Evaluation of Saliva as a Matrix for RT-PCR Analysis and Two Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. SARS-CoV-2 Detection Methods
2.2.1. Real-Time PCR Using Nasopharyngeal Swabs
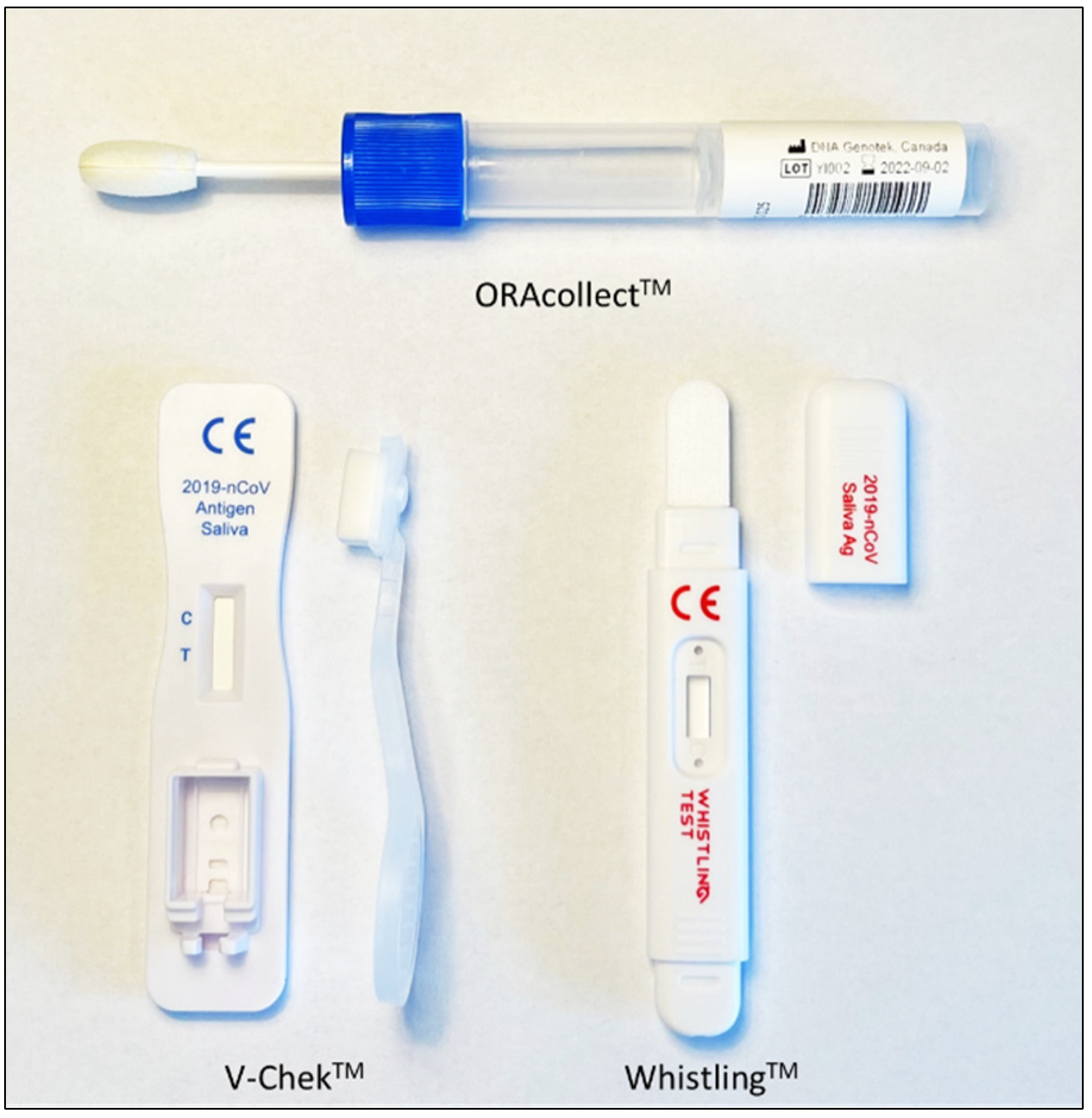
2.2.2. Real-Time PCR Using ORAcollectTM
2.2.3. AgRDT Using V-ChekTM and WhistlingTM Test
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. ORAcollectTM Compared to Nasopharyngeal Sample
3.2. V-ChekTM
3.3. WhistlingTM Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsack, J.C.; Coravos, A.; Bakker, J.P.; Bent, B.; Dowling, A.V.; Fitzer-Attas, C.; Godfrey, A.; Godino, J.G.; Gujar, N.; Izmailova, E.; et al. Verification, analytical validation, and clinical validation (V3): The foundation of determining fit-for-purpose for Biometric Monitoring Technologies (BioMeTs). NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi Karkan, S.; Maleki Baladi, R.; Shahgolzari, M.; Gholizadeh, M.; Shayegh, F.; Arashkia, A. The evolving direct and indirect platforms for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 300, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.F.; Selvam, K.; Jeffry, A.J.N.; Salmi, M.F.; Najib, M.A.; Norhayati, M.N.; Aziah, I. Performance of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Warren, J.L.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J.; et al. Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Options for the Use of Rapid Antigen Detection Tests for COVID-19 in the EU/EEA—First Update; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mestdagh, P.; Gillard, M.; Dhillon, S.K.; Pirnay, J.P.; Poels, J.; Hellemans, J.; Hutse, V.; Vermeiren, C.; Boutier, M.; De Wever, V.; et al. Evaluating Diagnostic Accuracy of Saliva Sampling Methods for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Reveals Differential Sensitivity and Association with Viral Load. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, G.; Hsiao, N.-y.; Iranzadeh, A.; Doolabh, D.; Enoch, A.; Chu, C.-y.; Williamson, C.; Brink, A.; Hardie, D. Saliva swabs are the preferred sample for Omicron detection. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M. HKUMed finds Omicron SARS-CoV-2 can infect faster and better than Delta in human bronchus but with less severe infection in lung. Braz. J. Implantol. Health Sci. 2022, 4, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Recommendations for National SARS-CoV-2 Testing Strategies and Diagnostic Capacities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A Coefficient of Agreement for Nominal Scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan-Galito, S.; Tarantini, F.S.; Tomlin, H.; Jenkins, H.; Thompson, J.L.; Scales, D.; Stroud, A.; Tellechea Lopez, A.; Hassall, J.; McTernan, P.G.; et al. Saliva for COVID-19 Testing: Simple but Useless or an Undervalued Resource? Front. Virol. 2021, 1, 778790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikos, A.; Caruana, G.; Brouillet, R.; Miroz, J.-P.; Abed-Maillard, S.; Stieger, G.; Opota, O.; Croxatto, A.; Vollenweider, P.; Bart, P.