Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and Its Endolysin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Bacteriophage Isolation and Purification
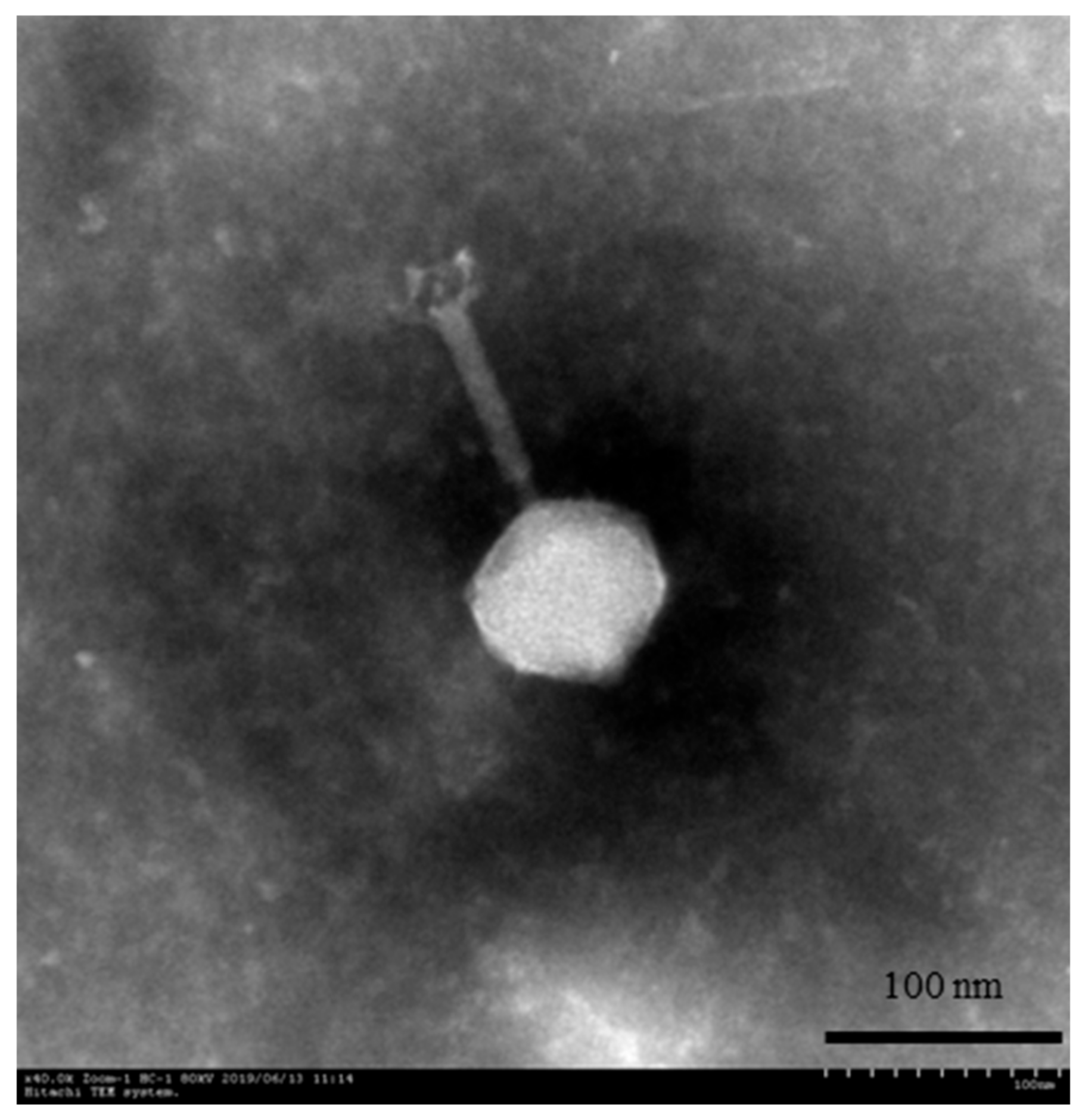
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Determination of the Host Range
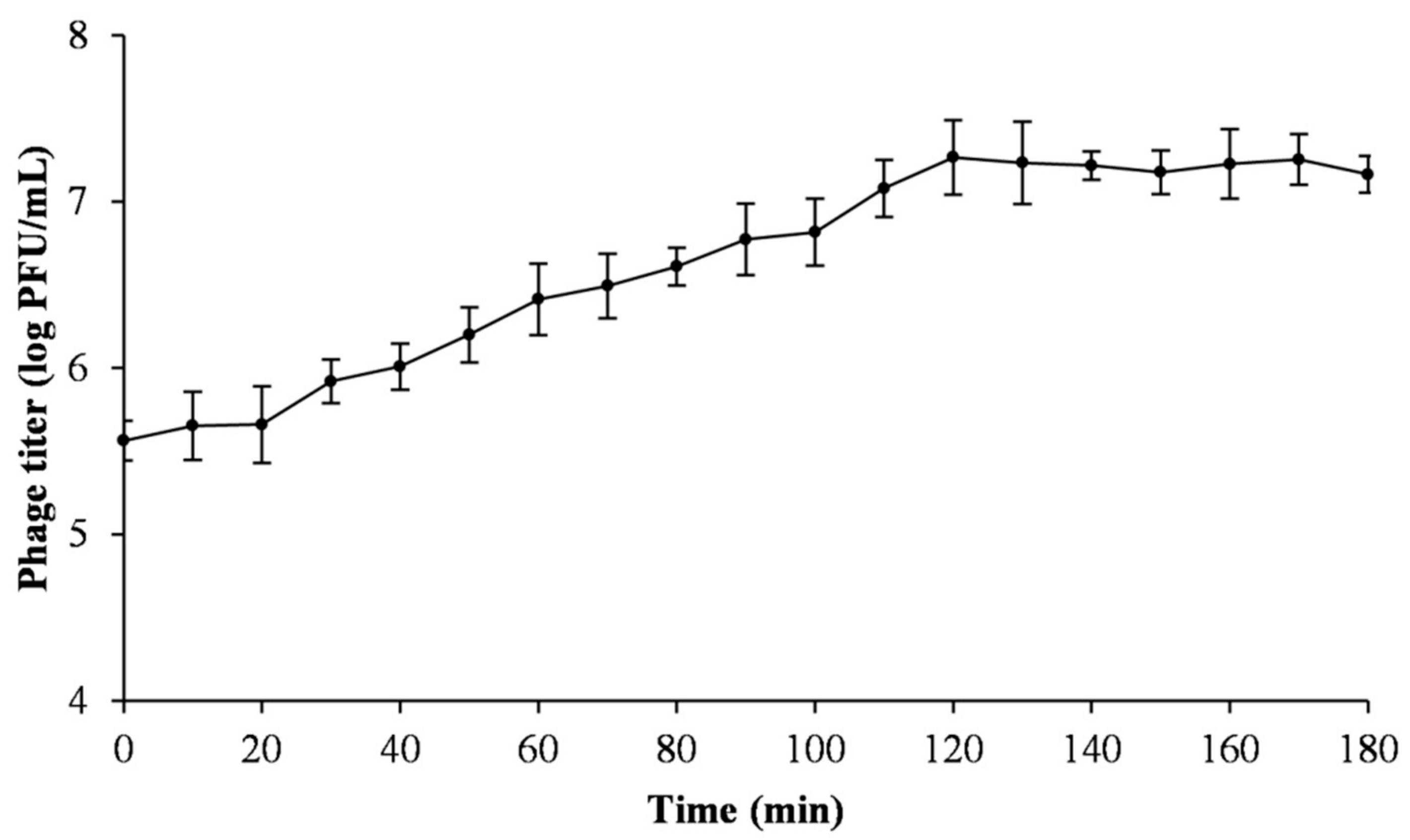
2.5. One-Step Growth Curve
2.6. Phage Stability
2.7. Bacteriophage DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
2.9. Identification, Cloning, Expression, and Purification of the Endolysin LysPN09 from Phage PN09
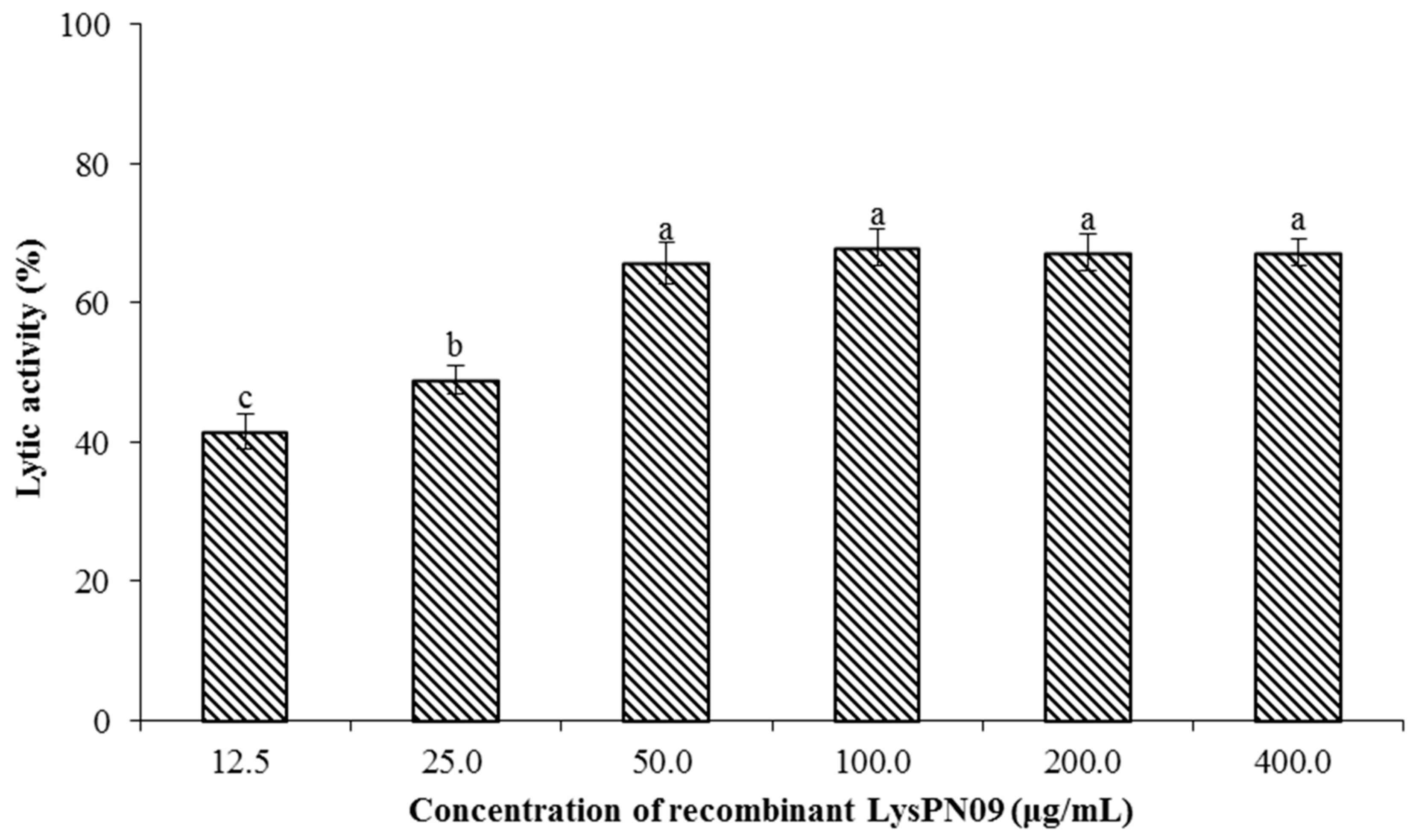
2.10. Antibacterial Activity and Lytic Spectrum of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09
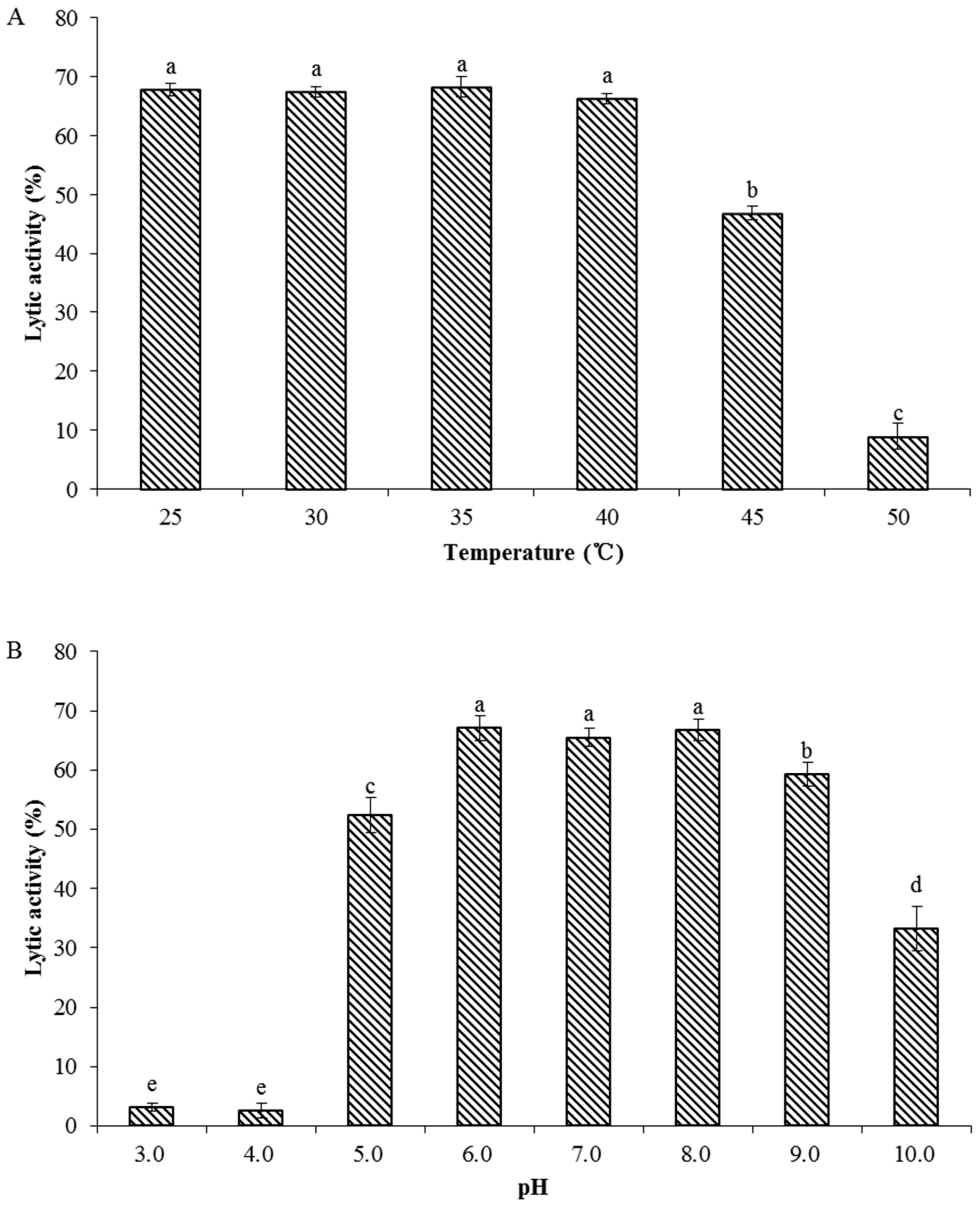
2.11. Biochemical Characterization of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09
2.12. Antibacterial Activity of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09 in Combination with EDTA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phage Morphology
3.2. Host Range of the Bacteriophage PN09
3.3. One-Step Growth Curve
3.4. Phage Stability
3.5. Genome Analysis of Phage PN09
3.6. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of LysPN09
3.7. Antibacterial Activity and Lytic Spectrum of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09
3.8. Biochemical Characterization of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09
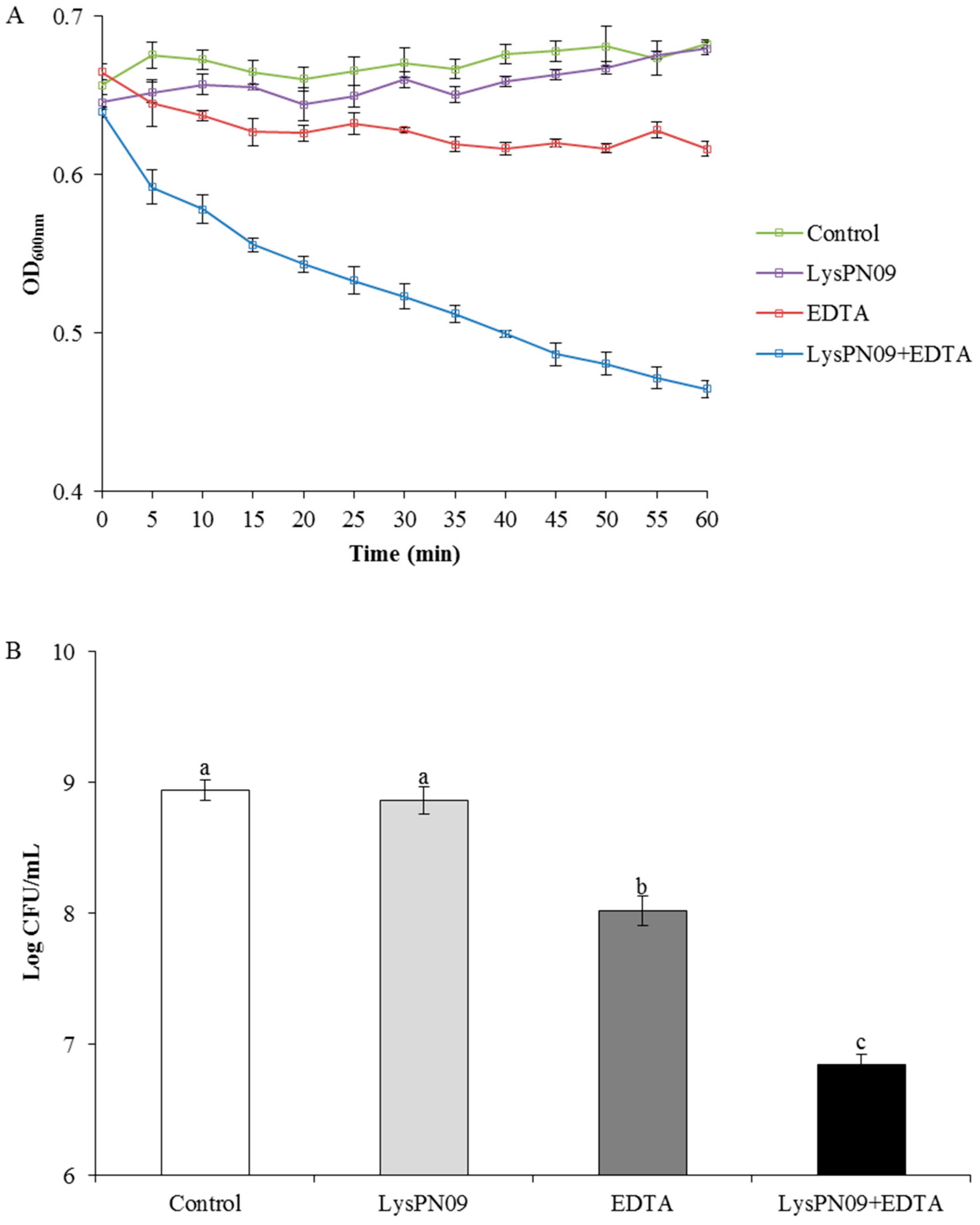
3.9. Antibacterial Activity of Recombinant Endolysin LysPN09 in Combination with EDTA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donati, I.; Cellini, A.; Buriani, G.; Mauri, S.; Kay, C.; Tacconi, G.; Spinelli, F. Pathways of flower infection and pollen-mediated dispersion of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae, the causal agent of kiwifruit bacterial canker. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.; Jung, J.; Hur, J. Current status of occurrence of major diseases on kiwifruits and their control in Korea. Acta Hortic. 2003, 610, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, Y.; Serizawa, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Tsuyumu, S.; Goto, M. