Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Biopsy of RRP Lesions
2.2. Mucosal Squamous Epithelial Cell Culture
2.3. Organotypic Epithelial Raft Culture
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT–qPCR)
2.5. Determination of HPV Strain by RT–qPCR
2.6. Southern Blot Analysis
2.7. 2D Culture on Coverslips with EdU Incorporation
2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.9. Confocal Imaging
2.10. Quantification of EdU and DAPI-Positive Cells
2.11. Statistical Methods
3. Results
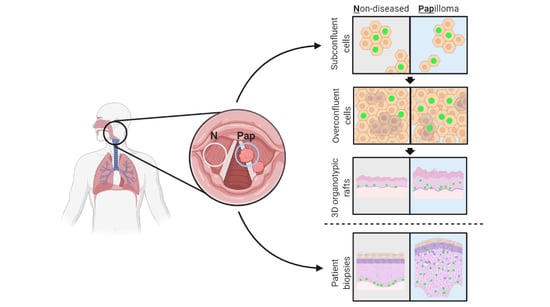
3.1. Establishing a Pipeline of Patient-Derived 2D Primary Cells and 3D Organotypic Rafts to Study JoRRP
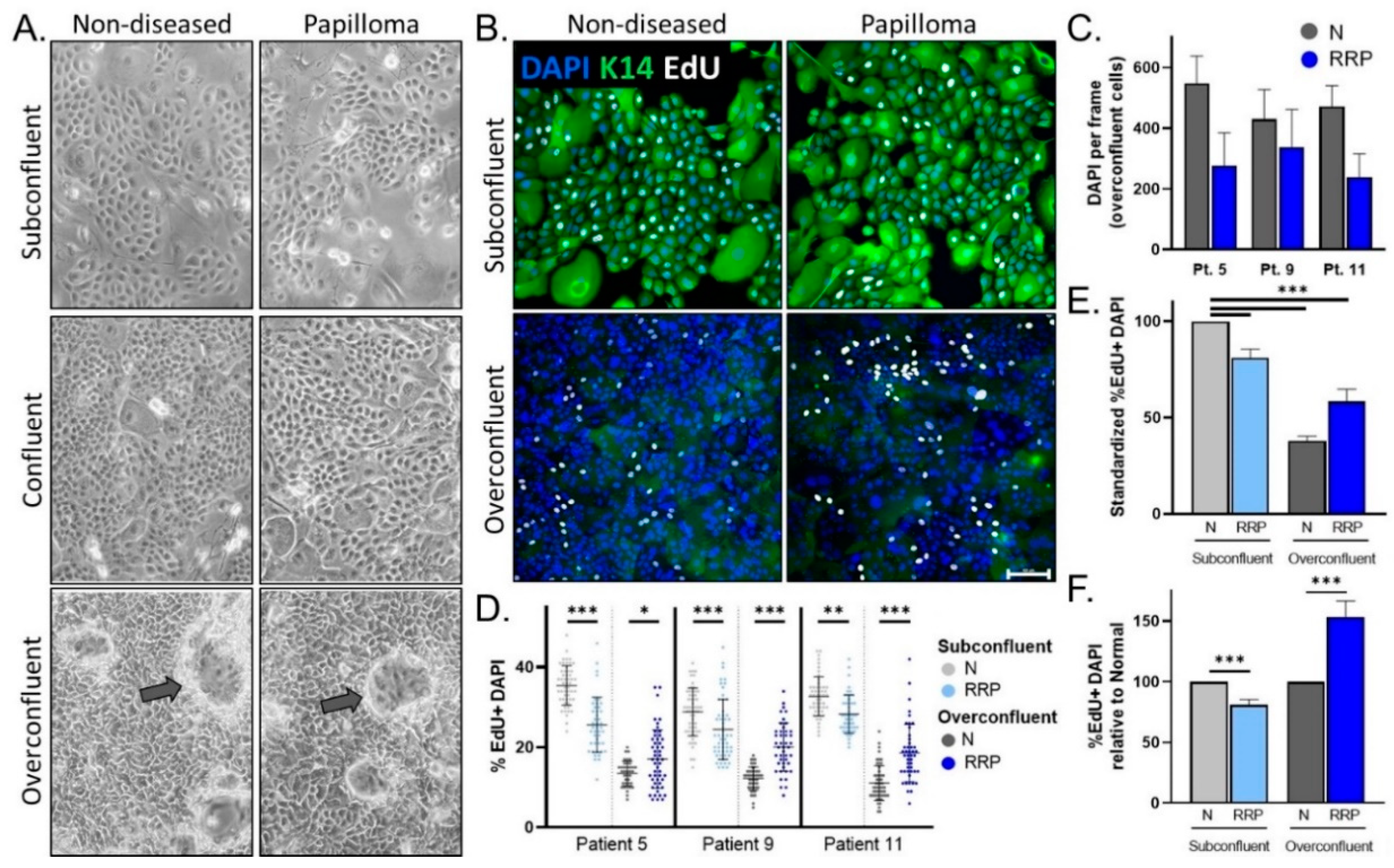
3.2. Papilloma versus Non-Diseased Primary Cells Exhibit Diminished Growth in Standard 2D Tissue Culture
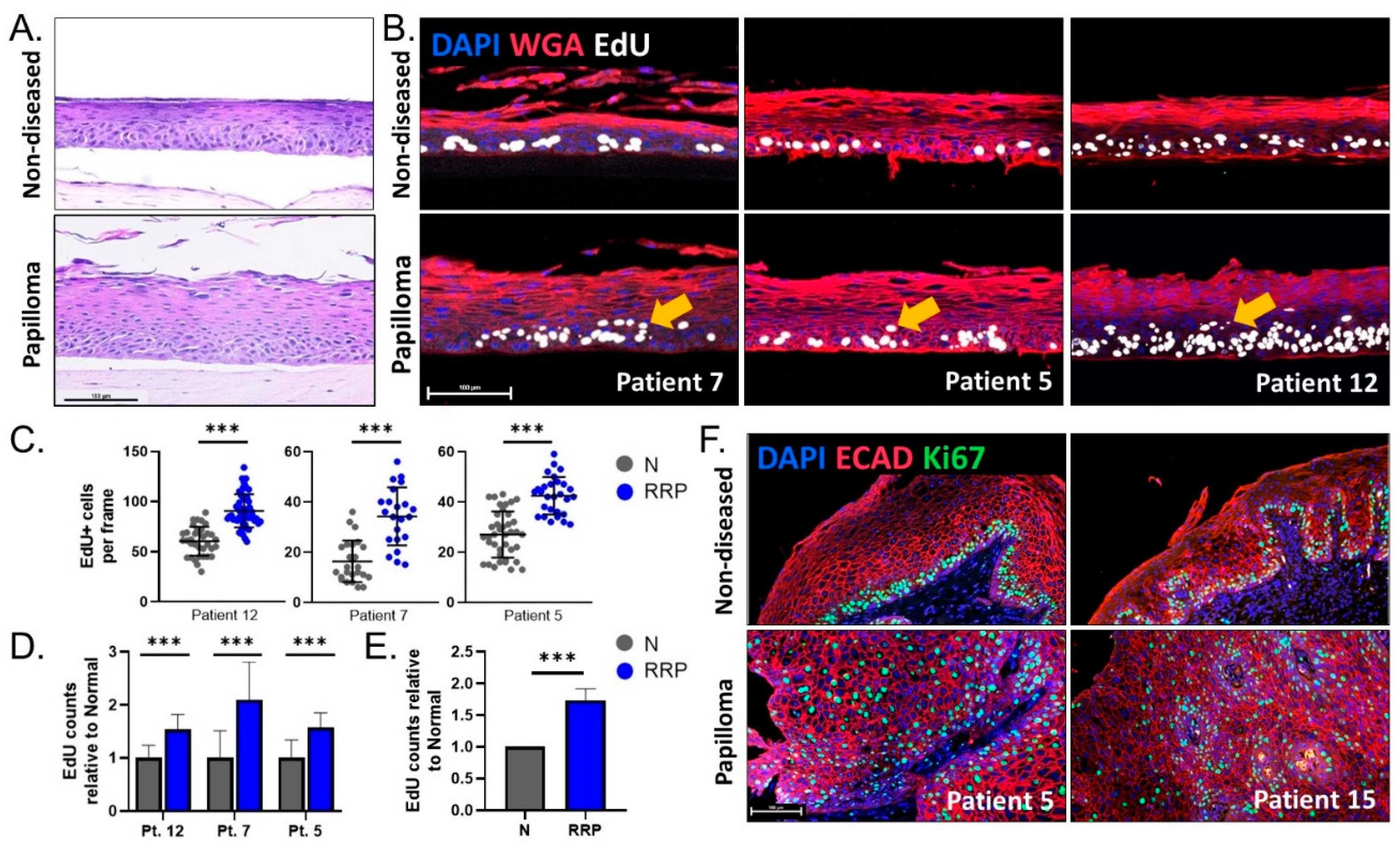
3.3. Engineered 3D Organotypic Raft Models Recapitulate Disease Phenotypes Observed in Patient Biopsies
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venkatesan, N.N.; Pine, H.S.; Underbrink, M.P. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 45, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkay, C.S.; Wiatrak, B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A review. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Akre, H.; Lie, K.A.; Jebsen, P.; Sandvik, L.; Brøndbo, K. Risk Factors for Aggressive Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in Adults and Juveniles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egawa, N.; Doorbar, J. The low-risk papillomaviruses. Virus Res. 2017, 231, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, M.J.; Thorsen, P.; Lindeberg, H.; Grant, L.A.; Shah, K.V. Condyloma in pregnancy is strongly predictive of juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Obs. Gynecol. 2003, 101, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Lie, K.A.; Akre, H.; Sandlie, L.E.; Jebsen, P.; Sandvik, L.; Nymoen, D.A.; Bzhalava, D.; Dillner, J.; Brøndbo, K. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: HPV genotypes and risk of high-grade laryngeal neoplasia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taliercio, S.; Cespedes, M.; Born, H.; Ruiz, R.; Roof, S.; Amin, M.R.; Branski, R.C. Adult-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review of Disease Pathogenesis and Implications for Patient Counseling. JAMA Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchinsky, F.J.; Valentino, W.L.; Ruszkay, N.; Powell, E.; Derkay, C.S.; Seedat, R.Y.; Uloza, V.; Dikkers, F.G.; Tunkel, D.E.; Choi, S.S.; et al. Age at diagnosis, but not HPV type, is strongly associated with clinical course in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasca, R.A.; Clarke, R.W. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ory, V.; Chapman, S.; Yuan, H.; Albanese, C.; Kallakury, B.; Timofeeva, O.A.; Nealon, C.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; et al. ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprynowicz, F.A.; Upadhyay, G.; Krawczyk, E.; Kramer, S.C.; Hebert, J.D.; Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Cheluvaraju, C.; Clapp, P.W.; Boucher, R.C., Jr.; et al. Conditionally reprogrammed cells represent a stem-like state of adult epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20035–20040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucs, A.V.; Wu, R.; Mullooly, V.; Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M. Constitutive overexpression of the oncogene Rac1 in the airway of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis patients is a targetable host-susceptibility factor. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Myers, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Woo, J.A.; Kallakury, B.; Ju, A.; Bazylewicz, M.; Carter, Y.M.; Albanese, C.; et al. Use of Reprogrammed Cells to Identify Therapy for Respiratory Papillomatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhilaiwi, F.; Paul, S.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Palechor-Ceron, N.; Wilson, K.; Guha, R.; Ferrer, M.; Grant, N.; et al. High-throughput screening identifies candidate drugs for the treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Papillomavirus Res. 2019, 8, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, H.R.; von Ranke, F.M.; Escuissato, D.L.; Araujo Neto, C.A.; Zanetti, G.; Hochhegger, B.; Souza, C.A.; Marchiori, E. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: A state-of-the-art review. Respir. Med. 2017, 126, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Bishop, J.A.; Akpeng, B.; Pai, S.I.; Best, S.R. Xenograft model for therapeutic drug testing in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2015, 124, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branski, R.C.; Dion, G.R.; Best, S. Letter to the Editor: Concerning “Xenograft Model for Therapeutic Drug Testing in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis”. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2016, 125, 947–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Norby, K.; Hayes, M.; Chiu, Y.F.; Sugden, B.; Lambert, P.F. Using Organotypic Epithelial Tissue Culture to Study the Human Papillomavirus Life Cycle. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2016, 41, 14b.8.1–14b.8.