An Importin-β-like Protein from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the RNA Silencing Suppressor P1b of the Cucumber Vein Yellowing Virus, Modulating Its Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Agroinfiltration
2.3. SIIIP1b Purification
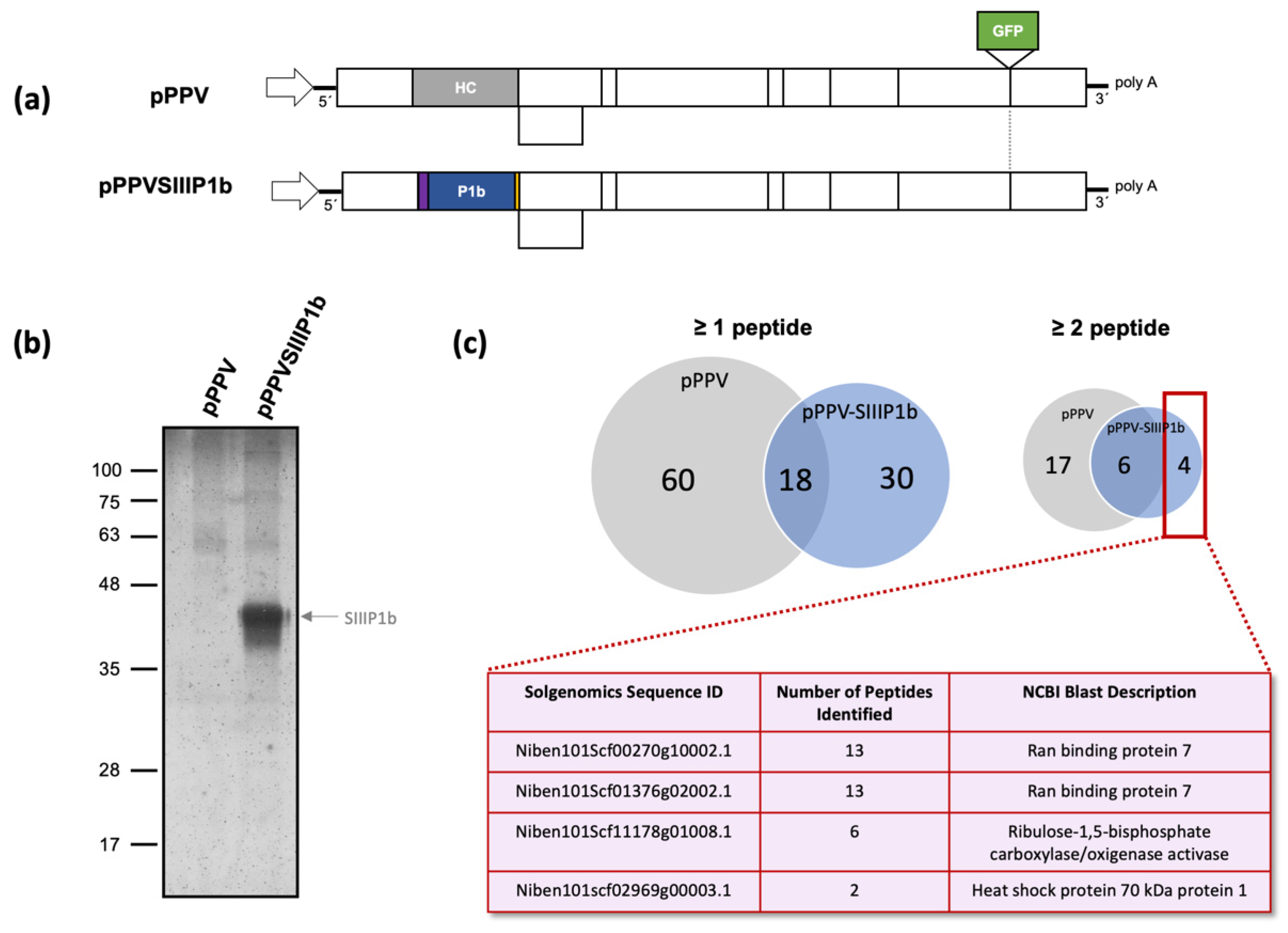
2.4. Mass Spectrometry Analyses
2.5. Image Analyses
2.6. Fluorescence Analysis
2.7. RT-PCR and -qPCR
3. Results
3.1. P1b Interacts with and Importin-β-Like Protein of Nicotiana benthamiana during Viral Infection
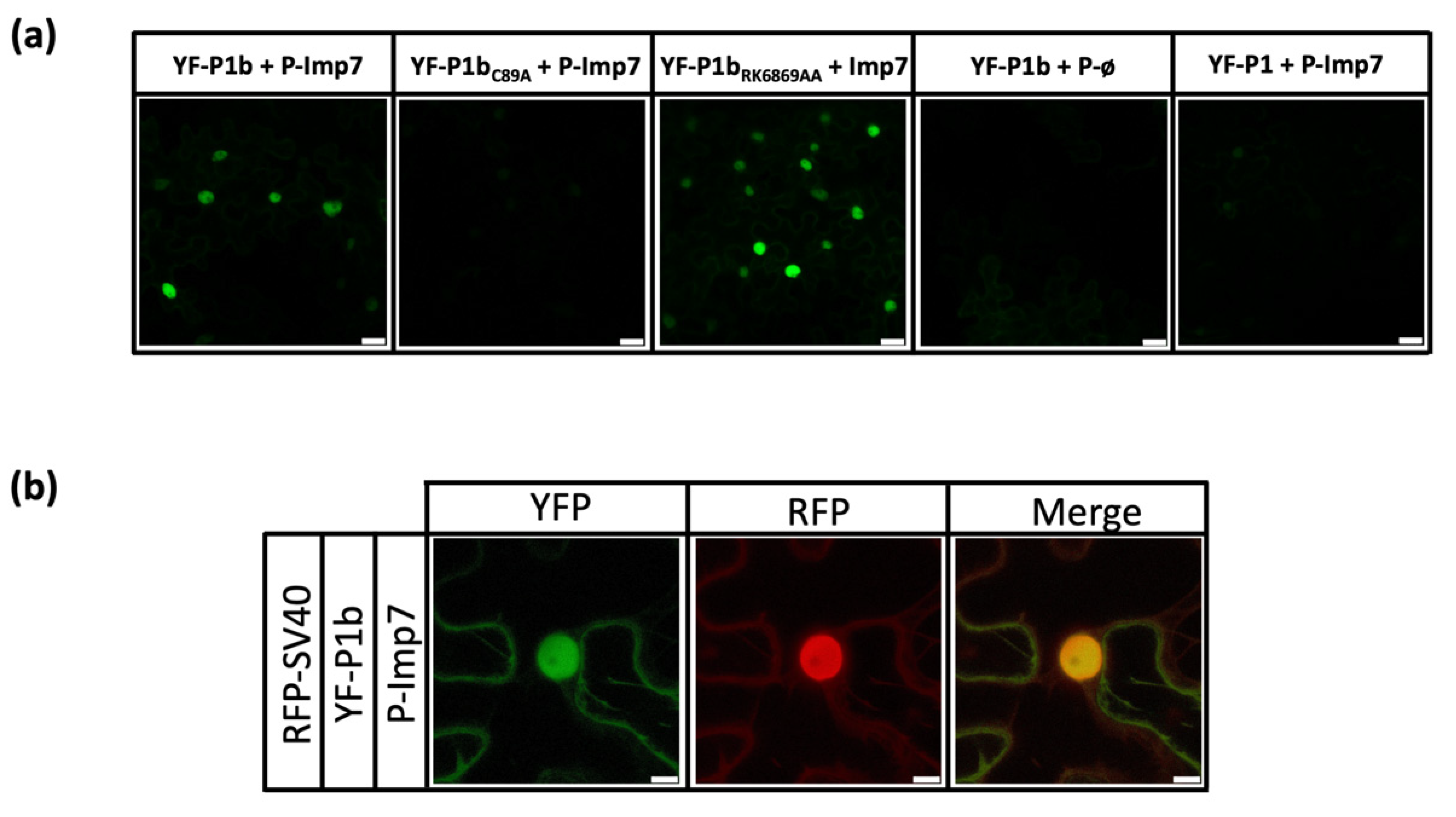
3.2. Interaction between NbImp7 and P1b Occurs in the Nucleus of the Cell, Depends on a Correct Folding of P1b, but Is Independent of Its Ability to Bind siRNA
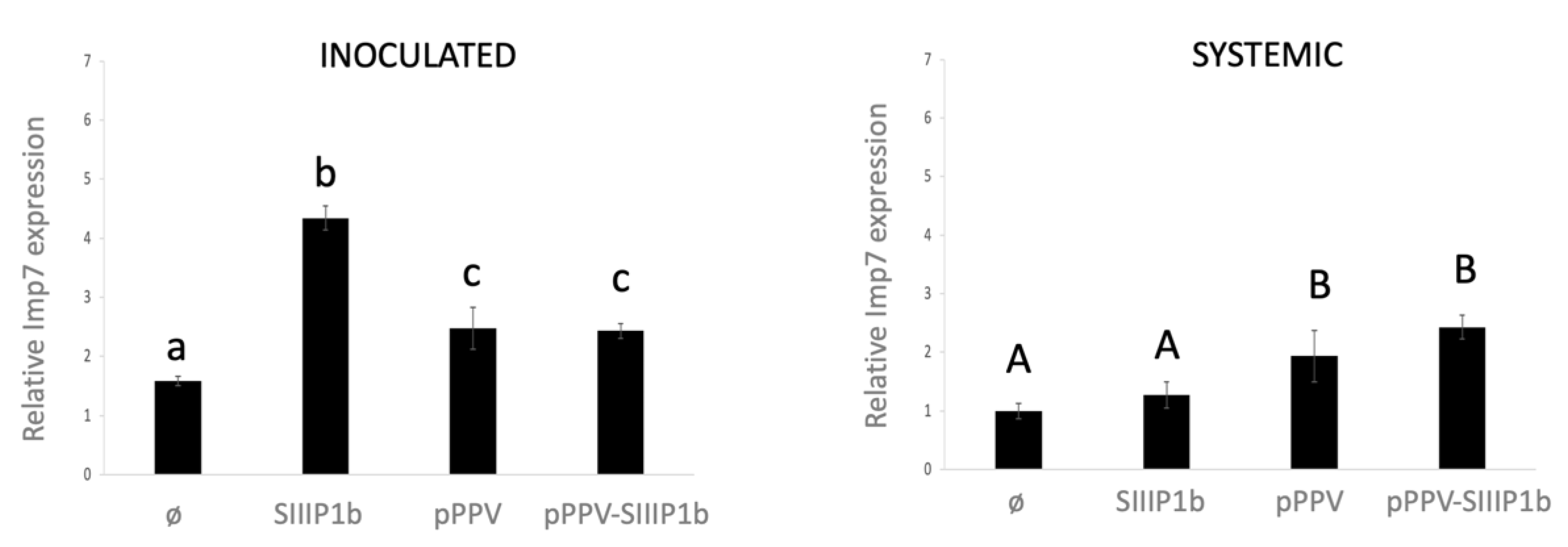
3.3. NbImp7 Is Overexpressed in the Plant after P1b Expression and during a Viral Infection
3.4. Expression of NbImp7 Interferes with P1b Ability to Suppress RNA Silencing
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Ruiz, H. Host factors against plant viruses. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1588–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; García, J.A. Molecular Plant-Plum Pox Virus Interactions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A. Dissecting the molecular network of virus-plant interactions: The complex roles of host factors. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollari, M.; De, S.; Wang, A.; Mäkinen, K. The potyviral silencing suppressor HCPro recruits and employs host ARGONAUTE1 in pro-viral functions. PLoS Path. 2020, 16, e1008965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.J.; Tadamura, K.; Murakami, T.; Inaba, J.I.; Kim, B.M.; Sato, M.; Atsumi, G.; Kuchitsu, K.; Masuta, C.; Nakahara, K.S. Rgs-CaM Detects and Counteracts Viral RNA Silencing Suppressors in Plant Immune Priming. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00761-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLeish, M.J.; Fraile, A.; García-Arenal, F. Evolution of plant-virus interactions: Host range and virus emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csorba, T.; Kontra, L.; Burgyán, J. Viral silencing suppressors: Tools forged to fine-tune host-pathogen coexistence. Virology 2015, 479–480, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mingot, A.; Valli, A.; Rodamilans, B.; San León, D.; Baulcombe, D.C.; García, J.A.; López-Moya, J.J. The P1N-PISPO trans-Frame Gene of Sweet Potato Feathery Mottle Potyvirus Is Produced during Virus Infection and Functions as an RNA Silencing Suppressor. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3543–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.H.; Hua, C.L.; Fang, Y.Y.; Guo, H.S. The dual edge of RNA silencing suppressors in the virus-host interactions. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revers, F.; García, J.A. Molecular biology of potyviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2015, 92, 101–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Hendrickson, R.C.; et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and the Statutes ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, A. Research Advances in Potyviruses: From the Laboratory Bench to the Field. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.S.; Sanfacon, H. Expanding Repertoire of Plant Positive-Strand RNA Virus Proteases. Viruses 2019, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodamilans, B.; Shan, H.; Pasin, F.; Garcia, J.A. Plant Viral Proteases: Beyond the Role of Peptide Cutters. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, B.Y.; Miller, W.A.; Atkins, J.F.; Firth, A.E. An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olspert, A.; Chung, B.Y.; Atkins, J.F.; Carr, J.P.; Firth, A.E. Transcriptional slippage in the positive-sense RNA virus family Potyviridae. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; Mingot, A.; San León, D.; Baulcombe, D.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. RNA polymerase slippage as a mechanism for the production of frameshift gene products in plant viruses of the Potyviridae family. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6965–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, C.; Hong, J.; Xiong, R.; Kasschau, K.D.; Zhou, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Wang, A. Formation of complexes at plasmodesmata for potyvirus intercellular movement is mediated by the viral protein P3N-PIPO. PLoS Path. 2010, 6, e1000962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, R.H.; Hajimorad, M.R. Mutational analysis of the putative pipo of soybean mosaic virus suggests disruption of PIPO protein impedes movement. Virology 2010, 400, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajamäki, M.L.; Streng, J.; Valkonen, J.P. Silencing suppressor protein VPg of a potyvirus interacts with the plant silencing-related protein SGS3. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, A. The potyvirus silencing suppressor protein VPg mediates degradation of SGS3 via ubiquitination and autophagy pathways. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodamilans, B.; Casillas, A.; García, J.A. P1 of Sweet Potato Feathery Mottle Virus Shows Strong Adaptation Capacity, Replacing P1-HCPro in a Chimeric Plum Pox Virus. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0015021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untiveros, M.; Olspert, A.; Artola, K.; Firth, A.E.; Kreuze, J.F.; Valkonen, J.P. A novel sweet potato potyvirus ORF is expressed via polymerase slippage and suppresses RNA silencing. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valli, A.A.; Gallo, A.; Rodamilans, B.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. The HCPro from the Potyviridae family: An enviable multitasking Helper Component that every virus would like to have. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 19, 744–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, S.; Pollari, M.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Association of host protein VARICOSE with HCPro within a multiprotein complex is crucial for RNA silencing suppression, translation, encapsidation and systemic spread of potato virus A infection. PLoS Path. 2020, 16, e1008956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Qiu, L.; Huang, W.; Xu, Q.; Zou, J.; Peng, Q.; Lin, H.; Xi, D. Chilli veinal mottle virus HCPro interacts with catalase to facilitate virus infection in Nicotiana tabacum. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5656–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanzibwa, D.R.; Tian, Y.; Mukasa, S.B.; Valkonen, J.P. Cassava brown streak virus (Potyviridae) encodes a putative Maf/HAM1 pyrophosphatase implicated in reduction of mutations and a P1 proteinase that suppresses RNA silencing but contains no HC-Pro. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6934–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, B.A.; Stenger, D.C.; Qu, F.; Morris, T.J.; Tatineni, S.; French, R. Tritimovirus P1 functions as a suppressor of RNA silencing and an enhancer of disease symptoms. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tatineni, S.; Qu, F.; Li, R.; Morris, T.J.; French, R. Triticum mosaic poacevirus enlists P1 rather than HC-Pro to suppress RNA silencing-mediated host defense. Virology 2012, 433, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caciagli, P.; Janssen, D.; Louro, D.; Vaira, A.M.; Winter, S. Cucumber vein yellowing virus (Ipomovirus). EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Valli, A.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. Recombination and gene duplication in the evolutionary diversification of P1 proteins in the family Potyviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Pasin, F.; Tzanetakis, I.E.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A.; Rodamilans, B. Truncation of a P1 leader proteinase facilitates potyvirus replication in a non-permissive host. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 19, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, H.; Pasin, F.; Valli, A.; Castillo, C.; Rajulu, C.; Carbonell, A.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A.; Rodamilans, B. The Potyviridae P1a leader protease contributes to host range specificity. Virology 2015, 476, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valli, A.; Martín-Hernández, A.M.; López-Moya, J.J.; García, J.A. RNA silencing suppression by a second copy of the P1 serine protease of Cucumber vein yellowing ipomovirus, a member of the family Potyviridae that lacks the cysteine protease HCPro. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10055–10063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valli, A.; Dujovny, G.; Garcia, J.A. Protease activity, self interaction, and small interfering RNA binding of the silencing suppressor p1b from cucumber vein yellowing ipomovirus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valli, A.; Oliveros, J.C.; Molnar, A.; Baulcombe, D.; García, J.A. The specific binding to 21-nt double-stranded RNAs is crucial for the anti-silencing activity of Cucumber vein yellowing virus P1b and perturbs endogenous small RNA populations. RNA 2011, 17, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.K.; Tatineni, S. Wheat streak mosaic virus P1 binds to dsRNAs without size and sequence specificity and a GW Motif Is crucial for suppression of RNA silencing. Viruses 2019, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.K.; Tatineni, S. RNA silencing suppression mechanisms of Triticum mosaic virus P1: dsRNA binding property and mapping functional motifs. Virus Res. 2019, 269, 197640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Sun, S.; Damaj, M.; Fu, H.; Gao, S. Diverse conserved domains and a positively selected site in the sugarcane streak mosaic virus P1 protein are essential for RNA silencing suppression and protein stability. