Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Wild, Terrestrial Mammals: A Review of Potential Synanthropic Vectors to Poultry Facilities
Abstract
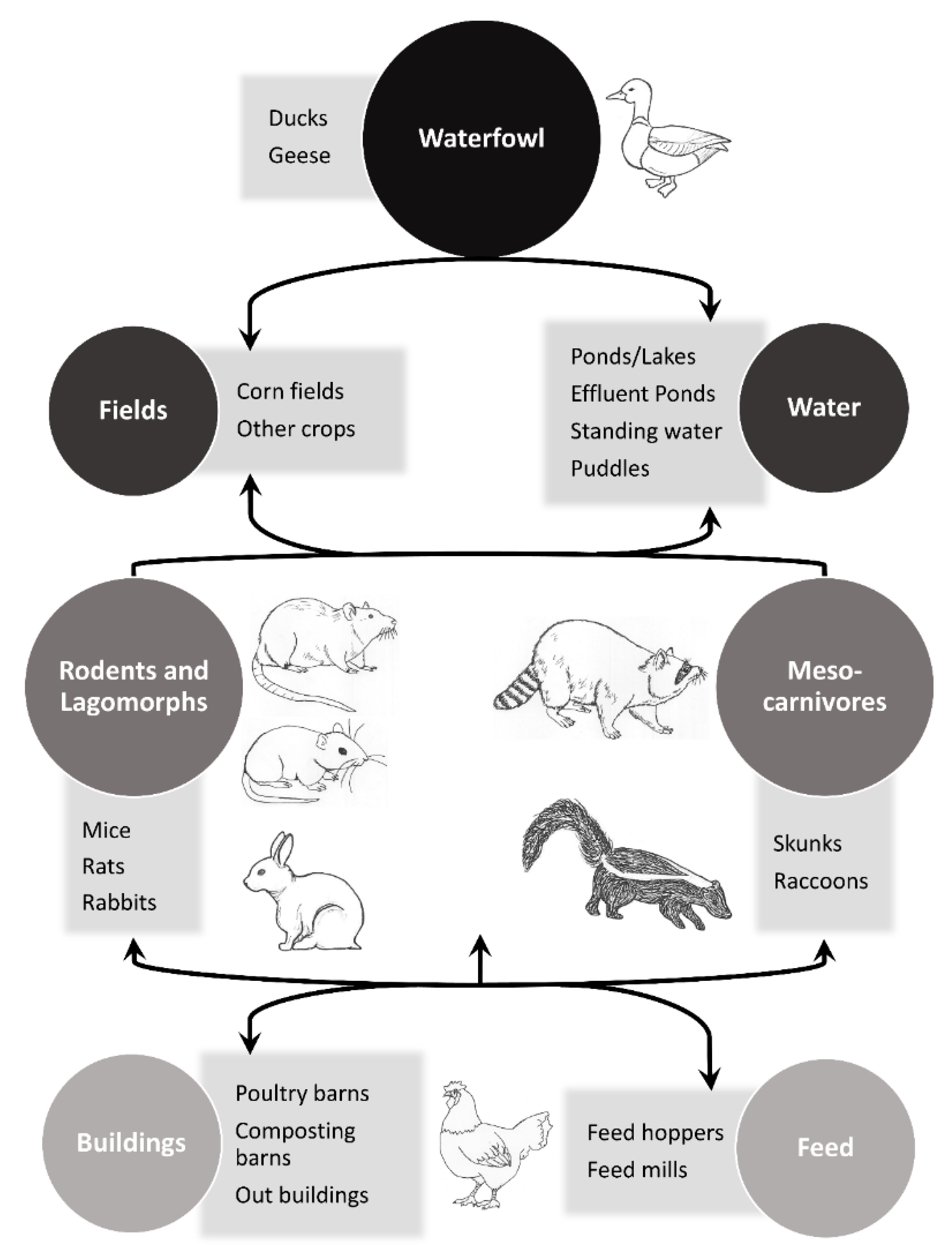
:1. Introduction
2. Antibody Detections
2.1. Lagomorphs
2.2. Procyonids
2.3. Canids
2.4. Felids
2.5. Mustelids
2.6. Rodents
2.7. Artiodactyls
3. Virus and Viral RNA Detections
4. Experimental Infections
5. Potential Mammalian Involvement in Outbreaks of IAV on Poultry Farms
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shriner, S.A.; Root, J.J.; Lutman, M.W.; Kloft, J.M.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J.; White, T.S.; Milleson, M.P.; Chandler, S.C.; Wolf, P.C.; et al. Surveillance for highly pathogenic H5 avian influenza A virus in synanthropic wildlife associated with poultry facilities during an acute outbreak. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Qi, X.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.F. H7N9: A low pathogenic avian influenza A virus infecting humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 5, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, D.A. Control of low pathogenicity avian influenza. In Avian Influenza; Swayne, D.E., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 513–536. [Google Scholar]
- Shriner, S.A.; VanDalen, K.K.; Mooers, N.L.; Ellis, J.W.; Sullivan, H.J.; Root, J.J.; Franklin, A.B. Low-pathogenic avian influenza viruses in wild house mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A.; Bentler, K.T.; Gidlewski, T.; Mooers, N.L.; Ellis, J.W.; Spraker, T.R.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J.; Franklin, A.B. Extended viral shedding of a low pathogenic avian influenza virus by striped skunks (Mephitis mephitis). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e70639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A.; Bentler, K.T.; Gidlewski, T.; Mooers, N.L.; Spraker, T.R.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J.; Franklin, A.B. Shedding of a low pathogenic avian influenza virus in a common synanthropic mammal—The cottontail rabbit. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Cheng, K.; Sun, W.; Xin, Y.; Cai, J.; Ma, R.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Sang, X.; et al. Lowly pathogenic avian influenza (H9N2) infection in plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae), Qinghai Lake, China. Veter. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Hall, J. Avian influenza in wild birds: Status as reservoirs, and risks to humans and agriculture. Ornithol. Monogr. 2006, 60, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McQuiston, J.H.; Garber, L.P.; Porter-Spalding, B.A.; Hahn, J.W.; Pierson, F.W.; Wainwright, S.H.; Senne, D.A.; Brignole, T.J.; Akey, B.L.; Holt, T.J. Evaluation of risk factors for the spread of low pathogenicity H7N2 avian influenza virus among commercial poultry farms. J. Am. Veter. Med Assoc. 2005, 226, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFarlane, R.; Sleigh, A.C.; McMichael, T.; McFarlane, R.A. Synanthropy of wild mammals as a determinant of emerging infectious diseases in the Asian–Australasian region. EcoHealth 2012, 9, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velkers, F.C.; Blokhuis, S.J.; Kroeze, E.J.B.V.; Burt, S.A. The role of rodents in avian influenza outbreaks in poultry farms: A review. Veter. Q. 2017, 37, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDalen, K.K.; Shriner, S.A.; Sullivan, H.J.; Root, J.J.; Franklin, A.B. Monitoring exposure to avian influenza viruses in wild mammals. Mammal Rev. 2009, 39, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reperant, L.; Rimmelzwaan, G.; Kuiken, T. Avian influenza viruses in mammals. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2009, 28, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T.; Siebert, U.; Wohlsein, P.; Vahlenkamp, T. Influenza A virus infections in marine mammals and terrestrial carnivores. Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2014, 126, 500–508. [Google Scholar]
- Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Harder, T.C. Influenza virus infections in mammals. Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2006, 119, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, E.V.; Kirilyuk, E.V.; Naidenko, S.V. Occurrence pattern of influenza A virus, Coxiella burnetii, Toxoplasma gondii, and Trichinella sp. in the Pallas cat and domestic cat and their potential prey under arid climate conditions. Arid. Ecosyst. 2016, 6, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilemetzidou, E.-S.; De Bruin, E.; Franz, M.; Aschenborn, O.H.K.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Van Beek, R.; Koopmans, M.; Greenwood, A.D.; Czirják, G.Á. Diet may drive influenza A virus exposure in African mammals. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 221, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J. What are the transmission mechanisms of influenza A viruses in wild mammals? J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 221, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Yin, W.; Wu, N.; Li, L.; Yan, Y.; Liao, M.; Huang, Y.; et al. Characterization of the H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus derived from wild pikas in China. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 8957–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuen, K.-Y.; Gao, P.; Guan, Y.; Ito, T.; Kawaoka, Y.; Markwell, D.; Takada, A.; Webster, R.G. Interspecies transmission of influenza viruses: H5N1 virus and a Hong Kong SAR perspective. Veter. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Prince, A.; Fawzy, A.; Abdou, N.-E.; Omar, L.; Fayed, A.; Salem, M. Sero-prevalence of avian influenza in animals and human in Egypt. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, J.S.; Bentler, K.T.; Landolt, G.; Elmore, S.A.; Minnis, R.B.; Campbell, T.A.; Barras, S.C.; Root, J.J.; Pilon, J.; Pabilonia, K.; et al. Influenza infection in wild raccoons. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horimoto, T.; Maeda, K.; Murakami, S.; Kiso, M.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Sashika, M.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Kawaoka, Y. Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection in feral raccoons, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, E.; Sashika, M.; Fujii, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Bui, V.N.; Ogawa, H.; Imai, K. Prevalence of multiple subtypes of influenza A virus in Japanese wild raccoons. Virus Res. 2014, 189, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemert, C.; Spivey, T.J.; Uher-Koch, B.D.; Atwood, T.C.; Sinnett, D.R.; Meixell, B.W.; Hupp, J.W.; Jiang, K.; Adams, L.G.; Gustine, D.D.; et al. Survey of arctic Alaskan wildlife for influenza A antibodies: Limited evidence for exposure of mammals. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-F.; Diao, F.-F.; Yu, J.-Y.; Zhang, F.-X.; Jiang, C.-Q.; Wang, J.-L.; Guo, S.-Y.; Cui, K.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wei, X.-H.; et al. Intraspecies and interspecies transmission of mink H9N2 influenza virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naidenko, S.V.; Hernandez-Blanco, J.A.; Pavlova, E.V.; Erofeeva, M.N.; Sorokin, P.A.; Litvinov, M.N.; Kotlyar, A.K.; Sulikhan, N.S.; Rozhnov, V.V. Primary study of seroprevalence to virus pathogens in wild felids of South Primorie, Russia. Can. J. Zool. 2018, 96, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Noh, J.Y.; Van Phan, L.; Kim, J.H.; Song, D.; Na, W.; Kang, A.; Nguyen, T.L.; Shin, J.-H.; et al. Serological evidence of H5-subtype influenza A virus infection in indigenous avian and mammalian species in Korea. Arch. Virol. 2017, 163, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songserm, T.; Amonsin, A.; Jam-On, R.; Sae-Heng, N.; Meemak, N.; Pariyothorn, N.; Payungporn, S.