Protective Immunity of COVID-19 Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Following Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Humoral and Cellular Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Samples
2.4. D-Dimer Quantitation
2.5. PRNT-SARS-CoV-2 Assay
2.6. Detection of Total Antibodies (IgG Anti-RBD)
2.7. IFN-γ ELISpot Assay
2.8. Activation-Induced Marker (AIM) Assay to Assess Memory Phenotypes for B and T Cells
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Does Not Induce D-Dimer Production
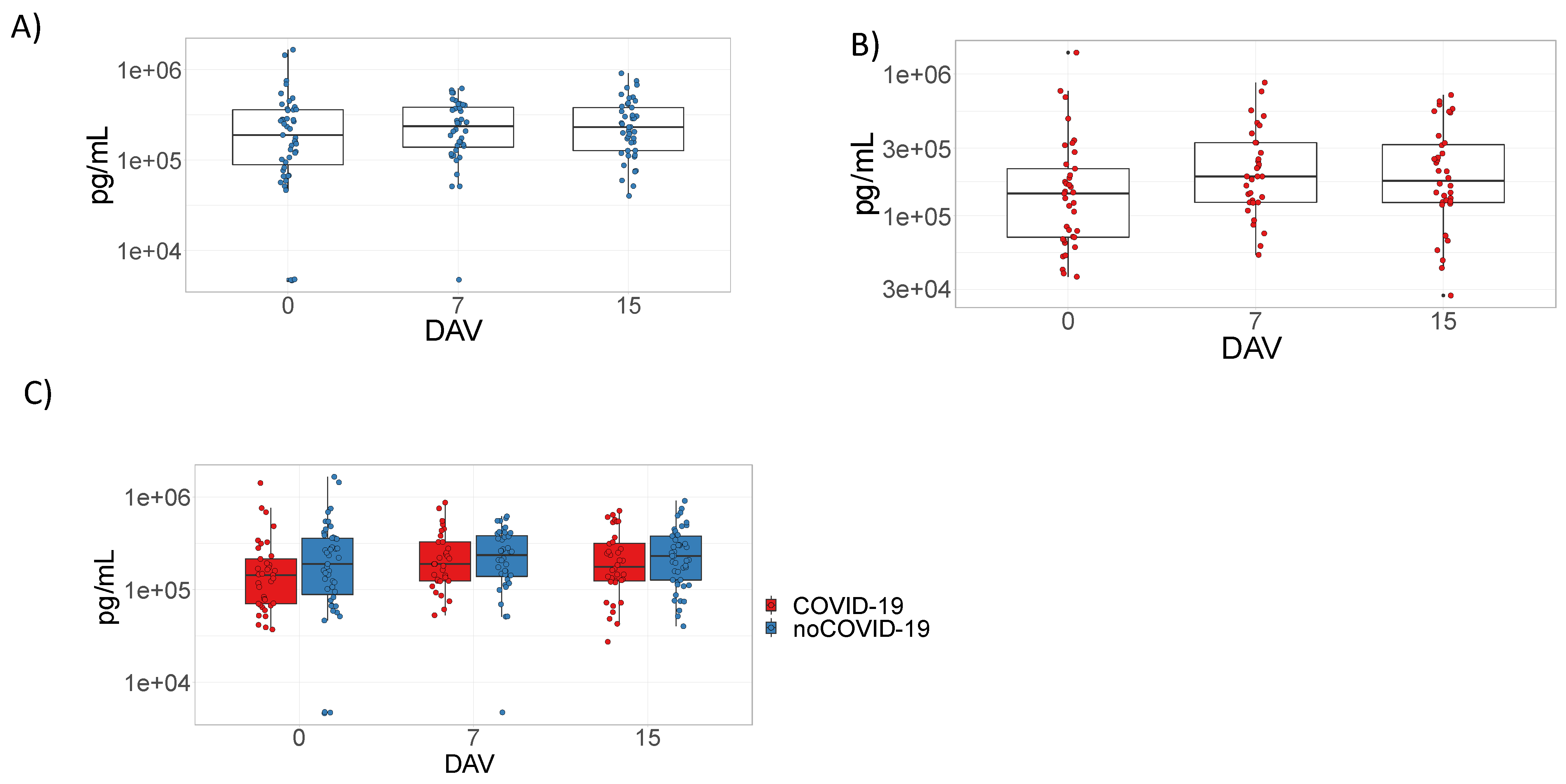
3.2. Analysis of the Humoral Response Elicited by ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
3.3. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Elicits Different Profiles of Cellular Response Dependent on Pre-Vaccination COVID-19 Status
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A Novel Coronavirus Outbreak of Global Health Concern. The Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard 2022; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, L.; Mescia, F.; Turner, L.; Hanson, A.L.; Kotagiri, P.; Dunmore, B.J.; Ruffieux, H.; De Sa, A.; Huhn, O.; Morgan, M.D.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis Reveals That Delayed Bystander CD8+ T Cell Activation and Early Immune Pathology Distinguish Severe COVID-19 from Mild Disease. Immunity 2021, 54, 1257–1275.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P. The T Cell Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.K.; Shin, E.-C. Phenotypes and Functions of SARS-CoV-2-Reactive T Cells. Mol. Cell. 2021, 44, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azkur, A.K.; Akdis, M.; Azkur, D.; Sokolowska, M.; Veen, W.; Brüggen, M.; O’Mahony, L.; Gao, Y.; Nadeau, K.; Akdis, C.A. Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 and Mechanisms of Immunopathological Changes in COVID-19. Allergy 2020, 75, 1564–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Ning, L.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, D.; Yuan, D.; Lausted, C.; Choi, J.; Dai, C.L.; Voillet, V.; Duvvuri, V.R.; Scherler, K.; Troisch, P.; et al. Multi-Omics Resolves a Sharp Disease-State Shift between Mild and Moderate COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 1479–1495.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Tang, X.-J.; Shi, Q.-L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.-J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.-J.; et al. Clinical and Immunological Assessment of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarrondo, F.J.; Fulcher, J.A.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Elliott, J.; Hofmann, C.; Hausner, M.A.; Ferbas, K.G.; Tobin, N.H.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Yang, O.O. Rapid Decay of Anti–SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Persons with Mild Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K.; et al. Robust Neutralizing Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Persist for Months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, B.J.; Ellebedy, A.H. The Germinal Centre B Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Candia, P.; Prattichizzo, F.; Garavelli, S.; Matarese, G. T Cells: Warriors of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodda, L.B.; Netland, J.; Shehata, L.; Pruner, K.B.; Morawski, P.A.; Thouvenel, C.D.; Takehara, K.K.; Eggenberger, J.; Hemann, E.A.; Waterman, H.R.; et al. Functional SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immune Memory Persists after Mild COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 169–183.