Genetic Characteristics and Phylogeographic Dynamics of Lagoviruses, 1988–2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Genomic Similarity Analysis
2.3. Phylogeographic Network Analysis
2.4. Recombination Analysis
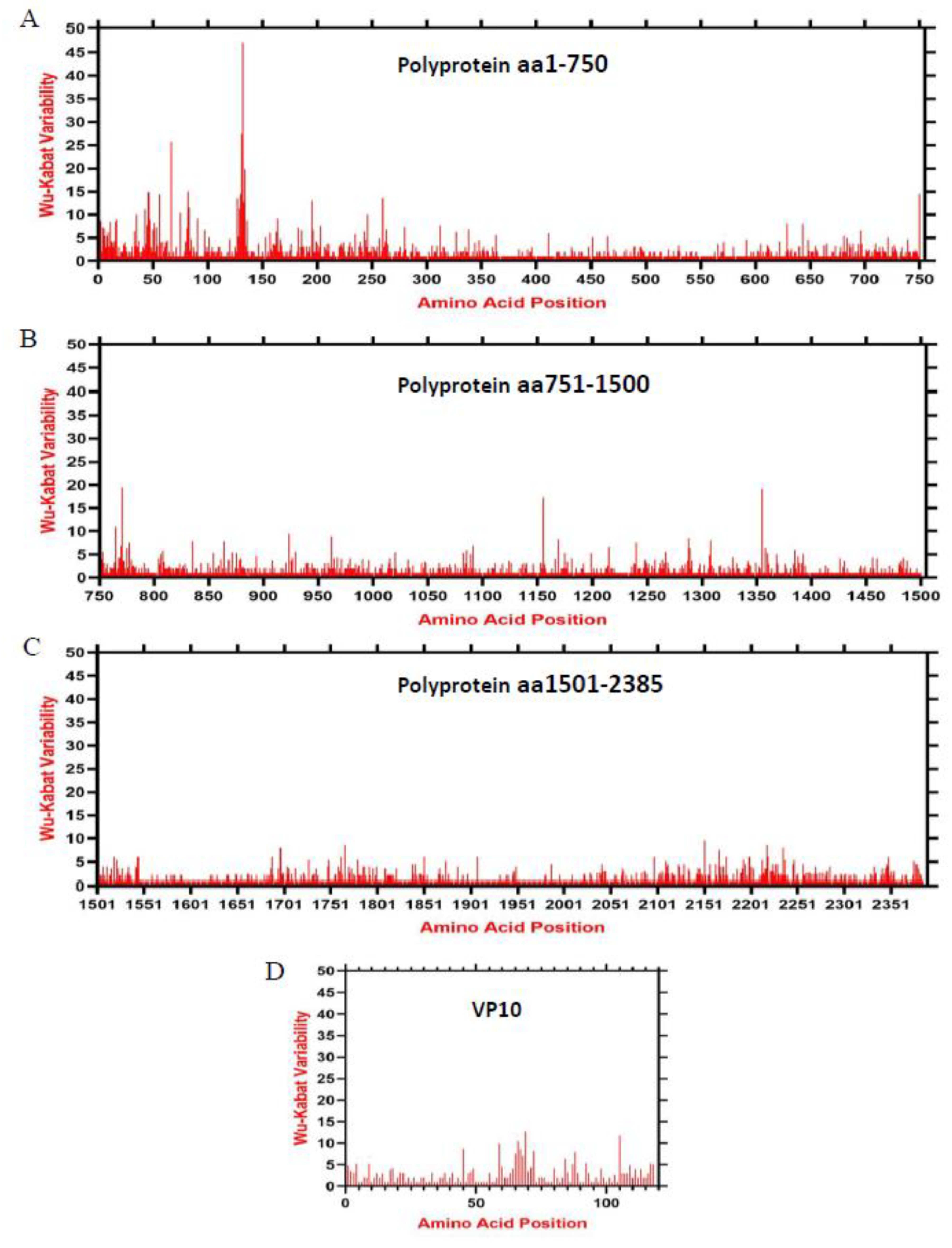
2.5. Amino Acids Variability Analysis
3. Results
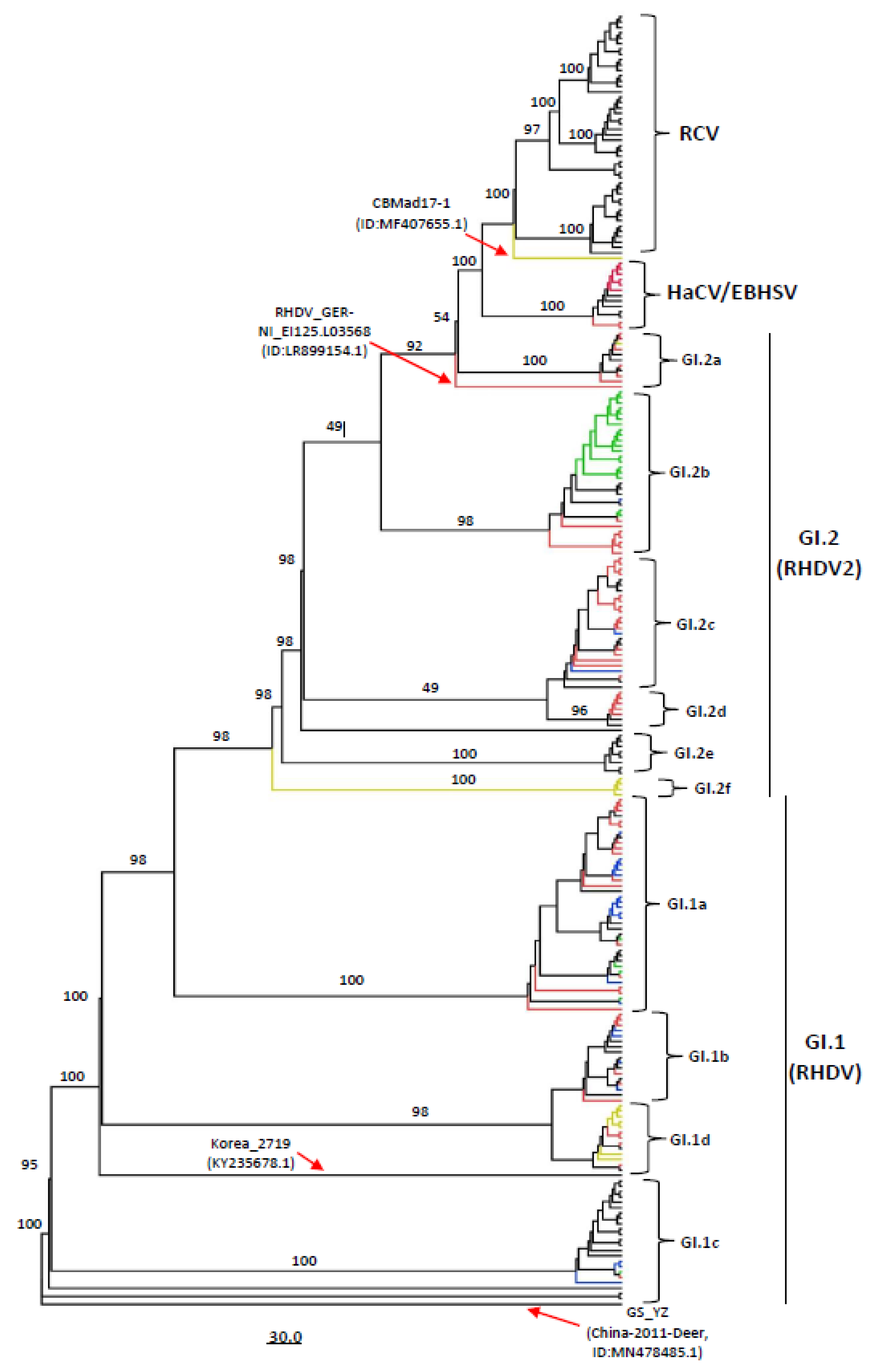
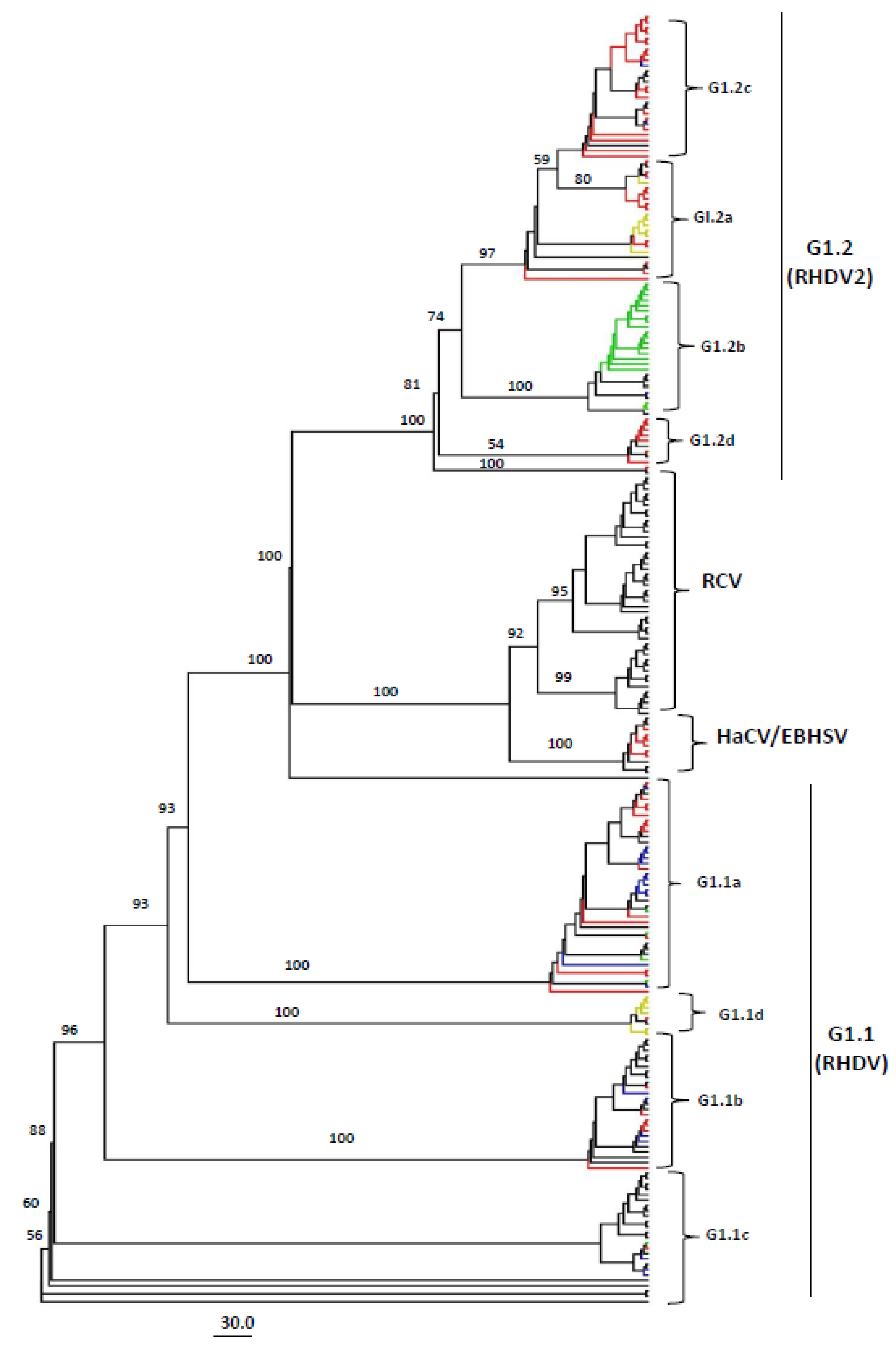
3.1. Genotyping of Lagoviruses Based on the Full-Length Genomes or Coding Sequences of VP60 and VP10
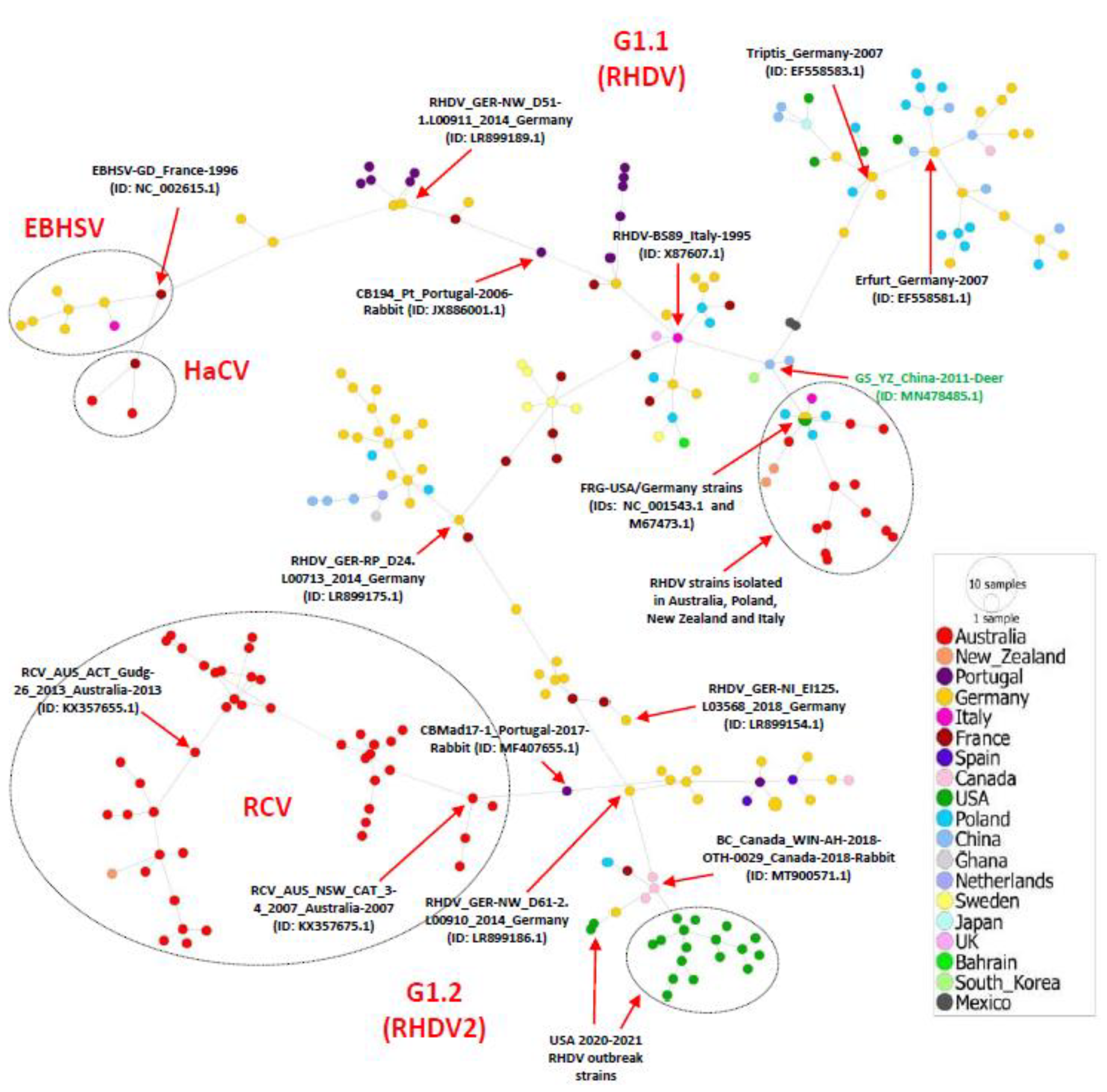
3.2. Phylogeographic Analysis of Full-Length Lagovirus Genomes
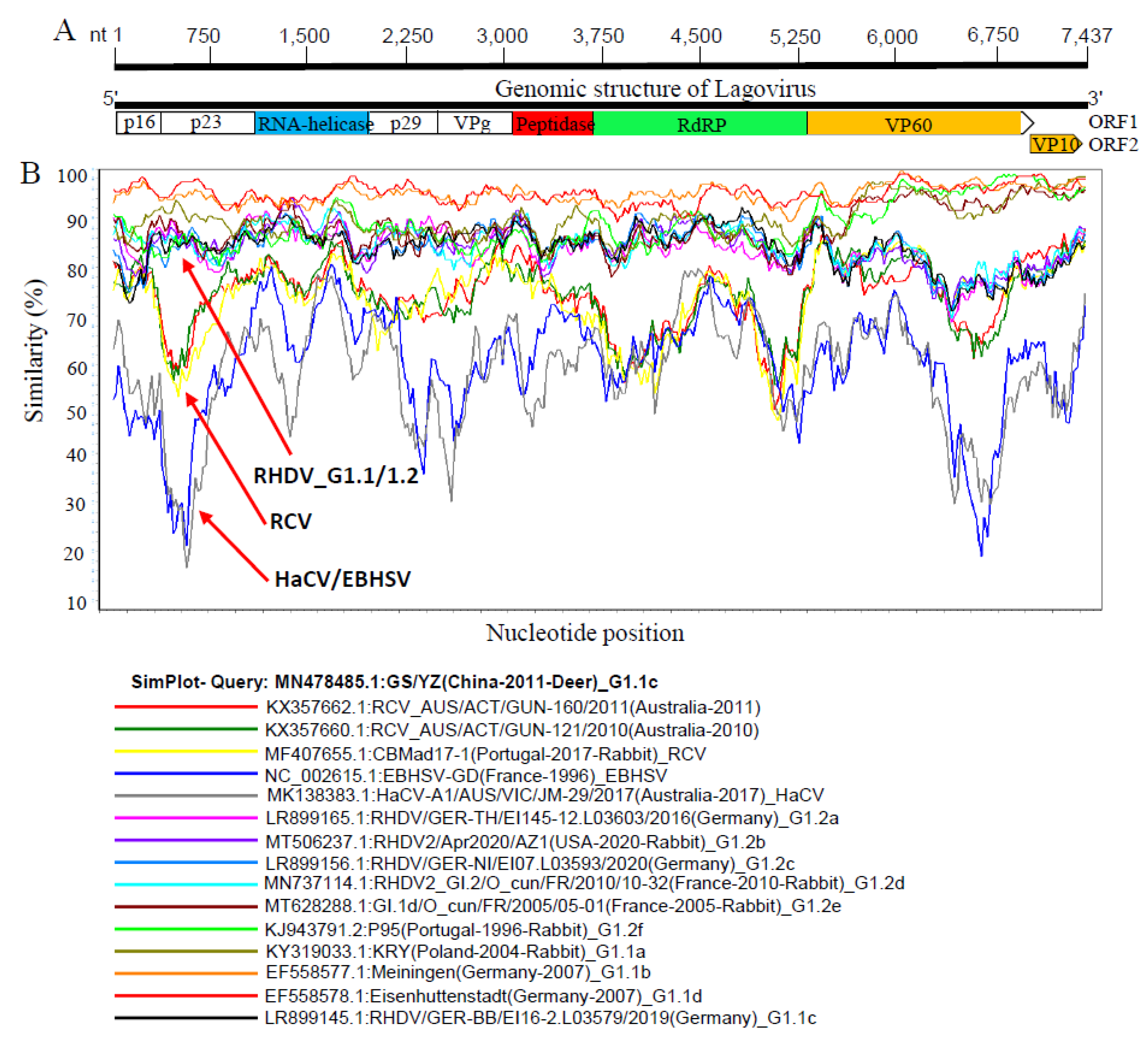
3.3. Recombination Pattern of Lagovirus Full-Length Genome
3.4. Amino Acids Variability Landscape of Lagovirus Proteins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavier-Widén, D.; Mörner, T. Epidemiology and diagnosis of the European brown hare syndrome in Scandinavian countries: A review. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1991, 10, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.J.; Xue, H.P.; Pu, B.Q.; Qian, N.H. A new viral disease in rabbit. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 1984, 16, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Cancellotti, F.M.; Renzi, M. Epidemiology and current situation of viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and the European brown hare syndrome in Italy. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1991, 10, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambagala, A.; Ababio, P.; Lamboo, L.; Goolia, M.; Lung, O.; Berhane, Y.; Odoom, T. Outbreak of Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 Infections, Ghana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Shimoda, H.; Kadekaru, S.; Henmi, C.; Une, Y. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus type 2 epidemic in a rabbit colony in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Wei, H.; Fan, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, M.; Qiu, R.; Zhu, W.; Xu, W.; Xue, J.; Wang, F. Emergence of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 in China in 2020. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Aguayo-Adán, J.A.; Santoro, S.; Abrantes, J.; Delibes-Mateos, M. Worldwide rapid spread of the novel rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (GI.2/RHDV2/b). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1762–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Van Der Loo, W.; Le Pendu, J.; Esteves, P.J. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): A review. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parra, F.; Prieto, M. Purification and characterization of a calicivirus as the causative agent of a lethal hemorrhagic disease in rabbits. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4013–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.-S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.M.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, L.; Fusi, P.; Lavazza, A.; Pacciarini, M.L.; Rossi, C. Detection and preliminary characterization of a new rabbit calicivirus related to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus but nonpathogenic. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8614–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Fages, M.-P.; Bertagnoli, S.; Gelfi, J.; Aubineau, J.; Roobrouck, A.; Botti, G.; Lavazza, A.; Marchandeau, S. Characterisation of a non-pathogenic and non-protective infectious rabbit lagovirus related to RHDV. Virology 2011, 410, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strive, T.; Wright, J.; Robinson, A. Identification and partial characterisation of a new lagovirus in Australian wild rabbits. Virology 2009, 384, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, N.L.; Trout, R.C.; Gould, E.A. Benign circulation of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus on Lambay Island, Eire. Virology 2007, 358, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahar, J.E.; Nicholson, L.; Eden, J.-S.; Duchêne, S.; Kerr, P.J.; Duckworth, J.; Ward, V.K.; Holmes, E.C.; Strive, T. Benign rabbit caliciviruses exhibit evolutionary dynamics similar to those of their virulent relatives. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9317–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capucci, L.; Fallacara, F.; Grazioli, S.; Lavazza, A.; Pacciarini, M.L.; Brocchi, E. A further step in the evolution of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: The appearance of the first consistent antigenic variant. Virus Res. 1998, 58, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Boucher, S.; Le Normand, B.; Plassiart, G.; Portejoie, Y.; Decors, A.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guérin, J.L.; Marchandeau, S. Detection of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Costa Carvalho, C.L. The Role of Wild Leporids as Reservoirs of Infectious Agents. Doctoral Thesis, University of Évora, Évora, Portugal, 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10174/21811 