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae pv. nov.: The causal bacterium of canker of kiwifruit in Japan. JPN J. Phytopathol. 1989, 55, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y. Outbreak and spread of bacterial canker in kiwifruit. J. Plant Pathol. 1994, 10, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Scortichini, M. Occurrence of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae on kiwifruit in Italy. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, G.; Renzi, M.; Mazzaglia, A. First report of bacterial canker ofActinidia deliciosacaused byPseudomonas syringaepv.actinidiaein Portugal. New Dis. Rep. 2010, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneste, J.L.; Poliakoff, F.; Audusseau, C.; Cornish, D.A.; Paillard, S.; Rivoal, C.; Yu, J. First Report of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae, the Causal Agent of Bacterial Canker of Kiwifruit in France. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwiartama, A. Resilience and transformation of the New Zealand kiwifruit industry in the face of Psa-V disease. J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 52, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, J.-E.; Jiang, Y.P.; Wang, R.L.; Wu, R.S. Predicting the potential distribution of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae in China using ensemble models. Plant Pathol. 2019, 69, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, T.; Sawada, H. Genome analysis of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae biovar 6, which produces the phytotoxins, phaseolotoxin and coronatine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, H.C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, H.; Zhong, C.; Rikkerink, E.H.; Templeton, M.D.; Straub, C.; Colombi, E.; et al. Origin and Evolution of the Kiwifruit Canker Pandemic. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Comprehensive prevention and control of kiwifruit canker disease. Fruit Grow. Friend. 2015, 10, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.; Sarojini, V. Pseudomonas syringaepv.actinidiae: Chemical control, resistance mechanisms and possible alternatives. Plant Pathol. 