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Vercruysse, T.; Sharma, S.; Ma, J.; Lemmens, V.; Van Looveren, D.; Arkalagud Javarappa, M.P.; Boudewijns, R.; Malengier-Devlies, B.; Liesenborghs, L.; et al. A Single-Dose Live-Attenuated YF17D-Vectored SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Candidate. Nature 2021, 590, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Peter, L.; Mercado, N.B.; McMahan, K.; Mahrokhian, S.H.; Nkolola, J.P.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. DNA Vaccine Protection against SARS-CoV-2 in Rhesus Macaques. Science 2020, 369, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doremalen, N.; Lambe, T.; Spencer, A.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Purushotham, J.N.; Port, J.R.; Avanzato, V.A.; Bushmaker, T.; Flaxman, A.; Ulaszewska, M.; et al. ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine Prevents SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in Rhesus Macaques. Nature 2020, 586, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A Preliminary Report of a Phase 1/2, Single-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.N.; Minassian, A.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Flaxman, A.L.; Folegatti, P.M.; Owens, D.R.; Voysey, M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Babbage, G.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine Administered in a Prime-Boost Regimen in Young and Old Adults (COV002): A Single-Blind, Randomised, Controlled, Phase 2/3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doremalen, N.; Lambe, T.; Sebastian, S.; Bushmaker, T.; Fischer, R.; Feldmann, F.; Haddock, E.; Letko, M.; Avanzato, V.A.; Rissanen, I.; et al. A Single-Dose ChAdOx1-Vectored Vaccine Provides Complete Protection against Nipah Bangladesh and Malaysia in Syrian Golden Hamsters. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryan, L.; Pulendran, B. The Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Dold, C.; Ewer, K.J.; Folegatti, P.M.; Gilbride, C.; Halkerston, R.; Hill, J.; Jenkin, D.; Stockdale, L.; et al. Phase 1/2 Trial of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 with a Booster Dose Induces Multifunctional Antibody Responses. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewer, K.J.; Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Sharpe, H.; Makinson, R.; Morter, R.; Flaxman, A.; Wright, D.; Bellamy, D.; Bittaye, M.; et al. T Cell and Antibody Responses Induced by a Single Dose of ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 (AZD1222) Vaccine in a Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Sobieszczyk, M.E.; Hirsch, I.; Sproule, S.; Robb, M.L.; Corey, L.; Neuzil, K.M.; Hahn, W.; Hunt, J.; Mulligan, M.J.; et al. Phase 3 Safety and Efficacy of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 NCoV-19) Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2348–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 NCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Palankar, R.; Wesche, J.; Handtke, S.; Wolff, M.; Aurich, K.; Lalk, M.; Methling, K.; Völker, U.; et al. Insights in ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia. Blood 2021, 138, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Theiler-Schwetz, V.; Trummer, C.; Krause, R.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. SARS-CoV-2 Reinfections: Overview of Efficacy and Duration of Natural and Hybrid Immunity. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibwana, M.G.; Moyo-Gwete, T.; Kwatra, G.; Mandolo, J.; Hermanaus, T.; Motlou, T.; Mzindle, N.; Ayres, F.; Chaponda, M.; Tembo, G.; et al. AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine Induces Robust Broadly Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses in Malawian Adults Previously Infected with SARS-CoV-2. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2018, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Melgaço, F.G.; Azamor, T.; Villar, L.M.; Ano Bom, A.P.D.; Melgaço, J.G. Impairment of CD4+ T and Memory B Cell Responses but Normal Memory CD8+T-Cell Activation on Crohn’s Disease after COVID-19 Vaccination: A Twin Case. Viruses 2021, 13, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) 2022; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022.
- Chung, H.; Noh, J.Y.; Koo, B.-S.; Hong, J.J.; Kim, H.K. SARS-CoV-2 Mutations Acquired during Serial Passage in Human Cell Lines Are Consistent with Several of Those Found in Recent Natural SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadesalingam, A.; Cantoni, D.; Wells, D.A.; Aguinam, E.T.; Ferrari, M.; Smith, P.; Chan, A.; Carnell, G.; Ohlendorf, L.; Einhauser, S.; et al. Paucity and Discordance of Neutralising Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 VOCs in Vaccinated Immunodeficient Patients and Health-Care Workers in the UK. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e416–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, M.; Shashidhar, J.; Deepika, G.; Ravikanth, V.; Krishna, V.V.; Sadhana, Y.; Pragathi, K.; Reddy, D.N. Immunological Memory and Neutralizing Activity to a Single Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine in Previously Infected Individuals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Barnes, C.O.; Finkin, S.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Cipolla, M.; Gaebler, C.; Lieberman, J.A.; et al. MRNA Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and Circulating Variants. Nature 2021, 592, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebinger, J.E.; Fert-Bober, J.; Printsev, I.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Prostko, J.C.; Frias, E.C.; Stewart, J.L.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Braun, J.G.; et al. Antibody Responses to the BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine in Individuals Previously Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct Antibody and Memory B Cell Responses in SARS-CoV-2 Naïve and Recovered Individuals after MRNA Vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatatos, L.; Czartoski, J.; Wan, Y.-H.; Homad, L.J.; Rubin, V.; Glantz, H.; Neradilek, M.; Seydoux, E.; Jennewein, M.F.; MacCamy, A.J.; et al. MRNA Vaccination Boosts Cross-Variant Neutralizing Antibodies Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Science 2021, 372, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaxman, A.; Marchevsky, N.G.; Jenkin, D.; Aboagye, J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Cappuccini, F.; et al. Reactogenicity and Immunogenicity after a Late Second Dose or a Third Dose of ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 in the UK: A Substudy of Two Randomised Controlled Trials (COV001 and COV002). Lancet 2021, 398, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamor, T.; da Silva, A.M.V.; Melgaço, J.G.; dos Santos, A.P.; Xavier-Carvalho, C.; Alvarado-Arnez, L.E.; Batista-Silva, L.R.; de Souza Matos, D.C.; Bayma, C.; Missailidis, S.; et al. Activation of an Effective Immune Response after Yellow Fever Vaccination Is Associated with the Genetic Background and Early Response of IFN-γ and CLEC5A. Viruses 2021, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.; McReynolds, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Ikram, A.; Ali, A.; Bashir, A.; Zohra, T.; Chang, W.L.W.; Hartigan-O’Connor, D.J.; et al. Immune Response Dynamics in COVID-19 Patients to SARS-CoV-2 and Other Human Coronaviruses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnke, Y.D.; Brodie, T.M.; Sallusto, F.; Roederer, M.; Lugli, E. The Who’s Who of T-Cell Differentiation: Human Memory T-Cell Subsets: HIGHLIGHTS. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bert, N.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Immunity in Cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and Uninfected Controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Coelho, C.H.; Zhang, Z.; Dan, J.M.; Yu, E.D.; Methot, N.; Bloom, N.I.; Goodwin, B.; Phillips, E.; Mallal, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Induces Immunological T Cell Memory Able to Cross-Recognize Variants from Alpha to Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, 847–859.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No COVID-19 (n = 58) | COVID-19 (n = 37) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (average ± SD) | 39.1 ± 8.7 | 37.1 ± 9.6 |
| BMI (average ± SD) | 30 ± 20.5 | 28.1 ± 5.1 |
| Sex (F/M) | 39/19 | 24/13 |
| COVID-19 clinical classification (asymptomatic/mild/severe) | 7/27/3 |
| Parameter Analyzed | 0 DAV (1st Dose) | 7 DAV | 15 DAV | 30 DAV | 90 DAV (2nd Dose) | 120 DAV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma D-Dimer | X | X | X | |||
| Plasma total anti-spike IgG | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Serum neutralizing antibodies | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| IFN-γ secretion by PBMC | X | X | X | X | X |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azamor, T.; Horbach, I.S.; Brito e Cunha, D.; Melgaço, J.G.; Silva, A.M.V.d.; Tubarão, L.N.; Azevedo, A.d.S.; Santos, R.T.; Alves, N.d.S.; Machado, T.L.; et al. Protective Immunity of COVID-19 Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Following Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Humoral and Cellular Investigation. Viruses 2022, 14, 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091916
Azamor T, Horbach IS, Brito e Cunha D, Melgaço JG, Silva AMVd, Tubarão LN, Azevedo AdS, Santos RT, Alves NdS, Machado TL, et al. Protective Immunity of COVID-19 Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Following Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Humoral and Cellular Investigation. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091916
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzamor, Tamiris, Ingrid Siciliano Horbach, Danielle Brito e Cunha, Juliana Gil Melgaço, Andréa Marques Vieira da Silva, Luciana Neves Tubarão, Adriana de Souza Azevedo, Renata Tourinho Santos, Nathalia dos Santos Alves, Thiago Lazari Machado, and et al. 2022. "Protective Immunity of COVID-19 Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Following Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Humoral and Cellular Investigation" Viruses 14, no. 9: 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091916
APA StyleAzamor, T., Horbach, I. S., Brito e Cunha, D., Melgaço, J. G., Silva, A. M. V. d., Tubarão, L. N., Azevedo, A. d. S., Santos, R. T., Alves, N. d. S., Machado, T. L., Silva, J., Souza, A. F. d., Bayma, C., Rocha, V. P., Frederico, A. B. T., Dias, B. d. M., Setatino, B. P., Denani, C. B., Campos, S. P. d. C., ... Missailidis, S. (2022). Protective Immunity of COVID-19 Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Following Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Humoral and Cellular Investigation. Viruses, 14(9), 1916. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091916







