The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Isolation, Propagation, Purification and Host Range Determination of vB_YenS_P840
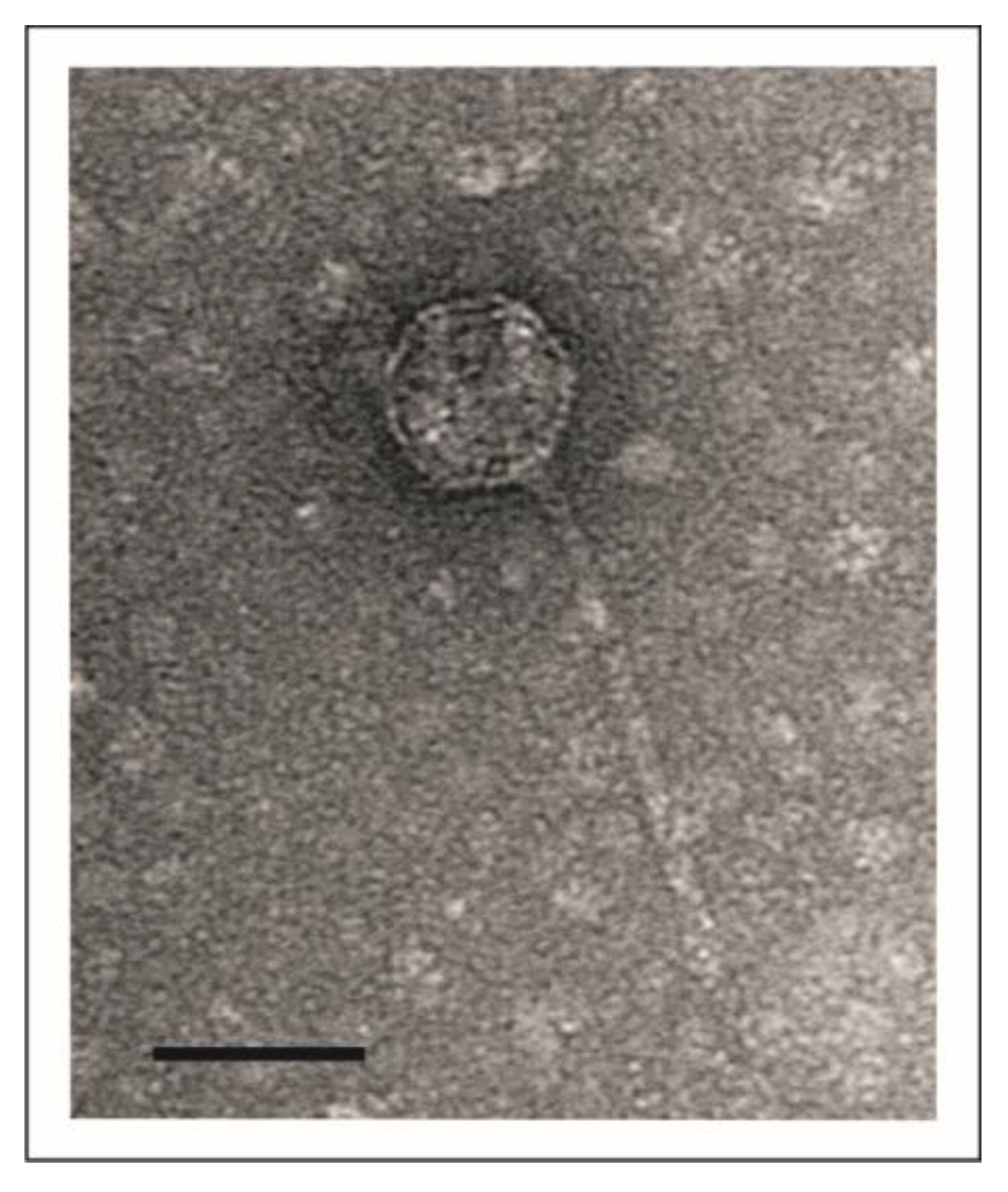
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Isolation of Phage DNA, Sequencing and Genome Annotation
2.5. Isolation and Analysis of Phage Mutants
2.6. Molecular Cloning and Activity of vB_YenS_P840 Repressor Genes
2.7. Resolution of the vB_YenS_P840 telRL Region by the PY54 Protelomerase
2.8. Insertion of vB_YenS_P840 Tail Fiber Genes into the PY54 Genome
2.9. Nucleotide sequence accession
3. Results
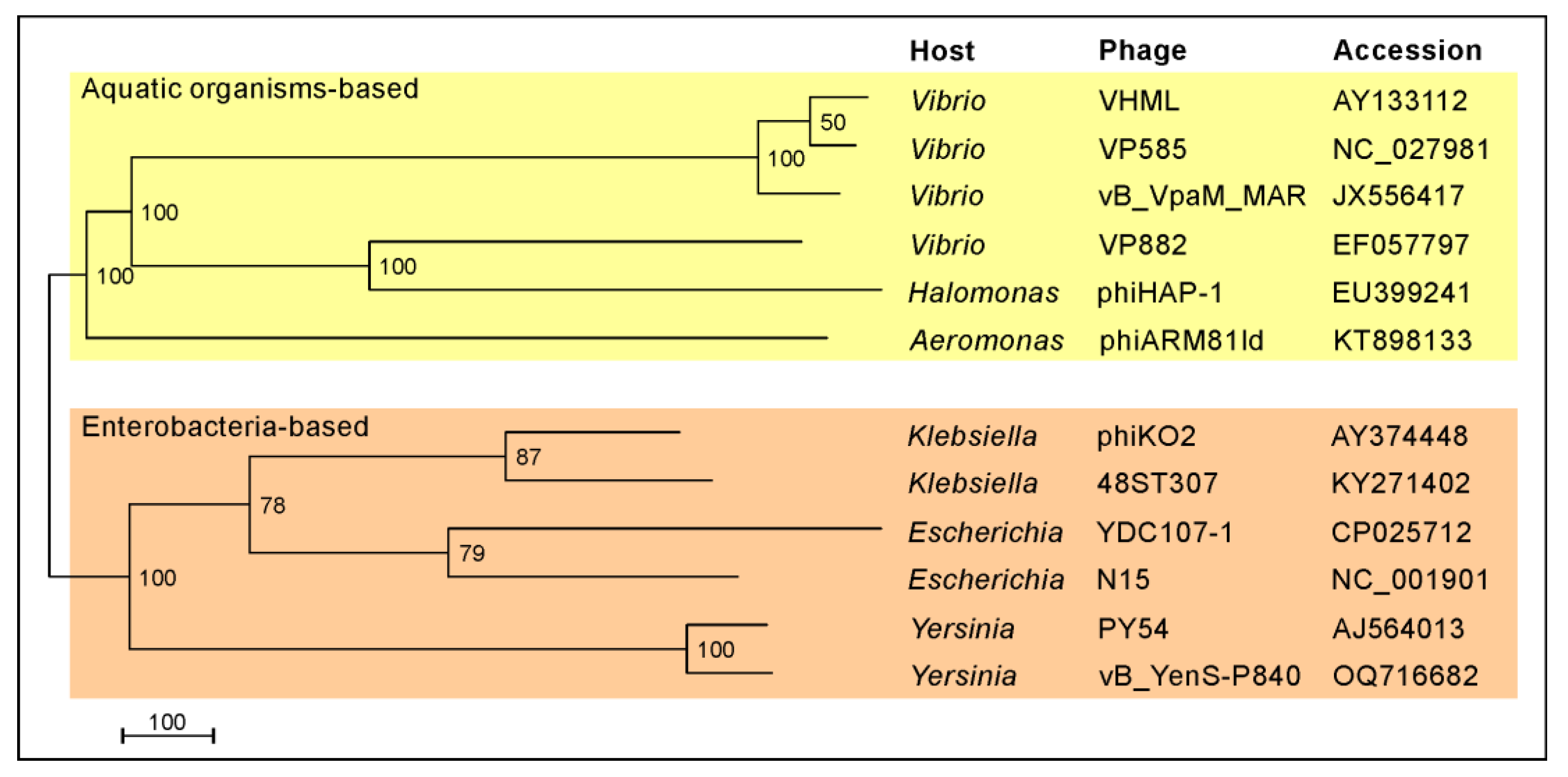
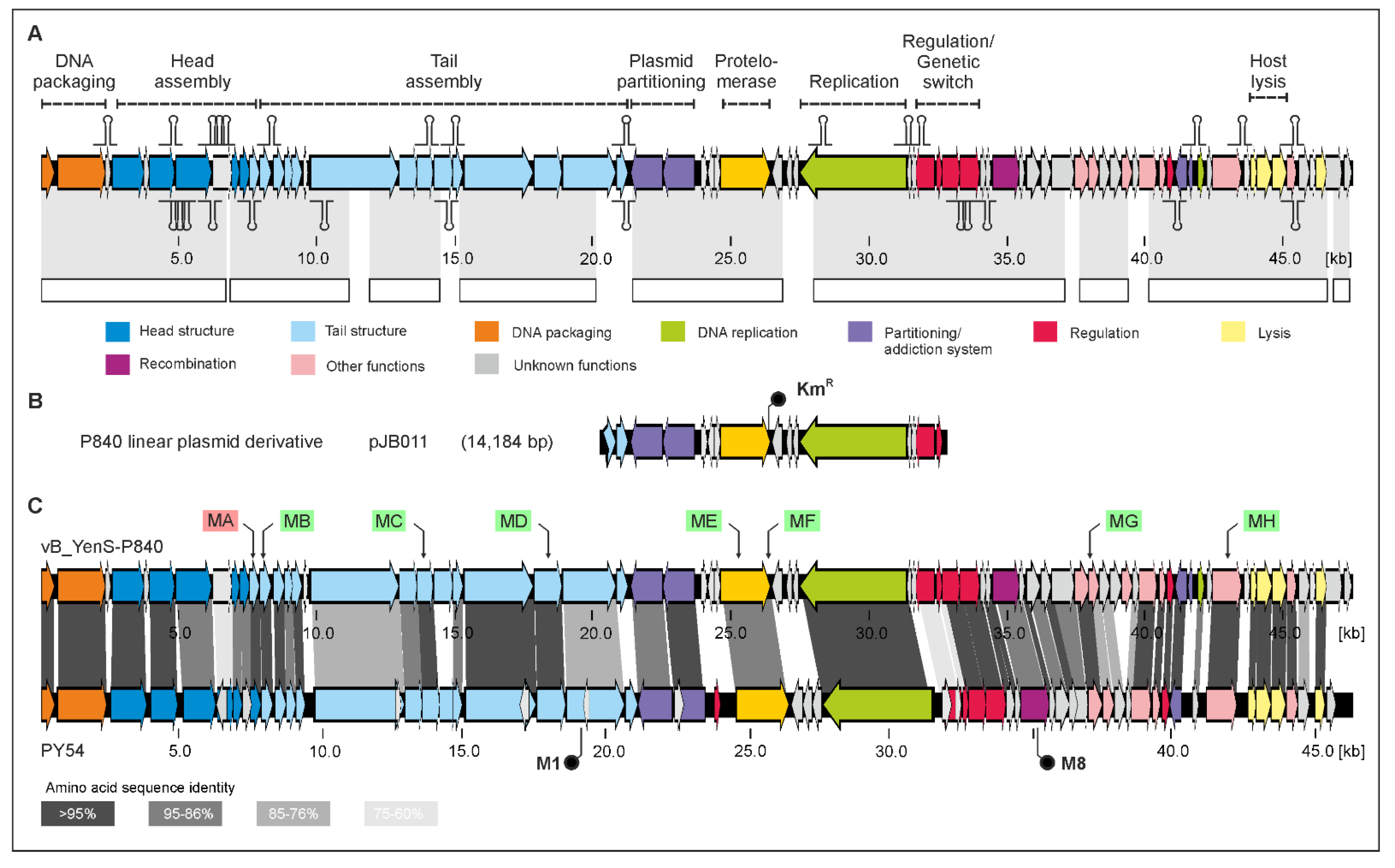
3.1. vB_YenS_P840 and PY54 Are Closely Related Telomere Phages
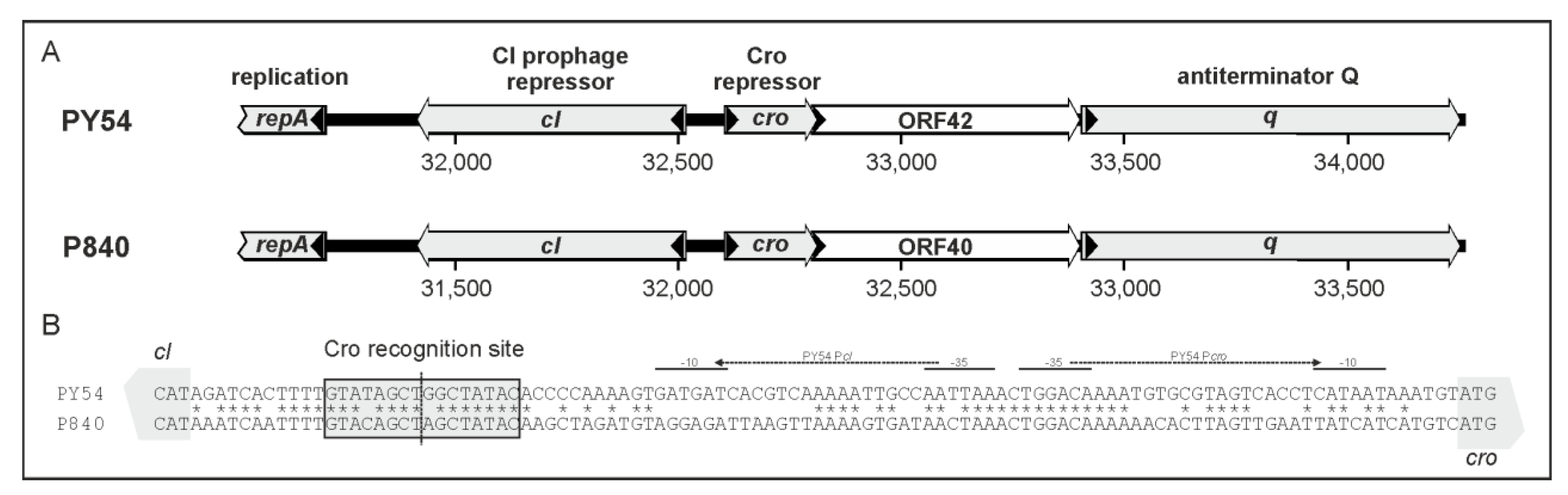
3.2. Phage vB_YenS_P840 Encodes Two Prophage Repressors and Three Proteins Stimulating the Lytic Cycle
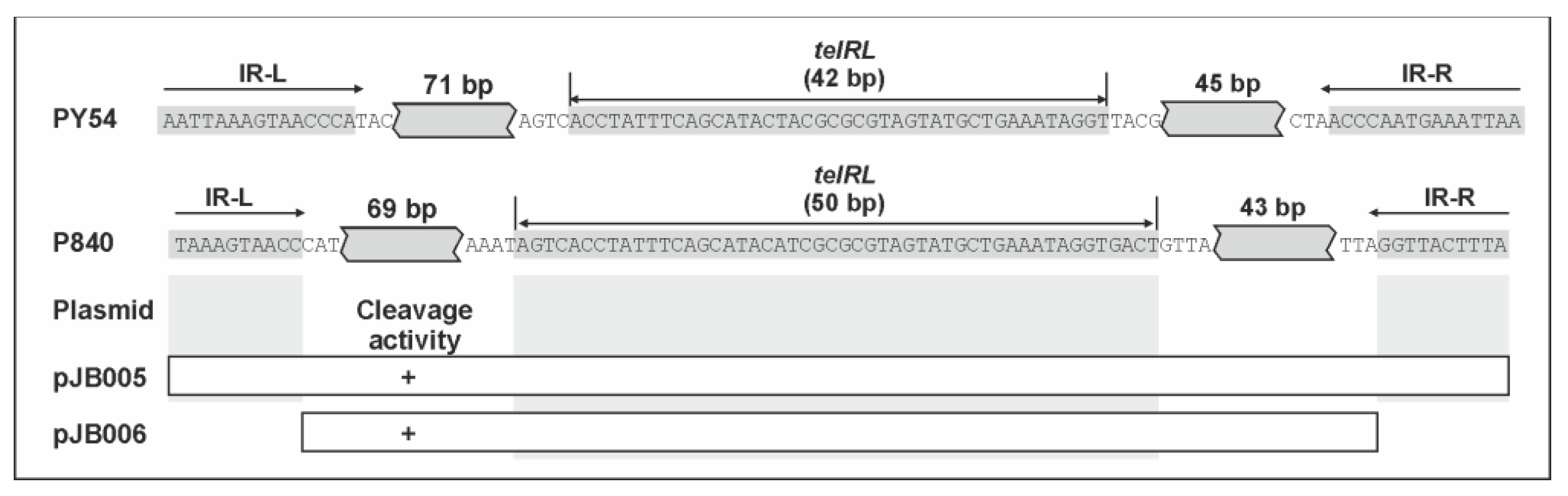
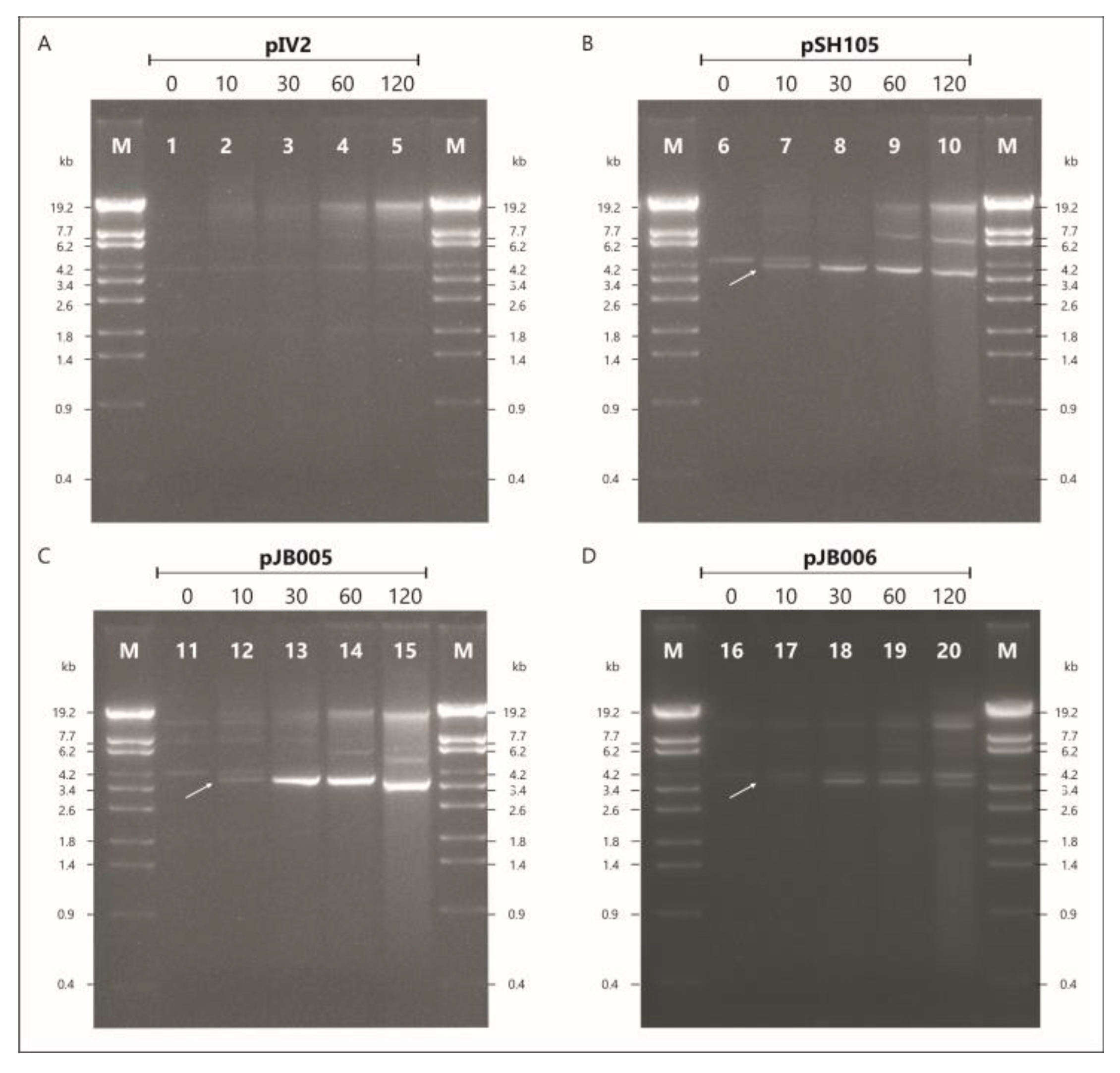
3.3. The vB_YenS_P840 telRL Site without Its Flanking Inverted Repeat Is a Substrate for the PY54 Protelomerase In Vivo
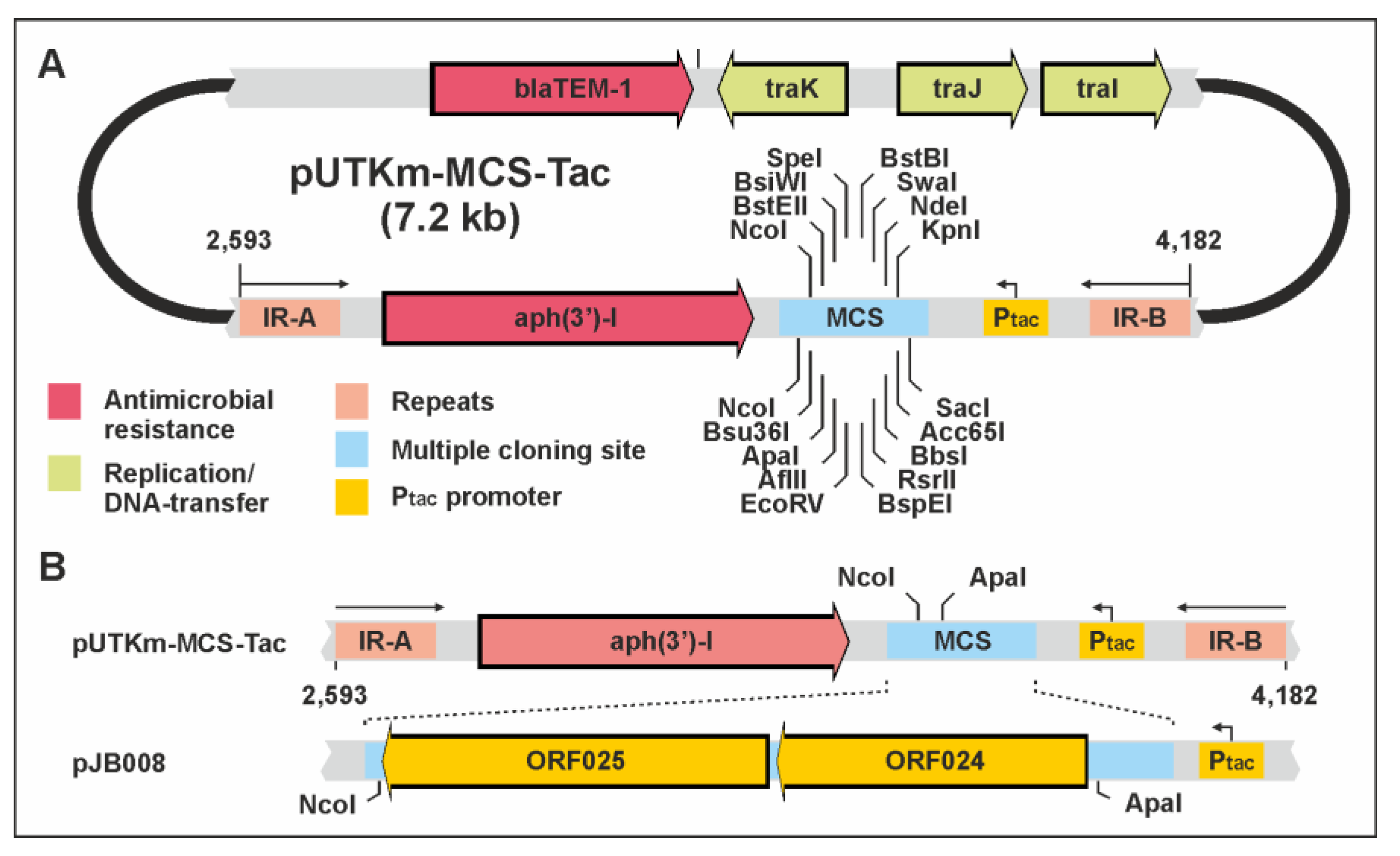
3.4. Two Tail Fiber Proteins of vB_YenS_P840 Are Sufficient to Change the PY54 Host Range
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rybchin, V.N.; Svarchevsky, A.N. The plasmid prophage N15: A linear DNA with covalently closed ends. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casjens, S.R.; Gilcrease, E.B.; Huang, W.M.; Bunny, K.L.; Pedulla, M.L.; Ford, M.E.; Houtz, J.M.; Hatfull, C.F.; Hendrix, R.W. The pKO2 linear plasmid prophage of Klebsiella oxytoca. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1818–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertwig, S.; Klein, I.; Lurz, R.; Lanka, E.; Appel, B. PY54, a linear plasmid prophage of Yersinia enterocolitica with covalently closed ends. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.A.; Kropinski, A.M.; Abbasifar, R.; Griffiths, M.W. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacteriophage vB_VpaM_MAR. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13138–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.-F.; Huang, C.-H.; Chang, C.-H.; Liao, W.-C.; Lin, I.-H.; Jian, W.-N.; Wu, Y.-G.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wong, H.-C. Characterization of a new plasmid-like prophage in a pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus O3:K6 strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobberley, J.M.; Authement, R.N.; Segall, A.M.; Paul, J.H. The temperate marine phage PhiHAP-1 of Halomonas aquamarina possesses a linear plasmid-like prophage genome. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6618–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, B.; Hammerl, J.A.; Espejo, R.T.; Hertwig, S. The linear plasmid prophage Vp58.5 of Vibrio parahaemolyticus is closely related to the integrating phage VHML and constitutes a new incompatibility group of telomere phages. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9313–9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakey, H.J.; Owens, L. A new bacteriophage, VHML, isolated from a toxin-producing strain of Vibrio harveyi in tropical Australia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, L.; Feudi, C.; Fortini, D.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Bonura, C.; Endimiani, A.; Mammina, C.; Ocampo, A.M.; Jimenez, J.N.; et al. Diversity, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance of the KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 clone. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, S.; Klein, I.; Schmidt, V.; Beck, S.; Hammerl, J.A.; Appel, B. Sequence analysis of the genome of the temperate Yersinia enterocolitica phage PY54. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 331, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravin, V.; Ravin, N.; Casjens, S.; Ford, M.E.; Hatfull, G.F.; Hendrix, R.W. Genomic sequence and analysis of the atypical temperate bacteriophage N15. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 299, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneke, J.; Ziegelin, G.; Lurz, R.; Lanka, E. The protelomerase of temperate Escherichia coli phage N15 has cleaving-joining activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7721–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneke, J.; Ziegelin, G.; Lurz, R.; Lanka, E. Phage N15 telomere resolution: Target requirements for recognition and processing by the protelomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10410–10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Roschanski, N.; Lurz, R.; Johne, R.; Lanka, E.; Hertwig, S. The Molecular Switch of Telomere Phages: High Binding Specificity of the PY54 Cro Lytic Repressor to a Single Operator Site. Viruses 2015, 7, 2771–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V. The antirepressor needed for induction of linear plasmid-prophage N15 belongs to the SOS regulon. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6333–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravin, N.V.; Svarchevsky, A.N.; Deho, G. The anti-immunity system of phage-plasmid N15: Identification of the antirepressor gene and its control by a small processed RNA. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Klein, I.; Lanka, E.; Appel, B.; Hertwig, S. Genetic and functional properties of the self-transmissible Yersinia enterocolitica plasmid pYE854, which mobilizes the virulence plasmid pYV. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lorenzo, V.; Herrero, M.; Jakubzik, U.; Timmis, K.N. Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gram-negative eubacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 6568–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; de Lorenzo, V.; Timmis, K.N. Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 6557–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Klein, I.; Appel, B.; Hertwig, S. Interplay between the temperate phages PY54 and N15, linear plasmid prophages with covalently closed ends. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8366–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, E.; Voigt, I.; Broll, H.; Appel, B. Use of a plasmid of a yersinia enterocolitica biogroup 1A strain for the construction of cloning vectors. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 79, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; El-Mustapha, S.; Bölcke, M.; Trampert, H.; Barac, A.; Jäckel, C.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Bölcke, S. Host Range, Morphology and Sequence Analysis of Ten Temperate Phages Isolated from Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäckel, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Reetz, J.; Kropinski, A.M.; Hertwig, S. Campylobacter group II phage CP21 is the prototype of a new subgroup revealing a distinct modular genome organization and host specificity. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäckel, C.; Hertwig, S.; Scholz, H.C.; Nöckler, K.; Reetz, J.; Hammerl, J.A. Prevalence, host range, and comparative genomic analysis of temperate Ochrobactrum phages. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osieka, V.; Grobbel, M.; Schmoger, S.; Szentiks, C.A.; Irrgang, A.; Käsbohrer, A.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Hammerl, J.A. Complete draft genome sequence of an Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-producing Citrobacter freundii strain recovered from the intestine of a house sparrow (Passer domesticus) in Germany 2017. Genome Announc 2018, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, I.L.; Fontana, W.; Stadler, P.F.; Bonhoeffer, L.S.; Tacker, M.; Schuster, P. Fast folding and comparison of RNA secondary structures. Monatsh. Chem. 1994, 125, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macke, T.J. RNAMotif, an RNA secondary structure definition and search algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4724–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Barac, A.; Jäckel, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Gadicherla, A.; Hertwig, S. Phage vB_YenS_P400, a Novel Virulent Siphovirus of Yersinia enterocolitica Isolated from Deer. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. VICTOR: Genome-based phylogeny and classification of prokaryotic viruses. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3396–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, F.; Braun, P.; Scholz, H.C.; Grass, G. Specific Detection of Yersinia pestis Based on Receptor Binding Proteins of Phages. Pathogens 2020, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filik, K.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Niedziółka-Jönson, J.; Roźniecka, E.; Ciekot, J.; Pyra, A.; Matyjaszczyk, I.; Skurnik, M.; Brzozowska, E. phiYeO3-12 phage tail fiber Gp17 as a promising high specific tool for recognition of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenic serotype O:3. AMB Express 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyra, A.; Filik, K.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Czarny, A.; Brzozowska, E. New Insights on the Feature and Function of Tail Tubular Protein B and Tail Fiber Protein of the Lytic Bacteriophage phiYeO3-12 Specific for Yersinia enterocolitica Serotype O:3. Molecules 2020, 25, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Pajunen, M.I.; Jun, J.W.; Skurnik, M. T4-like Bacteriophages Isolated from Pig Stools Infect Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia pestis Using LPS and OmpF as Receptors. Viruses 2021, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelin, G.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Lurz, R.; Hertwig, S.; Hammerl, J.; Appel, B.; Lanka, E. The repA gene of the linear Yersinia enterocolitica prophage PY54 functions as a circular minimal replicon in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V. Functional characterization of the repA replication gene of linear plasmid prophage N15. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V. Conversion of linear DNA with hairpin telomeres into a circular molecule in the course of phage N15 lytic replication. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 391, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference (Accession No.) | Description/Genotype | Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotype | Strains (Plasmid/Vector) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invitrogen | F- mcrA ∆(mrr-hsdRMS-mcrBC) φ80lacZ∆M15 ∆lacX74 recA1 araD139 ∆(ara-leu)7697 galU galK rpsL (StrR) endA1 nupG fhuA::IS2 (confers phage T1 resistance) | StrR | E. coli GeneHogs |
| [18,19] | Strain lysogenized with λpir phage containing the Tn5-based delivery plasmid pUTKm | AmpR, KmR | E. coli S17.1 λpir (pUTKm) |
| [20] | Bioserotype B2/O:5,27 strain lacking the virulence plasmid pYV | Y. enterocolitica 83/88/2 | |
| This work | Bioserotype B4/O:3 strain containing the vB_YenS_P840 (P840) prophage | Y. enterocolitica 18-YE00024 | |
| Reference (Accession no.) | Description | Antimicrobial resistance | Phages |
| This work (OQ716682) | P840 wildtype phage | None | vB_YenS_P840 |
| [3,10] | PY54 wildtype phage | None | PY54 |
