SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring in Wastewater Reveals Novel Variants and Biomarkers of Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
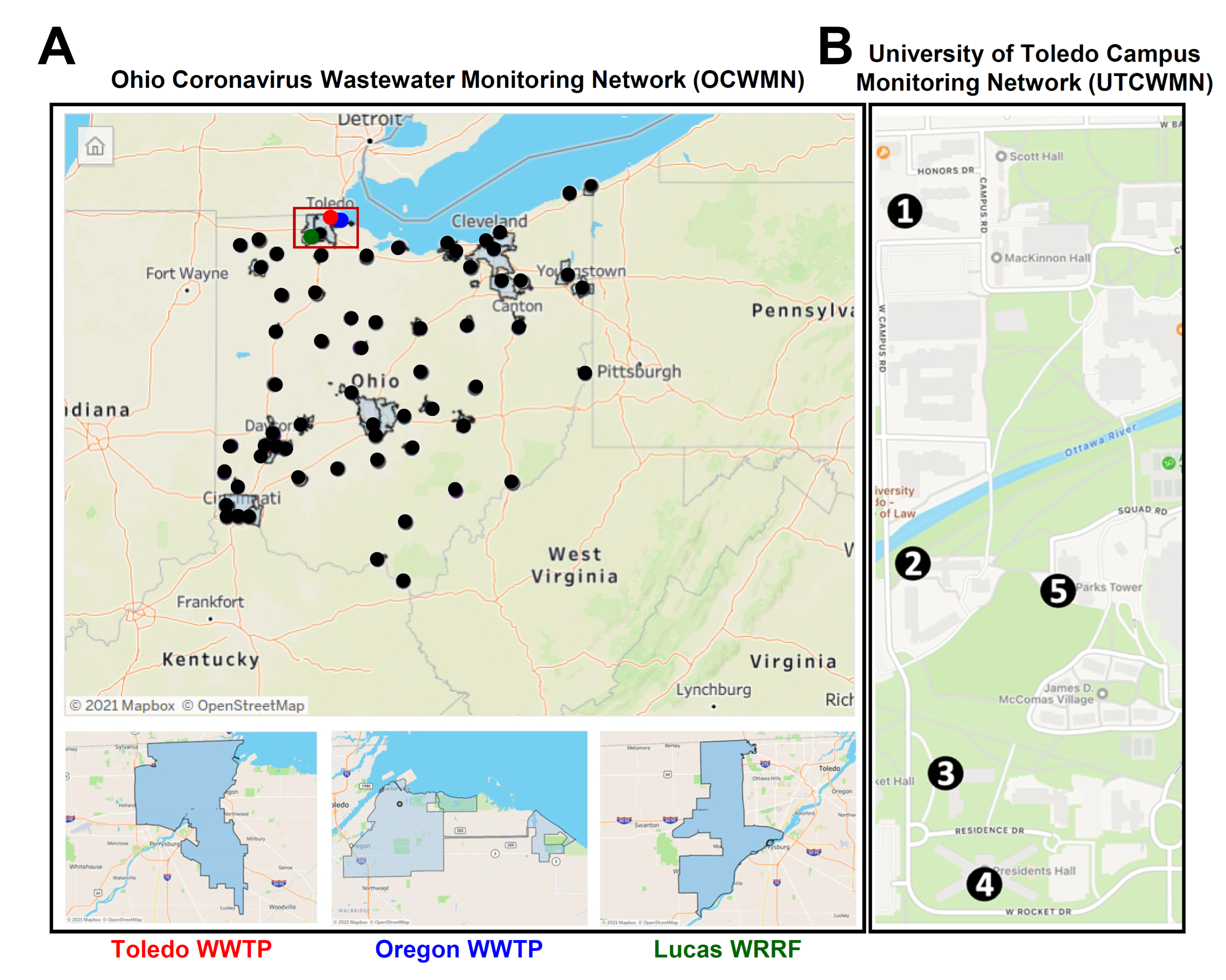
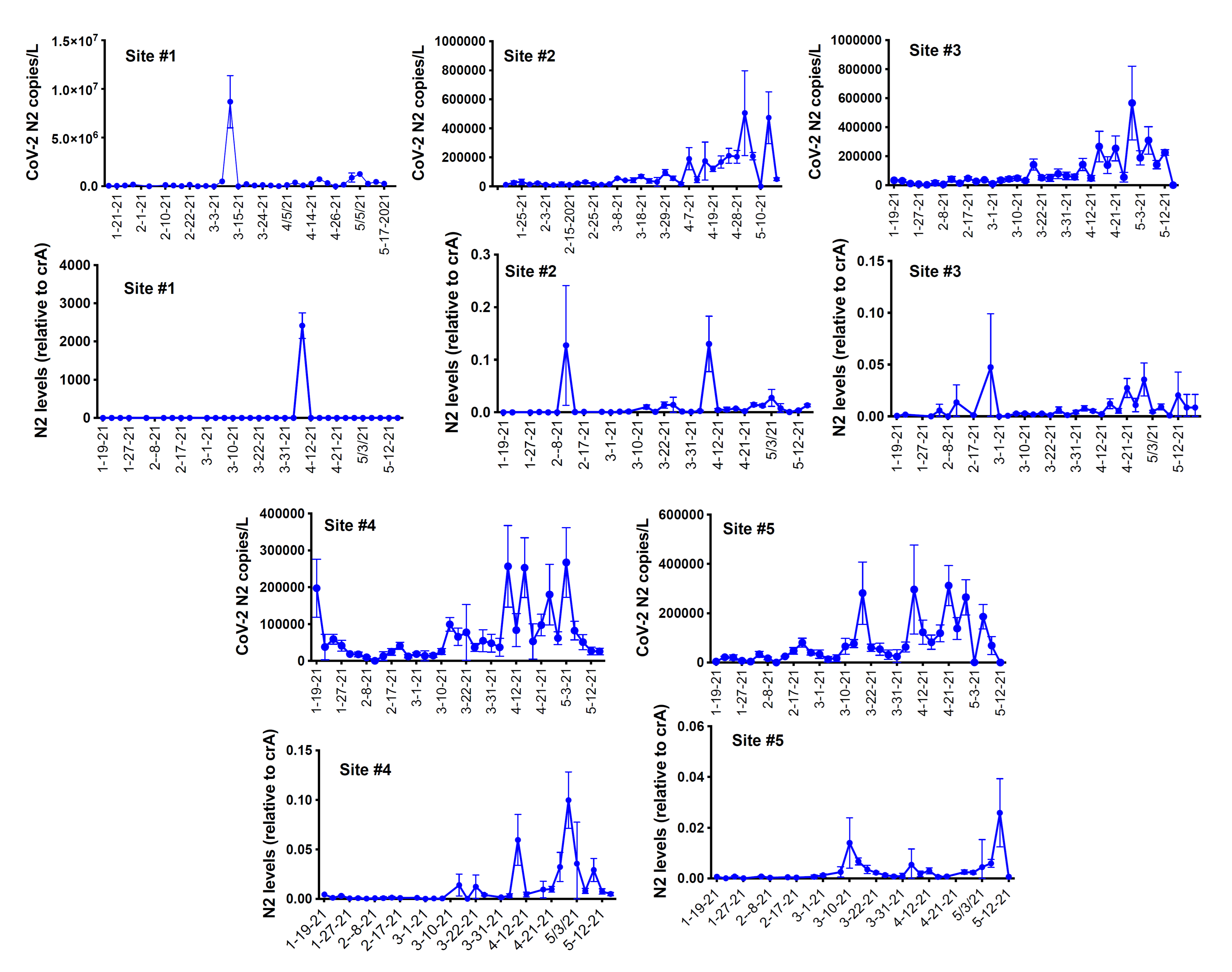
2.1. Ohio Wastewater Network and the University of Toledo Campus Monitoring Network
2.2. Wastewater Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Extraction from the Wastewater
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR Analyses of the SARS-CoV-2 Gene Copy Levels
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Genome Amplification and Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Microbiome Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
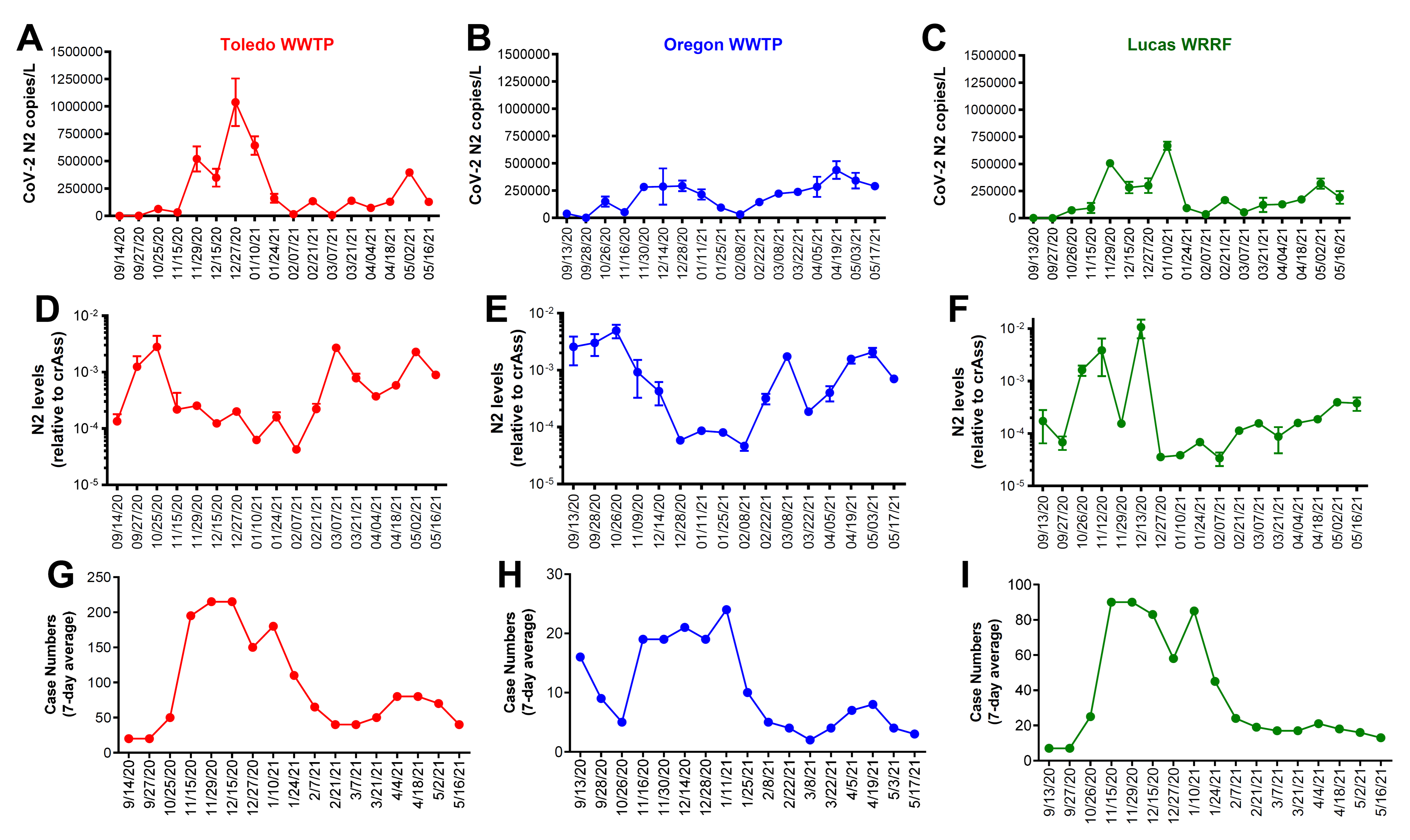
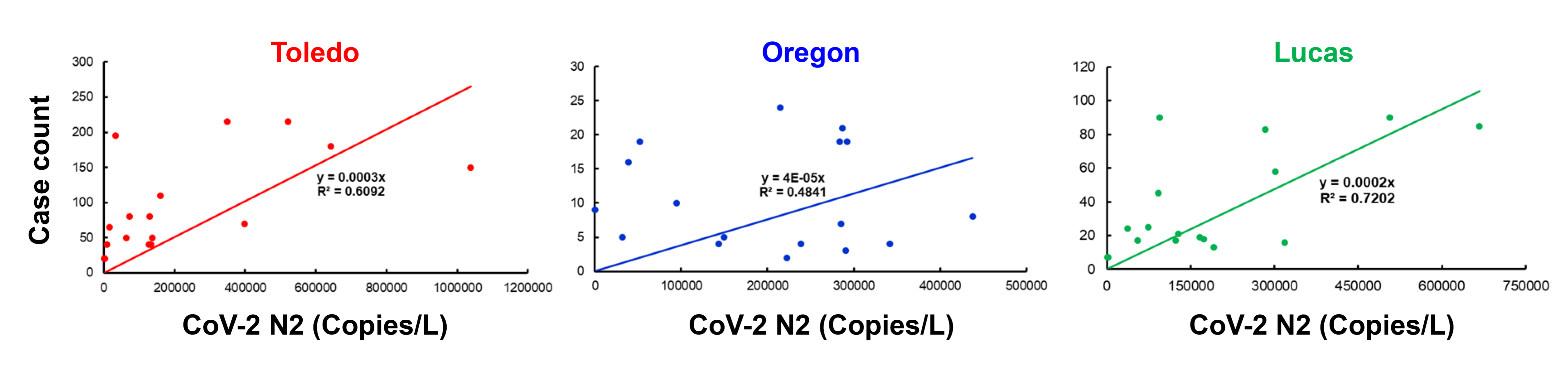
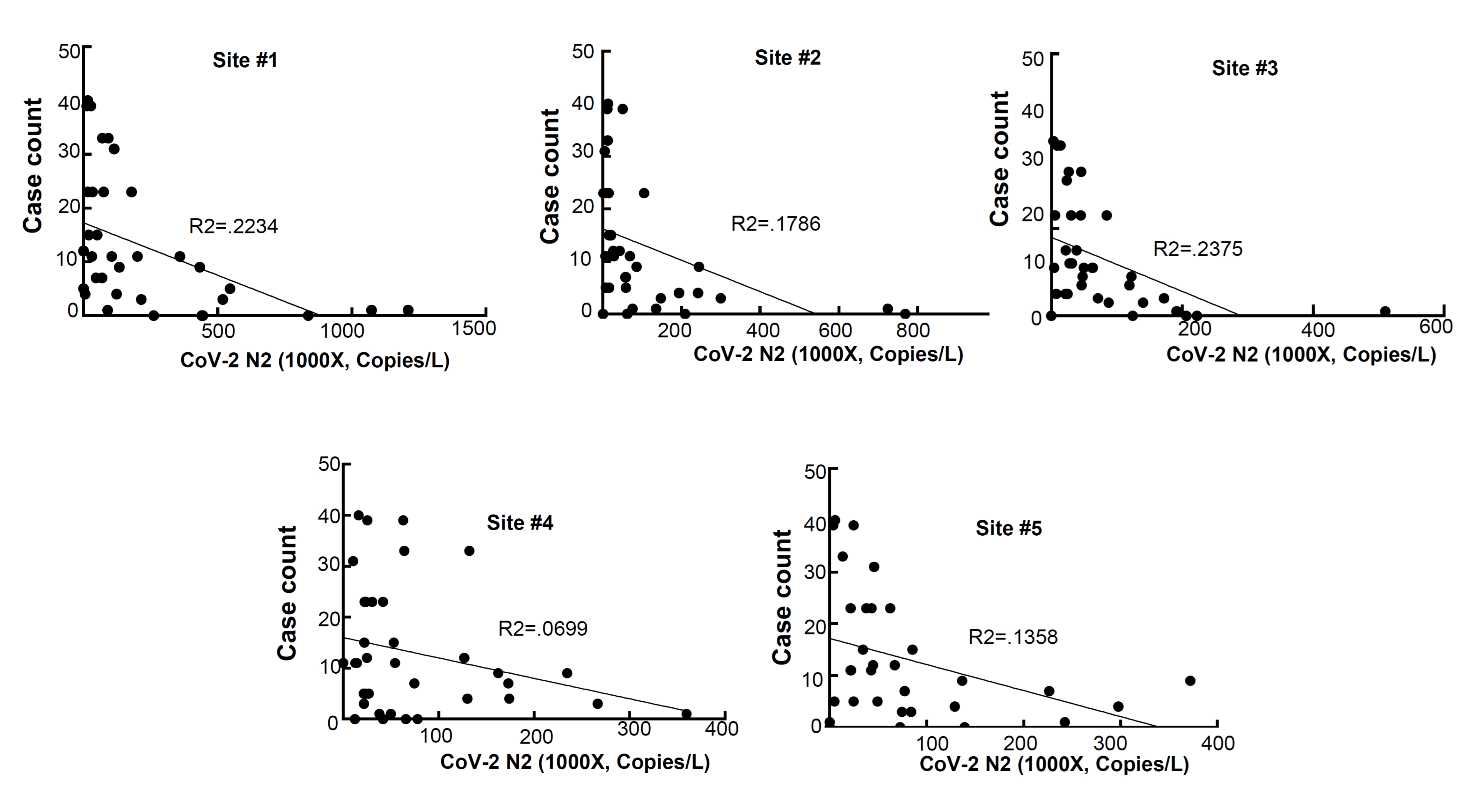
3.1. Correlation between the Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 Viral Gene Copies and the Case Counts
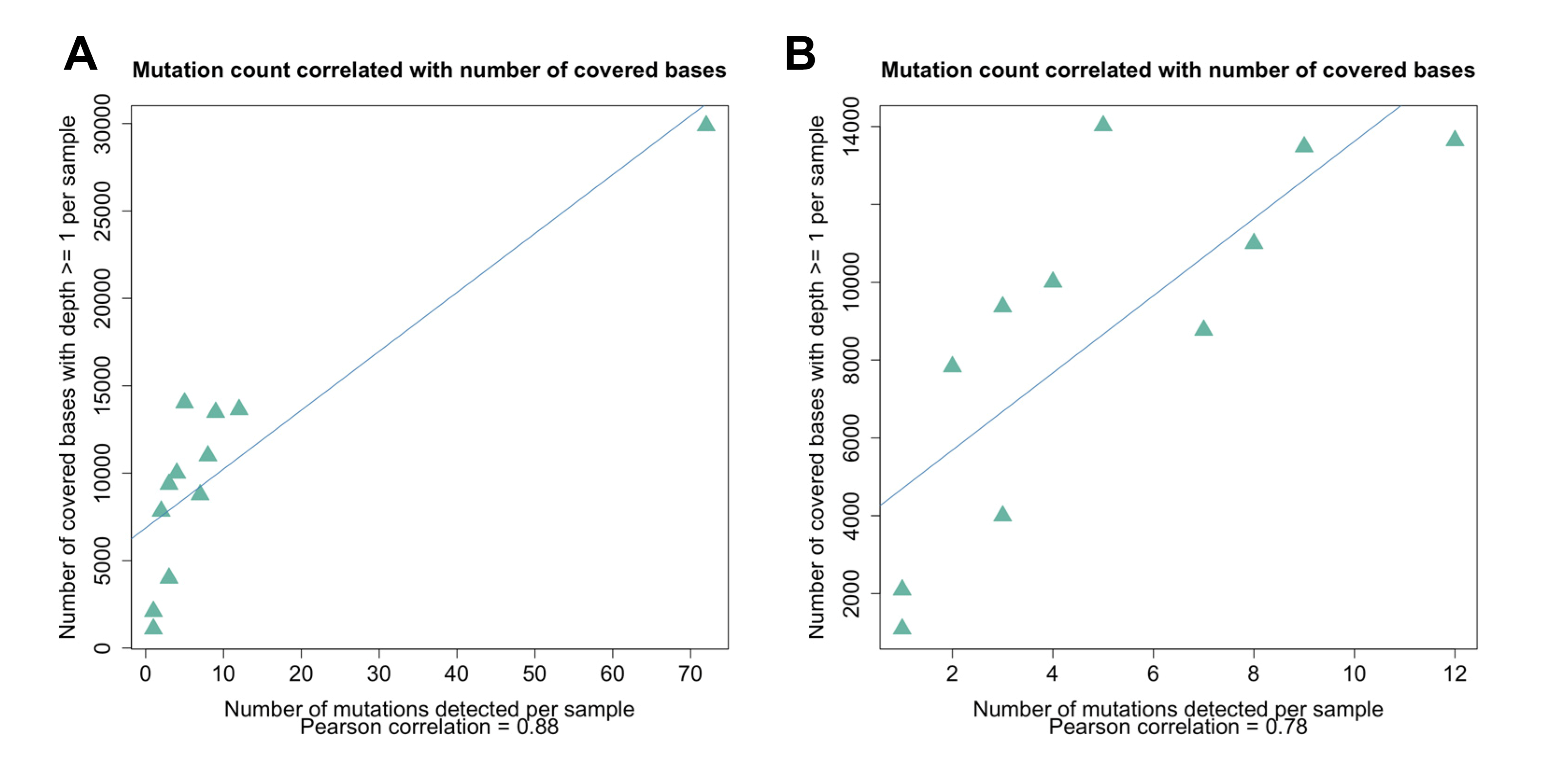
3.2. Sequence Analysis of the Wastewater Samples
3.3. Potential Bacterial Biomarkers to Strengthen Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soleimanian, S.; Alyasin, S.; Sepahi, N.; Ghahramani, Z.; Kanannejad, Z.; Yaghobi, R.; Karimi, M.H. An Update on Protective Effectiveness of Immune Responses After Recovery from COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 884879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. The humoral response and antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogharab, V.; Ostovar, M.; Ruszkowski, J.; Hussain, S.Z.M.; Shrestha, R.; Yaqoob, U.; Aryanpoor, P.; Nikkhoo, A.M.; Heidari, P.; Jahromi, A.R.; et al. Global burden of the COVID-19 associated patient-related delay in emergency healthcare: A panel of systematic review and meta-analyses. Glob. Health 2022, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Nishimura, A.; Noda, T.; Okabe, K.; Kusakabe, T.; Kanda, Y.; Nishida, M. Drug repurposing for the treatment of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 149, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnaggar, M.; Abomhya, A.; Elkhattib, I.; Dawoud, N.; Doshi, R. COVID-19 and liver diseases, what we know so far. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 3969–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.E.; Spiro, D.J.; Viboud, C. Projecting the SARS-CoV-2 transition from pandemicity to endemicity: Epidemiological and immunological considerations. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immunity: The first line of defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGrace, M.M.; Ghedin, E.; Frieman, M.B.; Krammer, F.; Grifoni, A.; Alisoltani, A.; Alter, G.; Amara, R.R.; Baric, R.S.; Barouch, D.H.; et al. Defining the risk of SARS-CoV-2 variants on immune protection. Nature 2022, 605, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Ji, X.; Suchard, M.A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Emerging viruses: Cross-species transmission of coronaviruses, filoviruses, henipaviruses, and rotaviruses from bats. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xie, C.; Bu, G.L.; Zhong, L.Y.; Zeng, M.S. Molecular characteristics, immune evasion, and impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Signal Transduct Target. Ther 2022, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Rao, Z. The Life of SARS-CoV-2 Inside Cells: Replication-Transcription Complex Assembly and Function. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Miao, J.; Guo, R.; Guo, J.; Fan, Z.; Kong, X.; Gao, R.; Yang, L. Mechanism of COVID-19 Causing ARDS: Exploring the Possibility of Preventing and Treating SARS-CoV-2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 931061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberberg, E.; Filep, J.G.; Ariel, A. Weathering the Storm: Harnessing the Resolution of Inflammation to Limit COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 863449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivshankar, P.; Karmouty-Quintana, H.; Mills, T.; Doursout, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Czopik, A.K.; Evans, S.E.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Yuan, X. SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Host Response, Immunity, and Therapeutic Targets. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1430–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, R.J.; Yu, W.C.; Peng, G.R.; Ye, C.H.; Hu, S.; Chong, P.C.T.; Yap, K.Y.; Lee, J.Y.C.; Lin, W.C.; Yu, S.H. The Role of Cytokines and Chemokines in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infections. