Whole Genomic Constellation of Avian Reovirus Strains Isolated from Broilers with Arthritis in North Carolina, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ARV Strain Isolation and Propagation
2.2. Genomic RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.3. ARV Full-Length Genome Amplification
2.4. ARV Whole Genome Sequencing and Raw-Data Processing
2.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.6. Detection of Recombination Incidence
3. Results
3.1. R18-37308 and R18-38167 Sequencing Data
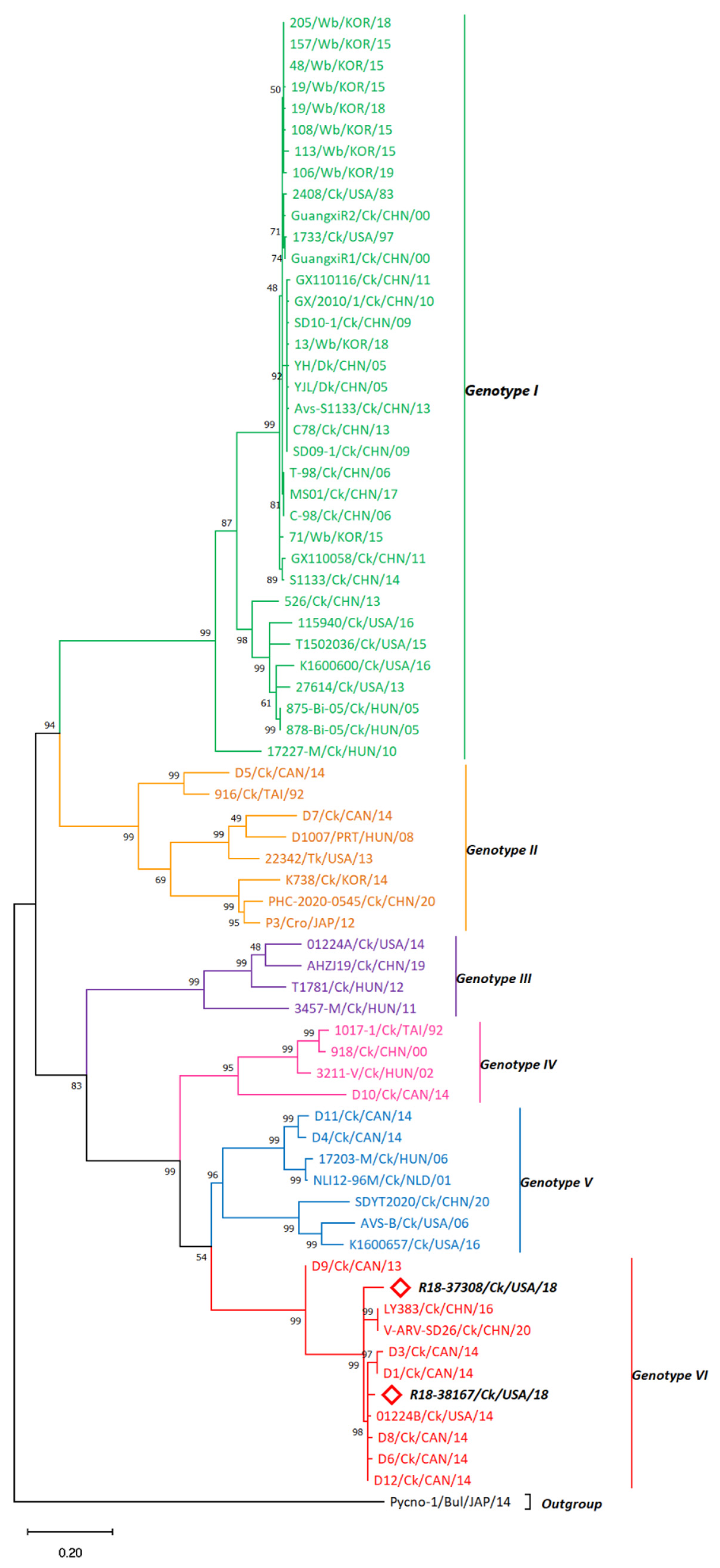
3.2. σC-Based Genotyping Determined That R18-37308 and R18-38167 Clustered with Genotype VI
3.3. Whole Genome Organization of the R18-37308 and R18-38167 Strains Show Conserved Terminal UTRs and the Lack of a Common Ancestor
3.3.1. The L-Class Genomic Segments
3.3.2. The M-Class Genomic Segments
3.3.3. The S-Class Genomic Segments
3.4. Visualization of the Whole Genome Alignment
3.5. Recombination Analysis Indicates the Novelty of the Study Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sterner, F.; Rosenberger, J.; Margolin, A.; Ruff, M. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. II. Clinical evaluation of chickens infected with two avian reovirus pathotypes. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heide, L. The history of avian reovirus. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gussem, J.; Swam, H.; Lievens, K.; De Herdt, P. Reovirus tenosynovitis in a flock of layer breeders. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, P.; Dewitt, W. Serological incidence of avian reovirus infection in broiler-breeders and progeny in Nova Scotia. Can. Vet. J. 1979, 20, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, A.; Bertoncin, P.; D’aprile, P.; Felluga, B. Ultrastructural histopathology of chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane infected with an avian reovirus. Avian Pathol. 1980, 9, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, M.; D’apirile, P.; Cancellotti, F. Biological and physico-chemical properties of the infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). Avian Pathol. 1973, 2, 135–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, M.E.C.; D’Andrea, E.; Calvert-Evers, J.; Paximadis, M.; Boccardo, G. Evidence for a phytoreovirus associated with tobacco exhibiting leaf curl symptoms in South Africa. Phytopathology 1999, 89, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.A.M.; da Silva, R.R.; Kaiano, J.H.L.; Silvestre, R.V.D.; de Souza Oliveira, D.; Linhares, A.C.; Gabbay, Y.B.; Mascarenhas, J.D.A.P. Detection of avian group D rotavirus using the polymerase chain reaction for the VP6 gene. J. Virol. Methods 2012, 185, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palya, V.; Glávits, R.; Dobos-Kovács, M.; Ivanics, É.; Nagy, E.; Bányai, K.; Szücs, G.; Dá, Á.; Benkö, M. Reovirus identified as cause of disease in young geese. Avian Pathol. 2003, 32, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangaspero, M.; Vanopdenbosch, E.; Nishikawa, H.; Tabbaa, D. Prevalence of antibodies against respiratory viruses (parainfluenza virus type 3, respiratory syncytial virus, reovirus and adenovirus) in relation to productivity in Syrian Awassi sheep. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1997, 29, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, R.; Alexander, V.; Whitford, W. Persistent reovirus infection of CHO cells resulting in virus resistance. J. Virol. 1976, 17, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.S.; Levy, M.G.; Ley, D.H.; Barnes, H.J.; Gerig, T.M. Experimental reproduction of enteritis in bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) with Cryptosporidium and reovirus. Avian Dis. 1987, 31, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, D.L.; Montgomery, R.D.; Maslin, W.R.; Wu, C.-C.; Jack, S.W. Reovirus associated with excessive mortality in young bobwhite quail. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, G.D.; Ley, D.; Levy, M.; Guy, J.; Barnes, H.J. Intestinal cryptosporidiosis and reovirus isolation from bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) with enteritis. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindevogel, H.; Meulemans, G.; Pastoret, P.-P.; Schwers, A.; Calberg-Bacq, C.-M. Reovirus Infection in the Pigeon; Annales de Recherches Vétérinaires: Paris, France, 1982; pp. 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R. Avian reovirus infections. Rev. Sci. Tech.