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Avian influenza H5N1 in naturally infected domestic cat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.E.; Sun, H.; Carrel, M.; Cunningham, F.L.; Baroch, J.A.; Hanson-Dorr, K.C.; Young, S.G.; Schmit, B.; Notling, J.M.; Yoon, K.J.; et al. US feral swine were exposed to both avian and swine influenza A viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01346-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maya-Badillo, B.A.; Ojeda-Flores, R.; Chaves, A.; Reveles-Félix, S.; Orta-Pineda, G.; Martínez-Mercado, M.J.; Saavedra-Montañez, M.; Segura-Velázquez, R.; Sanvicente, M.; Sánchez-Betancourt, J.I. Eco-epidemiological evidence of the transmission of avian and human influenza A viruses in wild pigs in Campeche, Mexico. Viruses 2020, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, J.R.; Macdonald, D.W. Foxes, Wolves, Jackals, and Dogs: An Action Plan for the Conservation of Canids; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 1990; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.-R.; Yang, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-G.; Wei, J.; Ma, W.-G.; Ren, Z.-G.; Guo, H.-L.; Wang, T.-C.; Mi, X.-Y.; Adili, G.; et al. Serological survey of avian influenza virus infection in non-avian wildlife in Xinjiang, China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunquist, M.; Sunquist, F. Wild Cats of the World; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, L. Wild Cats of the World; Bloomsbury Publishing Plc: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gordy, J.T.; Jones, C.A.; Rue, J.; Crawford, P.C.; Levy, J.K.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Tripp, R.A.; Tompkins, S.M. Surveillance of feral cats for influenza A virus in North Central Florida. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2011, 6, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Slavinski, S.; Schiff, C.; Merlino, M.; Daskalakis, D.; Liu, D.; Rakeman, J.L.; Misener, M.; Thompson, C.; Leung, Y.L.; et al. Outbreak of influenza A(H7N2) among cats in an animal shelter with cat-to-human transmission—New York City, 2016. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1927–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour, H.; Busquets, N.; Fernández-Aguilar, X.; Sánchez, A.; Ribas, M.P.; De Pedro, G.; Lizarraga, P.; Alarcia-Alejos, O.; Temiño, C.; Cabezón, Ó. Influenza A virus surveillance in the invasive American mink (Neovison vison) from freshwater ecosystems, Northern Spain. Zoonoses Public Health 2016, 64, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, P.E.; Samartino, L.E.; Stanchi, N.O.; Radman, N.E.; Parrado, E.J. Serology and protein electrophoresis for evidence of exposure to 12 mink pathogens in free-ranging American mink (Neovison vison) in Argentina. Veter. Q. 2017, 37, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, Y.; Yanagawa, R.; Noda, H. Experimental infection of mink with influenza A viruses. Arch. Virol. 1979, 62, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xuan, Y.; Shan, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Li, G.; Qiao, J. Avian influenza virus H9N2 infections in farmed minks. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, Y.; Xu, Y. Evolutionary status of the invasive American mink Neovison vison revealed by complete mitochondrial genome. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2016, 1, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.; Kidd, A.G.; Gorman, R.M.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I. Assessing the potential for impacts by feral mink on wild mink in Canada. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimi, N.A.; Sultana, R.; Muhsina, M.; Uddin, B.; Haider, N.; Nahar, N.; Zeidner, N.; Sturm-Ramirez, K.; Luby, S.P. Biosecurity conditions in small commercial chicken farms, Bangladesh 2011–2012. EcoHealth 2017, 14, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Teng, L.; Wu, Y. Habitat selection of the Chinese water deer (Hydropotes inermis) in Yancheng Reserve, Jiangsu Province. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2006, 26, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Choi, H.; Yoon, J.; Woo, C.; Chung, H.-M.; Kim, J.-T.; Shin, J.-H. Pathogens in water deer (Hydropotes inermis) in South Korea, 2010–2012. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pensaert, M.; Ottis, K.; Vandeputte, J.; Kaplan, M.M.; Bachmann, P.A. Evidence for the natural transmission of influenza A virus from wild ducks to swine and its potential importance for man. Bull. World Health Organ. 1981, 59, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Dong, G.; Li, K.; Lv, Z.; Huo, X.; He, H. Exposure to swine H1 and H3 and avian H5 and H9 influenza A viruses among feral swine in Southern China, 2009. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Gu, J.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-C.; Chen, X.-Y.; Li, Z.-K.; Lei, J.; Hu, B.-L.; Yan, L.; Xing, G.; Liao, M.; et al. Genetic characterization of H9N2 avian influenza virus in plateau pikas in the Qinghai Lake region of China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 162, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Xing, G.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, J.; Yan, L.; Lei, J.; Ji, S.; Hu, B.; Gray, G.C.; et al. Characterization of H7N2 avian influenza virus in wild birds and pikas in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, D.K.; Gorin, O.Z.; Yamnikova, S.S.; Zlobin, V.I.; Lvov, N.D.; Khasnatinov, M.A.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Chumakov, V.M.; Nepoklonov, Y.A.; Aliper, T.I. Isolation of influenza A viruses from wild birds and muskrat in the western area of east Asian migration route. Vopr. Virusol. 2001, 46, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lvov, D.K.; Yamnikova, S.S.; Fedyakina, I.T.; Lomakina, N.F.; Synitsyn, B.V.; Petrova, E.S.; Gambaryan, A.S.; Blinov, V.M.; Suarez, D.L.; Swayne, D.E.; et al. Evolution of H4, H5 influenza A viruses in natural ecosystems in Northern Eurasia (2000–2002). Int. Congr. Ser. 2004, 1263, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, M.A.; Delogu, M.; Sivay, M.; Sharshov, K.; Yurlov, A.; Cotti, C.; Shestopalov, A. Virological evaluation of avian influenza virus persistence in natural and anthropic ecosystems of Western Siberia (Novosibirsk Region, summer 2012). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, M.; Sharshov, K.; Suzuki, M.; Sobolev, I.; Sakoda, Y.; Alekseev, A.; Sivay, M.; Shestopalova, L.; Shchelkanov, M.; Shestopalov, A. Genetic characterization of an H2N2 influenza virus isolated from a muskrat in Western Siberia. J. Veter. Med Sci. 2017, 79, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, C.; Hill, N.J.; Puryear, W.B.; Rogers, B.; Mukherjee, J.; Leibler, J.H.; Rosenbaum, M.H.; Runstadler, J.A. Evidence of influenza A in wild Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Boston, Massachusetts. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, A.; Rahman, M.Z.; Hossain, M.E.; Rostal, M.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Hagan, E.; Islam, A.; Haider, N.; Daszak, P.; Epstein, J.H. Assessing viral diversity in peridomestic small mammals, Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 9th One Health Bangladesh Conference, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 September 2017; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Klopfleisch, R.; Wolf, P.; Wolf, C.; Harder, T.; Starick, E.; Niebuhr, M.; Mettenleiter, T.; Teifke, J.P. Encephalitis in a stone marten (Martes foina) after natural infection with highly pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H5N1. J. Comp. Pathol. 2007, 137, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, I.; Gyarmati, P.; Zohari, S.; Ramsay, K.W.; Metreveli, G.; Weiss, E.; Brytting, M.; Stivers, M.; Lindström, S.; Lundkvist, A.; et al. Molecular characterization of highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza viruses isolated in Sweden in 2006. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO. H5N1 Avian Influenza: Timeline of Major Events. Available online: https://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/H5N1_avian_influenza_update.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Roberton, S.; Bell, D.J.; Smith, G.; Nicholls, J.; Chan, K.; Nguyen, D.; Tran, P.; Streicher, U.; Poon, L.; Chen, H.; et al. Avian influenza H5N1 in viverrids: Implications for wildlife health and conservation. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Li, X.; Rider, P.; Fan, W.; Gu, H.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, F. Molecular characterization of highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza A viruses isolated from raccoon dogs in China. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, E.; Fujii, K.; Ogawa, H.; Imai, K. First detection of influenza A virus genes from wild raccoons in Japan. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, A.P.; Sojonky, K.R.; Scouras, A.P.; Bidulka, J.J. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in skunks, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britton, A.P.; Trapp, M.; Sabaiduc, S.; Hsiao, W.W.L.; Joseph, T.; Schwantje, H. Probable reverse zoonosis of influenza A(H1N1)pdm 09 in a striped skunk (Mephitis mephitis). Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 66, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, M.A.; Sharshov, K.; Gulyaeva, M.; Delogu, M.; Ciccarese, L.; Castrucci, M.R.; Shestopalov, A. Ecology of avian influenza viruses in Siberia. In Siberia: Ecology, Diversity and Environmental Impact; Nova Science Pub Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 83–160. [Google Scholar]
- Klingeborn, B.; Englund, L.; Rott, R.; Juntti, N.; Rockborn, G. An avian influenza A virus killing a mammalian species—The mink. Arch. Virol. 1985, 86, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Hou, G.; Peng, C.; Chen, J.; Shan, H. Characterization of H5N1 highly pathogenic mink influenza viruses in eastern China. Veter. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Sun, L.; Xiong, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, P.; Yu, H.; Yan, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. Semiaquatic mammals might be intermediate hosts to spread avian influenza viruses from avian to human. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belser, J.A.; Barclay, W.S.; Barr, I.; Fouchier, R.A.; Matsuyama, R.; Nishiura, H.; Peiris, M.; Russell, C.J.; Subbarao, K.; Zhu, H.; et al. Ferrets as models for influenza virus transmission studies and pandemic risk assessments. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Cheung, C.L.; Luo, S.W.; Li, P.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Butt, K.M.; et al. Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in Southern China. Science 2003, 302, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A.; Ellis, J.W.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J.; Franklin, A.B. When fur and feather occur together: Interclass transmission of avian influenza A virus from mammals to birds through common resources. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; Huang, C.; Sun, H.; Li, L.-X.; Su, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Distribution of sialic acid receptors and experimental infections with different subtypes of influenza A viruses in Qinghai-Tibet plateau wild pika. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A.; Ellis, J.W.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J. Low viral doses are sufficient to infect cottontail rabbits with avian influenza A virus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenbach, J.E.; Bowen, R.A. Transmission of avian influenza A viruses among species in an artificial barnyard. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanDalen, K.K.; Franklin, A.B.; Mooers, N.L.; Sullivan, H.J.; Shriner, S.A. Shedding light on avian influenza H4N6 infection in mallards: Modes of transmission and implications for surveillance. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental infection of peridomestic mammals with emergent H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) influenza A virus: Implications for biosecurity and wet markets. Virology 2016, 487, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Marlenee, N.L.; Bowen, R.A. Cottontail rabbits shed clade 2.3.4.4 H5 highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2823–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejeda, A.R.; Aiello, R.; Salomoni, A.; Berton, V.; Vascellari, M.; Cattoli, G. Susceptibility to and transmission of H5N1 and H7N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in bank voles (Myodes glareolus). Veter. Res. 2015, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, C.F. Experimental Infection of Raccoon, Skunk, and Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrels with Avian Derived Influenza A Viruses. Master’s Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- VanDalen, K.K.; Nemeth, N.M.; Thomas, N.O.; Barrett, N.L.; Ellis, J.W.; Sullivan, H.J.; Franklin, A.B.; Shriner, S.A. Experimental infections of Norway rats with avian-derived low-pathogenic influenza A viruses. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiono, T.; Okamatsu, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Ogasawara, K.; Endo, M.; Kuribayashi, S.; Shichinohe, S.; Motohashi, Y.; Chu, D.-H.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Experimental infection of highly and low pathogenic avian influenza viruses to chickens, ducks, tree sparrows, jungle crows, and black rats for the evaluation of their roles in virus transmission. Veter. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Bentler, K.T.; Shriner, S.A.; Mooers, N.L.; VanDalen, K.K.; Sullivan, H.J.; Franklin, A.B. Ecological routes of avian influenza virus transmission to a common mesopredator: An experimental evaluation of alternatives. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reperant, L.A.; Van Amerongen, G.; Van De Bildt, M.W.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Dobson, A.P.; Osterhaus, A.; Kuiken, T. Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N1) infection in red foxes fed infected bird carcasses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagyu, K.; Yanagawa, R.; Matsuura, Y.; Noda, H. Contact infection of mink with influenza A viruses of avian and mammalian origin. Arch. Virol. 1981, 68, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Yanagawa, R.; Kida, H. Contact infection of mink with 5 subtypes of avian influenza virus. Arch. Virol. 1983, 77, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, C.; Han, K.-Y.; Zhang, F.-X.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Ling, Z.-S.; Zhang, X.-X.; Jiang, S.-J.; Xie, Z.-J. Molecular characterization of H9N2 influenza virus isolated from mink and its pathogenesis in mink. Veter. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, S.; Kromm, M.M.; Vanbeusekom, E.T.; Sorley, E.J.; Sundaram, M.E.; VanderWaal, K.; Bowers, J.W.J.; Papinaho, P.A.; Osterholm, M.T.; Bender, J. Epidemiologic investigation of highly pathogenic H5N2 avian influenza among upper Midwest U.S. turkey farms, 2015. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grear, D.A.; Dusek, R.J.; Walsh, D.P.; Hall, J.S. No evidence of infection or exposure to highly pathogenic avian influenzas in peridomestic wildlife on an affected poultry facility. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.D.; Azeem, S.; Lundy, C.W.; Sato, Y.; Guo, B.; Blanchong, J.A.; Gauger, P.C.; Marks, D.R.; Yoon, K.