| [3,10] | Lytic deficient PY54 transposon mutant | KmR | PY54 mutant C |
| [3,10] | Wildtype-like PY54 transposon mutant | KmR | PY54-mutant O |
| This work | Wildtype-like P840 transposon mutant | KmR | PY54 mutant M1 (tfp) |
| This work | Wildtype-like P840 transposon mutant | KmR | PY54 mutant M8 (tfp) |
| Reference (Accession no.) | Description | Antimicrobial resistance | Plasmid/vector |
| [18,19] | E. coli suicide mutagenesis vector | AmpR, KmR | pUTKm |
| This work (OQ474598) | pUTKm containing a MCS and Ptac promoter | AmpR, KmR | pUTKm-MCS-Tac |
| This work | pUTKm-MCS-Tac with P840 ORF24 and 25 (ApaI/NcoI) | AmpR, KmR | pJB008 |
| [14] | E. coli cloning vector | AmpR, CatR | pMS470∆8cat |
| This work | pMS470∆8cat with P840 cI (NdeI/HindIII) | AmpR, CatR | pJB001 |
| This work | pMS470∆8cat with P840 cro (NdeI/HindIII) | AmpR, CatR | pJB002 |
| This work | pMS470∆8cat with P840 ORF40 (NdeI/HindIII) | AmpR, CatR | pJB003 |
| This work | pMS470∆8cat with P840 antA (NdeI/HindIII) | AmpR, CatR | pJB004 |
| This work | pMS470∆8cat with P840 q (NdeI/SphI) | AmpR, CatR | pJB010 |
| [21] | Yersinia cloning vector | KmR | pIV2 |
| This work | pIV2 with P840 palIR (HindIII) | KmR | pJB005 |
| This work | pIV2 with P840 palIRw (BamHI) | KmR | pJB006 |
| MoBiTec, Göttingen | E. coli cloning vector | AmpR | pMCS5 |
| This work | pMCS5 with P840 ORF 24 and 25 (ApaI/NcoI) | AmpR | pJB007 |
| This work | vB_YenS_P840 mutant MF-derived miniplasmid (AflII/KanI) | KmR | pJB011 |
| [3] | pBR329 with PY54 palIR (BamHI/HindIII) | AmpR, CatR | pSH105 |
| Lysogenization | Lytic Behaviour | Affected Gene | Resistance Marker Position | Mutant ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | − | ORF11 (tail completion protein) | 7768 [KmR] | MA |
| + | + | ORF12 (tail protein) | 8208 [CatR] | MB |
| + | + | ORF19 (phage minor tail component) | 13,866 [CatR] | MC |
