Interaction Network of Porcine Circovirus Type 3 and 4 Capsids with Host Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.5. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
2.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Pull-Down Assays
2.7. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
2.8. Construction and Analysis of a Protein-Protein Interaction Network
2.9. GO and KEGG Pathway Analyses
3. Results
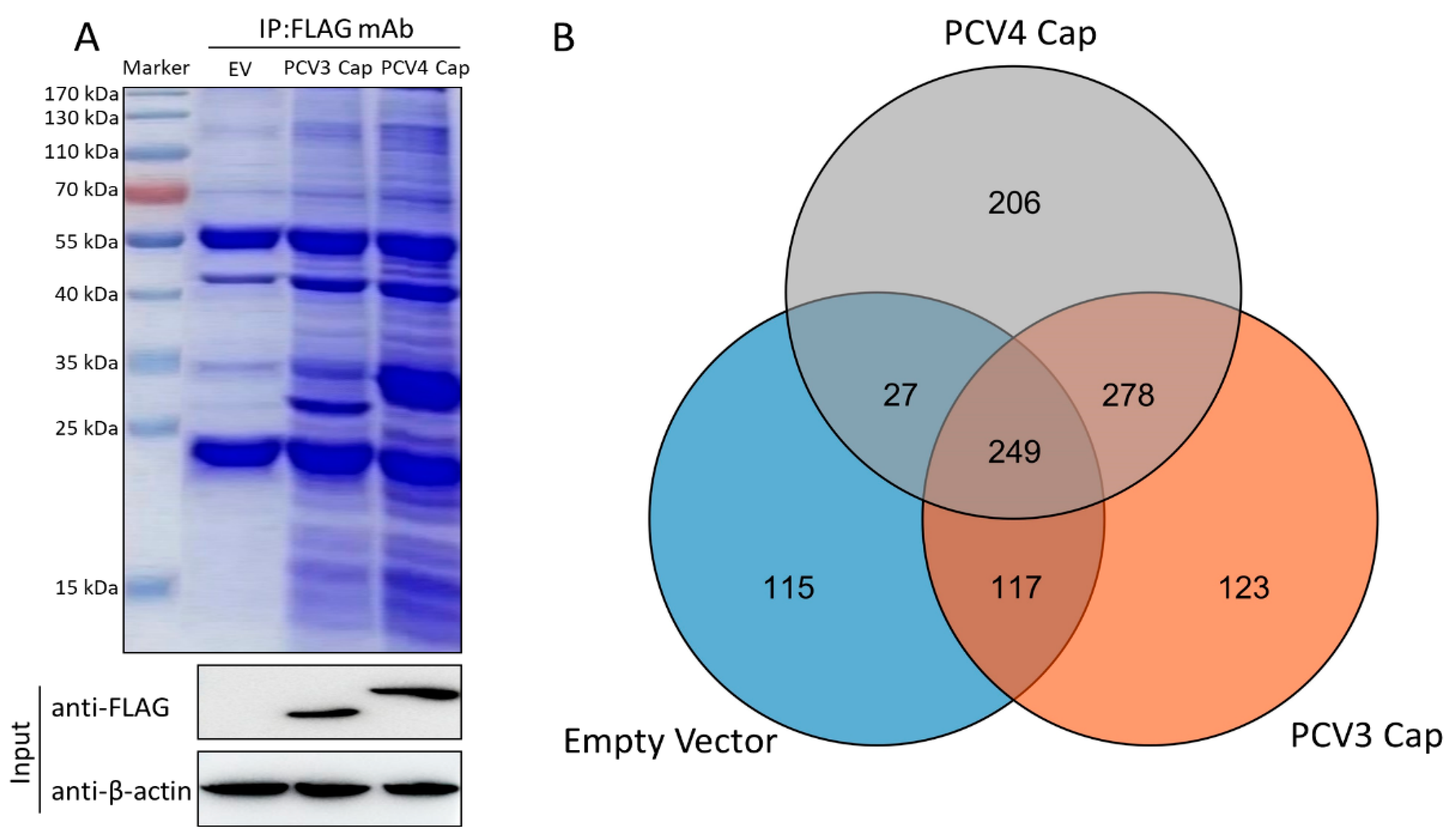
3.1. Characterization of Cap-Host Protein Interactions via Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
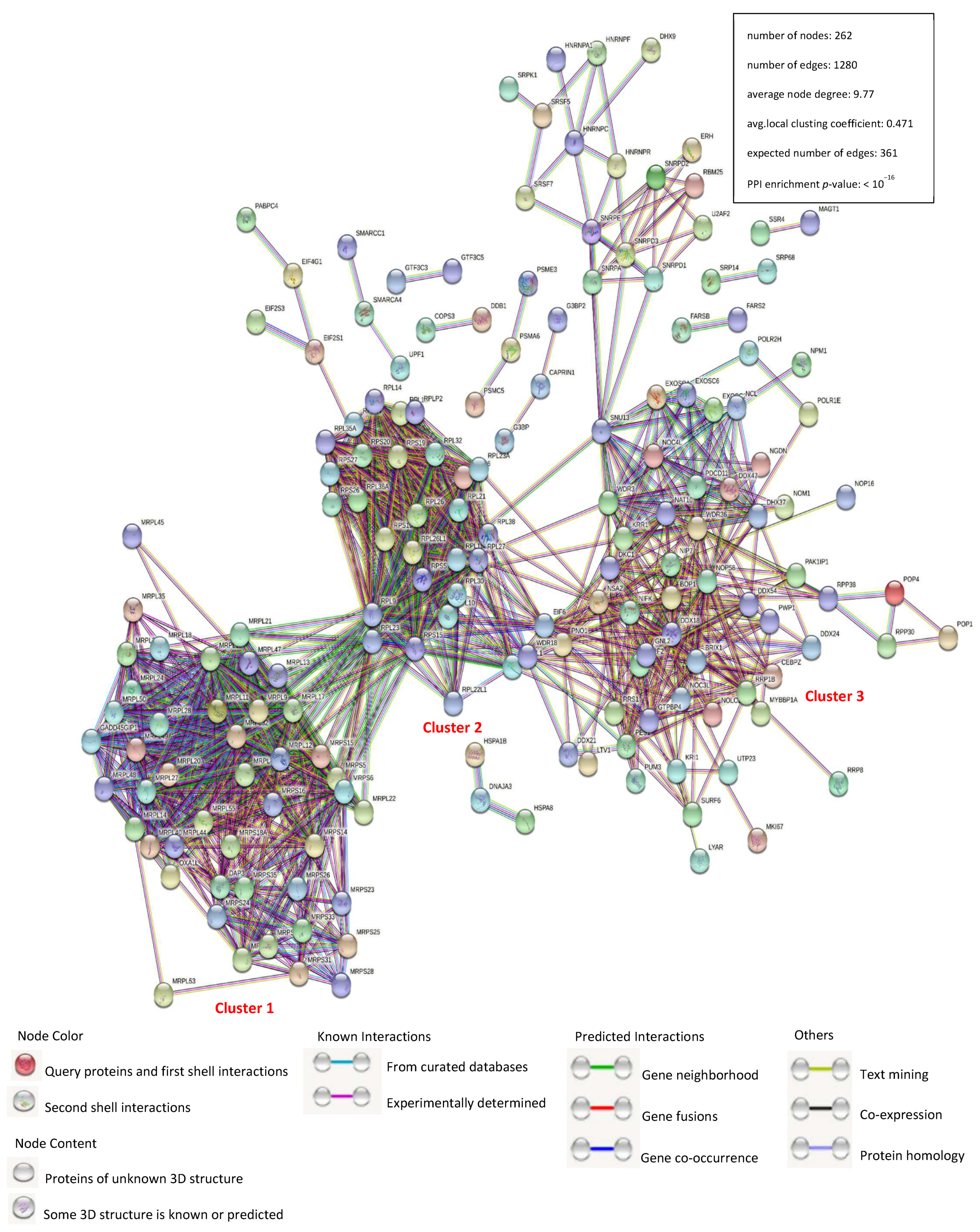
3.2. Construction of a Protein–Protein Interaction Network
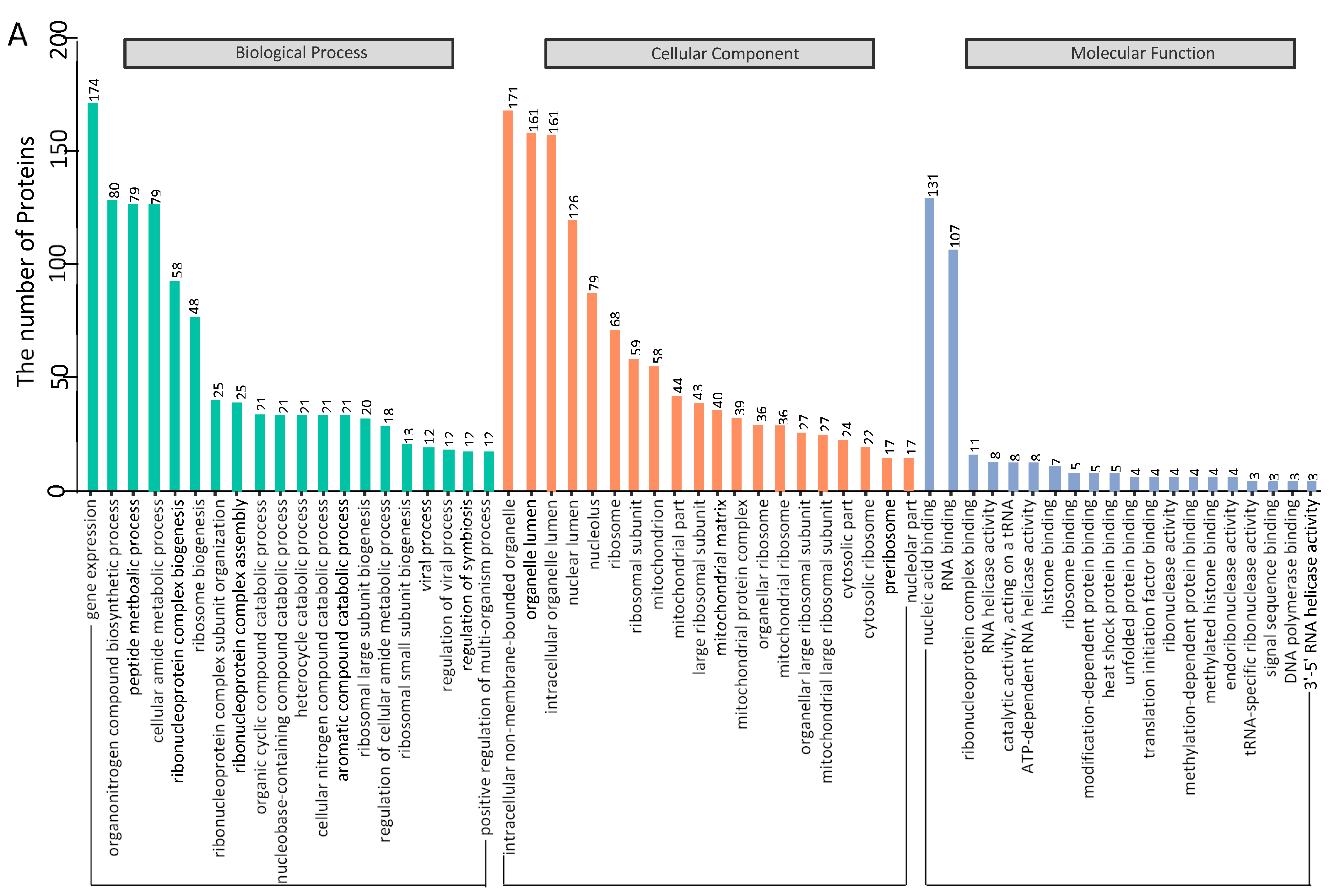
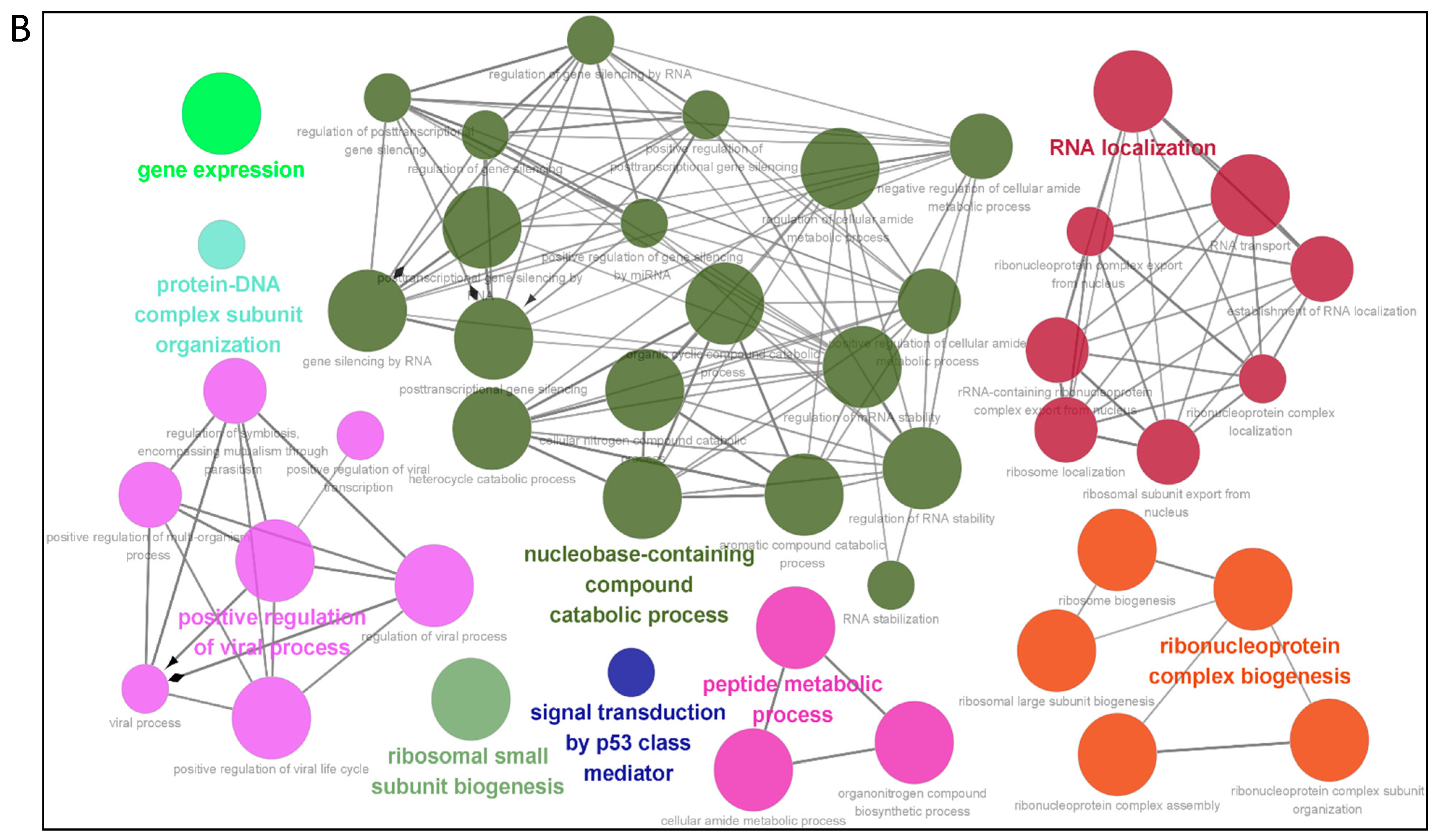
3.3. Gene Ontology Annotation
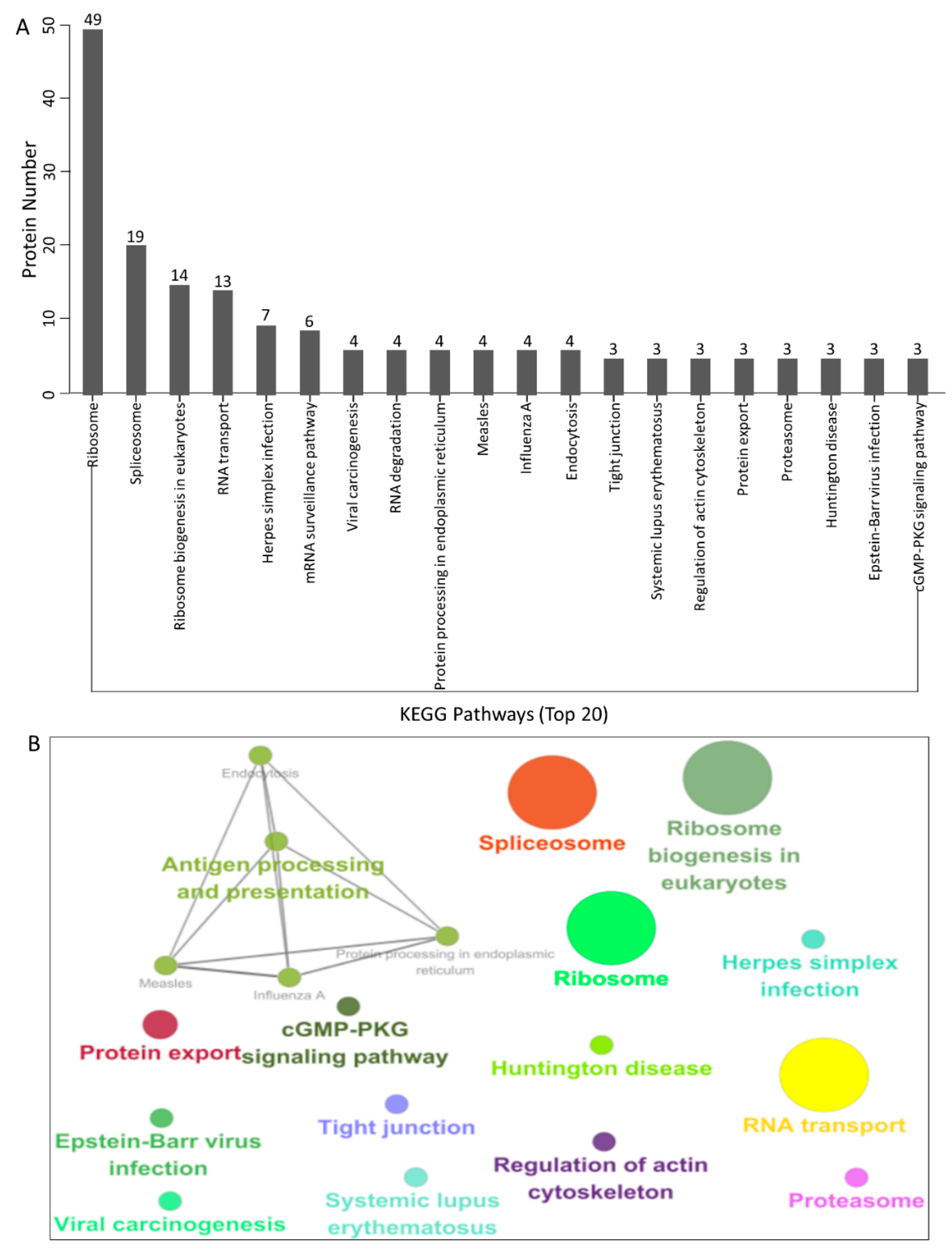
3.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment
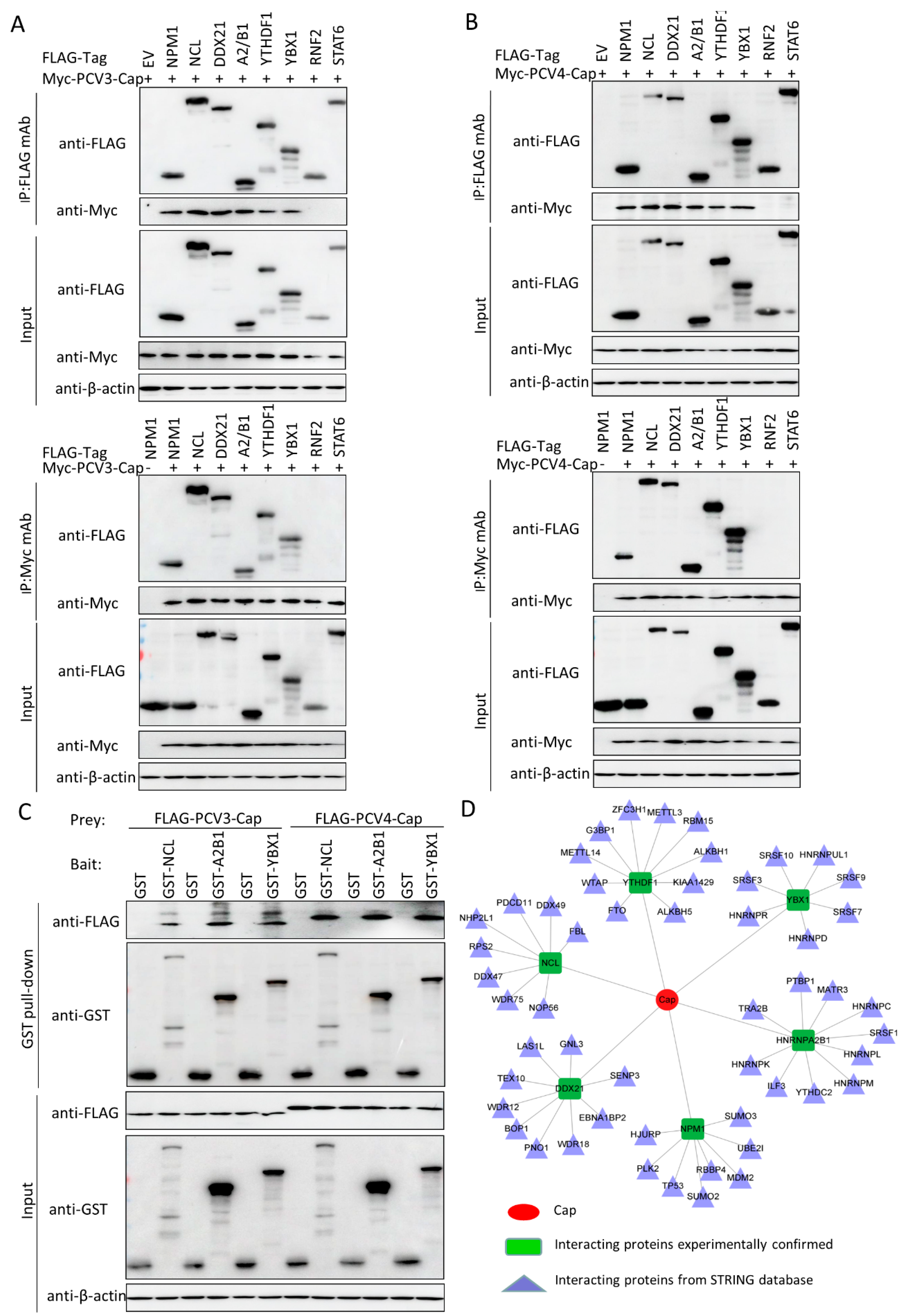
3.5. Validation of the Interactions between Host Proteins and PCV3 or PCV4 Capsid Proteins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitbart, M.; Delwart, E.; Rosario, K.; Segales, J.; Varsani, A. ICTV Report Consortium ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Circoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1997–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Hu, W.Q.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, T.N.; Zhou, J.Y.; Opriessnig, T.; Xiao, C.T. Novel circovirus species identified in farmed pigs designated as Porcine circovirus 4, Hunan province, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 67, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.; Chae, C. First isolation and genetic characterization of porcine circovirus type 3 using primary porcine kidney cells. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 241, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opriessnig, T.; Karuppannan, A.K.; Castro, A.M.; Xiao, C.-T. Porcine circoviruses: Current status, knowledge gaps and challenges. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischer, I.; Gelderblom, H.R.; Vettermann, W.; Koch, M.A. A very small porcine virus with circular single-stranded DNA. Nature 1982, 295, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, G.M.; McNeilly, F.; Kennedy, S.; Daft, B.; Clarke, E.G.; Ellis, J.A.; Haines, D.M.; Meehan, B.M.; Adair, B.M. Isolation of Porcine Circovirus-like Viruses from Pigs with a Wasting Disease in the USA and Europe. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1998, 10, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phan, T.G.; Giannitti, F.; Rossow, S.; Marthaler, D.; Knutson, T.P.; Li, L.; Deng, X.; Resende, T.; Vannucci, F.; Delwart, E. Detection of a novel circovirus PCV3 in pigs with cardiac and multi-systemic inflammation. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palinski, R.; Piñeyro, P.; Shang, P.; Yuan, F.; Guo, R.; Fang, Y.; Byers, E.; Hause, B.M. A Novel Porcine Circovirus Distantly Related to Known Circoviruses Is Associated with Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome and Reproductive Failure. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01879-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.; She, R.; Ren, X.; Tian, J.; Quan, R.; Hou, L.; Li, Z.; et al. Induction of Porcine Dermatitis and Nephropathy Syndrome in Piglets by Infection with Porcine Circovirus Type 3. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02045-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Du, Q.; Han, Z.; Bi, J.; Lan, T.; Wang, W.; Zheng, M. Detection and genetic characterization of porcine circovirus 4 (PCV4) in Guangxi, China. Gene 2020, 773, 145384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xie, N.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, J. Development and application of a quadruplex real-time PCR assay for differential detection of porcine circoviruses (PCV1 to PCV4) in Jiangsu province of China from 2016 to 2020. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Z.; Yu, C.; Xie, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, P.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Rong, F.; et al. Retrospective surveillance of porcine circovirus 4 in pigs in Inner Mongolia, China, from 2016 to 2018. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, J.; Zheng, H.; Xu, T.; Hou, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, L.; Chen, H. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Porcine circovirus 4 in Henan and Shanxi Provinces of China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Do, H.; Huynh, T.; Park, Y.; Park, B.; Chung, H. Molecular-based detection, genetic characterization and phylogenetic analysis of porcine circovirus 4 from Korean domestic swine farms. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, A.L.; Lin, L.L.; Nayar, G.P.S. Nucleotide Sequence of Porcine Circovirus Associated with Postweaning Multisystemic Wasting Syndrome in Pigs. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5262–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, A.K. Transcriptional analysis of porcine circovirus type 2. Virology 2003, 305, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.-Y.; Chen, Q.-X.; Ye, J.-X.; Shen, H.-G.; Chen, T.-F.; Shang, S.-B. Serological Investigation and Genomic Characterization of PCV2 Isolates from Different Geographic Regions of Zhejiang Province in China. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankertz, A.; Mankertz, J.; Wolf, K.; Buhk, H.J. Identification of a protein essential for replication of porcine circovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankertz, A.; Hillenbrand, B. Replication of porcine circovirus type 1 requires two proteins encoded by the viral rep gene. Virology 2001, 279, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, A.K. Rolling-circle replication of an animal circovirus genome in a theta-replicating bacterial plasmid in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8686–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawagitgul, P.; Morozov, I.; Bolin, S.R.; Harms, P.A.; Sorden, S.D.; Paul, P.S. Open reading frame 2 of porcine circovirus type 2 encodes a major capsid protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Mahe, D.; Cariolet, R.; Keranflec’h, A.; Baudouard, M.A.; Cordioli, P.; Albina, E.; Jestin, A. Protection of swine against post-weaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) by porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) proteins. Vaccine 2003, 21, 4565–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenaux, M.; Opriessnig, T.; Halbur, P.G.; Elvinger, F.; Meng, X.J. Two amino acid mutations in the capsid protein of type 2 porcine circovirus (PCV2) enhanced PCV2 replication in vitro and attenuated the virus in vivo. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13440–13446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmusk, S.; Fossum, C.; Berg, M. Porcine circovirus type 2 replicase binds the capsid protein and an intermediate filament-like protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Yu, T.; Li, J.; Dong, W.; Ojha, N.K.; Jin, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhou, J. Protein interactions network of porcine circovirus Type 2 capsid with host proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, I.; Kwang, J. Characterization of a previously unidentified viral protein in porcine circovirus type 2-infected cells and its role in virus-induced apoptosis. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8262–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, N.; Jin, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J. Identification and functional analysis of the novel ORF4 protein encoded by porcine circovirus type 2. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Q.; Guo, K.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y. Identification of putative ORF5 protein of porcine circovirus type 2 and functional analysis of GFP-fused ORF5 protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Cai, S.; Ao, C.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y. Identification and functional analysis of the novel ORF6 protein of porcine circovirus type 2 in vitro. Vet. Res. Commun. 2017, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, L.; Williamson, A.L.; Rybicki, E.P. The capsid protein of beak and feather disease virus binds to the viral DNA and is responsible for transporting the replication-associated protein into the nucleus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7219–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asensio, N.C.; Giner, E.M.; De Groot, N.S.; Burgas, M.T. Centrality in the host–pathogen interactome is associated with pathogen fitness during infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermin, G.; Tennant, P. Host-Virus Interactions: Battles between Viruses and Their Hosts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 245. [Google Scholar]