-J.; Adelman, J.S. Evaluating the role of wild songbirds or rodents in spreading avian influenza virus across an agricultural landscape. PeerJ 2017, 5, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nettles, V.F.; Wood, J.M.; Webster, R.G. Wildlife surveillance associated with an outbreak of lethal H5N2 avian influenza in domestic poultry. Avian Dis. 1985, 29, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler, D.J.; Kradel, D.C.; Davison, S.; Ziegler, A.F.; Singletary, D.; DeBok, P.; Castro, A.E.; Lu, H.; Eckroade, R.; Swayne, D.; et al. Epidemiology, production losses, and control measures associated with an outbreak of avian influenza subtype H7N2 in Pennsylvania (1996–98). Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Gonzales, J.L. Quantification of visits of wild fauna to a commercial free-range layer farm in the Netherlands located in an avian influenza hot-spot area assessed by video-camera monitoring. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 67, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Killian, M.L.; Torchetti, M.K.; Hines, N.; Yingst, S.; Deliberto, T.; Lee, D.-H. Outbreak of H7N8 Low pathogenic avian influenza in commercial turkeys with spontaneous mutation to highly pathogenic avian influenza. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00457-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, J.W.; Shriner, S.A.; McLean, H.E.; Petersen, L.; Root, J.J. Inventory of wildlife use of mortality pits as feeding sites: Implications of pathogen exposure. Hum.-Wildl. Interact. 2017, 11, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, V.L.; Drake, J.M.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Brown, J.D.; Pedersen, K.; Rohani, P. Dissecting a wildlife disease hotspot: The impact of multiple host species, environmental transmission and seasonality in migration, breeding and mortality. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A. Influenza A viruses in peridomestic mammals. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2123, pp. 415–428. [Google Scholar]



| Common Name a | Scientific Name | Location | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plateau pika | Ochotona curzoniae | China | [7,19] |
| Daurian pika | O. dauurica | Russia | [16] |
| “Rats” | Presumably Rattus sp. | Hong Kong | [20] |
| “Sewage rats” | Presumably Rattus sp. | Egypt | [21] |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | U.S. | [4] |
| Transbaikal hamster b | Cricetulus pseudogriseus | Russia | [16] |
| Campbell’s dwarf hamster b | Phodopus campbelli | Russia | [16] |
| Brandt’s vole | Lasiopodomys brandtii | Russia | [16] |
| Mongolian gerbil | Meriones unguiculatus | Russia | [16] |
| Daurian souslik | Spermophilus dauricus | Russia | [16] |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | U.S. | [22] |
| Japan | [23,24] | ||
| Arctic fox | Vulpes lagopus | U.S. | [25] |
| “Fox” c | Not listed | China | [26] |
| Black-backed jackal | Canis mesomelas | Namibia | [17] |
| Raccoon dog c | Nyctereutes procyonoides | China | [26] |
| Far-eastern wild cat | Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus | Russia | [27] |
| Leopard cat | Prionailurus bengalensis | Korea | [28] |
| American mink | Neovison vison | Spain | [38] |
| Water deer | Hydropotes inermis | Korea | [28] |
| Feral swine | Sus scrofa | U.S. | [30] |
| Mexico | [31] |
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Type | Subtype | Location | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plateau pika | Ochotona curzoniae | Virus | H5N1 | China | [19] |
| Virus | H9N2 | China | [49] | ||
| Virus | H7N2 | China | [50] | ||
| Muskrat | Ondatra zibethicus | Virus | H13N6 | Russia | [51] |
| Virus | H4N6 | Russia | [52] | ||
| Virus | H2N2 | Russia | [53,54] | ||
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | RNA a | ND b | U.S. | [55] |
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | RNA | ND b | Bangladesh | [56] |
| House mouse | Mus musculus | RNA | ND b | Bangladesh | [56] |
| Asian house shrew | Suncus murinus | RNA | ND b | Bangladesh | [56] |
| Stone marten | Martes fonia | RNA/Virus | H5N1 | Germany | [57] |