2013, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lallo, G.; Evangelisti, M.; Mancuso, F.; Ferrante, P.; Marcelletti, S.; Tinari, A.; Superti, F.; Migliore, L.; D’Addabbo, P.; Frezza, D.; et al. Isolation and partial characterization of bacteriophages infectingPseudomonas syringaepv.actinidiae, causal agent of kiwifruit bacterial canker. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twort, F. An investigation on the nature of ultra-microscopic viruses. Lancet 1915, 186, 1241–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüssow, H. What is needed for phage therapy to become a reality in Western medicine? Virology 2012, 434, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, R.A.; Pitman, A.R.; Fineran, P.C. Advances in Bacteriophage-Mediated Control of Plant Pathogens. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, R.A.; Taylor, C.; Moreno, A.V.H.; Visnovsky, S.B.; Petty, N.K.; Pitman, A.R.; Fineran, P.C. Identification of Bacteriophages for Biocontrol of the Kiwifruit Canker Phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2216–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.A.M.; Pereira, C.; Barreal, M.E.; Gallego, P.P.; Balcão, V.M.; Almeida, A. Use of phage ϕ6 to inactivate Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae in kiwifruit plants: In vitro and ex vivo experiments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstmans, H.; Criel, B.; Briers, Y. Synthetic biology of modular endolysins. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 624–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hu, K.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mu, D.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, D.; Shi, Y. A Novel Phage PD-6A3, and Its Endolysin Ply6A3, With Extended Lytic Activity against Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. An Endolysin LysSE24 by Bacteriophage LPSE1 Confers Specific Bactericidal Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Strains. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.C.B.; Chen, X.; Ho, M.K.Y.; Xia, J.; Leung, S.S.Y. Bacteriophage-derived endolysins to target gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briers, Y.; Walmagh, M.; Lavigne, R. Use of bacteriophage endolysin EL188 and outer membrane permeabilizers against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Rubio, L.; Gerstmans, H.; Thorpe, S.; Mesnage, S.; Lavigne, R.; Briers, Y. DUF3380 Domain from a Salmonella Phage Endolysin Shows PotentN-Acetylmuramidase Activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4975–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Ni, P.; Deng, B.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, D. Isolation and characterisation of phages against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Plant Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ni, P.; Liu, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Tian, P.; Shi, X.; Wang, D. A Bacterial Surface Display System Expressing Cleavable Capsid Proteins of Human Norovirus: A Novel System to Discover Candidate Receptors. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoulinskaia, G.V.; Odinokova, I.V.; Zimin, A.A.; Lysanskaya, V.Y.; Feofanov, S.A.; Stepnaya, O.A. Identification and characterization of the metal ion-dependent l-alanoyl-d-glutamate peptidase encoded by bacteriophage T5. TFEBS J. 2009, 276, 7329–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; King, A.M.Q.; Harrach, B.; Harrison, R.L.; Knowles, N.J.; Kropinski, A.M.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; Mushegian, A.R.; et al. Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2016). Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2921–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Rao, X.; Hu, F.; Lu, S. Characterization and Genomic Analyses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Podovirus TC6: Establishment of Genus Pa11virus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y. Biocontrol Potential of a Lytic Bacteriophage PE204 against Bacterial Wilt of Tomato. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasiah, S.; Bhavsar, J.; Thapar, K.; Liles, M.; Schoenfeld, T.; Wommack, K.E. Phages across the biosphere: Contrasts of viruses in soil and aquatic environments. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, H.S.; Kim, G.