Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Determinants and Role in Plant Defense
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viral Isolates and Arabidopsis Thaliana Ecotypes
2.2. Construction of CMV Pseudorecombinants
2.3. Time Course of CMV Multiplication in Co-1
2.4. Use of Molecular Markers to Detect RCY1 in Arabidopsis Genomic DNA
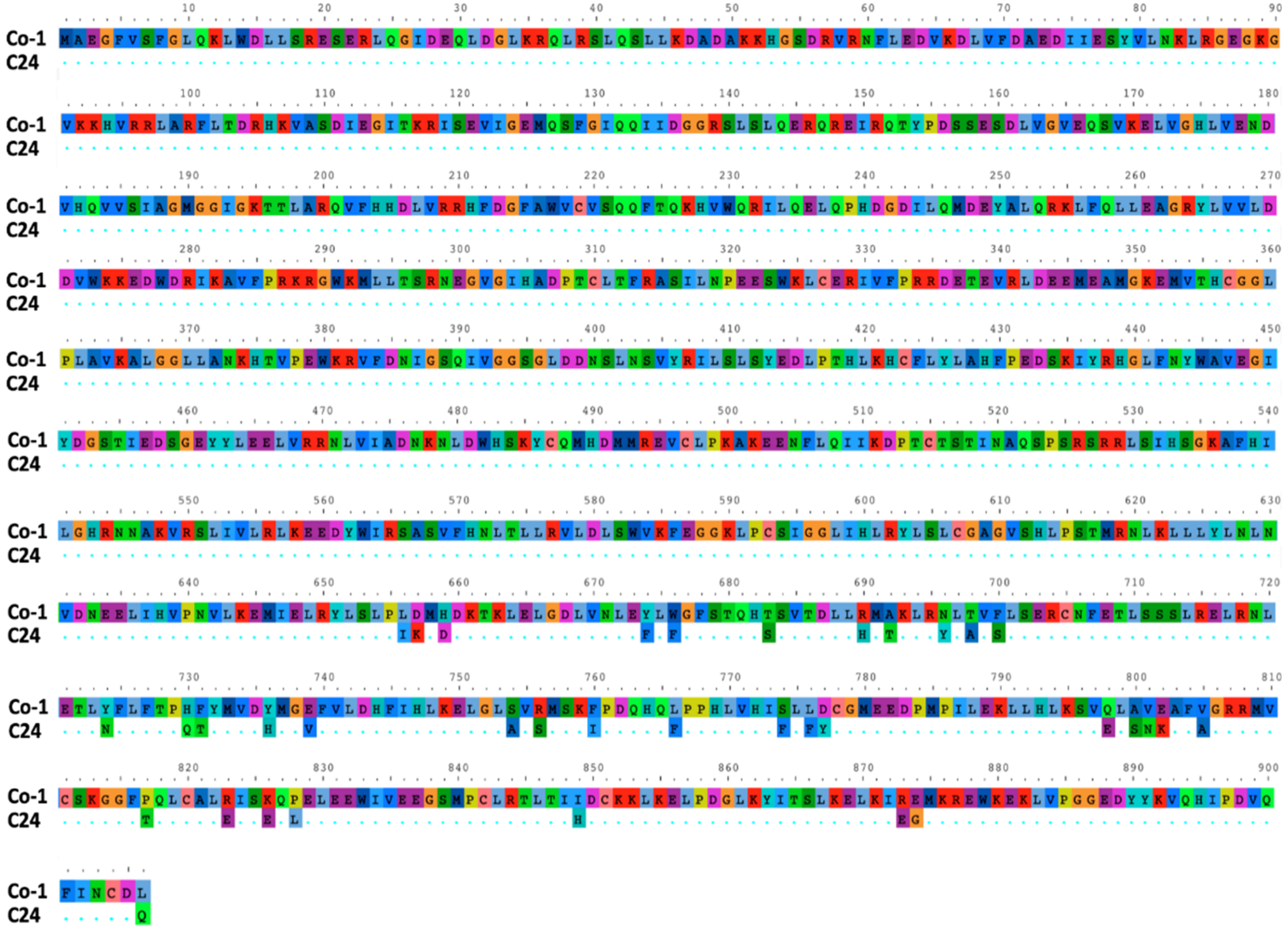
2.5. Sequencing of the RCY1 Gene in Co-1 Plants
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
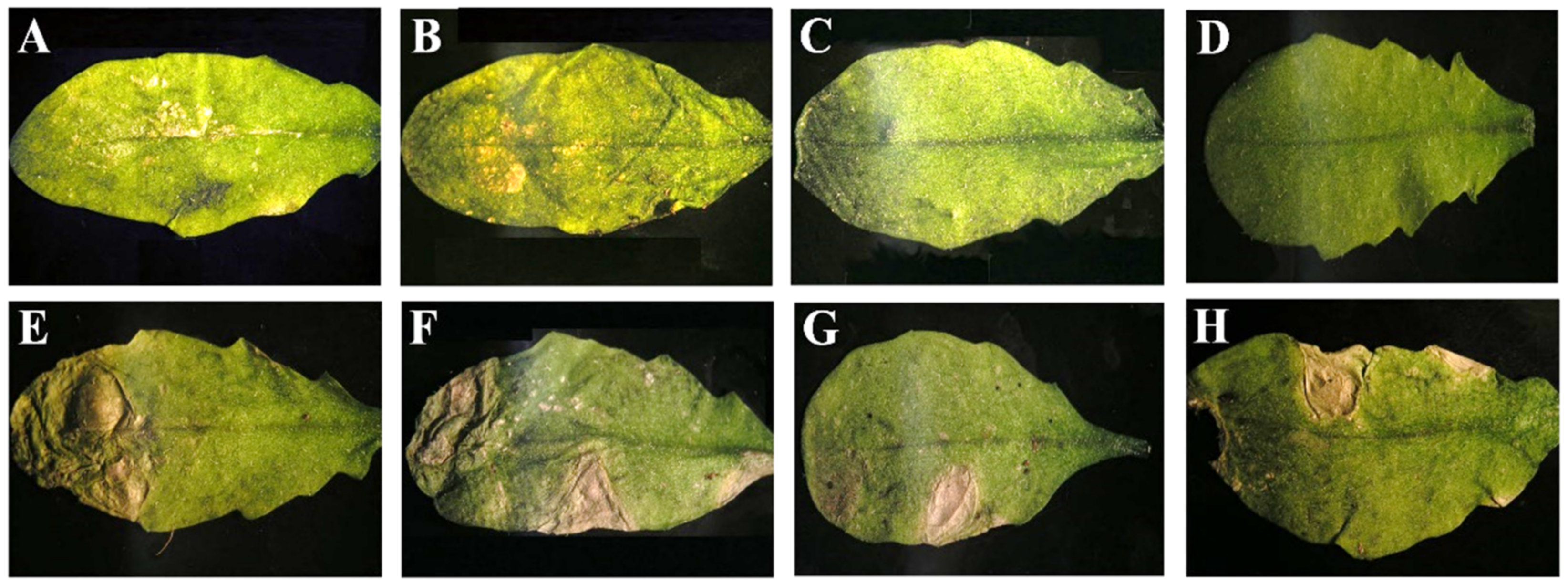
3.1. Genetic Determinants in CMV of Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis Co-1
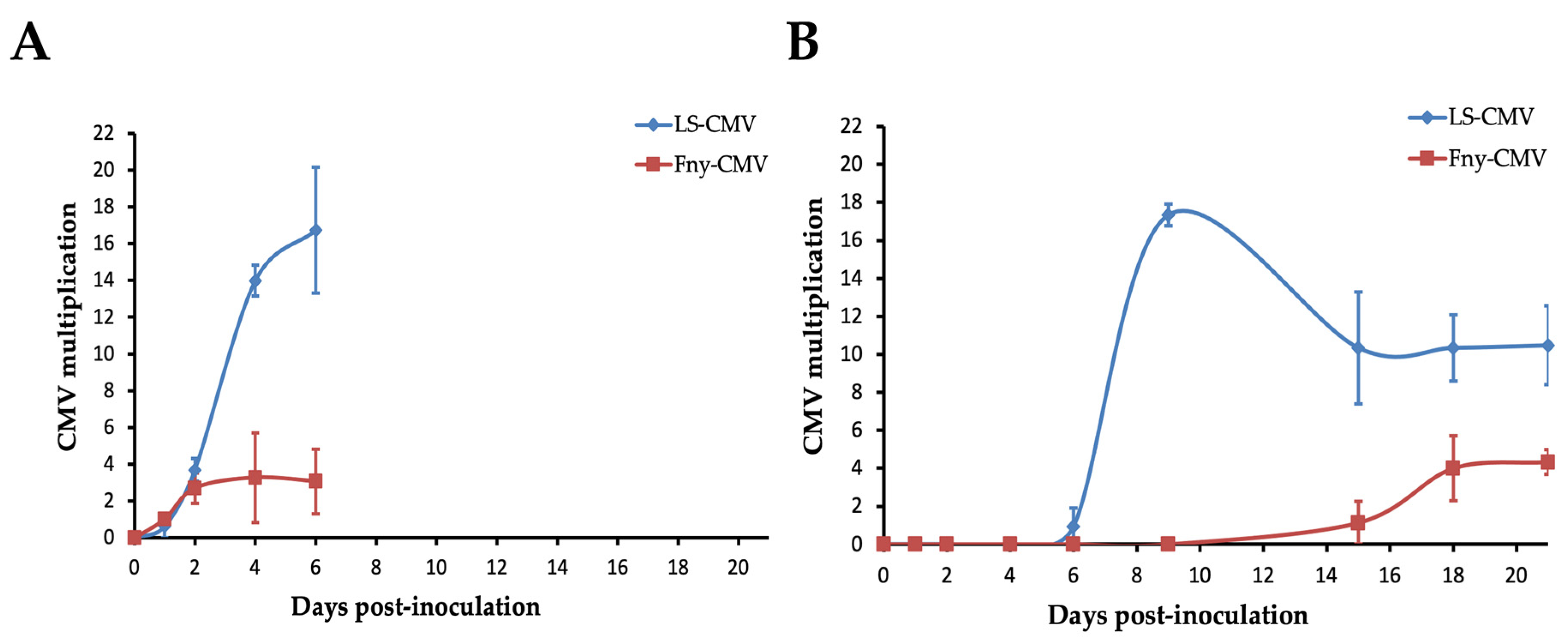
3.2. Systemic Necrosis Reduces CMV Multiplication
3.3. Systemic Necrosis in Co-1 Is Induced by Subgroup I CMV Isolates
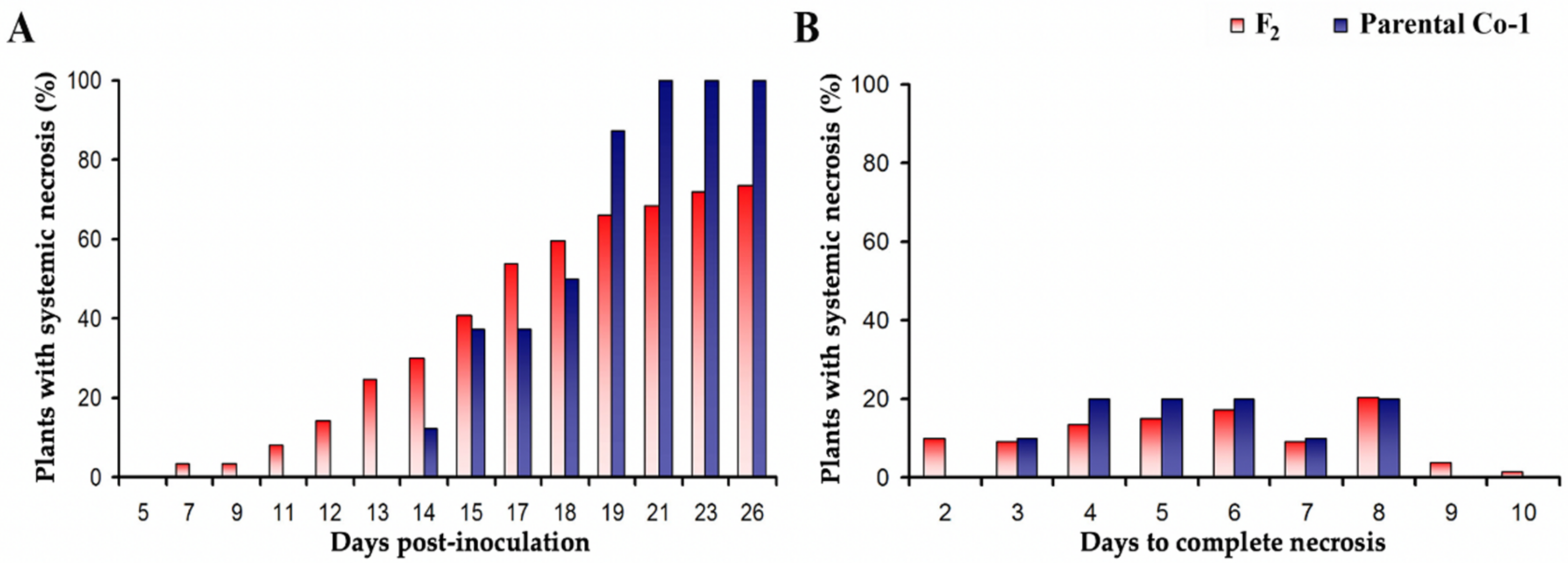
3.4. Genetic Determinants in Arabidopsis of CMV-Induced Systemic Necrosis
3.5. Screening of the Frequency of CMV-Induced Systemic Necrosis in the Arabidopsis Population of the Iberian Peninsula
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ristaino, J.B.; Anderson, P.K.; Bebber, D.P.; Brauman, K.A.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Fedoroff, N.V.; Finegold, C.; Garrett, K.A.; Gilligan, C.A.; Jones, C.M.; et al. The persistent threat of emerging plant disease pandemics to global food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022239118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, C.M.; McCullough, A.J.; Johnson, H.A.; Newton, L.A.; Borer, E.T. Invasive annual grasses indirectly increase virus incidence in California native perennial bunchgrasses. Oecologia 2005, 145, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palukaitis, P.; Yoon, J.-Y. R gene mediated defense against viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sett, S.; Prasad, A.; Prasad, M. Resistance genes on the verge of plant–virus interaction. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.E. Population biology of emerging and re-emerging pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, s3–s7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraile, A.; García-Arenal, F. The Coevolution of Plants and Viruses: Resistance and Pathogenicity. Adv. Virus Res. 2010, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagán, I.; García-Arenal, F. Tolerance