Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Virus Classification and Structure
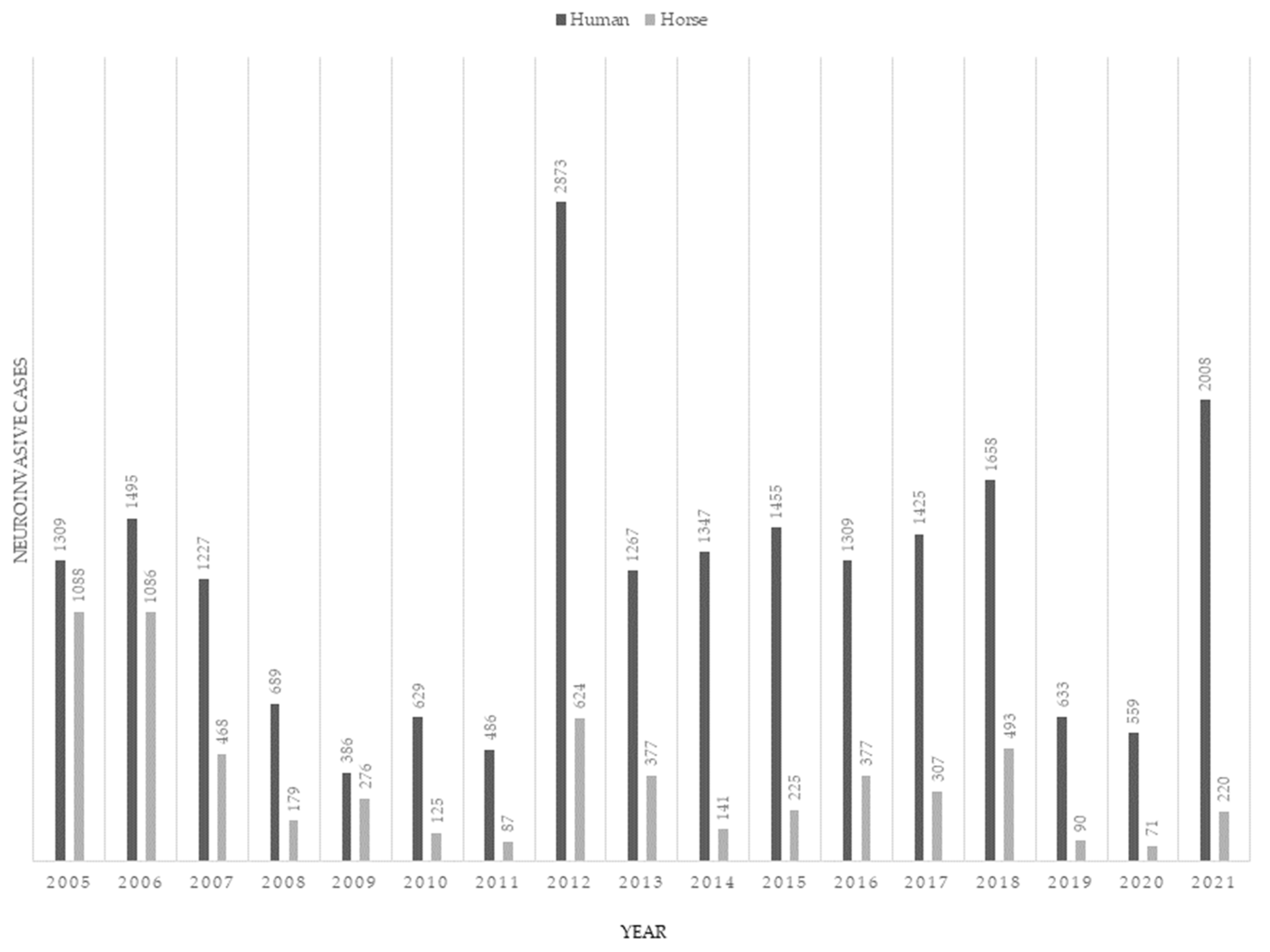
3. Epidemiology
3.1. Risk Factors for Human and Horse Exposure
3.1.1. Macroscale Factors
3.1.2. Microscale Factors
3.2. Transmission to Humans and Horses
4. Comparative Clinical Disease
4.1. Viral Kinetics
4.2. Clinical Syndromes
4.3. Demographics and Outcomes
4.4. West Nile Fever
4.5. West Nile Neuroinvasive Disease
4.6. Extra-Neural Symptoms
4.7. Long-Term Recovery
5. Comparative Clinicopathological Features
5.1. Clinical Pathology
5.2. Pathology
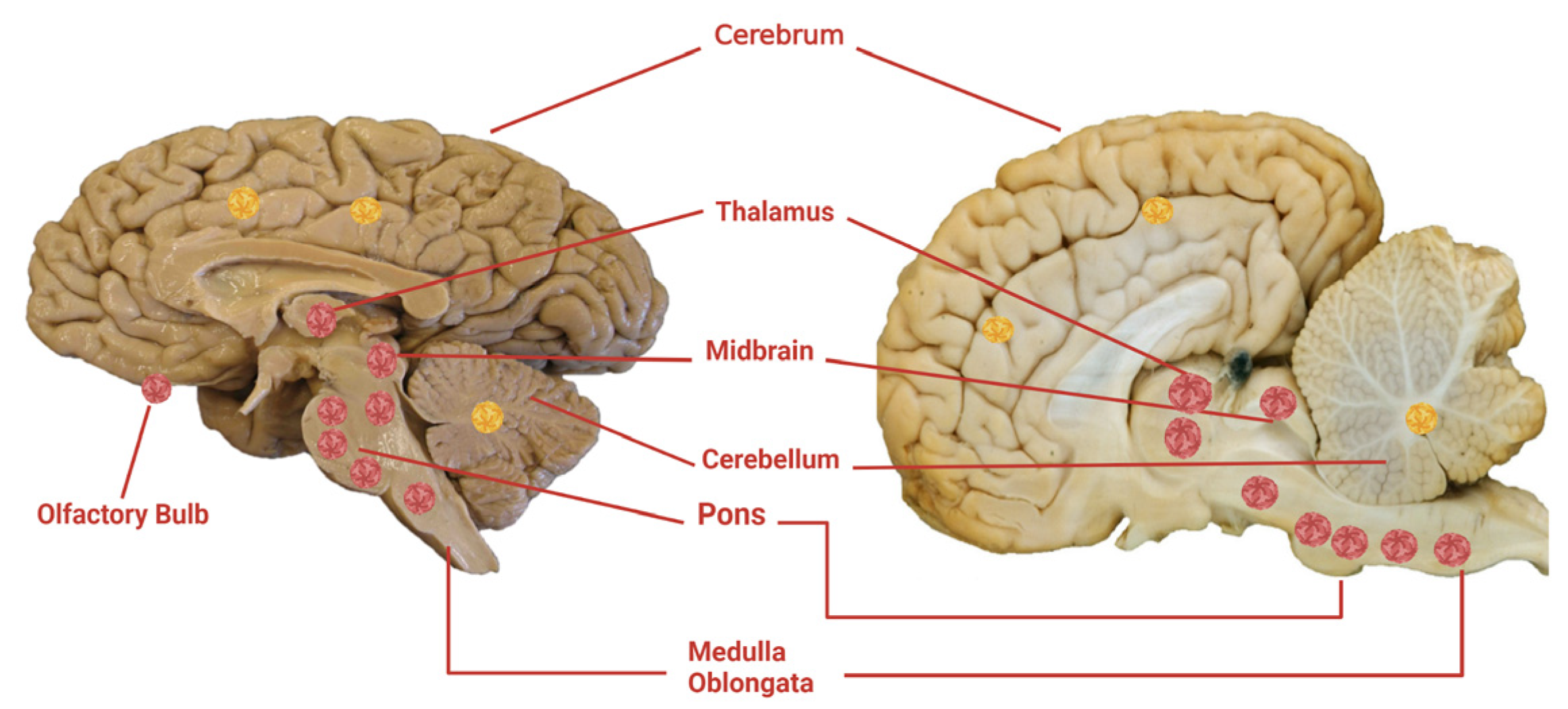
5.2.1. Gross Pathology
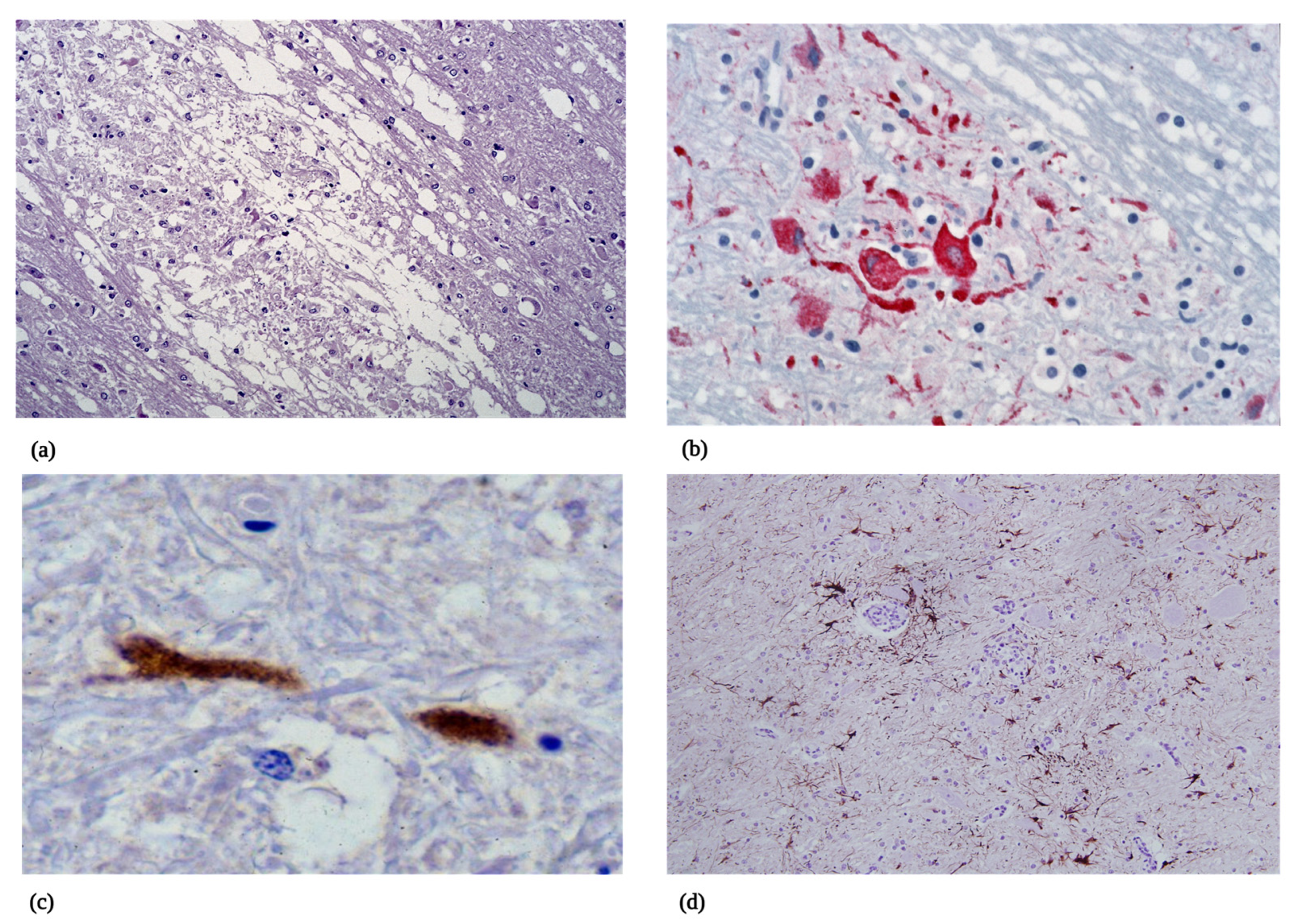
5.2.2. Microscopic Pathology
6. Diagnosis of WNV
6.1. Detection of WNV Antibody
6.1.1. Serosurveillance
6.1.2. Serodiagnosis of Clinical Disease
6.2. Other Diagnostic Modalities
7. Vaccines and Therapeutics against WNV
7.1. Vaccines
7.2. Therapeutics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hurlbut, H.S.; Rizk, F.; Taylor, R.M.; Work, T.H. A study of the ecology of West Nile virus in Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1956, 5, 579–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jupp, P.G.; McIntosh, B.M. Quantitative experiments on the vector capability of Culex (Culex) univittatus Theobald with West Nile and Sindbis viruses. J. Med. Entomol. 1970, 7, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, L.; Mouchet, J.; Rageau, J.; Hannoun, C.; Joubert, L.; Oudar, J.; Beytout, D. Epidemiology of the West Nile virus: Study of an outbreak in Camargue. II. Outline of the physical, biological and human environment. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. 1968, 114, 521–538. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G.; Blackburn, N.K.; Thompson, D.L.; Meenehan, G.M. Sindbis and West Nile virus infections in the Witwatersrand-Pretoria region. S. Afr. Med. J. 1986, 70, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Roehrig, J.T.; Deubel, V.; Smith, J.; Parker, M.; Steele, K.; Crise, B.; Volpe, K.E.; Crabtree, M.B.; Scherret, J.H.; et al. Origin of the West Nile virus responsible for an outbreak of encephalitis in the northeastern United States. Science 1999, 286, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byas, A.D.; Ebel, G.D. Comparative Pathology of West Nile Virus in Humans and Non-Human Animals. Pathogens 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Olivares, J.; Wood, J. West Nile virus infection of horses. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockx, B.; van Asten, L.; van den Wijngaard, C.; Godeke, G.J.; Goehring, L.; Vennema, H.; van der Avoort, H.; van Pelt, W.; Koopmans, M. Syndromic surveillance in the Netherlands for the early detection of West Nile virus epidemics. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2006, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, A.; Hendrikx, P.; Sabatier, P. West Nile virus outbreak detection using syndromic monitoring in horses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, R.S.; Leblond, A.; Lecollinet, S.; Tritz, P.; Cantile, C.; Kutasi, O.; Zientara, S.; Pradier, S.; van Galen, G.; Speybroek, N.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of West Nile Fever in Equids by classification and regression tree (CART) analysis and comparative study of clinical appearance in three European countries. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faverjon, C.; Andersson, M.G.; Decors, A.; Tapprest, J.; Tritz, P.; Sandoz, A.; Kutasi, O.; Sala, C.; Leblond, A. Evaluation of a Multivariate Syndromic Surveillance System for West Nile Virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faverjon, C.; Vial, F.; Andersson, M.G.; Lecollinet, S.; Leblond, A. Early detection of West Nile virus in France: Quantitative assessment of syndromic surveillance system using nervous signs in horses. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedell, R.; Andersson, M.G.; Faverjon, C.; Marcillaud-Pitel, C.; Leblond, A.; Mostad, P. Surveillance of animal diseases through implementation of a Bayesian spatio-temporal model: A simulation example with neurological syndromes in horses and West Nile Virus. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 162, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithburn, K.C.; Hughes, T.P.; Burke, A.W.; Paul, J.H. A neurotropic virus isolated from the blood of a native of Uganda. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1940, 20, 471–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, T.J.; Hahn, C.S.; Galler, R.; Rice, C.M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1990, 44, 649–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, M.A. The molecular biology of West Nile Virus: A new invader of the western hemisphere. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 371–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kim, B.S.; Chipman, P.R.; Rossmann, M.G.; Kuhn, R.J. Structure of West Nile virus. Science 2003, 302, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khromykh, A.A.; Westaway, E.G. Completion of kunjin virus-rna sequence and recovery of an infectious rna transcribed from stably cloned full-length cdna. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Ebel, G.D.; Deubel, V.; Kerst, A.J.; Murri, S.; Meyer, R.; Bowen, M.; McKinney, N.; Morrill, W.E.; Crabtree, M.B.; et al. Complete genome sequences and phylogenetic analysis of West Nile virus strains isolated from the United States, Europe, and the Middle East. Virology 2002, 298, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z.; Halouzka, J. West Nile fever—A reemerging mosquito-borne viral disease in Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgue, B.; Murri, S.; Triki, H.; Deubel, V.; Zeller, H.G. West Nile in the Mediterranean basin: 1950–2000. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgue, B.; Murri, S.; Zientara, S.; Durand, B.; Durand, J.P.; Zeller, H. West Nile outbreak in horses in southern France, 2000: The return after 35 years. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgue, B.; Zeller, H.; Deubel, V. The ecology and epidemiology of West Nile virus in Africa, Europe and Asia. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trock, S.C.; Meade, B.J.; Glaser, A.L.; Ostlund, E.N.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Cropp, B.C.; Kulasekera, V.; Kramer, L.D.; Komar, N. West Nile virus outbreak among horses in New York State, 1999 and 2000. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Edmonds, J.H.; Prow, N.A.; Gu, X.; Davis, R.; Hornitzky, C.; Arzey, K.E.; Finlaison, D.; Hick, P.; et al. Characterization of virulent West Nile virus Kunjin strain, Australia, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.A.; Fegan, M.; O’Riley, K.; Motha, J.; Warner, S. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Murray Valley encephalitis virus and West Nile virus (Kunjin subtype) from an arbovirus disease outbreak in horses in Victoria, Australia, in 2011. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzon, L.; Franchin, E.; Squarzon, L.; Lavezzo, E.; Toppo, S.; Martello, T.; Bressan, S.; Pagni, S.; Cattai, M.; Piazza, A.; et al. Genome sequence analysis of the first human west nile virus isolated in italy in 2009. Eurosurveillance 2009, 14, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzon, L.; Pacenti, M.; Franchin, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Martello, T.; Squarzon, L.; Toppo, S.; Fiorin, F.; Marchiori, G.; Russo, F.; et al. New endemic West Nile virus lineage 1a in northern Italy, July 2012. