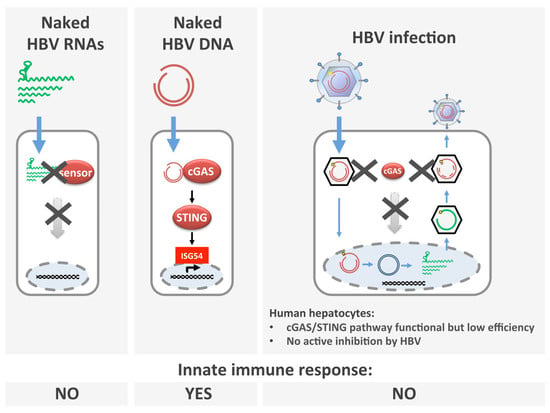
Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Ethics Statements
2.2. HepG2-hNTCP Overexpressing cGAS and STING
2.3. Hepatitis B Virus Production and Infection
2.4. Other Viruses and Viral Vectors
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Reagents
2.7. Preparation and Quantification of Viral Nucleic Acids for Transfection Experiments
2.8. Transfections
2.9. Western Blots
2.10. IRF3 Nuclear Translocation Assays
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Microscope Image Acquisition
3. Results
3.1. HBV DNAs but not RNAs are Immunostimulatory
3.2. Virion-Associated HBV DNA is Sensed by the cGAS/STING Pathway
3.3. Hepatocytes Express Low Levels of the DNA Sensors Compared to Immune Cells
3.4. Hepatocytes are Competent for Sensing HBV DNA
3.5. HBV DNA is not Sensed During Productive Infection of Hepatocytes
3.6. HBV Does not Inhibit the Innate Immune Response to Foreign DNA in Hepatocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Sastre, A. Ten Strategies of Interferon Evasion by Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.K.; Gack, M.U. Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.-L.; Liao, F. Melanoma Differentiation–Associated Gene 5 Senses Hepatitis B Virus and Activates Innate Immune Signaling To Suppress Virus Replication. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3264–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA Sensor RIG-I Dually Functions as an Innate Sensor and Direct Antiviral Factor for Hepatitis B Virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shlomai, A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ramanan, V.; Bhatta, A.; De Jong, Y.P.; Bhatia, S.N.; Rice, C.M. Modeling host interactions with hepatitis B virus using primary and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12193–12198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luangsay, S.; Gruffaz, M.; Isorce, N.; Testoni, B.; Michelet, M.; Faure-Dupuy, S.; Maadadi, S.; Ait-Goughoulte, M.; Parent, R.; Rivoire, M.; et al. Early inhibition of hepatocyte innate responses by hepatitis B virus. J. Hepatology 2015, 63, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Trippler, M.; Real, C.I.; Werner, M.; Luo, X.; Schefczyk, S.; Kemper, T.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Ladiges, Y.; Treckmann, J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus particles activate toll-like receptor 2 signaling initial upon infection of primary human hepatocytes. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hösel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltjes, A.; Van Montfoort, N.; Biesta, P.J.; Brouw, M.L.O.D.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Van Der Laan, L.J.W.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Boonstra, A.; Woltman, A.M. Kupffer Cells Interact With Hepatitis B Surface Antigen In Vivo and In Vitro, Leading to Proinflammatory Cytokine Production and Natural Killer Cell Function. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 211, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verrier, E.R.; Yim, S.-A.; Heydmann, L.; El Saghire, H.; Bach, C.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Mailly, L.; Durand, S.C.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Evasion From Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate–Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase Sensing in Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, F.; Tang, L.; Shu, S.; Sehgal, M.; Sheraz, M.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; et al. Activation of Stimulator of Interferon Genes in Hepatocytes Suppresses the Replication of Hepatitis B Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winer, B.Y.; Gaska, J.M.; Lipkowitz, G.; Bram, Y.; Parekh, A.; Parsons, L.; Leach, R.; Jindal, R.; Cho, C.H.; Shrirao, A.; et al. Analysis of Host Responses to Hepatitis B and Delta Viral Infections in a Micro-scalable Hepatic Co-culture System. Hepatology 2019, 71, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.K.; Nandakumar, R.; Stadler, D.; Malo, A.; Valls, R.M.; Wang, F.; Reinert, L.S.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Hollensen, A.K.; Mikkelsen, J.G.; et al. Lack of immunological DNA sensing in hepatocytes facilitates hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2016, 64, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stacey, A.R.; Norris, P.J.; Qin, L.; Haygreen, E.A.; Taylor, E.; Heitman, J.; Lebedeva, M.; DeCamp, A.; Li, D.; Grove, D.; et al. Induction of a Striking Systemic Cytokine Cascade prior to Peak Viremia in Acute Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection, in Contrast to More Modest and Delayed Responses in Acute Hepatitis B and C Virus Infections. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, C.; Peppa, D.; Khanna, P.; Nebbia, G.; Jones, M.; Brendish, N.; Lascar, R.M.; Brown, D.; Gilson, R.; Tedder, R.J.; et al. Temporal Analysis of Early Immune Responses in Patients With Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansako, H.; Ueda, Y.; Okumura, N.; Satoh, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Ikeda, M.; Kato, N. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthetase-STING signaling pathway is required for both the innate immune response against HBV and the suppression of HBV assembly. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Dupuy, S.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D. Interplay between the Hepatitis B Virus and Innate Immunity: From an Understanding to the Development of Therapeutic Concepts. Viruses 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Imanishi, H.; Morisaki, H.; Liu, W.; Nakamura, H.; Morisaki, T.; Hada, T. Recombinant HBsAg inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 expression and IL-18 production by interfering with the NFkappaB pathway in a human monocytic cell line, THP-1. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ni, C.; Song, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Jia, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, K.; Xu, Y.; et al. The Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Disrupts Innate Immunity by Downregulating Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real, C.I.; Lu, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Trippler, M.; Hossbach, M.; Deckert, J.; Jahn-Hofmann, K.; Ickenstein, L.M.; John, M.J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus genome replication triggers toll-like receptor 3-dependent interferon responses in the absence of hepatitis B surface antigen. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.-P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2008, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Kato, N.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes through interference with interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and dampening of the interaction between TBK1/IKKepsilon and DDX3. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ryu, W.-S. Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Blocks Pattern Recognition Receptor Signaling via Interaction with DDX3: Implications for Immune Evasion. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.; An, B.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Z.; An, F.; Yu, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Impairment of the retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-IFN-? signaling pathway in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jung, S.Y.; Hodgson, A.J.; Madden, C.R.; Qin, J.; Slagle, B.L. Hepatitis B Virus Regulatory HBx Protein Binds to Adaptor Protein IPS-1 and Inhibits the Activation of Beta Interferon. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Cao, W.; Han, T.; Ren, S.; Feng, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Broering, R.; Lu, M.; Zhu, Y. Inducible Rubicon facilitates viral replication by antagonizing interferon production. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Bornscheuer, T.; Volz, T.; Allweiss, L.; Bockmann, J.-H.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M. Hepatitis B Virus Limits Response of Human Hepatocytes to Interferon-α in Chimeric Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase Disrupts K63-Linked Ubiquitination of STING To Block Innate Cytosolic DNA-Sensing Pathways. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suslov, A.; Boldanova, T.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.F.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis B Virus Does Not Interfere With Innate Immune Responses in the Human Liver. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mutz, P.; Metz, P.; Lempp, F.A.; Bender, S.; Qu, B.; Schöneweis, K.; Seitz, S.; Tu, T.; Restuccia, A.; Frankish, J.; et al. HBV Bypasses the Innate Immune Response and Does Not Protect HCV From Antiviral Activity of Interferon. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1791–1804.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D Viruses Exploit Sodium Taurocholate Co-transporting Polypeptide for Species-Specific Entry into Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, M.A.; Chen, M.L.; Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, S.K.; Otto, M.J.; Barker, C.S.; Zaifert, K.; Wang, G.H.; Guo, J.T.; Seeger, C.; King, R.W. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: A novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Yamabe, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, T.; Tada, K. Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1). Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankan, A.K.; Schmidt, T.; Chauhan, D.; Goldeck, M.; Höning, K.; Gaidt, M.; Kubarenko, A.V.; Andreeva, L.; Hopfner, K.-P.; Hornung, V. Cytosolic RNA:DNA hybrids activate the cGAS –STING axis. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, M.; Pawlita, M. High-throughput detection and multiplex identification of cell contaminations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, M.-K.H.; Boost, K.A.; Leckel, K.; Beecken, W.-D.; Engl, T.; Jonas, D.; Oppermann, E.; Hilgard, P.; Markus, B.H.; Bechstein, W.-O.; et al. Controlled and reversible induction of differentiation and activation of adult human hepatocytes by a biphasic culture technique. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, L.; Gerossier, L.; Ducroux, A.; Dion, S.; Deng, Q.; Michel, M.-L.; Buendia, M.-A.; Hantz, O.; Neuveut, C. HBx relieves chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of hepatitis B viral cccDNA involving SETDB1 histone methyltransferase. J. Hepatology 2015, 63, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempp, F.A.; Urban, S. Inhibitors of Hepatitis B Virus Attachment and Entry. Intervirology 2014, 57, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staib, C.; Drexler, I.; Ohlmann, M.; Wintersperger, S.; Erfle, V.; Sutter, G. Transient Host Range Selection for Genetic Engineering of Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara. BioTechniques 2000, 28, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosma, A.; Bühler, S.; Nagaraj, R.; Staib, C.; Hammarin, A.-L.; Wahren, B.; Goebel, F.D.; Erfle, V.; Sutter, G. Neutralization Assay Using a Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Vector Expressing the Green Fluorescent Protein Is a High-Throughput Method To Monitor the Humoral Immune Response against Vaccinia Virus. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ducroux, A.; Benhenda, S.; Rivière, L.; Semmes, O.J.; Benkirane, M.; Neuveut, C. The Tudor Domain Protein Spindlin1 Is Involved in Intrinsic Antiviral Defense against Incoming Hepatitis B Virus and Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grandvaux, N.; Servant, M.J.; Tenoever, B.; Sen, G.C.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Transcriptional Profiling of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Target Genes: Direct Involvement in the Regulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakaya, T.; Sato, M.; Hata, N.; Asagiri, M.; Suemori, H.; Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, N.; Taniguchi, T. Gene Induction Pathways Mediated by Distinct IRFs during Viral Infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strähle, L.; Marq, J.-B.; Brini, A.; Hausmann, S.; Kolakofsky, D.; Garcin, D. Activation of the Beta Interferon Promoter by Unnatural Sendai Virus Infection Requires RIG-I and Is Inhibited by Viral C Proteins. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12227–12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, P.; Wang, W.; Cao, H.; Avogadri, F.; Dai, L.; Drexler, I.; Joyce, J.A.; Li, X.-D.; Chen, Z.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara Triggers Type I IFN Production in Murine Conventional Dendritic Cells via a cGAS/STING-Mediated Cytosolic DNA-Sensing Pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nassal, M. Hepatitis B viruses: Reverse transcription a different way. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paijo, J.; Döring, M.; Spanier, J.; Grabski, E.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Schmidt, T.; Witte, G.; Messerle, M.; Hornung, V.; Kaever, V.; et al. cGAS Senses Human Cytomegalovirus and Induces Type I Interferon Responses in Human Monocyte-Derived Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, K.; Riess, M.; König, R. Role of Innate Genes in HIV Replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 419, 69–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoh, S.M.; Schneider, M.; Seifried, J.; Soonthornvacharin, S.; Akleh, R.E.; Olivieri, K.C.; de Jesus, P.D.; Ruan, C.; de Castro, E.; Ruiz, P.A.; et al. PQBP1 Is a Proximal Sensor of the cGAS-Dependent Innate Response to HIV-1. Cell 2015, 161, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kell, A.M.; Gale, M. RIG-I in RNA virus recognition. Virology 2015, 479–480, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, A.; Robb, G.B.; Chan, S.-H. mRNA capping: Biological functions and applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7511–7526. [Google Scholar]