-Off. Int. Epizoot. 2000, 19, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, M.; Qi, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X. Genetic and pathogenic characterisation of 11 avian reovirus isolates from northern China suggests continued evolution of virulence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaña-Labrin, S.; Hauck, R.; Figueroa, A.; Stoute, S.; Shivaprasad, H.; Crispo, M.; Corsiglia, C.; Zhou, H.; Kern, C.; Crossley, B. Genotypic characterization of emerging avian reovirus genetic variants in California. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxler, S.; Rigomier, P.; Bilic, I.; Liebhart, D.; Prokofieva, I.; Robineau, B.; Hess, M. Identification of a new reovirus causing substantial losses in broiler production in France, despite routine vaccination of breeders. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lublin, A.; Goldenberg, D.; Rosenbluth, E.; Heller, E.D.; Pitcovski, J. Wide-range protection against avian reovirus conferred by vaccination with representatives of four defined genotypes. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8683–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, H.; Linneman, E.; Gauthiersloan, V.; Collet, T. Isolation and characterization of reovirus field isolates from clinical cases of viral arthritis. In Proceedings of the 62nd of the Western Poultry Disease Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 30 March–1 April 2013; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, H.; Durairaj, V.; Gauthiersloan, V.; Linneman, E. Genotypic analysis of avian reoviruses from clinical submissions of viral arthritis. In Proceedings of the 64th of the Western Poultry Disease Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 22–25 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, E.; Sellers, H.S.; Linneman, E. Pathogenesis of two variant reoviruses from clinical cases of tenosynovitis. In Proceedings of the 63rd of the Western Poultry Disease Conference, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 1–5 April 2014; pp. 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Tang, Y.; Dunn, P.A.; Wallner-Pendleton, E.A.; Lin, L.; Knoll, E.A. Isolation and molecular characterization of newly emerging avian reovirus variants and novel strains in Pennsylvania, USA, 2011–2014. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, L.; Gupta, A.; Fricke, J.; Lockerbie, B.; Popowich, S.; Gomis, S. Isolation and characterization of avian reoviruses by phylogenetic analysis and restriction enzyme fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). In Proceedings of the 65th of the Western Poultry Disease Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–27 April 2016; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Palomino-Tapia, V.; Mitevski, D.; Inglis, T.; van der Meer, F.; Abdul-Careem, M.F. Molecular characterization of emerging avian reovirus variants isolated from viral arthritis cases in Western Canada 2012–2017 based on partial sigma (σ) C gene. Virology 2018, 522, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.C. Reovirus infections. Dis. Poult. 2013, 351–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, A.; Balk, F.; Born, L.; van Roozelaar, D.; Heijmans, J.; Gielkens, A.; ter Huurne, A. Classification of Dutch and German avian reoviruses by sequencing the σ C protein. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joklik, W.K. Structure and function of the reovirus genome. Microbiol. Rev. 1981, 45, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, H.; Cursiefen, D.; Becht, H. Structural and growth characteristics of two avian reoviruses. Arch. Virol. 1975, 48, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, R.; Benavente, J. Protein coding assignment of avian reovirus strain S1133. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6775–6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, R.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Mallo, M.; Benavente, J. Intracellular posttranslational modifications of S1133 avian reovirus proteins. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2974–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.P.; Su, B.S.; Shien, J.H.; Liu, H.J.; Lee, L.H. The sequence and phylogenetic analysis of avian reovirus genome segments M1, M2, and M3 encoding the minor core protein μA, the major outer capsid protein μB, and the nonstructural protein μNS. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 133, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, R.; Meanger, J.; Enriquez, C.E.; Wilcox, G.E. Avian reovirus proteins associated with neutralization of virus infectivity. Virology 1993, 194, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, T.J. Protein coding assignment of the S genes of the avian reovirus S1133. Virology 1985, 141, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gallardo, R. Molecular epidemiology of reoviruses in California. In Proceedings of the 66th of the Western Poultry Disease Conference, Sacramento, CA, USA, 20–22 March 2017; pp. 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, H.S. Avian reoviruses from clinical cases of tenosynovitis: An overview of diagnostic approaches and 10-year review of isolations and genetic characterization. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heggen-Peay, C.; Cheema, M.; Ali, R.; Schat, K.; Qureshi, M. Interactions of poult enteritis and mortality syndrome-associated reovirus with various cell types in vitro. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Coster, W.; D’hert, S.; Schultz, D.T.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C. NanoPack: Visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, C.; Brudno, M.; Schwartz, J.R.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.S.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Visualizing global DNA sequence alignments of arbitrary length. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Taylor, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Bioinformatics 1992, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.O.; Shelton, D.C.; Munro, D.A. Infectious synovitis control by medication-effect of strain differences and pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Am. J. Vet. Res 1957, 18, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, N.; Kerr, K. Some characteristics of an avian arthritis viral agent. Avian Dis. 1966, 10, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.R.; Friedman, M.; Olson, N. Electron microscopic study of an avian reovirus that causes arthritis. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1972, 41, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibenge, F.S.; Jones, R.A.; Savage, C.E. Effects of experimental immunosuppression on reovirus-induced tenosynovitis in light-hybrid chickens. Avian Pathol. 1987, 16, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, R.; Fletcher, O.; Rowland, G.N.; Gaudry, D.; Villegas, P. Malabsorption syndrome in broiler chickens. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, M.A.; Davis, J.F.; McNulty, M.S.; Brown, J.; Player, E.C. Enteritis (so-called runting stunting syndrome) in Georgia broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Pomeroy, B. Isolation and characterization of an enterovirus from baby chicks having an enteric infection II. Physical and chemical characteristics and ultrastructure. Avian Dis. 1967, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, M.; Felluga, B.; Borghi, G.; Baroni, A. The Crawley agent: An avian reovirus. Arch. Für Die Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967, 21, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Qu, L.; Xiang, W.; Guo, D.; Yuan, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, C. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the S-class genome segments of a duck orthoreovirus. Acta Virol. 2007, 51, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, P.C.; Chiou, Y.F.; Liu, H.J.; Song, C.H.; Su, Y.P.; Lee, L.H. Genetic variation of the λA and λC protein encoding genes of avian reoviruses. Res. Vet. Sci. 2007, 83, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Su, H.Y.; Huang, P.; Lee, L.H.; Liu, H.J. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of P10-and P17-encoding genes of avian reovirus. Avian Dis. 2005, 49, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Lee, L.H.; Hsu, H.W.; Kuo, L.C.; Liao, M.H. Molecular evolution of avian reovirus:: Evidence for genetic diversity and reassortment of the S-class genome segments and multiple cocirculating lineages. Virology 2003, 314, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.M.; Cheng, H.L.; Ke, L.Y.; Ji, W.T.; Chulu, J.L.; Liao, M.H.; Chang, T.J.; Liu, H.J. Development of a quantitative Light Cycler real-time RT-PCR for detection of avian reovirus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 133, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzastek, K.; Sellers, H.S.; Kapczynski, D.R. A Universal, Single-Primer Amplification Protocol to Perform Whole-Genome Sequencing of Segmented dsRNA Avian Orthoreoviruses. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.T.; Lahmers, K.K.; Sellers, H.S.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Poulson, R.L.; Saliki, J.T.; Tompkins, S.M.; Padykula, I.; Siepker, C.; Howerth, E.W. Randomly primed, strand-switching, MinION-based sequencing for the detection and characterization of cultured RNA viruses. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mase, M.; Gotou, M.; Inoue, D.; Masuda, T.; Watanabe, S.; Iseki, H. Genetic analysis of avian reovirus isolated from chickens in Japan. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanaty, A.; Mosaad, Z.; Elfeil, W.M.; Badr, M.; Palya, V.; Shahein, M.A.; Rady, M.; Hess, M. Isolation and Genotypic Characterization of New Emerging Avian Reovirus Genetic Variants in Egypt. Poultry 2023, 2, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, R.A. Molecular Characterization of Variant Avian Reoviruses and Their Relationship with Antigenicity and Pathogenicity. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markis, M. Evaluation of Pathogenicity and Antigenicity of Avian Reoviruses and Disease Control Through Vaccination. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, D.; Rosenberger, J. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. III. Host factors affecting virulence and persistence. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, J.; Sterner, F.; Botts, S.; Lee, K.; Margolin, A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian reoviruses. I. Pathogenicity and antigenic relatedness of several avian reovirus isolates. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, D. Complete sequence of a reovirus associated with necrotic focus formation in the liver and spleen of Muscovy ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Day, J.M.; Jackwood, M.W.; Spackman, E. Enteric viruses detected by molecular methods in commercial chicken and turkey flocks in the United States between 2005 and 2006. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styś-Fijoł, N.; Kozdruń, W.; Czekaj, H. Detection of avian reoviruses in wild birds in Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 61, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ayalew, L.E.; Ahmed, K.A.; Mekuria, Z.H.; Lockerbie, B.; Popowich, S.; Tikoo, S.K.; Ojkic, D.; Gomis, S. The dynamics of molecular evolution of emerging avian reoviruses through accumulation of point mutations and genetic re-assortment. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, D.; Jones, J.D.; Studholme, D.J. Application of’next-generation’sequencing technologies to microbial genetics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, L.; Sebastian, A.; Lu, H. Detection and characterization of two co-infection variant strains of avian orthoreovirus (ARV) in young layer chickens using next-generation sequencing (NGS). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, H.S. Current limitations in control of viral arthritis and tenosynovitis caused by avian reoviruses in commercial poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalew, L.E.; Gupta, A.; Fricke, J.; Ahmed, K.A.; Popowich, S.; Lockerbie, B.; Tikoo, S.K.; Ojkic, D.; Gomis, S. Phenotypic, genotypic and antigenic characterization of emerging avian reoviruses isolated from clinical cases of arthritis in broilers in Saskatchewan, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bányai, K.; Dandár, E.; Dorsey, K.M.; Mató, T.; Palya, V. The genomic constellation of a novel avian orthoreovirus strain associated with runting-stunting syndrome in broilers. Virus Genes 2011, 42, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Xie, Z.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Pang, Y.; Deng, X.; Xie, Z.; Fan, Q.; Luo, S.; Feng, J. Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of an avian reovirus genome. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.K.; Sharafeldin, T.A.; Porter, R.E.; Goyal, S.M. Molecular characterization of L class genome segments of a newly isolated turkey arthritis reovirus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.J.; Farsetta, D.L.; Kim, J.; Noble, S.; Broering, T.J.; Nibert, M.L. Mammalian reovirus L3 gene sequences and evidence for a distinct amino-terminal region of the λ1 protein. Virology 1999, 258, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fang, Q.; Attoui, H.; Biagini, J.F.P.; Zhu, Z.; de Micco, P.; de Lamballerie, X. Sequence of genome segments 1, 2, and 3 of the grass carp reovirus (Genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 274, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavente, J.; Martínez-Costas, J. Avian reovirus: Structure and biology. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, J.; Martınez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J.; Vakharia, V.N. Cloning, expression, and characterization of avian reovirus guanylyltransferase. Virology 2002, 296, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Coombs, K.M. Conserved structure/function of the orthoreovirus major core proteins. Virus Res. 2009, 144, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Timinskas, A.; Butkus, V.; Janulaitis, A. Sequence motifs characteristic for DNA [cytosine-N4] and DNA [adenine-N6] methyltransferases. Classification of all DNA methyltransferases. Gene 1995, 157, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, S.K.; Marthaler, D.; Verma, H.; Sharafeldin, T.A.; Jindal, N.; Porter, R.E.; Goyal, S.M. Phylogenetic analysis, genomic diversity and classification of M class gene segments of turkey reoviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, L.; Shatkin, A.J. Reovirus polypeptide sigma 3 and N-terminal myristoylation of polypeptide mu 1 are required for site-specific cleavage to mu 1C in transfected cells. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaña-Labrin, S.; Jerry, C.; Roh, H.; Da Silva, A.; Corsiglia, C.; Crossley, B.; Rejmanek, D.; Gallardo, R. Avian reoviruses of the same genotype induce different pathology in chickens. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsman, J.; Top, D.; Boutilier, J.; Duncan, R. Extensive syncytium formation mediated by the reovirus FAST proteins triggers apoptosis-induced membrane instability. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8090–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelón, G.; Labrada, L.A.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. Modification of late membrane permeability in avian reovirus-infected cells: Viroporin activity of the S1-encoded nonstructural p10 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 17789–17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.K.; Verma, H.; Sharafeldin, T.A.; Porter, R.E.; Jindal, N.; Ziegler, A.; Goyal, S.M. Characterization of S class gene segments of a newly isolated turkey arthritis reovirus. Virology 2014, 464, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, M.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of partial S1 genes of avian orthoreovirus isolates in Shandong province during 2015–2017. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.G.; Fox, G.C.; Parrado, X.L.H.; Llamas-Saiz, A.L.; Costas, C.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J.; van Raaij, M.J. Structure of the carboxy-terminal receptor-binding domain of avian reovirus fibre sigmaC. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 354, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, D.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Chacón, R.; Puga, B.; Piantino Ferreira, A. Emerging new avian reovirus variants from cases of enteric disorders and arthritis/tenosynovitis in Brazilian poultry flocks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Iglesias, L.; Lostale-Seijo, I.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. Different intracellular distribution of avian reovirus core protein sigmaA in cells of avian and mammalian origin. Virology 2012, 432, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardado-Calvo, P.; Vazquez-Iglesias, L.; Martinez-Costas, J.; Llamas-Saiz, A.L.; Schoehn, G.; Fox, G.C.; Hermo-Parrado, X.L.; Benavente, J.; van Raaij, M.J. Crystal structure of the avian reovirus inner capsid protein σA. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11208–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Iglesias, L.; Lostalé-Seijo, I.; Martínez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. Avian reovirus sigmaA localizes to the nucleolus and enters the nucleus by a nonclassical energy-and carrier-independent pathway. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10163–10175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, W.