Genotype Diversity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in the Czech Republic in 2021/2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
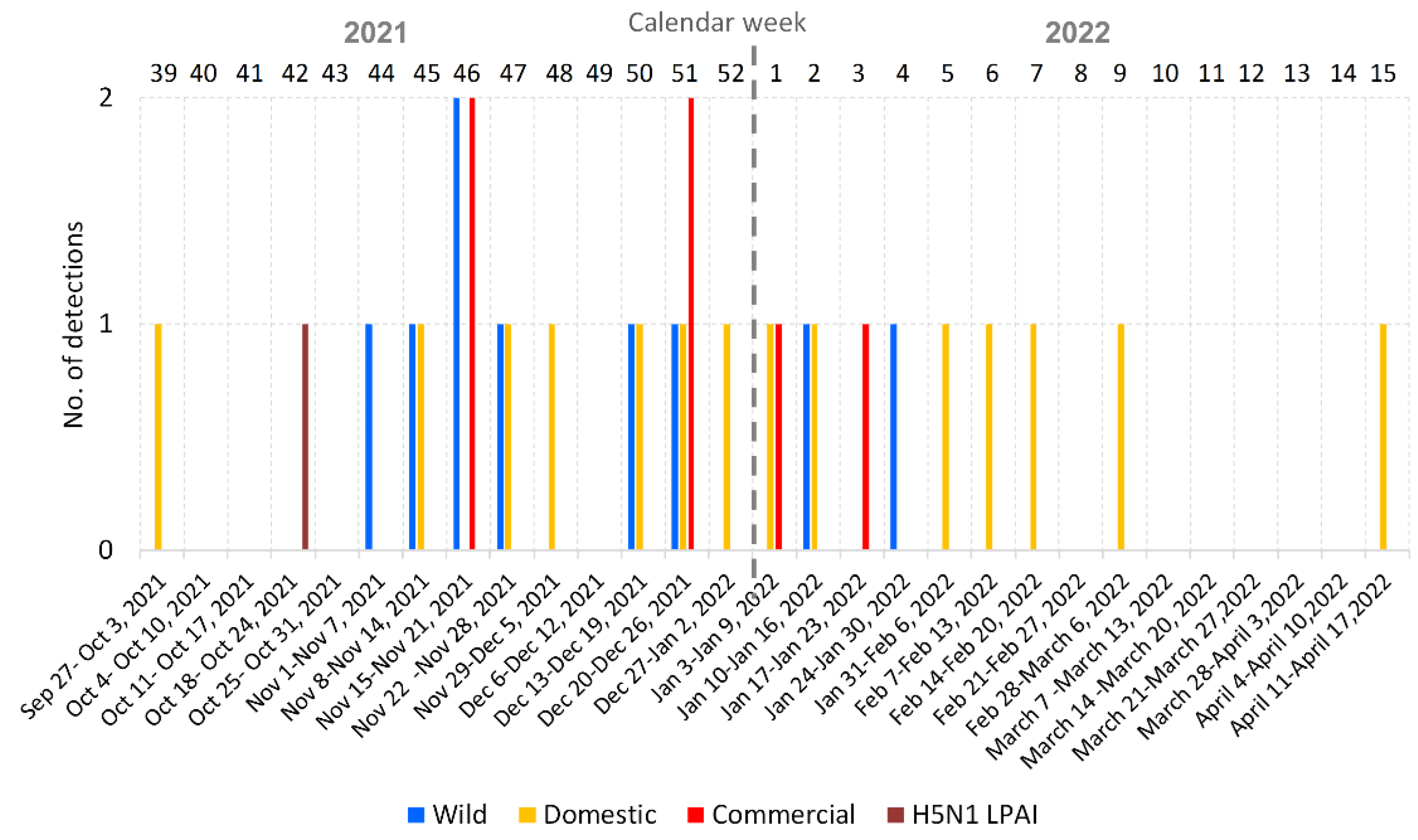
3.1. Overview of the 2021/2022 Avian Influenza Season in the Czech Republic
3.2. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Detected AIV Viruses
3.3. Genotype Diversity of the Czech H5N1 2021/2022 Viruses
3.4. Molecular Epidemiology of the Czech H5N1 2021/2022 Viruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview March–June 2022. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7415. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Brown, I.; Mulatti, P.; Smietanka, K.; Staubach, C.; Willeberg, P.; Adlhoch, C.; Candiani, D.; et al. Scientific report on the avian influenza overview October 2016–August 2017. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 5018. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview December 2021–March 2022. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7289. [Google Scholar]
- Poultrymed. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20221021094717/https://www.poultrymed.com/Poultrymed/Templates/showpage.asp?DBID=1&LNGID=1&TMID=178&FID=2948&PID=0&IID=79782 (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Lewis, N.S.; Banyard, A.C.; Whittard, E.; Karibayev, T.; Al Kafagi, T.; Chvala, I.; Byrne, A.; Meruyert Akberovna, S.; King, J.; Harder, T.; et al. Emergence and spread of novel H5N8, H5N5 and H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2020. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview August–December 2020. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6379. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview December 2020–February 2021. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6497. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview February–May 2021. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6951. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview May–September 2021. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7122. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlmann, A.; King, J.; Fusaro, A.; Zecchin, B.; Banyard, A.C.; Brown, I.H.; Byrne, A.M.P.; Beerens, N.; Liang, Y.; Heutink, R.; et al. Has Epizootic Become Enzootic? Evidence for a Fundamental Change in the Infection Dynamics of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza in Europe, 2021. mBio 2022, 30, e0060922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Černíková, L.; Stará, M. A new clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza genotype detected in Europe in 2021. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority; ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control); EURL (European Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza); Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; et al. Scientific report: Avian influenza overview September–December 2021. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 7108. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, A.; Černíková, L.; Stará, M.; Hofmannová, L.; Sedlák, K. Genotype Uniformity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N8 in the Czech Republic in 2021. Viruses 2022, 14, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Dán, Á.; Černíková, L.; Vitásková, E.; Křivda, V.; Horníčková, J.; Masopust, R.; Sedlák, K. Microevolution and independent incursions as main forces shaping H5 Hemagglutinin diversity during a H5N8/H5N5 highly pathogenic avian influenza outbreak in Czech Republic in 2017. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Černíková, L.; Kunteová, K.; Dirbáková, Z.; Thomas, S.S.; Slomka, M.J.; Dán, Á.; Varga, T.; Máté, M.; Jiřincová, H.; et al. A universal RT-qPCR assay for “One Health” detection of influenza A viruses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, M.J.; Pavlidis, T.; Banks, J.; Shell, W.; McNally, A.; Essen, S.; Brown, I.H. Validated H5 Eurasian real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and its application in H5N1 outbreaks in 2005–2006. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, M.J.; Coward, V.J.; Banks, J.; Löndt, B.Z.; Brown, I.H.; Voermans, J.; Koch, G.; Handberg, K.J.; Jørgensen, P.H.; Cherbonnel-Pansart, M.; et al. Identification of sensitive and specific avian influenza polymerase chain reaction methods through blind ring trials organized in the European Union. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payungporn, S.; Chutinimitkul, S.; Chaisingh, A.; Damrongwantanapokin, S.; Buranathai, C.; Amonsin, A.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Single step multiplex real-time RT-PCR for H5N1 influenza A virus detection. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arctic Network. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20221021094307/https://artic.network/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Samtools. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20221021094039/http://www.htslib.org/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Influenza Research Database. Available online: https://web.archive.org/save/https://www.fludb.org/brc/analysis_landing.spg?decorator=influenza (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Kazunori, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EMMBOS: Union Manual. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20221021093806/https://www.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/emboss/help/union (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- To, T.-H.; Jung, M.; Lycett, S.; Gascuel, O. Fast dating using least-squares criteria and algorithms. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dohna, H.; Cardona, C.J.; Miller, J.; Carpenter, T.E. Emergence and Genetic Variation of Neuraminidase Stalk Deletions in Avian Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wei, C.J.; Kong, W.P.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.; Smith, D.F.; Nabel, G.J. Immunization by avian H5 influenza hemagglutinin mutants with altered receptor binding specificity. Science 2007, 317, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.M.; Blixt, O.; Stevens, J.; Lipatov, A.S.; Davis, C.T.; Collins, B.E.; Cox, N.J.; Paulson, J.C.; Donis, R.O. In vitro evolution of H5N1 avian influenza virus toward human-type receptor specificity. Virology 2012, 422, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Ellakany, H.F.; Kawashita, N.; Mizuike, R.; Hiramatsu, H.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ikuta, K. Acquisition of Human-Type Receptor Binding Specificity by New H5N1 Influenza Virus Sublineages during Their Emergence in Birds in Egypt. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ishaq, M.; Prudence, M.; Xi, X.; Hu, T.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Single mutation at the amino acid position 627 of PB2 that leads to increased virulence of an H5N1 avian influenza virus during adaptation in mice can be compensated by multiple mutations at other sites of PB2. Virus Res. 2009, 144, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Deng, G.; Song, J.; Tian, G.; Suo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Bu, Z.; Kawaoka, Y.; Chen, H. Two amino acid residues in the matrix protein M1 contribute to the virulence difference of H5N1 avian influenza viruses in mice. Virology 2009, 384, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, G.; Herwig, A.; Klenk, H.D. Interaction of polymerase subunit PB2 and NP with importin alpha1 is a determinant of host range of influenza A virus. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, A.; Van der Meer, F.; Stegeman, A.; Koch, G. Evolutionary Analysis of Inter-Farm Transmission Dynamics in a Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Epidemic. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouwstra, R.J.; Koch, G.; Heutink, R.; Harders, F.; Van der Spek, A.; Elbers, A.R.; Bossers, A. Phylogenetic analysis of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N8) virus outbreak strains provides evidence for four separate introductions and one between-poultry farm transmission in the Netherlands, November 2014. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatesh, D.; Brouwer, A.; Goujgoulova, G.; Ellis, R.; Seekings, J.; Brown, I.H.; Lewis, N.S. Regional Transmission and Reassortment of 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Viruses in Bulgarian Poultry 2017/18. Viruses 2020, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.G.; Guan, Y.; Peiris, M.; Walker, D.; Krauss, S.; Zhou, N.N.; Govorkova, E.A.; Ellis, T.M.; Dyrting, K.C.; Sit, T.; et al. Characterization of H5N1 influenza viruses that continue to circulate in geese in southeastern China. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, B.; Liang, J.; You, R.; Han, L.; Mei, K.; Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X.; Gao, P.; et al. Pathogenicity and transmissibility of a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus H5N6 isolated from a domestic goose in Southern China. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 212, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmietanka, K.; Świętoń, E.; Kozak, E.; Wyrostek, K.; Tarasiuk, K.; Tomczyk, G.; Konopka, B.; Welz, M.; Domańska-Blicharz, K.; Niemczuk, K. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N8 in Poland in 2019–2020. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Cha, R.M.; Kye, S.J.; Lee, Y.N.; Kim, N.Y.; Baek, Y.G.; Heo, G.B.; Sagong, M.; Lee, K.N.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Pathogenicity of H5N8 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus in Chickens and Ducks from South Korea in 2020–2021. Viruses 2021, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoizec, A.; Niqueux, E.; Thomas, R.; Daniel, P.; Schmitz, A.; Le Bouquin, S. Airborne Detection of H5N8 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Genome in Poultry Farms, France. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filaire, F.; Lebre, L.; Foret-Lucas, C.; Vergne, T.; Daniel, P.; Lelièvre, A.; De Barros, A.; Jbenyeni, A.; Bolon, P.; Paul, M.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus in Dust Samples from Poultry Farms, France, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Baas, C.; Lexmond, P.; Waldenström, J.; Wallensten, A.; Fransson, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Beyer, W.E.; Schutten, M.; Olsen, B.; et al. Spatial, temporal, and species variation in prevalence of influenza A viruses in wild migratory birds. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallensten, A.; Munster, V.J.; Latorre-Margalef, N.; Brytting, M.; Elmberg, J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Fransson, T.; Haemig, P.D.; Karlsson, M.; Lundkvist, A.; et al. Surveillance of influenza A virus in migratory waterfowl in northern Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, V.G.; Chen, R.; Spiro, D.J.; Sengamalay, N.; Zaborsky, J.; Ghedin, E.; Nolting, J.; Swayne, D.E.; Runstadler, J.A.; Happ, G.M.; et al. The evolutionary genetics and emergence of avian influenza viruses in wild birds. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, A.; Cerníková, L.; Jiřincová, H.; Havlíčková, M.; Horníčková, J. Local-scale diversity and between-year “frozen evolution” of avian influenza A viruses in nature. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Strain ID | Collection Date | Category | Bird Species | Virus Strain and GISAID acc. No. | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18520 | 2021-09-27 | Backyard poultry | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/18520-1/2021|EPI_ISL_5323346 | B |