- Devarkar, S.C.; Wang, C.; Miller, M.T.; Ramanathan, A.; Jiang, F.; Khan, A.G.; Patel, S.S.; Marcotrigiano, J. Structural basis for m7G recognition and 2’-O-methyl discrimination in capped RNAs by the innate immune receptor RIG-I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Hepatitis B virus replication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lien, J.M.; Aldrich, C.E.; Mason, W.S. Evidence that a capped oligoribonucleotide is the primer for duck hepatitis B virus plus-strand DNA synthesis. J. Virol. 1986, 57, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imam, H.; Khan, M.; Gokhale, N.S.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Kim, G.-W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M.; Siddiqui, A. N6-methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B virus RNA differentially regulates the viral life cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8829–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durbin, A.F.; Wang, C.; Marcotrigiano, J.; Gehrke, L. RNAs Containing Modified Nucleotides Fail To Trigger RIG-I Conformational Changes for Innate Immune Signaling. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, X.; Nguyen, D.; Mentzer, L.; Adams, C.; Lee, H.; Ashley, R.; Hafenstein, S.; Hu, J. Secretion of Genome-Free Hepatitis B Virus—Single Strand Blocking Model for Virion Morphogenesis of Para-retrovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.T.; Sahu, G.K.; Whitehead, W.E.; Greenberg, R.; Shih, C. The Mechanism of an Immature Secretion Phenotype of a Highly Frequent Naturally Occurring Missense Mutation at Codon 97 of Human Hepatitis B Virus Core Antigen. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 5731–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Shu, W.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Gao, B.; Xiong, S. Nuclear Sensor Interferon-Inducible Protein 16 Inhibits the Function of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA by Integrating Innate Immune Activation and Epigenetic Suppression. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Clark, D.N.; Liu, K.; Xu, X.-D.; Guo, J.-T.; Hu, J. Viral DNA-Dependent Induction of Innate Immune Response to Hepatitis B Virus in Immortalized Mouse Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Name | Citation | Supplier | Authentication Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | Figure 3 | Gift from Prof S.Urban, Heidelberg, Germany | Cell line authentication performed by Eurofins Genomics, using Applied BiosystemsTM AmpFLSTRTM IdentifilerTM Plus PCR Amplification Kit with 16 markers |
| HepG2-hNTCP | Figures 3–6 | Gift from Prof S.Urban, Heidelberg, Germany [33] | Cell line authentication performed by Eurofins Genomics, using Applied BiosystemsTM AmpFLSTRTM IdentifilerTM Plus PCR Amplification Kit with 16 markers |
| HepaRG-hNTCP | Figure 3 | Gift from Prof S.Urban, Heidelberg, Germany | Multiplexion cell contamination assay (Heidelberg, Germany) as described [39] |
| HepAD38 | Figure 1 (for HBV RNAs and replication intermediate extraction) | Gift from Prof E Hild, Langen, Germany | Release of HBV particles (qPCR + infectivity test) |
| THP1 | Figures 2 and 3 | Gift from Prof V. Hornung, Munich, Germany | Cell line authentication by Eurofins Genomics on 24.03.2017 |
| THP1 ΔSTING | Figure 2 | Gift from Prof V. Hornung, Munich, Germany | Western blot |
| THP1 ΔcGAS | Figure 2 | Gift from Prof V. Hornung, Munich, Germany | Western blot |
| THP1 ΔMAVS | Figure 2 | Gift from Prof V. Hornung, Munich, Germany | Western blot |
| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Supplier | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBV_RC_F | CACTCTATGGAAGGCGGGTA | Eurofins Genomics | qPCR for quantification of HBV stocks |
| HBV_RC_R | TGCTCCAGCTCCTACCTTGT | Eurofins Genomics | qPCR for quantification of HBV stocks |
| HBV RNA 3 F | GCTTTCACTTTCTCGCCAAC | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| HBV RNA 3 R | GAGTTCCGCAGTATGGATCG | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| ISG54_F | GGTGGCAGAAGAGGAAGATT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| ISG54_R | TAGGCCAGTAGGTTGCACAT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| IFNλ-1_F | CGCCTTGGAAGAGTCACTCA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| IFNλ-1_R | GAAGCCTCAGGTCCCAATTC | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| cGAS_F | CAAGAAGGCCTGCGCATTCA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| cGAS_R | GAGAAGGATAGCCGCCATGT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| STING_F | GATATCTGCGGCTGATCCTG | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| STING_R | GCTGTAAACCCGATCCTTGA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| IFI16_F | CGCTTGAAGACCTGGCTGAA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| IFI16_R | TGACAGTGCTGCTTGTGGAG | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| PQBP1_F | TCTGGAGCCTGAACCAGAGGAA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| PQBP1_R | TCCAACCTGGTGGCCTCGTAGT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| RIG-I_F | CCTACCTACATCCTGAGCTACAT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| RIG-I_R | TCTAGGGCATCCAAAAAGCCA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| MAVS_F | GGTGCTCACCAAGGTGTCTG | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| MAVS_R | AGGAGGTGCTGGCACTGATG | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| MDA5_F | AGAGTGGCTGTTTACATTGCC | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| MDA5_R | GCTGTTCAACTAGCAGTACCTT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| TLR3_F | ACCTCCAGCACAATGAGCTA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| TLR3_R | TCCAGCTGAACCTGAGTTCC | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| RPL13A_F | CCT GGA GGA GAA GAG GAA AGA GA | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| RPL13A_R | TTG AGG ACC TCT GTG TAT TTG TCA A | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| TBP_F | GGAGCTGTGATGTGAAGT | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| TBP_R | TACGTCITCTTCCTGAATCC | Eurofins Genomics | RT-qPCR |
