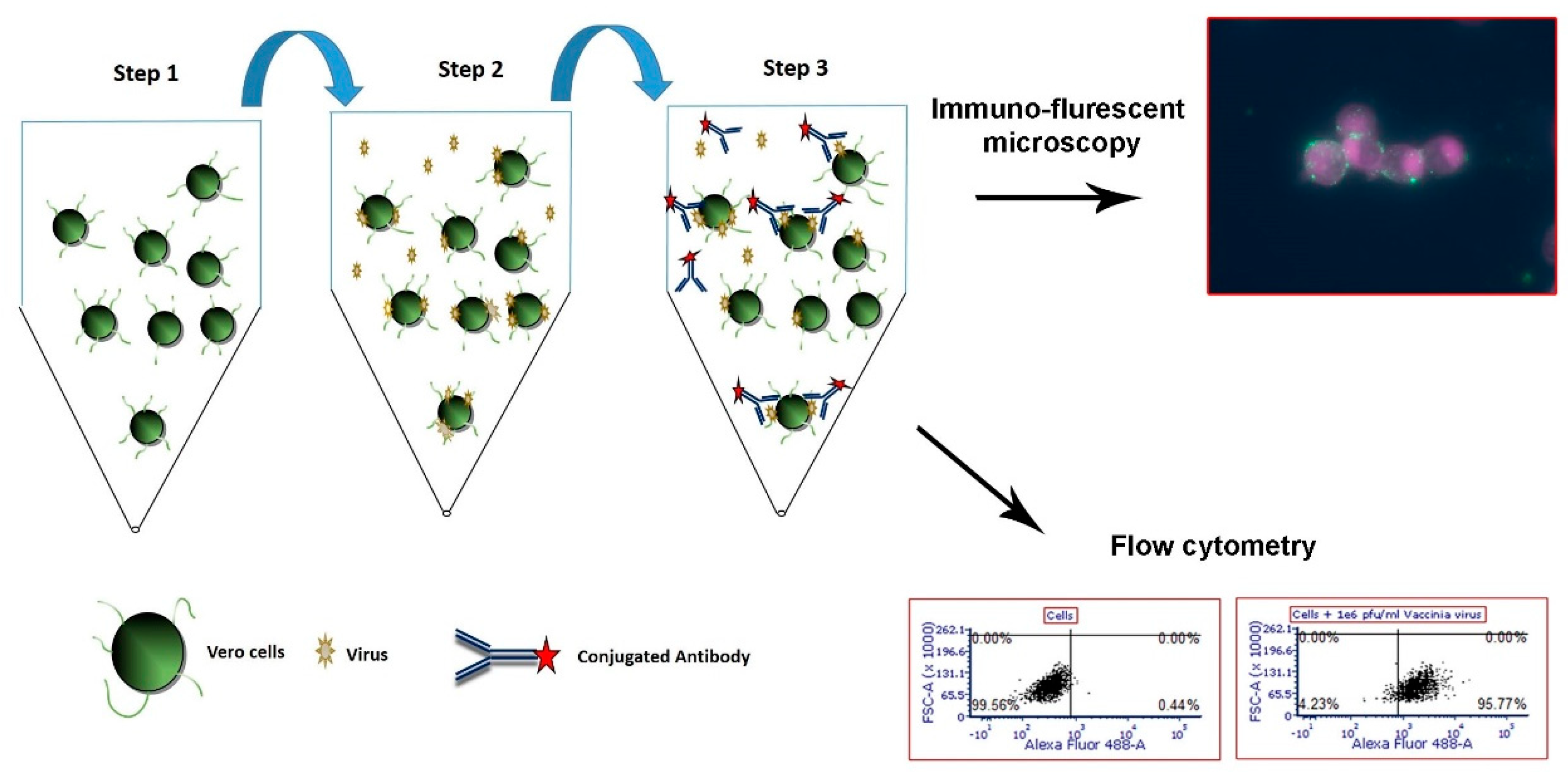
2.4. Flow Cytometry Cell-based Capture Assay for Adenovirus, West Nile Virus and MVA
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.6. Immuno-Fluorescence Microscopy Assays for the Detection of MVA and West Nile Virus after Capture with Vero Cells
2.7. Negative Staining Electron Microscopy Analysis of MVA and Adenovirus after Capture with Vero Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of a Cell-based Immunoassay for the Detection of MVA, West Nile Virus and Adenovirus
3.2. Adaptation of the Cell-Based Assay to Human Serum Samples
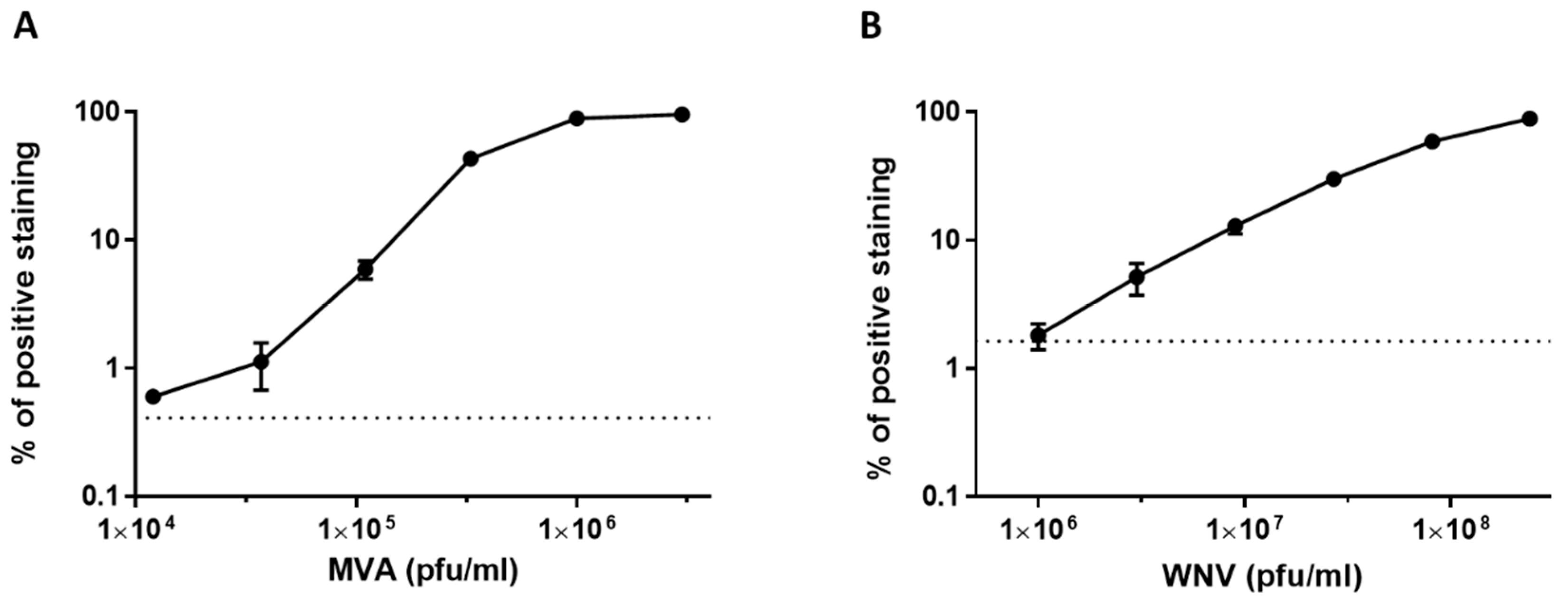
3.3. Dose Response Analysis of MVA and West Nile Virus Spiked into Human Serum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boonham, N.; Kreuze, J.; Winter, S.; Van Der Vlugt, R.; Bergervoet, J.; Tomlinson, J.; Mumford, R. Methods in virus diagnostics: From ELISA to next generation sequencing. Virus Res. 2014, 186, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, S.V.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Biswas, S.; Hewlett, I. Current Approaches for Diagnosis of Influenza Virus Infections in Humans. Viruses 2016, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lippé, R. Flow Virometry: A Powerful Tool to Functionally Characterize Viruses. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01765-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonsdale, R.; Pau, M.; Oerlemans, M.; Ophorst, C.; Vooys, A.; Havenga, M.; Goudsmit, J.; UytdeHaag, F.; Marzio, G. A rapid method for immunotitration of influenza viruses using flow cytometry. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 110, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeth, C.R.; White, L.J.; Johnston, R.E.; De Silva, A.M. Flow Cytometry-Based Assay for Titrating Dengue Virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3267–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.K.; Homann, D. Accelerated and Improved Quantification of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV) Titers by Flow Cytometry. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.-P.; Zhang, Z.-L.; He, R.; Lin, Y.; Xie, M.; Wang, H.; Pang, D.-W. Robust and Highly Sensitive Fluorescence Approach for Point-of-Care Virus Detection Based on Immunomagnetic Separation. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2358–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, K.-Y.; Hung, L.-Y.; Huang, T.-B.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Lei, H.-Y.; Lee, G.-B. Rapid detection of influenza A virus infection utilizing an immunomagnetic bead-based microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3900–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.-Y.; Huang, T.-B.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Yeh, C.-S.; Lei, H.-Y.; Lee, G.-B. A microfluidic immunomagnetic bead-based system for the rapid detection of influenza infections: From purified virus particles to clinical specimens. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, A.; Satoh, K.; Murata, M.; Hikata, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Virus Concentration Using Sulfonated Magnetic Beads to Improve Sensitivity in Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakudo, A.; Onodera, T. Virus capture using anionic polymer-coated magnetic beads (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, K. Virus concentration using polyethyleneimine-conjugated magnetic beads for improving the sensitivity of nucleic acid amplification tests. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 114, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, E.; Kogi, M.; Oshizawa, T.; Furuta, B.; Satoh, K.; Iwata, A.; Murata, M.; Hikata, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Optimization of the virus concentration method using polyethyleneimine-conjugated magnetic beads and its application to the detection of human hepatitis A, B and C viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 143, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patramool, S.; Bernard, E.; Hamel, R.; Natthanej, L.; Chazal, N.; Surasombatpattana, P.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Daoust, S.; Thongrungkiat, S.; Thomas, F.; et al. Isolation of infectious chikungunya virus and dengue virus using anionic polymer-coated magnetic beads. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, B.; Kojima, A.; Sata, T.; Katano, H. Virus detection using Viro-Adembeads, a rapid capture system for viruses, and plaque assay in intentionally virus-contaminated beverages. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 63, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sakudo, A.; Ikuta, K. Efficient capture of infectious H5 avian influenza virus utilizing magnetic beads coated with anionic polymer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achdout, H.; Lustig, S.; Israely, T.; Erez, N.; Politi, B.; Tamir, H.; Israeli, O.; Waner, T.; Melamed, S.; Paran, N. Induction, treatment and prevention of eczema vaccinatum in atopic dermatitis mouse models. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4245–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erster, O.; Melamed, S.; Paran, N.; Weiss, S.; Khinich, Y.; Gelman, B.; Solomony, A.; Laskar-Levy, O. First Diagnosed Case of Camelpox Virus in Israel. Viruses 2018, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shlomo, L.; Maik-Rachline, G.; Paran, N.; Melamed, S.; Israely, T.; Erez, N.; Orr, N.; Reuveny, S.; Ordentlich, A.; Laub, O.; et al. Effective post-exposure protection against lethal orthopoxviruses infection by vaccinia immune globulin involves induction of adaptive immune response. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, S.; Olshevsky, U.; Ben-Nathan, D.; Lachmi, B.-E.; Malkinson, M.; Kobiler, D.; Halevy, M. A Live Attenuated West Nile Virus Strain as a Potential Veterinary Vaccine. Viral Immunol. 2000, 13, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblum, N.; Sterk, V.V.; Paderski, B. West Nile fever; the clinical features of the disease and the isolation of West Nile virus from the blood of nine human cases. Am. J. Hyg. 1954, 59, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brien, J.D.; LaZear, H.M.; Diamond, M.S. Propagation, Quantification, Detection, and Storage of West Nile Virus. Curr. Protocols Microbiol. 