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 832394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovito, R.; Augello, M.; Ben-Haim, A.; Bono, V.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Marchetti, G. Hallmarks of Severe COVID-19 Pathogenesis: A Pas de Deux Between Viral and Host Factors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 912336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Hsu, M.T.; Lee, M.Y.; Chou, C.K. Gastrointestinal Involvement in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xiong, C.; Qian, H. Direct mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-induced cardiomyocyte damage: An update. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Wong, F.; Couch, L.S.; Wang, B.X. Cardiac Complications of COVID-19 in Low-Risk Patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasek, S.M.; Pepper, I.L.; Innes, G.K.; Slinski, S.; Ruedas, M.; Sanchez, A.; Brierley, P.; Betancourt, W.Q.; Stark, E.R.; Foster, A.R.; et al. Population level SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding rates determined via wastewater-based epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmalbaf, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Niasar, M.S.; Shoraka, S.; Yadegar, A.; Baradaran Ghavami, S.; Shahrokh, S.; Moshari, M.; Malekpour, H.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Genome in Stool and Plasma Samples of Laboratory Confirmed Iranian COVID-19 Patients. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 865129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.H.; Ni, W.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.J.; Li, G.J.; Wang, W.D.; Tong, J.N.; Song, X.F.; Wing-Kin Wong, G.; Xing, Q.S. Prolonged viral shedding in feces of pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Jacobo, L.R.; Islam, G.; Desaulniers, J.P.; Kirkwood, A.E.; Simmons, D.B.D. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins in Wastewater Samples by Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5062–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron-Navarro, R.; Linares-Hernandez, I.; Castillo-Suarez, L.A. The impact of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) in water: Potential risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 52651–52674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Cutrupi, F.; Segata, N.; Manara, S.; Pinto, F.; Malpei, F.; Bruni, L.; La