| HBV_quant_F | TGTCAACACTAATATGGGCCTAA | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of HBV RNA and DNA |
| HBV_quant_R | AGGGGCATTTGGTGGTCTAT | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of HBV RNA and DNA |
| HBV_st | TGTCAACACTAATATGGGCCTAAAGTTCAGGCAACTCTTGTGGTTTCACATTTCTTGTCTCACTTTTGGAAGAGAAACAGTTATAGAGTATTTGGTGTCTTTCGGAGTGTGGATTCGCACTCCTCCAGCTTATAGACCACCAAATGCCCCT | Integrated DNA Technologies, BvBA | standard for quantification of HBV RNA and DNA |
| MVAgfp_F | AGCACGACTTCTTCAAGTCC | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of MVAgfp DNA |
| MVAgfp_R | GTTGTAGTTGTACTCCAGCTTG | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of MVAgfp DNA |
| MVAgfp_st | AGCACGACTTCTTCAAGTCCGCCATGCCCGAAGGCTACGTCCAGGAGCGCACCATCTTCTTCAAGGACGACGGCAACTACAAGACCCGCGCCGAGGTGAAGTTCGAGGGCGACACCCTGGTGAACCGCATCGAGCTGAAGGGCATCGACTTCAAGGAGGACGGCAACATCCTGGGGCACAAGCTGGAGTACAACTACAAC | Integrated DNA Technologies, BvBA | standard for quantification of MVAgfp DNA |
| SeV_F | TTCATTATCATCCCGTGAGA | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of SeV RNA |
| SeV_R | CCAGTGATCCATCATCAATC | Eurofins Genomics | quantification of SeV RNA |
| SeV_st | TTCATTATCATCCCGTGAGATCAGGAACCTGAGGGTTATCACAAAAACTTTATTAGACAGGTTTGAGGATATTATACATAGTATAACGTATAGATTCCTCACCAAAGAGATAAAGATTTTGATGAAGATTTTAGGGGCAGTCAAGATGTTCGGGGCCAGGCAAAATGAATACACGACCGTGATTGATGATGGATCACTGG | Integrated DNA Technologies, BvBA | standard for quantification of SeV RNA |
| SeV n.ac. from Particles | MVA n.ac. from Particles | HBV n.ac. from Particles | HepaD38 RNA | HBV R.I. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral DNA (copies/cell) | 5.0E+03 | 5.0E+03 | 5.0E+03 | ||
| Viral RNA (cDNA-equivalent copies/cell) | 2.8E+01 | 2.3E+01 | 1.3E+04 |
| Name | Supplier | Cat No. | Clone No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti phospho S386-IRF3 (rabbit) | Abcam | ab76493 | EPR2346 |
| Anti IRF3 (rabbit) | Epitomics | 2241-1 | EP2419Y |
| Anti beta-actin (mouse) | Sigma-Aldrich | A5441 | AC-15 |
| Anti beta-tubulin (mouse) | Sigma-Aldrich | 075K4875 | TUB 2.1 |
| Anti GAPDH (rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | 2118 | 14C10 |
| Anti MAVS (rabbit) | Abcam | Ab25084 | |
| Anti STING (rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | 13647 | D2P2F |
| Anti cGAS (rabbit) | Cell Signaling Technology | 15102 | D1D3G |
| Anti-mouse HRP | Cell Signaling Technology | 7076S | |
| Anti-rabbit HRP | Cell Signaling Technology | 7074S |
| Name | Citation | Supplier | Cat No. | Clone No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti IRF3 (rabbit) | IRF3 translocation assay, Figure 6 | Cell Signaling Technology | 11904S | D6I4C |
| anti HBc (mouse) | IRF3 translocation assay, Figure 6 | gift from Prof. S. Urban, Heidelberg | M312 | |
| anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 | IRF3 translocation assay, Figure 6 | Invitrogen | A11008 | |
| anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 555 | IRF3 translocation assay, Figure 6 | Thermo Fischer Scientific | A21422 | |
| Anti-HBc (rabbit) | Figure S5 | Dako, Agilent | B0586 | |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG(H+L), Alexa Fluor 546 | Figure S5 | Thermo Fischer Scientific | A-11010 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauterbach-Rivière, L.; Bergez, M.; Mönch, S.; Qu, B.; Riess, M.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Liese, J.; Hornung, V.; Urban, S.; König, R. Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060592
Lauterbach-Rivière L, Bergez M, Mönch S, Qu B, Riess M, Vondran FWR, Liese J, Hornung V, Urban S, König R. Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060592
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauterbach-Rivière, Lise, Maïwenn Bergez, Saskia Mönch, Bingqian Qu, Maximilian Riess, Florian W. R. Vondran, Juliane Liese, Veit Hornung, Stephan Urban, and Renate König. 2020. "Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes" Viruses 12, no. 6: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060592
APA StyleLauterbach-Rivière, L., Bergez, M., Mönch, S., Qu, B., Riess, M., Vondran, F. W. R., Liese, J., Hornung, V., Urban, S., & König, R. (2020). Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. Viruses, 12(6), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060592