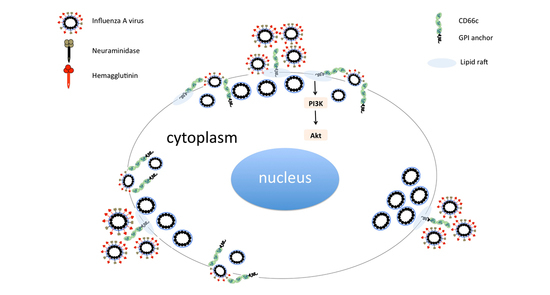
The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza A Virus
Abstract
Share and Cite
Rahman, S.K.; Ansari, M.A.; Gaur, P.; Ahmad, I.; Chakravarty, C.; Verma, D.K.; Sharma, A.; Chhibber, S.; Nehal, N.; Wirth, D.; et al. The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050726
Rahman SK, Ansari MA, Gaur P, Ahmad I, Chakravarty C, Verma DK, Sharma A, Chhibber S, Nehal N, Wirth D, et al. The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza A Virus. Viruses. 2021; 13(5):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050726
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Shah Kamranur, Mairaj Ahmed Ansari, Pratibha Gaur, Imtiyaz Ahmad, Chandrani Chakravarty, Dileep Kumar Verma, Anshika Sharma, Sanjay Chhibber, Naila Nehal, Dagmar Wirth, and et al. 2021. "The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza A Virus" Viruses 13, no. 5: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050726
APA StyleRahman, S. K., Ansari, M. A., Gaur, P., Ahmad, I., Chakravarty, C., Verma, D. K., Sharma, A., Chhibber, S., Nehal, N., Wirth, D., & Lal, S. K. (2021). The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza A Virus. Viruses, 13(5), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13050726