| duck | A/duck/Czech_Republic/18520-2/2021|EPI_ISL_5323347 | ||||
| 20689 | 2021-10-22 | Commercial farms | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/20689-27T/2021|EPI_ISL_6511912 | LPAI |
| goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/20689-28T/2021|EPI_ISL_6512576 | ||||
| 21312 | 2021-11-01 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/21312/2021|EPI_ISL_6328409 | A1 |
| 22224 | 2021-11-12 | Backyard poultry | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/22224-2T/2021|EPI_ISL_7224437 | A2 |
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/22224-3K/2021|EPI_ISL_7224454 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/22224-3T/2021|EPI_ISL_7224463 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/22224-4T/2021|EPI_ISL_7224472 | |||||
| 22380 | 2021-11-15 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/22380/2021|EPI_ISL_9603920 | C |
| 22477 | 2021-11-12 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/22477-1/2021|EPI_ISL_9603916 | A1 |
| A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/22477-2/2021|EPI_ISL_9603918 | |||||
| 22608 * | 2021-11-18 | Commercial farms | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/22608-1/2021|EPI_ISL_8515478 | A2 |
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/22608-1T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603795 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/22608-2/2021|EPI_ISL_8515479 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/22608-2T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603819 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/22608-3T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603901 | |||||
| 22684 | 2021-11-15 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/22684/2021|EPI_ISL_9603922 | A1 |
| 22750 * | 2021-11-19 | Commercial farms | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/22750/2021|EPI_ISL_9603924 | A2 |
| 23404 | 2021-11-25 | Backyard poultry | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23404-2K/2021|EPI_ISL_7626484 | A1 |
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23404-4K/2021|EPI_ISL_7626506 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23404-2T/2021|EPI_ISL_7626512 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23404-4T/2021|EPI_ISL_7626513 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23404/2021|EPI_ISL_8515480 | |||||
| 23458 * | 2021-11-26 | Commercial farms | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/23458-1K/2021|EPI_ISL_9603780 | A2 |
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/23458-2T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603767 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/23458-4T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603775 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/23458-5T/2021|EPI_ISL_9603769 | |||||
| 23589 | 2021-11-29 | Backyard poultry | Muscovy duck | A/duck/Czech_Republic/23589-1T/2021|EPI_ISL_7626514 | A2 |
| chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23589-1T/2021|EPI_ISL_7626526 | ||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23589-3/2021|EPI_ISL_7626532 | |||||
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/23589-4/2021|EPI_ISL_7626533 | |||||
| 23608 $ | 2021-11-28 | Wild birds | grey heron | A/grey heron/Czech_Republic/23608/2021|EPI_ISL_8515481 | D |
| A/grey heron/Czech_Republic/23608-1K/2021|EPI_ISL8515482 | |||||
| 23609 $ | 2021-11-28 | Wild birds | great egret | A/great egret/Czech_Republic/23609/2021|EPI_ISL_8515483 | D |
| 24893 * | 2021-12-14 | Commercial farms | goose | N.A | N.A |
| 24894 * | 2021-12-14 | Commercial farms | goose | N.A | N.A |
| 24895 * | 2021-12-14 | Commercial farms | goose | N.A | N.A |
| 24898 * | 2021-12-14 | Commercial farms | goose | N.A | N.A |