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Lopes, A.M.; Correia, J.; Abrantes, J.; Melo, P.; Ramada, M.; Magalhães, M.J.; Alves, P.C.; Esteves, P.J. Is the new variant RHDV replacing genogroup 1 in Portuguese wild rabbit populations? Viruses 2014, 7, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvete, C.; Sarto, P.; Calvo, A.J.; Monroy, F.; Calvo, J.H. Could the new rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus variant (RHDVb) be fully replacing classical RHD strains in the Iberian Peninsula? World Rabbit Sci. 2014, 22, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavadini, P.; Molinari, S.; Pezzoni, G.; Chiari, M.; Brocchi, E.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L. Identification of a new non-pathogenic lagovirus in Lepus europeaus. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress for Veterinary Virology and 9th Annual Epizone Meeting “Changing Viruses in a Changing World”, Montpellier, France, 31 August–3 September 2015; pp. 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, P.J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Cavadini, P.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Guitton, J.S.; Lavazza, A.; Lemaitre, E.; Letty, J.; Lopes, A.M.; et al. Emergence of pathogenicity in lagoviruses: Evolution from pre-existing nonpathogenic strains or through a species jump? PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droillard, C.; Lemaitre, E.; Chatel, M.; Guitton, J.-S.; Marchandeau, S.; Eterradossi, N.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. First complete genome sequence of a hare calicivirus strain isolated from Lepus europaeus. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01224-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahar, J.E.; Hall, R.N.; Shi, M.; Mourant, R.; Huang, N.; Strive, T.; Holmes, E.C. The discovery of three new hare lagoviruses reveals unexplored viral diversity in this genus. Virus Evol. 2019, 5, vez005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohlinger, V.F.; Haas, B.; Meyers, G.; Weiland, F.; Thiel, H.J. Identification and characterization of the virus causing rabbit hemorrhagic disease. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3331–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodak, L.; Smid, B.; Valicek, L.; Vesely, T.; Stepanek, J.; Hampl, J.; Jurak, E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of antibodies to rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus and determination of its major structural proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirblich, C.; Meyers, G.; Ohlinger, V.F.; Capucci, L.; Eskens, U.; Haas, B.; Thiel, H.J. European brown hare syndrome virus: Relationship to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus and other caliciviruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5164–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyers, G.; Wirblich, C.; Thiel, H.