-A.; et al. Sensitivity of Rapid Antigen Testing and RT-PCR Performed on Nasopharyngeal Swabs versus Saliva Samples in COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients: Results of a Prospective Comparative Trial (RESTART). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruana, G.; Croxatto, A.; Kampouri, E.; Kritikos, A.; Opota, O.; Foerster, M.; Brouillet, R.; Senn, L.; Lienhard, R.; Egli, A.; et al. Implementing SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Testing in the Emergency Ward of a Swiss University Hospital: The INCREASE Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Emergency use authorization (EUA) summary ORAcollect. In RNA Device Models (ORAcollect·RNA ORE-100 and ORACOLLECT·RNA or-100); Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Meyer, J.; Goris, H.; Mortelé, O.; Spiessens, A.; Hans, G.; Jansens, H.; Goossens, H.; Matheeussen, V.; Vandamme, S.; Antwerp University Hospital (UZA), 2650 Edegem, Belgium. Effect of ORAcollectTM extraction volume on the ΔCt between saliva and nasopharyngeal swab SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR results. Unpublished work. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- De Meyer, J.; Goris, H.; Mortelé, O.; Spiessens, A.; Hans, G.; Jansens, H.; Goossens, H.; Matheeussen, V.; Vandamme, S.; Antwerp University Hospital (UZA), 2650 Edegem, Belgium. Detection of RNAseP in discordant saliva samples. Unpublished work. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jegerlehner, S.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Jent, P.; Bittel, P.; Nagler, M. Diagnostic accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 saliva antigen testing in a real-life clinical setting. International J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 119, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasomsub, E.; Watcharananan, S.P.; Boonyawat, K.; Janchompoo, P.; Wongtabtim, G.; Suksuwan, W.; Sungkanuparph, S.; Phuphuakrat, A. Saliva sample as a non-invasive specimen for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 285.e1–285.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobaño, C.; Alonso, S.; Vidal, M.; Jiménez, A.; Rubio, R.; Santano, R.; Barrios, D.; Tomas, G.P.; Melé Casas, M.; Hernández García, M.; et al. Multiplex Antibody Analysis of IgM, IgA and IgG to SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva and Serum from Infected Children and their Close Contacts. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igloi, Z.; Velzing, J.; Huisman, R.; Geurtsvankessel, C.; Comvalius, A.; Ijpelaar, J.; van Beek, J.; Ensing, R.; Boelsums, T.; Koopmans, M.; et al. Clinical evaluation of the SD Biosensor SARS-CoV-2 saliva antigen rapid test with symptomatic and asymptomatic, non-hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Grosser, R.; Wisplinghoff, F.