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Koh, Y.J.; Jung, J.S. Molecular Characteristics of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae Strains Isolated in Korea and a Multiplex PCR Assay for Haplotype Differentiation. Plant Pathol. J. 2014, 30, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, X. Identification of novel bacteriophage vB_EcoP-EG1 with lytic activity against planktonic and biofilm forms of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, H.; Tremblay, D.; Moineau, S. Long-term bacteriophage preservation. WFCC Newslett. 2004, 38, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jończyk, E.; Kłak, M.; Międzybrodzki, R.; Górski, A. The influence of external factors on bacteriophages—Review. Folia Microbiol. 2011, 56, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relationship between the morphology of bacteriophages and their persistence in the environment. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 129–132. [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, S.; Volckaert, A.; Venneman, S.; Declercq, B.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Allonsius, C.N.; Van Malderghem, C.; Jang, H.B.; Briers, Y.; Noben, J.P.; et al. Characterization of Novel Bacteriophages for Biocontrol of Bacterial Blight in Leek Caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. porri. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, H.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Pang, M.; Sun, L.; Zhou, X. Application of a phage in decontaminating Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oysters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 275, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, R.A.; Acedo, E.L.; Young, V.L.; Chen, D.; Tong, B.; Taylor, C.; Easingwood, R.A.; Pitman, A.R.; Kleffmann, T.; Bostina, M.; et al. Genome, Proteome and Structure of a T7-Like Bacteriophage of the Kiwifruit Canker Phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. Viruses 2015, 7, 3361–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelcher, M.; Donovan, D.M.; Loessner, M.J. Bacteriophage endolysins as novel antimicrobials. Futur. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1147–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Feng, C.; Ren, J.