Rosa, G. SARS-CoV-2 from faeces to wastewater treatment: What do we know? A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liang, T.J. Is SARS-CoV-2 Also an Enteric Pathogen with Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission? A COVID-19 Virological and Clinical Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, K.; Chen, W.; Bivins, A.; Lowry, S.; Bibby, K. Contribution of SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding routes to RNA loads in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, P.; Dash, S.; Honda, R.; Sonne, C.; Kumar, M. Sewage surveillance for SARS-CoV-2: Molecular detection, quantification, and normalization factors. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 28, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivins, A.; North, D.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmed, W.; Alm, E.; Been, F.; Bhattacharya, P.; Bijlsma, L.; Boehm, A.B.; Brown, J.; et al. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology: Global Collaborative to Maximize Contributions in the Fight Against COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7754–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, M.; Keely, S.P.; Jahne, M.; Wheaton, E.; Hart, C.; Smith, B.; Garland, J.; Varughese, E.A.; Braam, A.; Wiechman, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 monitoring at three sewersheds of different scales and complexity demonstrates distinctive relationships between wastewater measurements and COVID-19 case data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Davis, A.; Jones, D.; Lemeshow, S.; Tu, H.; He, F.; Ru, P.; Pan, X.; Bohrerova, Z.; Lee, J. Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 monitoring as a community-level COVID-19 trend tracker and variants in Ohio, United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, G.; Heijnen, L.; Elsinga, G.; Italiaander, R.; Brouwer, A. Presence of SARS-Coronavirus-2 RNA in Sewage and Correlation with Reported COVID-19 Prevalence in the Early Stage of the Epidemic in The Netherlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidhaas, J.; Aanderud, Z.T.; Roper, D.K.; VanDerslice, J.; Gaddis, E.B.; Ostermiller, J.; Hoffman, K.; Jamal, R.; Heck, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater with COVID-19 disease burden in sewersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, A.; Wu, F.; Bushman, M.; Zhang, J.; Imakaev, M.; Chai, P.R.; Duvallet, C.; Endo, N.; Erickson, T.B.; Armas, F.; et al. Metrics to relate COVID-19 wastewater data to clinical testing dynamics. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safford, H.R.; Shapiro, K.; Bischel, H.N. Opinion: Wastewater analysis can be a powerful public health tool-if it’s done sensibly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119600119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Wu, Z.J.; Chen, Y.B.; Gao, H.; Lv, L.X.; Guo, F.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Luo, R.; Huang, C.J.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, S.; Stollman, N.; Bozkurt, H.S.; Dave, S.; Papoutsis, A.J.; Daniels, J.; Barrows, B.D.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Borody, T.J. Lost microbes of COVID-19: Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium depletion and decreased microbiome diversity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.L.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Fung, K.S.C.; et al. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Miyani, B.; Spooner, M.; Gentry, Z.; Jacobi, S.; David, R.E.; Withington, S.; McFarland, S.; et al. Five-week warning of COVID-19 peaks prior to the Omicron surge in Detroit, Michigan using wastewater surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Paital, S.; Raizada, P.; Ahamad, T.; Khan, A.A.P.; Thakur, S.; Singh, P.; Hussain, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Nadda, A.K. Surveillance of omicron variants through wastewater epidemiology: Latest developments in environmental monitoring of pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Gutierrez, V.; Hassard, F.; Vu, M.; Leitao, R.; Burczynska, B.; Wildeboer, D.; Stanton, I.; Rahimzadeh, S.; Baio, G.; Garelick, H.; et al. Monitoring occurrence of SARS-CoV-2 in school populations: A wastewater-based approach. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchi, N.B.; Hinton, D.R.; Stohlman, S.A.; Kapil, P.; Fensterl, V.; Sen, G.C.; Bergmann, C.C. Ifit2 deficiency results in uncontrolled neurotropic coronavirus replication and enhanced encephalitis via impaired alpha/beta interferon induction in macrophages. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Varghese, M.; Kottapalli, A.; Fan, S.; Chakravarti, R.; Chattopadhyay, S. Transcriptional and Non-Transcriptional Activation, Posttranslational Modifications, and Antiviral Functions of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and Viral Antagonism by the SARS-Coronavirus. Viruses 2021, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An amplicon-based sequencing framework for accurately measuring intrahost virus diversity using PrimalSeq and iVar. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilm, A.; Aw, P.P.K.; Bertrand, D.; Yeo, G.H.T.; Ong, S.H.; Wong, C.H.; Khor, C.C.; Petric, R.; Hibberd, M.L.; Nagarajan, N. LoFreq: A sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2012, 40, 11189–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiagen. DNeasy PowerSoil pro Kit Handbook; Qiagen: Hilden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Glier, M.; Kuchinski, K.; Ross-Van Mierlo, T.; McVea, D.; Tyson John, R.; Prystajecky, N.; Ziels Ryan, M.; Cristea Ileana, M. Assessing Multiplex Tiling PCR Sequencing Approaches for Detecting Genomic Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater. mSystems 2021, 6, e0106821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.M.; Gnanakaran, S.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W.; Hengartner, N.; Giorgi, E.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Foley, B.; et al. Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: Evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus. Cell 2020, 182, 812–827.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; He, S.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Kang, S. Structural Insight Into the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein C-Terminal Domain Reveals a Novel Recognition Mechanism for Viral Transcriptional Regulatory Sequences. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 624765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, K.R.; Rennick, L.J.; Nambulli, S.; Robinson-McCarthy, L.R.; Bain, W.G.; Haidar, G.; Duprex, W.P. Recurrent deletions in the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein drive antibody escape. Science 2021, 371, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Avenarius, M.R.; Kubatko, L.; Hunt, M.; Pan, X.; Ru, P.; Garee, J.; Thomas, K.; Mohler, P.; Pancholi, P.; et al. Distinct Patterns of Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variants including N501Y in Clinical Samples in Columbus Ohio. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodcroft, E.B.; Domman, D.B.; Snyder, D.J.; Oguntuyo, K.Y.; Van Diest, M.; Densmore, K.H.; Schwalm, K.C.; Femling, J.; Carroll, J.L.; Scott, R.S.; et al. Emergence in late 2020 of multiple lineages of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein variants affecting amino acid position 677. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z. Structure and Function of N-Terminal Zinc Finger Domain of SARS-CoV-2 NSP2. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, Y.; Tahvildari, A.; Arbabi, M.; Vazife, F.; Sechi, L.A.; Bonjar, A.H.S.; Jamshidi, P.; Nasiri, M.J.; Mirsaeidi, M. Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Roles of Gut Microbiota in COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 804644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Li, A.Y.L.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.T.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients with COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, R.C.; Gauthier, J.; Hernandez, M.C.; Abraham, G.E.; Robinson, T.O.; Williams, H.B.; Sloan, M.; Owings, A.; Laird, H.; Christian, T.; et al. The gut microbiome of COVID-19 recovered patients returns to uninfected status in a minority-dominated United States cohort. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1926840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Ma, K.; Luo, W.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Tong, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Roseburia intestinalis: A Beneficial Gut Organism from the Discoveries in Genus and Species. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 757718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia—A new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Park, J.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Wallstrom, G.; Labaer, J.; Adams, J.B.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Reduced incidence of Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Sample Count | Gene | AA Pos | Ave Alt Freq | Med Alt Freq | Ref AA | Alt AA | Toledo | Lucas | Oregon | UT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | orf1ab | 265 | 100.0% | 100.0% | T | I | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | orf1ab | 314 | 100.0% | 