2013, 31, 15D.3.1–15D.3.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paran, N.; Suezer, Y.; Lustig, S.; Israely, T.; Schwantes, A.; Melamed, S.; Katz, L.; Preuß, T.; Hanschmann, K.-M.; Kalinke, U.; et al. Postexposure Immunization with Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara or Conventional Lister Vaccine Provides Solid Protection in a Murine Model of Human Smallpox. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, A.; Gelderblom, H.R.; Eisendle, K.; Romani, N.; Pauli, G. Pitfalls in diagnosing human poxvirus infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 38, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E. Detection and identification of viruses by electron microscopy. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 2005, 4, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan, A.K.; Martins, T.B.; Hill, H.R.; Litwin, C.M.; Stipanovich, P.J.; Louro, A.P.; Roberson, J.; Eltoum, I.; Ascp), S.; Chhieng, D.C. Detection of IgG and IgM to West Nile Virus: Development of an Immunofluorescence Assay. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 119, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordignon, J.; Ferreira, S.C.P.; Caporale, G.M.M.; Carrieri, M.L.; Kotait, I.; Lima, H.C.; Zanetti, C.R. Flow cytometry assay for intracellular rabies virus detection. J. Virol. Methods 2002, 105, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorov, B.; Rabilloud, J.; Lawrence, P.; Gerlier, D. Rapid Titration of Measles and Other Viruses: Optimization with Determination of Replication Cycle Length. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-X.; Li, X.-F.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Guo, Y.-H.; Hao, W.; Che, X.-Y.; Qin, C.-F.; Fu, N. Development of a Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA for West Nile Virus Detection Using Monoclonal Antibodies against Non-Structural Protein 1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.; Pauly, D.; Zydek, M.; Miller, L.; Piesker, J.; Laue, M.; Lisdat, F.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G.; Nitsche, A. Development of a Genus-Specific Antigen Capture ELISA for Orthopoxviruses—Target Selection and Optimized Screening. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milrot, E.; Makdasi, E.; Politi, B.; Israely, T.; Laskar, O. A Cell-Based Capture Assay for Rapid Virus Detection. Viruses 2020, 12, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101165
Milrot E, Makdasi E, Politi B, Israely T, Laskar O. A Cell-Based Capture Assay for Rapid Virus Detection. Viruses. 2020; 12(10):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101165
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilrot, Elad, Efi Makdasi, Boaz Politi, Tomer Israely, and Orly Laskar. 2020. "A Cell-Based Capture Assay for Rapid Virus Detection" Viruses 12, no. 10: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101165
APA StyleMilrot, E., Makdasi, E., Politi, B., Israely, T., & Laskar, O. (2020). A Cell-Based Capture Assay for Rapid Virus Detection. Viruses, 12(10), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101165