| 25203 | 2021-12-16 | Backyard poultry | guinea fowl | N.A | N.A |
| 25322 * | 2021-12-19 | Commercial farms | goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/25322-179/2021|EPI_ISL_12150664 | A2 |
| A/goose/Czech Republic/25322-229/2021|EPI_ISL_12325995 | |||||
| A/goose/Czech_Republic/25322-205/2021|EPI_ISL_12150666 | |||||
| 25324 * | 2021-12-19 | Commercial farms | goose | N.A | N.A |
| 25338 | 2021-12-18 | Wild birds | grey heron | A/grey_heron/Czech_Republic/25338-1/2021|EPI_ISL_12223688 | D |
| A/grey_heron/Czech_Republic/25338-2/2021|EPI_ISL_12223734 | |||||
| 25429 | 2021-12-20 | Backyard poultry | chicken | N.A | N.A |
| 25690 | 2021-12-22 | Commercial farms | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/25690/2021|EPI_ISL_9603929 | C |
| 25702 | 2021-12-20 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/25702-2/2021|EPI_ISL_9603927 | A1 |
| 25827 | 2021-12-25 | Commercial farms | pheasant | A/pheasant/Czech_Republic/25827-1/2021|EPI_ISL_9603931 | A1 |
| A/pheasant/Czech_Republic/25827-2/2021|EPI_ISL_9603937 | |||||
| A/pheasant/Czech_Republic/25827-3/2021|EPI_ISL_9603939 | |||||
| 61 | 2021-12-31 | Backyard poultry | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/61-1/2022|EPI_ISL_11327088 | A2 |
| A/chicken/Czech_Republic/61-2/2022|EPI_ISL_11327089 | |||||
| 63 | 2022-01-03 | Backyard poultry | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/63/2022|EPI_ISL_11327090 | A1 |
| 65 | 2022-01-03 | Commercial farms | mallard | N.A | N.A |
| 785 | 2022-01-10 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/785-/2022|EPI_ISL_12139999 | A2 |
| A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/785-/2022|EPI_ISL_9603943 | |||||
| 913 | 2022-01-12 | Backyard poultry | chicken | A/chicken/Czech_Republic/913/2022|EPI_ISL_12150658 | A2 |
| goose | A/goose/Czech_Republic/913/2022|EPI_ISL_12150657 | ||||
| duck | A/duck/Czech_Republic/913/2022|EPI_ISL_12140437 | ||||
| 1814 | 2022-01-22 | Commercial farms | duck | N.A | N.A |
| 2755 | 2022-01-29 | Wild birds | mute swan | A/mute_swan/Czech_Republic/2755/2022|EPI_ISL_12150661 | A1 |
| 2968 | 2022-02-04 | Backyard poultry | chicken | HA|A/chicken/Czech_Republic/2968/2022|EPI_ISL_13955171 | E |
| 3306 | 2022-02-09 | Backyard poultry | duck | HA|A/duck/Czech_Republic/3306-1/2022|EPI_ISL_12324302 | F |
| HA|A/chicken/Czech_Republic/3306-2/2022|EPI_ISL_12325210 | |||||
| 4060 | 2022-02-18 | Backyard poultry | chicken | N.A | N.A |
| 4919 | 2022-03-01 | Backyard poultry | N.A | N.A | N.A |
| 8028 | 2022-04-13 | Backyard poultry | chicken | HA|A/chicken/Czech_Republic/8028-1/2022|EPI_ISL_13955204 | E |
| HA|A/chicken/Czech_Republic/8028-2/2022|EPI_ISL_13967740 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagy, A.; Stará, M.; Černíková, L.; Hofmannová, L.; Sedlák, K. Genotype Diversity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in the Czech Republic in 2021/2022. Viruses 2023, 15, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020293
Nagy A, Stará M, Černíková L, Hofmannová L, Sedlák K. Genotype Diversity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in the Czech Republic in 2021/2022. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020293
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagy, Alexander, Martina Stará, Lenka Černíková, Lada Hofmannová, and Kamil Sedlák. 2023. "Genotype Diversity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in the Czech Republic in 2021/2022" Viruses 15, no. 2: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020293
APA StyleNagy, A., Stará, M., Černíková, L., Hofmannová, L., & Sedlák, K. (2023). Genotype Diversity, Wild Bird-to-Poultry Transmissions, and Farm-to-Farm Carryover during the Spread of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in the Czech Republic in 2021/2022. Viruses, 15(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020293





