Transmission, Strain Diversity, and Zoonotic Potential of Chronic Wasting Disease
Abstract
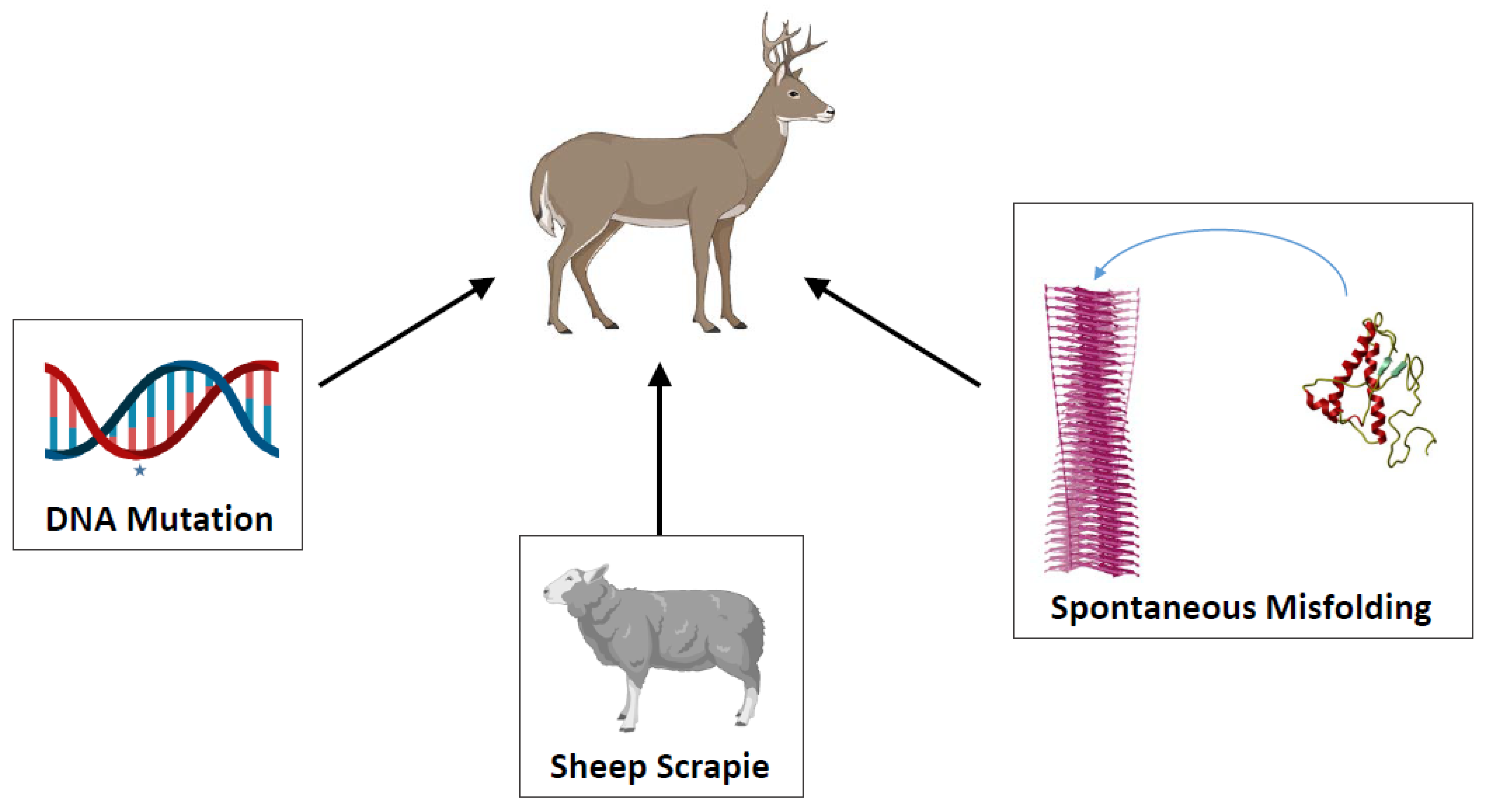
:1. Background
2. Mechanisms and Routes Responsible for the Efficient Natural Spreading of CWD
3. CWD Strain Diversity
4. Species Barrier and CWD Zoonotic Potential
5. Strategies for Minimizing CWD Spreading: Is Eradication of CWD a Possibility?
5.1. Surveillance
5.2. Selective Breeding
5.3. Implementation of High-Sensitivity Tests for CWD Prion Detection
5.4. Selective Animal Culling
5.5. Prion Decontamination
5.6. Treatment for CWD
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collinge, J. Prion diseases of humans and animals: Their causes and molecular basis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritzkow, S.; Gorski, D.; Ramirez, F.; Soto, C. Prion Dissemination through the Environment and Medical Practices: Facts and Risks for Human Health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0005919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soto, C. Prion Hypothesis: The end of the Controversy? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, C. Transmissible Proteins: Expanding the Prion Heresy. Cell 2012, 149, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, L.; LeVine, H.; Jucker, M. Koch’s postulates and infectious proteins. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 112, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, L.E.; Pritzkow, S.; Winter, S.N.; Grear, D.A.; Kirchgessner, M.S.; Dominguez-Villegas, E.; Machado, G.; Townsend Peterson, A.; Soto, C. The ecology of chronic wasting disease in wildlife. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: A spongiform encephalopathy. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spraker, T.R.; Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S.; Getzy, D.M.; Adrian, W.J.; Schoonveld, G.G.; Spowart, R.A.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Miller, J.M.; Merz, P.A. Spongiform encephalopathy in free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus), white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) in northcentral Colorado. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, D.R.; Kauffman, M.J.; Schumaker, B.A.; Lindzey, F.G.; Cook, W.E.; Kreeger, T.J.; Grogan, R.G.; Cornish, T.E. Chronic Wasting Disease Drives Population Decline of White-Tailed Deer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.S.; Miller, M.W. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in non-domestic animals: Origin, transmission and risk factors. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2003, 22, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S. Chronic wasting disease of cervids. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 284, 193–214. [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee, J.J.; Smith, J.D.; Kunkle, R.A. White-tailed deer are susceptible to the agent of sheep scrapie by intracerebral inoculation. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassmann, E.D.; Frese, R.D.; Greenlee, J.J. Second passage of chronic wasting disease of mule deer to sheep by intracranial inoculation compared to classical scrapie. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richt, J.A.; Hall, S.M. BSE case associated with prion protein gene mutation. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benestad, S.L.; Telling, G.C. Chronic wasting disease: An evolving prion disease of cervids. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hazards, E.P.O.B.; Ricci, A.; Allende, A.; Bolton, D.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; Fernandez Escamez, P.S.; Girones, R.; Herman, L.; Koutsoumanis, K.; et al. Chronic wasting disease (CWD) in cervids. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04667. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.J. Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) in Cervids and the Consequences of a Mutable Protein Conformation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12474–12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Velasquez, C.D.; Aiken, J.; McKenzie, D. Chronic wasting disease: A cervid prion infection looming to spillover. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, N.A.; Brandt, A.L.; Novakofski, J.E.