Patient and Clinical Factors at Admission Affect the Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies Six Months after Recovering from COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
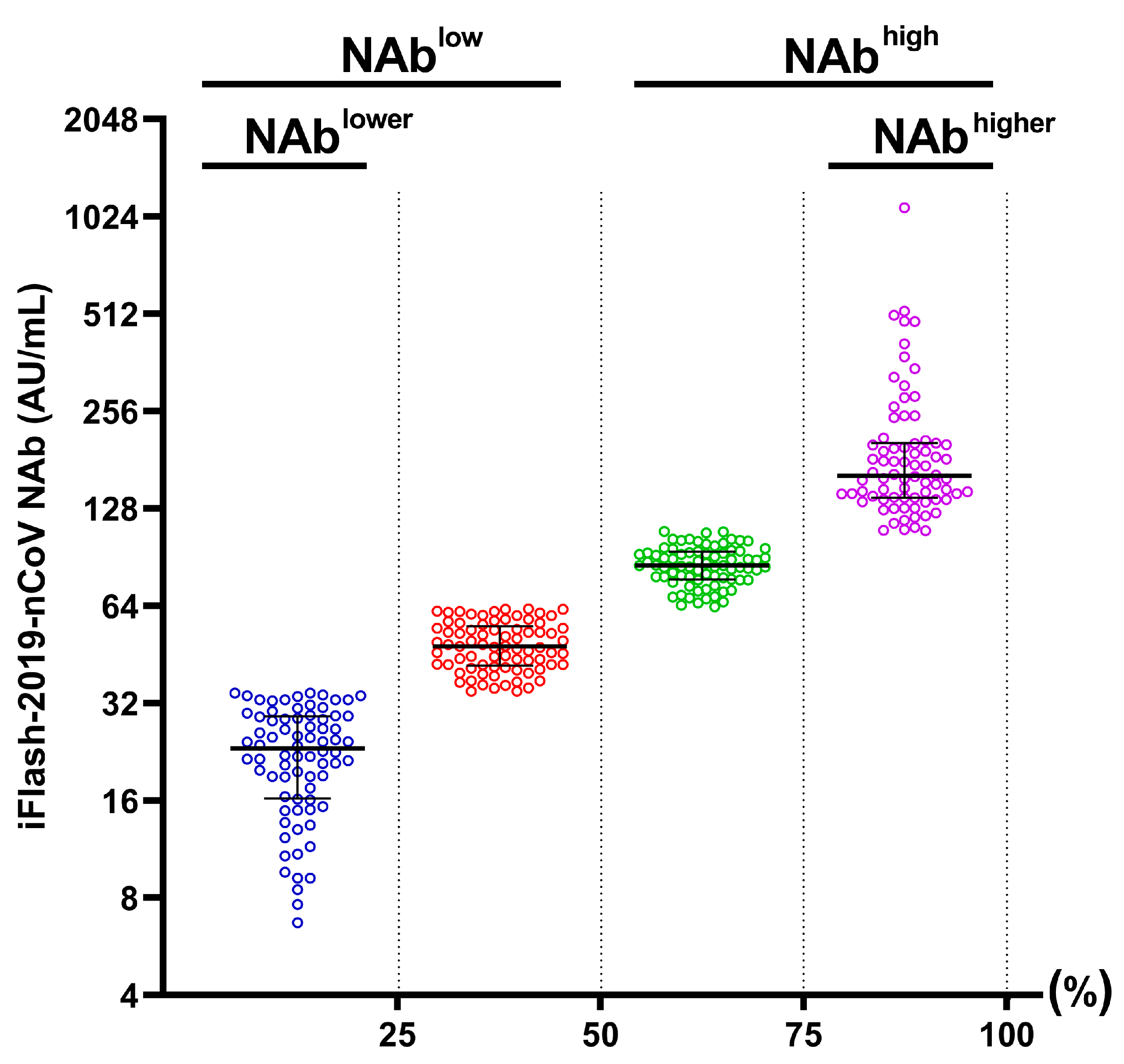
2.3. Classification of Patients
2.4. Neutralizing Antibody Assay
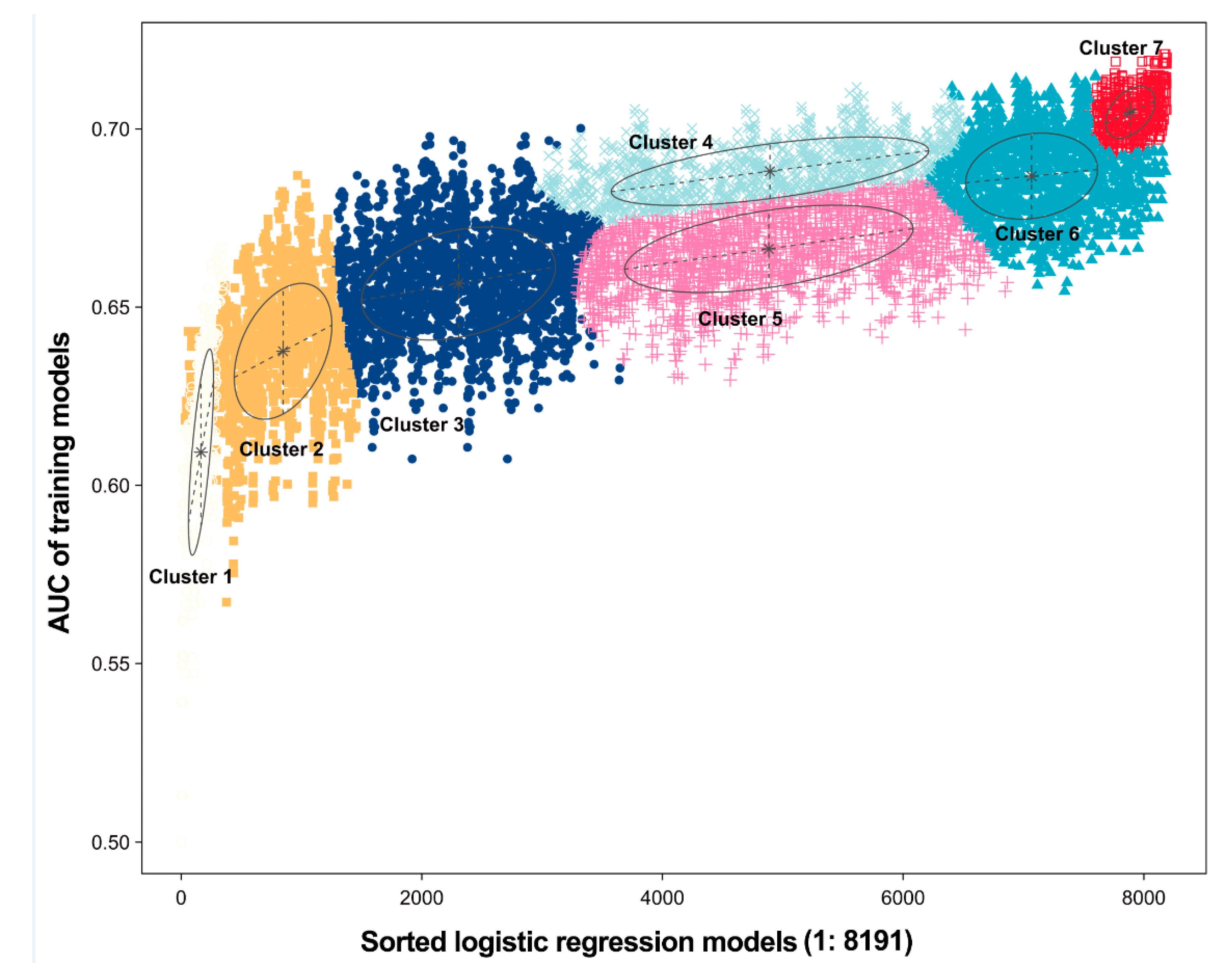
2.5. Model for Predicting Levels of COVID-19 NAb
2.6. Statistical Method
3. Results
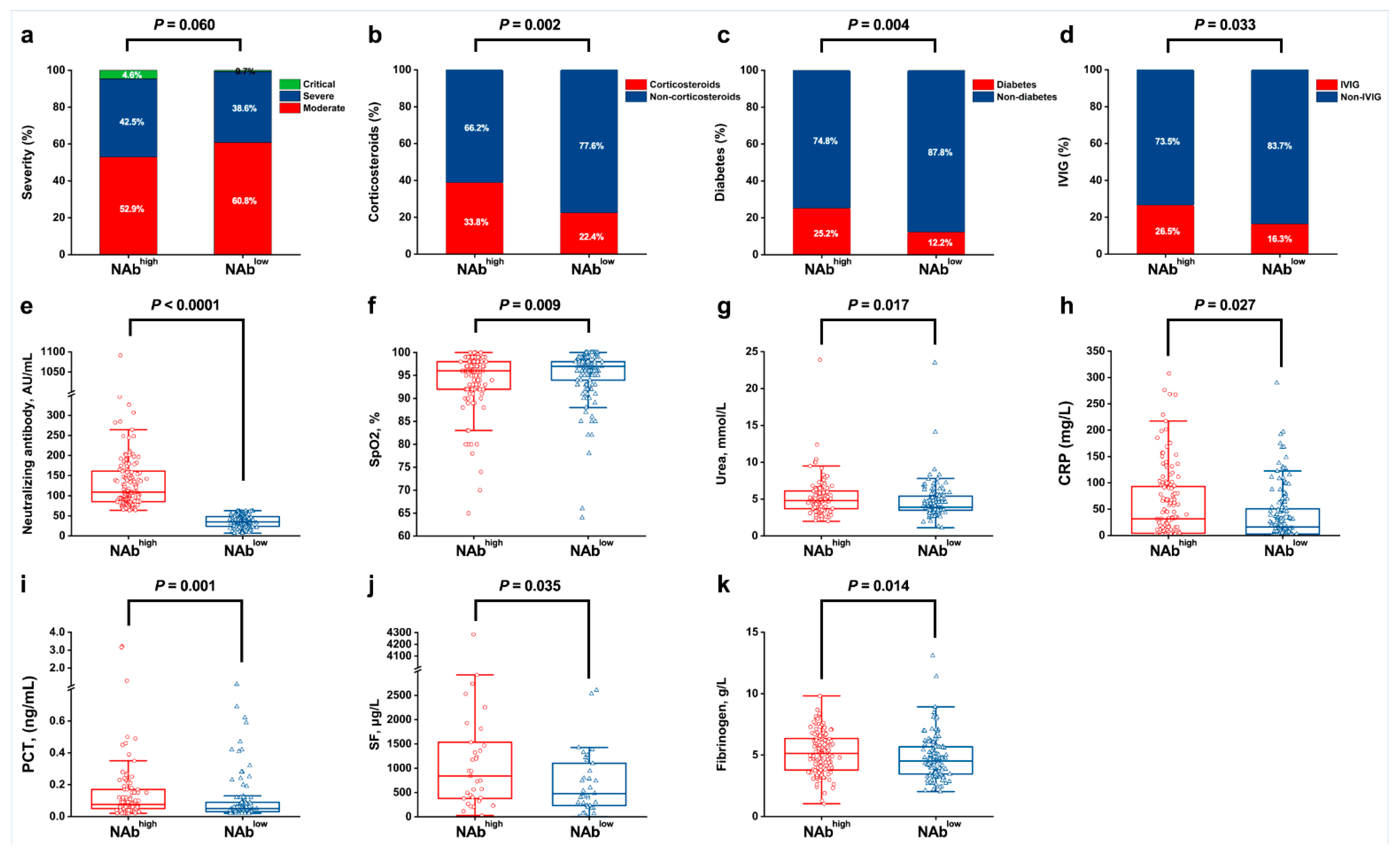
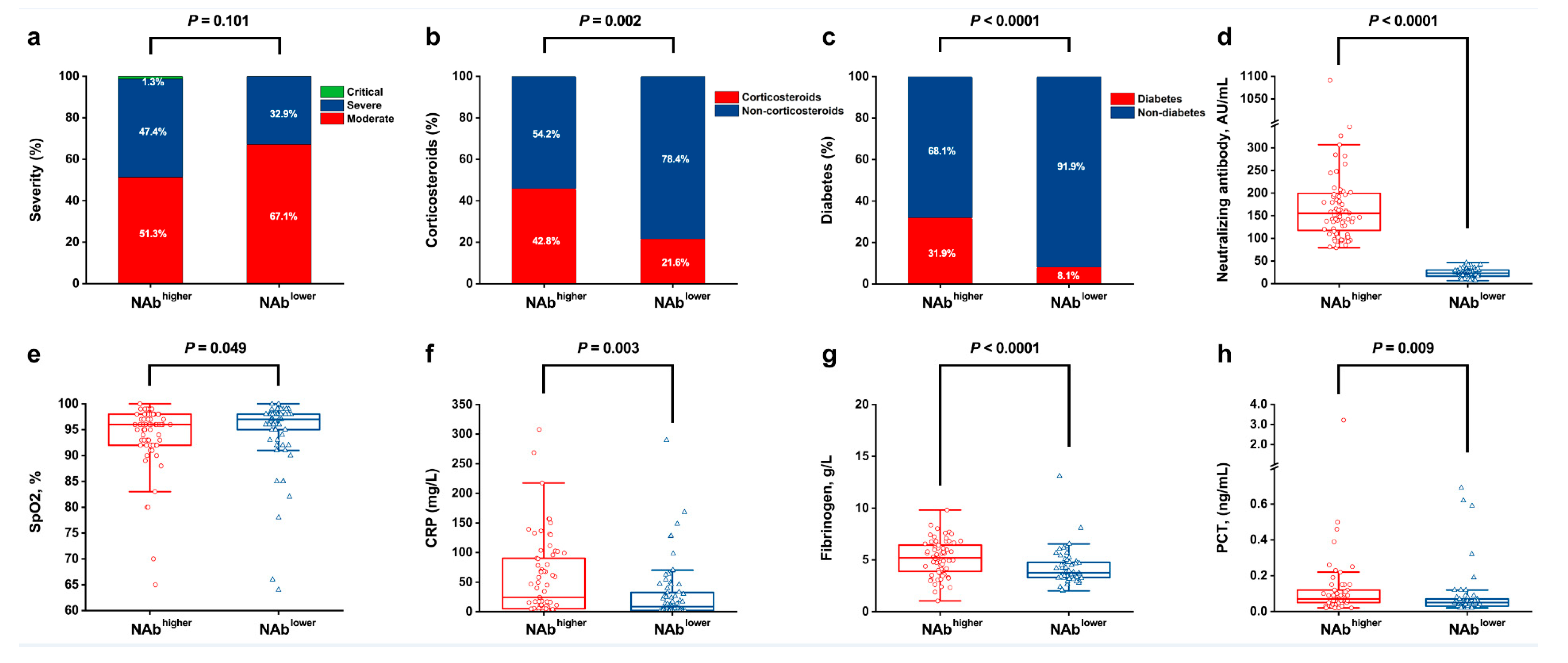
3.1. Factors at Admission Associated with NAbhigh and NAblow
3.2. The Relationship between Long-Term Serum NAb Levels and Clinical Indicators
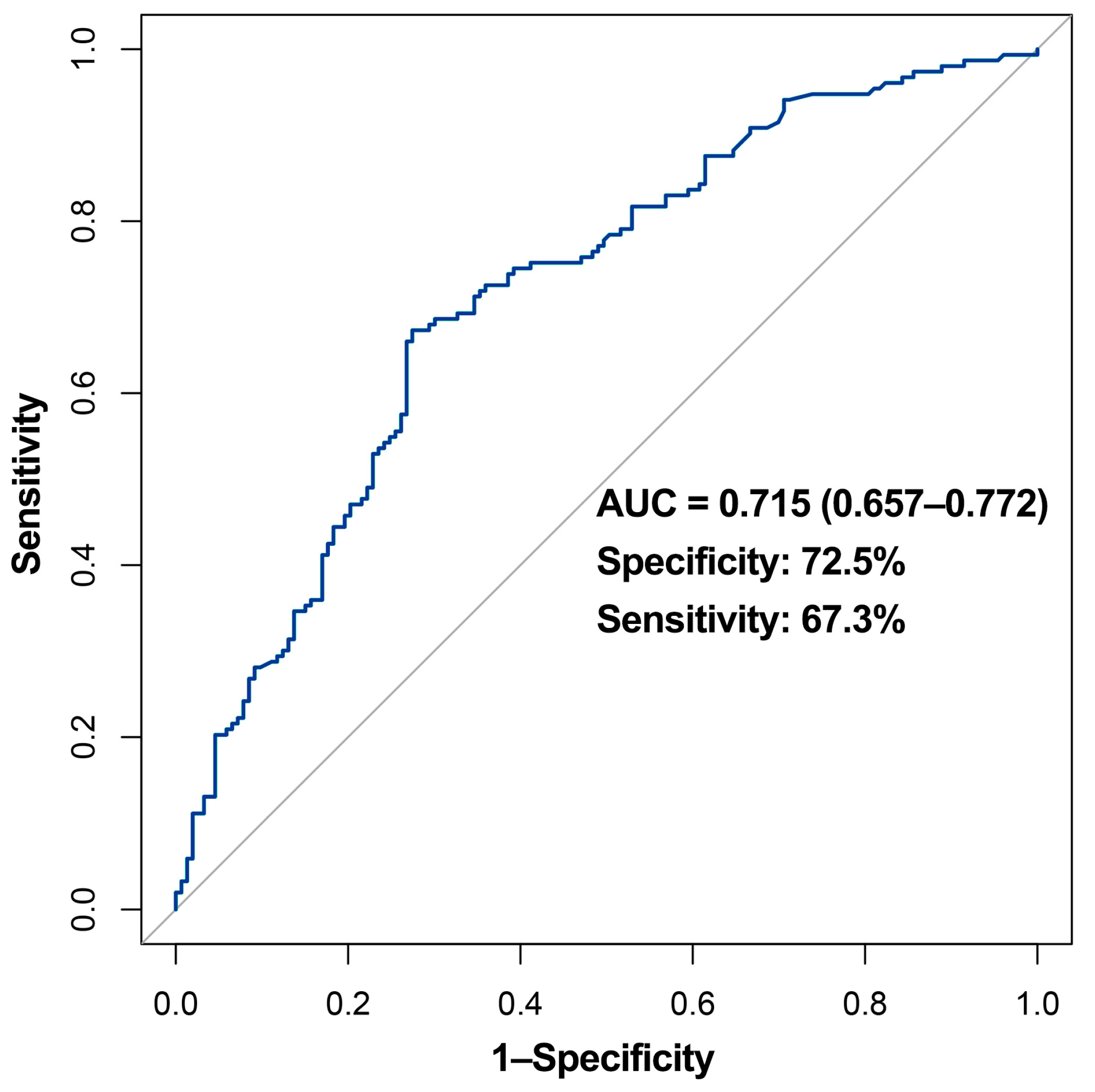
3.3. Model for Predicting Long-Term NAb Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoshkam, Z.; Aftabi, Y.; Stenvinkel, P.; Paige Lawrence, B.; Rezaei, M.H.; Ichihara, G.; Fereidouni, S. Recovery scenario and immunity in COVID-19 disease: A new strategy to predict the potential of reinfection. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 31, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, D.; Juno, J.A.; Khoury, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J.; Davenport, M.P. Prospects for durable immune control of SARS-CoV-2 and prevention of reinfection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muecksch, F.; Wise, H.; Batchelor, B.; Squires, M.; Semple, E.; Richardson, C.; McGuire, J.; Clearly, S.; Furrie, E.; Greig, N.; et al. Longitudinal Serological Analysis and Neutralizing Antibody Levels in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Convalescent Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Dowell, A.C.; Pearce, H.; Verma, K.; Long, H.M.; Begum, J.; Aiano, F.