Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Correlates with but Does Not Predict Neutralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Cell Lines
2.4. ELISA
2.5. Virus Capture Assay
2.6. Virus Neutralization Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Virus Capture Assay
3.2. Recognition of S Glycoproteins at the Surface of Pseudoviral Particles is Required but not Sufficient to Neutralize
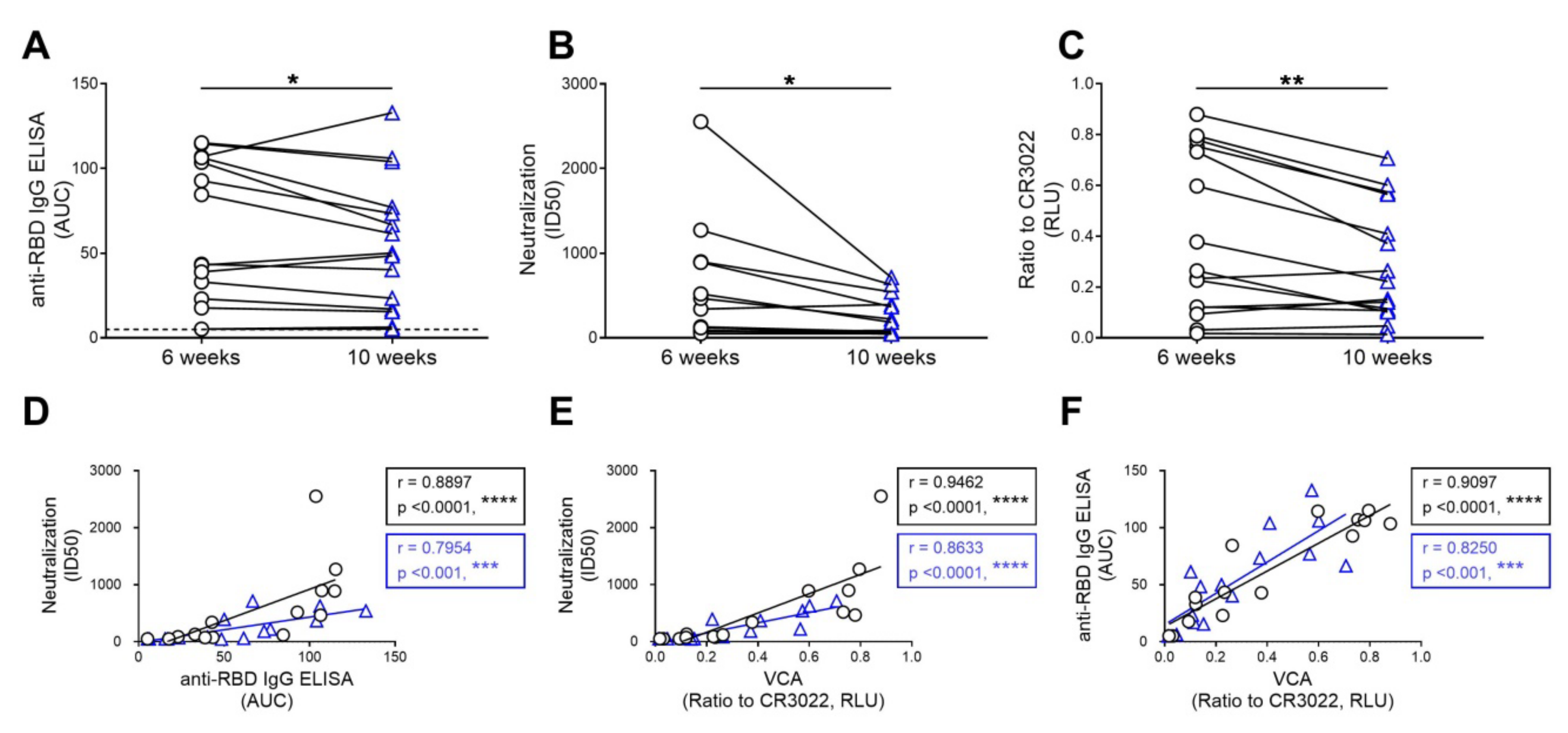
3.3. The Capacity of Convalescent Plasma to Bind to the S Glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 and Neutralize Pseudoviral Particles Decreases Over Time
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, J.; Bao, L.; Shi, Y. Convalescent plasma as a potential therapy for COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Seok, H.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.K.; Chung, C.R.; Kang, E.S.; et al. Challenges of convalescent plasma infusion therapy in Middle East respiratory coronavirus infection: A single centre experience. Antivir. Ther. 2018, 23, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, I.F.; To, K.K.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, K.L.; Chan, K.; Yan, W.W.; Liu, R.; Watt, C.L.; Chan, W.M.; Lai, K.Y.; et al. Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2011, 52, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wong, R.; Soo, Y.O.; Wong, W.S.; Lee, C.K.; Ng, M.H.; Chan, P.; Wong, K.C.; Leung, C.B.; Cheng, G. Use of convalescent plasma therapy in SARS patients in Hong Kong. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, E.M.; Shoham, S.; Casadevall, A.; Sachais, B.S.; Shaz, B.; Winters, J.L.; van Buskirk, C.; Grossman, B.J.; Joyner, M.; Henderson, J.P.; et al. Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casadevall, A.; Joyner, M.J.; Pirofski, L.A. A Randomized Trial of Convalescent Plasma for COVID-19-Potentially Hopeful Signals. J. Am. Med Assoc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, A.; Pirofski, L.A. The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joyner, M.J.; Wright, R.S.; Fairweather, D.; Senefeld, J.W.; Bruno, K.A.; Klassen, S.A.; Carter, R.E.; Klompas, A.M.; Wiggins, C.C.; Shepherd, J.R.; et al. Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5000 patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Liu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Qu, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Meng, S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9490–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurlburt, N.K.; Wan, Y.-H.; Stuart, A.B.; Feng, J.; McGuire, A.T.; Stamatatos, L.; Pancera, M. Structural basis for potent neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and role of antibody affinity maturation. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydoux, E.; Homad, L.J.; MacCamy, A.J.; Parks, K.R.; Hurlburt, N.K.; Jennewein, M.F.; Akins, N.R.; Stuart, A.B.; Wan, Y.-H.; Feng, J.; et al. Characterization of neutralizing antibodies from a SARS-CoV-2 infected individual. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Laumaea, A.; Anand, S.P.; Prévost, J.; Gasser, R.; Goyette, G.; Medjahed, H.; Perreault, J.; Tremblay, T.; Lewin, A.; et al. Decline of humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike in convalescent individuals. mBio 2020, 11, e02590-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, J.; Gasser, R.; Beaudoin-Bussieres, G.; Richard, J.; Duerr, R.; Laumaea, A.; Anand, S.P.; Goyette, G.; Benlarbi, M.; Ding, S.; et al. Cross-sectional evaluation of humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; et al. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wu, N.C.; Zhu, X.; Lee, C.D.; So, R.T.Y.; Lv, H.; Mok, C.K.P.; Wilson, I.A. A highly conserved cryptic epitope in the receptor-binding domains of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Science 2020, 368, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Yu, J.; Rapp, M.