-J. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus--molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of a calicivirus genome. Virology 1991, 184, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhai, Y.; Xu, W.; Zheng, D.; Sun, F. Cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of two types of wild rabbit hemorrhagic disease viruses characterized the structural features of Lagovirus. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, K.; Baker, T.S.; Schulten, K.; et al. Atomic model of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Droillard, C.; Lemaitre, E.; Chatel, M.; Quéméner, A.; Briand, F.-X.; Guitton, J.-S.; Marchandeau, S.; Pendu, J.; Eterradossi, N.; Gall-Reculé, G. Genetic diversity and evolution of Hare Calicivirus (HaCV), a recently identified lagovirus from Lepus europaeus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 82, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Balseiro, A.; Muguerza, M.A.; Rosell, J.M.; Casais, R.; Álvarez, Á.L.; Parra, F. Variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in young rabbits, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlinger, V.; Haas, B. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD): Characterization of the causative calicivirus. Vet. Res. 1993, 24, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henning, J.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Davies, P.; Schnitzler, F.-R. Influence of weather conditions on fly abundance and its implications for transmission of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in the North Island of New Zealand. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, N.L.; Boag, B.; Moss, S.R.; Turner, S.L.; Trout, R.C.; White, P.J.; Hudson, P.J.; Gould, E.A. Long-term survival of New Zealand rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus RNA in wild rabbits, revealed by RT-PCR and phylogenetic analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 11, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G.; Boilletot, E.; Arnauld, C.; Morisse, J.P.; Rasschaert, D. Molecular epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus outbreaks in France during 1988 to 1995. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 Pt 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Gall-Recule, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Laurent, S.; de Boisséson, C.; Portejoie, Y.; Rasschaert, D. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France between 1993 and 2000, and the characterisation of RHDV antigenic variants. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.R.; Turner, S.L.; Trout, R.C.; White, P.J.; Hudson, P.; Desai, A.; Armesto, M.; Forrester, N.L.; Gould, E.A. Molecular epidemiology of Rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83 Pt 10, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, N.; Bascuñana, C.R.; Ballagi-Pordaány, A.; Gavier-Wideén, D.; Uhleén, M.; Belaák, S. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease and European brown hare syndrome viruses by comparison of sequences from the capsid protein gene. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lole, K.S.; Bollinger, R.C.; Paranjape, R.S.; Gadkari, D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Novak, N.G.; Ingersoll, R.; Sheppard, H.W.; Ray, S.C. Full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes from subtype C-infected seroconverters in India, with evidence of intersubtype recombination. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Boronat, M.; Diez-Rivero, C.M.; Reinherz, E.L.; Reche, P.A. PVS: A web server for protein sequence variability analysis tuned to facilitate conserved epitope discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36 (Suppl. S2), W35–W41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabat, E.; Wu, T.T.; Bilofsky, H. Unusual distributions of amino acids in complementarity determining (hypervariable) segments of heavy and light chains of immunoglobulins and their possible roles in specificity of antibody-combining sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 6609–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szillat, K.P.; Höper, D.; Beer, M.; König, P. Full-genome sequencing of German rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus uncovers recombination between RHDV (GI.2) and EBHSV (GII.1). Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Lopes, A.M.; Lemaitre, E.; Ahola, H.; Banihashem, F.; Droillard, C.; Marchandeau, S.; Esteves, P.J.; Neimanis, A.