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, K.; He, P.; Guo, X.; Qin, J. A Novel Antimicrobial Endolysin, LysPA26, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Characterization of Endolysin LysECP26 Derived from rV5-like Phage vB_EcoM-ECP26 for Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1552–1558. [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. | Species | Strain | Location | Source | Biovar | Host Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae | JH1401-1 | Shanghai | Hongyang | 3 | + |
| 2 | JH1401-2 | Shanghai | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 3 | JH1402-2 | Shanghai | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 4 | JH1402-4 | Shanghai | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 5 | JH1403-1-1 | Shanghai | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 6 | 4LH1402-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 7 | 4LH1403-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 8 | 4LH1404-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 9 | 4LH3401-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 10 | 4LH3402-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 11 | 8LH1401-1 | Zhejiang | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 12 | GX05 | Guizhou | Donghong | 3 | + | |
| 13 | BYJX-1 | Guizhou | Jinxia | 3 | + | |
| 14 | BYHJG | Guizhou | Hort-16A | 3 | + | |
| 15 | SCJY02-1 | Sichuan | Jinyan | 3 | + | |
| 16 | LH4-2 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 17 | LH1-2 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 18 | LSHY2-1 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 19 | LH3-2 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 20 | LH2-3 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 21 | LH5-2 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 22 | JSHY-4 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 23 | JSHY-6 | Sichuan | Hongyang | 3 | + | |