-R.; Huang, J.-W.; Chen, I.-C.; Chang, Y.-K.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-D.; Liao, T.-L.; Nielsen, B.L. Oncolytic avian reovirus σA-modulated fatty acid metabolism through the PSMB6/Akt/SREBP1/acetyl-CoA carboxylase pathway to increase energy production for virus replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 273, 109545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Antigenic analysis monoclonal antibodies against different epitopes of σB protein of Muscovy duck reovirus. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Yuan, S.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, Z.; Su, L.; Yee, M.; Zhang, X. Genetic variation analysis of the sigma B protein gene of novel duck reovirus in southeastern China from 2011 to 2020. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 303, 114479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demene, H.; Dong, C.; Ottmann, M.; Rouyez, M.; Jullian, N.; Morellet, N.; Mely, Y.; Darlix, J.; Fournie-Zaluski, M. 1H NMR structure and biological studies of the His23. fwdarw. Cys mutant nucleocapsid protein of HIV-1 indicate that the conformation of the first zinc finger is critical for virus infectivity. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 11707–11716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.H.; Li, Y.J.; Su, Y.P.; Lee, L.H.; Liu, H.J. Epitope mapping and functional analysis of sigma A and sigma NS proteins of avian reovirus. Virology 2005, 332, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, P.F.; Hu, L.; Knowlton, J.J.; Lahr, R.M.; Moreno, R.A.; Berman, A.J.; Prasad, B.V.; Dermody, T.S. Reovirus nonstructural protein σNS acts as an RNA stability factor promoting viral genome replication. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Raghunathan, K.; Taylor, G.M.; French, A.J.; Tenorio, R.; Fernández de Castro, I.; Risco, C.; Parker, J.S.; Dermody, T.S. Reovirus nonstructural protein σNS recruits viral RNA to replication organelles. Mbio 2021, 12, e0140821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Choi, Y.-R.; Park, J.-Y.; Wei, B.; Shang, K.; Zhang, J.-F.; Jang, H.-K.; Cha, S.-Y.; Kang, M. Isolation and genomic characterization of avian reovirus from wild birds in South Korea. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 794934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Genomic Segment | Length (bp) | ORF Localization | Similarity (%) to S1133 * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | R18-37308 | R18-38167 | ||
| L1 | 3959 | 22 | 2903 | 88.67 | 88.68 |
| L2 | 3830 | 15 | 3794 | 83.46 | 89.79 |
| L3 | 3907 | 13 | 3870 | 74.25 | 74.12 |
| M1 | 2283 | 13 | 2211 | 88.30 | 88.04 |
| M2 | 2158 | 30 | 2060 | 85.14 | 84.53 |
| M3 | 1996 | 25 | 1932 | 82.07 | 82.07 |
| S1 | 1643 | 31 | 321 | 74.39 | 75.09 |
| 293 | 733 | 80.77 | 80.58 | ||
| 630 | 1610 | 86.49 | 86.49 | ||
| S2 | 1324 | 16 | 1266 | 91.54 | 91.54 |
| S3 | 1202 | 31 | 1134 | 87.27 | 88.10 |
| S4 | 1192 | 24 | 1127 | 82.63 | 82.47 |
| Strain | σC-Based Genotype | Whole-Genome-Based Genotyping |
|---|---|---|
| R18-37308 | VI | L1-III/L2-Id/L3-II/M1-IIIa/M2-II/M3-II/S1-VI/S2-I/S3-Ic/S4-II * |
| R18-38167 | VI | L1-III/L2-II/L3-II/M1-IIIa/M2-II/M3-II/S1-VI/S2-I/S3-Ib/S4-II |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nour, I.; Alvarez-Narvaez, S.; Harrell, T.L.; Conrad, S.J.; Mohanty, S.K. Whole Genomic Constellation of Avian Reovirus Strains Isolated from Broilers with Arthritis in North Carolina, USA. Viruses 2023, 15, 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112191
Nour I, Alvarez-Narvaez S, Harrell TL, Conrad SJ, Mohanty SK. Whole Genomic Constellation of Avian Reovirus Strains Isolated from Broilers with Arthritis in North Carolina, USA. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112191
Chicago/Turabian StyleNour, Islam, Sonsiray Alvarez-Narvaez, Telvin L. Harrell, Steven J. Conrad, and Sujit K. Mohanty. 2023. "Whole Genomic Constellation of Avian Reovirus Strains Isolated from Broilers with Arthritis in North Carolina, USA" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112191
APA StyleNour, I., Alvarez-Narvaez, S., Harrell, T. L., Conrad, S. J., & Mohanty, S. K. (2023). Whole Genomic Constellation of Avian Reovirus Strains Isolated from Broilers with Arthritis in North Carolina, USA. Viruses, 15(11), 2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112191