| “Mink” | Neovison visonc | Virus | H5N1 | Sweden | [58,59] |
| “Mink” | Not reported d | Virus | H9N2 | China | [26] |
| Owston’s civet | Chrotogale owstoni | Virus | H5N1 | Vietnam | [60] |
| Raccoon dog | Nyctereutes procyonoides | Virus | H5N1 | China | [61] |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | RNA | ND b | Japan | [62] |
| Striped skunk | Mephitis mephitis | RNA/Virus | H1N1 e | Canada | [63,64] |
| Feral swine | Sus scrofa | RNA | H5N2 | Mexico | [31] |
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Subtype | Pathotype b* | Exposure Method | Maximum Titer f* | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plateau pika | Ochotona curzoniae | H5N1 a | HP | IN c* | ND | [72] |
| H9N2 b | LP | IN | 4.8 h* | [7] | ||
| Cottontail rabbit | Sylvilagus sp. | H4N6 c | LP | IN | 7.2 | [73] |
| H7N9 d | LP | IN | 5.8 | [76] | ||
| H5N8 e | HP | IN | 3.5 | [77] | ||
| H5N2 f | HP | IN | 3.9 | [77] | ||
| H5N2 g | HP | IN | 5.3 | [77] | ||
| House mouse | Mus musculus | H3N6 h | LP | IN | 2.4 i* | [4] |
| H3N8 i | LP | IN | 4.5 i* | [4] | ||
| H4N6 j | LP | IN | 4.3 i* | [4] | ||
| H4N8 k | LP | IN | 2.1 i* | [4] | ||
| H6N2 l | LP | IN | 2.1 i* | [4] | ||
| Bank vole | Myodes glareolus | H7N1 m | HP | IN | 4.9 | [78] |
| H5N1 n | HP | IN | 6.6 | [78] | ||
| Thirteen-lined ground squirrel | Ictidomys tridecemlineatusa* | H3N8 o | LP | IN | ND g* | [79] |
| Norway rat | Rattus norvegicus | H6N2 l | LP | IN | 3.5 i* | [80] |
| H4N8 k | LP | IN | 1.7 i* | [80] | ||
| H4N6 j | LP | IN | 4.8 i* | [80] | ||
| H3N8 i | LP | IN | 5.5 i* | [80] | ||
| Black rat | Rattus rattus | H5N1 p | HP | IN | 3.0 j* | [81] |
| Raccoon | Procyon lotor | H4N6 c | LP | Virus-laden water | 4.2 | [82] |
| H7N9 d | LP | IN | 5.2 | [76] | ||
| H4N8 k | LP | IN | 1.1 | [22] | ||
| Striped skunk | Mephitis | H4N6 c | LP | IN | 6.0 | [5] |
| H7N9 d | LP | IN | 6.4 | [76] | ||
| H1N1 q | LP | ICE d*/IN | ND | [79] | ||
| H3N8 o | LP | ICE/IN | ND | [79] | ||
| Red fox | Vulpes vulpes | H5N1 r | HP | IT or BC e* | 5.2 | [83] |
| “Fox” | Not listed | H9N2 s | LP | IN or Contact | Negative | [26] |
| Mink | Neovison vison | H9N2 t | LP | IN | ND | [41] |
| H7N2 u | LP | IN or Contact | 7.2 k* | [40,84] | ||
| H4N1 v | LP | IN | 4.5 k* | [40] | ||
| H3N8 w | LP | IN | 6.3 | [85] | ||
| H11N4 x | LP | IN | 5.3 | [85] | ||
| H7N7 y | Not reported | IN | 5.5 | [85] | ||
| H8N4 z | LP | IN | 6.0 | [85] | ||
| H5N3 aa | Not reported | IN | 4.5 | [85] | ||
| H9N2 bb | LP | IN | 4.3 | [85] | ||
| “Mink” | Not listed | H9N2 s | LP | IN or Contact | 4.2 | [26] |
| “Mink” | Not listed | H9N2 cc | LP | IN | 4.5 | [86] |
| Raccoon dog | Nyctereutes procyonoides | H9N2 s | LP | IN or Contact | Negative | [26] |
| Feral swine | Sus Scrofa | H3N2 dd | LP | IN | 2.5 | [30] |
| H6N2 ee | LP | IN | ND | [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Root, J.J.; Shriner, S.A. Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Wild, Terrestrial Mammals: A Review of Potential Synanthropic Vectors to Poultry Facilities. Viruses 2020, 12, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121352
Root JJ, Shriner SA. Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Wild, Terrestrial Mammals: A Review of Potential Synanthropic Vectors to Poultry Facilities. Viruses. 2020; 12(12):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121352
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoot, J. Jeffrey, and Susan A. Shriner. 2020. "Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Wild, Terrestrial Mammals: A Review of Potential Synanthropic Vectors to Poultry Facilities" Viruses 12, no. 12: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121352
APA StyleRoot, J. J., & Shriner, S. A. (2020). Avian Influenza A Virus Associations in Wild, Terrestrial Mammals: A Review of Potential Synanthropic Vectors to Poultry Facilities. Viruses, 12(12), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12121352