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. Retrospective Analysis Shows That Most RHDV GI.1 Strains Circulating Since the Late 1990s in France and Sweden Were Recombinant GI.3P-GI.1d Strains. Genes 2020, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Droillard, C.; Lopes, A.M.; Lemaitre, E.; Lucas, P.; Blanchard, Y.; Marchandeau, S.; Esteves, P.J.; Le Gall-Reculé, G. Recombination at the emergence of the pathogenic rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeier, H.; Reimann, I.; Köllner, B.; Granzow, H. Pathogenic, antigenic and molecular properties of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) isolated from vaccinated rabbits: Detection and characterization of antigenic variants. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.K.; Xu, L.; Moran, K.; Mohamed, F.; Boston, T.; Pauszek, S.J.; Vierra, D.A.; Faburay, B.; Dodd, K.A.; Barrette, R.W. Coding-Complete Genome Sequences of Emerging Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus Type 2 Isolates Detected in 2020 in the United States. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e01064-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Qi, R.; Veldkamp, L.; Ijzer, J.; Kik, M.L.; Zhu, J.; Tang, A.; Dong, D.; Shi, Y.; van Oers, M.M.; et al. Immunogenicity in Rabbits of Virus-Like Particles from a Contemporary Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus Type 2 (GI.2/RHDV2/b) Isolated in The Netherlands. Viruses 2019, 11, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Parra, F. Spread of new variant RHDV in domestic rabbits on the Iberian Peninsula. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucci, L.; Cavadini, P.; Schiavitto, M.; Lombardi, G.; Lavazza, A. Increased pathogenicity in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 (RHDV2). Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansman, G.S.; Jiang, X.J.; Green, K.Y. Caliciviruses: Molecular and Cellular Virology; Horizon Scientific Press: Norfolk, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, N.L.; Moss, S.R.; Turner, S.L.; Schirrmeier, H.; Gould, E.A. Recombination in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus: Possible impact on evolution and epidemiology. Virology 2008, 376, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Van Der Loo, W. Evidence for recombination in the major capsid gene VP60 of the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV). Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.M.; Dalton, K.P.; Magalhães, M.J.; Parra, F.; Esteves, P.; Holmes, E.; Abrantes, J. Full genomic analysis of new variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus revealed multiple recombination events. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96 Pt 6, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikschofsky, H.; Schirrmeier, H.; Keil, G.M.; Lange, B.; Polowick, P.L.; Keller, W.; Broer, I. Pea-derived vaccines demonstrate high immunogenicity and protection in rabbits against rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, A.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Guo, H.; Liu, G. Construction and immunogenicity of novel bivalent virus-like particles bearing VP60 genes of classic RHDV (GI. 1) and RHDV2 (GI. 2). Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Ulrich, R.; Franzke, K.; Müller, M.; Köllner, B. Crude extracts of recombinant baculovirus expressing rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 VLPs from both insect and rabbit cells protect rabbits from rabbit hemorrhagic disease caused by RHDV2. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.; Ulrich, R.; Schinköthe, J.; Müller, M.; Köllner, B. Characterization of protective humoral and cellular immune responses against RHDV2 induced by a new vaccine based on recombinant baculovirus. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Europe | Middle East | Africa | Asia | America | Oceania | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHDV | GI.1a | Germany (15), Poland (12) | - | - | China (7), Japan (1) | USA (4), Canada (1) | - | 40 |
| GI.1b | Germany (6), Poland (4), France (3), Italy (1), UK (1), Sweden (1) | Bahrain (1) | - | - | - | - | 17 | |
| GI.1c | Poland (3), Germany (1), Italy (1) | - | - | China (2) | Mexico (2), USA (1) | Australia (12), New Zealand (2) | 24 | |
| GI.1d | Portugal (7), Germany (4), France (2) | - | - | South Korea (1) | - | - | 14 | |
| RHDV2 | GI.2a | Germany (6), Portugal (1), Spain (2) | - | - | - | Canada (1) | - | 10 |
| GI.2b | Germany (7), Poland (1), France (1) | - | - | - | USA (19), Canada (3) | - | 31 | |
| GI.2c | Germany (17), Portugal (2), France (1), Netherland (1) | - | Ghana (1) | China (3) | - | - | 25 | |
| GI.2d | Germany (5), France (3) | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | |
| GI.2e | Sweden (5), France (3) | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | |
| GI.2f | Poland (4) | - | - | - | - | - | 4 | |
| RCV | Portugal (1) | Australia (44), New Zealand (1) | 46 | |||||
| HaCV/EBHSV | Germany (8), Italy (1), France (2) | Australia (2) | 13 | |||||
| Total | 132 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 31 | 61 | 240 | |
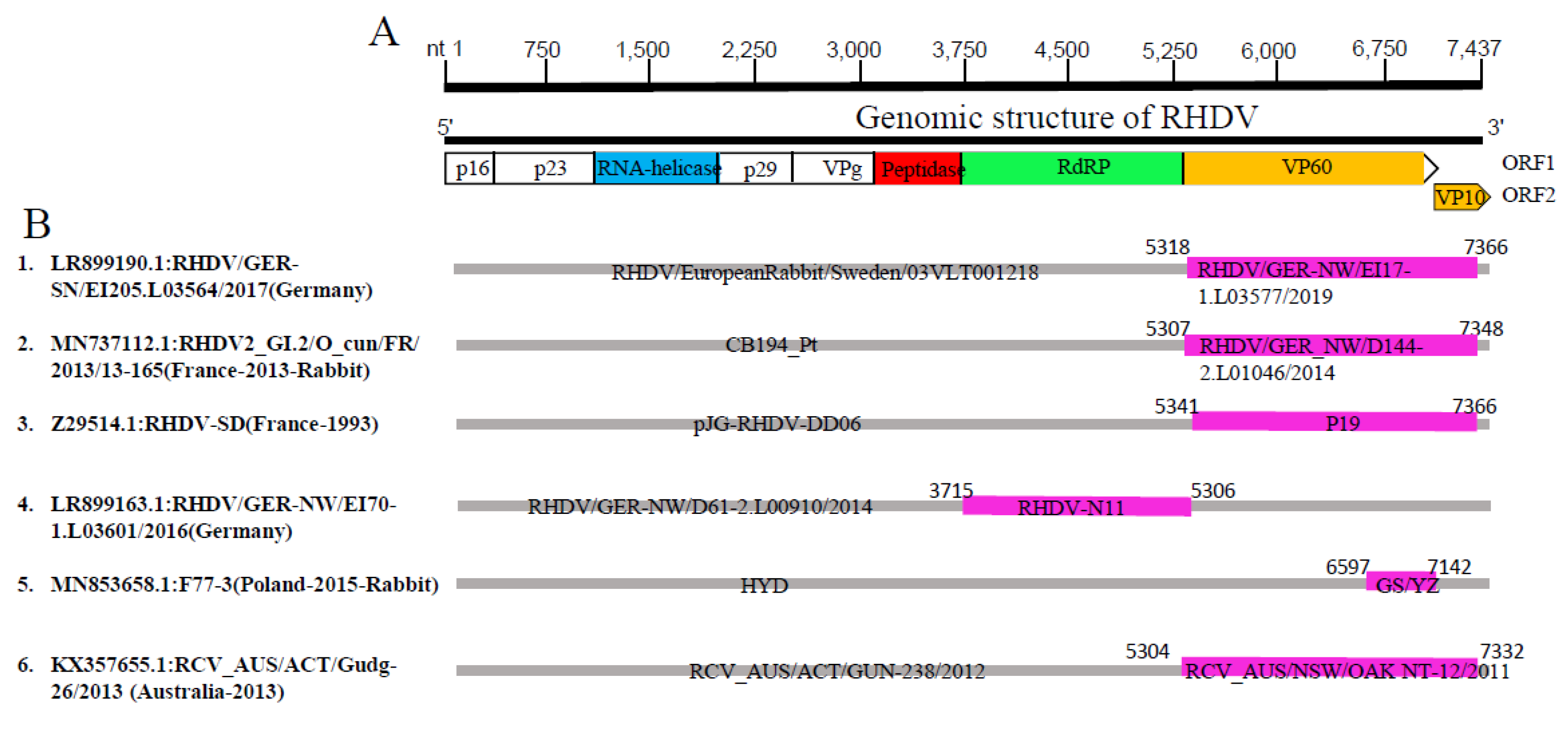