to Plant Pathogens: Theory and Experimental Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.K.; Cunningham, A.A.; Patel, N.G.; Morales, F.J.; Epstein, P.R.; Daszak, P. Emerging infectious diseases of plants: Pathogen pollution, climate change and agrotechnology drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.I.; Jones, A.T. Responses of Plants to Viruses: Proposals for the Use of Terms. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.D. Tolerance of parasites and disease in plants and its significance in host-parasite interactions. Adv. Plant Pathol. 1986, 5, 161–198. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara, K.S.; Masuta, C. Interaction between viral RNA silencing suppressors and host factors in plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehl, A.; Heinlein, M. Perception of double-stranded RNA in plant antiviral immunity. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangl, J.L.; Jones, J.D.G. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 2001, 411, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Parker, J.E. Deciphering plant–pathogen communication: Fresh perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Dodds, P.; Pryor, T. Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ronde, D.; Butterbach, P.; Kormelink, R. Dominant resistance against plant viruses. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C.; Vincent, S.J. Strain-Specific Hypersensitive and Extreme Resistance Phenotypes Elicited by Potato virus Y Among 39 Potato Cultivars Released in Three World Regions Over a 117-Year Period. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, V.; Julio, E.; Candresse, T.; Cotucheau, J.; Decorps, C.; Volpatti, R.; Moury, B.; Glais, L.; de Borne, F.D.; Decroocq, V.; et al. NtTPN1: A RPP8-like R gene required for Potato virus Y-induced veinal necrosis in tobacco. Plant J. 2018, 95, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, D.A.; van Bentum, S.; Suzuki, M.; Ando, S.; Takahashi, H.; Miyashita, S. Plant death caused by inefficient induction of antiviral R-gene-mediated resistance may function as a suicidal population resistance mechanism. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.