| 24 | LG1-1 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 25 | LG4-1 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 26 | LG1-3 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 27 | LG2-3 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 28 | LG4-3 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 29 | LG3-3 | Sichuan | Guichang | 3 | + | |
| 30 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ATCC17802 | − | |||
| 31 | Salmonella derby | 58 | − | |||
| 32 | Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC29213 | − | |||
| 33 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CMCC 10104 | − | |||
| 34 | Escherichia coli | BL21 (DE3) | − | |||
| 35 | DH5α | − |
| No. | Strain | Lytic Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JH1401-1 | 62.81.1 |
| 2 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JH1401-2 | 51.52.1 |
| 3 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JH1402-2 | 59.21.4 |
| 4 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JH1402-4 | 62.71.3 |
| 5 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JH1403-1-1 | 62.90.6 |
| 6 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 4LH1402-1 | 59.72.0 |
| 7 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 4LH1403-1 | 68.11.2 |
| 8 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 4LH1404-1 | 64.71.6 |
| 9 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 4LH3401-1 | 58.42.9 |
| 10 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 4LH3402-1 | 61.72.0 |
| 11 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae 8LH1401-1 | 55.62.2 |
| 12 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae GX05 | 67.21.1 |
| 13 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae BYJX-1 | 65.12.9 |
| 14 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae BYHJG | 57.02.1 |
| 15 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae SCJY02-1 | 64.70.4 |
| 16 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LH4-2 | 60.13.5 |
| 17 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LH1-2 | 59.13.1 |
| 18 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LSHY2-1 | 58.71.7 |
| 19 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LH3-2 | 66.40.7 |
| 20 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LH2-3 | 62.61.7 |
| 21 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LH5-2 | 64.61.3 |