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.; Valli, A.; Martín-Trillo, M.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A.; Rodamilans, B. Sterol isomerase HYDRA1 interacts with RNA silencing suppressor P1b and restricts potyviral infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.I.; Eskelin, K.; Basic, M.; De, S.; Lohmus, A.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. Molecular insights into the function of the viral RNA silencing suppressor HCPro. Plant J. 2016, 85, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, X.; Guo, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Gong, Z.; Schumaker, K.S.; Guo, Y. SAD2, an importin -like protein, is required for UV-B response in Arabidopsis by mediating MYB4 nuclear trafficking. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3805–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verslues, P.E.; Guo, Y.; Dong, C.H.; Ma, W.; Zhu, J.K. Mutation of SAD2, an importin beta-domain protein in Arabidopsis, alters abscisic acid sensitivity. Plant J. 2006, 47, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, R.; Xin, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, C.; Shi, H.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Y. An importin beta protein negatively regulates MicroRNA activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3565–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodamilans, B.; Valli, A.; Mingot, A.; San Leon, D.; Lopez-Moya, J.J.; Garcia, J.A. An atypical RNA silencing suppression strategy provides a snapshot of the evolution of sweet potato-infecting potyviruses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. A simple, fast and efficient method for cloning blunt DNA fragments. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 4094–4097. [Google Scholar]
- Azimzadeh, J.; Nacry, P.; Christodoulidou, A.; Drevensek, S.; Camilleri, C.; Amiour, N.; Parcy, F.; Pastuglia, M.; Bouchez, D. Arabidopsis TONNEAU1 proteins are essential for preprophase band formation and interact with centrin. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Kawamukai, M.; Koizumi, N.; Nakagawa, T. Development of a series of gateway binary vectors possessing a tunicamycin resistance gene as a marker for the transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Soriano, M.; Pallás, V.; Navarro, J.A. A model for transport of a viral membrane protein through the early secretory pathway: Minimal sequence and endoplasmic reticulum lateral mobility requirements. Plant J. 2014, 77, 863–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, M.T.; Voinnet, O.; Baulcombe, D.C. Initiation and maintenance of virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, F.; Bedoya, L.C.; Bernabé-Orts, J.M.; Gallo, A.; Simón-Mateo, C.; Orzaez, D.; García, J.A. Multiple T-DNA delivery to plants using novel mini binary vectors with compatible replication origins. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 1962–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, K.I.; Basic, M.