| + | + | ORF23 (tail fiber protein 1) | 18,593 [KmR] | MD |
| + | + | ORF31 (TelN) | 25,125 [KmR] | ME |
| + | + | intergenic (between telN ORF31 and ORF32) | 26,449 [KmR] | MF |
| + | + | ORF50 (helicase, polymerase, exon.) | 38,159 [CatR] | MG |
| + | + | ORF62 (adenine methylase) | 42,479 [CatR] | MH |
| Lysis (pfu/mL) | Lysogenization (cfu/mL) | vB_YenS_P840 Insert | Construct in Y. enterocolitica 83/88/2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.27 × 106 | 1.20 × 106 | cI (ORF38) | pJB001 |
| 9.21 × 106 | - | cro (ORF39) | pJB002 |
| 4.71 × 106 | 2.55 × 106 | PY54-ORF42 (ORF40) | pJB003 |
| 6.76 × 106 | - | antA (ORF57) | pJB004 |
| 7.0 × 106 | - | q (ORF41) | pJB010 |
| 4.90 × 106 | 3.54 × 104 | - | None |
| 4.71 × 106 | 4.29 × 103 | None | pMS470Δ8cat |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bräuer, J.A.; Hammerl, J.A.; El-Mustapha, S.; Fuhrmann, J.; Barac, A.; Hertwig, S. The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences. Viruses 2023, 15, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102019
Bräuer JA, Hammerl JA, El-Mustapha S, Fuhrmann J, Barac A, Hertwig S. The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences. Viruses. 2023; 15(10):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102019
Chicago/Turabian StyleBräuer, Julia Anabell, Jens Andre Hammerl, Sabrin El-Mustapha, Julius Fuhrmann, Andrea Barac, and Stefan Hertwig. 2023. "The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences" Viruses 15, no. 10: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102019
APA StyleBräuer, J. A., Hammerl, J. A., El-Mustapha, S., Fuhrmann, J., Barac, A., & Hertwig, S. (2023). The Novel Yersinia enterocolitica Telomere Phage vB_YenS_P840 Is Closely Related to PY54, but Reveals Some Striking Differences. Viruses, 15(10), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15102019