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzon, L.; Papa, A.; Pacenti, M.; Franchin, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Squarzon, L.; Masi, G.; Martello, T.; Testa, T.; Cusinato, R.; et al. Genome Sequencing of West Nile Virus from Human Cases in Greece, 2012. Viruses 2013, 5, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehender, G.; Veo, C.; Ebranati, E.; Carta, V.; Rovida, F.; Percivalle, E.; Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; Calzolari, M.; Lavazza, A.; et al. Reconstructing the recent West Nile virus lineage 2 epidemic in Europe and Italy using discrete and continuous phylogeography. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzon, L.; Pacenti, M.; Franchin, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Masi, G.; Squarzon, L.; Pagni, S.; Toppo, S.; Russo, F.; Cattai, M.; et al. Whole genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of West Nile virus lineage 1 and lineage 2 from human cases of infection, Italy, August 2013. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzon, L.; Papa, A.; Lavezzo, E.; Franchin, E.; Pacenti, M.; Sinigaglia, A.; Masi, G.; Trevisan, M.; Squarzon, L.; Toppo, S.; et al. Phylogenetic characterization of Central/Southern European lineage 2 West Nile virus: Analysis of human outbreaks in Italy and Greece, 2013–2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 1122.e1–1122.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzon, L. Ongoing and emerging arbovirus threats in Europe. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 107, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadieu, E.; Bahuon, C.; Lowenski, S.; Zientara, S.; Coulpier, M.; Lecollinet, S. Differential virulence and pathogenesis of West Nile viruses. Viruses 2013, 5, 2856–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciota, A.T.; Kramer, L.D. Vector-virus interactions and transmission dynamics of West Nile virus. Viruses 2013, 5, 3021–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolsá-García, M.J.; Wehmeyer, M.L.; Lühken, R.; Roiz, D. Worldwide transmission and infection risk of mosquito vectors of West Nile, St. Louis encephalitis, Usutu and Japanese encephalitis viruses: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, F.J.; Davis, C.T.; Tesh, R.B.; Barrett, A.D. Phylogeography of West Nile virus: From the cradle of evolution in Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2964–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uelmen, J.A.; Irwin, P.; Bartlett, D.; Brown, W.; Karki, S.; Ruiz, M.O.; Fraterrigo, J.; Li, B.; Smith, R.L. Effects of Scale on Modeling West Nile Virus Disease Risk. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Tran, A.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Linard, C.; Soti, V. Pathogenic landscapes: Interactions between land, people, disease vectors, and their animal hosts. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2010, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakoulias, N.W.; Schopflocher, D.P.; Svenson, L.W. Modelling geographic variations in West Nile virus 2. Can. J. Public Health 2006, 97, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, B.F.; Langerhans, R.B.; Ryberg, W.A.; Landesman, W.J.; Griffin, N.W.; Katz, R.S.; Oberle, B.J.; Schutzenhofer, M.R.; Smyth, K.N.; de St, M.A.; et al. Ecological correlates of risk and incidence of West Nile virus in the United States 81. Oecologia 2009, 158, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugumaran, R.; Larson, S.R.; Degroote, J.P. Spatio-temporal cluster analysis of county-based human West Nile virus incidence in the continental United States. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Candeloro, L.; Ippoliti, C.; Monaco, F.; De Massis, F.; Bruno, R.; Di Sabatino, D.; Danzetta, M.L.; Benjelloun, A.; Belkadi, B.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Identification of Areas Suitable for West Nile Disease in the Mediterranean Basin and Central Europe. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, A.; L’Ambert, G.; Balanca, G.; Pradier, S.; Grosbois, V.; Balenghien, T.; Baldet, T.; Lecollinet, S.; Leblond, A.; Gaidet-Drapier, N. An Integrative Eco-Epidemiological Analysis of West Nile Virus Transmission. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, B.V.; Turner, K.W.; Hunter, F.F. Geospatial Analysis and Seasonal Distribution of West Nile Virus Vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) in Southern Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, A.; Davis, J.K.; Wimberly, M.C. Identifying Environmental Risk Factors and Mapping the Distribution of West Nile Virus in an Endemic Region of North America. Geohealth 2018, 2, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.A.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; McVey, D.S.; Scoglio, C.M. A spatio-temporal individual-based network framework for West Nile virus in the USA: Spreading pattern of West Nile virus. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Brown, W.M.; Uelmen, J.; Ruiz, M.O.; Smith, R.L. The drivers of West Nile virus human illness in the Chicago, Illinois, USA area: Fine scale dynamic effects of weather, mosquito infection, social, and biological conditions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moirano, G.; Richiardi, L.; Calzolari, M.; Merletti, F.; Maule, M. Recent rapid changes in the spatio-temporal distribution of West Nile Neuro-invasive Disease in Italy. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carrasco, J.M.; Muñoz, A.R.; Olivero, J.; Segura, M.; Real, R. Predicting the spatio-temporal spread of West Nile virus in Europe. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uelmen, J.A.; Irwin, P.; Brown, W.M.; Karki, S.; Ruiz, M.O.; Li, B.; Smith, R.L. Dynamics of data availability in disease modeling: An example evaluating the trade-offs of ultra-fine-scale factors applied to human West Nile virus disease models in the Chicago area, USA. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calistri, P.; Giovannini, A.; Hubalek, Z.; Ionescu, A.; Monaco, F.; Savini, G.; Lelli, R. Epidemiology of west nile in europe and in the mediterranean basin. Open Virol. J. 2010, 4, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, A.; Allepuz, A.; Napp, S.; Soler, M.; Selga, I.; Aranda, C.; Casal, J.; Pages, N.; Hayes, E.B.; Busquets, N. Ecological surveillance for West Nile in Catalonia (Spain), learning from a five-year period of follow-up 66. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejek, J.; Jungbauer, C.; Aberle, S.W.; Allerberger, F.; Bagó, Z.; Camp, J.V.; Dimmel, K.; de Heus, P.; Kolodziejek, M.; Schiefer, P.; et al. Integrated analysis of human-animal-vector surveillance: West Nile virus infections in Austria, 2015–2016. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganzenberg, S.; Sieg, M.; Ziegler, U.; Pfeffer, M.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Hörügel, U.; Groschup, M.H.; Lohmann, K.L. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors for Equine West Nile Virus Infections in Eastern Germany, 2020. Viruses 2022, 14, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, Y.; Kaufman, Z.; Mannasse, B.; Koren, R.; Katz-Likvornik, S.; Orshan, L.; Glatman-Freedman, A.; Mendelson, E. West Nile virus outbreak in Israel in 2015: Phylogenetic and geographic characterization in humans and mosquitoes. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihi, H.; Chatti, N.; Ben Mhadheb, M.; Gharbi, J.; Abid, N. Phylodynamic and phylogeographic analysis of the complete genome of the West Nile virus lineage 2 (WNV-2) in the Mediterranean basin. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carrasco, J.M.; Muñoz, A.R.; Olivero, J.; Segura, M.; Real, R. Mapping the Risk for West Nile Virus Transmission, Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaddle, J.P.; Calos, S.E. Increased avian diversity is associated with lower incidence of human West Nile infection: Observation of the dilution effect 92. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchardt, S.M.; Feist, M.A.; Miller, T.; Lo, T.S. Epidemiology of West Nile virus in the highly epidemic state of North Dakota, 2002–2007. Public Health Rep. 2010, 125, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, S.E.; Magori, K.; Drake, J.M. Regional differences in the association between land cover and West Nile virus disease incidence in humans in the United States 43. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreadis, T.G. The contribution of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes to transmission and persistence of West Nile virus in North America. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2012, 28, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, A.M.; Pape, W.J. Predicting human West Nile virus infections with mosquito surveillance data 3. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.M.; Young, K.I.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; Hanley, K.A.; Peters, D.P.C. Vector Surveillance, Host Species Richness, and Demographic Factors as West Nile Disease Risk Indicators. Viruses 2021, 13, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Docherty, D.E.; McLean, R.G.; Zody, M.C.; Qu, J.; Yang, X.; Birren, B.W.; Malboeuf, C.M.; Newman, R.M.; et al. Fluid Spatial Dynamics of West Nile Virus in the United States: Rapid Spread in a Permissive Host Environment. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, C.; de Azevedo, T.S.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F. Impact of climate change on West Nile virus distribution in South America. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 116, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Campos, Z.; Juliano, R.; Velez, J.; Nogueira, R.M.; Komar, N. Serological evidence of widespread circulation of West Nile virus and other flaviviruses in equines of the Pantanal, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, M.C.; Boston, R.C. Irrigation linked to a greater incidence of human and veterinary West Nile virus cases in the United States from 2004 to 2006. Prev. Vet. Med. 2009, 89, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.P.; Wittich, C.A.; Fosgate, G.; Srinivasan, R. Environmental risk factors for equine West Nile virus disease cases in Texas. Vet. Res. Commun. 2009, 33, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisanzio, D.; Martello, E.; Izenour, K.; Stevens, K.; Kaur, R.; McKenzie, B.A.; Kraemer, M.; Reithinger, R.; Zohdy, S. Arboviral diseases and poverty in Alabama, 2007–2017. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberg, T.L.; Anderson, M.E.; Drebot, M.A.; Vooght, M.T.; Findlater, A.R.; Curry, P.S.; Campbell, C.A.; Osei, W.D. Seroprevalence of West Nile virus in Saskatchewan’s Five Hills Health Region, 2003. Can. J. Public Health 2006, 97, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, L.; Barker, C.M.; Moore, C.G.; Pape, W.J.; Winters, A.M.; Cheronis, N. Irrigated agriculture is an important risk factor for West Nile virus disease in the hyperendemic Larimer-Boulder-Weld area of north central Colorado. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, D.W.; Dykstra, E.A.; Brauner, J.M.; Duffy, A.; Reed, C.; Martin, E.; Peterson, W.; Carrière, Y.; Dutilleul, P.; Owen, J.P. West nile virus prevalence across landscapes is mediated by local effects of agriculture on vector and host communities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, L.M.; Sheu, J.J.; Day, J.F.; Maruniak, J.E.; Seino, K.; Zaretsky, H.; Long, M.T. Environmental risk factors associated with West Nile virus clinical disease in Florida horses. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2009, 23, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardelis, M.R.; Turell, M.J.; Dohm, D.J.; O’Guinn, M.L. Vector competence of selected North American Culex and Coquillettidia mosquitoes for West Nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Dohm, D.J.; Webb, J.P.; Sardelis, M.R. Vector competence of Culex tarsalis from Orange County, California, for West Nile virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2002, 2, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; Dohm, D.J.; Sardelis, M.R.; Oguinn, M.L.; Andreadis, T.G.; Blow, J.A. An update on the potential of north American mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) to transmit West Nile Virus 189. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Walther, D. Vector Potential of Mosquito Species (Diptera: Culicidae) Occurring in Central Europe. In Mosquito-Borne Diseases: Implications for Public Health; Benelli, G., Mehlhorn, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Faraji, A.; Healy, K.; Andreadis, T.G. West Nile Virus Mosquito Vectors in North America. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, C.G.; Stark, L.M.; Jeter, W.C.; Oliveri, R.L.; Brooks, R.G.; Conti, L.A.; Wiersma, S.T. Surveillance results from the first West Nile virus transmission season in Florida, 2001. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribar, L.J.; Vlach, J.J.; Demay, D.J.; Stark, L.M.; Stoner, R.L.; Godsey, M.S.; Burkhalter, K.L.; Spoto, M.C.; James, S.S.; Smith, J.M.; et al. Mosquitoes infected with West Nile virus in the Florida Keys, Monroe County, Florida, USA. J. Med. Entomol. 2003, 40, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godsey, M.S.; Blackmore, M.S.; Panella, N.A.; Burkhalter, K.; Gottfried, K.; Halsey, L.A.; Rutledge, R.; Langevin, S.A.; Gates, R.; Lamonte, K.M.; et al. West Nile virus epizootiology in the southeastern United States, 2001. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005, 5, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailly, P.; Balenghien, T.; Ezanno, P.; Fontenille, D.; Toty, C.; Tran, A. Role of the repartition of wetland breeding sites on the spatial distribution of Anopheles and Culex, human disease vectors in southern France. Parasit. Vectors. 2011, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, V.; Tran, A.; Durand, B. Predictive modeling of West Nile virus transmission risk in the Mediterranean Basin: How far from landing? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 11, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jupp, P.G. The ecology of West Nile virus in South Africa and the occurrence of outbreaks in humans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körsten, C.; Al-Hosary, A.A.; Schäfer, M.; Tews, B.A.; Werner, D.; Kampen, H.; Vasic, A.; Silaghi, C. Vector Competence of German Aedes punctor (Kirby, 1837) for West Nile Virus Lineages 1 and 2. Viruses 2022, 14, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, N. West Nile virus surveillance using sentinel birds 20. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, N.; Langevin, S.; Hinten, S.; Nemeth, N.; Edwards, E.; Hettler, D.; Davis, B.; Bowen, R.; Bunning, M. Experimental infection of North American birds with the New York 1999 strain of West Nile virus 18. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, N.; Young, G.; Ndaluka, C.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Komar, N.; Bowen, R. Persistent West Nile virus infection in the house sparrow (Passer domesticus). Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komar, N.; Panella, N.A.; Young, G.R.; Brault, A.C.; Levy, C.E. Avian hosts of West Nile virus in Arizona 51. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, S.A.; Brault, A.C.; Panella, N.A.; Bowen, R.A.; Komar, N. Variation in virulence of West Nile virus strains for house sparrows (Passer domesticus). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apperson, C.S.; Hassan, H.K.; Harrison, B.A.; Savage, H.M.; Aspen, S.E.; Farajollahi, A.; Crans, W.; Daniels, T.J.; Falco, R.C.; Benedict, M.; et al. Host feeding patterns of established and potential mosquito vectors of West Nile virus in the eastern United States 232. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2004, 4, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Uzcátegui, N.Y.; Gould, E.A.; Nuttall, P.A. Ixodid and argasid tick species and west nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, H.J.; Gorham, C.H.; Machain-Williams, C.; Loroño-Pino, M.A.; James, A.M.; Marlenee, N.L.; Winn, B.; Beaty, B.J.; Blair, C.D. Experimental transmission of West Nile virus (Flaviviridae: Flavivirus) by Carios capensis ticks from North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005, 5, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.B.; Komar, N.; Nasci, R.S.; Montgomery, S.P.; O’Leary, D.R.; Campbell, G.L. Epidemiology and transmission dynamics of West Nile virus disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez-Richarte, Á.; Ortiz de Salazar, M.I.; Giménez-Richarte, M.P.; Collado, M.; Fernández, P.L.; Clavijo, C.; Navarro, L.; Arbona, C.; Marco, P.; Ramos-Rincon, J.M. Transfusion-transmitted arboviruses: Update and systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, L.A.; Pelzel, A.M.; Rush, B.R.; Wright, A.M.; Galgut, B.I.; Hennager, S.G.; King, A.O.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L. Babesia equi-induced anemia in a Quarter Horse and subsequent regulatory response. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 242, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandriani, S.; Skewes-Cox, P.; Zhong, W.; Ganem, D.E.; Divers, T.J.; Van Blaricum, A.J.; Tennant, B.C.; Kistler, A.L. Identification of a previously undescribed divergent virus from the Flaviviridae family in an outbreak of equine serum hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1407–E1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, A.; Quinlivan, M.; Nelly, M.; Patterson, H.; Kenna, R.; Garvey, M.; Gildea, S.; Lyons, P.; Flynn, M.; Galvin, P.; et al. Diagnosis of equine infectious anaemia during the 2006 outbreak in Ireland. Vet. Rec. 2007, 161, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, M.; Human, S.; van Niekerk, S.; Williams, J.; van Eeden, C.; Freeman, F. Fatal neurologic disease and abortion in mare infected with lineage 1 West Nile virus, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Laboratory-acquired West Nile virus infections—United States, 2002. JAMA 2003, 289, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, M.; Steyl, J.; Human, S.; Weyer, J.; Zaayman, D.; Blumberg, L.; Leman, P.A.; Paweska, J.; Swanepoel, R. Transmission of West Nile virus during horse autopsy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.P.; Wright, D.J.; Custer, B.; Tobler, L.H.; Stramer, S.L.; Kleinman, S.H.; Prince, H.E.; Bianco, C.; Foster, G.; Petersen, L.R.; et al. West Nile virus infections projected from blood donor screening data, United States, 2003. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Factor, D.L.; Tkachenko, N.; Templeton, S.M.; Crall, N.D.; Pape, W.J.; Bauer, M.J.; Ambruso, D.R.; Dickey, W.C.; Marfin, A.A. West Nile viremic blood donors and risk factors for subsequent West Nile fever. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2007, 7, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.P.; Kleinman, S.H.; Tobler, L.H.; Kamel, H.T.; Norris, P.J.; Walsh, I.; Matud, J.L.; Prince, H.E.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Wright, D.J.; et al. Virus and antibody dynamics in acute west nile virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Elmansoury, H.K. Natural and experimental infection of egyptian equines with west nile virus. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1963, 57, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunning, M.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Cropp, C.B.; Sullivan, K.G.; Davis, B.S.; Komar, N.; Godsey, M.S.; Baker, D.; Hettler, D.L.; Holmes, D.A.; et al. Experimental infection of horses with West Nile virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, L.; Bowen, R.A.; Karaca, K.; Murray, M.J.; Gordy, P.W.; Loosmore, S.M.; Audonnet, J.C.; Nordgren, R.M.; Minke, J.M. Assessment of the efficacy of a single dose of a recombinant vaccine against West Nile virus in response to natural challenge with West Nile virus-infected mosquitoes in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siger, L.; Bowen, R.; Karaca, K.; Murray, M.; Jagannatha, S.; Echols, B.; Nordgren, R.; Minke, J.M. Evaluation of the efficacy provided by a Recombinant Canarypox-Vectored Equine West Nile Virus vaccine against an experimental West Nile Virus intrathecal challenge in horses. Vet. Ther. 2006, 7, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.T.; Gibbs, E.P.; Mellencamp, M.W.; Bowen, R.A.; Seino, K.K.; Zhang, S.; Beachboard, S.E.; Humphrey, P.P. Efficacy, duration, and onset of immunogenicity of a West Nile virus vaccine, live Flavivirus chimera, in horses with a clinical disease challenge model. Equine Vet. J. 2007, 39, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, K.K.; Long, M.T.; Gibbs, E.P.; Bowen, R.A.; Beachboard, S.E.; Humphrey, P.P.; Dixon, M.A.; Bourgeois, M.A. Comparative efficacies of three commercially available vaccines against West Nile Virus (WNV) in a short-duration challenge trial involving an equine WNV encephalitis model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, R.A.; Bosco-Lauth, A.; Syvrud, K.; Thomas, A.; Meinert, T.R.; Ludlow, D.R.; Cook, C.; Salt, J.; Ons, E. Protection of horses from West Nile virus Lineage 2 challenge following immunization with a whole, inactivated WNV lineage 1 Vaccine. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5455–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; Bosco-Lauth, A.; Hartwig, A.E.; Uddin, M.J.; Barcelon, J.; Suen, W.W.; Wang, W.; Hall, R.A.; Bowen, R.A. Characterization of non-lethal West Nile Virus (WNV) infection in horses: Subclinical pathology and innate immune response. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 103, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, R.; Nemeth, N. Experimental infections with West Nile virus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 20, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacenti, M.; Sinigaglia, A.; Franchin, E.; Pagni, S.; Lavezzo, E.; Montarsi, F.; Capelli, G.; Barzon, L. Human West Nile Virus Lineage 2 Infection: Epidemiological, Clinical, and Virological Findings. Viruses 2020, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heus, P.; Kolodziejek, J.; Camp, J.V.; Dimmel, K.; Bagó, Z.; Hubálek, Z.; van den Hoven, R.; Cavalleri, J.V.; Nowotny, N. Emergence of West Nile virus lineage 2 in Europe: Characteristics of the first seven cases of West Nile neuroinvasive disease in horses in Austria. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonry, J.H.; Brown, C.B.; Cropp, C.B.; Co, J.K.; Bennett, S.N.; Nerurkar, V.R.; Kuberski, T.; Gubler, D.J. West Nile virus detection in urine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.W.; Shing, E.; Nelder, M.; Sander, B. Epidemiologic and clinical parameters of West Nile virus infections in humans: A scoping review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunning, M.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Cropp, B.; Sullivan, K.; Davis, B.; Komar, N.; Godsey, M.; Baker, D.; Hettler, D.; Holmes, D.; et al. Experimental infection of horses with West Nile virus and their potential to infect mosquitoes and serve as amplifying hosts. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.O.; Koers, E.; Baraniuk, S.; Herrington, E.; Carter, H.; Sierra, M.; Kilborn, C.; Arafat, R. Risk factors for encephalitis from West Nile Virus: A matched case-control study using hospitalized controls. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 56, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.; Baraniuk, S.; Resnick, M.; Arafat, R.; Kilborn, C.; Cain, K.; Shallenberger, R.; York, T.L.; Martinez, D.; Hellums, J.S.; et al. Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile virus infection. Epidemiol. Infect. 2006, 134, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.R.; Murray, K.O. Risk factors for West Nile virus infection and disease in populations and individuals. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.; Mostashari, F.; Fine, A.; Miller, J.; O’Leary, D.; Murray, K.; Huang, A.; Rosenberg, A.; Greenberg, A.; Sherman, M.; et al. The outbreak of West Nile virus infection in the New York City area in 1999. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.P.; Florescu, S.A.; Hasbun, R.; Harxhi, A.; Evendar, R.; Kahraman, H.; Neuberger, A.; Codreanu, D.; Zaharia, M.F.; Tosun, S.; et al. Prediction of unfavorable outcomes in West Nile virus neuroinvasive infection—Result of a multinational ID-IRI study. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 122, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.P.; Florescu, S.A.; Cotar, A.I.; Badescu, D.; Ceianu, C.S.; Zaharia, M.; Tardei, G.; Codreanu, D.; Ceausu, E.; Ruta, S.M. Re-emergence of severe West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease in humans in Romania, 2012 to 2017-implications for travel medicine. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantile, C.; Di Guardo, G.; Eleni, C.; Arispici, M. Clinical and neuropathological features of West Nile virus equine encephalomyelitis in Italy. Equine Vet. J. 2000, 32, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, M.; Human, S.; Zaayman, D.; Gerdes, G.H.; Williams, J.; Steyl, J.; Leman, P.A.; Paweska, J.T.; Setzkorn, H.; Rous, G.; et al. Lineage 2 west nile virus as cause of fatal neurologic disease in horses, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Long, M.; Getman, L.; Giguere, S.; MacKay, R.; Lester, G.; Alleman, A.; Wamsley, H.; Franklin, R.; Jacks, S.; et al. West Nile Virus encephalomyelitis in horses: 46 cases (2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 222, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; Baird, J.D.; DeLay, J.; Kenney, D.G.; Staempfli, H.R.; Viel, L.; Parent, J.; Smith-Maxie, L.; Poma, R. West Nile virus encephalomyelitis in horses in Ontario: 28 cases. Can. Vet. J. 2003, 44, 469–473. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.P.; Levy, M.; Thacker, H.L.; Ash, M.; Norman, S.K.; Moore, G.E.; Webb, P.W. Investigation of an outbreak of encephalomyelitis caused by West Nile virus in 136 horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, L.A.; Khaitsa, M.L.; Dyer, N.W.; Stoltenow, C.L. Evaluation of an outbreak of West Nile virus infection in horses: 569 cases (2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.P.; Schuermann, J.A.; Highfield, L.D.; Murray, K.O. Characteristics of an outbreak of West Nile virus encephalomyelitis in a previously uninfected population of horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 118, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, O.; Bakonyi, T.; Lecollinet, S.; Biksi, I.; Ferenczi, E.; Bahuon, C.; Sardi, S.; Zientara, S.; Szenci, O. Equine encephalomyelitis outbreak caused by a genetic lineage 2 West Nile virus in Hungary. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, O.E.; Fehérvári, P.; Tolnai, C.H.; Forgách, P.; Malik, P.; Jerzsele, Á.; Wagenhoffer, Z.; Szenci, O.; Korbacska-Kutasi, O. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestation of West Nile Virus Infections of Equines in Hungary, 2007–2020. Viruses 2022, 14, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, P.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Morley, P.S.; Wilmot, D.D.; Steffen, D.J.; Cunningham, W.E.; Salman, M.D. Outcome of equids with clinical signs of West Nile virus infection and factors associated with death. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.J.; Finlaison, D.S.; Gu, X.; Hick, P.M.; Moloney, B.J.; Wright, T.; Kirkland, P.D. Clinical and epidemiological features of West Nile virus equine encephalitis in New South Wales, Australia, 2011. Aust. Vet. J. 2019, 97, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbu, A.; Ceianu, C.S.; Panculescu-Gatej, R.I.; Vazquez, A.; Tenorio, A.; Rebreanu, R.; Niedrig, M.; Nicolescu, G.; Pistol, A. Outbreak of West Nile virus infection in humans, Romania, July to October 2010. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutasi, O.; Fehér, O.; Sárdi, S.; Balogh, N.; Nagy, A.; Moravszki, L.; Bódai, E.; Szenci, O. Characterisation of the cerebrospinal fluid of horses with West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease. Acta Vet. Hung. 2020, 68, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snook, C.; Hyman, S.; Del Piero, F.; Palmer, J.; Ostlund, E.; Barr, B.; Desrochers, A.; Reilly, L. West Nile virus encephalomyelitis in eight horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, K.L.; Sieg, M.; Landmann, M.; Ganzenberg, S.; Arnold, C.; Vahlenkamp, T.; Ulrich, R.G. West-Nile-Virus infections in 12 horses in east-central Germany. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. G Grosstiere. Nutztiere. 2022, 50, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, C.M.; Honarmand, S.; Louie, J.K.; Glaser, C.A. Risk factors for West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease, California, 2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1918–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostashari, F.; Bunning, M.L.; Kitsutani, P.T.; Singer, D.A.; Nash, D.; Cooper, M.J.; Katz, N.; Liljebjelke, K.A.; Biggerstaff, B.J.; Fine, A.D.; et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: Results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet 2001, 358, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Foster, G.A.; Dodd, R.Y.; Petersen, L.R.; Stramer, S.L. West Nile fever characteristics among viremic persons identified through blood donor screening. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejvar, J.J. Clinical manifestations and outcomes of West Nile virus infection. Viruses 2014, 6, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Marfin, A.A. Manifestations of West Nile neuroinvasive disease. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, F.M.; Thompson, P.N.; Venter, M. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation of West Nile Virus Infection in Horses in South Africa, 2016–2017. Pathogens 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.E.; DeBiasi, R.; Goade, D.E.; Haaland, K.Y.; Harrington, J.A.; Harnar, J.B.; Pergam, S.A.; King, M.K.; DeMasters, B.K.; Tyler, K.L. West Nile virus neuroinvasive disease. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnis, D.S.; Conetta, R.; Waldman, G.; Teixeira, A.A. The West Nile virus encephalitis outbreak in the United States (1999–2000)—From flushing, New York, to beyond its borders. West Nile Virus Detect. Surveill. Control 2001, 951, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Sampathkumar, P. West Nile virus: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and prevention 260. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Leis, A.A.; Stokic, D.S.; Van Gerpen, J.A.; Marfin, A.A.; Webb, R.; Haddad, M.B.; Tierney, B.C.; Slavinski, S.A.; Polk, J.L.; et al. Acute flaccid paralysis and West Nile virus infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamanolis, D.P.; Leslie, M.J.; Caveny, E.A.; Guarner, J.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.R. Neuropathological findings in West Nile virus encephalitis: A case report. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.W.; Tomlinson, G.; Loeb, M.; Sander, B. Health-related quality of life in persons with West Nile virus infection: A longitudinal cohort study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Jampol, L.M. Systemic and intraocular manifestations of West Nile virus infection. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2005, 50, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberger, V.S.; Augsburger, J.J.; Hutchins, R.K.; Miller, S.A.; Horwitz, J.A.; Bergmann, M. Chorioretinal lesions in nonfatal cases of West Nile virus infection. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowers, M.Y.; Lang, R.; Nassar, F.; Ben-David, D.; Giladi, M.; Rubinshtein, E.; Itzhaki, A.; Mishal, J.; Siegman-Igra, Y.; Kitzes, R.; et al. Clinical characteristics of the West Nile fever outbreak, Israel, 2000. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racsa, L.; Gander, R.; Chung, W.; Southern, P.; Le, J.; Beal, S.; Lee, F.; Cavuoti, D.; Reisch, J.; Alatoom, A. Clinical features of West Nile virus epidemic in Dallas, Texas, 2012. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, J.M.; Winpisinger, K.; Mattson, B.J.; Duffy, R.; Moolenaar, R.L. The epidemiology and early clinical features of West Nile virus infection. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2005, 23, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamino, V.; Escribano-Romero, E.; Gutiérrez-Guzmán, A.V.; Blázquez, A.B.; Saiz, J.C.; Höfle, U. Oculopathologic findings in flavivirus-infected gallinaceous birds. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, A.V.; Oster, S.; McMullen, R.J., Jr.; Shaw, G.C.; Dubielzig, R.R.; Teixeira, L.B.C.; Bellah, J.R.; Moore, P.A.; Boveland, S.D. Clinical and pathologic evaluation of chorioretinal lesions in wild owl species. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2022, 25, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, A.M.; Cruz-Martinez, L.A.; Ponder, J.B.; Redig, P.T.; Glaser, A.L.; Klauss, G.; Schoster, J.V.; Wunschmann, A. Ophthalmologic and oculopathologic findings in red-tailed hawks and Cooper’s hawks with naturally acquired West Nile virus infection 2. JAVMA J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 231, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünschmann, A.; Armién, A.G.; Khatri, M.; Martinez, L.C.; Willette, M.; Glaser, A.; Alvarez, J.; Redig, P. Ocular Lesions in Red-Tailed Hawks (Buteo jamaicensis) with Naturally Acquired West Nile Disease. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, P.J.; Konewko, P.; Wold, K.S.; Mariani, P.; Goli, S.; Bergloff, P.; Crosby, R.D. Long-term clinical and neuropsychological outcomes of West Nile virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.O.; Nolan, M.S.; Ronca, S.E.; Datta, S.; Govindarajan, K.; Narayana, P.A.; Salazar, L.; Woods, S.P.; Hasbun, R. The Neurocognitive and MRI Outcomes of West Nile Virus Infection: Preliminary Analysis Using an External Control Group. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherhead, J.E.; Miller, V.E.; Garcia, M.N.; Hasbun, R.; Salazar, L.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Murray, K.O. Long-term neurological outcomes in West Nile virus-infected patients: An observational study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejvar, J.J. The long-term outcomes of human West Nile virus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sejvar, J.J.; Curns, A.T.; Welburg, L.; Jones, J.F.; Lundgren, L.M.; Capuron, L.; Pape, J.; Reeves, W.C.; Campbel, G.L. Neurocognitive and functional outcomes in persons recovering from West Nile virus illness. J. Neuropsychol. 2008, 2, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.B.; Sejvar, J.J.; Zaki, S.R.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Bode, A.V.; Campbell, G.L. Virology, pathology, and clinical manifestations of West Nile virus disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouffard, J.P.; Riudavets, M.A.; Holman, R.; Rushing, E.J. Neuropathology of the brain and spinal cord in human West Nile virus infection. Clin. Neuropathol. 2004, 23, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wamsley, H.L.; Alleman, A.R.; Porter, M.B.; Long, M.T. Findings in cerebrospinal fluids of horses infected with West Nile virus: 30 cases (2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, A.; Banet, C.; Sutton, G.A.; Yadin, H.; Hadar, S.; Brill, A. Clinical signs of West Nile virus encephalomyelitis in horses during the outbreak in Israel in 2000. Vet. Rec. 2002, 151, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantile, C.; Del Piero, F.; Di Guardo, G.; Arispici, M. Pathologic and immunohistochemical findings in naturally occuring West Nile virus infection in horses. Vet. Pathol. 2001, 38, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; van Niekerk, S.; Human, S.; van Wilpe, E.; Venter, M. Pathology of fatal lineage 1 and 2 West Nile virus infections in horses in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2014, 85, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tber, A. West Nile fever in horses in Morocco. Bull. De L’Office Int. Des Epizoot. 1996, 11, 867–869. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, B.A.; Armbrustmacher, V. West Nile encephalitis: The neuropathology of four fatalities. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, B.A.; Nields, H.; Armbrustmacher, V.; Asnis, D.S. Muscle weakness in west Nile Encephalitis Is Due to Destruction of Motor Neurons. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 628–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, W.J.; Guarner, J.; Layton, M.; Fine, A.; Miller, J.; Nash, D.; Campbell, G.L.; Roehrig, J.T.; Gubler, D.J.; Zaki, S.R. The role of pathology in an investigation of an outbreak of West Nile encephalitis in New York, 1999. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarner, J.; Shieh, W.J.; Hunter, S.; Paddock, C.D.; Morken, T.; Campbell, G.L.; Marfin, A.A.; Zaki, S.R. Clinicopathologic study and laboratory diagnosis of 23 cases with West Nile virus encephalomyelitis. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, T.W.; Prayson, R.A.; Ruiz, A.I.; Isada, C.M.; Gordon, S.M. The neuropathology of West Nile virus meningoencephalitis. A report of two cases and review of the literature. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 119, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratkin, J.D.; Leis, A.A.; Stokic, D.S.; Slavinski, S.A.; Geiss, R.W. Spinal cord neuropathology in human West Nile virus infection. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2004, 128, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leis, A.A.; Fratkin, J.; Stokic, D.S.; Harrington, T.; Webb, R.M.; Slavinski, S.A. West Nile poliomyelitis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omalu, B.I.; Shakir, A.A.; Wang, G.; Lipkin, W.I.; Wiley, C.A. Fatal fulminant pan-meningo-polioencephalitis due to West Nile virus. Brain Pathol. 2003, 13, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kerst, A.J.; Nasci, R.S.; Godsey, M.S.; Mitchell, C.J.; Savage, H.M.; Komar, N.; Panella, N.A.; Allen, B.C.; Volpe, K.E.; et al. Rapid detection of west nile virus from human clinical specimens, field-collected mosquitoes, and avian samples by a TaqMan reverse transcriptase-PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kerst, A.J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification assays for rapid detection of West Nile and St. Louis encephalitis viruses 320. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4506–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, K.T.; Vetter, D.E. Detection of West Nile Virus Envelope Protein in Brain Tissue with an Immunohistochemical Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2585, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, J.; Shimizu, S.; Shibahara, T.; Isobe, T.; Yamada, M.; Tanimura, N. Development of monoclonal antibodies to West Nile virus and their application in immunohistochemistry. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplu, N.; Oğuzoğlu, T.; Ural, K.; Albayrak, H.; Ozan, E.; Ertürk, A.; Epikmen, E.T. West Nile Virus Infection in Horses: Detection by Immunohistochemistry, In Situ Hybridization, and ELISA. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 52, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennick, K.; McKnight, C.; Patterson, J.; Latimer, K.; Maes, R.; Wise, A.; Kiupel, M. Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry for Eastern equine encephalitis virus and West Nile virus in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded brain tissue of horses. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcambre, G.H.; Liu, J.; Streit, W.J.; Shaw, G.P.J.; Vallario, K.; Herrington, J.; Wenzlow, N.; Barr, K.L.; Long, M.T. Phenotypic characterisation of cell populations in the brains of horses experimentally infected with West Nile virus. Equine Vet. J. 2017, 49, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besselaar, T.G.; Blackburn, N.K.; Aldridge, N. Comparison of an antibody-capture IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with IgM-indirect immunofluorescence for the diagnosis of acute Sindbis and West Nile infections. J. Virol. Methods 1989, 25, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blitvich, B.J.; Bowen, R.A.; Marlenee, N.L.; Hall, R.A.; Bunning, M.L.; Beaty, B.J. Epitope-blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of west nile virus antibodies in domestic mammals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2676–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, R.J.; Anderson, B.L.; Litwin, C.M. Evaluation of a new commercial enzyme immunoassay for the detection of IgM antibodies to West Nile virus using a ratio method to eliminate nonspecific reactivity. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Ko, Y.J.; Nah, J.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, S.Y.; Yoon, K.J.; Joo, Y.S. Monoclonal antibody-based competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting and quantifying West Nile virus-neutralizing antibodies in horse sera. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olufemi, O.T.; Barba, M.; Daly, J.M. A Scoping Review of West Nile Virus Seroprevalence Studies among African Equids. Pathogens 2021, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, J.; Nishi, H.; Matsuda, H.; Tsunemitsu, H.; Shimiz, S. Cross-reactivity of Japanese encephalitis virus-vaccinated horse sera in serodiagnosis of West Nile virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joó, K.; Bakonyi, T.; Szenci, O.; Sárdi, S.; Ferenczi, E.; Barna, M.; Malik, P.; Hubalek, Z.; Fehér, O.; Kutasi, O. Comparison of assays for the detection of West Nile virus antibodies in equine serum after natural infection or vaccination. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 183, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calisher, C.H.; Karabatsos, N.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Shope, R.E.; Porterfield, J.S.; Westaway, E.G.; Brandt, W.E. Antigenic relationships between flaviviruses as determined by cross-neutralization tests with polyclonal antisera. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70 Pt 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjelloun, A.; El Harrak, M.; Belkadi, B. West Nile Disease Epidemiology in North-West Africa: Bibliographical Review. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e153–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eybpoosh, S.; Fazlalipour, M.; Baniasadi, V.; Pouriayevali, M.H.; Sadeghi, F.; Ahmadi Vasmehjani, A.; Karbalaie Niya, M.H.; Hewson, R.; Salehi-Vaziri, M. Epidemiology of West Nile Virus in the Eastern Mediterranean region: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.B.C.; Olufemi, O.T.; Daly, J.M.; Barba, M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of seroprevalence studies of West Nile virus in equids in Europe between 2001 and 2018. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Emeribe, A.U.; Ghamba, P.E.; Omosigho, P.O.; Bello, Z.M.; Oderinde, B.S.; Fasogbon, S.A.; Olayemi, L.; Daneji, I.M.; Musa, M.H.; et al. Distribution pattern and prevalence of West Nile virus infection in Nigeria from 1950 to 2020: A systematic review. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Khater, E.I.M.; Xue, J.B.; Ghallab, E.H.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Jiang, T.G.; Li, S.Z. Epidemiology of Mosquito-Borne Viruses in Egypt: A Systematic Review. Viruses 2022, 14, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ometto, T.; Durigon, E.L.; de, A.J.; Aprelon, R.; de Aguiar, D.M.; Cavalcante, G.T.; Melo, R.M.; Levi, J.E.; de Azevedo Junior, S.M.; Petry, M.V.; et al. West Nile virus surveillance, Brazil, 2008–2010. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaoui, R.; Lecollinet, S.; Lancelot, R. Mapping the serological prevalence rate of West Nile fever in equids, Tunisia. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Bocanegra, I.; Arenas-Montes, A.; Jaén-Téllez, J.A.; Napp, S.; Fernández-Morente, M.; Arenas, A. Use of sentinel serosurveillance of mules and donkeys in the monitoring of West Nile virus infection. Vet. J. 2012, 194, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongoh, M.N.; Khaitsa, M.L.; Dyer, N.W. Environmental and ecological determinants of West Nile virus occurrence in horses in North Dakota, 2002. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 135, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, R.L.; Waldner, C.; Epp, T.; Wright, J.; Whitehead, S.M.; Bangura, H.; Young, E.; Townsend, H.G. Prediction of human cases of West Nile virus by equine cases, Saskatchewan, Canada, 2003. Prev. Vet. Med. 2006, 76, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, Y.; Sofer, D.; Bucris, E.D.; Mendelson, E. Surveillance and Diagnosis of West Nile Virus in the Face of Flavivirus Cross-Reactivity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, H.E.; Tobler, L.H.; Yeh, C.; Gefter, N.; Custer, B.; Busch, M.P. Persistence of West Nile virus-specific antibodies in viremic blood donors. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 1228–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Nash, D.; Maldin, B.; Labowitz, A.; Martin, D.A.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Campbell, G.L. Persistence of virus-reactive serum immunoglobulin m antibody in confirmed west nile virus encephalitis cases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B.; Long, M.; Gosche, D.G.; Schott, H.M.; Hines, M.T.; Rossano, M.; Sellon, D.C. Immunoglobulin M-capture enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay testing of cerebrospinal fluid and serum from horses exposed to West Nile virus by vaccination or natural infection. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.H.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Rodeheaver, R.M.; Ostlund, E.N.; Pedersen, D.D.; Moorhead, R.G.; Stricklin, J.B.; Dewell, R.D.; Roach, S.D.; Long, R.E.; et al. Immunologic responses to West Nile virus in vaccinated and clinically affected horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 226, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostlund, E.N.; Andresen, J.E.; Andresen, M. West Nile encephalitis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2000, 16, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.T.; Jeter, W.; Hernandez, J.; Sellon, D.C.; Gosche, D.; Gillis, K.; Bille, E.; Gibbs, E.P. Diagnostic performance of the equine IgM capture ELISA for serodiagnosis of West Nile virus infection. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2006, 20, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibzadeh, S.M.; Gold, C.B.; Keggan, A.E.; Perkins, G.A.; Glaser, A.L.; Dubovi, E.J.; Wagner, B. West Nile virus-specific immunoglobulin isotype responses in vaccinated and infected horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 76, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Carvajal, F.; Bravo-Barriga, D.; Martín-Cuervo, M.; Aguilera-Sepúlveda, P.; Ferraguti, M.; Jiménez-Clavero, M.; Llorente, F.; Alonso, J.M.; Frontera, E. Serological evidence of co-circulation of West Nile and Usutu viruses in equids from western Spain. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, O.; Bakonyi, T.; Barna, M.; Nagy, A.; Takács, M.; Szenci, O.; Joó, K.; Sárdi, S.; Korbacska-Kutasi, O. Serum neutralising antibody titres against a lineage 2 neuroinvasive West Nile Virus strain in response to vaccination with an inactivated lineage 1 vaccine in a European endemic area. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 227, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmerly, S.A. Diagnosis and treatment of west nile infections. Ochsner. J. 2003, 5, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, C.B.; Trikamji, B.V.; Mathisen, G.E.; Mishra, S.K. Southern California neuroinvasive West Nile virus case series. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.B.; Trikamji, B.; Mathisen, G.; Yim, C.; Zipser, B.; Mishra, S. MRI Ventral Nerve Root Enhancement in Five Patients Presenting With Extremity Weakness Secondary to Neuroinvasive West Nile Virus. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2016, 18, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Reina, C.; Martínez-Moya, M.; Piñero-González de la Peña, P.; Caro-Domínguez, P. Neuroinvasive disease due to West Nile virus: Clinical and imaging findings associated with a re-emerging pathogen. Radiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 64, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, K.A.; Gordon, S.M.; Prayson, R.A.; Ruggierri, P.M. West Nile virus meningoencephalitis: MR imaging findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrett, K.S. Special Diagnostic Techniques in Equine Neurology (Radiography, Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging). Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2022, 38, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.A.; Hallowell, T.C. Magnetic resonance imaging, clinicopathologic findings, and clinical progression of a puppy with confirmed Eastern equine encephalitis virus. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.; Hathaway, D.; Jennings, N.; Champ, D.; Chiang, Y.W.; Chu, H.J. Equine vaccine for West Nile virus. Dev. Biol. 2003, 114, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.A.; Haque, M.; Stanfield, B.; Andrews, F.M.; Roy, A.A.; Kousoulas, K.G. A recombinant fusion protein consisting of West Nile virus envelope domain III fused in-frame with equine CD40 ligand induces antiviral immune responses in horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 198, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Ge, J.; Hua, R.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.; Sun, E.; Wu, D.; et al. Newcastle disease virus-vectored West Nile fever vaccine is immunogenic in mammals and poultry. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bardelli, M.; Espinosa, D.A.; Pedotti, M.; Ng, T.-S.; Bianchi, S.; Simonelli, L.; Lim, E.X.Y.; Foglierini, M.; Zatta, F.; et al. A Human Bi-specific Antibody against Zika Virus with High Therapeutic Potential. Cell 2017, 171, 229–241.e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.C.; Ricardo, R.C.; Santos, N.C. Dengue, West Nile, and Zika Viruses: Potential Novel Antiviral Biologics Drugs Currently at Discovery and Preclinical Development Stages. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, E.R.; Long, M.T. Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance. Viruses 2023, 15, 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061230
Schwarz ER, Long MT. Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Erika R., and Maureen T. Long. 2023. "Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061230
APA StyleSchwarz, E. R., & Long, M. T. (2023). Comparison of West Nile Virus Disease in Humans and Horses: Exploiting Similarities for Enhancing Syndromic Surveillance. Viruses, 15(6), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061230