| Event Serial Number | Recombinant | Minor Parent | Major Parent | Detection Methods | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GenBank ID: Virus Name (Country-Year) | Genotype | GenBank ID: Virus Name (Country-Year) | Genotype | GenBank ID: Virus Name (Country-Year) | Genotype | R | G | B | M | C | S | T | |
| 1 | LR899190.1:RHDV/GER-SN/EI205.L03564/2017(Germany) | GI.2e | LR899142.1:RHDV/GER-NW/EI17-1.L03577/2019 (Germany) | GI.2c | MT819375.1:RHDV/EuropeanRabbit/Sweden/03VLT001218 (Swden-2003-Rabbit) | GI.2b | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 2 | MN737112.1:RHDV2_GI.2/O_cun/FR/2013/13-165(France-2013-Rabbit) | GI.1d | LR899187.1:RHDV/GER_NW/D144-2.L01046/2014 (Germany) | GI.2c | JX886001.1:CB194_Pt (Potugal-2006-Rabbit) | GI.1d | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 3 | * Z29514.1:RHDV-SD(France-1993) | GI.1d | KY765610.1:P19 (Portugal-1994-Rabbit) | GI.2a | EF363035.1:pJG-RHDV-DD06 (Germany-2007) | GI.1b | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| 4 | LR899163.1:RHDV/GER-NW/EI70-1.L03601/2016(Germany) | GI.2f | KM878681.1:RHDV-N11 (Spain-2014-Rabbit) | GI.2c | LR899186.1:RHDV/GER-NW/D61-2.L00910/2014 (Germany) | GI.2f | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | * MN853658.1:F77-3(Pland-2015-Rabbit) | GI.1a | MN478485.1:GS/YZ (China-2011-Deer) | GI.1c | JF412629.1:HYD (China-2005-Rabbit) | GI.1a | + | − | + | − | − | + | + |
| 6 | KX357655.1:RCV_AUS/ACT/Gudg-26/2013(Autralia-2013) | RCV | KX357681.1:RCV_AUS/NSW/OAK NT-12/2011 (Autralia-2011) | RCV | KX357663.1:RCV_AUS/ACT/GUN-238/2012 (Autralia-2012) | RCV | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, P.T.; Bahoussi, A.N.; Yang, C.; Yao, G.; Dong, L.; Wu, C.; Xing, L. Genetic Characteristics and Phylogeographic Dynamics of Lagoviruses, 1988–2021. Viruses 2023, 15, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040815
Shah PT, Bahoussi AN, Yang C, Yao G, Dong L, Wu C, Xing L. Genetic Characteristics and Phylogeographic Dynamics of Lagoviruses, 1988–2021. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040815
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Pir Tariq, Amina Nawal Bahoussi, Caiting Yang, Guanhan Yao, Li Dong, Changxin Wu, and Li Xing. 2023. "Genetic Characteristics and Phylogeographic Dynamics of Lagoviruses, 1988–2021" Viruses 15, no. 4: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040815
APA StyleShah, P. T., Bahoussi, A. N., Yang, C., Yao, G., Dong, L., Wu, C., & Xing, L. (2023). Genetic Characteristics and Phylogeographic Dynamics of Lagoviruses, 1988–2021. Viruses, 15(4), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040815