- Finsterbusch, T.; Steinfeldt, T.; Doberstein, K.; Rodner, C.; Mankertz, A. Interaction of the replication proteins and the capsid protein of porcine circovirus type 1 and 2 with host proteins. Virology 2009, 386, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; He, J.; Yan, Y. Differential proteome analysis of host cells infected with porcine circovirus type 2. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5111–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P. Hsp70 positively regulates porcine circovirus type 2 replication in vitro. Virology 2013, 447, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.J.; Xu, C.M.; Song, Z.B.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.F.; Bai, J.; Wang, X.W. Vimentin modulates infectious porcine circovirus type 2 in PK-15 cells. Virus Res. 2018, 243, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lin, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, N.; Jin, Y.; Liao, M.; Zhou, J. Circovirus transport proceeds via direct interaction of the cytoplasmic dynein IC1 subunit with the viral capsid protein. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2777–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Du, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.-L.; Tong, D.; et al. Cellular p32 Is a Critical Regulator of Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Nuclear Egress. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00979-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Dai, Y.D.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.X.; Dong, W.R.; Jin, Y.L.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Gu, J.Y. Nucleolar protein NPM1 is essential for circovirus replication by binding to viral capsid. Virulence 2020, 11, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W.; Jin, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhou, J. The serine-48 residue of nucleolar phosphoprotein nucleophosmin-1 plays critical role