BHK-21 Cell Clones Differ in Chikungunya Virus Infection and MXRA8 Receptor Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Viruses
2.4. Plaque Assays
2.5. Infectious Center Assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Electroporation Efficiency
2.8. RT-PCR and Quantitative PCR
2.9. Rescue Experiments
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
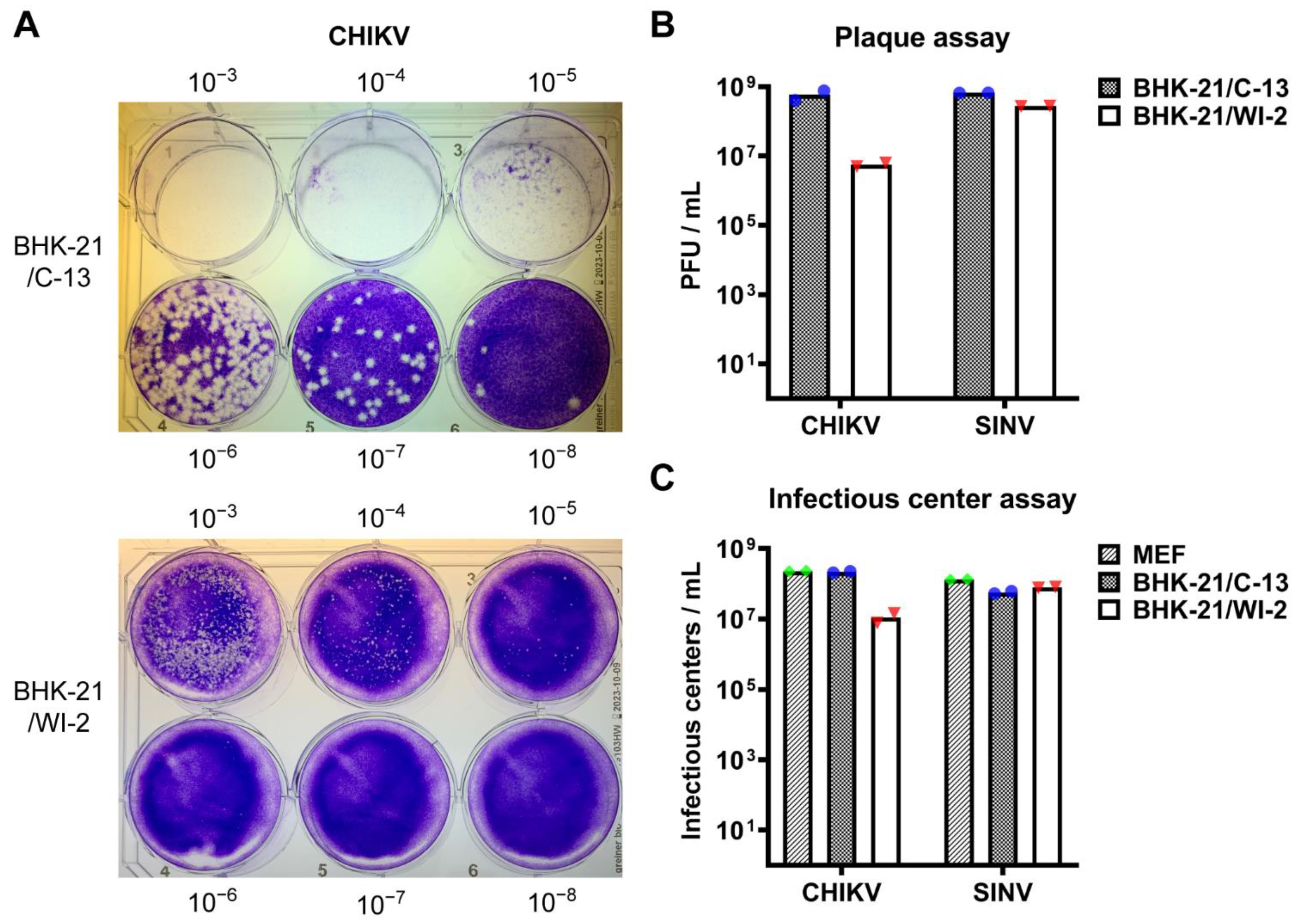
3.1. BHK-21/WI-2 Cells Are Less Susceptible to CHIKV Than Are BHK-21/C-13 Cells
3.2. Electroporation Efficiency of Alphavirus RNA into BHK-21/WI-2 and BHK-21/C-13 Cells
3.3. Expression of MXRA8 RNA in BHK-21/WI-2 and BHK-21/C-13 Cells
3.4. Exogenous Expression of Either Human MXRA8 or Hamster MXRA8 Rescues CHIKV Infection of BHK-21/WI-2 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, A.M.; Brault, A.C.; Shirako, Y.; Strauss, E.G.; Kang, W.; Strauss, J.H.; Weaver, S.C. Evolutionary relationships and systematics of the alphaviruses. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10118–10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, R.J. Togaviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication. In Fields Virology: Emerging Viruses, 7th ed.; Howley, P.M., Knipe, D.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 170–193. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.A.; Dermody, T.S. Chikungunya virus: Epidemiology, replication, disease mechanisms, and prospective intervention strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mason, P.J.; Haddow, A.J. An epidemic of virus disease in Southern Province, Tanganyika Territory, in 1952-53; an additional note on Chikungunya virus isolations and serum antibodies. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 51, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Winegar, R.; Manger, I.D.; Forrester, N.L. Alphaviruses: Population genetics and determinants of emergence. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enserink, M. Infectious diseases. Chikungunya: No longer a third world disease. Science 2007, 318, 1860–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, O.; Albert, M.L. Biology and pathogenesis of chikungunya virus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazeille, M.; Moutailler, S.; Coudrier, D.; Rousseaux, C.; Khun, H.; Huerre, M.; Thiria, J.; Dehecq, J.S.; Fontenille, D.; Schuffenecker, I.; et al. Two Chikungunya Isolates from the Outbreak of La Reunion (Indian Ocean) Exhibit Different Patterns of Infection in the Mosquito, Aedes albopictus. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.A. Chikungunya on the move. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, T.E. Reemergence of chikungunya virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11644–11647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, R.S.; Wan, J.J.; Kielian, M. The Alphavirus Exit Pathway: What We Know and What We Wish We Knew. Viruses 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, A.C.; Basore, K.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. A molecular understanding of alphavirus entry. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielian, M. Mechanisms of Virus Membrane Fusion Proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kielian, M.; Chanel-Vos, C.; Liao, M. Alphavirus entry and membrane fusion. Viruses 2010, 2, 796–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Kim, A.S.; Fox, J.M.; Nair, S.; Basore, K.; Klimstra, W.B.; Rimkunas, R.; Fong, R.H.; Lin, H.; Poddar, S.; et al. Mxra8 is a receptor for multiple arthritogenic alphaviruses. Nature 2018, 557, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basore, K.; Kim, A.S.; Nelson, C.A.; Zhang, R.; Smith, B.K.; Uranga, C.; Vang, L.; Cheng, M.; Gross, M.L.; Smith, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of Chikungunya Virus in Complex with the Mxra8 Receptor. Cell 2019, 177, 1725–1737.e1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhao, Z.; Chai, Y.; Jin, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, F.; Liu, S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; et al. Molecular Basis of Arthritogenic Alphavirus Receptor MXRA8 Binding to Chikungunya Virus Envelope Protein. Cell 2019, 177, 1714–1724.e1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Earnest, J.T.; Kim, A.S.; Winkler, E.S.; Desai, P.; Adams, L.J.; Hu, G.; Bullock, C.; Gold, B.; Cherry, S.; et al. Expression of the Mxra8 Receptor Promotes Alphavirus Infection and Pathogenesis in Mice and Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2647–2658.e2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, M.; Macpherson, I. Syrian Hamster Fibroblast Cell Line Bhk21 and Its Derivatives. Nature 1964, 203, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, B.T.; Faulkner, P. Altered pattern of viral RNA synthesis in cells infected with standard and defective Sindbis virus. Virology 1973, 51, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.R.; Mohamed Hussain, K.; Chu, J.J.H. Macropinocytosis dependent entry of Chikungunya virus into human muscle cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Hodge, H.M.; Campbell, W.E., Jr. Growth of chikungunya virus in baby hamster kidney cell (BHK-21-clone 13) suspension cultures. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 21, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaheri, A.; Sedwick, W.D.; Plotkin, S.A.; Maes, R. Cytopathic effect of rubella virus in RHK21 cells and growth to high titers in suspension culture. Virology 1965, 27, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, I.; Stoker, M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology 1962, 16, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt, M.A. Generation of VSV pseudotypes using recombinant DeltaG-VSV for studies on virus entry, identification of entry inhibitors, and immune responses to vaccines. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helenius, A.; Soderlund, H. Stepwise dissociation of the Semliki Forest Virus membrane with triton X-100. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 307, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaud, J.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Atasheva, S.; Rasalouskaya, A.; White, J.P.; Diamond, M.S.; Weaver, S.C.; Frolova, E.I.; Frolov, I. IFIT1 Differentially Interferes with Translation and Replication of Alphavirus Genomes and Promotes Induction of Type I Interferon. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardwick, J.M.; Levine, B. Sindbis virus vector system for functional analysis of apoptosis regulators. Meth. Enzym. 2000, 322, 492–508. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, W.J.; Gidwitz, S.; Ayers, V.K.; Schoepp, R.J.; Johnston, R.E. Conformational alteration of Sindbis virion glycoproteins induced by heat, reducing agents, or low pH. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3504–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liljestrom, P.; Lusa, S.; Huylebroeck, D.; Garoff, H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: The small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4107–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.S.; Zimmerman, O.; Fox, J.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Basore, K.; Zhang, R.; Durnell, L.; Desai, C.; Bullock, C.; Deem, S.L.; et al. An Evolutionary Insertion in the Mxra8 Receptor-Binding Site Confers Resistance to Alphavirus Infection and Pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 428–440.e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljestrom, P.; Garoff, H. A new generation of animal cell expression vectors based on the Semliki Forest virus replicon. Biotechnology 1991, 9, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Stillman, E.A.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses from DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayakar, H.R.; Murti, K.G.; Whitt, M.A. Mutations in the PPPY motif of vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein reduce virus budding by inhibiting a late step in virion release. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9818–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashem, A.M.; Algaissi, A.; Almahboub, S.A.; Alfaleh, M.A.; Abujamel, T.S.; Alamri, S.S.; Alluhaybi, K.A.; Hobani, H.I.; AlHarbi, R.H.; Alsulaiman, R.M.; et al. Early Humoral Response Correlates with Disease Severity and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2020, 12, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, T.; Lecuit, M. Focus on Chikungunya pathophysiology in human and animal models. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlen, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, A.; Kampf, C.; Sjostedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudeep, A.B.; Vyas, P.B.; Parashar, D.; Shil, P. Differential susceptibility & replication potential of Vero E6, BHK-21, RD, A-549, C6/36 cells & Aedes aegypti mosquitoes to three strains of chikungunya virus. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 771–777. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G.C.; Zothner, C.; Remenyi, R.; Merits, A.; Stonehouse, N.J.; Harris, M. Evaluation of a range of mammalian and mosquito cell lines for use in Chikungunya virus research. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, P.; Dowd, K.A.; Brien, J.D.; Edeling, M.A.; Gorlatov, S.; Johnson, S.; Lee, I.; Akahata, W.; Nabel, G.J.; Richter, M.K.; et al. Development of a highly protective combination monoclonal antibody therapy against Chikungunya virus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.; Kielian, M. BHK-21 Cell Clones Differ in Chikungunya Virus Infection and MXRA8 Receptor Expression. Viruses 2021, 13, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060949
Yin P, Kielian M. BHK-21 Cell Clones Differ in Chikungunya Virus Infection and MXRA8 Receptor Expression. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060949
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Peiqi, and Margaret Kielian. 2021. "BHK-21 Cell Clones Differ in Chikungunya Virus Infection and MXRA8 Receptor Expression" Viruses 13, no. 6: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060949
APA StyleYin, P., & Kielian, M. (2021). BHK-21 Cell Clones Differ in Chikungunya Virus Infection and MXRA8 Receptor Expression. Viruses, 13(6), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13060949