| 22 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JSHY-4 | 55.31.4 |
| 23 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae JSHY-6 | 58.92.1 |
| 24 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG1-1 | 58.41.9 |
| 25 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG4-1 | 60.61.5 |
| 26 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG1-3 | 54.53.3 |
| 27 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG2-3 | 58.21.9 |
| 28 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG4-3 | 61.22.6 |
| 29 | Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae LG3-3 | 63.31.2 |
| 30 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus ATCC17802 | 1.21.1 |
| 31 | Salmonella derby 58 | −0.80.5 |
| 32 | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC29213 | −1.20.7 |
| 33 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa CMCC 10104 | 8.42.0 |
| 34 | Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) | 1.20.9 |
| 35 | Escherichia coli DH5α | 2.41.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, P.; Wang, L.; Deng, B.; Jiu, S.; Ma, C.; Zhang, C.; Almeida, A.; Wang, D.; Xu, W.; Wang, S. Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and Its Endolysin. Viruses 2021, 13, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040631
Ni P, Wang L, Deng B, Jiu S, Ma C, Zhang C, Almeida A, Wang D, Xu W, Wang S. Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and Its Endolysin. Viruses. 2021; 13(4):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040631
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Peien, Lei Wang, Bohan Deng, Songtao Jiu, Chao Ma, Caixi Zhang, Adelaide Almeida, Dapeng Wang, Wenping Xu, and Shiping Wang. 2021. "Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and Its Endolysin" Viruses 13, no. 4: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040631
APA StyleNi, P., Wang, L., Deng, B., Jiu, S., Ma, C., Zhang, C., Almeida, A., Wang, D., Xu, W., & Wang, S. (2021). Characterization of a Lytic Bacteriophage against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae and Its Endolysin. Viruses, 13(4), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13040631