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. One-step purification of twin-strep-tagged proteins and their complexes on strep-tactin resin cross-linked with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate (BS3). J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 86, 51536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, F.; Kulasekaran, S.; Natale, P.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A. Rapid fluorescent reporter quantification by leaf disc analysis and its application in plant-virus studies. Plant Methods 2014, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koressaar, T.; Lepamets, M.; Kaplinski, L.; Raime, K.; Andreson, R.; Remm, M. Primer3_masker: Integrating masking of template sequence with primer design software. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shi, L.; Han, C.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in virus-infected Nicotiana benthamiana using quantitative real-time PCR. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, A.; Dujovny, G.; García, J.A.; Valli, A. The Cucumber vein yellowing virus silencing suppressor P1b can functionally replace HCPro in Plum pox virus infection in a host-specific manner. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maliogka, V.I.; Calvo, M.; Carbonell, A.; García, J.A.; Valli, A. Heterologous RNA-silencing suppressors from both plant- and animal-infecting viruses support plum pox virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukao, Y. Protein-protein interactions in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.F.; Wei, W.L.; Hong, S.F.; Fang, R.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, P.C.; Sanobar, N.; Wang, H.P.; Sulistio, M.; Wu, C.T.; et al. Investigation of the effects of P1 on HC-pro-mediated gene silencing suppression through genetics and omics approaches. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohozková, J.; Sebela, M.; Nvrátil, M. P1 peptidase of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus contains non-canonical C2H2 zinc finger and may act in a truncated form. J. Plant Mol. Breed. 2014, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardo, L.G.; de Souza, G.B.; Alves, M.S. Trnascriptomics of plant-virus interactions: A review. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2019, 31, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, A.; Lakatos, L.; García-Chapa, M.; López-Moya, J.J.; Burgyan, J. Viral protein inhibits RISC activity by argonaute binding through conserved WG/GW motifs. PLoS Path. 2010, 6, e1000996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayers, C.N.; Palukaitis, P.; Carr, J.P. Subcellular distribution analysis of the cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81 Pt 1, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, S.; Soler, N.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.; Fagoaga, C.; López, C.; Navarro, L.; Moreno, P.; Peña, L.; Flores, R. Citrus tristeza virus p23: Determinants for nucleolar localization and their influence on suppression of RNA silencing and pathogenesis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, S.; Men, S.; Kang, Z.; Hong, J.; Wei, C.; Hong, W.; Li, Y. A non-structural protein encoded by Rice Dwarf Virus targets to the nucleus and chloroplast and inhibits local RNA silencing. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, G.; Azevedo, J.; Moissiard, G.; Geldreich, A.; Himber, C.; Bureau, M.; Fukuhara, T.; Keller, M.; Voinnet, O. Nuclear import of CaMV P6 is required for infection and suppression of the RNA silencing factor DRB4. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2591–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, F.; Daros, J.A. Tobacco etch virus protein P1 traffics to the nucleolus and associates with the host 60S ribosomal subunits during infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10725–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahara, K.S.; Masuta, C.; Yamada, S.; Shimura, H.; Kashihara, Y.; Wada, T.S.; Meguro, A.; Goto, K.; Tadamura, K.; Sueda, K.; et al. Tobacco calmodulin-like protein provides secondary defense by binding to and directing degradation of virus RNA silencing suppressors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10113–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brodersen, P.; Sakvarelidze-Achard, L.; Bruun-Rasmussen, M.; Dunoyer, P.; Yamamoto, Y.Y.; Sieburth, L.; Voinnet, O. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 2008, 320, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, B.; Sanfacon, H. Temperature-dependent symptom recovery in Nicotiana benthamiana plants infected with tomato ringspot virus is associated with reduced translation of viral RNA2 and requires ARGONAUTE 1. Virology 2014, 456, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasin, F.; Simón-Mateo, C.; García, J.A. The hypervariable amino-terminus of P1 protease modulates potyviral replication and host defense responses. PLoS Path. 2014, 10, e1003985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Barcelo, C.; Darós, J.A.; Elena, S.F. Compensatory molecular evolution of HC-Pro, an RNA-silencing suppressor from a plant RNA virus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, B.; Bedoya, L.; García, J.A.; Rodamilans, B. An Importin-β-like Protein from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the RNA Silencing Suppressor P1b of the Cucumber Vein Yellowing Virus, Modulating Its Activity. Viruses 2021, 13, 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122406
García B, Bedoya L, García JA, Rodamilans B. An Importin-β-like Protein from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the RNA Silencing Suppressor P1b of the Cucumber Vein Yellowing Virus, Modulating Its Activity. Viruses. 2021; 13(12):2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122406
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Beatriz, Leonor Bedoya, Juan Antonio García, and Bernardo Rodamilans. 2021. "An Importin-β-like Protein from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the RNA Silencing Suppressor P1b of the Cucumber Vein Yellowing Virus, Modulating Its Activity" Viruses 13, no. 12: 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122406
APA StyleGarcía, B., Bedoya, L., García, J. A., & Rodamilans, B. (2021). An Importin-β-like Protein from Nicotiana benthamiana Interacts with the RNA Silencing Suppressor P1b of the Cucumber Vein Yellowing Virus, Modulating Its Activity. Viruses, 13(12), 2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13122406