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Hoschler, K.; Brooks, T.; et al. Robust SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity is maintained at 6 months following primary infection. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röltgen, K.; Powell, A.E.; Wirz, O.F.; Stevens, B.A.; Hogan, C.A.; Najeeb, J.; Hunter, M.; Wang, H.; Sahoo, M.K.; Huang, C.; et al. Defining the features and duration of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with disease severity and outcome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrondo, F.J.; Fulcher, J.A.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Elliott, J.; Hofmann, C.; Hausner, M.A.; Ferbas, K.G.; Tobin, N.H.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Yang, O.O. Rapid Decay of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Persons with Mild COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.N.; Zhu, F.; Ong, S.W.X.; Young, B.E.; Fong, S.-W.; Le Bert, N.; Tan, C.W.; Tiu, C.; Zhang, J.; Tan, S.Y.; et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody responses and duration of immunity: A longitudinal study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e240–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Feng, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Leng, Z.; Tong, X.; Zhou, W.; et al. Seroprevalence and humoral immune durability of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Wuhan, China: A longitudinal, population-level, cross-sectional study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Ye, B.; Zhao, M.; Zhan, J.; Dong, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; et al. One-year sustained cellular and humoral immunities of COVID-19 convalescents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Marmar, T.; Xu, Q.; Tu, J.; Li, T.; Han, J.; Xu, D.; Shen, T. Cardiac Troponin I association with critical illness and death risk in 726 seriously ill COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHC. National Health Commission of China. Chinese Management Guideline for COVID-19 (version 7.0). Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb1989.shtml (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Tenbusch, M.; Schumacher, S.; Vogel, E.; Priller, A.; Held, J.; Steininger, P.; Beileke, S.; Irrgang, P.; Brockhoff, R.; Salmanton-García, J.; et al. Heterologous prime–boost vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1212–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y.; Qian, C.; Wang, X.; Cheng, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific immune response in COVID-19 convalescent individuals. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Gillot, C.; Di Chiaro, L.; Eucher, C.; Elsen, M.; Van Eeckhoudt, S.; David, C.; Morimont, L.; Dogné, J.-M.; Douxfils, J. Neutralizing Antibodies in COVID-19 Patients and Vaccine Recipients after Two Doses of BNT162b2. Viruses 2021, 13, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Weng, T.; Wu, J.; Dai, C.; Luo, R.; Chen, K.; Zhu, M.; Lu, X.