-H.; Inukai, T.; Suehiro, N.; Natsuaki, T.; Masuta, C. Fine genetic mapping of the TuNI locus causing systemic veinal necrosis by turnip mosaic virus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 110, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, K.-T.; Ishihara, T.; Hase, S.; Kusano, T.; Shah, J.; Takahashi, H. Single amino acid alterations in Arabidopsis thaliana RCY1 compromise resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus, but differentially suppress hypersensitive response-like cell death. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 62, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Ozeki, J.; Yamaji, Y.; Maejima, K.; Senshu, H.; Himeno, M.; Okano, Y.; Kagiwada, S.; Namba, S. Viral-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Plants Involves Both Programmed Cell Death and the Inhibition of Viral Multiplication, Which Are Regulated by Independent Pathways. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Schiff, M.; Czymmek, K.; Tallóczy, Z.; Levine, B.; Dinesh-Kumar, S. Autophagy Regulates Programmed Cell Death during the Plant Innate Immune Response. Cell 2005, 121, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofius, D.; Li, L.; Hafrén, A.; Coll, N.S. Autophagy as an emerging arena for plant–pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escriu, F.; Perry, K.L.; García-Arenal, F. Transmissibility of Cucumber mosaic virus by Aphis gossypii Correlates with Viral Accumulation and Is Affected by the Presence of Its Satellite RNA. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamonje, F.O.; Donnelly, R.; Tungadi, T.D.; Murphy, A.M.; Pate, A.E.; Woodcock, C.; Caulfield, J.; Mutuku, J.M.; Bruce, T.J.A.; Gilligan, C.A.; et al. Different Plant Viruses Induce Changes in Feeding Behavior of Specialist and Generalist Aphids on Common Bean That Are Likely to Enhance Virus Transmission. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, H.R. Cereal aphid movement: General principles and simulation modelling. Mov. Ecol. 2013, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palukaitis, P.; García-Arenal, F. Cucumber Mosaic Virus; APS Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, M.B.; Pathirana, S.; Wu, H.-J.; Kachroo, P.; Klessig, D.F. Members of the Arabidopsis HRT/RPP8 Family of Resistance Genes Confer Resistance to Both Viral and Oomycete Pathogens. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Miller, J.; Nozaki, Y.; Takeda, M.; Shah, J.; Hase, S.; Ikegami, M.; Ehara, Y.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. RCY1, an Arabidopsis thaliana RPP8/HRT family resistance gene, conferring resistance to cucumber mosaic virus requires salicylic acid, ethylene and a novel signal transduction mechanism. Plant J. 2002, 32, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagán, I.; Fraile, A.; Fernandez-Fueyo, E.; Montes, N.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; García-Arenal, F. Arabidopsis thaliana as a model for the study of plant–virus co-evolution. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, N.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; García-Arenal, F. Cucumber mosaic virus infection as a potential selective pressure on Arabidopsis thaliana populations. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Goto, N.; Ehara, Y. Hypersensitive response in cucumber mosaic virus-inoculated Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1994, 6, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, J.; Fraile, A.; Sacristán, S.; Malpica, J.M.; García-Arenal, F. Role of recombination in the evolution of natural populations of Cucumber mosaic virus, a tripartite RNA plant virus. Virology 2005, 332, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, T.M.; Palukaitis, P. Construction of full-length cDNA clones of cucumber mosaic virus RNAs 1, 2 and 3: Generation of infectious RNA transcripts. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1990, 222, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hanada, K.; Palukaitis, P. Mapping Local and Systemic Symptom Determinants of Cucumber Mosaic Cucumovirus in Tobacco. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 3185–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lot, H.; Marrou, J.; Quiot, J.B.; Esvan, C. Contribution à l’étude du virus de la mosaïque du concombre (CMV). Méthode de purification rapide du virus. Ann. Phytopathol. 1972, 4, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves, D.; Providenti, R.; Edwards, M.C. Tomato white leaf: The relation of an apparent satellite RNA and Cucumber mosaic virus. Phytopathology 1982, 72, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyes, D.C.; Zayed, A.M.; Ascenzi, R.; McCaskill, A.J.; Hoffman, N.E.; Davis, K.R.; Görlach, J. Growth stage-based phenotypic analysis of Arabidopsis: A model for high throughput functional genomics in plants. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, N.; Cobos, A.; Gil-Valle, M.; Caro, E.; Pagán, I. Arabidopsis thaliana Genes Associated with Cucumber mosaic virus Virulence and Their Link to Virus Seed Transmission. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharbel, T.F.; Haubold, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Genetic isolation by distance in Arabidopsis thaliana: Biogeography and postglacial colonization of Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagán, I.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; García-Arenal, F. The Relationship of Within-Host Multiplication and Virulence in a Plant-Virus System. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Takahashi, H.; Suzuki, M.; Natsuaki, K.; Shigyo, T.; Hino, K.; Teraoka, T.; Hosokawa, D.; Ehara, Y. Mapping the Virus and Host Genes Involved in the Resistance Response in Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Infected Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagán, I.; García-Arenal, F. Tolerance of Plants to Pathogens: A Unifying View. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S.; Miyashita, S.; Takahashi, H. Plant defense systems against cucumber mosaic virus: Lessons learned from CMV–Arabidopsis interactions. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, P.; Liu, H.; Kachroo, A. Salicylic acid: Transport and long-distance immune signaling. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 42, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofius, D.; Munch, D.; Bressendorff, S.; Mundy, J.; Petersen, M. Role of autophagy in disease resistance and hypersensitive response-associated cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Shoji, H.; Ando, S.; Kanayama, Y.; Kusano, T.; Takeshita, M.; Suzuki, M.; Masuta, C. RCY1-Mediated Resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus Is Regulated by LRR Domain-Mediated Interaction with CMV(Y) Following Degradation of RCY1. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, M.T.; Zitter, T.A. Determination of cucumber mosaic virus titer in muskmelon by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and correlation with aphid transmission. Plant Dis. 1990, 74, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, A.; Montes, N.; López-Herranz, M.; Gil-Valle, M.; Pagán, I. Within-Host Multiplication and Speed of Colonization as Infection Traits Associated with Plant Virus Vertical Transmission. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01078-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufty, R.C. A Genetic Analysis of the Association Between Resistance toMeloidogyne incognitaand a Necrotic Response to Infection by a Strain of Potato Virus Y in Tobacco. Phytopathology 1983, 73, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chen, P.; Buss, G.R.; Tolin, S.A. Genetic study of a lethal necrosis to soybean mosaic virus in PI 507389 soybean. J. Hered. 2003, 94, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraile, A.; Alonso-Prados, J.L.; Aranda, M.A.; Bernal, J.J.; Malpica, J.M.; García-Arenal, F. Genetic exchange by recombination or reassortment is infrequent in natural populations of a tripartite RNA plant virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Microsatellite | Symptom | RPP8 Allele | Heterozygous | RCY1 Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nga 129 | ||||
| Systemic necrosis | 8 | 61 | 22 | |
| Lamina reduction | 14 | 5 | 1 | |
| CIW 9 | ||||
| Systemic necrosis | 10 | 62 | 20 | |
| Lamina reduction | 13 | 5 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagán, I.; García-Arenal, F. Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Determinants and Role in Plant Defense. Viruses 2022, 14, 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122790
Pagán I, García-Arenal F. Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Determinants and Role in Plant Defense. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122790
Chicago/Turabian StylePagán, Israel, and Fernando García-Arenal. 2022. "Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Determinants and Role in Plant Defense" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122790
APA StylePagán, I., & García-Arenal, F. (2022). Cucumber Mosaic Virus-Induced Systemic Necrosis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Determinants and Role in Plant Defense. Viruses, 14(12), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122790