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Chronic Wasting Disease In Cervids: Prevalence, Impact And Management Strategies. Vet. Med. 2019, 10, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.; Powers, J.; Seelig, D.M.; Hoover, C.; Haley, N.J.; Hayes-Klug, J.; Anderson, K.; Stewart, P.; Goldmann, W.; et al. Mother to offspring transmission of chronic wasting disease in reeves’ muntjac deer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, J.D.; Goldmann, W.; Hunter, N. Evidence in sheep for pre-natal transmission of scrapie to lambs from infected mothers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selariu, A.; Powers, J.G.; Nalls, A.; Brandhuber, M.; Mayfield, A.; Fullaway, S.; Wyckoff, C.A.; Goldmann, W.; Zabel, M.M.; Wild, M.A.; et al. In utero transmission and tissue distribution of chronic wasting disease-associated prions in free-ranging Rocky Mountain elk. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 3444–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramm, C.; Gomez-Gutierrez, R.; Soto, C.; Telling, G.; Nichols, T.; Morales, R. In Vitro detection of Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) prions in semen and reproductive tissues of white tailed deer bucks (Odocoileus virginianus). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.; Hoover, C.E.; Pulscher, L.A.; Hoover, E.A.; Mathiason, C.K. Infectious Prions in the Pregnancy Microenvironment of Chronic Wasting Disease-Infected Reeves’ Muntjac Deer. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00501-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.E.; Mayfield, A.; Crum, J.M.; Keel, M.K.; Hoover, E.A.; Ruder, M.G.; Mathiason, C.K. Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions in Fetal Tissues of Free-Ranging White-Tailed Deer. Viruses 2021, 13, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Kunkle, R.; Greenlee, M.H.; Nicholson, E.; Richt, J.; Hamir, A.; Waters, W.R.; Greenlee, J. Horizontal Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease in Reindeer. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S. Prion disease: Horizontal prion transmission in mule deer. Nature 2003, 425, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, N.J.; Seelig, D.M.; Zabel, M.D.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.A. Detection of CWD prions in urine and saliva of deer by transgenic mouse bioassay. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiason, C.K.; Powers, J.G.; Dahmes, S.J.; Osborn, D.A.; Miller, K.V.; Warren, R.J.; Mason, G.L.; Hays, S.A.; Hayes-Klug, J.; Seelig, D.M.; et al. Infectious prions in the saliva and blood of deer with chronic wasting disease. Science 2006, 314, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramm, C.; Pritzkow, S.; Lyon, A.; Nichols, T.; Morales, R.; Soto, C. Detection of Prions in Blood of Cervids at the Asymptomatic Stage of Chronic Wasting Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denkers, N.D.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.A. Minor oral lesions facilitate transmission of chronic wasting disease. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1396–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denkers, N.D.; Hayes-Klug, J.; Anderson, K.R.; Seelig, D.M.; Haley, N.J.; Dahmes, S.J.; Osborn, D.A.; Miller, K.V.; Warren, R.J.; Mathiason, C.K.; et al. Aerosol transmission of chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1890–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denkers, N.D.; Seelig, D.M.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.A., Jr. Aerosol and Nasal Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease in Cervidized Mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, J.G.; Lessard, P.; Tamguney, G.; Freyman, Y.; Deering, C.; Letessier, F.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Transmission and detection of prions in feces. J. Infect. Dis 2008, 198, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamguney, G.; Miller, M.W.; Wolfe, L.L.; Sirochman, T.M.; Glidden, D.V.; Palmer, C.; Lemus, A.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Asymptomatic deer excrete infectious prions in faeces. Nature 2009, 461, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulford, B.; Spraker, T.R.; Wyckoff, A.C.; Meyerett, C.; Bender, H.; Ferguson, A.; Wyatt, B.; Lockwood, K.; Powers, J.; Telling, G.C.; et al. Detection of PrPCWD in feces from naturally exposed Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) using protein misfolding cyclic amplification. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.M.; Tennant, J.M.; Haley, N.J.; Denkers, N.D.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Detection of chronic wasting disease prion seeding activity in deer and elk feces by real-time quaking-induced conversion. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haley, N.J.; Mathiason, C.K.; Carver, S.; Zabel, M.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.A. Detection of chronic wasting disease prions in salivary, urinary, and intestinal tissues of deer: Potential mechanisms of prion shedding and transmission. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S.; Hobbs, N.T.; Wolfe, L.L. Environmental sources of prion transmission in mule deer. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, K.A.; Hoover, C.E.; Denkers, N.D.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Modified Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification Overcomes Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion Assay Inhibitors in Deer Saliva To Detect Chronic Wasting Disease Prions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00947-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davenport, K.A.; Mosher, B.A.; Brost, B.M.; Henderson, D.M.; Denkers, N.D.; Nalls, A.V.; McNulty, E.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Assessment of Chronic Wasting Disease Prion Shedding in Deer Saliva with Occupancy Modeling. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01243-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, D.M.; Manca, M.; Haley, N.J.; Denkers, N.D.; Nalls, A.V.; Mathiason, C.K.; Caughey, B.; Hoover, E.A. Rapid antemortem detection of CWD prions in deer saliva. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyckoff, A.C.; Kane, S.; Lockwood, K.; Seligman, J.; Michel, B.; Hill, D.; Ortega, A.; Mangalea, M.R.; Telling, G.C.; Miller, M.W.; et al. Clay Components in Soil Dictate Environmental Stability and Bioavailability of Cervid Prions in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giachin, G.; Narkiewicz, J.; Scaini, D.; Ngoc, A.T.; Margon, A.; Sequi, P.; Leita, L.; Legname, G. Prion protein interaction with soil humic substances: Environmental implications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.B.; Booth, C.J.; Pedersen, J.A. Fate of prions in soil: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Shimozaki, N.; Yamamura, T.; Murayama, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Mohri, S. Sensitive detection of scrapie prion protein in soil. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.H.; Lee, S.; Somerville, R.A.; McKenzie, D.; Benson, C.H.; Pedersen, J.A. Transport of the pathogenic prion protein through soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seidel, B.; Thomzig, A.; Buschmann, A.; Groschup, M.H.; Peters, R.; Beekes, M.; Terytze, K. Scrapie Agent (Strain 263K) can transmit disease via the oral route after persistence in soil over years. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.J.; Phillips, K.E.; Schramm, P.T.; McKenzie, D.; Aiken, J.M.; Pedersen, J.A. Prions Adhere to Soil Minerals and Remain Infectious. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.; Gajdusek, D.C. Survival of scrapie virus after 3 years’ interment. Lancet 1991, 337, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Pedersen, J.A.; Chappell, R.J.; McKenzie, D.; Aiken, J.M. Oral Transmissibility of Prion Disease Is Enhanced by Binding to Soil Particles. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, R.A.; Fernie, K.; Smith, A.; Bishop, K.; Maddison, B.C.; Gough, K.C.; Hunter, N. BSE infectivity survives burial for five years with only limited spread. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, T.A.; Pulford, B.; Wyckoff, A.C.; Meyerett, C.; Michel, B.; Gertig, K.; Hoover, E.A.; Jewell, J.E.; Telling, G.C.; Zabel, M.D. Detection of protease-resistant cervid prion protein in water from a CWD-endemic area. Prion 2009, 3, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritzkow, S.; Morales, R.; Moda, F.; Khan, U.; Telling, G.C.; Hoover, E.; Soto, C. Grass plants bind, retain, uptake, and transport infectious prions. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritzkow, S.; Morales, R.; Camacho, M.; Soto, C. Uptake, Retention, and Excretion of Infectious Prions by Experimentally Exposed Earthworms. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 3151–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzkow, S.; Morales, R.; Lyon, A.; Concha-Marambio, L.; Urayama, A.; Soto, C. Efficient prion disease transmission through common environmental materials. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flechsig, E.; Hegyi, I.; Enari, M.; Schwarz, P.; Collinge, J.; Weissmann, C. Transmission of scrapie by steel-surface-bound prions. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, B.C.; Baker, C.A.; Terry, L.A.; Bellworthy, S.J.; Thorne, L.; Rees, H.C.; Gough, K.C. Environmental sources of scrapie prions. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11560–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carta, M.; Aguzzi, A. Molecular foundations of prion strain diversity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 72, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartz, J.C. Prion Strain Diversity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a024349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parchi, P.; Castellani, R.; Capellari, S.; Ghetti, B.; Young, K.; Chen, S.G.; Farlow, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sima, A.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Molecular basis of phenotypic variability in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.; Abid, K.; Soto, C. The prion strain phenomenon: Molecular basis and unprecedented features. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1772, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angers, R.C.; Kang, H.E.; Napier, D.; Browning, S.; Seward, T.; Mathiason, C.; Balachandran, A.; McKenzie, D.; Castilla, J.; Soto, C.; et al. Prion strain mutation determined by prion protein conformational compatibility and primary structure. Science 2010, 328, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowell, J.; Hughson, A.; Caughey, B.; Bessen, R.A. Host Determinants of Prion Strain Diversity Independent of Prion Protein Genotype. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10427–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duque Velasquez, C.; Kim, C.; Haldiman, T.; Kim, C.; Herbst, A.; Aiken, J.; Safar, J.G.; McKenzie, D. Chronic wasting disease (CWD) prion strains evolve via adaptive diversification of conformers in hosts expressing prion protein polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4985–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.; Tatum, T.; Hwang, S.; Vrentas, C.; West Greenlee, M.H.; Kong, Q.; Nicholson, E.; Greenlee, J. Novel Strain of the Chronic Wasting Disease Agent Isolated From Experimentally Inoculated Elk With LL132 Prion Protein. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, J.; Christiansen, J.R.; Moreno, J.A.; Kane, S.J.; Khaychuk, V.; Gallegos, J.; Kim, S.; Telling, G.C. Primary structural differences at residue 226 of deer and elk PrP dictate selection of distinct CWD prion strains in gene-targeted mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12478–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hannaoui, S.; Triscott, E.; Duque Velasquez, C.; Chang, S.C.; Arifin, M.I.; Zemlyankina, I.; Tang, X.; Bollinger, T.; Wille, H.; McKenzie, D.; et al. New and distinct chronic wasting disease strains associated with cervid polymorphism at codon 116 of the Prnp gene. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifin, M.I.; Hannaoui, S.; Chang, S.C.; Thapa, S.; Schatzl, H.M.; Gilch, S. Cervid Prion Protein Polymorphisms: Role in Chronic Wasting Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazami-Goudarzi, K.; Andreoletti, O.; Vilotte, J.L.; Beringue, V. Review on PRNP genetics and susceptibility to chronic wasting disease of Cervidae. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.W.; Wolfe, L.L.; Sirochman, T.M.; Sirochman, M.A.; Jewell, J.E.; Williams, E.S. Survival patterns in white-tailed and mule deer after oral inoculation with a standardized, conspecific prion dose. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J.; Herbst, A.; Duque-Velasquez, C.; Vanderloo, J.P.; Bochsler, P.; Chappell, R.; McKenzie, D. Prion protein polymorphisms affect chronic wasting disease progression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Johnson, J.; Vanderloo, J.P.; Keane, D.; Aiken, J.M.; McKenzie, D. Prion protein polymorphisms in white-tailed deer influence susceptibility to chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87 Pt 7, 2109–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.J.; Merrett, K.; Buros Stein, A.; Simpson, D.; Carlson, A.; Mitchell, G.; Staskevicius, A.; Nichols, T.; Lehmkuhl, A.D.; Thomsen, B.V. Estimating relative CWD susceptibility and disease progression in farmed white-tailed deer with rare PRNP alleles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jewell, J.E.; Conner, M.M.; Wolfe, L.L.; Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S. Low frequency of PrP genotype 225SF among free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86 Pt 8, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, K.I.; Besser, T.E.; Miller, M.W.; Cline, T.F.; Spraker, T.R.; Jenny, A.L.; Wild, M.A.; Zebarth, G.L.; Williams, E.S. PrP genotypes of captive and free-ranging Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) with chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 10, 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.J.; Samuel, M.D.; Johnson, C.J.; Adams, M.; McKenzie, D.I. Emerging prion disease drives host selection in a wildlife population. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirisinu, L.; Tran, L.; Chiappini, B.; Vanni, I.; Di Bari, M.A.; Vaccari, G.; Vikoren, T.; Madslien, K.I.; Vage, J.; Spraker, T.; et al. Novel Type of Chronic Wasting Disease Detected in Moose (Alces alces), Norway. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benestad, S.L.; Mitchell, G.; Simmons, M.; Ytrehus, B.; Vikoren, T. First case of chronic wasting disease in Europe in a Norwegian free-ranging reindeer. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikoren, T.; Vage, J.; Madslien, K.I.; Roed, K.H.; Rolandsen, C.M.; Tran, L.; Hopp, P.; Veiberg, V.; Heum, M.; Moldal, T.; et al. First Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease in a Wild Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) in Europe. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonno, R.; Di Bari, M.A.; Pirisinu, L.; D’Agostino, C.; Vanni, I.; Chiappini, B.; Marcon, S.; Riccardi, G.; Tran, L.; Vikoren, T.; et al. Studies in bank voles reveal strain differences between chronic wasting disease prions from Norway and North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31417–31426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Kim, S.; Kane, S.J.; Crowell, J.; Sun, J.L.; Christiansen, J.; Saijo, E.; Moreno, J.A.; DiLisio, J.; Burnett, E.; et al. Adaptive selection of a prion strain conformer corresponding to established North American CWD during propagation of novel emergent Norwegian strains in mice expressing elk or deer prion protein. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barria, M.A.; Telling, G.C.; Gambetti, P.; Mastrianni, J.A.; Soto, C. Generation of a New Form of Human PrPSc in Vitro by Interspecies Transmission from Cervid Prions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7490–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritzkow, S.; Gorski, D.; Ramirez, F.; Telling, G.C.; Benestad, S.L.; Soto, C. North American and Norwegian Chronic Wasting Disease prions exhibit different potential for interspecies transmission and zoonotic risk. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 225, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.A.; Vorberg, I.; Priola, S.A. Species barriers in prion diseases-brief review. In Infectious Diseases from Nature: Mechanisms of Viral Emergence and Persistence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, T.D.; Sigurdson, C.J. Cross-species transmission of CWD prions. Prion 2016, 10, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.J.; Smith, J.D.; Richt, J.A.; Greenlee, J.J. Raccoons accumulate PrP(Sc) after intracranial inoculation of the agents of chronic wasting disease or transmissible mink encephalopathy but not atypical scrapie. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2019, 31, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.J.; West Greenlee, M.H.; Kondru, N.; Manne, S.; Smith, J.D.; Kunkle, R.A.; Kanthasamy, A.; Greenlee, J.J. Experimental Transmission of the Chronic Wasting Disease Agent to Swine after Oral or Intracranial Inoculation. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00926-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenlee, J.J.; Nicholson, E.M.; Smith, J.D.; Kunkle, R.A.; Hamir, A.N. Susceptibility of cattle to the agent of chronic wasting disease from elk after intracranial inoculation. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamir, A.N.; Kunkle, R.A.; Cutlip, R.C.; Miller, J.M.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Williams, E.S.; Miller, M.W.; Stack, M.J.; Chaplin, M.J.; Richt, J.A. Experimental transmission of chronic wasting disease agent from mule deer to cattle by the intracerebral route. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2005, 17, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamir, A.N.; Kunkle, R.A.; Cutlip, R.C.; Miller, J.M.; Williams, E.S.; Richt, J.A. Transmission of chronic wasting disease of mule deer to Suffolk sheep following intracerebral inoculation. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigurdson, C.J.; Mathiason, C.K.; Perrott, M.R.; Eliason, G.A.; Spraker, T.R.; Glatzel, M.; Manco, G.; Bartz, J.C.; Miller, M.W.; Hoover, E.A. Experimental chronic wasting disease (CWD) in the ferret. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Spongiform encephalopathies in Cervidae. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1992, 11, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collinge, J. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1999, 354, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Huang, S.; Zou, W.; Vanegas, D.; Wang, M.; Wu, D.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, M.; Bai, H.; Deng, H.; et al. Chronic wasting disease of elk: Transmissibility to humans examined by transgenic mouse models. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7944–7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamguney, G.; Giles, K.; Bouzamondo-Bernstein, E.; Bosque, P.J.; Miller, M.W.; Safar, J.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Transmission of elk and deer prions to transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9104–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandberg, M.K.; Al-Doujaily, H.; Sigurdson, C.J.; Glatzel, M.; O’Malley, C.; Powell, C.; Asante, E.A.; Linehan, J.M.; Brandner, S.; Wadsworth, J.D.; et al. Chronic wasting disease prions are not transmissible to transgenic mice overexpressing human prion protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91 Pt 10, 2651–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, J.D.F.; Joiner, S.; Linehan, J.M.; Jack, K.; Al-Doujaily, H.; Costa, H.; Ingold, T.; Taema, M.; Zhang, F.; Sandberg, M.K.; et al. Humanised transgenic mice are resistant to chronic wasting disease prions from Norwegian reindeer and moose. J. Infect. Dis. 2022; (In press). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.F.; Kincaid, A.E.; Bessen, R.A.; Bartz, J.C. Interspecies Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions to Squirrel Monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13794–13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Race, B.; Meade-White, K.D.; Miller, M.W.; Barbian, K.D.; Rubenstein, R.; LaFauci, G.; Cervenakova, L.; Favara, C.; Gardner, D.; Long, D.; et al. Susceptibilities of nonhuman primates to chronic wasting disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Race, B.; Williams, K.; Orru, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Lubke, L.; Chesebro, B. Lack of Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease to Cynomolgus Macaques. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00550-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czub, S.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Stahl-Hennig, C.; Beekes, M.; Schaetzl, H.; Motzkus, D. First evidence of intracranial and peroral transmission or chronic wasting disease (CWD) into Cynomolgus macaques: A work in progress. In Prion 2017 Deciphering Neurodegenerative Disorders; Taylor & Francis: Edingurgh, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barria, M.A.; Libori, A.; Mitchell, G.; Head, M.W. Susceptibility of Human Prion Protein to Conversion by Chronic Wasting Disease Prions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barria, M.A.; Balachandran, A.; Morita, M.; Kitamoto, T.; Barron, R.; Manson, J.; Knight, R.; Ironside, J.W.; Head, M.W. Molecular barriers to zoonotic transmission of prions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davenport, K.A.; Henderson, D.M.; Bian, J.; Telling, G.C.; Mathiason, C.K.; Hoover, E.A. Insights into Chronic Wasting Disease and Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy Species Barriers by Use of Real-Time Conversion. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9524–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mawhinney, S.; Pape, W.J.; Forster, J.E.; Anderson, C.A.; Bosque, P.; Miller, M.W. Human prion disease and relative risk associated with chronic wasting disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, J.Y.; Maddox, R.A.; Harvey, A.R.; Schonberger, L.B.; Belay, E.D. Travel history, hunting, and venison consumption related to prion disease exposure, 2006–2007 FoodNet Population Survey. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.; Donner, R.; Merrett, K.; Miller, M.; Senior, K. Selective Breeding for Disease-Resistant PRNP Variants to Manage Chronic Wasting Disease in Farmed Whitetail Deer. Genes 2021, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.; Groschup, M.H. TSE eradication in small ruminants--quo vadis? Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2005, 118, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Bueler, H.; Aguzzi, A.; Sailer, A.; Greiner, R.A.; Autenried, P.; Aguet, M.; Weissmann, C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell 1993, 73, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richt, J.A.; Kasinathan, P.; Hamir, A.N.; Castilla, J.; Sathiyaseelan, T.; Vargas, F.; Sathiyaseelan, J.; Wu, H.; Matsushita, H.; Koster, J.; et al. Production of cattle lacking prion protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N. Amplification Techniques for the Detection of Misfolded Prion Proteins in Experimental and Clinical Samples. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2020, 130, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erana, H.; Charco, J.M.; Gonzalez-Miranda, E.; Garcia-Martinez, S.; Lopez-Moreno, R.; Perez-Castro, M.A.; Diaz-Dominguez, C.M.; Garcia-Salvador, A.; Castilla, J. Detection of Pathognomonic Biomarker PrP(Sc) and the Contribution of Cell Free-Amplification Techniques to the Diagnosis of Prion Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNulty, E.; Nalls, A.V.; Mellentine, S.; Hughes, E.; Pulscher, L.; Hoover, E.A.; Mathiason, C.K. Comparison of conventional, amplification and bio-assay detection methods for a chronic wasting disease inoculum pool. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandel, J.P.; Culeux, A.; Grznarova, K.; Levavasseur, E.; Lamy, P.; Privat, N.; Welaratne, A.; Denouel, A.; Laplanche, J.L.; Haik, S. Amplification techniques and diagnosis of prion diseases. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, N.J.; Richt, J.A. Evolution of Diagnostic Tests for Chronic Wasting Disease, a Naturally Occurring Prion Disease of Cervids. Pathogens 2017, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, R.; Duran-Aniotz, C.; Diaz-Espinoza, R.; Camacho, M.V.; Soto, C. Protein misfolding cyclic amplification of infectious prions. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramm, C.; Soto, P.; Nichols, T.A.; Morales, R. Chronic wasting disease (CWD) prion detection in blood from pre-symptomatic white-tailed deer harboring PRNP polymorphic variants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, E.E.; Nalls, A.V.; Xun, R.; Denkers, N.D.; Hoover, E.A.; Mathiason, C.K. In vitro detection of haematogenous prions in white-tailed deer orally dosed with low concentrations of chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Hannaoui, S.; John, T.R.; Dudas, S.; Czub, S.; Gilch, S. Real-time Quaking-induced Conversion Assay for Detection of CWD Prions in Fecal Material. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 29, 56373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, A.M.; Henderson, D.M.; Nalls, A.V.; Wilham, J.M.; Caughey, B.W.; Hoover, E.A.; Kincaid, A.E.; Bartz, J.C.; Mathiason, C.K. In vitro detection of prionemia in TSE-infected cervids and hamsters. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uehlinger, F.D.; Johnston, A.C.; Bollinger, T.K.; Waldner, C.L. Systematic review of management strategies to control chronic wasting disease in wild deer populations in North America. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjerovic, M.B.; Green, M.L.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.; Novakofski, J. The importance of localized culling in stabilizing chronic wasting disease prevalence in white-tailed deer populations. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, L.L.; Watry, M.K.; Sirochman, M.A.; Sirochman, T.M.; Miller, M.W. Evaluation of a Test and Cull Strategy for Reducing Prevalence of Chronic Wasting Disease in Mule Deer (Odocoileus Hemionus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haley, N.J.; Henderson, D.M.; Donner, R.; Wyckoff, S.; Merrett, K.; Tennant, J.; Hoover, E.A.; Love, D.; Kline, E.; Lehmkuhl, A.D.; et al. Management of chronic wasting disease in ranched elk: Conclusions from a longitudinal three-year study. Prion 2020, 14, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mysterud, A.; Rolandsen, C.M. A reindeer cull to prevent chronic wasting disease in Europe. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1343–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M. Inactivation of transmissible degenerative encephalopathy agents: A review. Vet. J. 2000, 159, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secker, T.J.; Leighton, T.G.; Offin, D.G.; Birkin, P.R.; Herve, R.C.; Keevil, C.W. A cold water, ultrasonically activated stream efficiently removes proteins and prion-associated amyloid from surgical stainless steel. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Dehen, C.; Perrin, A.; Thomas, V.; Igel-Egalon, A.; Burke, P.A.; Deslys, J.P.; Comoy, E. Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization of surface prion contamination. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 85, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Ito, H.; Furuta, T.; Ikuta, K.; Sakudo, A. Degradation and destabilization of abnormal prion protein using alkaline detergents and proteases. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Suyama, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Akagawa, M.; Murayama, Y.; Horii, H.; Takata, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Mohri, S. Assessment of prion inactivation by fenton reaction using protein misfolding cyclic amplification and bioassay. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2069–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyama, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Akagawa, M.; Murayama, Y.; Horii, H.; Takata, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Mohri, S. Prion inactivation by the Maillard reaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, M.; Miwa, T.; Horii, H.; Takata, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Nishizawa, K.; Watanabe, M.; Shinagawa, M.; Murayama, Y. Characterization of a proteolytic enzyme derived from a Bacillus strain that effectively degrades prion protein. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belondrade, M.; Jas-Duval, C.; Nicot, S.; Bruyere-Ostells, L.; Mayran, C.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Torres, J.M.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Beringue, V.; et al. Correlation between Bioassay and Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification for Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Decontamination Studies. mSphere 2020, 5, e00649-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belondrade, M.; Nicot, S.; Beringue, V.; Coste, J.; Lehmann, S.; Bougard, D. Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Abnormal Prion Protein on Steel Surfaces by Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification: Application to Prion Decontamination Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moudjou, M.; Castille, J.; Passet, B.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Vilotte, J.L.; Rezaei, H.; Beringue, V.; Igel-Egalon, A. Improving the Predictive Value of Prion Inactivation Validation Methods to Minimize the Risks of Iatrogenic Transmission With Medical Instruments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 591024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzkow, S.; Wagenfuhr, K.; Daus, M.L.; Boerner, S.; Lemmer, K.; Thomzig, A.; Mielke, M.; Beekes, M. Quantitative detection and biological propagation of scrapie seeding activity in vitro facilitate use of prions as model pathogens for disinfection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zattoni, M.; Legname, G. Tackling prion diseases: A review of the patent landscape. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, V.L.; Caughey, B. Recent advances in prion chemotherapeutics. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sassoon, J.; Sadowski, M.; Wisniewski, T.; Brown, D.R. Therapeutics and prion disease: Can immunisation or drugs be effective? Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, F.; Mathiason, C.K.; Yim, L.; Wong, K.; Hayes-Klug, J.; Nalls, A.; Peyser, D.; Estevez, V.; Denkers, N.; Xu, J.; et al. Mucosal immunization with an attenuated Salmonella vaccine partially protects white-tailed deer from chronic wasting disease. Vaccine 2015, 33, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, M.E.; Griebel, P.; Huizenga, M.L.; Lockwood, S.; Hansen, C.; Potter, A.; Cashman, N.; Mapletoft, J.W.; Napper, S. Accelerated onset of chronic wasting disease in elk (Cervus canadensis) vaccinated with a PrP(Sc)-specific vaccine and housed in a prion contaminated environment. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7737–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, S.E.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Bartz, J.C. Prions in the environment: Occurrence, fate and mitigation. Prion 2008, 2, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Cervid Species | Polymorphisms |
|---|---|
| White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) | G37V, G96S, G96R, A123T, Q230L |
| Mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) | D20G, S225F, Q226K |
| Elk (Cervus canadensis) | M132L, E226 |
| Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) | V2M, Del 84-91, G129S, S138N, Y153F, V169M, N176D, S225Y, P242L |
| Red deer (Cervus elaphus) | G59S, T98A, P168S, M208I, Q226E, I247L |
| Moose (Alces alces) | T36N, S100R, K109Q, M209I |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pritzkow, S. Transmission, Strain Diversity, and Zoonotic Potential of Chronic Wasting Disease. Viruses 2022, 14, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071390
Pritzkow S. Transmission, Strain Diversity, and Zoonotic Potential of Chronic Wasting Disease. Viruses. 2022; 14(7):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071390
Chicago/Turabian StylePritzkow, Sandra. 2022. "Transmission, Strain Diversity, and Zoonotic Potential of Chronic Wasting Disease" Viruses 14, no. 7: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071390
APA StylePritzkow, S. (2022). Transmission, Strain Diversity, and Zoonotic Potential of Chronic Wasting Disease. Viruses, 14(7), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071390