100.0% | P | L | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | S | 614 | 100.0% | 100.0% | D | G | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | orf3a | 57 | 100.0% | 100.0% | Q | H | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | N | 199 | 97.6% | 99.8% | P | L | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | N | 203 | 99.9% | 99.9% | R | K | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | N | 204 | 100.0% | 100.0% | G | R | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | N | 205 | 9.1% | 9.1% | T | I | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | N | 235 | 99.9% | 99.9% | S | F | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGowan, J.; Borucki, M.; Omairi, H.; Varghese, M.; Vellani, S.; Chakravarty, S.; Fan, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Siddiquee, M.; Thissen, J.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring in Wastewater Reveals Novel Variants and Biomarkers of Infection. Viruses 2022, 14, 2032. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092032
McGowan J, Borucki M, Omairi H, Varghese M, Vellani S, Chakravarty S, Fan S, Chattopadhyay S, Siddiquee M, Thissen JB, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring in Wastewater Reveals Novel Variants and Biomarkers of Infection. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):2032. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092032
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGowan, Jenna, Monica Borucki, Hicham Omairi, Merina Varghese, Shahnaz Vellani, Sukanya Chakravarty, Shumin Fan, Srestha Chattopadhyay, Mashuk Siddiquee, James B. Thissen, and et al. 2022. "SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring in Wastewater Reveals Novel Variants and Biomarkers of Infection" Viruses 14, no. 9: 2032. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092032
APA StyleMcGowan, J., Borucki, M., Omairi, H., Varghese, M., Vellani, S., Chakravarty, S., Fan, S., Chattopadhyay, S., Siddiquee, M., Thissen, J. B., Mulakken, N., Moon, J., Kimbrel, J., Tiwari, A. K., Taylor, R. T., Kang, D.-W., Jaing, C., Chakravarti, R., & Chattopadhyay, S. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring in Wastewater Reveals Novel Variants and Biomarkers of Infection. Viruses, 14(9), 2032. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092032