in subcellular localization and interaction with porcine circovirus type 3 capsid protein. Veter Res. 2021, 52, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, L.; Dai, B.; Feng, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, J. The Nucleolar Localization Signal of Porcine Circovirus Type 4 Capsid Protein Is Essential for Interaction With Serine-48 Residue of Nucleolar Phosphoprotein Nucleophosmin-1. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, T.; Dittmar, M.T. CDC42 use in viral cell entry processes by RNA viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 6526–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkert, K.; Echard, A. Rab35 GTPase: A central regulator of phosphoinositides and F-actin in endocytic recycling and beyond. Traffic 2016, 17, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, R.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, W.; Wu, S.; Cao, L.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Fan, X.-G.; Yan, Z.; et al. HMGB1 in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2014, 40, 1–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, Y.; Li, X.; Fang, W. PCV2 Induces Reactive Oxygen Species to Promote Nucleocytoplasmic Translocation of the Viral DNA Binding Protein HMGB1 To Enhance Its Replication. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00238-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Deng, Z.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, Y.; Fang, W.; Li, X. Porcine Circovirus 2 Manipulates the PERK-ERO1α Axis of the Endoplasmic Reticulum To Favor Its Replication by Derepressing Viral DNA from HMGB1 Sequestration within Nuclei. J. Virol. 2021, 95, JVI0100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderem, A.; Adkins, J.N.; Ansong, C.; Galagan, J.; Kaiser, S.; Korth, M.J.; Law, G.L.; McDermott, J.G.; Proll, S.C.; Rosenberger, C.; et al. A Systems Biology Approach to Infectious Disease Research: Innovating the Pathogen-Host Research Paradigm. mBio 2011, 2, e00325-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, X.; Chan, E.Y.; Li, Y.; Diamond, D.L.; Korth, M.J.; Katze, M.G. Virus–host interactions: From systems biology to translational research. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Q.; Miller-Jensen, K. Systems biology of virus-host signaling network interactions. BMB Rep. 2012, 45, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. Spliceosome Structure and Function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-K.; Chen, C.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, S.-W.; Shih, S.-R.; Kuo, R.-L. Cellular hnRNP A2/B1 interacts with the NP of influenza A virus and impacts viral replication. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.M.; Zhou, J.H.; Du, Y.C. hnRNP A2/B1 interacts with influenza A viral protein NS1 and inhibits virus replication potentially through suppressing NS1 RNA/protein levels and NS1 mRNA nuclear export. Virology 2014, 449, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, H.; Ajamian, L.; Valiente-Echeverria, F.; Levesque, K.; Rigby, W.F.; Mouland, A.J. Depletion of hnRNP A2/B1 overrides the nuclear retention of the HIV-1 genomic RNA. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1714–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Roizman, B.; Zhou, G.G. hnRNPA2B1 Associated with Recruitment of RNA into Exosomes Plays a Key Role in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Release from Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00367-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wen, M.; Cao, X. Nuclear hnRNPA2B1 initiates and amplifies the innate immune response to DNA viruses. Science 2019, 365, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaca, A.; Fardilha, M.; Silva, E.D.C.E.; Cunha, C. The heterogeneous ribonuclear protein C interacts with the hepatitis delta virus small antigen. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechtawewat, T.; Songprakhon, P.; Limjindaporn, T.; Puttikhunt, C.; Kasinrerk, W.; Saitornuang, S.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T.; Noisakran, S. Role of human heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1/C2 in dengue virus replication. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, S.; Singh, N.; Sengupta, N.; Fatima, M.; Seth, P.; Mahadevan, A.; Shankar, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis virus induces human neural stem/progenitor cell death by elevating GRP78, PHB and hnRNPC through ER stress. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; et al. The Nuclear Matrix Protein SAFA Surveils Viral RNA and Facilitates Immunity by Activating Antiviral Enhancers and Super-enhancers. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Product | Sense Primer (5′ to 3′) | Antisense Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PCV3 Cap | ATGAGACACAGAGCTATATTC | TTAGAGAACGGACTTGTAACGAATC |
| PCV4 Cap | ATGCCAATCAGATCTAGGTACA | TTATCCCTGTTTGGGGTAGTTAACA |
| NPM1 | ATGGAAGATTCGATGGATAT | TTAAAGAGACTTCCTCCACT |
| NCL | ATGGTAAAGCTCGCAAAGGCC | CTATTCAAACTTGGTCTTCTTTCCT |
| DDX21 | ATGCCGGGGAAACTTCGTAGT | TTACTGTCCAAACGCTTTGCT |
| hnRNPA2/B1 | ATGGAGAAAACTTTAGAAACTGT | TCAATATCGGCTTCTCCCTCCAT |
| YTHDF1 | ATGTCGGCCACCAGCGTGGACC | TTATTGTTTGTTTCGATTCTGCCGT |
| YBX1 | ATGAGCAGCGAGGCCGAGA | TTACTCAGCCCCGCCCTGCTCA |
| RNF2 | ATGTCTCAGGCTGTGCAGACAAAT | TCATTTGTGCTCCTTTGTGGGT |
| STAT6 | ATGTCTCTGTGGGGTCTGGTCTCCAAAAT | TCACCAACTGGGGTTAGCCCTTAGGT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dai, B.; Feng, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, J. Interaction Network of Porcine Circovirus Type 3 and 4 Capsids with Host Proteins. Viruses 2022, 14, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050939
Zhou J, Wang Y, Zhou L, Qiu Y, Zhao J, Dai B, Feng X, Hou L, Liu J. Interaction Network of Porcine Circovirus Type 3 and 4 Capsids with Host Proteins. Viruses. 2022; 14(5):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050939
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jianwei, Yongxia Wang, Linyi Zhou, Yonghui Qiu, Jie Zhao, Beining Dai, Xufei Feng, Lei Hou, and Jue Liu. 2022. "Interaction Network of Porcine Circovirus Type 3 and 4 Capsids with Host Proteins" Viruses 14, no. 5: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050939
APA StyleZhou, J., Wang, Y., Zhou, L., Qiu, Y., Zhao, J., Dai, B., Feng, X., Hou, L., & Liu, J. (2022). Interaction Network of Porcine Circovirus Type 3 and 4 Capsids with Host Proteins. Viruses, 14(5), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050939