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, V.; Urciuolo, F.; Netti, P.A.; Imparato, G. In Vitro Organotypic Systems to Model Tumor Microenvironment in Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Related Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCance, D.J.; Kopan, R.; Fuchs, E.; Laimins, L.A. Human papillomavirus type 16 alters human epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7169–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S.; Malis, D.J.; Zalzal, G.; Wiatrak, B.J.; Kashima, H.K.; Coltrera, M.D. A staging system for assessing severity of disease and response to therapy in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, R.P.; Derkay, C.S.; Burke, B.L.; Lawson, M.L. Reliability of a staging assessment system for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, C.; Frattini, M.G.; Hudson, J.B.; Laimins, L.A. Biosynthesis of human papillomavirus from a continuous cell line upon epithelial differentiation. Science 1992, 257, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbun, M.A.; Meyers, C. Temporal usage of multiple promoters during the life cycle of human papillomavirus type 31b. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Tan, Q.; Xirasagar, S.; Bandaru, S.; Gopalan, V.; Mohamoud, Y.; Huyen, Y.; McBride, A.A. The Papillomavirus Episteme: A central resource for papillomavirus sequence data and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D571–D578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Protein Atlas. Available online: www.proteinatlas.org (accessed on 28 October 2020).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bedard, M.C.; Brusadelli, M.G.; Carlile, A.; Ruiz-Torres, S.; Lodin, H.; Lee, D.; Kofron, M.; Lambert, P.F.; Lane, A.; Ameziane, N.; et al. Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010068
Bedard MC, Brusadelli MG, Carlile A, Ruiz-Torres S, Lodin H, Lee D, Kofron M, Lambert PF, Lane A, Ameziane N, et al. Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Viruses. 2021; 13(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleBedard, Mary C., Marion G. Brusadelli, Adrean Carlile, Sonya Ruiz-Torres, Hannah Lodin, Denis Lee, Matthew Kofron, Paul F. Lambert, Adam Lane, Najim Ameziane, and et al. 2021. "Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis" Viruses 13, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010068
APA StyleBedard, M. C., Brusadelli, M. G., Carlile, A., Ruiz-Torres, S., Lodin, H., Lee, D., Kofron, M., Lambert, P. F., Lane, A., Ameziane, N., Bahassi, E. M., Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K. A., de Alarcon, A., Smith, D. F., & Wells, S. I. (2021). Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Viruses, 13(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010068