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chan, J.F.; Sahi, V.; Figueroa, A.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Nature 2020, 584, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.F.; Zhao, F.; Huang, D.; Beutler, N.; Burns, A.; He, W.T.; Limbo, O.; Smith, C.; Song, G.; Woehl, J.; et al. Isolation of potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and protection from disease in a small animal model. Science 2020, 369, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Gasser, R.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Medjahed, H.; Tolbert, W.D.; Sodroski, J.; Pazgier, M.; Finzi, A. CD4 Incorporation into HIV-1 Viral Particles Exposes Envelope Epitopes Recognized by CD4-Induced Antibodies. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, A.; Finzi, A.; Pancera, M.; Courter, J.R.; Smith, A.B., 3rd; Sodroski, J. Identification of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Envelope Glycoprotein Variant Resistant to Cold Inactivation. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4476–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desormeaux, A.; Coutu, M.; Medjahed, H.; Pacheco, B.; Herschhorn, A.; Gu, C.; Xiang, S.H.; Mao, Y.; Sodroski, J.; Finzi, A. The highly conserved layer-3 component of the HIV-1 gp120 inner domain is critical for CD4-required conformational transitions. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2549–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finzi, A.; Xiang, S.H.; Pacheco, B.; Wang, L.; Haight, J.; Kassa, A.; Danek, B.; Pancera, M.; Kwong, P.D.; Sodroski, J. Topological layers in the HIV-1 gp120 inner domain regulate gp41 interaction and CD4-triggered conformational transitions. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, B.; Alsahafi, N.; Debbeche, O.; Prevost, J.; Ding, S.; Chapleau, J.P.; Herschhorn, A.; Madani, N.; Princiotto, A.; Melillo, B.; et al. Residues in the gp41 Ectodomain Regulate HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Conformational Transitions Induced by gp120-Directed Inhibitors. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, Q.X.; Tang, X.J.; Shi, Q.L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.J.; et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, J.; Graham, C.; Merrick, B.; Acors, S.; Steel, K.J.A.; Hemmings, O.; O’Bryne, A.; Kouphou, N.; Pickering, S.; Galao, R.; et al. Longitudinal evaluation and decline of antibody responses in SARS-CoV-2 infection. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, S.; Laumaea, A.; Benlarbi, M.; Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Gasser, R.; Medjahed, H.; Pancera, M.; Stamatatos, L.; McGuire, A.T.; Bazin, R.; et al. Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Correlates with but Does Not Predict Neutralization. Viruses 2020, 12, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111214
Ding S, Laumaea A, Benlarbi M, Beaudoin-Bussières G, Gasser R, Medjahed H, Pancera M, Stamatatos L, McGuire AT, Bazin R, et al. Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Correlates with but Does Not Predict Neutralization. Viruses. 2020; 12(11):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111214
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Shilei, Annemarie Laumaea, Mehdi Benlarbi, Guillaume Beaudoin-Bussières, Romain Gasser, Halima Medjahed, Marie Pancera, Leonidas Stamatatos, Andrew T. McGuire, Renée Bazin, and et al. 2020. "Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Correlates with but Does Not Predict Neutralization" Viruses 12, no. 11: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111214
APA StyleDing, S., Laumaea, A., Benlarbi, M., Beaudoin-Bussières, G., Gasser, R., Medjahed, H., Pancera, M., Stamatatos, L., McGuire, A. T., Bazin, R., & Finzi, A. (2020). Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 S Glycoprotein Correlates with but Does Not Predict Neutralization. Viruses, 12(11), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111214