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q.; et al. Dynamic Characteristic Analysis of Antibodies in Patients with COVID-19: A 13-Month Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 708184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Campos, P.; Blankenhaus, B.; Mota, C.; Gomes, A.; Serrano, M.; Ariotti, S.; Costa, C.; Nunes-Cabaço, H.; Mendes, A.M.; Gaspar, P.; et al. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in COVID-19 patients and healthy volunteers up to 6 months post disease onset. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 2025–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Yue, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Disease severity dictates SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legros, V.; Denolly, S.; Vogrig, M.; Boson, B.; Siret, E.; Rigaill, J.; Pillet, S.; Grattard, F.; Gonzalo, S.; Verhoeven, P.; et al. A longitudinal study of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients reveals a high correlation between neutralizing antibodies and COVID-19 severity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhu, F. Glycosylated hemoglobin is associated with systemic inflammation, hypercoagulability, and prognosis of COVID-19 patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 164, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Bhowmik, B.; do Vale Moreira, N.C. COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Ji, J.; Wen, C. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: The Current Evidence and Treatment Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Yang, L.; Luo, R.G.; Xu, J.F. Corticosteroid administration for viral pneumonia: COVID-19 and beyond. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, D.M.G.; Criner, G.J.; Papi, A.; Singh, D.; Anzueto, A.; Martinez, F.J.; Agusti, A.A.; Vogelmeier, C.F. Global Initiative for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. The 2020 GOLD Science Committee Report on COVID-19 and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-D.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Kursat Azkur, A.; Azkur, D.; Gan, H.; Sun, Y.-L.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Marmar, T.; Xu, Q.; Tu, J.; Yin, Y.; Tao, Q.; Chen, H.; Shen, T.; Xu, D. Predictive indicators of severe COVID-19 independent of comorbidities and advanced age: A nested case-control study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo Marin, B.; Aghagoli, G.; Lavine, K.; Yang, L.; Siff, E.J.; Chiang, S.S.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dumenco, L.; Savaria, M.C.; Aung, S.N.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020, 135, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Ou, J.; Qiu, X.; Jie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Cao, J.; Tan, M.; Xu, W.; Zheng, F.; et al. A Tool for Early Prediction of Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Multicenter Study Using the Risk Nomogram in Wuhan and Guangdong, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Liu, M.; Wang, A.; Lu, L.; Wang, Q.; Gu, C.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Xia, S.; Ling, Y.; et al. Evaluating the Association of Clinical Characteristics with Neutralizing Antibody Levels in Patients Who Have Recovered from Mild COVID-19 in Shanghai, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.-F.; Xu, C.; Tang, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody levels are correlated with severity of COVID-19 pneumonia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.-X.; Tang, X.-J.; Shi, Q.-L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.-J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.-J.; et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Pang, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Xu, D.; Shen, T. Patient and Clinical Factors at Admission Affect the Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies Six Months after Recovering from COVID-19. Viruses 2022, 14, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14010080
Li X, Pang L, Yin Y, Zhang Y, Xu S, Xu D, Shen T. Patient and Clinical Factors at Admission Affect the Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies Six Months after Recovering from COVID-19. Viruses. 2022; 14(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinjie, Ling Pang, Yue Yin, Yuqi Zhang, Shuyun Xu, Dong Xu, and Tao Shen. 2022. "Patient and Clinical Factors at Admission Affect the Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies Six Months after Recovering from COVID-19" Viruses 14, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14010080
APA StyleLi, X., Pang, L., Yin, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, S., Xu, D., & Shen, T. (2022). Patient and Clinical Factors at Admission Affect the Levels of Neutralizing Antibodies Six Months after Recovering from COVID-19. Viruses, 14(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14010080





