Quinazolinone-Peptido-Nitrophenyl-Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of G Compounds
2.2. Molecular Cloning and Protein Expression of Mpro
2.3. In Vitro Mpro Inhibition Assay
2.4. Bio-Layer Interferometry Binding Kinetics Assay
2.5. Molecular Docking
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Fragment-Based G-Compounds
3.2. Mpro Inhibition Assay
3.3. Pharmacological and Bioavailability of the Synthesized Compounds
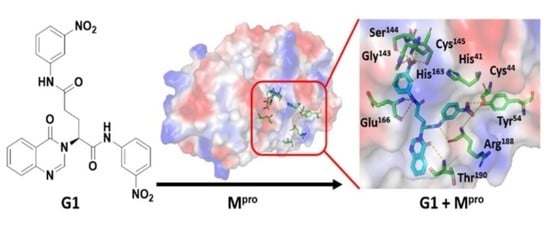
3.4. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, D.E.; Hiatt, J.; Bouhaddou, M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Ulferts, S.; Braberg, H.; Jureka, A.S.; Obernier, K.; Guo, J.Z.; Batra, J.; et al. Comparative host-coronavirus protein interaction networks reveal pan-viral disease mechanisms. Science 2020, 370, eabe9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In Coronaviruses; Maier, H.J., Bickerton, E., Britton, P., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Yang, X.L.; Chmura, A.A.; Zhu, G.; Epstein, J.H.; Mazet, J.K.; Hu, B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2013, 503, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ullrich, S.; Nitsche, C. The SARS-CoV-2 main protease as drug target. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rao, Z. Structural biology of SARS- CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.-S.; Chakraborty, C. Probable molecular mechanism of remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19: Need to Know more. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, W.P.; Holman, W.; Bush, J.A.; Almazedi, F.; Malik, M.; Eraut, N.C.J.E.; Morin, M.J.; Szewczyk, L.J.; Painter, G.R. Human Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Molnupiravir, a Novel Broad-Spectrum Oral Antiviral Agent with Activity against SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2021, 65, e02428-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.S.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, D.Q.; Guo, H.; Sirois, S.; Chou, K.C. Polyprotein cleavage mechanism of SARS-CoV Mpro and chemical modification of the octapeptide. Peptides 2004, 25, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Mujwar, S. Repurposing metocurine as main protease inhibitor to develop novel antiviral therapy for COVID-19. Struct. Chem. 2020, 36, 2487–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, H.M.; Dilnessa, T.; Jin, T. Structural Basis of Potential Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 622898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, F.; Zeng, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.; McCormick, P.J.; et al. Structural Basis of the Main Proteases of Coronavirus Bound to Drug Candidate PF-07321332. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0201321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodarahmi, G.A.; Rahmani Khajouei, M.; Hakimelahi, G.H.; Abedi, D.; Jafari, E.; Hassanzadeh, F. Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic evaluation of some new 2,3-disubstituted 4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 7, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Zaib, S.; Batool, S.; Abbas, N.; Ashraf, Z.; Iqbal, J.; Saeed, A. Quinazolines and quinazolinones as ubiquitous structural fragments in medicinal chemistry: An update on the development of synthetic methods and pharmacological diversification. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 2361–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birhan, Y.S.; Bekhit, A.A.; Hymete, A. In vivo antimalarial evaluation of some 2,3-disubstituted-4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toledo-Sherman, L.; Deretey, E.; Slon-Usakiewicz, J.J.; Ng, W.; Dai, J.R.; Foster, J.E.; Redden, P.R.; Uger, M.D.; Liao, L.C.; Pasternak, A.; et al. Frontal affinity chromatography with MS detection of EphB2 tyrosine kinase receptor. 2. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors via coupling with virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3221–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Kashaw, S.K.; Jain, N.; Rajak, H.; Soni, A.; Stables, J. Design and synthesis of some novel 3-[5-(4-substituted) phenyl-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole-2yl]-2-phenylquinazoline-4 (3 H)-ones as possible anticonvulsant agent. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.L.; Zocco, D.; Sundrud, M.S.; Hendrick, M.; Edenius, M.; Yum, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.K.; Cortese, J.F.; Wirth, D.; et al. Halofuginone and other febrifugine derivatives inhibit prolyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, K.Z.; Yasuo, N.; Sekijima, M. Screening for Inhibitors of Main Protease in SARS-CoV-2: In Silico and In Vitro Approach Avoiding Peptidyl Secondary Amides. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ye, F.; Feng, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Huang, B.; Niu, P.; et al. Both Boceprevir and GC376 efficaciously inhibit SARS-CoV-2 by targeting its main protease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, W.; Khan, M.B.; Fischer, C.; Arutyunova, E.; Lamer, T. Feline coronavirus drug inhibits the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 and blocks virus replication. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Petter, R.C.; Baillie, T.A.; Whitty, A. The resurgence of covalent drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moynihan, M.M.; Murkin, A.S. Cysteine Is the General Base That Serves in Catalysis by Isocitrate Lyase and in Mechanism-Based Inhibition by 3-Nitropropionate. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, T.A. Targeted Covalent Inhibitors for Drug Design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13408–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Kreitler, D.F.; Gulick, A.M.; Murkin, A.S. The Nitro Group as a Masked Electrophile in Covalent Enzyme Inhibition. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiche, Y.; Malashock, D.; Pinkerton, A.; Pons, J. Determining kinetics and affinities of protein interactions using a parallel realtime label-free biosensor, the Octet. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 377, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.B.; Duncan, T.M. Bio-layer Interferometry for Measuring Kinetics of Protein-protein Interactions and Allosteric Ligand Effects. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 84, e51383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, B.C.; Over, B.; Giordanetto, F.; Kihlberg, J. Oral druggable space beyond the rule of 5: Insights from drugs and clinical candidates. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1115–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doak, B.C.; Kihlberg, J. Drug discovery beyond the rule of 5—Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, E.C.; Santana, K.; Josino, L.; Lima, E.; Lima, A.H.; de Souza de Sales, J.C. Predicting cell-penetrating peptides using machine learning algorithms and navigating in their chemical space. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kügler, J.; Schmelz, S.; Gentzsch, J.; Haid, S.; Pollmann, E.; van den Heuvel, J.; Franke, R.; Pietschmann, T.; Heinz, D.W.; Collins, J. High affinity peptide inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS3-4A protease refractory to common resistant mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 39224–39232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Shaikh, M.; Tul-Wahab, A.; Ur-Rahman, A. In silico identification of potential inhibitors of key SARS-CoV-2 3CL hydrolase (Mpro) via molecular docking, MMGBSA predictive binding energy calculations, and molecular dynamics simulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmezayen, A.D.; Al-Obaidi, A.; Sahin, A.T.; Yelekci, K. Drug repurposing for coronavirus (COVID-19): In silico screening of known drugs against coronavirus 3CL hydrolase and protease enzymes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 2980–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, L.; Kumari, A.; Srivastava, M.; Singh, M.; Asthana, S. Identification of potential molecules against COVID-19 main protease through structure-guided virtual screening approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 3662–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitrit, A.; Zaidman, D.; Kalid, O.; Bloch, I.; Doron, D.; Yarnizky, T.; Buch, I.; Segev, I.; Ben-Zeev, E.; Segev, E.; et al. Conserved interactions required for inhibition of the main protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Gallo, G.; Campos, C.B.; Hardy, L.; Würtele, M. Biochemical screening for SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Kim, Y.; Liu, H.; Kankanamalage, A.C.G.; Eckstrand, C.; Groutas, W.C.; Bannasch, M.; Meadows, J.M.; Chang, K.O. Efficacy of a 3C-like protease inhibitor in treating various forms of acquired feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| KD (M) | kon (1/Ms) | koff (1/s) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 2.60 × 10−5 ± 1.49 × 10−7 | 1.25 × 102 ± 4.99 × 10−1 | 3.25 × 10−3 ± 1.33 × 10−5 | 0.9913 |
| G4 | 2.55 × 10−5 ± 7.59 × 10−7 | 1.62 × 104 ± 3.50 × 102 | 4.13 × 10−1 ± 8.44 × 10−3 | 0.971 |
| Name | Lipinski’s Rules | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW <500 | HBA <10 | HBD ≤5 | Mlog P ≤4.15 | Lipinski’s Volations | Bioavailability Score | |
| G1 | 516.46 | 8 | 2 | 1.63 | 2 | 0.17 |
| G2 | 546.48 | 10 | 0 | 2.31 | 2 | 0.17 |
| G3 | 548.46 | 10 | 4 | −0.13 | 2 | 0.17 |
| G4 | 548.46 | 10 | 2 | 0.41 | 2 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giang, H.-N.-H.; Chou, F.-P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, S.-C.; Huang, S.-C.; Wu, T.; Hue, B.-T.-B.; Lin, H.-C.; Wu, T.-K. Quinazolinone-Peptido-Nitrophenyl-Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Viruses 2023, 15, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020287
Giang H-N-H, Chou F-P, Chen C-Y, Chou S-C, Huang S-C, Wu T, Hue B-T-B, Lin H-C, Wu T-K. Quinazolinone-Peptido-Nitrophenyl-Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020287
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiang, Huynh-Nguyet-Huong, Feng-Pai Chou, Ching-Yun Chen, Shen-Chieh Chou, Sheng-Cih Huang, Tuoh Wu, Bui-Thi-Buu Hue, Hong-Cheu Lin, and Tung-Kung Wu. 2023. "Quinazolinone-Peptido-Nitrophenyl-Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease" Viruses 15, no. 2: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020287
APA StyleGiang, H.-N.-H., Chou, F.-P., Chen, C.-Y., Chou, S.-C., Huang, S.-C., Wu, T., Hue, B.-T.-B., Lin, H.-C., & Wu, T.-K. (2023). Quinazolinone-Peptido-Nitrophenyl-Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Viruses, 15(2), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020287