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Wiesmuller, G.; Schildgen, O.; Schildgen, V. SARS-CoV-2, CT-Values, and Infectivity-Conclusions to Be Drawn from Side Observations. Viruses 2021, 13, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congrave-Wilson, Z.; Lee, Y.; Jumarang, J.; Perez, S.; Bender, J.M.; Bard, J.D.; Pannaraj, P.S. Change in Saliva RT-PCR Sensitivity Over the Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA 2021, 326, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, Y.; Suda, Y.; Yano, K. A case report of SARS-CoV-2 confirmed in saliva specimens up to 37 days after onset: Proposal of saliva specimens for COVID-19 diagnosis and virus monitoring. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.-W.; Tsang, O.T.-Y.; Leung, W.-S.; Tam, A.R.; Wu, T.-C.; Lung, D.C.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Cai, J.-P.; Chan, J.M.-C.; Chik, T.S.-H.; et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.-K.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Poon, R.W.-S.; Chan, K.-H.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Yuen, K.-Y.; To, K.K.-W. Evaluating the use of posterior oropharyngeal saliva in a point-of-care assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ORAcollectTM (RT-PCR) | V-ChekTM (AgRDT) | Whistling TestTM (AgRDT) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| True positives | 100 (28.8%) | 1 (1.9%) | 5 (4.1%) |
| True negatives | 218 (62.8%) | 37 (68.5%) | 47 (38.2%) |
| False positives | 8 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| False negatives | 21 (6.1%) | 12 (22.2%) | 50 (40.7%) |
| Invalid results | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (7.4%) | 21 (17.1%) |
| Total number of samples | 347 | 54 | 123 |
| Sensitivity | 82.6% | 7.7% | 9.1% |
| Specificity b | 96.5%/99.1% b | 100% | 100% |
| NPV a | 91.3% | 66.9% | 67.3% |
| PPV a,b | 92.6%/98.0% b | 100% | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Meyer, J.; Goris, H.; Mortelé, O.; Spiessens, A.; Hans, G.; Jansens, H.; Goossens, H.; Matheeussen, V.; Vandamme, S. Evaluation of Saliva as a Matrix for RT-PCR Analysis and Two Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2022, 14, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091931
De Meyer J, Goris H, Mortelé O, Spiessens A, Hans G, Jansens H, Goossens H, Matheeussen V, Vandamme S. Evaluation of Saliva as a Matrix for RT-PCR Analysis and Two Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091931
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Meyer, Julie, Hanne Goris, Olivier Mortelé, An Spiessens, Guy Hans, Hilde Jansens, Herman Goossens, Veerle Matheeussen, and Sarah Vandamme. 2022. "Evaluation of Saliva as a Matrix for RT-PCR Analysis and Two Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2" Viruses 14, no. 9: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091931
APA StyleDe Meyer, J., Goris, H., Mortelé, O., Spiessens, A., Hans, G., Jansens, H., Goossens, H., Matheeussen, V., & Vandamme, S. (2022). Evaluation of Saliva as a Matrix for RT-PCR Analysis and Two Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses, 14(9), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14091931






